Spatial Estimation of Biogas and Compost Potential for Sustainable Livestock Manure Management in Bangladesh
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Processing
2.2. Theoretical Assessment
2.2.1. Available Manure Generation
2.2.2. Biogas, Electricity, and Biofertilizer Potential
× Energy content in biogas × η
| Livestock Types | Manure Generation Rate (kg/Head/Day) | Availability Coefficient (%) | TS of Manure (%) | Biogas Yield (m3 kg−1 TS) | DM (% of Manure) | VS (% of DM) | CH4 Content (% of Biogas) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large Animal | 19 | 50 | 25 | 0.60 | 25 | 80 | 60 |
| Small Animal | 0.8 | 13 | 25 | 0.40 | 18 | 80 | 45 |
| Poultry | 0.045 | 90 | 29 | 0.80 | 10 | 70 | 60 |
2.2.3. Compost Production Potential and Synthetic Fertilizer Replacement
2.2.4. GHG Emissions Reduction Potential of Biogas
× CH4 density (0.717kg/m3)
potential of CH4
× SEF
from biogas (in CO2eq)
2.2.5. GHG Emissions Reduction Potential of Compost
2.2.6. Nutrient Leach-Out Reduction Potential of Biogas and Compost
| TN (kgha−1) | TP (kgha−1) | Country | Soil Type | Crops | Others | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.3 | 0.29 | Finland | Peat soil | Cereals, barley | Subsurface drainage | [80] |
| 21.7 | 0.30 | Norway | Mineral soil | Perennial grass | Subsurface drainage | [81] |
| 2.41 | 0.64 | China | - | Cereals | Runoff | [82] |
| 25 | 0.30 | Finland | Peat soil | Grass | Subsurface drainage | [83] |
| 39–191 | 0.9–2.4 | Sweden | Garden plants | Surface runoff | [84] | |
| 3.3–30.4 | 0.11–0.32 | Argentina | No-tillage | Cover crops | Rainfall | [85] |
| 4.3 | 0.04 | Sweden | Silty loam | Barley, grass | Subsurface | [86] |
| 28.5–40.0 | 0.7–4.3 | East Asia | - | Rice, paddy | Subsurface | [87] |
| 4.5–12.9 | 0.5–2.6 | East Asia | - | Rice, paddy | Surface runoff | [87] |
2.3. Spatial Analysis
2.3.1. Symbology Analysis
2.3.2. Hot Spot Analysis
3. Results
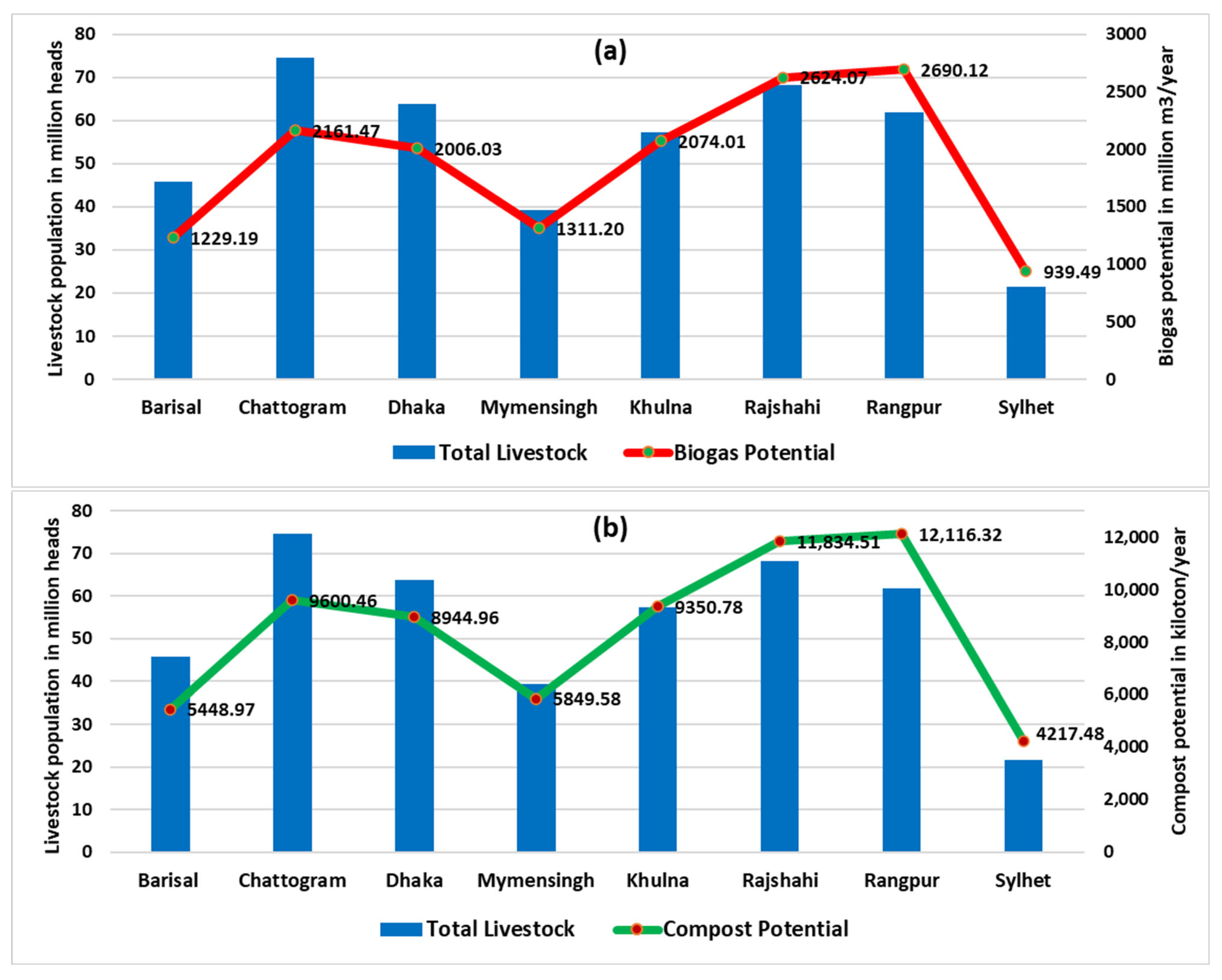
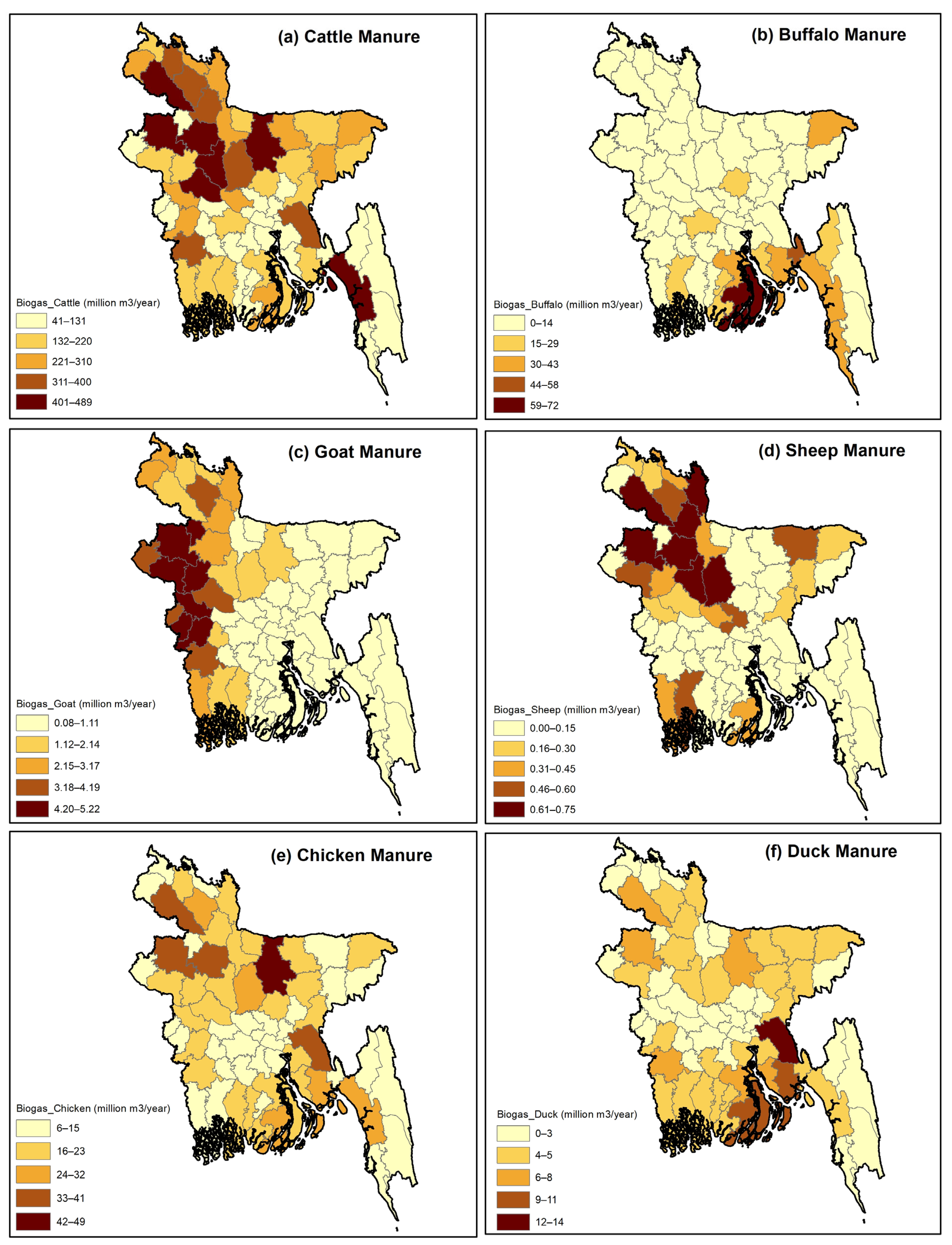
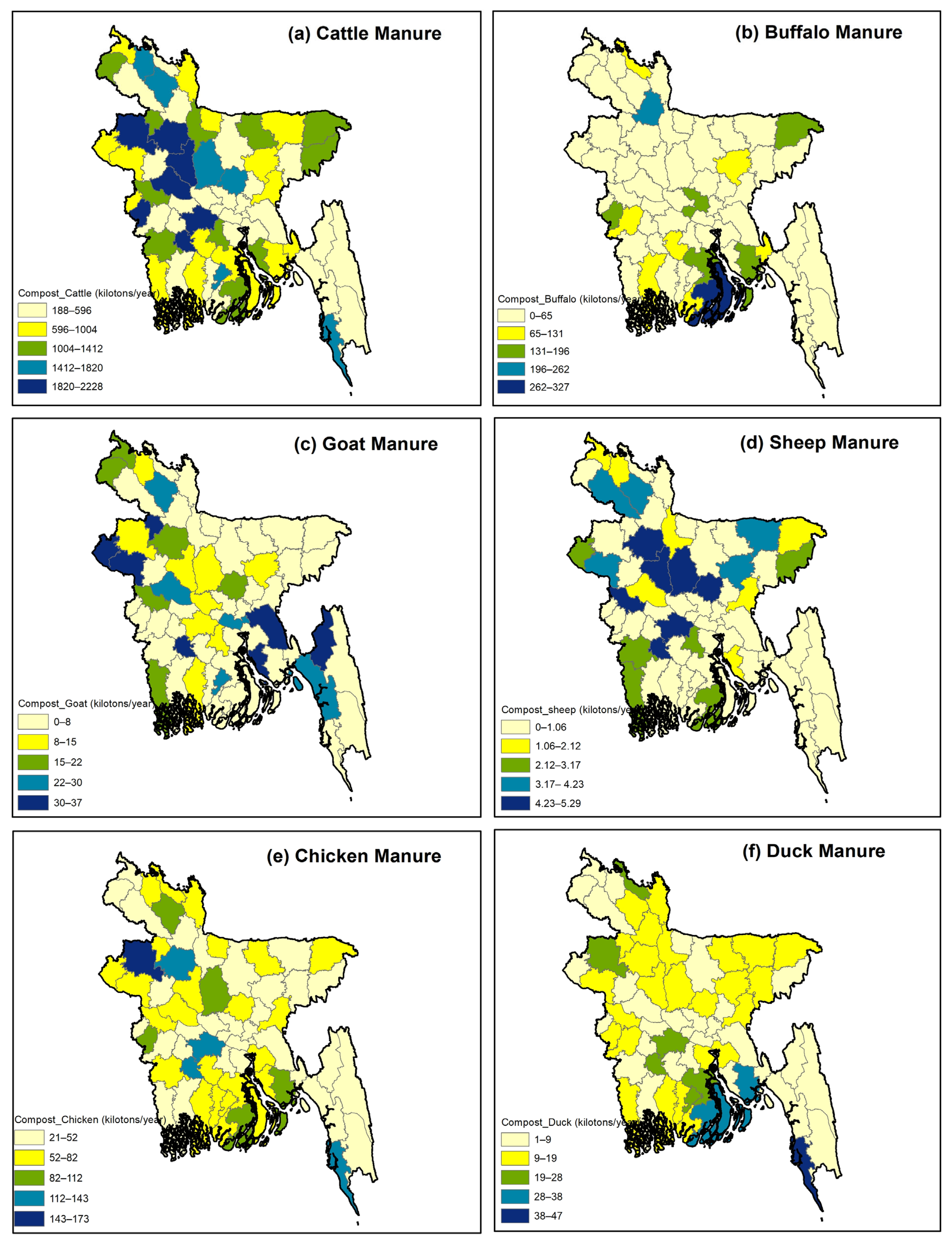
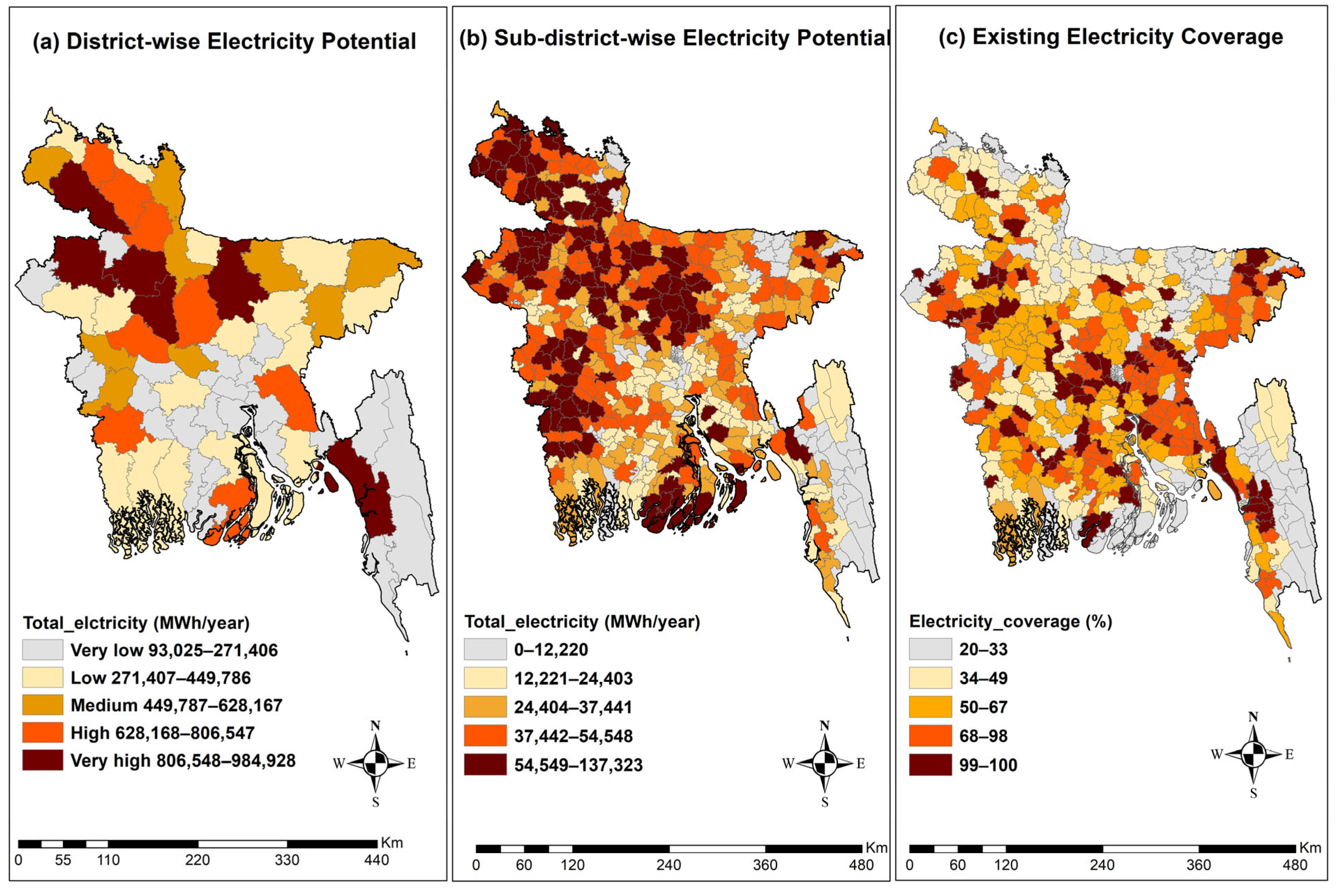
3.1. Regional Pattern of Biogas and Compost Potential
3.2. Hot Spot Identification
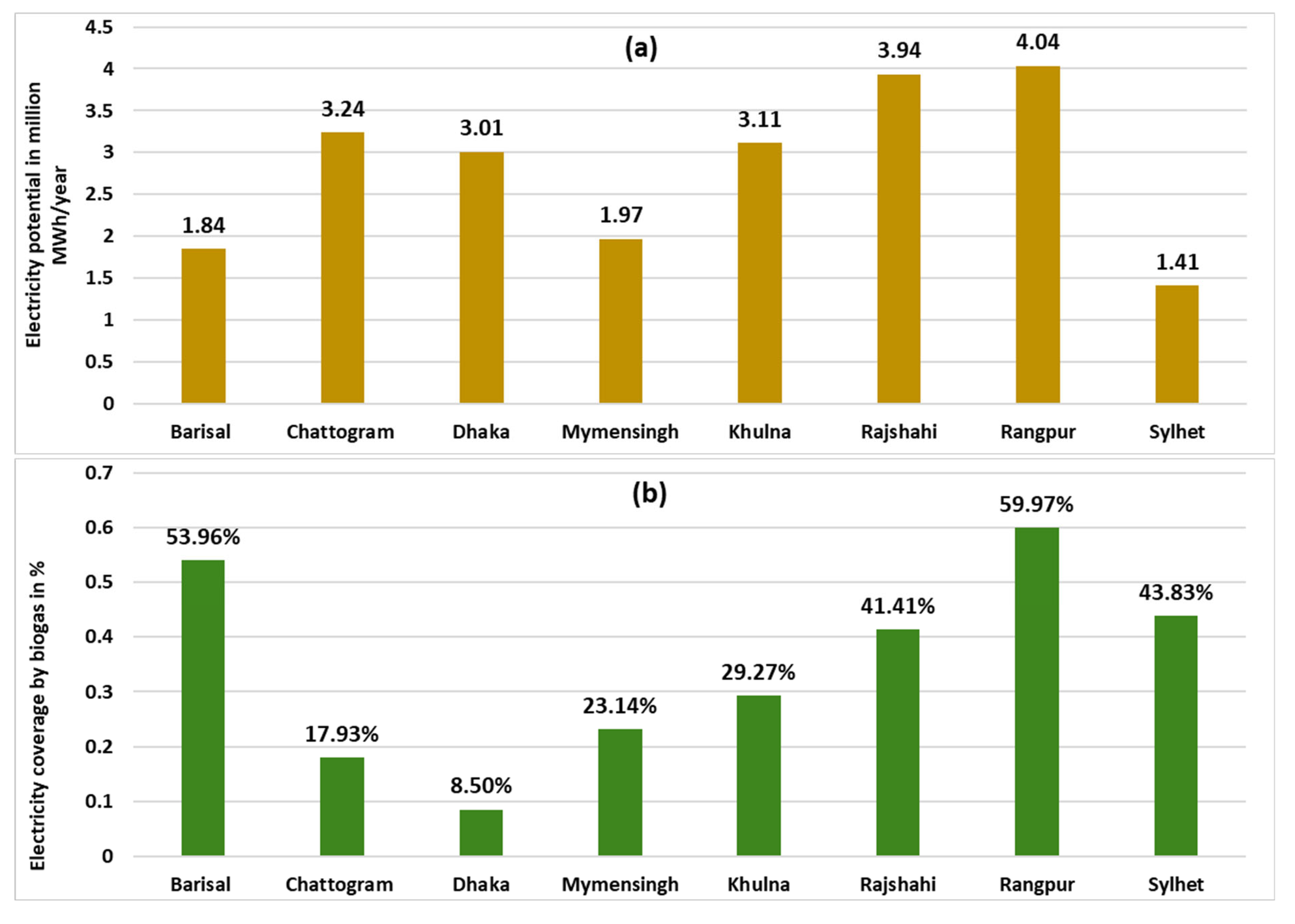
3.3. Electricity Potential
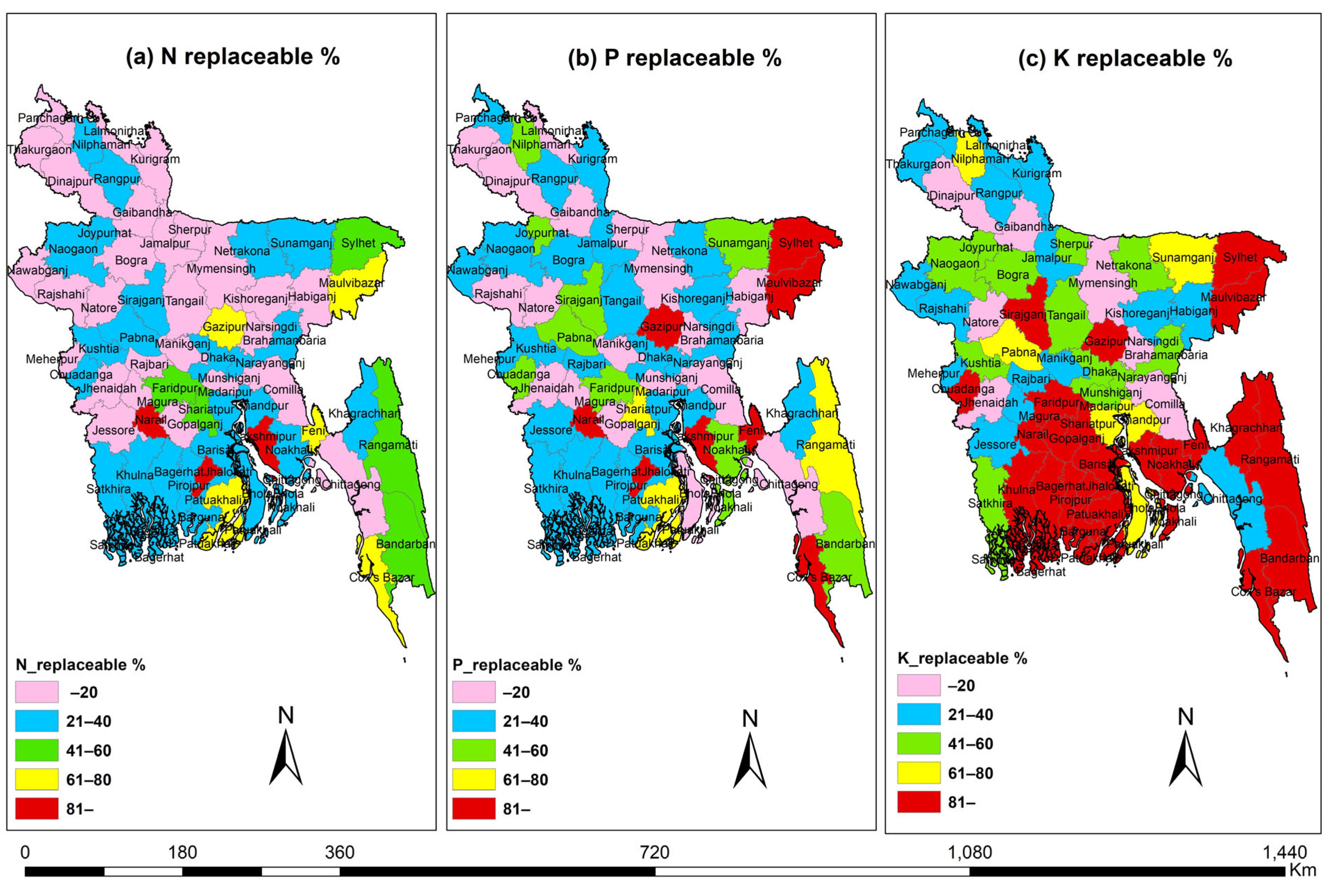
3.4. Synthetic Fertilizer Replacement
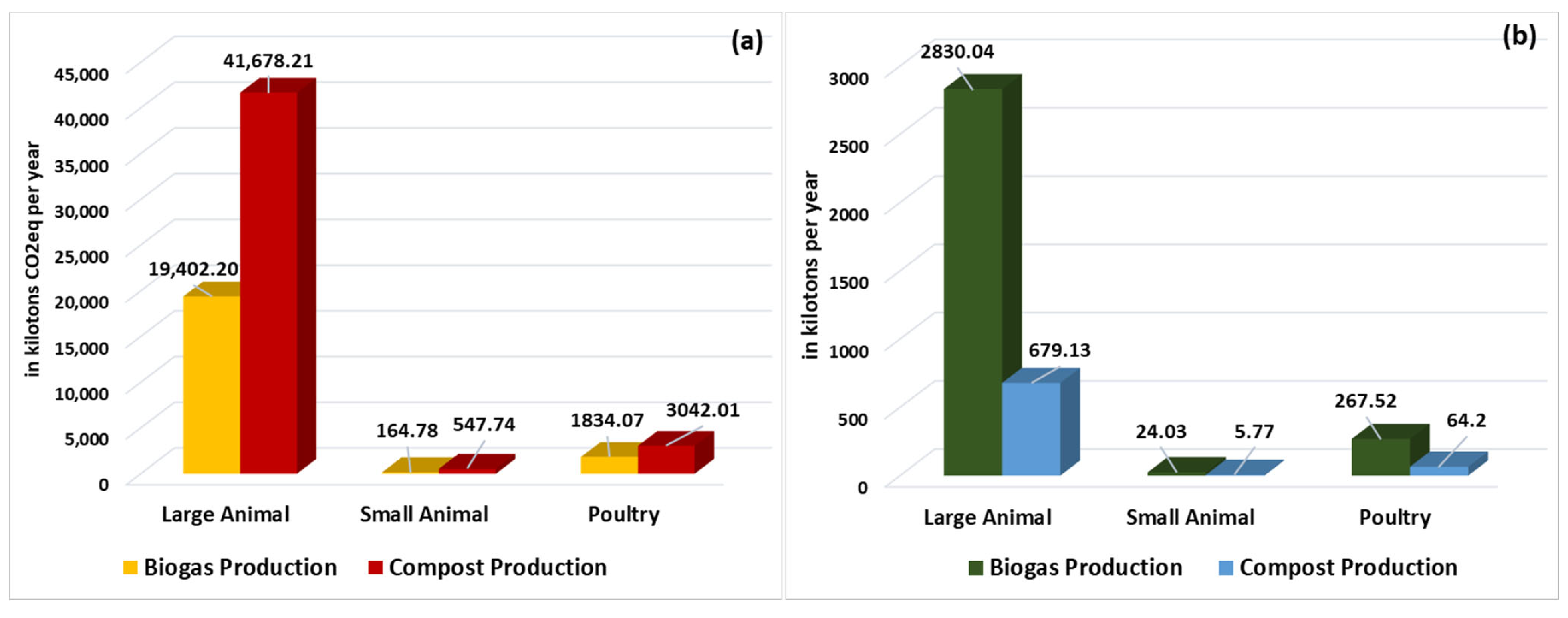
3.5. GHG Emissions and Nutrient Leach-Out Reduction Potential
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
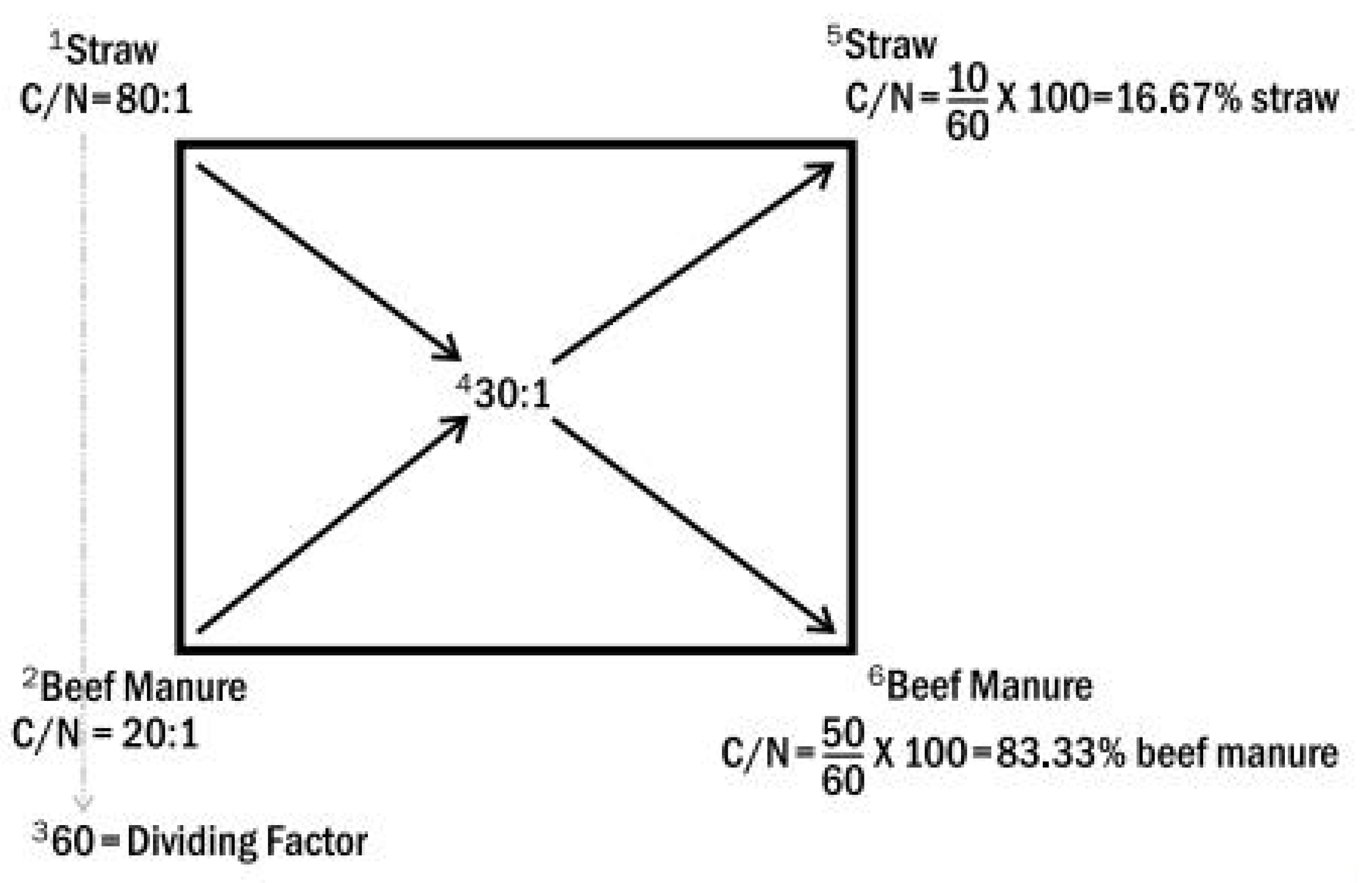
Appendix B
| Manure | C/N Ranges [15,98] | C/N (This Study) | % of Manure | % of Rice Straw | Total Available Manure (in kg) | Compost Production (in kg) | Final Compost Production (in kg) (After 50% Mass Reduction) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large Animal | 18–20:1 | 18:1 | 80.645 | 19.355 | 90,876,153,648.85 | 112,686,655,897.88 | 56,343,327,948.94 |
| Small Animal | 16–18:1 | 16:1 | 78.125 | 21.875 | 108,460,030.91 | 138,828,839.56 | 69,412,919.78 |
| Poultry | 6–7:1 | 6:1 | 67.567 | 32.432 | 5,552,972,364.02 | 8,218,468,133.88 | 4,109,234,066.94 |
References
- DLS. Livestock Economy at a Glance; Department of Livestock Services: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2024. Available online: http://dls.portal.gov.bd/sites/default/files/files/dls.portal.gov.bd/page/ee5f4621_fa3a_40ac_8bd9_898fb8ee4700/2023-07-23-12-04-afbcccb96f8b27d4bab6501aa8c2c2ff.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2025).
- FAO. Livestock and Environment Statistics: Manure and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Global, Regional and Country Trends, 1990-2018; Report No.: FAOSTAT Analytical Brief Series No. 14; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020; Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/f0cebfdd-725e-4d7a-8e14-3ba8fb1486a7/content (accessed on 7 December 2024).
- Searchinger, T.; Waite, R.; Hanson, C.; Ranganathan, J. Creating a Sustainable Food Future “A Menu of Solutions to Feed Nearly 10 Billion People by 2050”; World Reaserch Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Available online: https://agritrop.cirad.fr/593176/1/WRR_Food_Full_Report_0.pdf (accessed on 25 December 2024).
- Mahal, Z.; Yabar, H.; Mizunoya, T. Spatial Assessment of Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Eutrophication Potential from Livestock Manure in Bangladesh. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock. ILMM Draft National Integrated Livestock Manure Management (ILMM) Policy; Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- BLRI. Bangladesh Livestock Research Institute. 2023. Available online: https://blri.gov.bd/ (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- MoEF. The National Environment Policy; Ministry of Environment and Forest, the Government of Bangladesh: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2018. Available online: https://moef.gov.bd/site/page/1c05e31e-1bb0-46ce-95a3-6ee3c82b439f/%E0%A6%AA%E0%A6%B0%E0%A6%BF%E0%A6%AC%E0%A7%87%E0%A6%B6-%E0%A6%A8%E0%A7%80%E0%A6%A4%E0%A6%BF,%E0%A6%86%E0%A6%87%E0%A6%A8-%E0%A6%93-%E0%A6%AC%E0%A6%BF%E0%A6%A7%E0%A6%BF (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Legislative and Parliamentary Affairs Division Ministry of Law, Justice and Parliamentary Affairs. Laws of Bangladesh. 2024. Available online: http://bdlaws.minlaw.gov.bd/laws-of-bangladesh.html?lang=en (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Venier, F.; Yabar, H. Renewable energy recovery potential towards sustainable cattle manure management in Buenos Aires Province: Site selection based on GIS spatial analysis and statistics. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 1317–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahal, Z.; Yabar, H. A Spatial Modeling Approach for Optimizing the Locations of Large-Scale Biogas Plants from Livestock Manure in Bangladesh. Land 2025, 14, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktar, K.; Yabar, H.; Mizunoya, T.; Islam, M.M. Application of GIS in Introducing Community-Based Biogas Plants from Dairy Farm Waste: Potential of Renewable Energy for Rural Areas in Bangladesh. Geomatics 2024, 4, 384–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiki, S.Y.A.; Uddin, M.N.; Mofijur, M.; Fattah, I.M.R.; Ong, H.C.; Lam, S.S.; Kumar, P.S.; Ahmed, S.F. Theoretical calculation of biogas production and greenhouse gas emission reduction potential of livestock, poultry and slaughterhouse waste in Bangladesh. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, T.; Chowdhury, H.; Hossain, N.; Ahmed, A.; Hossen, M.S.; Chowdhury, P.; Thirugnanasambandam, M.; Saidur, R. Latest advancements on livestock waste management and biogas production: Bangladesh’s perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Zhan, X.; Lee, D.J. Recent advancements in sustainable management of livestock waste and rural environment (LSW-2020). Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 316, 123958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary, A.K. Composting Animal Manures: A Guide to the Process and Management of Animal Manure Compost|NDSU Agriculture 2022. Available online: https://www.ndsu.edu/agriculture/extension/publications/composting-animal-manures-guide-process-and-management-animal-manure-compost (accessed on 24 May 2024).
- Bayu, W.; Rethman, N.F.G.; Hammes, P.S. The Role of Animal Manure in Sustainable Soil Fertility Management in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Review. J. Sustain. Agric. 2005, 25, 113–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, G.R.; Cook, A.R.; Posner, J.L.; Hedtcke, J.L.; Hall, J.A.; Baldock, J.O. Linking Wisconsin Dairy and Grain Farms via Manure Transfer for Corn Production. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finance Division, Ministry of Finance. Economic Review. 2024. Available online: https://mof.portal.gov.bd/site/page/28ba57f5-59ff-4426-970a-bf014242179e/Bangladesh-Economic-Review (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Islam, K.N.; Sarker, T.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F.; Atri, A.C.; Alam, M.S. Renewable energy generation from livestock waste for a sustainable circular economy in Bangladesh. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 139, 110695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehra, M.; Jain, S. Estimation of renewable biogas energy potential from livestock manure: A case study of India. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2023, 22, 101432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afotey, B.; Sarpong, G.T. Estimation of biogas production potential and greenhouse gas emissions reduction for sustainable energy management using intelligent computing technique. Meas. Sens. 2022, 25, 100650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, D.S.; Kulay, L. A prospective study on the environmental feasibility of supplying electricity to the Brazilian Amazon through biogas power generation. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 55, 102962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deublein, D.; Steinhauser, A. (Eds.) Biogas from Waste and Renewable Resources: An Introduction, 1st ed.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerová, M.; Šimon, T.; Stehlík, M.; Madaras, M.; Koubová, M.; Smatanová, M. Long-term application of biogas digestate improves soil physical properties. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 231, 105715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordahl, S.L.; Preble, C.V.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Scown, C.D. Greenhouse Gas and Air Pollutant Emissions from Composting. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 2235–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Xu, F.; Ge, X.; Li, Y. Improving the sustainability of organic waste management practices in the food-energy-water nexus: A comparative review of anaerobic digestion and composting. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 89, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ArcGIS Online 2024. Available online: https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-d&q=arcgis+online (accessed on 13 November 2024).
- DLS. Department of Livestock Services 2024. Available online: https://dls.gov.bd/ (accessed on 24 April 2024).
- Abdeshahian, P.; Lim, J.S.; Ho, W.S.; Hashim, H.; Lee, C.T. Potential of biogas production from farm animal waste in Malaysia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afazeli, H.; Jafari, A.; Rafiee, S.; Nosrati, M. An investigation of biogas production potential from livestock and slaughterhouse wastes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcioğlu, A.O.; Türker, U. Status and potential of biogas energy from animal wastes in Turkey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deublein, D.; Steinhauser, A. Biogas from Waste and Renewable Resources. In Biogas from Waste and Renewable Resources; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, P.; Paul, N.; Joardder, M.; Khan, M.; Sarker, M. Feasibility analysis of implementing anaerobic digestion as a potential energy source in Bangladesh. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 65, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, M.; Ortiz, I.; Rodríguez, L.; Muñoz, G. Ni–Co bimetallic catalyst for hydrogen production in sewage treatment plants: Biogas reforming and tars removal. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 14456–14468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.P. Techno-Economic Feasibility Study of a Small-Scale Biogas Plant for Treating Market Waste in the City of El Alto KTH School of Industrial Engineering and Management Energy Technology EGI-2014-083MSC Division of Energy and Climate SE-100 44 STOCKHOLM. 2014. Available online: http://kth.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:741758/FULLTEXT01.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2024).
- Ngumah, C.; Ogbulie, J.; Orji, J.; Amadi, E. Potential of Organic Waste for Biogas and Biofertilizer Production in Nigeria. Environ. Res. Eng. Manag. 2013, 63, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, I.M.; Ghazi, T.I.M.; Omar, R. Anaerobic digestion technology in livestock manure treatment for biogas production: A review. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorollahi, Y.; Kheirrouz, M.; Asl, H.F.; Yousefi, H.; Hajinezhad, A. Biogas production potential from livestock manure in Iran. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitenbeck, G.A.; Schellinger, D. Calculating the Reduction in Material Mass And Volume during Composting. Compos. Sci. Util. 2004, 12, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikumo, H. Estimation of Potential Supply of Livestock Waste Compost to Replace Chemical Fertilizer Use in Japan Based on 2000 Census of Agriculture. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2005, 39, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- DAE. Department of Agricultural Extension-Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh 2024. Available online: https://dae.gov.bd/ (accessed on 9 July 2024).
- Cestonaro, T.; Costa, M.S.S.d.M.; Costa, L.A.d.M.; Pereira, D.C.; Rozatti, M.A.; Martins, M.F.L. Addition of cattle manure to sheep bedding allows vermicomposting process and improves vermicompost quality. Waste Manag. 2017, 61, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, Z.; Bahar, M.; Sarkar, B.; Donne, S.W.; Wade, P.; Bolan, N. Assessment of the fertilizer potential of biochars produced from slow pyrolysis of biosolid and animal manures. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 155, 105043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C. Available Nutrients and Value for Manure; The Ontario Ministry of Agriculture and Food and the Ministry of Rural Affairs: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2013; Available online: https://fieldcropnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Nutrient-Value-of-Manure.pdf (accessed on 26 December 2024).
- Leikam, D.F.; Lamond, R.E. Estimating Manure Nutrient Availability Report, No.: MF-2562; Kansas State University, Department of Agronomy: Manhattan, KS, USA, 2003; Available online: https://bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/download/estimating-manure-nutrient-availability_MF2562 (accessed on 26 December 2024).
- Raza, S.T.; Tang, J.L.; Ali, Z.; Yao, Z.; Bah, H.; Iqbal, H.; Ren, X. Ammonia Volatilization and Greenhouse Gases Emissions during Vermicomposting with Animal Manures and Biochar to Enhance Sustainability. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 18, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mendonça Costa, M.S.M.; Bernardi, F.H.; de Mendonça Costa, L.A.; Pereira, D.C.; Lorin, H.E.F.; Rozatti, M.A.T.; Carneiro, L.J. Composting as a cleaner strategy to broiler agro-industrial wastes: Selecting carbon source to optimize the process and improve the quality of the final compost. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 2084–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Chang, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Yang, H.; Fu, G. Potential use of anaerobically digested manure slurry to suppress Phytophthora root rot of chilli pepper. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 168, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slepetiene, A.; Volungevicius, J.; Jurgutis, L.; Liaudanskiene, I.; Amaleviciute-Volunge, K.; Slepetys, J.; Ceseviciene, J. The potential of digestate as a biofertilizer in eroded soils of Lithuania. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfa, M.; Adie, D.; Igboro, S.; Oranusi, U.; Dahunsi, S.; Akali, D. Assessment of biofertilizer quality and health implications of anaerobic digestion effluent of cow dung and chicken droppings. Renew. Energy 2014, 63, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezemagu, I.; Ejimofor, M.; Menkiti, M.; Diyoke, C. Biofertilizer production via composting of digestate obtained from anaerobic digestion of post biocoagulation sludge blended with saw dust: Physiochemical characterization and kinetic study. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, J.; Vinken, T.; Hamelin, L.; De Boer, I. Comparing environmental consequences of anaerobic mono- and co-digestion of pig manure to produce bio-energy—A life cycle perspective. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 125, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G.; Fazekas, I.; Szabo, S.; Szabo, G.; Buday, T.; Paladi, M.; Kisari, K.; Kerenyi, A. The Carbon Footprint of a Biogas Power Plant. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2014, 13, 2867–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayodele, T.; Ogunjuyigbe, A.; Alao, M. Economic and environmental assessment of electricity generation using biogas from organic fraction of municipal solid waste for the city of Ibadan, Nigeria. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 203, 718–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Agriculture, Forestry and Other Land Use. 2006. Available online: https://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/public/2006gl/vol4.html (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Kaygusuz, K. Renewable and sustainable energy use in Turkey: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2002, 6, 339–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, B. Chapter 3—Natural Gas. In Energy Sources Amsterdam; Viswanathan, B., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebel, E.D.; Finnegan, C.J.; Ouyang, Z.; Jackson, R.B. Methane and NOx Emissions from Natural Gas Stoves, Cooktops, and Ovens in Residential Homes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2529–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.; Boldrin, A.; Christensen, T.; Scheutz, C. Greenhouse gas emissions from home composting of organic household waste. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, J.; Cuhls, C. Greenhouse gas emissions from mechanical and biological waste treatment of municipal waste. Environ. Technol. 2003, 24, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.; Chang, C.; Larney, F.J. Carbon, Nitrogen Balances and Greenhouse Gas Emission during Cattle Feedlot Manure Composting. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellebrand, H. Emission of Nitrous Oxide and other Trace Gases during Composting of Grass and Green Waste. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1998, 69, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowrońska, M.; Filipek, T. Life cycle assessment of fertilizers: A review. Int. Agrophysics 2014, 28, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaugh, T.J.; Vance, E.D.; Gaudreault, C.; Fox, T.R.; Allen, H.L.; Stape, J.L.; Rubilar, R.A. Carbon Emissions and Sequestration from Fertilization of Pine in the Southeastern United States. For. Sci. 2012, 58, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brentrup, F.; Hoxha, A.; Christensen, B. Carbon footprint analysis of mineral fertilizer production in Europe and other world regions. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Life Cycle Assessment of Food (LCA Food 2016), Dublin, Ireland, 19–21 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.; Haglund, C. Life Cycle Inventory (LCI) of Fertiliser Production: Fertiliser Products Used in Sweden and Western Europe; SIK: Gothenburg, Sweden, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A.G.; Audsley, E.; Sandars, D.L. Environmental burdens of producing bread wheat, oilseed rape and potatoes in England and Wales using simulation and system modelling. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2010, 15, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Geng, Y.; Hong, J.; Yang, D.; Ma, X. Life cycle assessment of potash fertilizer production in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 138, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, E.; Trois, C. GHG emission factors developed for the recycling and composting of municipal waste in South African municipalities. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2520–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phong, N.T. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Composting and Anaerobic Digestion Plants. Vietnam. J. Sci. Technol. 2012, 54, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Mulbry, W.; White, J.; Kondrad, S. Pile mixing increases greenhouse gas emissions during composting of dairy manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2904–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luske, B. Reduced GHG Emissions Due to Compost Production and Compost Use in Egypt Comparing Two Scenarios; Report No.: 2010-016 LbD; Louis Bolk Instituu: Bunnik, The Netherlands, 2010; Available online: https://orgprints.org/id/eprint/17480/4/17480.pdf (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- McDougall, F.R.; White, P.; Franke, M.; Hindle, P. (Eds.) Integrated Solid Waste Management: A Life Cycle Inventory; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK; Malden, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkerley, D. Effects of rainfall intensity fluctuations on infiltration and runoff: Rainfall simulation on dryland soils, Fowlers Gap, Australia. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 26, 2211–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Guo, L.; Yu, Y.; Luo, D.; Fan, B.; Chu, G. Storm runoff generation in headwater catchments on the Chinese Loess Plateau after long-term vegetation rehabilitation. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 748, 141375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Tian, X.; Geng, Y.; Santagata, R.; Zhuang, M.; Chen, W.; Yang, S.; Ulgiati, S. Sustainability assessment in the anthropocentric watershed based on emergy and decomposition methods: A case study of Erhai Lake Basin, southwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, T.; He, B. Runoff-related nutrient loss affected by fertilization and cultivation in sloping croplands: An 11-year observation under natural rainfall. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 319, 107549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybowski, D.; Dzierzbicka-Glowacka, L.A.; Pietrzak, S.; Juszkowska, D.; Puszkarczuk, T. Estimation of nitrogen leaching load from agricultural fields in the Puck Commune with an interactive calculator. PeerJ Life Environ. 2020, 8, e8899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.R.; Kundu, D.K.; Dey, P.; Singh, P.; Mahapatra, B.S. Effect of balanced fertilizers on soil quality and lentil yield in Gangetic alluvial soils of India. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 156, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yli-Halla, M.; Lötjönen, T.; Kekkonen, J.; Virtanen, S.; Marttila, H.; Liimatainen, M.; Saari, M.; Mikkola, J.; Suomela, R.; Joki-Tokola, E. Thickness of peat influences the leaching of substances and greenhouse gas emissions from a cultivated organic soil. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 806, 150499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kløve, B.; Sveistrup, T.E.; Hauge, A. Leaching of nutrients and emission of greenhouse gases from peatland cultivation at Bodin, Northern Norway. Geoderma 2010, 154, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhou, H.; Chen, L.; Shen, Z. The pollution risk assessment of nitrogen and phosphorus loss in surface runoff from farmland fertilizer. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2017, 36, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.; Yli-Halla, M.; Marttila, H.; Lötjönen, T.; Liimatainen, M.; Kekkonen, J.; Läpikivi, M.; Klöve, B.; Joki-Tokola, E. Leaching of nitrogen, phosphorus and other solutes from a controlled drainage cultivated peatland in Ruukki, Finland. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 904, 166769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieczko, A.K.; van de Vlasakker, P.C.; Tonderski, K.; Metson, G.S. Seasonal nitrogen and phosphorus leaching in urban agriculture: Dominance of non-growing season losses in a Southern Swedish case study. Urban For. Urban Green. 2022, 79, 127823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portela, S.I.; Reixachs, C.; Torti, M.J.; Beribe, M.J.; Giannini, A.P. Contrasting effects of soil type and use of cover crops on nitrogen and phosphorus leaching in agricultural systems of the Argentinean Pampas. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 364, 108897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norberg, L.; Linefur, H.; Andersson, S.; Blomberg, M.; Kyllmar, K. Nutrient losses over time via surface runoff and subsurface drainage from an agricultural field in northern Sweden. J. Environ. Qual. 2022, 51, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Hu, K.; Wang, S.; Zhou, M.; Hayashi, K.; Wang, H.; Zhan, X.; Jian, Y.; et al. Importance of subsurface fluxes of water, nitrogen and phosphorus from rice paddy fields relative to surface runoff. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESRI. Hot Spot Analysis (Getis-Ord Gi*) (Spatial Statistics)—ArcGIS Pro | Documentation. 2024. Available online: https://pro.arcgis.com/en/pro-app/latest/tool-reference/spatial-statistics/hot-spot-analysis.htm (accessed on 8 July 2024).
- BPDB. Bangladesh Power Development Board. 2024. Available online: http://www.bpdb.gov.bd/site/page/d2d5afd4-9f20-4c05-9102-a7c7de13798e/- (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Mahbub, A.A.; Islam, A.R.M.T. Current status of running renewable energy in Bangladesh and future prospect: A global comparison. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, C.; Sieverding, H.L.; Asato, C.M.; Gonzalez-Estrella, J.; Litzen, D.; Gilcrease, P.C.; Stone, J.J. Life cycle assessment of portable two-stage anaerobic digestion of mixed food waste and cardboard. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 139, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadiyala, A.; Kommalapati, R.; Huque, Z. Evaluation of the Life Cycle Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Different Biomass Feedstock Electricity Generation Systems. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.; Zerhusen, B.; Zehetmeier, M.; Effenberger, M. Distribution of specific greenhouse gas emissions from combined heat-and-power production in agricultural biogas plants. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 133, 105443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, A.; Azapagic, A. Life cycle environmental impacts of generating electricity and heat from biogas produced by anaerobic digestion. Energy 2014, 70, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwu, S.N.; Harding, K.; Enweremadu, C.C. Comparative life cycle assessment of enhanced anaerobic digestion of agro-industrial waste for biogas production. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 345, 131178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA. CO2 Emissions From Fuel Combustion Highlights; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2013; p. 112. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/en/publications/co2-emissions-from-fuel-combustion-2013_co2_fuel-2013-en.html (accessed on 18 November 2024).
- Vaneeckhaute, C.; Meers, E.; Michels, E.; Buysse, J.; Tack, F. Ecological and economic benefits of the application of bio-based mineral fertilizers in modern agriculture. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 49, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rynk, R.; van de Kamp, M.; Willson, G.B.; Singley, M.E.; Richard, T.L.; Kolega, J.J.; Gouin, F.R.; Laliberty, L., Jr.; Kay, D.; Murphy, D.M.; et al. On-Farm Composting Handbook (NRAES 54); Northeast Regional Agricultural Engineering Service: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]







| Components | N (%) | P (%) | K (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large animal manure | 2.7 | 0.624 | 0.6 | [42] |
| 1.79 | 1.68 | 6.17 | [43] | |
| 0.92 | 0.33 | 0.66 | [44] | |
| 0.55 | 0.90 | 0.50 | [45] | |
| Small animal manure | 1.94 | 0.99 | 0.38 | [43] |
| 1.82 | 0.59 | 1.11 | [46] | |
| 1.04 | 0.28 | 1.01 | [44] | |
| Poultry manure | 4.52 | 1.68 | 2.12 | [43] |
| 2.7 | 1.32 | 1.45 | [44] | |
| 1.65 | 2.40 | 1.7 | [45] | |
| Biofertilizer/Compost | 3.3 | 0.92 | 2.1 | [47] |
| 2.1 | 0.94 | 3.67 | [48] | |
| 0.72 | 0.16 | 0.29 | [49] | |
| 6.1 | 2.7 | 5.5 | [24] | |
| 2.36 | 2.37 | - | [50] | |
| 0.22 | 0.012 | 0.03 | [51] |
| Nutrients | N | P | K | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loss of nutrients during composting (%) | 40 | 10 | 20 | [40] |
| Nutrient bioavailability for agricultural plants (%) | 40 | 80 | 90 | [40] |
| Emission Factor (kg CO2eq/kg Fertilizer) | Type of Fertilizer | Country/Region | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.6 | Urea | Europe | [63] |
| 3.1 | USA | [64] | |
| 1.9/2.7 | Europe/Russia, USA | [65] | |
| 4 | Sweden and Western Europe | [66] | |
| 3.5 | United Kingdom | [67] | |
| 1.3–1.8 | Ammonium phosphate | Sweden and Western Europe | [66] |
| 1.4/1.7 | Europe/Russia, USA | [65] | |
| 1 | Single superphosphate | Sweden | [66] |
| 0.6 | United Kingdom | [67] | |
| 0.4–0.54 | Triple superphosphate | Europe, Russia, USA | [65] |
| 1 | Sweden | [66] | |
| 1.2 | United Kingdom | [67] | |
| 0.14–0.25 | Potassium chloride | China | [68] |
| Emission Factor (kgCO2eq/kg Compost) | Waste Type | Authors |
|---|---|---|
| 0.172–0.186 | Municipal waste | [69] |
| 0.18 | Biowaste | [70] |
| 0.239 | Household waste | [59] |
| 0.145–0.173 | Dairy manure | [71] |
| 0.413 | Municipal waste | [60] |
| 0.423 | Cattle manure | [61] |
| 0.164 | Organic waste | [72] |
| 0.381 | Grass and green waste | [62] |
| 0.229 | Livestock manure | [25] |
| 0.323 | Solid waste | [73] |
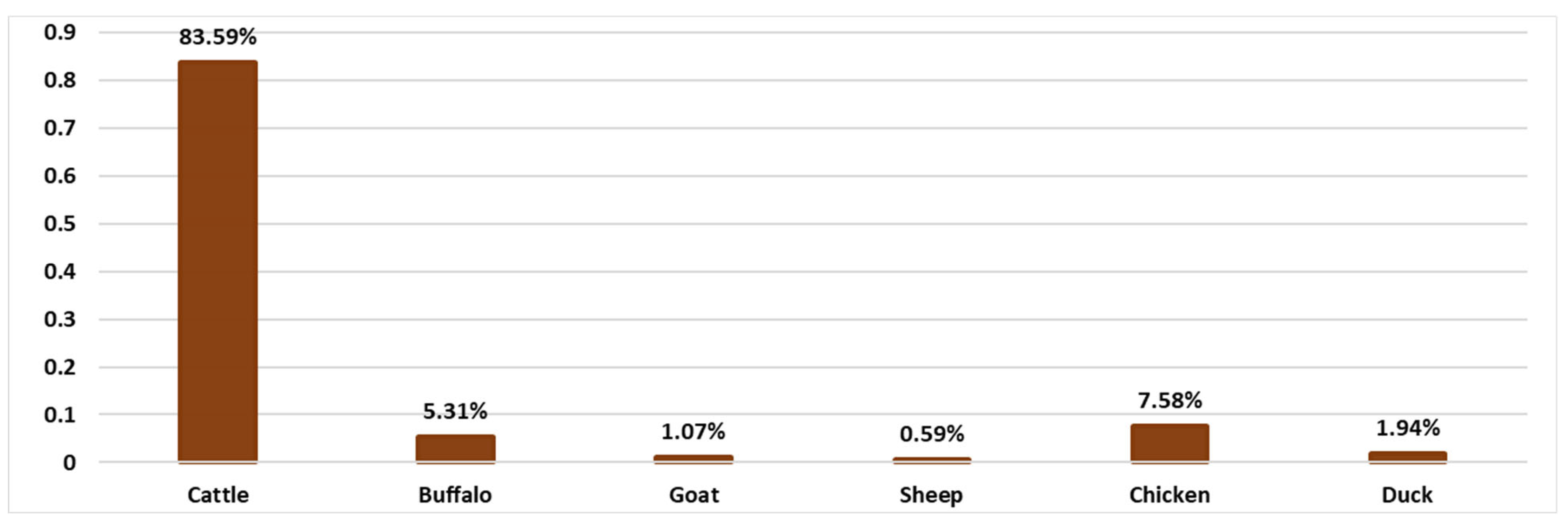
| Manure Potentiality | Cattle | Buffalo | Goats | Sheep | Chickens | Ducks | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manure generation (million tons/year) | 188.819 | 11.528 | 8.618 | 1.208 | 5.645 | 1.156 | 216.98 |
| Available manure (million tons/year) | 94.409 | 5.764 | 1.120 | 0.157 | 5.081 | 1.04 | 107.57 |
| Biogas (million m3/year) | 12,847.06 | 784.36 | 101.64 | 14.24 | 1069.33 | 218.96 | 15,035.59 |
| Electricity (MWh/year) | 23.12 | 1.41 | 0.202 | 0.028 | 1.924 | 0.394 | 27.064 |
| Biofertilizer (kilotons/year) | 12,273.26 | 749.33 | 104.86 | 14.69 | 294.68 | 60.34 | 13,497.17 |
| Compost (kilotons/year) | 58,534.03 | 3573.72 | 717.02 | 100.47 | 3759.76 | 769.86 | 67,363.03 |
| Synthetic fertilizer supply (kilotons/year) | 692.81 | 43.24 | 643.78 | 90.21 | 609.28 | 125.76 | 2202.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahal, Z.; Yabar, H. Spatial Estimation of Biogas and Compost Potential for Sustainable Livestock Manure Management in Bangladesh. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6753. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126753
Mahal Z, Yabar H. Spatial Estimation of Biogas and Compost Potential for Sustainable Livestock Manure Management in Bangladesh. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6753. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126753
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahal, Zinat, and Helmut Yabar. 2025. "Spatial Estimation of Biogas and Compost Potential for Sustainable Livestock Manure Management in Bangladesh" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6753. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126753
APA StyleMahal, Z., & Yabar, H. (2025). Spatial Estimation of Biogas and Compost Potential for Sustainable Livestock Manure Management in Bangladesh. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6753. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126753






