Improved Adaptive Constant False Alarm Rate Detector Based on Fuzzy Theory for Multiple-Target Scenario
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. VI-CFAR
2.2. Improved VI-CFAR
2.2.1. FOSTA-CFAR
2.2.2. KLQ-CFAR
2.2.3. Composition of Improved VI-CFAR Detection Algorithm
3. Simulation Results
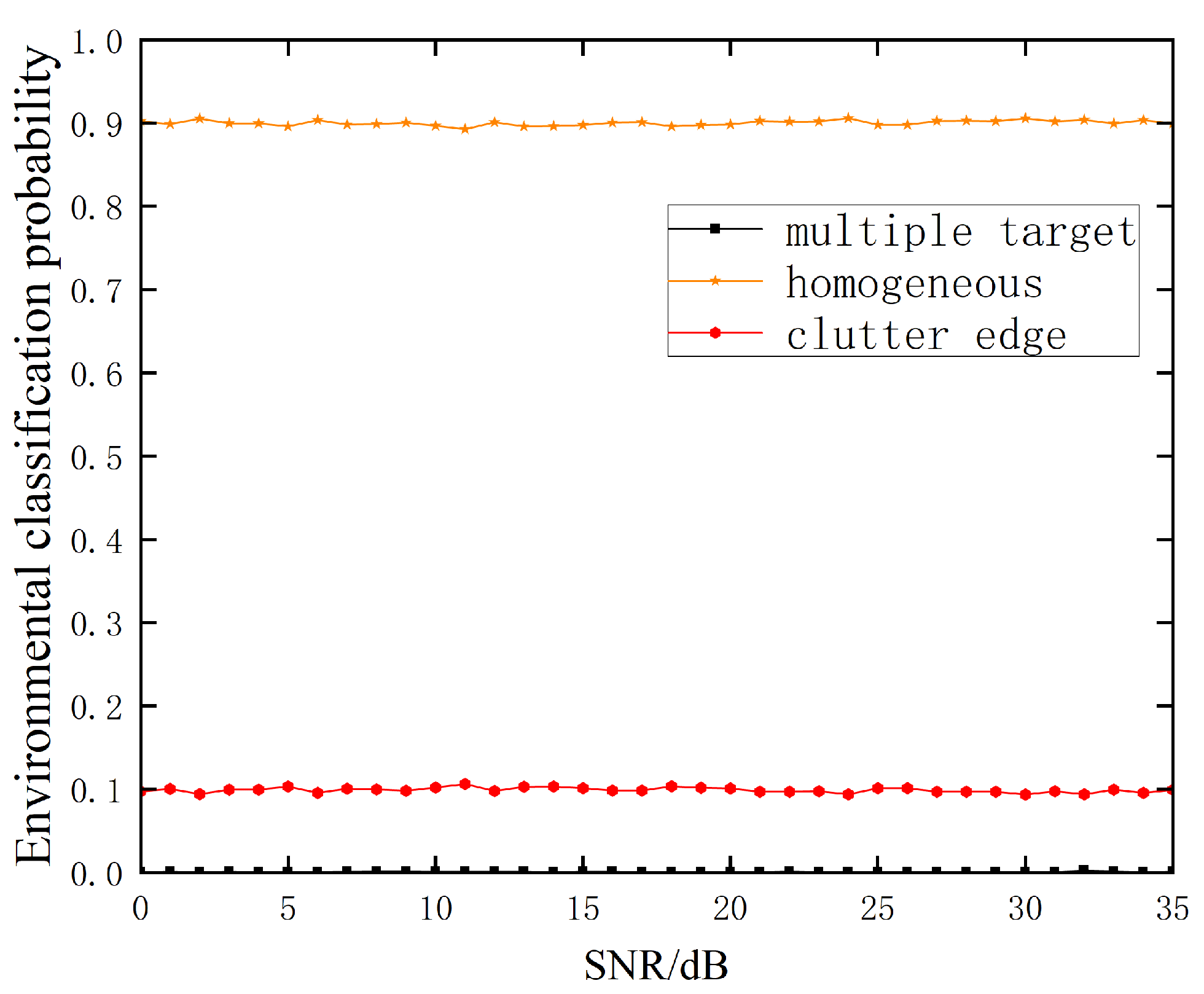
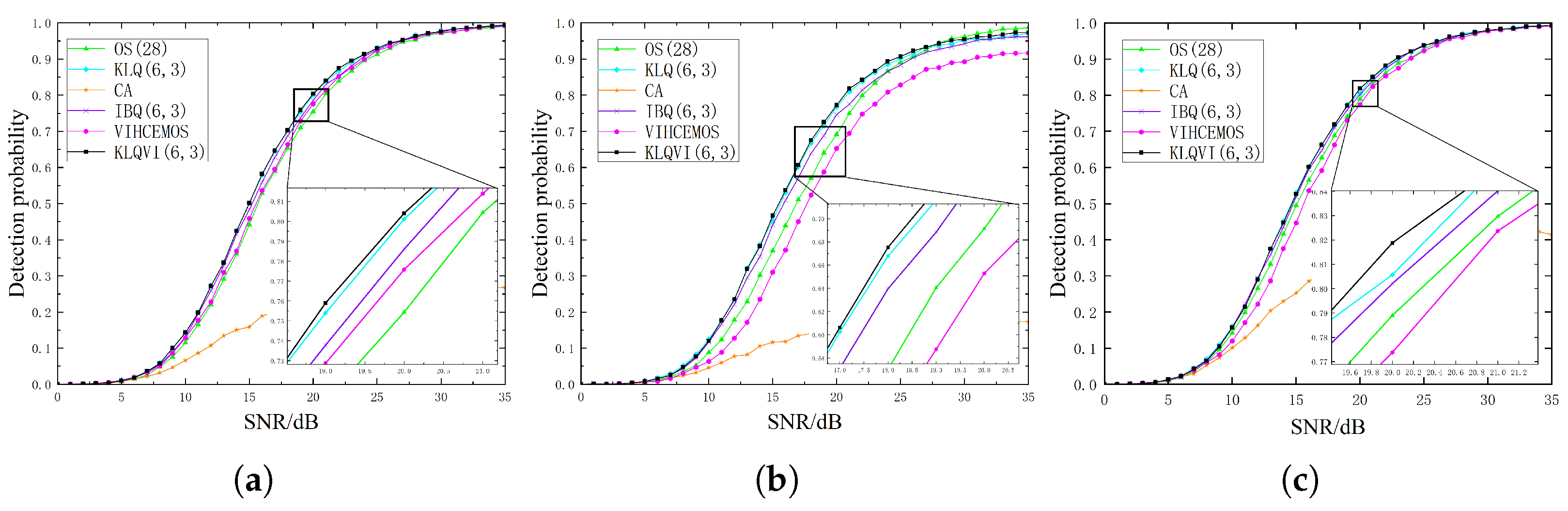
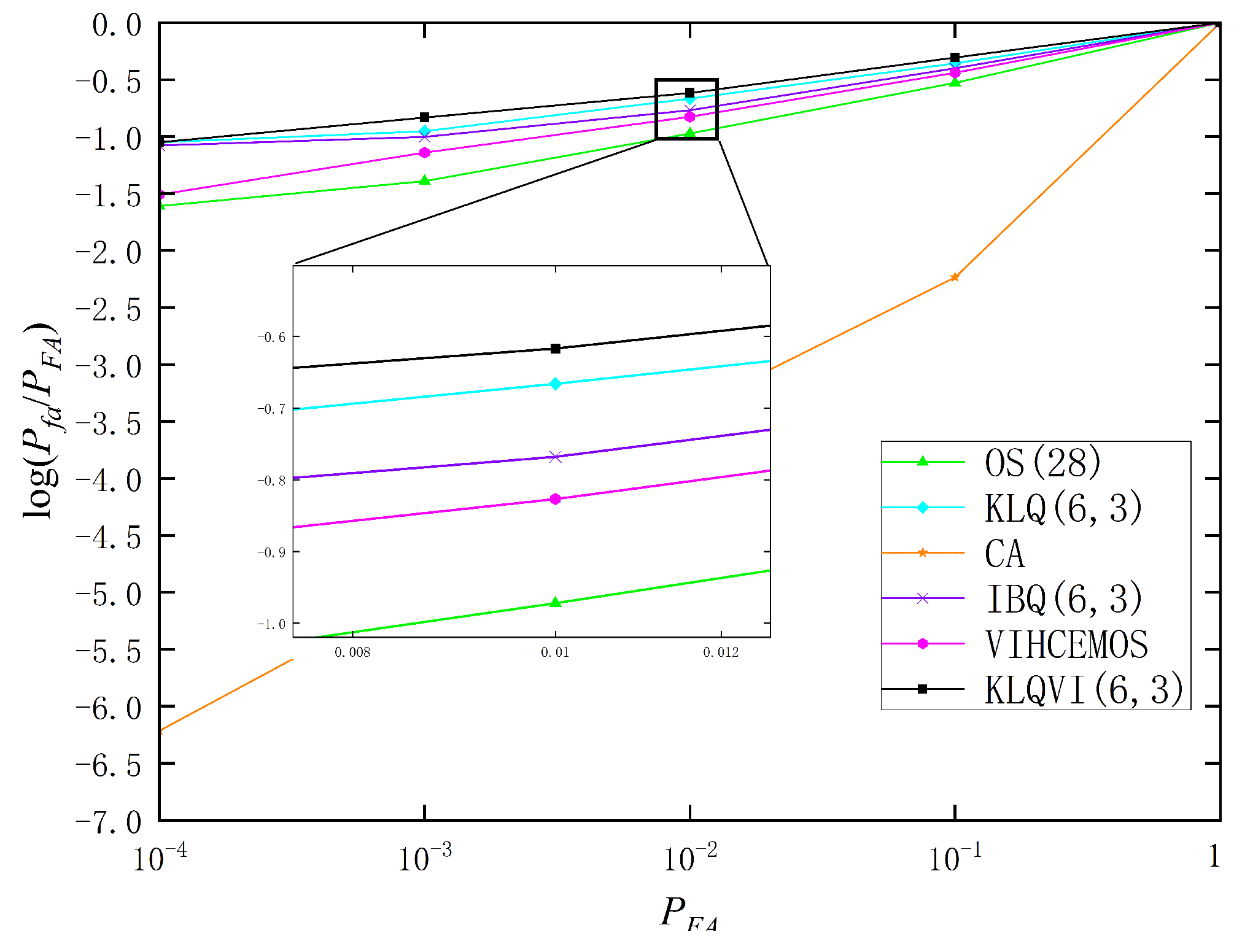
3.1. Homogeneous Environment
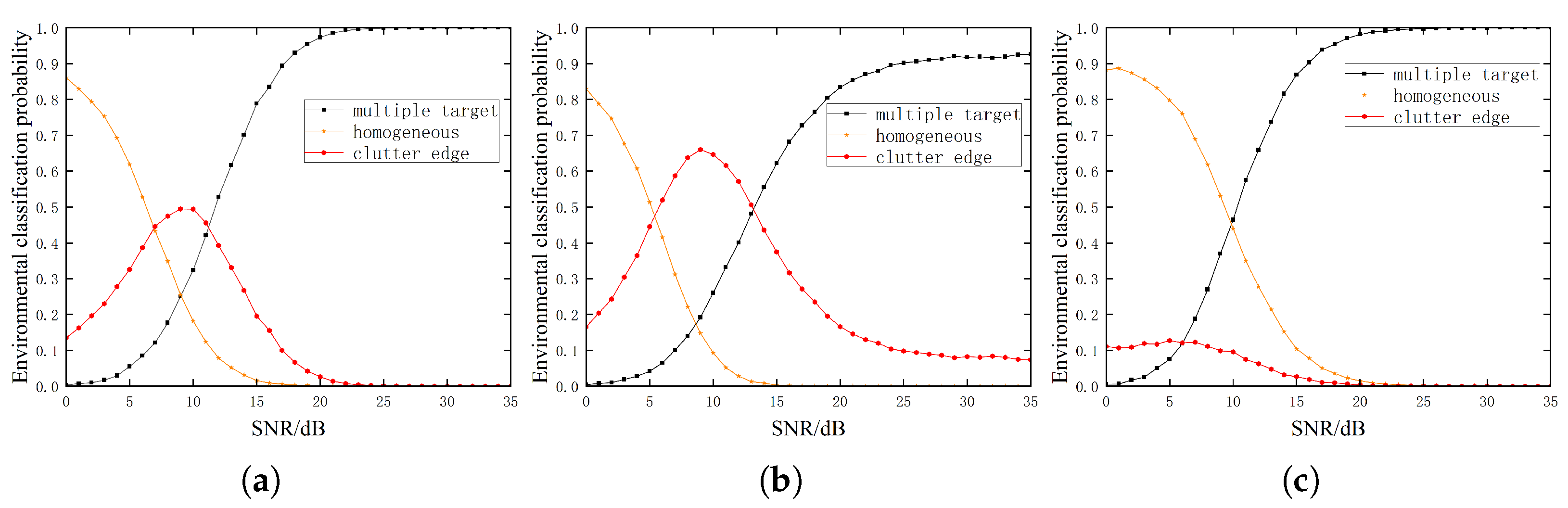
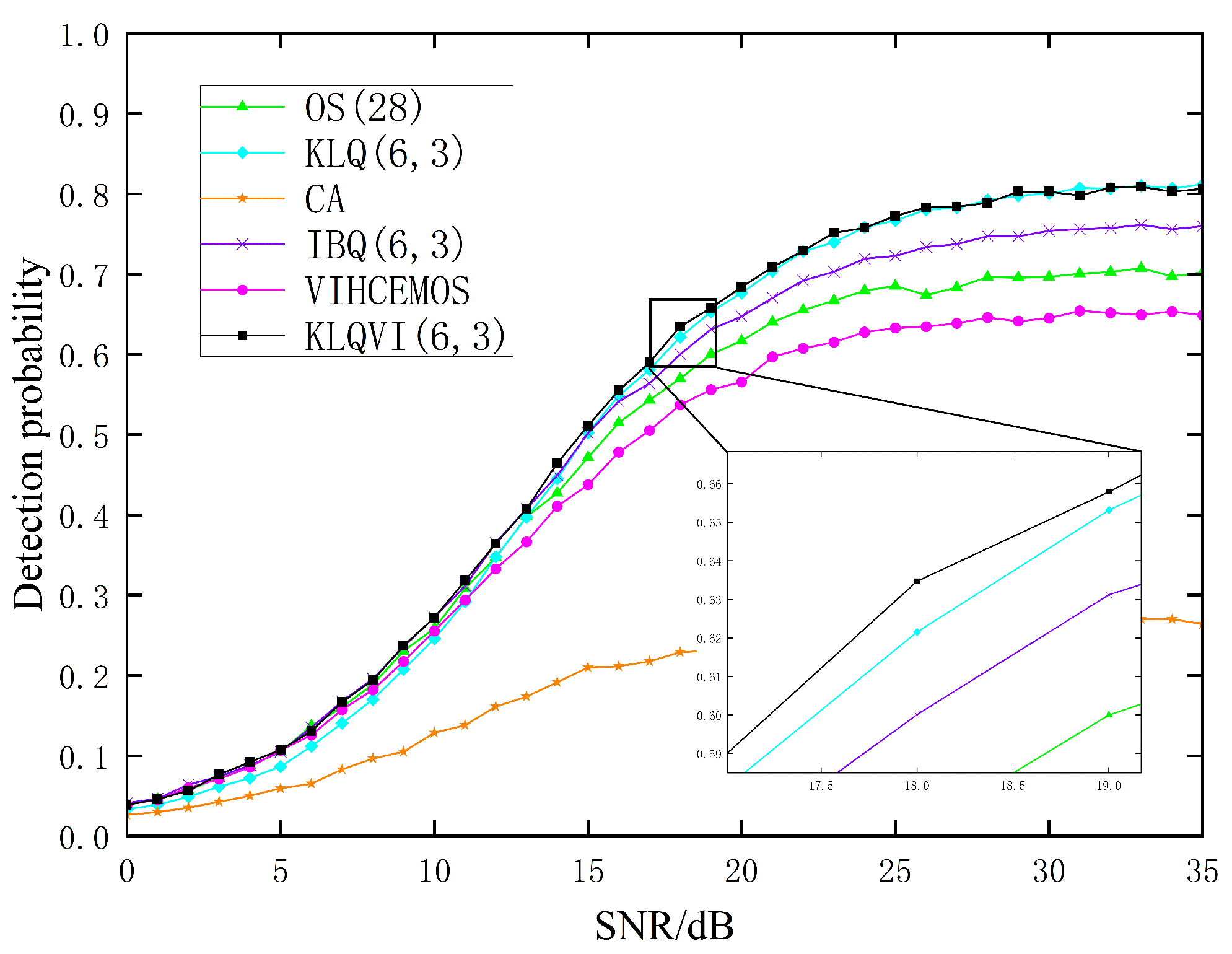
3.2. Multiple-Target Environment
3.3. Clutter Edge Environment
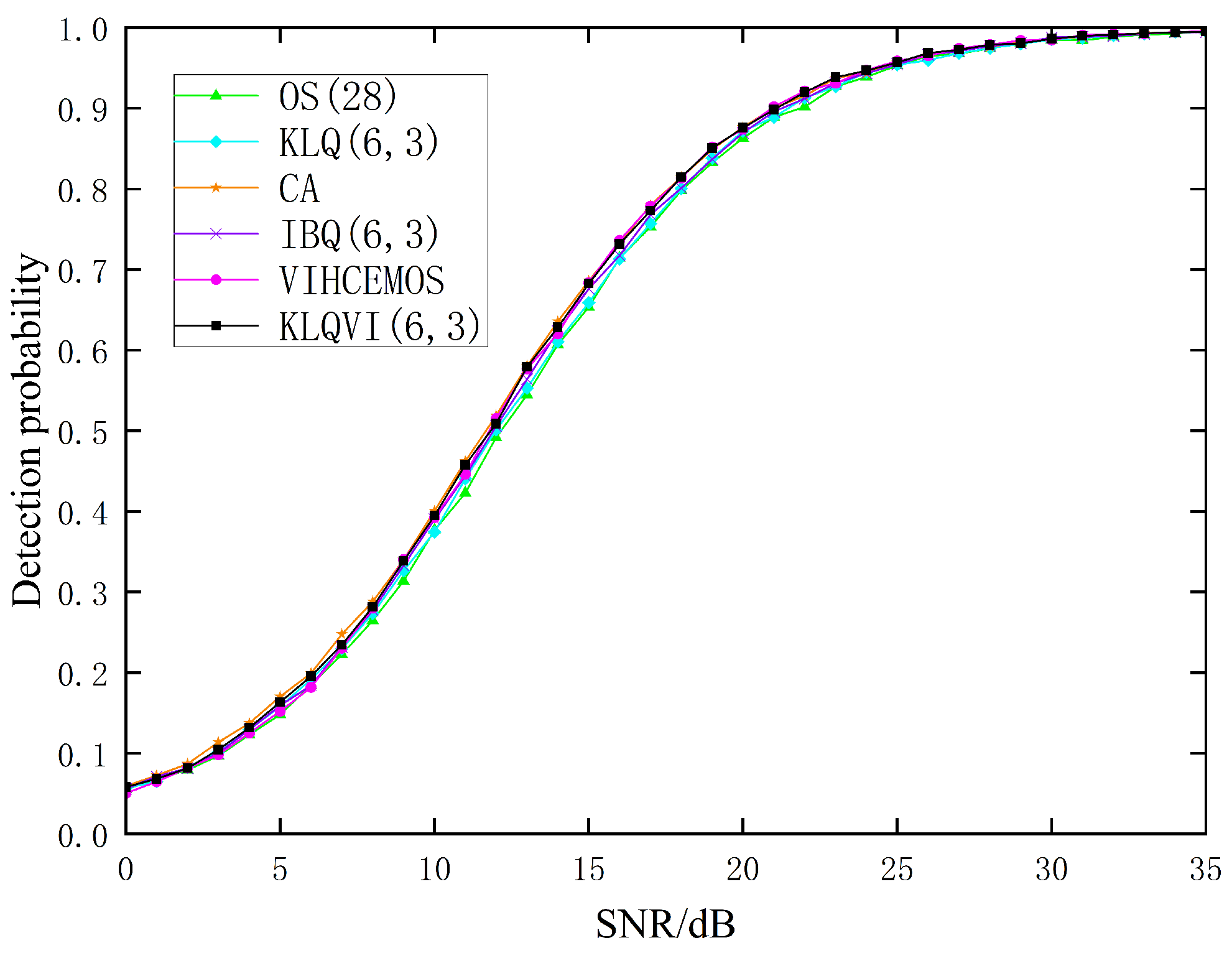
3.4. Performance of KLQVI-CFAR Based on Real Clutter Data
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wen, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Yao, T.; Tang, Y. A CFAR-enhanced ship detector for SAR images based on YOLOv5s. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Zhang, T.; Shao, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Shi, J.; Wei, S.; Zhang, X. CFAR-DP-FW: A CFAR-guided dual-polarization fusion framework for large-scene SAR ship detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 7242–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Roy, S.; Xing, G. MIMO-SAR: A hierarchical high-resolution imaging algorithm for mmWave FMCW radar in autonomous driving. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 7322–7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Hwang, J.N.; Xing, G.; Liu, H. RODNet: A real-time radar object detection network cross-supervised by camera-radar fused object 3D localization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2021, 15, 954–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, C.; Wang, C.; Wen, B.; Hou, Y.; Lai, Y. An improved CA-CFAR method for ship target detection in strong clutter using UHF radar. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, L.P.J.; García, F.D.A.; Alvarado, M.C.L.; Fraidenraich, G.; de Lima, E.R. A general CA-CFAR performance analysis for weibull-distributed clutter environments. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4025305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, D.S.; García, F.D.A.; Machado, R.; Santos Filho, J.C.S.; Saotome, O. Ca-cfar performance in k-distributed sea clutter with fully correlated texture. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1500505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baadeche, M.; Soltani, F. Closed-form expressions of P FA of mean level CFAR detectors for multiple-pulse gamma-distributed radar clutter. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 14, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahed, M.; Kenane, E.; Khalfa, A.; Djahli, F. Exact closed-form P fa expressions for CA-and GO-CFAR detectors in Gamma-distributed radar clutter. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 59, 4674–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalgh, W.; Lachenbruch, P.A. A generalized quantile estimator. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 1982, 11, 2217–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xie, J. Robust CFAR detector based on KLQ estimator for multiple-target scenario. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5104716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adak, S.; Cangi, H.; Yilmaz, A.S.; Arifoglu, U. Development software program for extraction of photovoltaic cell equivalent circuit model parameters based on the Newton–Raphson method. J. Comput. Electron. 2023, 22, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.E.; Varshney, P.K. Intelligent CFAR processor based on data variability. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2000, 36, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuping, L.; Feng, D.; Ranwei, L. Robust Centralized CFAR Detection for Multistatic Sonar Systems. Chin. J. Electron. 2021, 30, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.C.; Wang, Z.X.; Huang, Y.; Wei, H.X.; Liu, Y. VIHCEMOS-CFAR Detector Based on Improved VI-CFAR. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2613, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Jianzhong, W.; Haiyan, Z. Improved constant false alarm detector based on OSVI-CFAR. J. Electron. Meas. Instrum. 2018, 32, 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Xiu, C. Adaptive Constant False Alarm Detector Based on Composite Fuzzy Fusion Rules. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Liu, A.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, C. Target Detection Method for High-Frequency Surface Wave Radar RD Spectrum Based on (VI) CFAR-CNN and Dual-Detection Maps Fusion Compensation. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, N. A robust variability index CFAR detector for Weibull background. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 59, 2053–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihan, M.Y.; Nossair, Z.B.; Mubarak, R.I. An improved CFAR algorithm for multiple environmental conditions. Signal Image Video Process. 2024, 18, 3383–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csajbók, Z.E.; Mihálydeák, T. Fuzziness in partial approximation framework. In Proceedings of the 2013 Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems, Krakow, Poland, 8–11 September 2013; pp. 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Hannusch, C.; Mihálydeák, T. Algebraic structures gained from rough approximation in incomplete information systems. In Proceedings of the FedCSIS, Sofia, Bulgaria, 4–7 September 2022; Communication Papers. pp. 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- De, A.K.; Chakraborty, D.; Biswas, A. Literature review on type-2 fuzzy set theory. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 9049–9068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Guan, J.; Huang, Y.; Jian, T. Radar Target Detection and CFAR Processing; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Xie, J. An Improved Quantile Estimator with Its Application in CFAR Detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 3507705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
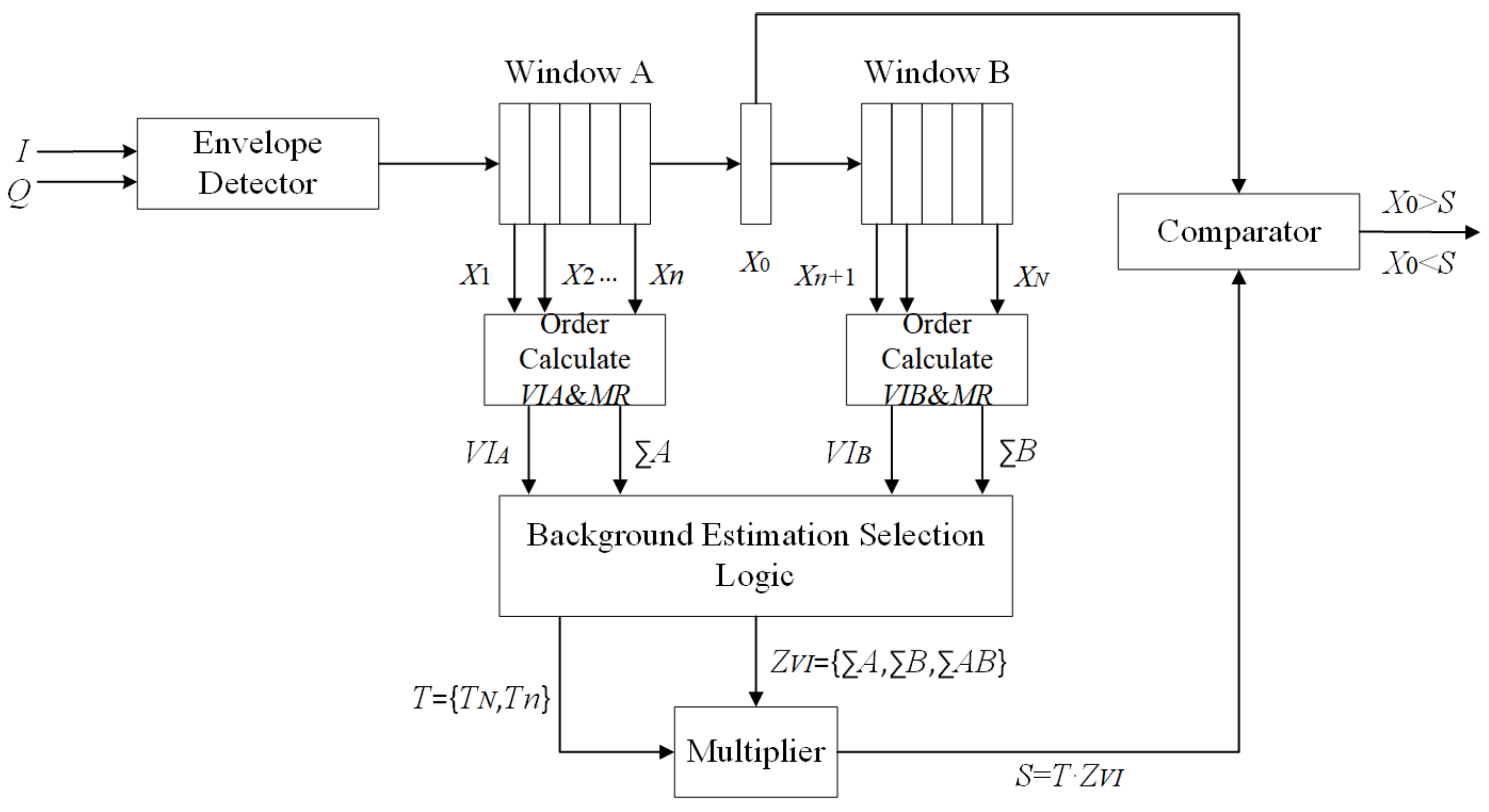
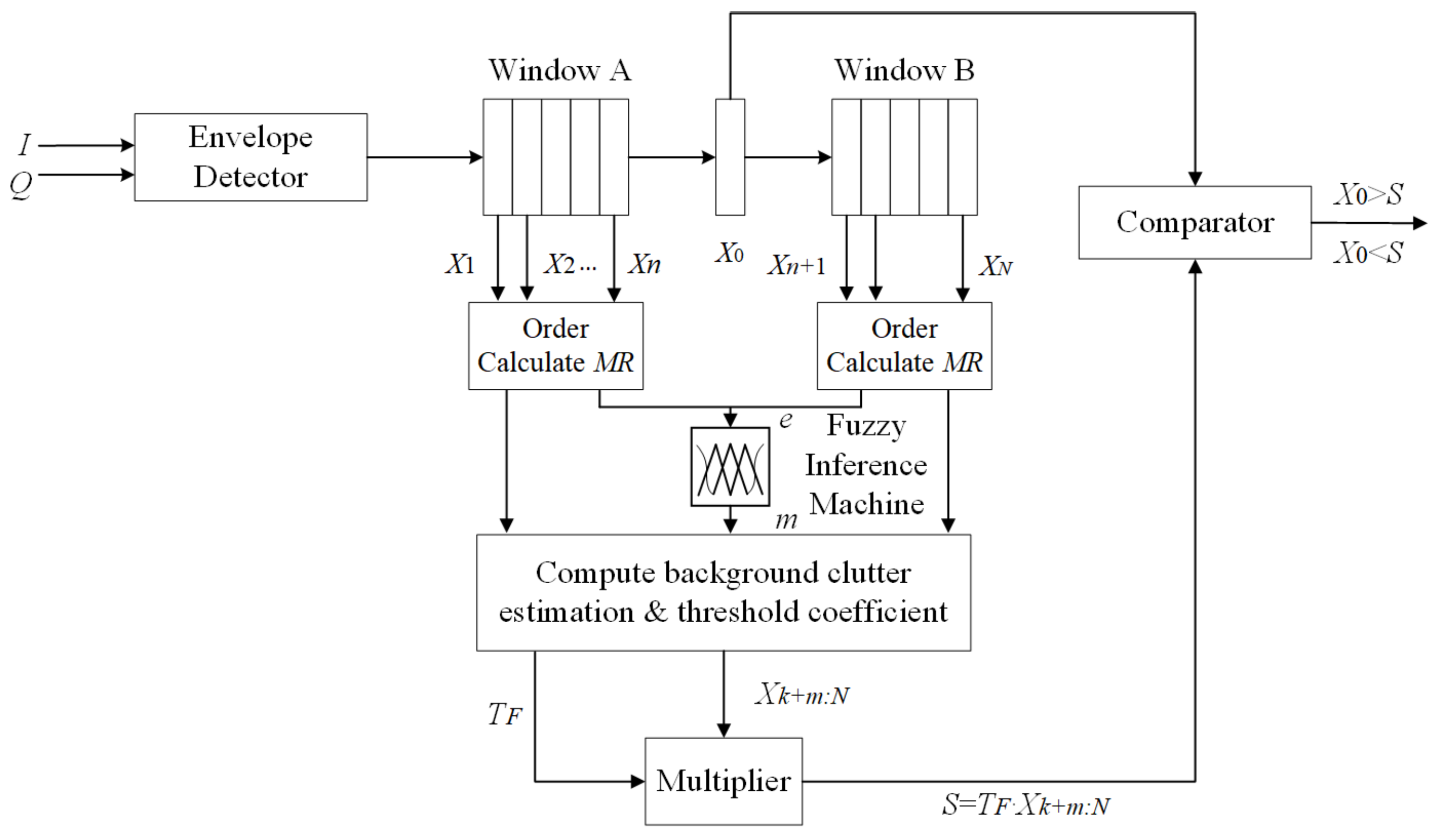



| Leading Window Variable? | Lagging Window Variable? | Different Means? | VI-CFAR Adaptive Threshold | Equivalent CFAR Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | No | No | CA | |
| No | No | Yes | GO | |
| No | Yes | - | CA | |
| Yes | No | - | CA | |
| Yes | Yes | - | SO |
| e | |||||
| m |
| Leading Window Variable? | Lagging Window Variable? | Different Means? | VI-CFAR Adaptive Threshold | Equivalent CFAR Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | No | No | CA | |
| No | No | Yes | FOSTA | |
| No | Yes | - | KLQ | |
| Yes | No | - | KLQ | |
| Yes | Yes | - | KLQ |
| Detector | CA | KLQ(6,3) | OS(28) | IBQ(6,3) | VIHCEMOS | KLQVI(6,3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average detection probability | 0.6755 | 0.6613 | 0.6519 | 0.6623 | 0.6705 | 0.6710 |
| Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between groups | 8.1 × | 2 | 4.1 × | 30.8367 | 1.0671 × |
| Within group | 3.5 × | 27 | 1.3 × | ||
| Total | 1.2 × | 29 |
| Environment | CA | KLQ(6,3) | OS(28) | IBQ(6,3) | VIHCEMOS | KLQVI(6,3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three interferences in the leading window | 0.1189 | 0.3492 | 0.3128 | 0.3382 | 0.3233 | 0.3497 |
| Four interferences in the lagging window | 0.1068 | 0.5270 | 0.5003 | 0.5145 | 0.4582 | 0.5296 |
| One interference in each of the leading and lagging windows | 0.4029 | 0.9414 | 0.9341 | 0.9395 | 0.9305 | 0.9427 |
| Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between groups | 6.9 × | 2 | 3.5 × | 618.5880 | 2.812 × |
| Within group | 1.5 × | 27 | 5.6 × | ||
| Total | 7.1 × | 29 |
| Pd = 0.5 | CA | KLQ(6,3) | OS(28) | IBQ(6,3) | VIHCEMOS | KLQVI(6,3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR/dB | – | 15.58 | 16.84 | 15.83 | 17.71 | 15.49 |
| Number of Interferences | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OS(28) | 0.8276 | 0.8135 | 0.7886 | 0.7534 | 0.7052 | 0.3203 |
| KLQ(6,3) | 0.8345 | 0.8237 | 0.8122 | 0.7997 | 0.7475 | 0.6443 |
| CA | 0.8475 | 0.5441 | 0.3503 | 0.2306 | 0.1611 | 0.1016 |
| IBQ(6,3) | 0.8369 | 0.8206 | 0.8055 | 0.7833 | 0.7387 | 0.5901 |
| VIHCEMOS | 0.8377 | 0.7836 | 0.7819 | 0.7748 | 0.7661 | 0.6869 |
| KLQVI(6,3) | 0.8414 | 0.8186 | 0.8141 | 0.8021 | 0.7684 | 0.6958 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Xiu, C. Improved Adaptive Constant False Alarm Rate Detector Based on Fuzzy Theory for Multiple-Target Scenario. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6693. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126693
Yang X, Xiu C. Improved Adaptive Constant False Alarm Rate Detector Based on Fuzzy Theory for Multiple-Target Scenario. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6693. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126693
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xudong, and Chunbo Xiu. 2025. "Improved Adaptive Constant False Alarm Rate Detector Based on Fuzzy Theory for Multiple-Target Scenario" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6693. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126693
APA StyleYang, X., & Xiu, C. (2025). Improved Adaptive Constant False Alarm Rate Detector Based on Fuzzy Theory for Multiple-Target Scenario. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6693. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126693






