Adsorption of Ibuprofen from Water Using Waste from Rose Geranium (Pelargonium graveolens) Stems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Preparation
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experiments
2.2.1. Preparation of Pelargonium Graveolens
2.2.2. Preparation of Stock Solution and Working Standards
2.2.3. Adsorption Experiments
2.2.4. Point Zero Charge
2.2.5. Reusability
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Data Management
3. Characterisation
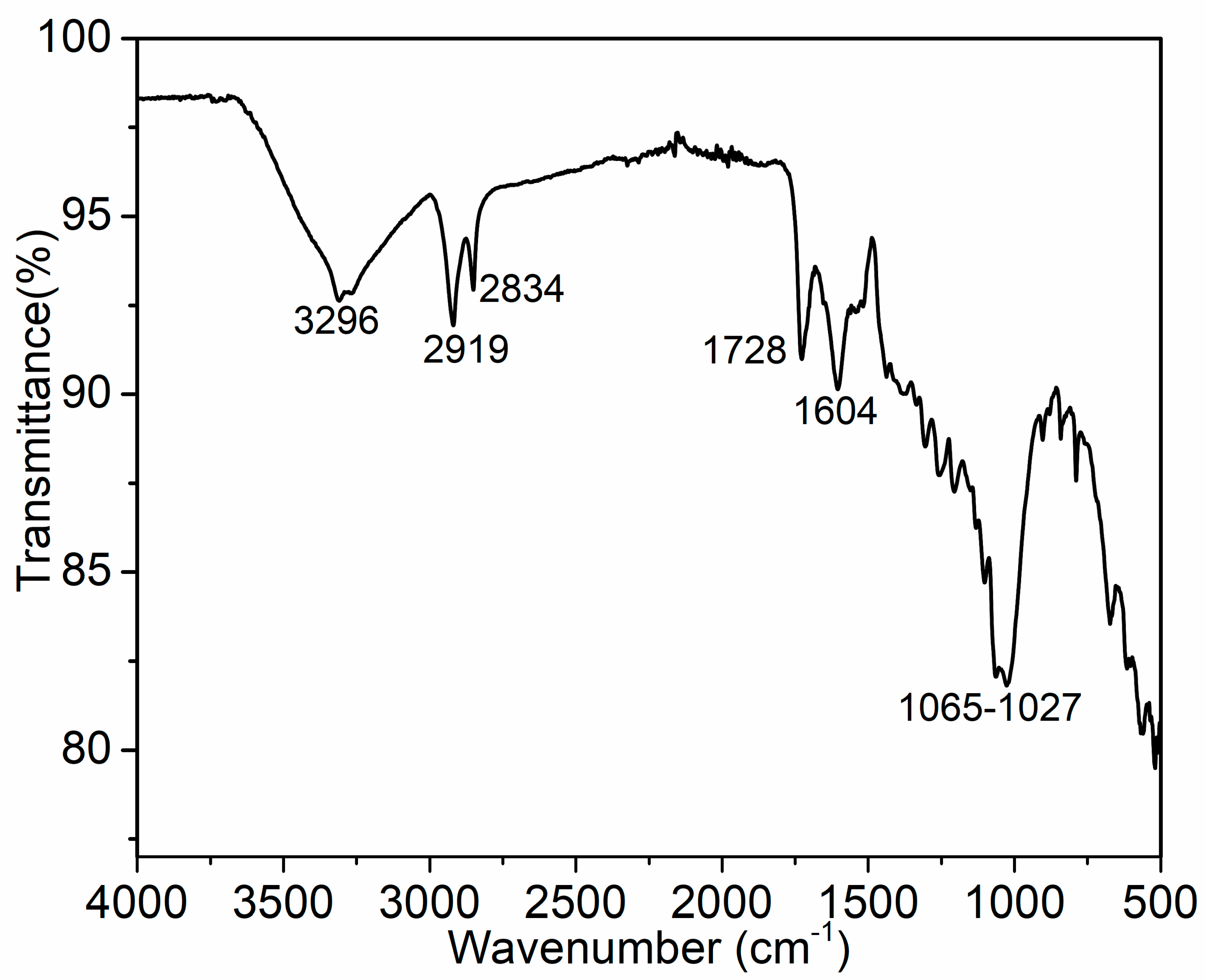
3.1. FTIR Analysis
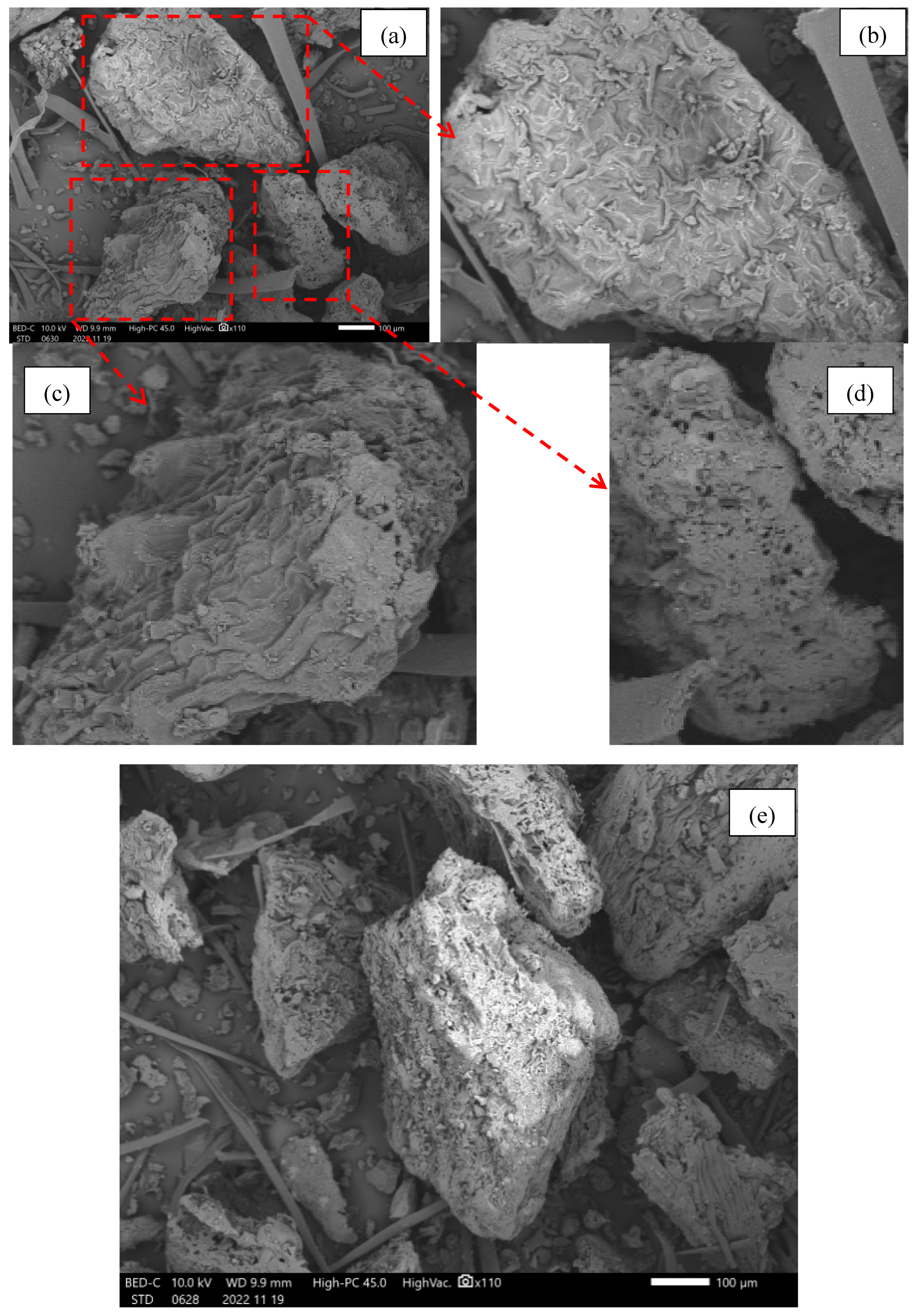
3.2. SEM-EDX Analysis
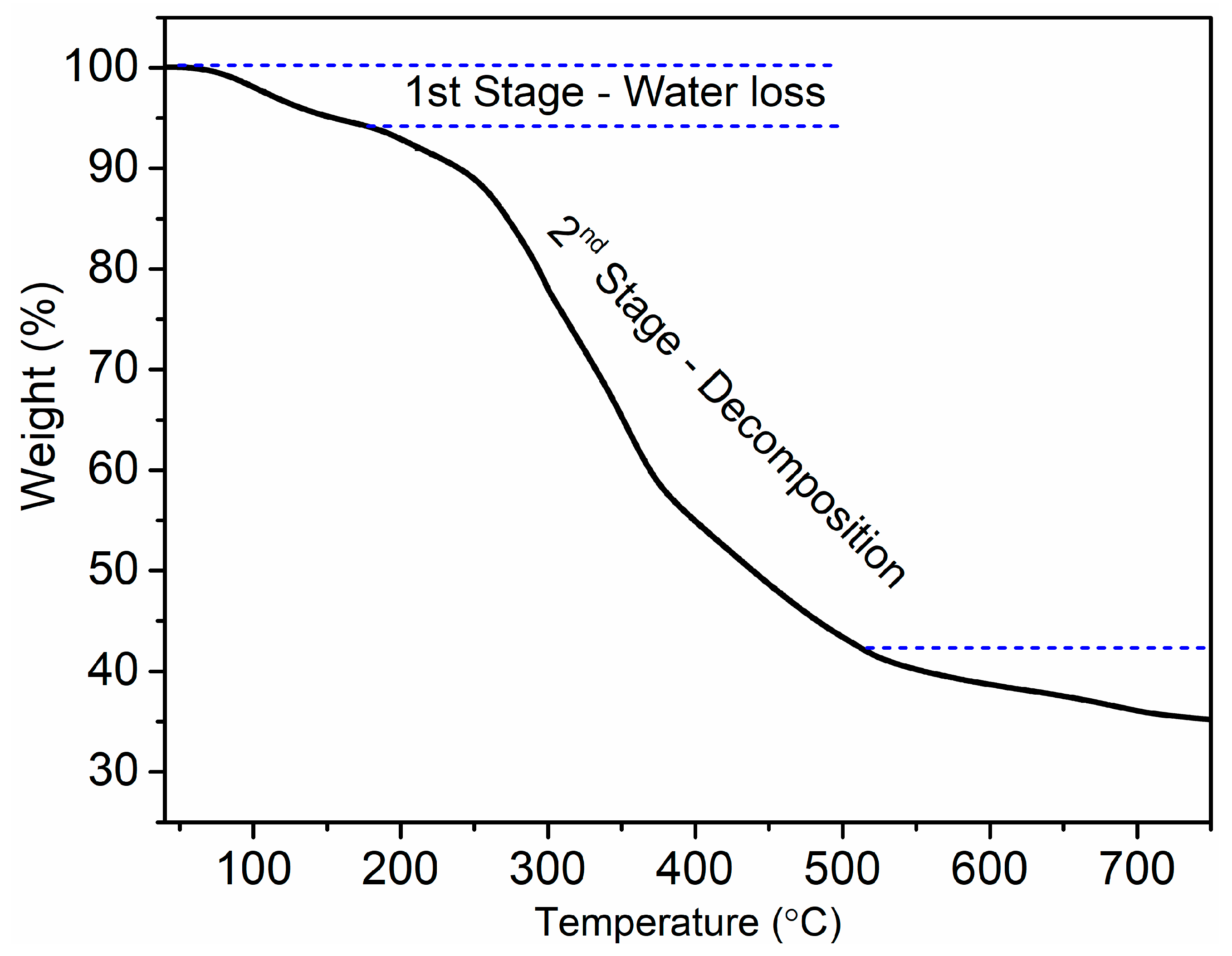
3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
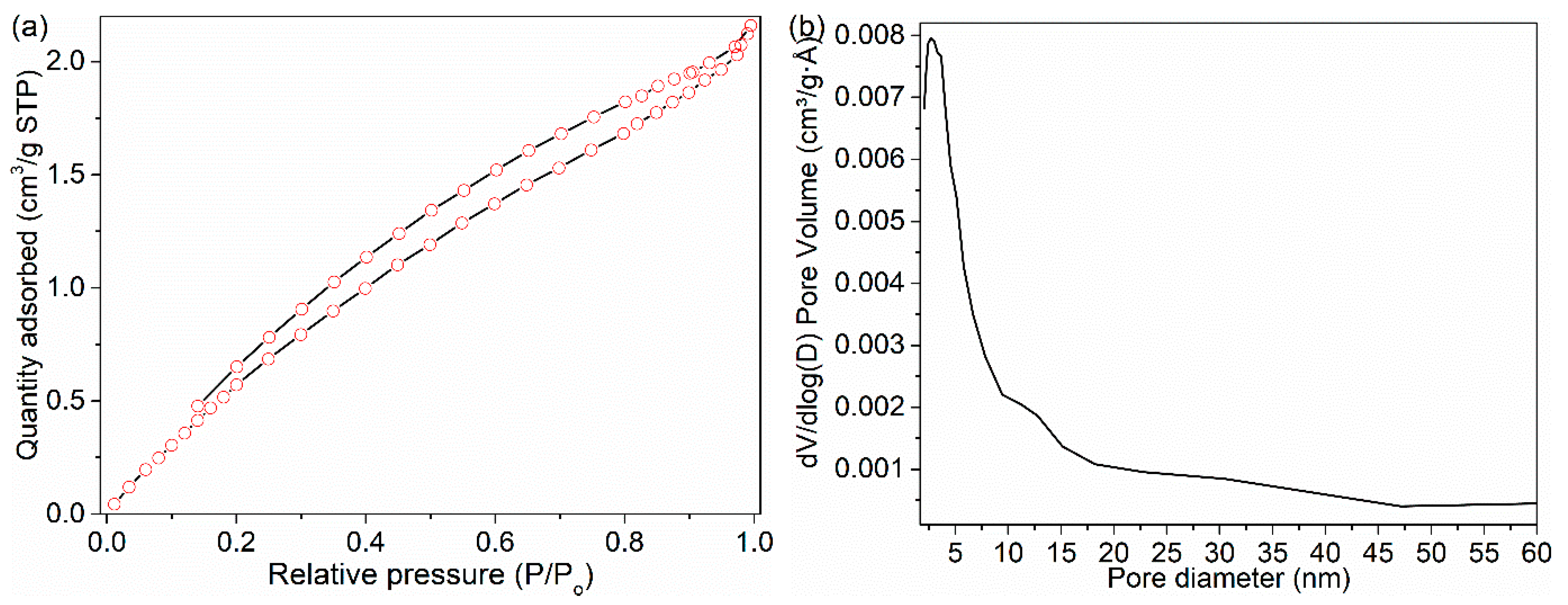
3.4. BET Analysis
3.5. Adsorption Results
3.5.1. Time Effect of SPG and Kinetic Models
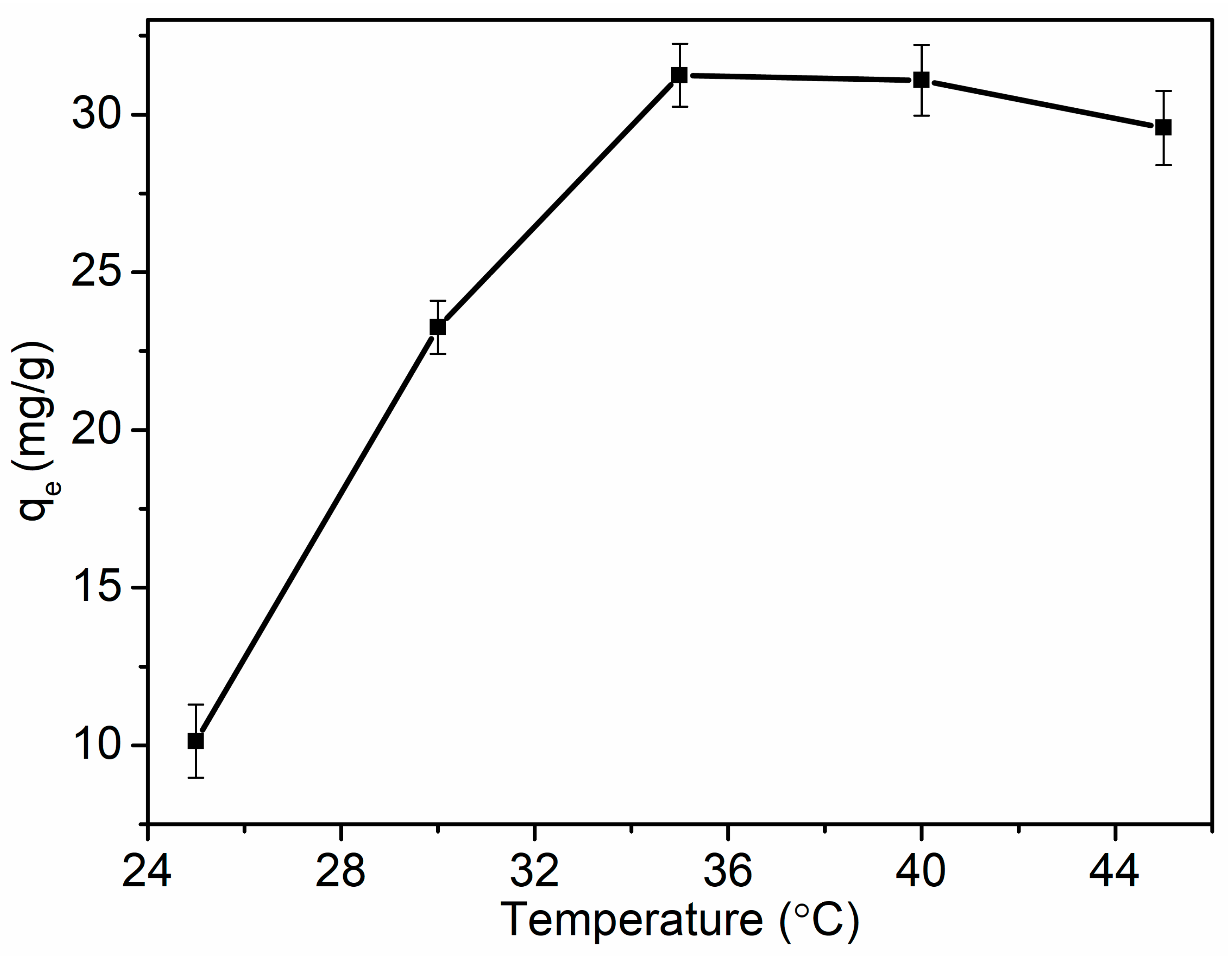
3.5.2. Temperature Effect and Thermodynamics of SPG
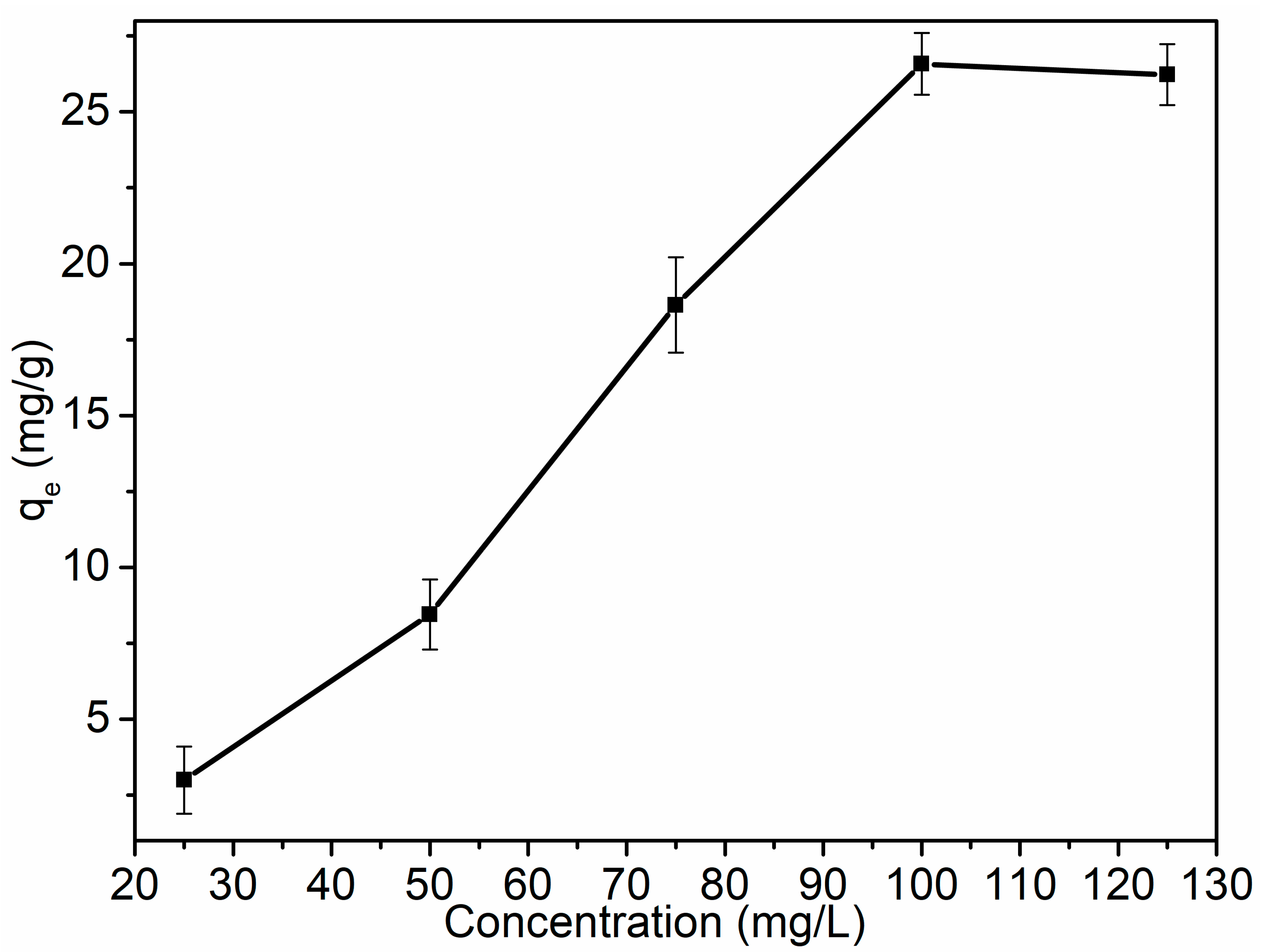
3.5.3. Concentration Effect and Isotherm Models for SPG
3.5.4. pH Effect of SPG
3.5.5. pH(PZC) of SPG
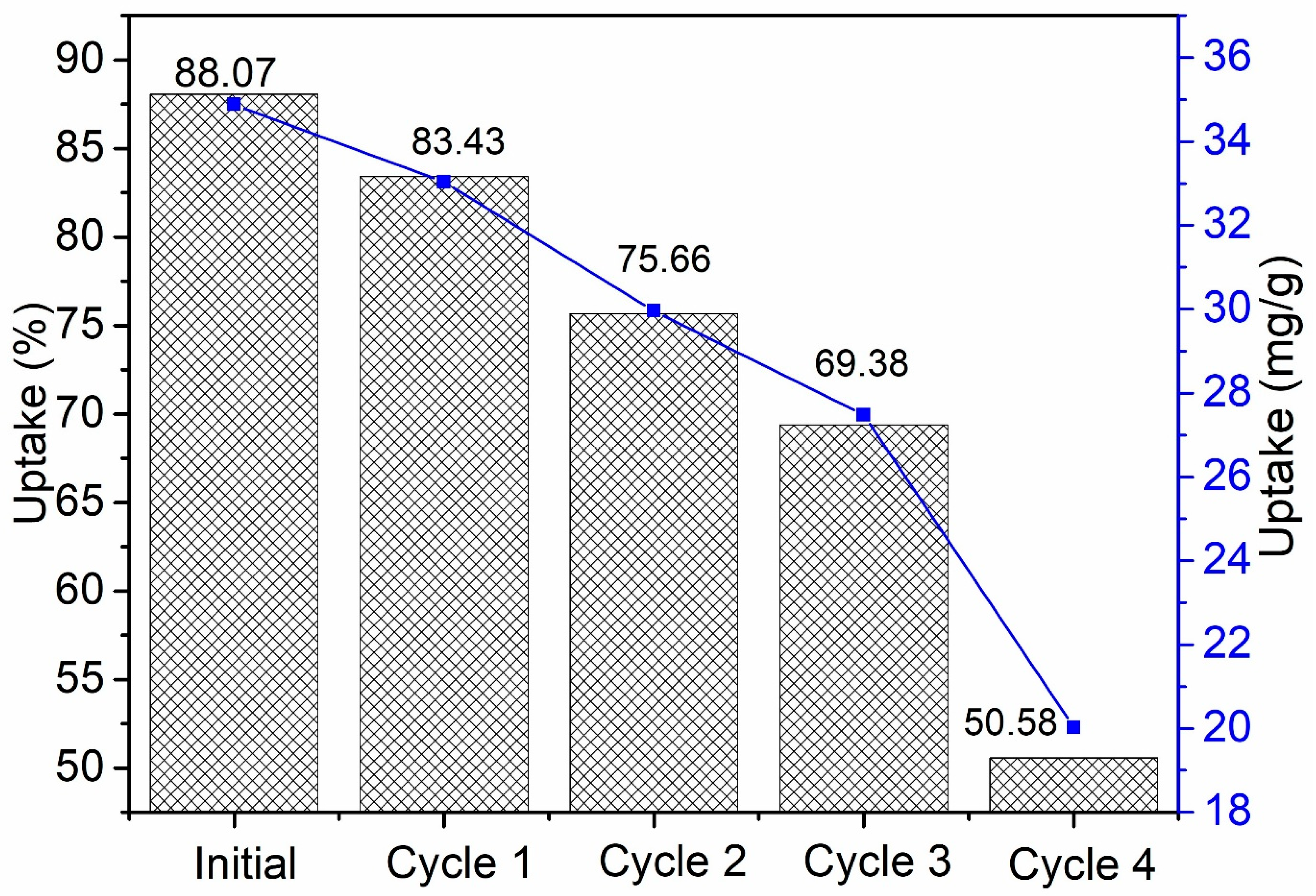
3.5.6. Reusability Study of SPG
3.5.7. Comparative Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munzhelele, E.P.; Mudzielwana, R.; Ayinde, W.B.; Gitari, W.M. Bodies of South Africa: A Review of Sources, Pathways, Occurrence, Effects, and Geographical Distribution. Water 2024, 16, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigonya, S.; Mokhotu, T.H.; Mokhena, T.C.; Makhanya, T.R. Mitigation of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory and Antiretroviral Drugs as Environmental Pollutants by Adsorption Using Nanomaterials as Viable Solution—A Critical Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y. Direct activation of petroleum pitch-based mesoporous carbon for phenol adsorption. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 702, 135020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Li, H. Kinetics and equilibrium study of phenol adsorption by activated carbon derived from pig blood. Carbon Trends 2023, 12, 100281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.L.; Ayati, A.; Farghali, M.; Krivosshapkin, P.; Tanhaei, B.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Krivoshapkina, E.; Taheri, P.; Tracey, C.; Al-Fatesh, A.; et al. Advanced adsorbents for ibuprofen removal from aquatic environments: A review. Environ. Chem. Letter. 2024, 22, 373–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, K.; Mahapatra, S.; Ali, M.H. Pharmaceutical wastewater as emerging contaminants (EC): Treatment technologies, impact on environment and human health. Energy Nexus 2022, 6, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogowska, J.; Zimmermann, A. Household Pharmaceutical Waste Disposal as a Global Problem—A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyam, S.; Patra, S. Innovations and challenges in adsorption-based wastewater remediation: A comprehensive review. Heliyon 2024, 10, 29573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokce, Y.; Aktas, Z. Nitric acid modification of activated carbon produced from waste tea and adsorption of methylene blue and phenol. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 313, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde, L.; Nabavi, M.S.; Escalera, E.; Antti, M.L.; Akhtar, F. Adsorption of heavy metals on natural zeolites: A review. Chemosphere 2023, 328, 138508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duwiejuah, A.B.; Adjei, E.F. Alhassan EH. Adsorption of toxic metals from greywater using coconut husk biochar and spent green tea. Heliyon 2024, 10, 38189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayoumi, L.; Khalil, M.; Ghareeb, D.; Chokr, A.; Bouaziz, M.; El-Dakdouki, M.H. Phytochemical constituents and therapeutic effects of the essential oil of rose geranium (Pelargonium hybrid) cultivated in Lebanon. S. Afr. J. Botany 2022, 147, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thillainayagam, B.P.; Saravanan, P.; Ravindiran, G.; Josephraj, J. Continuous sorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution using effective microorganisms-based water hyacinth waste compost in a packed column. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhatem, N.M.; Kameli, A.; Ferhat, M.A.; Saidi, F.; Mekarnia, M. Rose geranium essential oil as a source of new and safe anti-inflammatory drugs. Libyan J. Med. 2013, 7, 22520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmen, G.; Hnncu, G. Antimicrobial and Antifungal Activity of Pelargonium roseum Essential Oils. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 31, 511–514. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Li, Z.; Ni, T.; Li, S. Adsorption of low-cost absorption materials based on biomass (Cortaderia selloana flower spikes) for dye removal: Kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 229, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, P.V.; Rego, R.M.; Yap, P.L.; Losic, D.; Kurkuri, M.D. Unveiling cutting-edge advances in high surface area porous materials for the efficient removal of toxic metal ions from water. Prog. Mat. Sci. 2024, 146, 101314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.K.; Gu, S. The mechanism for thermal decomposition of cellulose and its main products. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 6496–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornaghi, H.L.; Ornaghi, F.G.; Neves, R.M.; Monticeli, F.; Bianchi, O. Mechanisms involved in thermal degradation of lignocellulosic fibers: A survey based on chemical composition. Cellulose 2020, 27, 4949–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, G.B.; Jamiu, W.; Okoro, H.K.; Okeola, F.O.; Adesina, A.K.; Feyisetan, O.A. Kinetics, Thermodynamics and Isothermal Modelling of Liquid Phase Adsorption of Methylene Blue onto Moringa Pod Husk Activated Carbon. S. Afr. J. Chem. 2019, 72, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhaleefa, A.; Ali, I.H.; Brima, E.I.; Shigidi, I.; Elhag, A.B.; Karama, B. Evaluation of the Adsorption Efficiency on the Removal of Lead(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Azadirachta indica Leaves as an Adsorbent. Processes 2021, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, J. A general kinetic model for adsorption: Theoretical analysis and modelling. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 288, 111100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandani, S. Kinetics of liquid phase batch adsorption experiments. Adsorption 2021, 27, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, S.N.; Ighalo, J.O.; Aniagor, C.O.; Igwegbe, C.A. Removal of ibuprofen from aqueous media by adsorption: A comprehensive review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Aikat, K.; Halder, G. Biosorptive uptake of ibuprofen by chemically modified Parthenium hysterophorus derived biochar: Equilibrium, kinetics, thermodynamics and modelling. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 92, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, C. Adsorption of cephalexin: A decade of progress in adsorbent development and mechanistic insights. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 318, 100357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamdod, A.S.; Kumar, M.V.P. Adsorption of methylene blue, methyl orange, and crystal violet on microporous coconut shell activated carbon and its composite with chitosan: Isotherms and kinetics. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 5274–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, T.; Paikaray, S.; Mahajan, P. Applicability of the equilibrium adsorption isotherms and the statistical tools on to them: A case study for the adsorption of fluoride onto Mg-Fe-CO3 LDH. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2603, 012056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozmuta, L.M.; Cozmuta, A.M.; Peter, A.; Nicula, C.; Nsimba, E.B.; Tutu, H. The influence of pH on the adsorption of lead by Na-clinoptilolite: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Water SA 2012, 38, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamin, M.; Ghouri, Z.K.; Rohman, N.; Syed, J.A.; Skelton, A.; Ahmed, K. Unravelling pH/pKa influence on pH-responsive drug carriers: Insights from ibuprofen-silica interactions and comparative analysis with carbon nanotubes, sulfasalazine, and alendronate. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2024, 128, 108720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayati, A.; Tanhaei, B.; Beiki, H.; Krivoshapkin, P.; Krivoshapkina, E.; Tracey, C. Insight into the adsorptive removal of ibuprofen using porous carbonaceous materials: A review. Chemosphere 2023, 323, 138241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labuto, G.; Carvalho, A.P.; Mestre, A.S.; dos Santos, M.S.; Modesto, H.R.; Martins, T.D.; Lemos, S.G.; da Silva, H.G.T.; Neide, E.; Carrilho, E.N.V.M.; et al. Individual and competitive adsorption of ibuprofen and caffeine from primary sewage effluent by yeast-based activated carbon and magnetic carbon nanocomposite. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 28, 100703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Chaubey, A.K.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D. Aqueous ibuprofen sorption by using activated walnut shell biochar: Process optimization and cost estimation. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2022, 1, 530–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Show, S.; Banerjee, S.; Halder, G. Mechanistic insight into sorptive elimination of ibuprofen employing bidirectional activated biochar from sugarcane bagasse: Performance evaluation and cost estimation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5287–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccar, R.; Sarra, M.; Bouzid, J.; Feki, M.; Blanquez, P. Removal of pharmaceutical compounds by activated carbon prepared from agricultural by-product. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 211–212, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedidi, H.; Reinert, L.; Leveque, J.M.; Soneda, Y.; Bellakhal, N.; Duclaux, N. The effects of the surface oxidation of activated carbon, the solution pH and the temperature on adsorption of ibuprofen. Carbon 2013, 54, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| EDX (Weight%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Mg | Ca | S | Cl | K |
| 61.22 | 37.83 | 0.11 | 0.28 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.33 |
| PFO | PSO | IPD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qo (mg/g) | 31.66 | qe (mg/g) | 27.23 | C (mg/g) | 27.23 |
| b (L/mg) | 0.102 | 1/n | 2.56 | Ki (g/g·min1/2) | 1.43 |
| R2 | 0.9918 | kf | 1.007 | R2 | 0.8187 |
| R2 | 0.8475 | EPA (%) | 23.44 | ||
| ESA (%) | 76.56 | ||||
| ∆Ho (KJ/mol) | ∆So (KJ/mol) | Temperature (K) | ∆Go (KJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| −1 × 10−3 | 3 × 10−3 | 25 | −4.88 |
| 30 | −2.87 | ||
| 35 | −2.10 | ||
| 40 | −1.97 | ||
| 45 | −1.89 |
| Langmuir | Freundlich | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Qo (mg/g) | 24.91 | qe (mg/g) | 2.4 |
| b (L/mg) | 0.0367 | 1/n | 3.12 |
| R2 | 0.9957 | kf | 0.053 |
| MPSD | 2.32 | R2 | 0.8836 |
| RMSE | 3.68 | MPSD | 17.69 |
| Experimental qe (mg/g) 26.58 | RMSE | 22.57 |
| Biosorbent | qe (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon/magnetite NP | 51.00 | [32] |
| Blend carbon | 45.58 | [5] |
| Pomegranate husk/Fe(II)–Fe(III) NP | 39.80 | |
| Stem of rose geranium | 34.88 | This study |
| Biochar from walnut shells | 30.10 | [33] |
| Hemp seeds-MnO/CuO | 26.50 | [4] |
| Sugarcane waste | 13.51 | [34] |
| Carbon from olive seeds | 9.090 | [35] |
| Mugwort leaves | 6.800 | [36] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shooto, N.D.; Thabede, P.M. Adsorption of Ibuprofen from Water Using Waste from Rose Geranium (Pelargonium graveolens) Stems. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7203. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137203
Shooto ND, Thabede PM. Adsorption of Ibuprofen from Water Using Waste from Rose Geranium (Pelargonium graveolens) Stems. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(13):7203. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137203
Chicago/Turabian StyleShooto, Ntaote David, and Patience Mapule Thabede. 2025. "Adsorption of Ibuprofen from Water Using Waste from Rose Geranium (Pelargonium graveolens) Stems" Applied Sciences 15, no. 13: 7203. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137203
APA StyleShooto, N. D., & Thabede, P. M. (2025). Adsorption of Ibuprofen from Water Using Waste from Rose Geranium (Pelargonium graveolens) Stems. Applied Sciences, 15(13), 7203. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137203







