Abstract
Aquaculture effluents are a growing source of water pollution, releasing suspended solids, organic matter, nitrogen, and phosphorus into aquatic environments. Recirculating aquaculture systems (RASs) have emerged as a more sustainable solution, allowing water to be continuously treated and reused. Within RASs, coagulation–flocculation is a key treatment step due to its simplicity and effectiveness. Tannin-based coagulants have gained attention as natural alternatives to traditional chemical agents. Although natural coagulants have been studied in aquaculture, only a few works explore their use in continuous-flow systems. This study evaluates a chestnut shell-based (CS) coagulant applied in continuous mode for the post-treatment of aquaculture effluent. The performance of CS was compared with Tanfloc, aluminum sulfate, and ferric chloride in removing color and dissolved organic carbon (DOC). At natural pH (6.5) and 50 mg·L−1, CS and Tanfloc achieved color removal of 61.0% and 65.5%, respectively, outperforming chemical coagulants. For DOC, Tanfloc and chemical coagulants removed 45–50%, while CS removed 32%. All coagulants removed over 90% of phosphorus, but nitrogen removal was limited (30–40%). These results highlight the potential of tannin-derived coagulants, particularly from agro-industrial residues, as sustainable solutions for aquaculture wastewater treatment in continuous systems.
1. Introduction
Aquaculture holds significant importance in the fisheries sector and serves as a vital source of nutrition for large populations globally. The industry experienced an average annual growth rate of 9.8% between 1980 and 2000 and 5.8% between 2000 and 2016 [1]. In 2022, global aquaculture production reached a record high of 130.9 million tons, comprising 94.4 million tons of aquatic animals and 36.5 million tons of algae (including seaweed and microalgae) [2,3]. The estimated farm-gate value of this production in 2022 was USD 312.8 billion, with aquatic animals accounting for USD 295.7 billion and algae for USD 17 billion [3]. However, this growth comes at a cost. A comprehensive report from the Food and Agriculture Organization highlights the ongoing depletion of marine fish stocks [4], being necessary to promote awareness about preserving global fishery resources. Measures such as fishing regulations and marine conservation efforts aim to achieve a balance between sustaining the environment and meeting food demands. Since the 1990s, wild-capture fisheries have reached a production plateau [5], making aquaculture a promising alternative to address the growing demand for seafood. Aquaculture has emerged as one of the most rapidly expanding industries in global food production [6], contributing 46% of the total aquatic food output in 2018 and providing 52% of the fish consumed worldwide [2].
Although aquaculture is widely regarded as a potential solution to meet global food demands, some researchers caution that its future growth may be hindered by several challenges, particularly the limited availability of high-quality water resources [7]. In this context, it is crucial to implement advanced monitoring strategies capable of detecting pollutants at very low concentrations. Biomonitoring approaches using living organisms have shown great promise for continuous environmental surveillance [8]. Additionally, emerging single-molecule detection tools offer ultrasensitive alternatives for identifying trace levels of toxic compounds, enabling more proactive and precise management of aquaculture systems [9]. Nevertheless, there is still a lack of comprehensive scientific research on the environmental implications of aquaculture practices. Key areas of concern include waste management, the use of growth-enhancing substances such as antibiotics and hormones, their impact on ecosystems, and the effectiveness of wastewater treatment techniques within the industry [7]. Aquaculture effluents are increasingly recognized as a significant source of pollution, releasing suspended solids, dissolved organic matter, nitrogen, phosphorus, and other harmful compounds into water bodies, which can pose serious environmental risks [10].
Among existing technologies, recirculating aquaculture systems (RASs) have become increasingly popular in modern aquaculture as they offer a more sustainable solution by continuously treating and reusing water through several purification stages. This process significantly reduces the need for fresh water inputs and minimizes pollutant concentrations in the effluents discharged. As the industry expands, regulatory requirements for effluent treatment are expected to become more stringent. For example, to produce 1000 tons of fish annually, approximately 3 tons of feed are required daily. Assuming a feed conversion ratio of 1.1 and a feed loss of 1%, the system could discharge roughly 35 kg of total phosphorus and 877 kg of total chemical oxygen demand (COD) each day [11]. Given the production of effluent with high pollutant charges and serious environmental risks [10], it is necessary to treat this water efficiently so it can be recycled into the system.
Effluent streams in RASs typically fall into two categories: one with high suspended solids, originating from drum filter and biofilter backwash, and another with lower solids content, resulting from water exchange overflow. Coagulation–flocculation is considered to be one of the most essential methods for wastewater treatment, being applied in different industrial sectors as demonstrated in the reviewer research of Hizam et al. [12], especially in aquaculture systems [7,13]. Conventional coagulants, such as those based on aluminum and iron, have notable drawbacks. These include the production of large volumes of sludge, strong pH dependency—which raises operational costs—and the presence of residual metals like aluminum and iron in the treated water [14]. As a result, there is growing interest in exploring alternative solutions, particularly those involving natural coagulants.
Environmentally friendly coagulants are designed to support sustainable development and green technology principles. Sourced from renewable biological origins such as plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria, these coagulants are typically biodegradable, non-toxic, non-corrosive, and economically viable [15]. Among them, tannin-based coagulants have garnered considerable scientific attention over the past decade [16]. Traditionally obtained from tree-derived biomass, tannin production can face certain limitations, including seasonal variability, storage difficulties, land use conflicts that may impact food production, and high water demands for cultivation [17]. Therefore, identifying alternative sources—particularly those derived from agricultural or vegetable residues—not only adds value to waste materials but also reinforces the circular economy framework.
Aquaculture is one of the main sectors where natural coagulants have been tested and applied for research purposes [14,18,19,20,21,22]. However, there is a research gap due to the predominance of lab-scale experiments conducted in batch mode, with most results obtained from jar tests. This study aims to evaluate the performance of a tannin-based coagulant derived from chestnut shells to treat real aquaculture wastewater under continuous flow conditions. The treatment was conducted in a laboratory-scale continuous coagulation/flocculation system, focusing on the removal of color, organic matter, phosphorus, and nitrogen from the final effluent of the Clarias gariepinus (African catfish) production line, which is recirculated back to the fish tank. For comparison, the chestnut shell-based coagulant was assessed alongside one commercial natural coagulant (Tanfloc SG) and two conventional chemical coagulants (Al2(SO4)3·14H2O and FeCl3·6H2O).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Coagulants
The preparation of a coagulant derived from chestnut shells begins with the extraction of tannins from the raw material, following established protocols found in the literature [23]. Residual chestnut shells were generously provided by Secas e Boas, a chestnut dehydration company based in Celorico da Beira, Portugal. After extraction, the tannins were obtained by freeze-drying the extract, which was stored at 4 °C until used in subsequent procedures. The chemical modification process was carried out according to methodologies previously described in the literature [24,25,26]. Specifically, 2 g of the freeze-dried tannins were dissolved in 7 mL of distilled water and stirred continuously while being heated to approximately 55 °C, resulting in a homogeneous solution after roughly one hour. In a separate step, a Mannich solution (MS) was prepared by mixing commercial aqueous formaldehyde (37% w/w, reagent grade, obtained from Absolve and distributed by JMS—Rebordosa, Portugal) with ammonium chloride (reagent grade, VWR Chemicals, Leuven, Belgium). This mixture was refluxed for 3 h and then cooled to 55 °C. After this, the MS was added to the tannin solution, and the temperature was raised to 85 °C. Although prior studies indicate the reaction between tannins and MS typically requires 5 to 8 h [25,26,27], a uniform and viscous product was achieved after just 3 h. More information regarding tannin-based coagulant production and characterization can be found in the work by Tomasi, et al. [25]. Additionally, Tanfloc SG was kindly supplied by TANAC (Montenegro, Brazil), and aluminum sulfate (Al2(SO4)3·14H2O) and ferric chloride (FeCl3·6H2O) were sourced from JMS Lda (Portugal) and Chem-Lab (Zedelgem, Belgium), respectively.
2.2. Water Samples
Aquaculture wastewater was collected from the aquaculture system at Leiria Polytechnic Institute in Leiria, Portugal, during the winter (February 2025). The entire system is shown in Figure 1. The operation of the aquaponics system relies on continuous water circulation. The cycle initiates in the fish tank (Tank 1), from which water flows into the drum filter (Tank 2) for mechanical filtration. Following this stage, the water enters the biological filter (Tank 3), where nitrifying bacteria convert ammonia into nitrate, rendering the water nutrient-rich for plant use. Next, the water moves to the grow bed, where plants are supported on floating rafts and absorb the available nutrients to support their development. From there, the flow proceeds to the sump reservoir (Tank 5), where a submersible pump returns the treated water to the fish tank, thus completing the cycle. An additional component—a conical sedimentation tank (Tank 6)—was integrated into the system to handle surplus water from the drum filter (Tank 2). This excess water, instead of being wasted, is redirected and reused through a connection between Tank 6 and the sump reservoir (Tank 5). The design takes advantage of gravity to facilitate water movement throughout the system. Water sampling focused on challenges frequently observed by system operators. The aquaculture system houses Clarias gariepinus, commonly known as the African catfish, a species widely farmed for its ability to thrive in high-density environments and tolerate low-quality water conditions [28]. Known for its adaptability, this species can withstand challenging factors such as low dissolved oxygen, elevated ammonia levels, and increased salinity [29]. However, a significant drawback of this setup is its rapid digestive process, which results in a higher production of organic waste and, consequently, a decline in water quality. The increased organic matter contributes to intensified water coloration, particularly in the sump reservoir (Tank 5), where the water took on a yellowish-brown hue. This coloration impaired the visibility of the fish when the water was returned to the main tank (Tank 1). To mitigate this issue, samples were specifically taken from Tank 5 just before the water was recirculated to the fish tank. Reducing color intensity at this point is essential for improving water clarity and ensuring better visibility of fish.
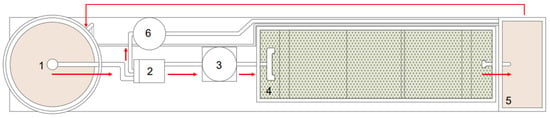
Figure 1.
Aquaculture system at the Leiria Polytechnic Institute. Components: (1) fish tank; (2) drum filter; (3) biological filter; (4) grow bed; (5) sump reservoir; and (6) conical sedimentation tank.
There is currently no specific regulatory framework that governs aquaponic systems. Nevertheless, the stability and efficiency of aquaponics rely heavily on maintaining appropriate water quality to support the three interconnected components: aquatic animals, plants, and nitrifying microorganisms. As outlined by Somerville, et al. [30], the conditions include maintaining a pH between 6 and 7, temperatures ranging from 18 to 30 °C, dissolved oxygen levels between 5 and 8 mg·L−1, and nitrate concentrations from 5 to 150 mg·L−1—equivalent to approximately 1.1 to 33.4 mg·L−1 of total nitrogen. Beyond these primary parameters, managing the availability of essential nutrients—especially potassium, magnesium, calcium, and iron—presents a significant horticultural challenge in aquaponic systems [31]. The water sample was analyzed for nutrient content (K, Mg, Na, Ca, N, and P), organic matter concentration, and color intensity, as presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Physicochemical properties of aquaculture wastewater.
2.3. Continuous Flow Experimental Setup and Operational Conditions
Laboratory-scale experiments were conducted in continuous flow mode under optimal pH and dosage conditions previously determined through jar testing by Tomasi et al. [14]. The experimental configuration was developed according to Edeline [32] and is illustrated in Figure 2. It included a 100 mL stirred reactor with a residence time of 5 min, where rapid mixing was facilitated using a magnetic stirrer. The aquaculture effluent was fed into the system at a constant flow rate of 20 mL·min−1 via a peristaltic pump, while the coagulant solution was introduced at a rate of 6.8 mL·min−1 using a dosing pump. The following optimal concentrations for each coagulant were used: Tanfloc at 25 mg·L−1 (pH 7), FeCl3·6H2O at 25 mg·L−1, Al2(SO4)3·14H2O at 20 mg·L−1, and the CS-based coagulant at 10 mg·L−1 (all at pH 8). To evaluate the influence of pH, different concentrations (20, 50, and 100 mg·L−1) were also applied under the natural pH of the water (around pH 6.5). Following coagulation, the mixture entered a 226 mL tubular reactor, designed to mimic the slow mixing phase, with an estimated residence time of 11 min. Settling took place in a U-shaped sedimentation tank equipped with dual outlet valves to separate sludge and the clarified effluent. After allowing the system to stabilize, effluent samples were collected after 45 min and analyzed for parameters such as final pH, color, dissolved organic carbon (DOC), natural organic matter (NOM), nitrite, total nitrogen, and phosphorus.
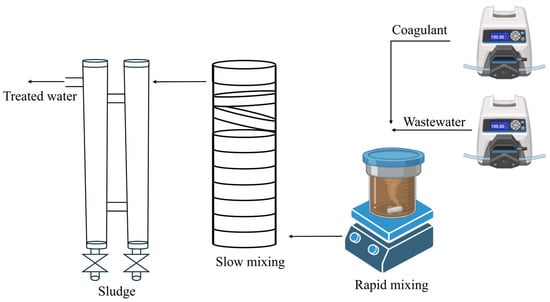
Figure 2.
Experimental setup used to perform coagulation–flocculation–sedimentation assays in continuous mode.
2.4. Analytical Methods
The pH of the samples was determined using a portable pH meter (HI 8424, HANNA Instruments, Padova, Italy). To evaluate dissolved organic carbon (DOC), samples were first filtered (Whatman Puradisc 25, pore size 0.7 µm) and then subjected to catalytic oxidation using a TOC-L analyzer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). True color was determined on filtered samples, following the standard method for clear liquids [33], which involves measuring absorbance at 400 nm using a UV/visible spectrophotometer, with results expressed as platinum-cobalt units. Alongside DOC, the presence of natural organic matter (NOM)—a heterogeneous group of organic compounds—was assessed by measuring UV absorbance at 254 nm [34] using a UV/vis spectrophotometer (VWR® UV-6300PC, Avantor, Radnor, PA, USA). Dissolved nitrogen was quantified using a SHIMADZU TOC-L/TNM-L analyzer, while nitrite, considered toxic to fish and associated with ‘brown blood disease’ [35], was quantified by the standard colorimetric method (4500-NO2− B) [33]. Total phosphorus was also determined based on established procedures (4500.B and E) [33]. For biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5), samples were analyzed using a BOD Sensor Set from Velp Scientifica (Usmate, Italy), where they were incubated in the dark for 5 days at 20 °C inside a thermostatically controlled cabinet. Metals and nutrients in both untreated and treated samples were quantified by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES) using a Thermo X Series system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Before analysis, samples were passed through a 0.45 µm syringe filter (Chromafil A-45/25, Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany) to eliminate particulate matter generated during coagulation, thus avoiding instrument clogging. Sludge quantification was performed by filtering a defined volume of treated water through a 1.5 µm glass microfiber filter (VWR), followed by drying at 60 °C for 24 h. The dry weight was recorded as the amount of sludge produced at the optimal dose of each coagulant. In a second step, sludge samples were acid digested (HCl/water solution 1:20 v/v), concentrated to under half their volume, then brought back to 50 mL and filtered. Finally, both water and sludge samples were analyzed for the presence of Al, Ca, Fe, and Mg.
3. Results
3.1. Coagulation–Flocculation in Continuous Mode
3.1.1. Color Removal
In aquaculture effluents, color is often caused by dissolved organic matter [36], making it important to understand the relationship between these two parameters. As previously mentioned, four coagulants—two natural and two chemicals—were tested in a lab-scale continuous flow system to assess whether this type of setup could be integrated into the existing aquaculture treatment plant. The goal is to improve water quality and enhance fish visibility for both researchers and operators working in this aquaculture facility. Table 2 presents the color, NOM, and DOC removal efficiency in continuous mode.

Table 2.
Comparison of coagulant efficiency on color, NOM, and DOC removal from aquaculture wastewater in continuous treatment mode.
The results presented in Table 2 indicate that all coagulants effectively reduced the wastewater’s initial color level. This is particularly important in the context of this study, as lowering the color enhances the ability to observe and take care of the fish more efficiently. In batch mode, chemical coagulants such as ferric chloride at a concentration of 75 mg·L−1 achieved a color reduction of approximately 95% [37], whereas, in this study’s continuous mode system, a reduction of around 70% was observed at a concentration of 100 mg·L−1. At pH 8 and a concentration of 25 mg·L−1 of ferric chloride (under batch mode conditions), color removal was approximately 15% [14]—about half of what was achieved under continuous mode using the same operational conditions. The Al-based coagulant, which was ineffective in removing color during jar tests as demonstrated by Tomasi et al. [14], showed the ability to reduce initial color levels in continuous mode, achieving over 60% color removal at a concentration of 100 mg·L−1 at natural pH. Although this coagulant is widely used, studies specifically addressing its effectiveness in color removal remain limited. Regarding the use of Tanfloc, results obtained at a concentration of 100 mg·L−1 in this study were comparable to those reported in the batch tests by Land, et al. [37]. While the batch mode achieved approximately 93% color removal, the continuous mode reached about 75%, confirming the coagulant’s effectiveness under both conditions. Similarly, the CS-based coagulant demonstrated good performance in continuous flow treatment. At lower concentrations, particularly 20 and 50 mg·L−1, it outperformed the chemical coagulants.
3.1.2. Organic Matter Removal
One of the main limitations of recirculating aquaculture systems (RASs) is the buildup of organic matter (OM), primarily originating from uneaten feed and fish feces [38]. This accumulation of organic matter can promote the growth of opportunistic bacteria, which may impair the performance of biofilters. Additionally, excess OM can degrade water quality, compromise fish welfare, and increase the demand for water treatment processes—ultimately raising operational costs [38]. Therefore, removing organic matter is crucial for maintaining fish health, optimizing system performance, and preserving the aquatic environment. Organic matter levels are typically monitored through measurements of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and UV absorbance at 254 nm (UV254), where DOC reflects overall organic load, and UV254 indicates the presence of natural organic matter (NOM) [34,39]. Table 2 shows the effectiveness of different coagulants in removing organic matter from aquaculture wastewater in continuous treatment mode while considering both the coagulant concentration and pH level.
Among the coagulants tested, Tanfloc achieved the highest DOC removal efficiency at pH 7 and a dosage of 25 mg·L−1. Among the chemical coagulants, aluminum sulfate showed a strong performance, particularly at pH 8 and 20 mg·L−1, while the ferric chloride exhibited lower DOC removal at pH 8 and 25 mg·L−1. The chestnut shell-based coagulant demonstrated good DOC removal (47.7%) in continuous flow mode. However, UV254 removal was lower compared to that obtained in batch mode (about 60% [14]). Overall, it can be confirmed that all the coagulants were efficient in organic matter removal when applied in continuous mode. These results are particularly promising, as natural coagulants are often associated with an increase in organic matter, as reported in the literature [40,41,42,43,44]. This increase is typically linked to their organic origin (e.g., chestnut shells) and the presence of compounds such as formaldehyde [43]. However, the potential for formaldehyde leaching into the treated water was previously investigated by Tomasi, et al. [25], and it was confirmed that formaldehyde does not leach.
The evaluation of BOD5 was also conducted to determine whether using natural coagulants increases the biodegradable organic load in the treated water. In the case of the initial BOD5 level, the untreated water initially exhibited a value close to 0 mg·L−1, as it corresponds to the final effluent, i.e., the water that has passed through all treatment stages and will be returned to the fish tank. However, this parameter increased with the addition of natural coagulants. When 10 mg·L−1 of CS was added at pH 8, the BOD5 increased to 5.4 mg·L−1. Similarly, the addition of 25 mg·L−1 of Tanfloc at pH 7 resulted in a BOD5 of 3.8 mg·L−1. Even though this parameter increased with the addition of natural coagulants, the reported values are not considered critical for the aquaculture system, as the BOD5 concentrations remain within the limits set by the Portuguese legislation (Annex XI) [45], which establishes an acceptable range of 3 to 6 mg·L−1 for fish farming waters.
3.1.3. Nutrients
In recirculating aquaculture systems (RASs), careful monitoring of phosphorus and nitrogen compounds is critical, as these nutrients directly influence fish health, plant development, and microbial dynamics within the system. This study specifically focuses on assessing the impact of these parameters—particularly nitrites—on the water quality of the fish tank based on the analyzed samples. Nitrites are of particular concern due to their high toxicity, even at low concentrations [35]. One of the fundamental requirements for the reuse of water in aquaculture is the implementation of nitrification processes [46], which ensure the continuous conversion of ammonium and nitrite to nitrate. The elimination of nitrite is essential, as its accumulation poses a serious threat to aquatic organisms, and in RASs, this is typically achieved through biofiltration units, such as the biofilter represented in Tank 3 (Figure 1). However, it remains crucial to verify whether nitrite is still present in the final treated water. If residual nitrite is present, it can diffuse across the gill membranes and enter the fish’s bloodstream, where it oxidizes hemoglobin to methemoglobin—a form that is unable to transport oxygen. This condition, known as “brown blood disease,” can lead to fish suffocation, even when dissolved oxygen levels in the water are otherwise adequate [47]. Nitrite levels after water treatment remained within the range of the initial concentration, and none of the coagulants caused an increase in this parameter. Aluminum and iron concentrations were also assessed to determine whether chemical coagulants influenced the presence of these metals in the treated water. Aluminum was detected only in samples treated with aluminum sulfate and Tanfloc, with concentrations ranging from 0.25 to 0.36 mg·L−1. While these values are within acceptable limits for short-term exposure, elevated aluminum levels can have adverse effects on recirculating systems [48,49]. Iron plays a vital role in various physiological processes in both fish and plants, serving as a key cofactor in enzymatic pathways such as chlorophyll biosynthesis, DNA synthesis, and nitrogen reduction [50]. According to Farooq, et al. [50], iron supplementation significantly improved the growth of Pangasianodon hypophthalmus, increasing from 6.32 g (without supplementation) to 7.66 g after 15 days and from 9.3 g to 12.3 g after 90 days with exposure to 1.5 mg·L−1 of iron. Although iron leaching into treated water can be a concern, in this case, its presence from an iron-based coagulant is not considered problematic and may even offer biological benefits. In addition to these analyses, the results for phosphorus (P), total nitrogen (N), calcium (Ca), and magnesium (Mg) are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Presence of nutrients in the aquaculture effluent before and after coagulation treatment.
As shown in Table 3, all coagulants tested were effective in removing more than 90% of the initial phosphorus concentration from the aquaculture effluent, demonstrating strong performance in phosphate reduction regardless of coagulant type. In contrast, the removal of total nitrogen was less pronounced. Although the observed reductions were low, this is an interesting result because of the common assumption that natural coagulants, such as tannin-based compounds, are less effective in nitrogen reduction—often attributed to the incorporation of quaternary nitrogen into their structure via the Mannich reaction during synthesis [16]—this study observed a measurable decrease in nitrogen levels even at higher coagulant dosages (e.g., 50 mg·L−1). Nonetheless, the extent of nitrogen removal was insufficient to approach the classic Redfield ratio of N:P = 16:1 (molar ratio), which is widely recognized as a stoichiometric benchmark for balanced nutrient availability for primary producers in aquatic ecosystems [51]. Maintaining the N:P ratio is crucial to prevent nutrient imbalances that can destabilize aquatic environments. In this study, nitrogen levels remained in excess both before and after treatment. In some cases, the relative excess of nitrogen increased following coagulation, as also observed in batch mode [14]. Therefore, phosphorus supplementation is recommended in the aquaculture system under study. Since the primary objective—color removal—was successfully achieved, the N:P ratio should now be adjusted by increasing the current phosphorus concentration.
The N:P disproportion creates a high risk for eutrophication and algal bloom formation, especially in systems where phosphorus becomes the limiting nutrient. Although phosphorus removal through coagulation/flocculation is generally considered beneficial in major treatment plants, in this case, the high removal efficiency may be seen as a drawback. The observed discrepancy between phosphorus and total nitrogen removal efficiencies can be attributed to the nature of the compounds involved. Natural coagulants are more effective at removing particulate matter and phosphate ions, which readily form insoluble complexes and flocs [16]. In contrast, nitrogen is often present in more stable, dissolved forms—such as ammonium, nitrate, and organic nitrogen—which are less responsive to coagulation-based removal [52]. Regarding nitrite (NO2−), concentrations remained relatively stable across all treatments, with only minor variations observed. This outcome is expected, as nitrite removal is primarily carried out by biological processes. However, it is important to confirm that the use of natural coagulants did not affect nitrite levels.
Regarding the mineral composition of the treated water, notable changes were observed in the concentrations of aluminum, calcium, iron, and magnesium. Calcium, which plays a vital role in fish osmoregulation [53] and directly contributes to overall water hardness, decreased significantly after treatment—from 71.5 mg·L−1 in the raw effluent to values ranging between 28.1 and 47.9 mg·L−1. A similar trend was observed for magnesium, with concentrations falling from 17.0 mg·L−1 in the untreated water to between 4.1 and 6.7 mg·L−1 post-treatment. These reductions are noteworthy, as calcium and magnesium are the primary contributors to water hardness, a parameter that influences fish physiology and overall aquaculture performance [54]. Water hardness requirements vary depending on the species cultivated. For instance, low hardness levels (50–100 mg·L−1 as CaCO3) have been associated with reduced feed efficiency and lower stress resistance in Micropterus salmoides [54], while levels around 400 mg·L−1 as CaCO3 are reported to improve stress tolerance and energy efficiency. Based on the initial concentrations of calcium and magnesium, the estimated hardness of the raw effluent was approximately 250 mg·L−1 as CaCO3, placing it within the ideal range of 100–400 mg·L−1 for aquaculture. After coagulation treatment, water hardness ranged from 99 to 137 mg·L−1, 109 to 112 mg·L−1, 87 to 123 mg·L−1, and 100 to 147 mg·L−1 for CS, Tanfloc, aluminum-based, and iron-based coagulants, respectively. These values also comply with Portuguese legal limits for aquaculture water (Annex XI), which allow a hardness range of 10–500 mg·L−1 [45]. Iron was detected only in the samples treated with ferric chloride, with concentrations reaching up to 1.1 mg·L−1. Iron is essential for various physiological processes in both fish and plants, acting as a crucial cofactor in several enzymatic pathways, including chlorophyll biosynthesis, DNA synthesis, and nitrogen reduction [50]. According to Farooq, et al. [50], supplementation with iron significantly enhanced the growth of Pangasianodon hypophthalmus—increasing from 6.32 g (without supplementation) to 7.66 g after 15 days, and from 9.3 g to 12.3 g after 90 days when exposed to 1.5 mg·L−1 of iron. Other authors have confirmed that iron supplementation can be beneficial for fish development [55,56,57]. However, its effectiveness is closely dependent on the fish species and the concentration of iron applied. Although iron leaching into treated water can be a concern, in this specific case, the presence of iron resulting from the use of an iron-based coagulant is not considered problematic and may, in fact, provide biological benefits.
4. Conclusions
Two natural and two conventional chemical coagulants were tested for the treatment of aquaculture wastewater. Among the natural coagulants, one was produced by extracting tannins from chestnut shells due to its availability in Portugal. The extracted tannins were chemically modified via the Mannich reaction using NH4Cl and formaldehyde. Addressing the research gap regarding the use of natural coagulants in continuous flow systems, this study evaluated their performance under optimal conditions (coagulant dosage and pH) and at different dosages under natural pH. The results demonstrated that all coagulants could remove color, organic matter, phosphorus, and nitrogen from raw aquaculture water. Although nitrogen removal rates were relatively low, the ability of natural coagulants to reduce nitrogen concentrations in continuous flow is a promising finding. Color reduction was particularly important for improving visibility in fish tanks, and the chestnut shell-derived coagulant outperformed the conventional ones in this aspect, showing high efficiency even at lower dosages. Another significant advantage of using the chestnut shell-based coagulant is the absence of residual aluminum in the treated water. Future studies should explore the combined use of different coagulants, as potential synergistic effects could enhance treatment efficiency and help optimize operational conditions for aquaculture wastewater treatment. Overall, this study confirms that chestnut shells are a valuable source for producing tannin-based coagulants, with proven efficiency in both batch and continuous flow treatments—bringing this natural solution a step closer to application at larger treatment scales.
Author Contributions
Investigation, I.T.T.; conceptualization, I.T.T.; methodology, I.T.T. and C.M.S.B.; visualization, I.T.T.; formal analysis, I.T.T.; data curation, I.T.T.; writing—original draft preparation, I.T.T.; validation, C.M.S.B. and R.A.R.B.; writing—review and editing, C.M.S.B. and R.A.R.B.; supervision, C.M.S.B. and R.A.R.B.; project administration, C.M.S.B.; funding acquisition, C.M.S.B. and R.A.R.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by UID/50020 of LSRE-LCM—Laboratory of Separation and Reaction Processes—Laboratory of Catalysis and Materials—funded by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, I.P./MCTES through national funds, and by ALiCE, LA/P/0045/2020 (DOI: 10.54499/LA/P/0045/2020). I.T.T. acknowledges the doctoral scholarship BD/11977/2022 (DOI: https://doi.org/10.54499/2022.11977.BD) awarded by the Portuguese Science and Technology Foundation (FCT).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to privacy restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lem, A.; Bjorndal, T.; Lappo, A. Economic Analysis of Supply and Demand for Food up to 2030—Special Focus on Fish and Fishery Products; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.-C.; Xu, S.-Y.; Deng, K.-H. Water Color Identification System for Monitoring Aquaculture Farms. Sensors 2022, 22, 7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.; Khan, M.A.; Nielsen, R.; Islam, N. Total factor productivity and technical efficiency differences of aquaculture farmers in Bangladesh: Do environmental characteristics matter? J. World Aquac. Soc. 2019, 51, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorella, K.J.; Okronipa, H.; Baker, K.; Heilpern, S. Contemporary aquaculture: Implications for human nutrition. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 70, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tom, A.P.; Jayakumar, J.S.; Biju, M.; Somarajan, J.; Ibrahim, M.A. Aquaculture wastewater treatment technologies and their sustainability: A review. Energy Nexus 2021, 4, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clasen, B.; Storck, T.R.; Tiecher, T.L. Aquatic biomonitoring: Importance, challenges, and limitations. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2022, 18, 597–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuello, C. Present and future opportunities in the use of atomic force microscopy to address the physico-chemical properties of aquatic ecosystems at the nanoscale level. Int. Aquat. Res. 2022, 14, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Hasan, H.A.; Othman, A.R.; Ismail, N.I. Aquaculture industry: Supply and demand, best practices, effluent and its current issues and treatment technology. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letelier-Gordo, C.O.; Fernandes, P.M. Coagulation of phosphorous and organic matter from marine, land-based recirculating aquaculture system effluents. Aquac. Eng. 2021, 92, 102144102144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hizam, M.; Noor, M.; Ngadi, N. Global research landscape on coagulation-flocculation for wastewater treatment: A 2000–2023 bibliometric analysis. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 64, 105696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, T.F.; Watanabe, W.O.; Losordo, T.M.; Whitehead, R.F.; Carroll, P.M. Evaluation of chemical polymers as coagulation aids to remove suspended solids from marine fish recirculating aquaculture system discharge using a geotextile bag. Aquac. Eng. 2020, 90, 102065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, I.T.; Santos, I.; Gozubuyuk, E.; Santos, O.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Botelho, C.M.S. A sustainable solution for aquaculture wastewater treatment: Evaluation of tannin-based and conventional coagulants. Chemosphere 2025, 377, 144320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyos-Martínez, P.L.d.; Merle, J.; Labidi, J.; Charrier, F.; Bouhtoury, E. Tannins extraction: A key point for their valorization and cleaner production. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 1138–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, I.T.; Machado, C.A.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Botelho, C.M.S.; Santos, S.C.R. Tannin-based coagulants: Current development and prospects on synthesis and uses. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasi, I.T.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Botelho, C.M.S. Environmental impact assessment of tannin-based coagulants production from chestnut shells. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 382, 125346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Hasan, H.A.; Othman, A.R.; Kurniawan, S.B. Aquaculture wastewater treatment using plant-based coagulants: Evaluating removal efficiency through the coagulation-flocculation process. Results Chem. 2024, 7, 101390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnena, M.K.; Konni, M.; Dwarapureddi, B.K.; Saritha, V. Blend of natural coagulants as a sustainable solution for challenges of pollution from aquaculture wastewater. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwegbe, C.A.; Ighalo, J.O.; Onukwuli, O.D.; Obiora-Okafo, I.A.; Anastopoulos, I. Coagulation-Flocculation of Aquaculture Wastewater Using Green Coagulant from Garcinia kola Seeds: Parametric Studies, Kinetic Modelling and Cost Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, S.B.; Imron, M.F.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Othman, A.R.; Hasan, H.A. Coagulation–flocculation of aquaculture effluent using biobased flocculant: From artificial to real wastewater optimization by response surface methodology. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyaene, I.H.; Onukwuli, O.D.; Babayemi, A.K.; Obiora-Okafo, I.A.; Ezeh, E.M. Application of Bio Coagulation–Flocculation and Soft Computing Aids for the Removal of Organic Pollutants in Aquaculture Effluent Discharge. Chem. Afr. 2024, 7, 455–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, I.T.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Botelho, C.M.S. Solid-Liquid Extraction of Polyphenols from Chestnut Shells: A Sustainable Approach for Coagulant Synthesis. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2024, 42, 101806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quamme, J.E.; Kemp, A.H. Stable Tannin Based Polymer Compound. U.S. Patent US4558080A, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi, I.T.; Santos, S.C.R.; Ribeiro, A.; Homem, V.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Botelho, C.M.S. Coagulants from chestnut shell tannins—Synthesis, characterization and performance on water treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 69, 106818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, L.H.; Decusati, O.G. Manufacturing Process for Quaternary Ammonium Tannate, a Vegetable Coagulating/Flocculating Agent. Brazil Patent 6478986, 12 December 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Carlqvist, K.; Arshadi, M.; Mossing, T.; Östman, U.; Brännström, H.; Halmemies, E.; Nurmi, J.; Lidén, G.; Börjesson, P. Life-cycle assessment of the production of cationized tannins from Norway spruce bark as flocculants in wastewater treatment. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2020, 14, 1270–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasch, J.; Palm, H.W. Economic Analysis and Improvement Opportunities of African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus) Aquaculture in Northern Germany. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisachov, A.; Nguyen, D.H.M.; Panthum, T.; Ahmad, S.F.; Singcha, W.; Ponjarat, J.; Jaisamut, K.; Srisapoome, P.; Duengkae, P.; Hatachote, S.; et al. Emerging importance of bighead catfish (Clarias macrocephalus) and north African catfish (C. gariepinus) as a bioresource and their genomic perspective. Aquaculture 2023, 573, 739585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerville, C.; Cohen, M.; Pantanella, E.; Stankus, A.; Lovatelli, A. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. In Small-Scale Aquaponic Food Production—Integrated Fish and Plant Farming; 2070-7010; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yep, B.; Zheng, Y. Aquaponic trends and challenges—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 1586–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edeline, F. Épuration Physico-Chimique des Eaux—Théorie et Technologie, 2nd ed.; INRAE: Paris, France, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; Association, A.P.H., Ed.; American Water Works Association and Water Environmental Federation: Denver, CO, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Okoro, B.U.; Sharifi, S.; Jesson, M.A.; Bridgeman, J. Natural organic matter (NOM) and turbidity removal by plant-based coagulants: A review. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinis, M.T.; Rocha, R.M. Introdução à Aquacultura, 1st ed.; Lidel—Edições Técnicas, Ed.; Lidel—Edições Técnicas, Lda: Lisboa, Portugal, 2021; p. 263. [Google Scholar]
- Kurniawan, S.B.; Imron, M.F.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Othman, A.R.; Purwanti, I.F.; Hasan, H.A. Treatment of real aquaculture effluent using bacteria-based bioflocculant produced by Serratia marcescens. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, T.M.S.; Veit, M.T.; Gonçalves, G.d.C.; Palácio, S.M.; Nascimento, J.C.Z.B.C.d.O.C.; Campos, E.G.P. Evaluation of a Coagulation/Flocculation Process as the Primary Treatment of Fish Processing Industry Wastewater. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Alarcón, P.; Gonzalez, S.V.; Simonsen, M.A.; Borrero-Santiago, A.R.; Sanchís, J.; Meriac, A.; Kolarevic, J.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Mikkelsen, Ø. Characterizing changes of dissolved organic matter composition with the use of distinct feeds in recirculating aquaculture systems via high-resolution mass spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 142326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilainen, A.; Gjessing, E.T.; Lahtinen, T.; Hed, L.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. An overview of the methods used in the characterization of natural organic matter (NOM) in relation to drinking water treatment. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justina, M.D.; Muniz, B.R.B.; Bröring, M.M.; Costa, V.J.; Skoronski, E. Using vegetable tannin and polyaluminium chloride as coagulants for dairy wastewater treatment: A comparative study. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 25, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, E.C.; Santos, S.C.R.; Pintor, A.M.A.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Botelho, C.M.S. Evaluation of a tannin-based coagulant on the decolorization of synthetic effluent. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polasek, P.; Wantenaar, C. The inability of organic coagulants to purify potable water to its best attainable quality. Water SA 2023, 43, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, I.T.; Ferreira, R.M.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Botelho, C.M.S. Natural coagulants from chestnut shells: A sustainable approach for textile wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2025, 376, 144286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-Heredia, J.; Sánchez-Martín, J.; Muñoz-Serrano, A.; Peres, J.A. Towards overcoming TOC increase in wastewater treated with Moringa oleifera seed extract. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 188, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decree Law No. 236/98. Available online: https://diariodarepublica.pt/dr/detalhe/decreto-lei/236-1998-430457 (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Neissi, A.; Rafiee, G.; Rahimi, S.; Farahmand, H.; Pandit, S.; Mijakovic, I. Enriched microbial communities for ammonium and nitrite removal from recirculating aquaculture systems. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molayemraftar, T.; Peyghan, R.; Jalali, M.R.; Shahriari, A. Single and combined effects of ammonia and nitrite on common carp, Cyprinus carpio: Toxicity, hematological parameters, antioxidant defenses, acetylcholinesterase, and acid phosphatase activities. Aquaculture 2022, 548, 737676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cui, Z.; Cui, H.; Bai, Y.; Yin, Z.; Qu, K. Hazardous substances and their removal in recirculating aquaculture systems: A review. Aquaculture 2023, 569, 739399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, K.A.; Trueman, B.; Halfyard, E.A.; Sterling, S.M. Detection and Prediction of Toxic Aluminum Concentrations in High-Priority Salmon Rivers in Nova Scotia. Environ. Toxicol Chem. 2024, 43, 2545–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, A.; Verma, A.K.; Hittinahalli, C.M.; Varghese, T.; Pathak, M.S. Iron supplementation in aquaculture wastewater and its impact on osmoregulatory, haematological, blood biochemical, and stress responses of pangasius with spinach in nutrient film technique based aquaponics. Aquaculture 2023, 567, 739250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Wan, L.; Song, C.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, X. Nitrogen and phosphorus turnover and coupling in ponds with different aquaculture species. Aquaculture 2023, 563, 738997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getahun, M.; Asaithambi, P.; Befekadu, A.; Alemayehu, E. Optimization of indigenous natural coagulants process for nitrate and phosphate removal from wet coffee processing wastewater using response surface methodology: In the case of Jimma Zone Mana district. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 100370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klykken, C.; Reed, A.K.; Dalum, A.S.; Olsen, R.E.; Moe, M.K.; Attramadal, K.J.K.; Boissonnot, L. Physiological changes observed in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) with nephrocalcinosis. Aquaculture 2022, 554, 738104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, N.; Egnew, N.; Quintero, H.; Kelly, A.; Sinha, A.K. The effects of water hardness on the growth, metabolic indicators and stress resistance of largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides. Aquaculture 2020, 527, 735469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shenawy, A.M.; Gad, D.M.; Yassin, S.A. Effect of Iron Nanoparticles on the Development of Fish Farm Feeds. Alex. J. Vet. Sci. 2019, 60, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Chauhan, R. Exploring the effects of iron nanoparticles in aquaculture: Review. Int. J. Adv. Biochem. Res. 2025, 9, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqwepu, O.; Salie, K.; Goosen, N. Evaluation of chelated iron and iron sulfate in the diet of African catfish, Clarias gariepinus to enhance iron excretion for application in integrated aquaponics systems. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2020, 51, 1034–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).