Ammonium and Phosphate Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Zeolite and Gravel: Kinetics and Adsorption Isotherms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design of Adsorption Kinetics
2.2. Experimental Design of Adsorption Isotherm
2.3. Thermodynamic Study
2.4. Chemical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
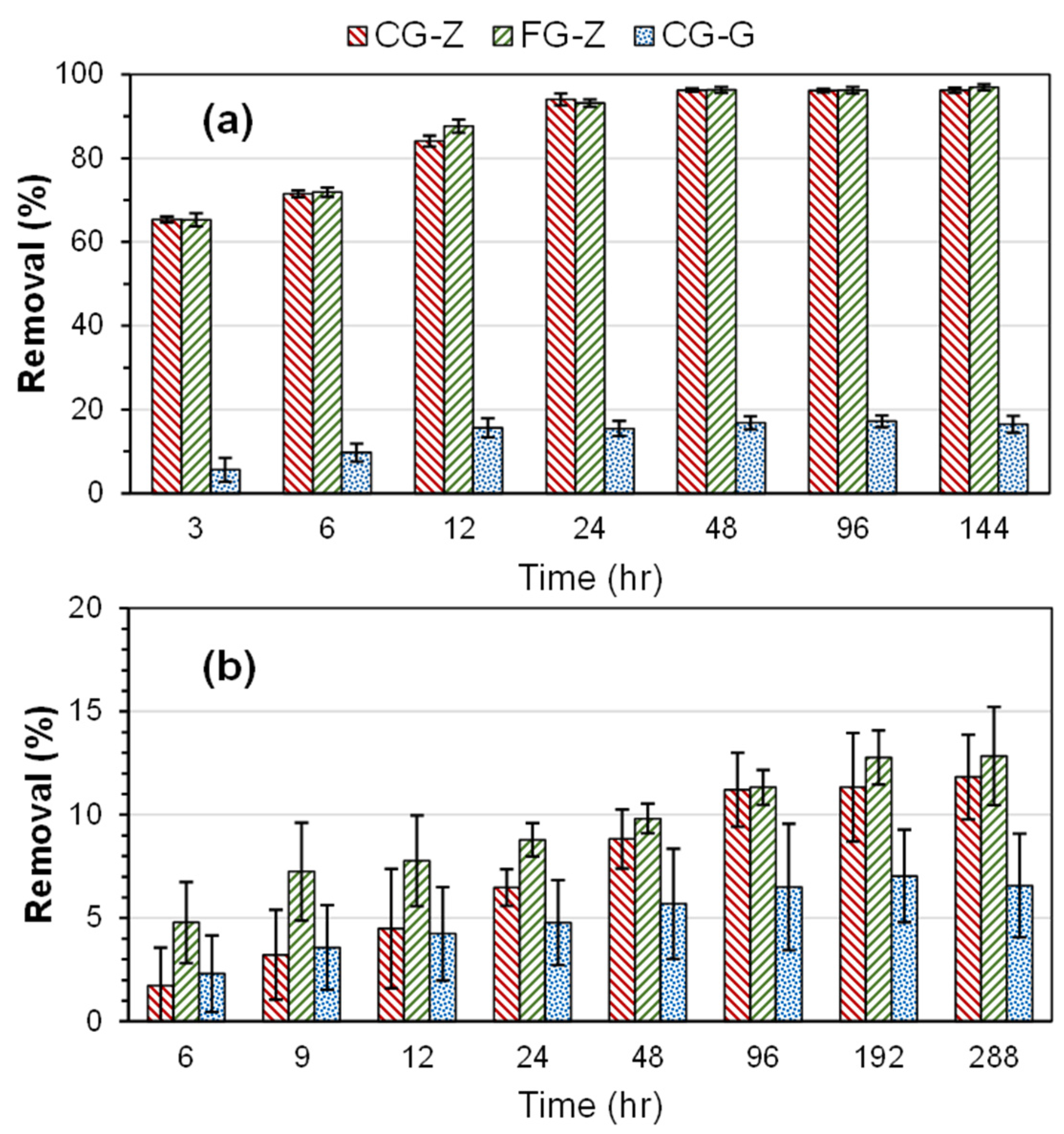
3.1. Adsorption Removal
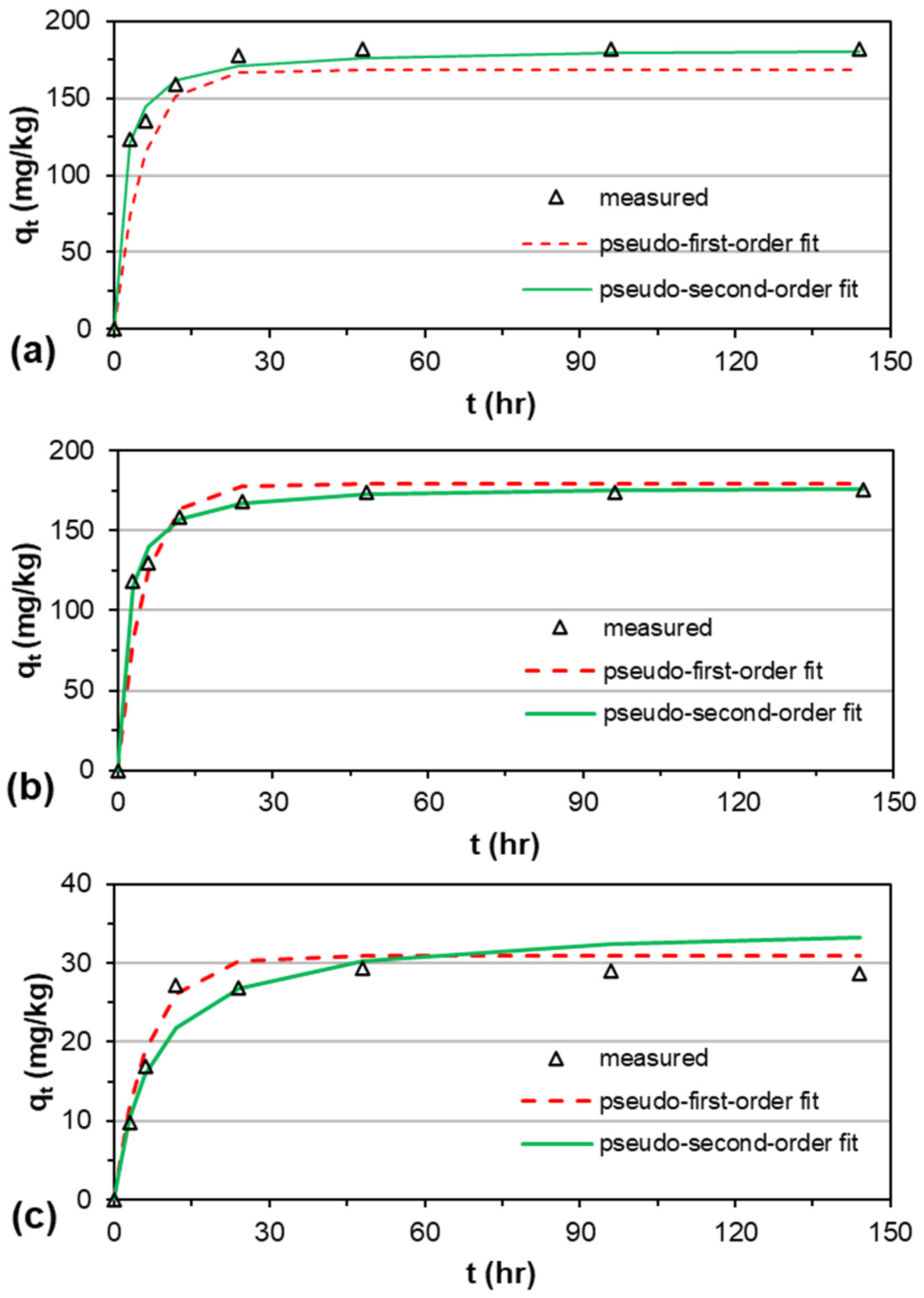
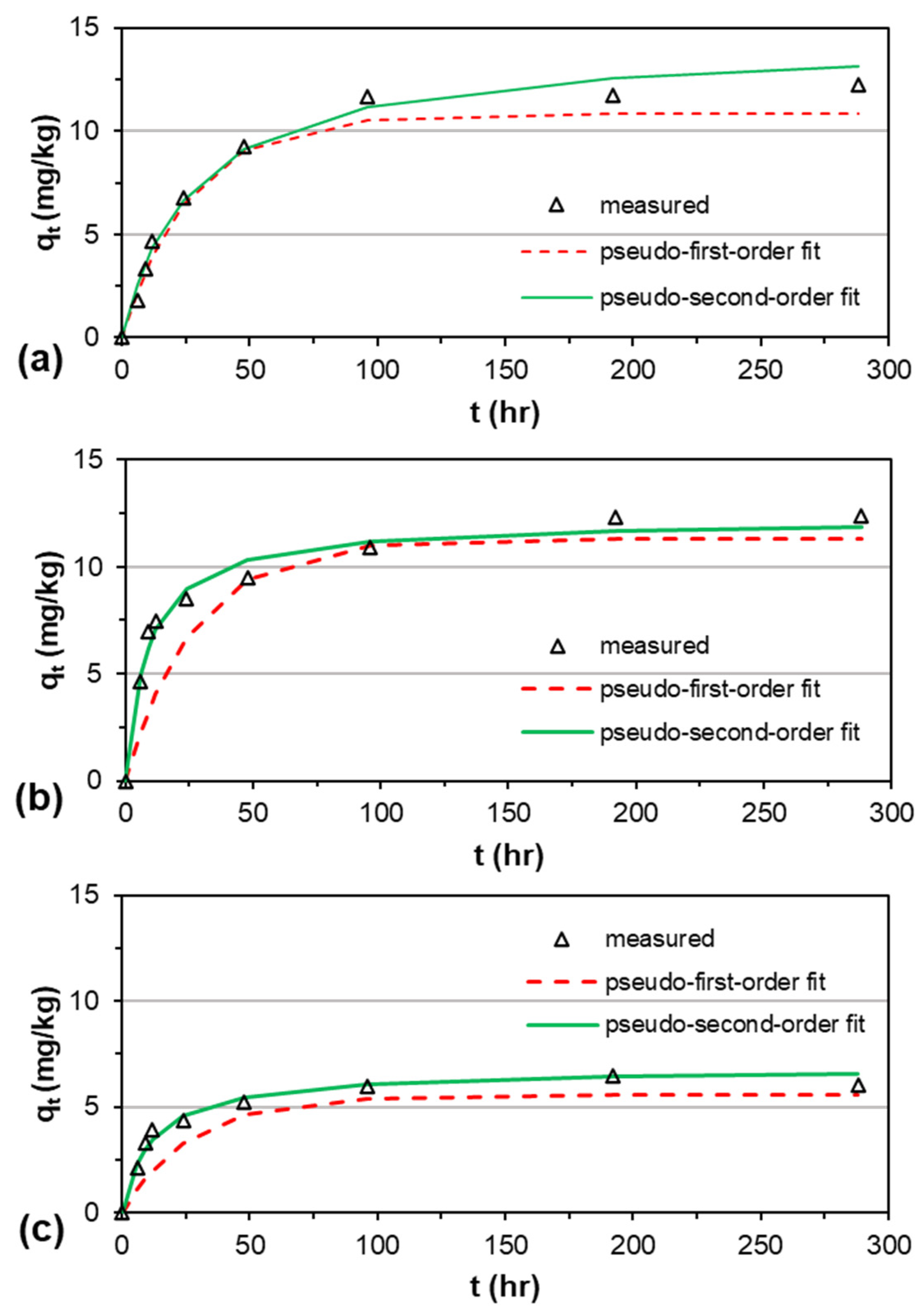
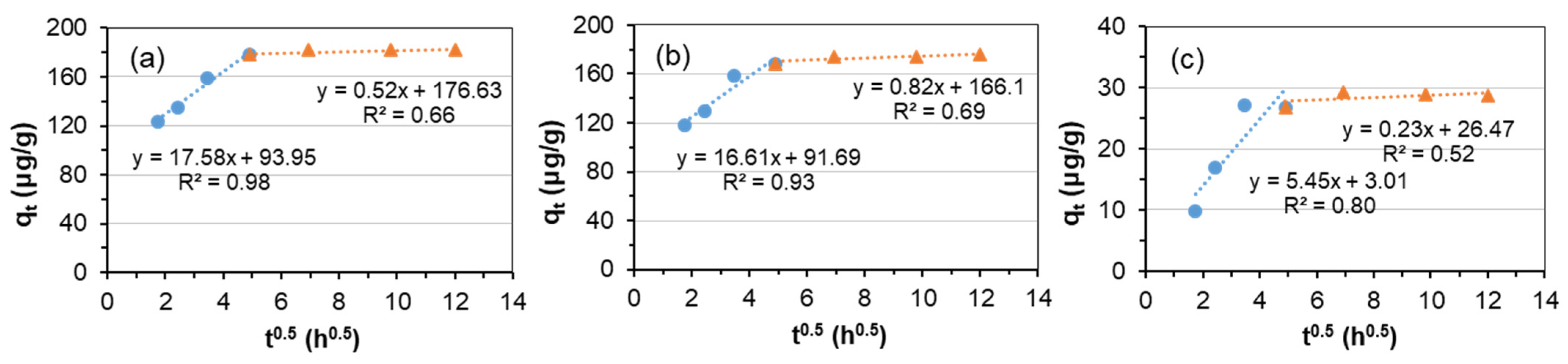
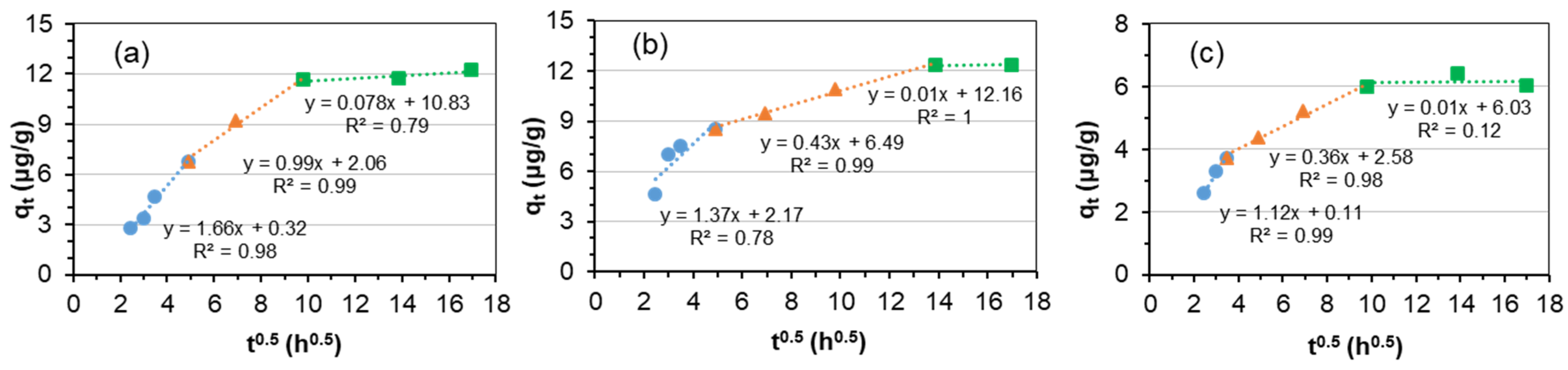
3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
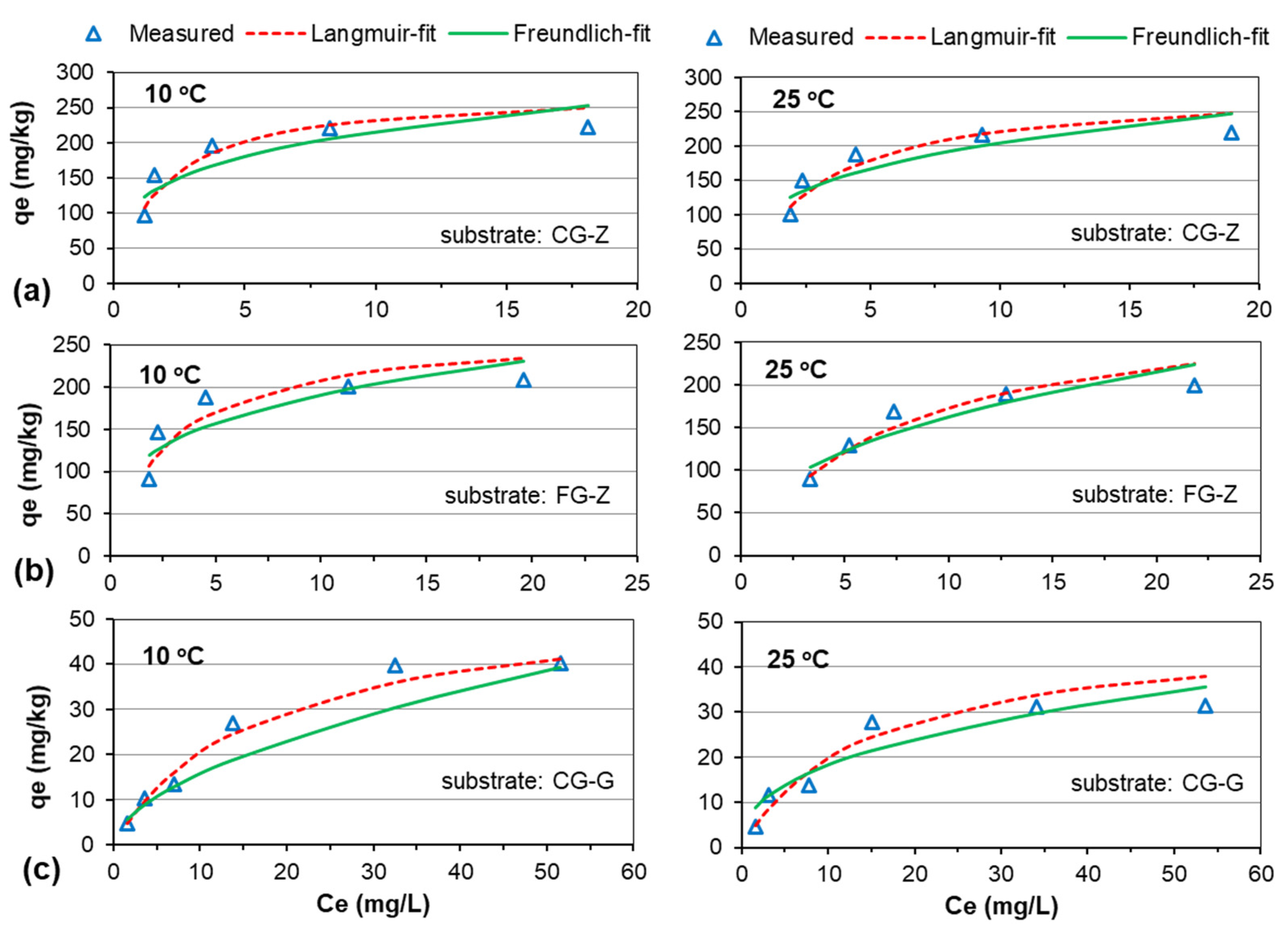
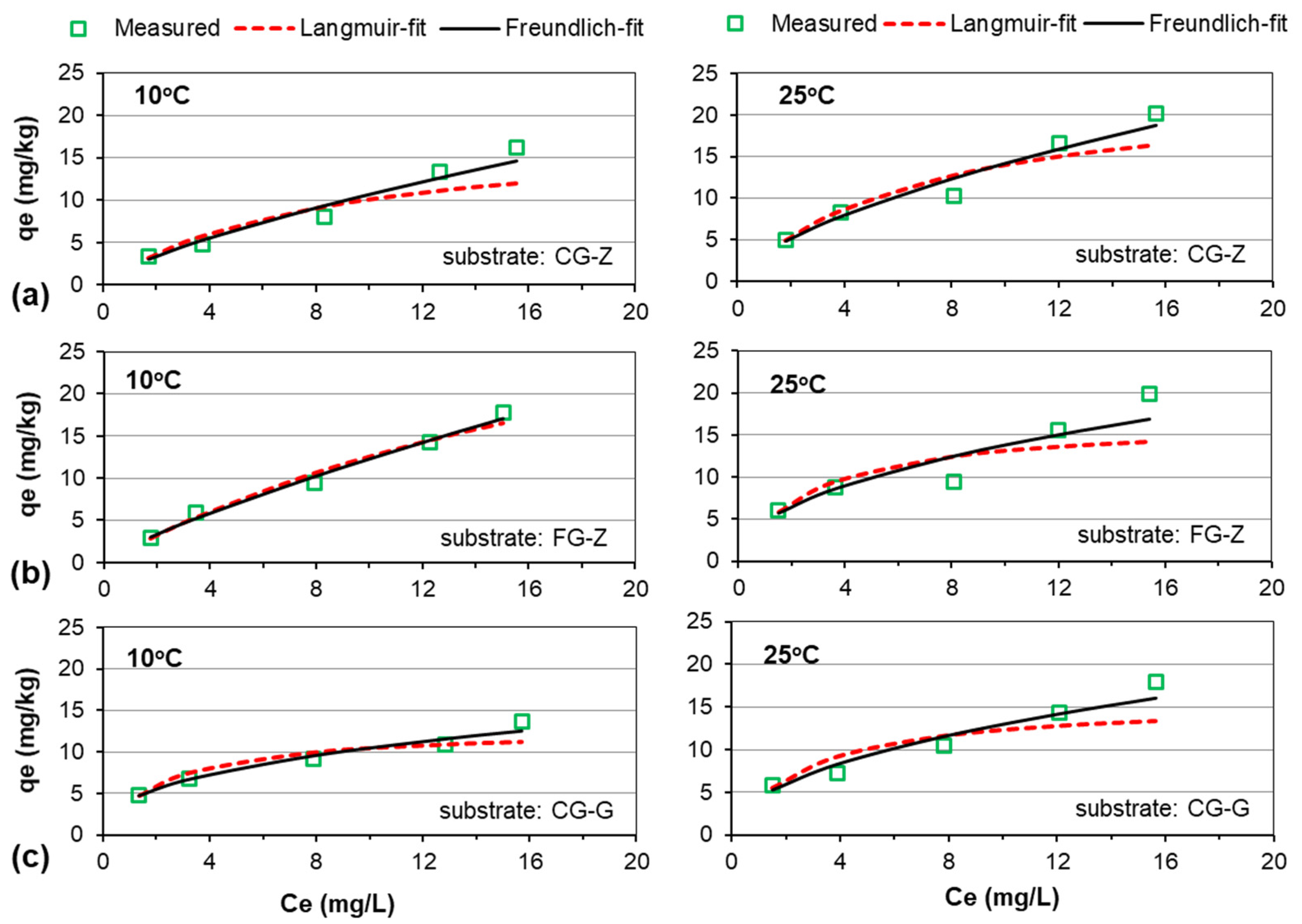
3.3. Adsorption Isotherms
3.4. Adsorption Thermodynamics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Zhao, D.; Ding, H. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal efficiency and denitrification kinetics of different substrates in constructed wetland. Water 2022, 14, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Q.; Wang, T.; Liao, J.; Shi, W.; Huang, Z.; Miao, H.; Wu, P.; Ruan, W. Operational performances and enzymatic activities for eutrophic water treatment by vertical-flow and horizontal-flow constructed wetlands. Water 2020, 12, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, I.; Darian, J.T.; Mokhtarani, B. Enhanced nitrogen adsorption capacity on Ca2+ ion-exchanged hierarchical X zeolite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 264, 118442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, G. Pathways of nitrogen and phosphorus utilization and removal from cyanobacteria wastewater by combining constructed wetlands with aerobic reactors. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Dong, J.H.; Huang, H.G.; Nie, J.X.; Du, X.; Tian, J.Y.; Zhang, W.X. Advanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal from groundwater by a composite functional particle-ceramic membrane bioreactor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 339, 126549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntountounakis, I.; Margaritou, I.-E.; Pervelis, I.; Kyrou, P.; Parlakidis, P.; Gikas, G.D. Pollutant removal efficiency of pilot-scale horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands treating landfill leachate. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muduli, M.; Choudharya, M.; Ray, S. A review on constructed wetlands for environmental and emerging contaminants removal from wastewater: Traditional and recent developments. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 30181–30220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melidis, P.; Gikas, G.D.; Akratos, C.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Dewatering of primary settled urban sludge in a vertical flow wetland. Desalination 2010, 250, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.; Bresciani, R.; Martinuzzi, N.; Masi, F. Online monitoring of a long-term full-scale constructed wetland for the treatment of winery wastewater in Italy. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlakidis, P.; Gounari, I.; Georgiou, A.; Adamidis, G.; Vryzas, Z.; Gikas, G.D. Removal of two triazole fungicides from agricultural wastewater in pilot-scale horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Agronomy 2023, 13, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retta, B.; Coppola, E.; Ciniglia, C.; Grilli, E. Constructed wetlands for the wastewater treatment: A review of Italian case studies. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaevangelou, V.; Gikas, G.D.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Effect of operational and design parameters on performance of pilot-scale vertical flow constructed wetlands treating university campus wastewater. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 5875–5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Wood, J.; Smith, D.; Thapa, A.; Aryal, N. A review on constructed treatment wetlands for removal of pollutants in the agricultural runoff. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Mao, W.; Pang, L.X.; Li, R.J.; Li, S.Q. Influence of Phragmites communis and Zizania aquatica on rhizosphere soil enzyme activity and bacterial community structure in a surface flow constructed wetland treating secondary domestic effluent in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 26141–26152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Long, Y.; Yu, G.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, S. A review on microorganisms in constructed wetlands for typical pollutant removal: Species, function, and diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 845725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Rodrigues, S.; Magalhães, M.; Rodrigues, K.; Pereira, L.; Marinho, G. A state-of-the-art review (2019–2023) on constructed wetlands for greywater treatment and reuse. Environ. Chall. 2024, 16, 100973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, A.; Ahn, Y. Constructed wetlands as sustainable ecotechnologies in decentralization practices: A review. Environ. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 180–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas Mendes, L.R. Edge-of-field technologies for phosphorus retention from agricultural drainage discharge. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H. Enhanced nitrogen removal of low C/N domestic wastewater using a biochar-amended aerated vertical flow constructed wetland. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitosa, A.P.; Rodrigues, K.; Martins, W.E.; Rodrigues, S.M.P.R.; Pereira, L.; Silva, G.M.M. Enhancing greywater treatment: High-efficiency constructed wetlands with seashell and ceramic brick substrates. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Dong, H.; Zeng, G. Application of zeolite in removing salinity/sodicity from wastewater: A review of mechanisms, challenges and opportunities. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 1435–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, H.; Du, L.; Fu, X.; Guo, D.; Chen, Y. Effect of macroporous zeolite substrate on denitrification in tidal flow constructed wetland. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Miao, Y.; Dong, J.; Shen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, C. Enhanced nitrogen removal and microbial analysis in partially saturated constructed wetland for treating anaerobically digested swine wastewater. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlakidis, P.; Tokamani, M.; Sandaltzopoulos, R.; Tokatlidis, I.; Sinapidou, E.; Vryzas, Z. Evaluation of the removal efficacy of three fungicides by biomixtures: Impact of bioaugmentation by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and zeolite fortification. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 104, 6089–6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhou, Q.; Tao, M.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wu, Z. Comparative study of microbial community structure in different filter media of constructed wetland. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Duan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yue, B. The removal efficiency of constructed wetlands filled with the zeolite-slag hybrid substrate for the rural landfill leachate treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 17547–17555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Xu, C.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Q. Enhanced nitrogen removal reliability and efficiency in integrated constructed wetland microcosms using zeolite. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2012, 6, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mashaqbeh, O.; Alsalhi, L.; Salaymeh, L.; Dotro, G.; Lyu, T. Treatment of pharmaceutical industry wastewater for water reuse in Jordan using hybrid constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 939, 173634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlakidis, P.; Mavropoulos, T.; Vryzas, Z.; Gikas, G.D. Fluopyram removal from agricultural equipment rinsing water using HSF pilot-scale constructed wetlands. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 29584–29596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Xu, Z.; Li, H. Clogging mechanism in vertical-flow constructed wetlands: Clogging cause and accumulation distribution characteristics. Environ. Sci. 2008, 29, 1508–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Sheng, L. Purification mechanism of sewage from constructed wetlands with zeolite substrates: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Bañuelos, G.; Yan, B.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, X.; Cheng, X. Constructed wetlands for saline wastewater treatment: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 98, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Ding, W. Ammonium removal from water by natural and modified zeolite: Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 55, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, N.; Srasra, E. Removal of phosphate ions from aqueous solution using Tunisian clays minerals and synthetic zeolite. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widiastuti, N.; Wu, H.; Ang, H.M.; Zhang, D. Removal of ammonium from greywater using natural zeolite. Desalination 2011, 277, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xiao, X.; Yan, B.; Yang, L. Ammonium removal from aqueous solutions by using natural Chinese (Chende) zeolite as adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Kinetic models for the sorption of dye from aqueous solution by wood. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 1998, 76, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gikas, G.D.; Vryzas, Z.; Koshis, Z. Experiments on fluometuron removal from simulated agricultural wastewater in porous media filters. Environ. Process. 2022, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J., Jr.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaya, D.; Valderrama, C.; Farran, A.; Armijos, C.; Cortina, J.L. Simultaneous phosphate and ammonium removal from aqueous solution by a hydrated aluminum oxide modified natural zeolite. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 271, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gikas, G.D. Water quality of drainage canals and assessment of nutrient loads using QUAL2Kw. Environ. Process. 2014, 1, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar]
- Aljeboree, A.M.; Alshirifi, A.N.; Alkaim, A.F. Kinetics and equilibrium study for the adsorption of textile dyes on coconut shell activated carbon. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3381–S3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.; Ramalingam, S.; Senthamarai, C.; Niranjanaa, M.; Vijayalakshmi, P.; Sivanesan, S. Adsorption of dye from aqueous solution by cashew nut shell: Studies on equilibrium isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics of interactions. Desalination 2010, 261, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Is the free energy change of adsorption correctly calculated? J. Chem. Eng. Data 2009, 54, 1981–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltalı, K.; Sarı, A.; Aydın, M. Removal of ammonium ion from aqueous solution by natural Turkish (Yıldızeli) zeolite for environmental quality. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste Water, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Montalvo, S.; Guerrero, L.; Milán, Z.; Borja, R. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal using a novel integrated system of natural zeolite and lime. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2011, 46, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, E.; Araya, F.; Vera, I.; Pozo, G.; Vidal, G. Phosphate removal using zeolite in treatment wetlands under different oxidation-reduction potentials. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 117, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlec, R.H.; Wallace, S.D. Treatment Wetlands, 2nd ed.; CRC Press/Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-1-56670-526-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Sheng, L.; Xu, J. Clogging mechanisms of constructed wetlands: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, I.; Araya, F.; Andrés, E.; Sáez, K.; Vidal, G. Enhanced phosphorus removal from sewage in mesocosm-scale constructed wetland using zeolite as medium and artificial aeration. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotoulas, A.; Agathou, D.; Triantaphyllidou, I.E.; Tatoulis, T.I.; Akratos, C.S.; Tekerlekopoulou, A.G.; Vayenas, D.V. Zeolite as a potential medium for ammonium recovery and second cheese whey treatment. Water 2019, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddeo, R.; Prajapati, S.; Lepistö, R. Optimizing ammonium adsorption on natural zeolite for wastewaters with high loads of ammonium and solids. J. Porous Mater. 2017, 24, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Ramos, R.; Aguilar-Armenta, G.; Gonzalez-Gutierrez, L.V.; Guerrero-Coronado, R.M.; Mendoza-Barron, J. Ammonia exchange on clinoptilolite from mineral deposits located in Mexico. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 79, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyath, A.M.; Mahbub, P.; Goonetilleke, A.; Adebajo, M.O.; Kokot, S.; Oloyede, A. Influence of physical and chemical parameters on the treatment of heavy metals in polluted stormwater using zeolite: A review. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2011, 3, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mery, C.; Guerrero, L.; Alonso-Gutiérrez, J.; Figueroa, M.; Lema, J.M.; Montalvo, S.; Borja, R. Evaluation of natural zeolite as microorganism support medium in nitrifying batch reactors: Influence of zeolite particle size. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2012, 47, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Senila, L.; Hoaghia, A.; Moldovan, A.; Török, I.A.; Kovacs, D.; Simedru, D.; Tomoiag, C.H.; Senila, M. The potential application of natural clinoptilolite-rich zeolite as support for bacterial community formation for wastewater treatment. Materials 2022, 15, 3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, M.; AbuKhadra, M.R.; Nasief, F.M.; El-Salam, H.A. Removal of ammonia from aqueous solutions, ground water, and wastewater using mechanically activated clinoptilolite and synthetic zeolite-a: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zhang, C. Study on phosphorus removal pathway in constructed wetlands with thermally modified sepiolite. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Tang, W.; Pei, Y. Constructed wetland substrates: A review on development, function mechanisms, and application in contaminants removal. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, R.; Cao, Y.; Wang, G.; Ji, L.; Xu, Y. Effects of different substrates on nitrogen and phosphorus removal in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 16229–16238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Rethinking of the intraparticle diffusion adsorption kinetics model: Interpretation, solving methods and applications. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, A.D.; Parameswaran, P. Ammonia adsorption and recovery from swine wastewater permeate using naturally occurring clinoptilolite. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 43, 102234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Hernández, R.; Padilla, I.; López-Andrés, S.; López-Delgado, A. Al-waste-based zeolite adsorbent used for the removal of ammonium from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1256197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho, I.; Licon, E.; Valderrama, C.; de Arespacochaga, N.; López-Palau, S.; Cortina, J.L. Recovery of ammonia from domestic wastewater effluents as liquid fertilizers by integration of natural zeolites and hollow fibre membrane contactors. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-B.; Lin, H. Ammonia nitrogen removal from aqueous solution using zeolite modified by microwave-sodium acetate. J. Cent. South Univ. 2016, 23, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yang, L.; Xue, Q.; Liu, J.; Hou, L.; Ding, L. Removal of ammonium from swine wastewater by zeolite combined with chlorination for regeneration. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 160, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Du, J.; Chen, P.; Huang, X.; Chen, O. Enhanced efficiency of swine wastewater treatment by the composite of modified zeolite and a bioflocculant enriched from biological sludge. Environ. Technol. 2017, 39, 3096–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Sartaj, M. Statistical analysis and optimization of ammonia removal from aqueous solution by zeolite using factorial design and response surface methodology. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakadevan, K.; Bavor, H.J. Phosphate adsorption characteristics of soils, slags and zeolite to be used as substrates in constructed wetland systems. Water Res. 1998, 32, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; Wang, L. Preferable adsorption of phosphate using lanthanum-incorporated porous zeolite: Characteristics and mechanism. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 426, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, L.; Zamora-Castro, S.A.; Vidal-Álvarez, M.; Marín-Muñiz, J.L. Role of wetland plants and use of ornamental flowering plants in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: A review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofiera, L.M.; Bose, P.; Kazner, C. Removal of heavy metals and bulk organics towards application in modified constructed wetlands using activated carbon and zeolites. Water 2024, 16, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, H.; Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; Cheng, H.; Wang, H.; Cao, L. Ammonia-nitrogen and phosphates sorption from simulated reclaimed waters by modified clinoptilolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 229, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshameri, A.; Yan, C.; Al-Ani, Y.; Dawood, A.S.; Ibrahim, A.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H. An investigation into the adsorption removal of ammonium by salt activated Chinese (Hulaodu) natural zeolite: Kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Substrate | qe,m mg/kg | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe,c mg/kg | k1 1/h | R2 | NOF | MAE | qe,c mg/kg | k2 kg/(mg h) | R2 | NOF | MAE | ||
| Ammonium | |||||||||||
| CG-Z | 181.87 | 168.57 | 0.083 | 0.94 | 0.14 | 18.51 | 181.81 | 0.0036 | 0.99 | 0.03 | 4.66 |
| FG-Z | 174.23 | 179.47 | 0.088 | 0.95 | 0.09 | 9.92 | 178.57 | 0.0034 | 0.99 | 0.03 | 2.87 |
| CG-G | 29.34 | 30.94 | 0.067 | 0.97 | 0.09 | 1.96 | 34.84 | 0.0039 | 0.87 | 0.13 | 2.26 |
| Phosphate | |||||||||||
| CG-Z | 11.76 | 10.84 | 0.0163 | 0.98 | 0.10 | 0.66 | 13.38 | 0.0025 | 0.98 | 0.07 | 0.46 |
| FG-Z | 12.35 | 11.30 | 0.0162 | 0.92 | 0.24 | 1.71 | 12.24 | 0.0093 | 0.95 | 0.06 | 0.53 |
| CG-G | 6.44 | 5.56 | 0.0159 | 0.92 | 0.29 | 1.04 | 6.82 | 0.0123 | 0.98 | 0.07 | 0.26 |
| Parameters | CG-Z | FG-Z | CG-G | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonium | ||||
| Kid1 | mg/(kg·h0.5) | 17.58 | 16.61 | 5.45 |
| C1 | mg/kg | 93.95 | 91.69 | 3.01 |
| R12 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.80 | |
| Kid2 | mg/(kg·h0.5) | 0.52 | 0.82 | 0.01 |
| C2 | mg/kg | 176.63 | 166.1 | 6.03 |
| R22 | 0.66 | 0.69 | 0.12 | |
| Phosphate | ||||
| Kid1 | mg/(kg·h0.5) | 1.66 | 1.37 | 1.12 |
| C1 | mg/kg | 0.32 | 2.17 | 0.11 |
| R12 | 0.98 | 0.78 | 0.99 | |
| Kid2 | mg/(kg·h0.5) | 0.99 | 0.43 | 0.36 |
| C2 | mg/kg | 2.06 | 6.49 | 2.58 |
| R22 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 | |
| Kid3 | mg/(kg·h0.5) | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| C3 | mg/kg | 10.83 | 12.16 | 6.03 |
| R32 | 0.79 | 1.0 | 0.12 |
| Substrate | T (°C) | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg/kg) | kL (L/mg) | R2 | 1/n | kF (mg/kg) | R2 | ||
| CG-Z | 10 | 275.02 | 0.548 | 0.89 | 0.26 | 118.03 | 0.74 |
| 25 | 286.93 | 0.340 | 0.88 | 0.29 | 103.87 | 0.76 | |
| FG-Z | 10 | 268.00 | 0.352 | 0.81 | 0.28 | 100.45 | 0.71 |
| 25 | 285.71 | 0.142 | 0.91 | 0.41 | 63.03 | 0.83 | |
| CG-G | 10 | 54.79 | 0.059 | 0.98 | 0.56 | 4.34 | 0.93 |
| 25 | 48.33 | 0.068 | 0.93 | 0.40 | 7.31 | 0.88 | |
| Substrate | T (°C) | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg/kg) | kL (L/mg) | R2 | 1/n | kF (mg/kg) | R2 | ||
| CG-Z | 10 | 18.14 | 0.12 | 0.90 | 0.72 | 2.05 | 0.97 |
| 25 | 23.71 | 0.14 | 0.90 | 0.63 | 3.34 | 0.96 | |
| FG-Z | 10 | 24.15 | 0.08 | 0.98 | 0.69 | 2.12 | 0.99 |
| 25 | 16.80 | 0.36 | 0.72 | 0.47 | 4.71 | 0.87 | |
| CG-G | 10 | 12.81 | 0.43 | 0.87 | 0.40 | 4.20 | 0.96 |
| 25 | 15.65 | 0.36 | 0.80 | 0.48 | 4.34 | 0.95 | |
| Substrate | T (K) | Kd | ΔG (kJ/mol) | ΔH (kJ/mol) | ΔS (kJ/(mol K)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonium | |||||
| CG-Z | 283 | 5.41 | −4.00 | 0.54 | 0.016 |
| 298 | 5.48 | −4.18 | |||
| FG-Z | 283 | 4.84 | −3.71 | 2.81 | 0.023 |
| 298 | 5.14 | −4.06 | |||
| CG-G | 283 | 1.10 | −0.22 | −16.79 | −0.059 |
| 298 | 0.77 | 0.66 | |||
| Orthophosphate | |||||
| CG-Z | 283 | 0.94 | 0.15 | 6.69 | 0.023 |
| 298 | 1.08 | −0.20 | |||
| FG-Z | 283 | 0.87 | 0.34 | 4.34 | 0.014 |
| 298 | 0.95 | 0.13 | |||
| CG-G | 283 | 0.56 | 1.36 | 20.09 | 0.066 |
| 0.86 | 0.37 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gikas, G.D.; Parlakidis, P.; Chamalis, N. Ammonium and Phosphate Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Zeolite and Gravel: Kinetics and Adsorption Isotherms. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7189. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137189
Gikas GD, Parlakidis P, Chamalis N. Ammonium and Phosphate Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Zeolite and Gravel: Kinetics and Adsorption Isotherms. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(13):7189. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137189
Chicago/Turabian StyleGikas, Georgios D., Paraskevas Parlakidis, and Neofytos Chamalis. 2025. "Ammonium and Phosphate Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Zeolite and Gravel: Kinetics and Adsorption Isotherms" Applied Sciences 15, no. 13: 7189. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137189
APA StyleGikas, G. D., Parlakidis, P., & Chamalis, N. (2025). Ammonium and Phosphate Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Zeolite and Gravel: Kinetics and Adsorption Isotherms. Applied Sciences, 15(13), 7189. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137189






