Abstract
Recent studies have highlighted the advantageous applications of the Marangoni effect in interfacial propulsion systems. Among these, optically driven Marangoni systems are particularly promising owing to their precise controllability and eco-friendly operation. Nevertheless, among these actuators, free movement still is limited by the interaction between light and actuators. In this work, we present a facile fabrication method for photothermal composites comprising polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) matrices embedded with carbon nanoparticles and Fe3O4 microparticles to achieve a dual-control micro-actuator. Experimental characterization confirmed the superior photothermal conversion efficiency of the composite material. Symmetrical structural configurations were engineered to achieve long-range (>15 cm), directionally programmable, and rotational motion under continuous near-infrared laser irradiation (808 nm, 2 W/cm2), while exhibiting magnetically responsive capabilities for trajectory modulation. Furthermore, the inherent viscoelasticity, mechanical flexibility, and enhanced tensile strength (up to 1.8 MPa) of the composite material enable propulsion of macroscopic payloads exceeding 50 g. The fabrication process demonstrates cost-effective, scalable, and environmentally sustainable characteristics, requiring neither complex equipment nor organic solvents. This strategy provides a paradigm shift for designing Marangoni effect-based photothermal actuators, with transformative potential in autonomous surface robotics and microfluidics applications.
1. Introduction
A micro-actuator based on the Marangoni effect presents significant potential for pioneering applications in the realm of self-driven and liquid surface robot development. In recent years, extensive research has demonstrated the unique advantages of the Marangoni effect in converting light, heat, and chemical energy into mechanical energy [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Owing to its substantial potential for practical applications in liquid surface transport, more and more researcher have focused on the Marangoni effect within the realms of self-assembly and self-propulsion [7,8,9,10,11,12]. This energy conversion is caused by inhomogeneous surface tension at the two-phase liquid interface, which is highly sensitive to variations in temperature and chemical composition. According to the Marangoni phenomenon, Marangoni actuators [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19] are an effective method for material transport.
In the field of interfacial self-assembly, the Marangoni effect emerges as a potent strategy for mitigating the coffee ring effect [20,21,22,23,24], which is related to chemical properties. The chemical driven Marangoni effect exhibits exceptional potential for driving substances across fluid surfaces [25]. For example, Cheng et al. developed a micro-boat propelled by isopropyl alcohol, investigating the feasibility of utilizing such micro-boats for the potential transport of target substances within microfluidic systems [26]. V.S. Akella et al. reported an experiment involving an agarose gel sheet embedded with camphoric acid, which spontaneously initiated movement in response to a surface tension gradient on the water surface [27]. However, a chemical-driven Marangoni effect presents some challenges, including environmental unfriendliness and long-distance movement.
Photoresponsive Marangoni actuators offer unique advantages to solve these problems [28]. Among previous micro-actuators, photothermal conversion materials played an important role in energy-autonomous microfluidic systems and drug delivery. In particular, carbon, as a high-performance photothermal conversion material, has garnered widespread attention from researchers for Marangoni actuators. For example, W. Wang et al. pioneered laser-induced graphene (LIG) strips with asymmetric adhesive-photothermal bifunctionality for Marangoni propulsion control [29]. In addition, Kwak et al. demonstrated a fuel-storage-integrated microvessel utilizing passive capillary triggering for on-demand ethanol release in Marangoni propulsion [30]. Furthermore, Maggi’s team achieved 62% photomechanical conversion efficiency in microgear arrays through optimized thermal capillary actuation at fluid interfaces and established a single-step laser ablation technique for fabricating Janus-structured floating devices with synergistic light absorption (>90% at 808 nm) and hydrodynamic drag reduction capabilities (42% reduction compared to smooth surfaces) [31]. Optical actuators exhibit efficient light-to-power conversion, and their capability for flexible and controllable transportation offers a novel direction for the development of new surface robot types. In addition, Yin et al. designed and prepared a dual-mode-driven Marangoni hydrogel actuator, which exhibits excellent ethanol loading capacity but also demonstrates both sustained motions [32]. Yao et al. developed anisotropic hydrogel actuators with multimodal stimuli-responsiveness, which consisted of clay nanosheets, Graphene Oxide (GO) nanosheets, and Fe3O4 nanoparticles [33]. However, due to low penetration of light, the movement of optical actuators is still restricted inside the liquid to a certain extent.
In this study, we demonstrate the preparation of hydrophobic materials with efficient photothermal effects for optical actuators, achieved through the direct incorporation of carbon black and Fe3O4 into PDMS. Triangular actuators were fabricated to validate the capability of directional control in free motions, and rotational motion can be realized by an optical actuator of symmetrical geometry. Furthermore, leveraging the unique adhesive properties of the material, the films were attached to the leaf’s end, thereby substituting the leaf petiole for photothermal propulsion. In addition, these actuators can achieve movement in the interface of both water and oil. This presents significant potential for pioneering applications in the realm of photothermal-driven and liquid surface robot development.
2. Materials and Methods
The devices were fabricated using a commercial PDMS elastomer (Sylgard 184 Silicone Elastomer, Dow Corning Corporation, Midland, MI, USA) along with commercially available carbon black powder and Fe3O4 powder (Kaili Metallurgical Research Institute, Tianjin, China). PDMS prepolymer was mixed with a curing agent (10:1 by weight), then carbon black powder and Fe3O4 powder were added and mixed thoroughly. The well-mixed composite was applied to a commercially available slide substrate and cured at 80 °C for 30 min. Therefore, films of 76 mm 26 mm were prepared for subsequent cutting processes. The composite films could be cut as required, and rectangular and triangular structures were prepared. Triangular drivers were made according to the above method.
Characterization and Measurement: SEM images were obtained using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) (Ultra Plus, Zeiss, Ober Kochen, Germany). DX-2700BH X-ray diffractometer provided the corresponding XRD spectra. The photothermal effect of the sample was obtained by measurement with a nano-photothermal tester (Nano Heat III, JY Tianjin, Tianjin, China). All temperature data were obtained from a non-contact infrared thermometer (smart sensor AS872D). The temperature rise in the samples was measured in air and water, respectively. Additionally, the relative thermal images were taken using an infrared camera model ST9450A+.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Properties of C/Fe3O4/PDMS Films
Figure 1a shows the preparation process of C/Fe3O4/PDMS films. Carbon and Fe3O4 powders are employed as additives and mixed with PDMS, which was mixed with a curing agent (10:1 by weight). The well-mixed composite was dropped on slide substrate and cured at 80 °C for 30 min. Figure 1b presents the XRD images of carbon and Fe3O4, confirming the amorphous nature of the C powder and the high purity of Fe3O4. The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of the samples illustrates obvious irregular folds in Figure 1c, which are attributed to the interaction between PDMS and Fe3O4. During heating, the internal energy of the Fe3O4/PDMS system increased and facilitated the formation of non-joint-chain dimethylsiloxane structures, thereby enhancing the adhesion properties of the materials [34]. As for the optical actuator, carbon black and Fe3O4 played crucial roles in thermal conversion. Figure 1d illustrates the superior tensile properties of the composite film. A uniform film, originally 73.4 mm in length, was readily stretched to 105 mm at a tensile rate of 1.43. In contrast, a PDMS film of the same length without any additives was stretched to only 88 mm, demonstrating less stretchability. These novel properties indicate the potential of this flexible, soft, and easily stretchable film to serve as a new type of robot skin in the domain of liquid surface-driven robotics. Notably, the cured films exhibit superior elasticity and are softer compared to pure PDMS films. Furthermore, the composite thin film holds significant potential in the realm of motion technology for optical driving transport actuators and small soft robots operating on liquid surfaces.
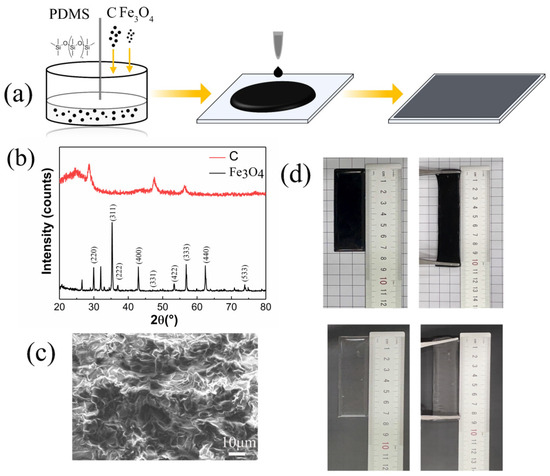
Figure 1.
Preparation process and properties of C/Fe3O4/PDMS film. (a) Preparation process of C/Fe3O4 /PDMS films. (b) XRD patterns of carbon and Fe3O4. (c) SEM image of film. (d) Optical photographs of tensile comparison between C/Fe3O4/PDMS film and pure PDMS film.
To further investigate the impact of Fe3O4 content on composite films, several samples with varying proportions were prepared (Table 1). All prepared film samples possessed identical specifications, with the carbon powder content fixed at a mass ratio of 1:20 to PDMS. The distinction lay in the mass ratios of PDMS to Fe3O4 powder, which were 10:1, 10:2, and 10:3, respectively, for samples designated as 1, 2, and 3 herein. However, when the ratio reaches 10:4, curing of the PDMS becomes challenging. The hydrophobic properties of the samples were also evaluated. The water contact angles of all samples exceeded 90 degrees, facilitating enhanced movement of the drives on the water surface. The instantaneous temperatures of the samples under laser irradiation (100 mW, 532 nm) were measured, and the temperature differences were derived by subtracting the ambient temperature. As anticipated, the Fe3O4 content was positively correlated with the temperature difference.

Table 1.
Basic information and test data about the samples.
3.2. Photothermal Property of C/Fe3O4/PDMS Film
To quantitatively characterize the photothermal property of the C/Fe3O4/PDMS film, systematic investigations were conducted using a nanoscale photothermal tester (with a laser wavelength of 808 nm and cyclic stability of 2%). Figure 2 shows photothermal properties of the C/Fe3O4/PDMS film. The temperature of the water surface was 24.5 °C, and the highest temperature detected by infrared imaging was distributed in the center of the triangular-shaped boat, up to 60.5 °C. This measurement was performed at room temperature and the boat was irradiated by a laser (100 mW, 532 nm) for one second. Similarly, the content of Fe3O4 and the temperature of the samples are positively correlated. As we suspected, a larger proportion of Fe3O4 can increase the heat absorption effect of the sample, and a higher power laser can bring a higher temperature change to the sample. Under 500 mW cm−2 laser irradiation, sample 3 warmed up at the fastest rate and reached the highest temperature at the end of the same one-minute test (Figure 2b). To investigate the heat absorption rates of the samples at different laser injection levels, the temperature variations in the three samples were tested under laser conditions of 250, 500, 750, and 1000 mW cm−2, respectively, as shown in Figure 2c. The increase in laser power significantly improves the heat absorption rate of the sample. In both sets of tests, sample 3 showed better photothermal performance compared to the others. This indicates that sample 3 will be able to provide a higher temperature gradient at the two-phase interface under laser irradiation, creating a higher Marangoni force and the best driving effect of the actuator. Subsequently, to explore the maximum value of the elevated temperature of sample 3 under laser irradiation, it was tested with lasers from 0 to 5000 mW cm−2, respectively, and the test results are shown in Figure 2d. The maximum temperature of the sample was obtained under 5000 mW cm−2 laser conditions at a room temperature of 25 °C environment. The above tests show that the boat prepared by the composite film can have a good enough photothermal effect, which is a prerequisite for generating sufficient Marangoni force on the water surface.
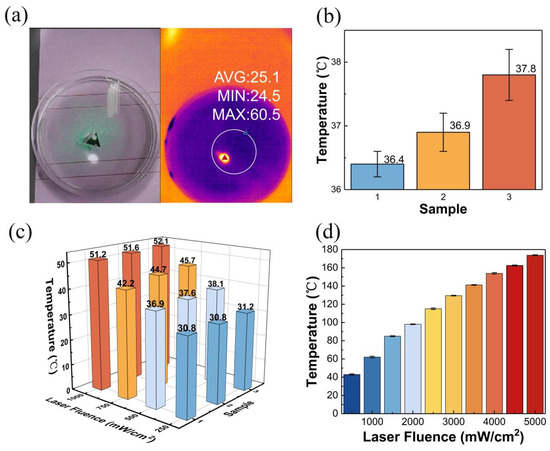
Figure 2.
Photothermal properties of C/Fe3O4/PDMS film. (a) Optical photo and thermal image of sample 3 irradiated by laser on water surface. (b) Maximum temperature changes in three samples after 60 s of irradiation by 500 mW cm−2. (c) Comparison of temperature changes in three samples after 60 s of irradiation at different laser powers. (d) Maximum temperature of sample 3 at different laser power.
3.3. The Motion Properties of the Actuators
To validate the photothermal-actuation hypothesis, micro-actuators with right-angled triangular geometry (length is 10 mm, thickness is 500 μm) were fabricated via cutting of the composite films, as shown in Figure 3a. The boat prepared by sample 3 was continuously irradiated by laser (100 mW, 532 nm) to achieve fast and smooth motion. The micro-actuators moved a distance of 40 mm at 7.8 s; the speed is about 5 mm s−1. In addition, the light-driven motion of the micro-actuators at the oil surface was also tested, as shown in Figure 3b. Among the three samples, processing time increased progressively from sample 3 (shortest duration) to sample 2 (intermediate duration), with sample 1 requiring the longest completion time and consequently demonstrating the lowest processing speed. The generation of these different gradients is related to the photothermal conversion of the samples. In other words, the speed of the boat is positively correlated with the temperature of its conversion from light. Sample 3 absorbs the most heat under laser irradiation, and transfers the highest temperature to the water surface, thus forming a larger Marangoni force on the surface. This further confirms the results of our tests on the photothermal properties of the above material.
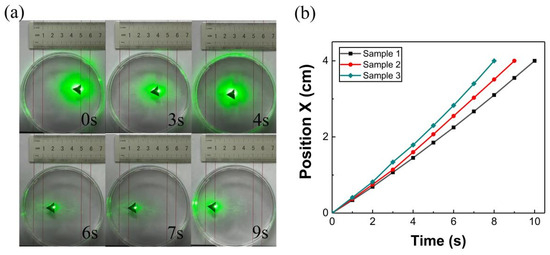
Figure 3.
The motion properties of the actuators. (a) The forward motion of the boat. (b) The time comparison of the three samples for 40 mm forward motion under green laser of 532 nm, 100 mW.
3.4. Directional Control and Maneuverability Analysis
To investigate whether the triangular drive can flexibly change its forward direction, a zigzag maze was built on the liquid surface (Figure 4). Red arrows indicate the direction of laser irradiation and the forward direction of the boat, and white dashed lines indicate the motion trajectory. With changing the laser spot position, the drive was propelled by the asymmetric Marangoni force, and a free and controlled motion in the direction was achieved. It is worth noting that either side of the triangular boat can be used to drive itself forward, so the boat can theoretically be driven in any direction at the two-phase interface. As shown in Figure 4a, the boat was initially placed at the entrance of the maze, and it could walk freely under laser driving. The maze movement was designed as a combination of three straight line movements and two turning points. The boat took 24 s to traverse the first straight line movement to reach the first turning point of the maze. The experimental configuration maintained laser irradiation on a stationary hull reference point, with real-time directional compensation synchronized to propulsion dynamics. This closed-loop implementation enabled gradual vessel navigation through the initial bend, achieving a 36 s completion duration for the curvilinear maneuver. At the first bend, the trajectory of the boat was approximated as an incomplete rotation, with the boat rotating 120 degrees counterclockwise under laser illumination, and the laser spot being fixed on the same point of the drive during this rotational motion. After taking 11 s, the boat went straight ahead to reach the second curve. Then we changed the position of laser irradiation, which directly changed the direction of the boat, so the second turn was faster than the first, taking almost only 3 s, since the boat did not perform any rotational movement during this direction change. In the end, the boat took about 20 s to reach the exit of the maze. The whole maze movement took 92 s, which was undoubtedly a rather long and continuous long-distance movement, the total movement distance of the boat was greater than 180 mm by rough calculation.
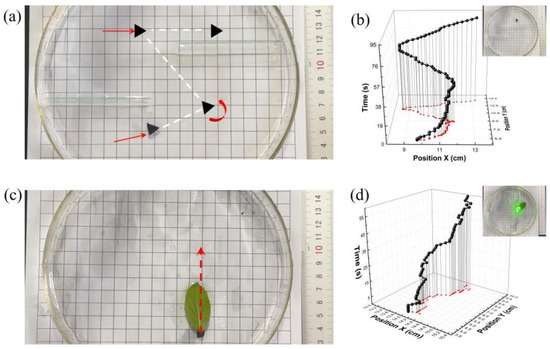
Figure 4.
(a) A schematic diagram of the zigzag maze track of the boat crossing water surface. (b) The motion of the boat’s final position traversing the maze. (c) A schematic diagram of the leaf’s forward trajectory driven by the composite film on the water surface. (d) The linear motion of the leaf.
Despite the variety of photothermal actuators that have been prepared, how to implement the actuators to transport large and bulky objects is also a great technical challenge. In our work, Marangoni thrusters adhered to other objects were prepared using the feature that thin film samples possess excellent adhesion (Figure 4b). Using the Marangoni force generated by the actuators, objects can be driven to walk freely. As an experimental verification, the sample 3 film was cut into a rectangle of 53 mm2, then it was glued to the end of the leaf to replace the petiole as a drive for transporting. The weight of the leaf used in the experiment was three times that of the pusher. When the pusher at the petiole was irradiated by laser (100 mW, 532 nm), it was rapidly warmed by the light, resulting in a local increase in water surface temperature. Nevertheless, the front of the leaf had no significant temperature change. The temperature gradient led to the Marangoni phenomenon, and the transfer of water drove the leaf to complete the forward motion. The position information during the movement in the figure was extracted from the movie, and the drive position was read once every second. As shown in the video, the thruster transported the leaf by as much as 50 mm under laser illumination during a continuous period of the 60 s. The inset shows the final position of the leaf at the end. But the leaf did not move exactly along a regular straight line, as the leaf possessed a complex geometry, which led to an imbalance in the Marangoni force, that manifested by the turning and irregular curvilinear motion of the leaf. So the position of the laser irradiation on the thruster was continuously adjusted to achieve the correction of the leaf’s forward direction. Although large transport mass and irregular surface hindered the growth of the transport speed, the drive still achieved good propulsion results. This has important implications for the development of thrusters that can transport large masses over long distances.
3.5. Rotational Movement of the Drives
Furthermore, in addition to planar linear motion, rotational motion can be achieved using efficient photothermal conversion films. Unlike conventional gear units with asymmetrical blades, the symmetrical triangular structure also allows for rotational motion. For example, a positive triangular device with the center point fixed is designed by a staple, as shown in Figure 5. Driven by the laser beam, the triangular device rotated in a counterclockwise direction ≈ 0.05 rad s−1, as shown by the arrows in Figure 5c. The drive did not rotate at a very high speed, and the friction from the center point counteracted some of the driving force. Interestingly, it denoted that the actuator would quickly rotate back in the opposite direction after removing the laser, possibly indicating the stress releasing after the light-driven forced rotation; the flexible film created torsional deformation in the rotation.
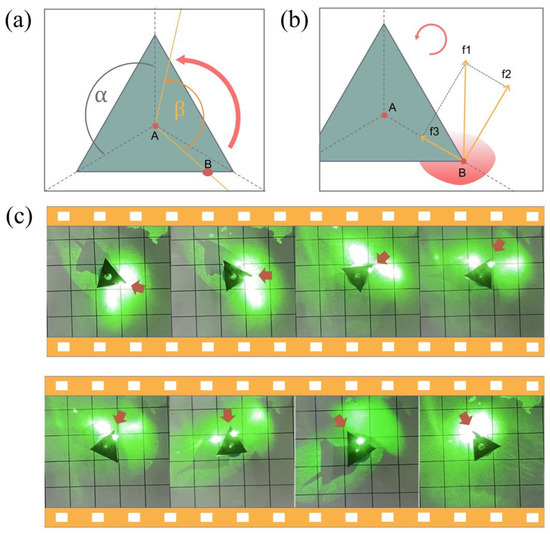
Figure 5.
(a) A schematic diagram of the rotational motion of the triangular actuator(A and B represent the center and a point at the edge of the triangle, respectively. f1 is Marangoni force, f2 and f3 denote two component force, respectively). (b) An analysis of the temperature distribution and tension of the rotating device at the water surface. (c) Passive rotation of the actuator, rotating 120 degrees counterclockwise under laser irradiation (532 nm, 100 mW). The irradiation continued for 7 s to drive the gear. See Video S5 of Supporting Information.
Similarly to the turning of the boat, which can flexibly choose different driving sides to change the forward direction, the rotation device can also change the laser tracking irradiation point to achieve flexible rotation movement. In the design, a full 360 degree rotation of the actuator was divided equally into three rotational movements of 120 degrees each (Figure 5a). In each segment, the laser beam was controlled to illuminate point B and rotated 120 degrees (angle), the actuator was then driven to rotate the same degrees (angle). Repeating this process three times achieved a complete rotational motion of the drive. And repeating the process over and over again achieved a combination of the reciprocating motion of the laser and the continuous rotational motion of the drive. Such a rotational motion is achieved by combining segmental motions, which is more flexible and practical for achieving a circular circumference in some cases where the laser is obscured.
To further understand the above rotational motion, the mechanical model of the triangular rotational structure is studied and shown in Figure 5b. Surface tension plays a critical role in interfacial motion and is influenced by the temperature, so we analyzed the temperature distribution and the forces on the rotating device. According to the Harkins formula [35], the surface tension decreases with increasing temperature, and it decreases more significantly in the region of higher relative temperature, so the temperature gradient between the liquid surface regions is sufficient to generate surface tension difference. The forces generated by the Marangoni effect at the interface (liquid/air) can be calculated as follows:
where the temperature derivative of surface tension (N mK−1) and the equation indicates that the shear stress on the surface is proportional to the temperature gradient. In the figure, point A indicated the fixed point of the triangle boat, point B indicated the action point of the laser, and the red area below point B indicated that the water surface was heated to a higher temperature. The direction of the force which generated the counterclockwise rotation was perpendicular to the line connecting the two points AB. Denoted by F1 as the total force applied to the drive, this force was equal to the sum of the Marangoni force and the drag force. Therefore, the decomposition force F3 parallel to the AB axis did not affect the rotational motion and could be ignored. Only the decomposition force F2 perpendicular to the AB line produced counterclockwise angular momentum. The moment of force F2 on point A can be calculated as follows:
where is the distance between the laser action point and the drive center point. The equation shows that the Marangoni force on the drive is proportional to the moment at the point of action. Further, we can obtain that the temperature gradient generated by the actuator at the liquid interface is proportional to the angular speed of the actuator rotation. Therefore, the drive rotates if the Marangoni force is sufficient to counteract the resistance. The imbalance in angular momentum leads to the rotation of the drive, and the key effect that causes this imbalance is the laser-induced asymmetric temperature distribution.
3.6. The Movement Caused by the Magnetic Field
The actuators can be magnetically driven because the composite material contains Fe3O4, which can be magnetically attracted. Driven by the magnet, the boat can achieve a simple three-dimensional motion, as shown in Figure 6. At the beginning of the experiment, the boat floated on the surface of the upper oil layer. Then a magnet was placed below the whole experimental setup, and the boat gradually sank to the oil–water interface under the attraction of the weak magnetic field (Figure 6a). The boat was always attracted first on one side, which may be due to the need for the boat to break the oil surface tension to get inside. In addition, the small boat can achieve linear motion on both water and oil surfaces under the action of a weak magnetic field (Figure 6b,c). The motion of the boat in oil was slower because the viscous force of oil is higher than that of water. It is worth noting that the magnetically driven boat has more motion direction perpendicular to the liquid surface compared to the light.
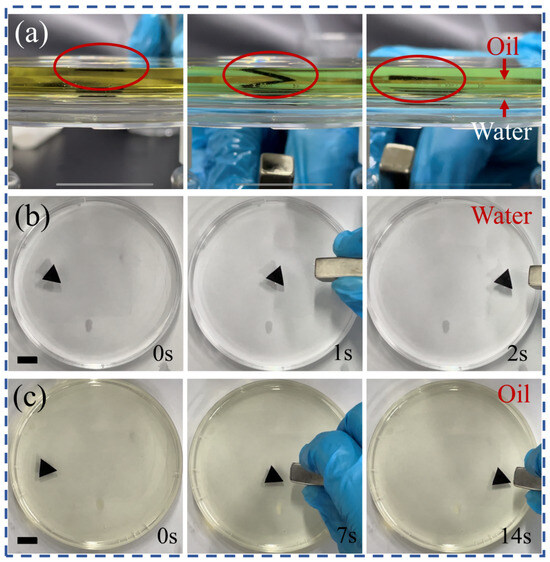
Figure 6.
(a) The actuator submerged down to the oil–water interface under the action of the magnetic field. (b) The linear motion of the boat on the water surface induced by a weak magnetic field. (c) The linear motion of the boat on the oil surface induced by a weak magnetic field.
4. Conclusions
In summary, we demonstrated the preparation of thin film materials using a simple method, with hydrophobous, viscous, and efficient photothermal conversion performances, for the development of optical actuators based on the Marangoni effect. With hydrophobic PDMS material as the main part, the addition of carbon and Fe3O4 added photothermal conversion properties and new adhesive properties to the composite. The actuator enabled free motions on the liquid surface under the action of the laser and magnetic fields. By generating Marangoni forces through laser beam irradiation, the actuator was used simultaneously to demonstrate the linear or rotational motion on the liquid surface. Furthermore, a Marangoni thruster was fabricated using the viscous properties of the composite material to drive large masses of irregularly shaped objects over long distances. The actuator can also achieve simple movement on the liquid surface and vertical sinking and floating movement under the action of the magnetic field. The resulting drive was stable and reusable, enabling long and continuous driving over long distances. We reported a simple and effective method for manufacturing highly efficient photothermal conversion materials and long-range light-driven actuators, showing great potential for cutting-edge applications.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app15126719/s1, Figure S1: Comparison of the temperature difference between Sample 3 and PDMS; Figure S2: Linear motion of the boat on an oil surface driven by the laser; Videos S1–S9: Movie of actuator.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.F.; methodology and software, writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z.; investigation, and resources, data curation, E.T. and J.Y.; writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Shanxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (202403021211093) and the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin (KHX2023-130).
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article or Supplementary Material.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Scriven, L.E.; Sternling, C.V. The Marangoni Effects. Nature 1960, 187, 186–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Lin, J.; Zhang, W.; Luo, Z.; Chen, L. Photo-thermoelectric generator integrated in graphene—Based actuator for self-powered sensing function. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 5376–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Gong, X.; Sun, Y.; Yi, N.; Wang, Z.; Weng, M.; Gao, X. Ultra-fast re-programmable actuator for use in multiple scenarios. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 508, 160978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, C.; Saglimbeni, F.; Dipalo, M.; Angelis, F.D.; Leonardo, R.D. Micromotors with asymmetric shape that efficiently convert light into work by thermocapillary effects. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Kar, A.; Kumar, R.J. Marangoni circulation by UV light modulation on sessile drop for particle agglomeration. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 873, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renney, C.; Brewer, A.; Mooibroek, T. Easy Demonstration of the Marangoni Effect by Prolonged and Directional Motion: “Soap Boat 2.0”. J. Chem. Educ. 2013, 90, 1353–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Xian, Y.; Shi, F. Precise Macroscopic Supramolecular Assembly by Combining Spontaneous Locomotion Driven by the Marangoni Effect and Molecular Recognition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 127, 8952–8956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, T.; Yamagami, T.; Nakata, H.; Okano, Y.J. pH-dependent motion of self-propelled droplets due to Marangoni effect at neutral pH. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. 2013, 29, 2554–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varanakkottu, S.N.; Anyfantakis, M.; Morel, M.; Rudiuk, S.; Baigl, D. Light-Directed Particle Patterning by Evaporative Optical Marangoni Assembly. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, T.; Nakata, H.J. Metal-Ion-Dependent Motion of Self-Propelled Droplets due to the Marangoni Effect. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 7100–7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikezoe, Y.; Washino, G.; Uemura, T.; Kitagawa, S.; Matsui, H. Autonomous motors of a metal-organic framework powered by reorganization of self-assembled peptides at interfaces. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 1081–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, H.; Chen, F.; Sun, H.; Dai, W.; Wei, Q.; Fu, L.; Yu, A.; Du, S.; et al. Layer-by-layer stacked graphene nanocoatings by Marangoni self-assembly for corrosion protection of stainless steel. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okawa, D.; Pastine, S.J.; Zettl, A.; FreChet, J.J. Surface tension mediated conversion of light to work. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 5396–5398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Hao, W.; Yu, S.; Feng, R.; Liu, Y.; Yu, F.; Tao, P.; Shang, W.; Wu, J.; Song, C.; et al. Vapor—Enabled propulsion for plasmonic photothermal motor at the liquid/air interface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 12362–12365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Grossiord, N.; Sol, J.A.H.P.; Debije, M.G.; Schenning, A.P.H.J. 3D Anisotropic Polyethylene as Light-Responsive Grippers and Surfing Divers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Qin, L.; Zhen, L.; Pan, Q.M. Controlled Movement of a Smart Miniature Submarine at Various Interfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24899–24904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Marmur, A.; Ikkala, O.; Ras, R.H.A. Vapour-driven Marangoni propulsion: Continuous, prolonged and tunable motion. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 2526–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Qiao, L.; Hao, L.J. Dramatic squat and trim phenomena of mm-scaled SU-8 boats induced by Marangoni effect. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2010, 9, 573–577. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, K.; Jaensson, N.; Buttinoni, I.; Volpe, G.; Isa, L. Microscale Marangoni Surfers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 098001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, H.; Rong, X.; Dong, G. Fabrication of Patterned Organic Semiconductor Thin Films by the Synergy of Marangoni and Coffee-Ring Effects. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2019, 35, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakashev, S.I.; Tsekov, R.J. Electro-Marangoni Effect in Thin Liquid Films. Langmuir 2011, 27, 2265–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.Y. Dewetting of liquid film via vapour-mediated Marangoni effect. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 872, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Larson, R.G. Marangoni Effect Reverses Coffee-Ring Depositions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7090–7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.H.; Stone, H.A. Uniform coating of self-assembled non-iridescent colloidal nanostructures using the Marangoni effect and polymers. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2018, 10, 054003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanton, X.; Cazabat, A.M. Spreading and Instabilities Induced by a Solutal Marangoni Effect. Langmuir 1998, 14, 2554–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Hao, L.; Liu, X. Propulsion of microboats using isopropyl alcohol as a propellant. J. Micromechanics Microengineering 2008, 18, 067002. [Google Scholar]
- Akella, V.S.; Singh, D.K.; Mandre, S.; Bandi, M.M. Dynamics of a Camphoric Acid boat at the air-water interface. Phys. Lett. A 2018, 382, 1176–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.L.; Zhu, Y.J.; Qin, D.D.; Xiong, Z.C. Light-Operated Dual-Mode Propulsion at the Liquid/Air Interface Using Flexible, Superhydrophobic, and Thermally Stable Photothermal Paper. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 12, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Han, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Han, D.-D.; Sun, H.-B. Laser-Induced Graphene Tapes as Origami and Stick-On Labels for Photothermal Manipulation via Marangoni Effect. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 31, 2006179–2006187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, B.; Choi, S.; Bae, J. Directional Motion on Water Surface with Keel Extruded Footpads Propelled by Marangoni Effect. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 6829–6836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.; Han, B.; Wang, H.; Han, D.D.; Wang, J.N.; Zhang, Y.L.; Sun, H.B. Direct Laser Writing of Superhydrophobic PDMS Elastomers for Controllable Manipulation via Marangoni Effect. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Song, Y.; He, S.; Fu, X.; Du, Z.; Yin, X. Dual—Mode driven Marangoni actuator with spontaneity and controllability as a soft robot. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 436, 137697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Yang, Y.; Huang, W.-Y.; Xiao, J.-J.; Meng, Z.-J.; Ou, Y.-Y.; He, X.-H.; Zhang, Y. Controllable Shape Morphing Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Robust Multi-Stimuli-Responsive Actuators. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 6371–6382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.H.; Ouzounian, M.; Hu, T.S.; Guo, Y.J.; Zhang, L.P.; Xu, Q. Gecko-inspired composite micro-pillars with both robust adhesion and enhanced dry self-cleaning property. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2019, 30, 2333–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkins, W.D.; Brown, F.E. The determination of surface tension and the weight of falling drops: The surface tension of water and benzene by the capillary height method. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1919, 41, 499–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).