Fusion-Based Localization System Integrating UWB, IMU, and Vision
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A tightly coupled UWB/IMU localization model based on a sliding-window factor graph is proposed. This model constructs a cost function for state estimation by leveraging the localization principles of both UWB and IMU.
- (2)
- An indoor UWB and stereo VIO fusion localization method based on the EKF is proposed to enable long-term, accurate, and reliable real-time localization.
2. Related Work
2.1. Visual–Inertial Odometry
2.2. UWB Positioning
2.3. Multi-Sensor Fusion Strategies
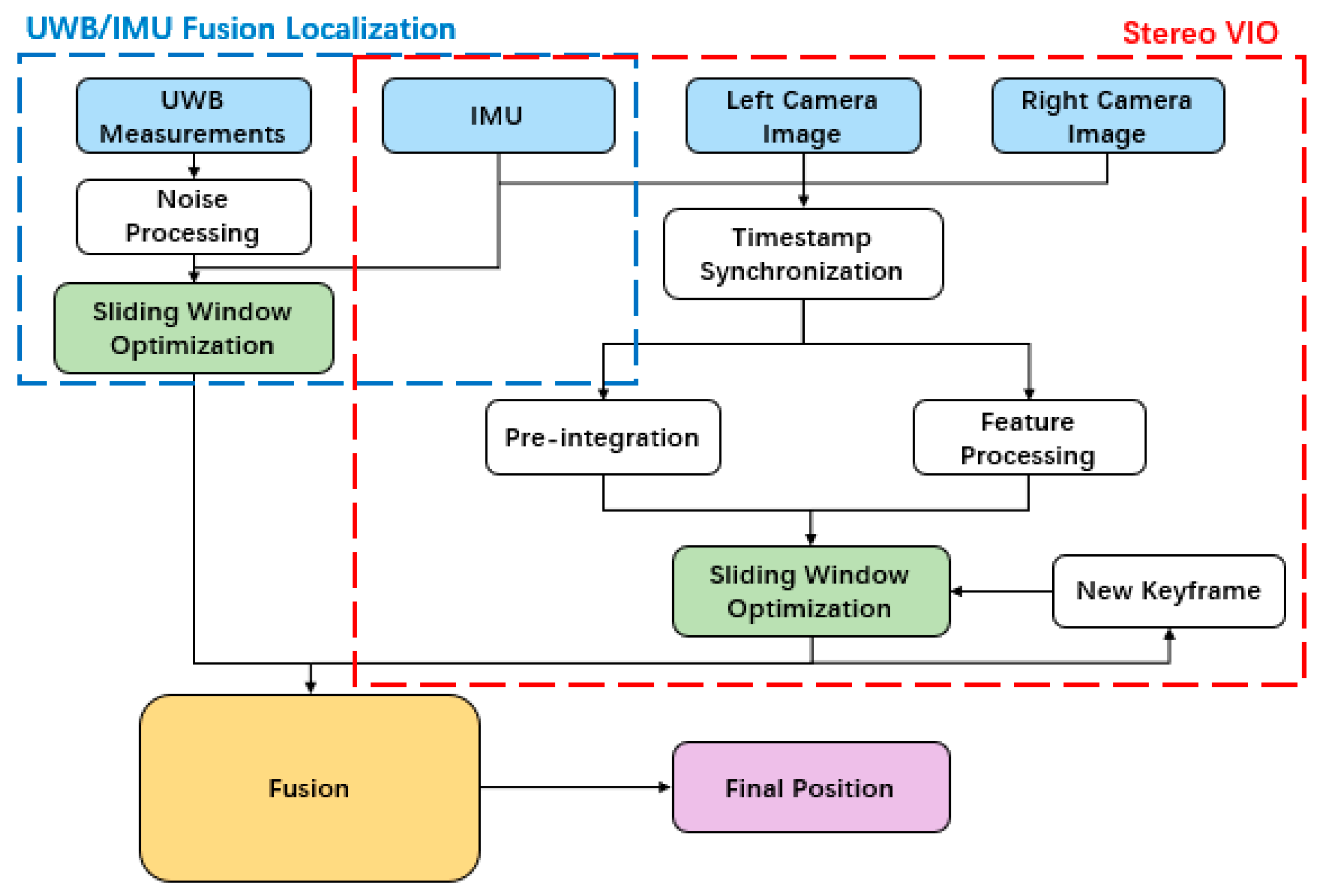
3. Tightly Coupled UWB/IMU Fusion Localization Based on Sliding-Window Factor Graph
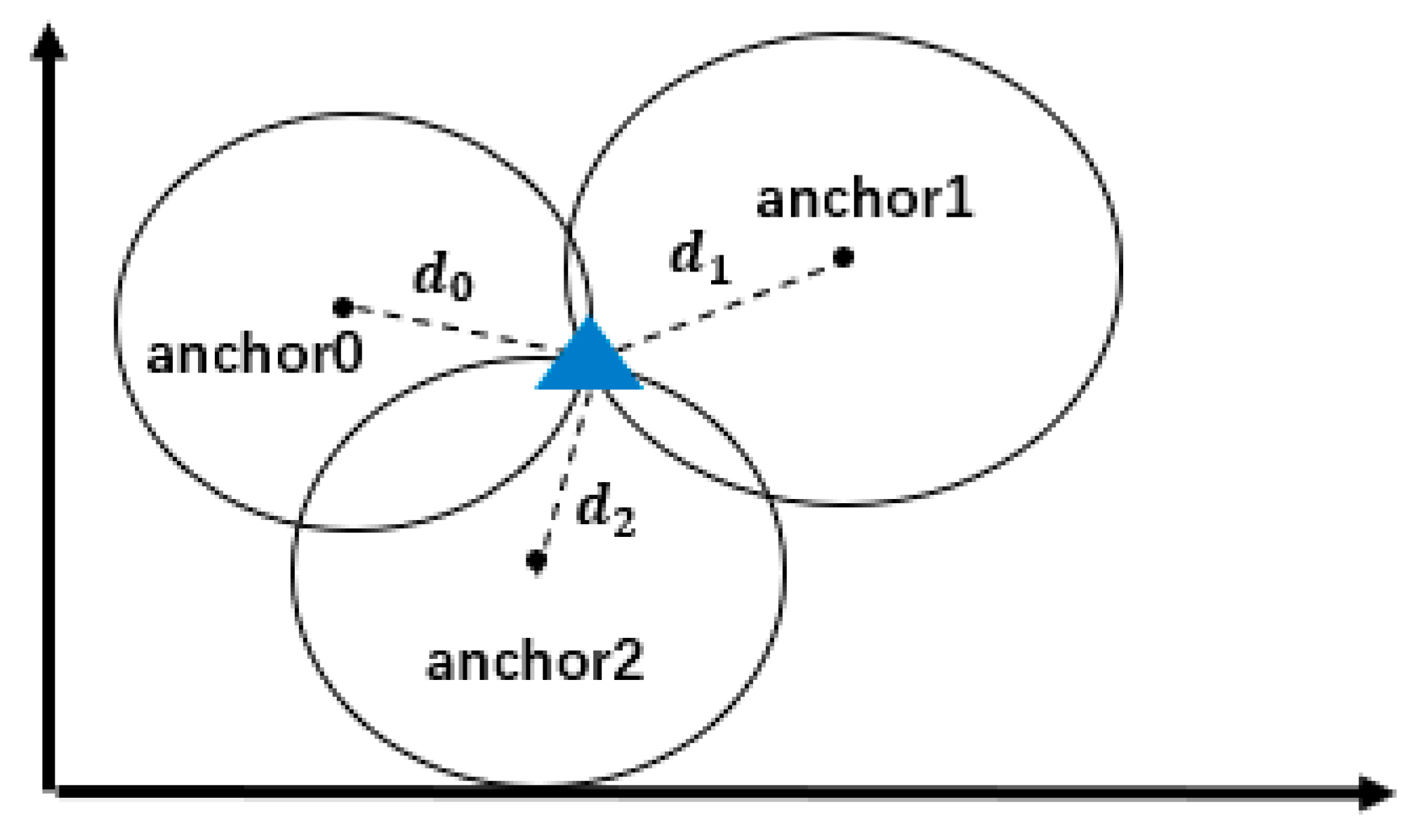
3.1. UWB Ranging Model
3.2. Factor Graph-Based Fusion Localization
3.3. UWB/IMU Fusion Localization
| Algorithm 1 DogLeg Method |
| 1: begin 2: intialize 3: While 4: compute 5: if or or 6: break 7: endif 8: 9: 10: 11: if 12: 13: elseif 14: 15: else 16: 17: 18: 19: 20: 21: 22: endif 23: if 24: break 25: endif 26: 27: 28: ; 29: 30: if 31: 32: elseif 33: 34: endif 35: 36: end |
4. Stereo VIO/UWB Fusion Localization Algorithm
4.1. State Model Construction
4.2. Observation Model Construction
4.3. Extended Kalman Filter
5. Experiments and Results Analysis
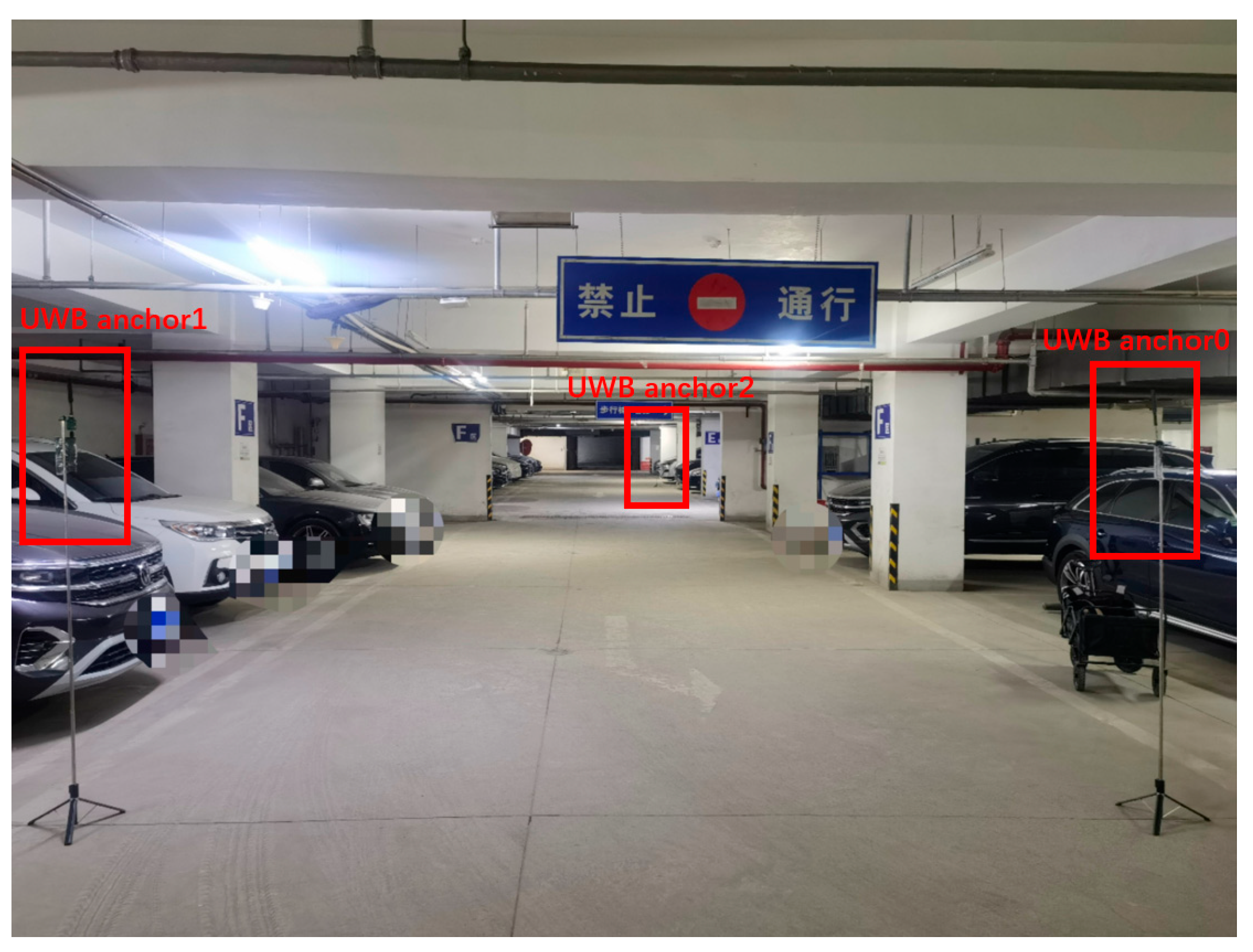
5.1. Experimental Platform Setup
5.1.1. Hardware Platform
5.1.2. Software Platform
5.2. Experiment and Analysis
5.2.1. Experimental Scenario
5.2.2. Localization Accuracy Evaluation Criteria
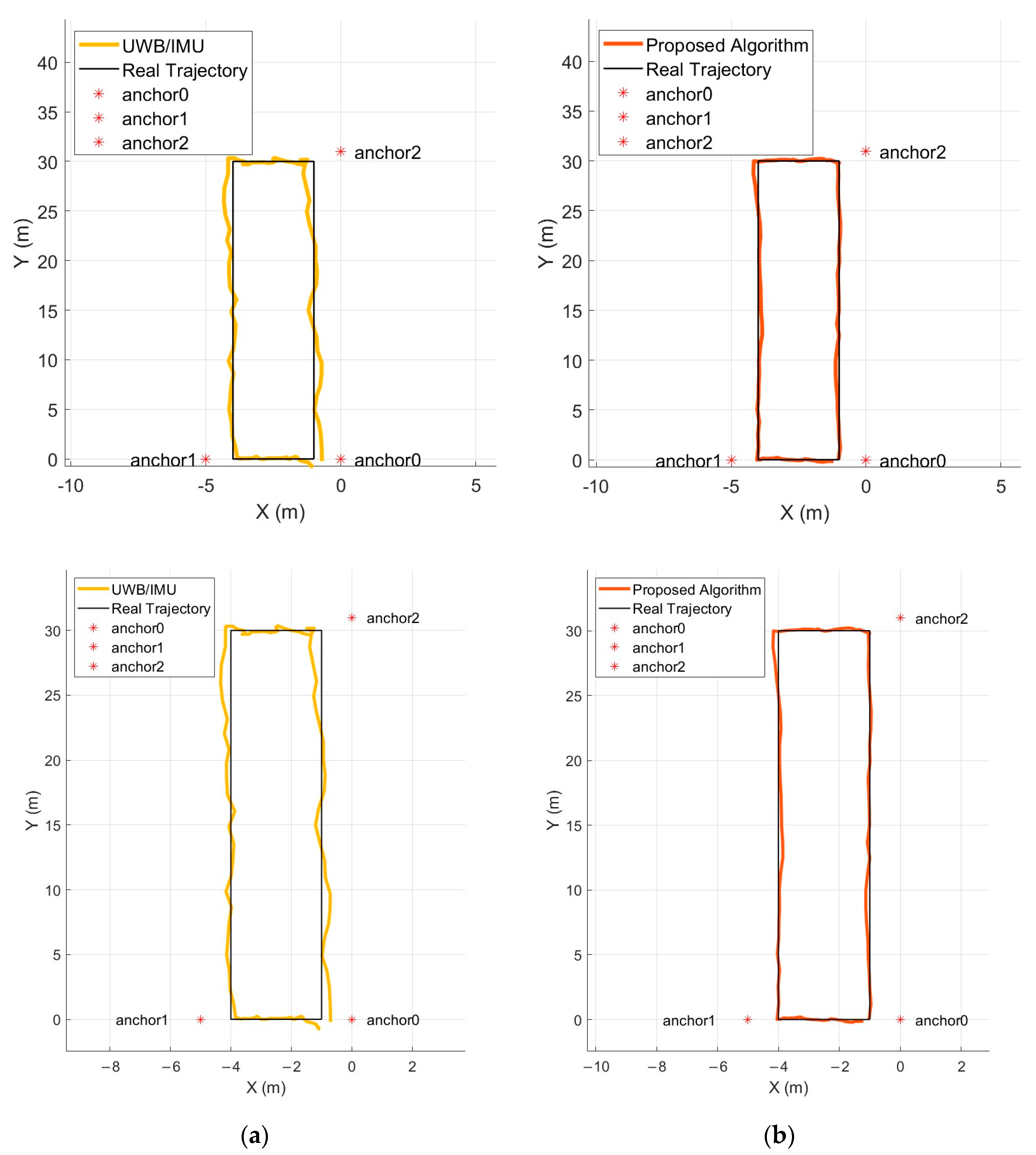
5.2.3. Results and Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, L.; Zhu, J.; Fu, Y.; Yu, Y. Integrity Monitoring for GNSS Precision Positioning. In Positioning and Navigation Using Machine Learning Methods; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2024; pp. 59–75. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, X.; Yu, B.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Jia, R.; Zhang, H.; Sheng, C.; Huang, L.; Wang, B. A New Array Pseudolites Technology for High Precision Indoor Positioning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 153269–153277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, K.; Shen, S. Decentralized visual-inertial-UWB fusion for relative state estimation of Aerial Swarm. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May 2020–31 August 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 8776–8782. [Google Scholar]
- Cadena, C.; Carlone, L.; Carrillo, H.; Latif, Y.; Scaramuzza, D.; Neira, J.; Reid, I.; Leonard, J.J. Past, Present, and Future of Simultaneous Localization and Mapping: Toward the Robust-Perception Age. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2016, 32, 1309–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benini, A.; Adriano, M.; Sauro, L. An imu/uwb/vision-based extended kalman filter for mini-uav localization in indoor environment using 802.15.4a wireless sensor network. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2013, 70, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmerico, J.; Davide, S. A benchmark comparison of monocular visual-inertial odometry algorithms for flying robots. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- William, S.; Banerjee, S.; Hoover, A. Using a map of measurement noise to improve UWB indoor position tracking. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2013, 62, 2228–2236. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.; Cui, X.; Li, W.; Xia, Y.; Lu, M. Visual-UWB Navigation System for Unknown Environments. In Proceedings of the 31st International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2018), Miami, FL, USA, 24–28 September 2018; pp. 3111–3121. [Google Scholar]
- Leutenegger, S.; Lynen, S.; Bosse, M.; Siegwart, R.; Furgale, P. Keyframe-based visual–inertial odometry using nonlinear optimization. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2015, 34, 314–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourikis, A.I.; Stergios, I.R. A multi-state constraint Kalman filter for vision-aided inertial navigation. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Rome, Italy, 10–14 April 2007; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Tardós, J.D. Visual-Inertial Monocular SLAM With Map Reuse. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Li, P.; Shen, S. Vins-mono: A robust and versatile monocular visual-inertial state estimator. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2018, 34, 1004–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloesch, M.; Omari, S.; Hutter, M.; Siegwart, R. Robust visual inertial odometry using a direct EKF-based approach. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September 2015–2 October 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, C.; Elvira, R.; Rodríguez, J.J.; Montiel, J.M.; Tardós, J.D. Orb-slam3: An accurate open-source library for visual, visual–inertial, and multimap slam. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021, 37, 1874–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geneva, P.; Eckenhoff, K.; Lee, W.; Yang, Y.; Huang, G. OpenVINS: A Research Platform for Visual-Inertial Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May 2020–31 August 2020; pp. 4666–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T. Research on AGV Navigation and Positioning System Based on UWB, IMU and Vision Fusion. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Prorok, A.; Martinoli, A. Accurate indoor localization with ultra-wideband using spatial models and collaboration. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2014, 33, 547–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecht, H.; David, P.; Emmeric, T.; Claude, O.; Davy, P.G.; Martine, L. An indoor variance-based localization technique utilizing the UWB estimation of geometrical propagation parameters. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 2522–2533. [Google Scholar]
- Taponecco, L.; D’Amico, A.A.; Mengali, U. Joint TOA and AOA estimation for UWB localization applications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2011, 10, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, C.; Zhou, T. UWB indoor positioning algorithm based on TDOA technology. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME), Qingdao, China, 23–25 August 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, C.L.; Steinhagen, B.; Homburg, J.D.; Adams, M.; Hesse, M.; Rückert, U. Identification of NLOS and multi-path conditions in UWB localization using machine learning methods. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Bu, L.; Song, X. Integrated navigation in indoor NLOS environment based on Kalman filter. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Electronic Information Technology and Computer Engineering, Xiamen, China, 22–24 October 2021; pp. 586–590. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Deng, Z.; Wang, G.; Yan, J. Time difference of arrival location method based on improved snake optimization algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 8th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 9–12 December 2022; pp. 482–486. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, B.; Pang, Z.; Åkerberg, J.; Neander, J.; Hancke, G. Experimental study of UWB-based high precision localization for industrial applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Ultra-WideBand (ICUWB), Paris, France, 1–3 September 2014; pp. 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niitsoo, A.; Edelhäußer, T.; Mutschler, C. Convolutional neural networks for position estimation in tdoa-based locating systems. In Proceedings of the Nternational Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Nantes, France, 24–27 September 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Fang, X.; Liang, L.; Du, J. Research on indoor positioning system algorithm based on UWB technology. Meas. Sens. 2024, 33, 101121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, T.-M.; Xie, L. Range-focused fusion of camera-IMU-UWB for accurate and drift-reduced localization. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 1678–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyqvist, H.E.; Skoglund, M.A.; Hendeby, G.; Gustafsson, F. Pose estimation using monocular vision and inertial sensors aided with ultra wide band. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Banff, AB, Canada, 13–16 October 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaveni, B.V.; Reddy, K.S.; Reddy, P.R. Indoor positioning and tracking by coupling IMU and UWB with the extended Kalman filter. IETE J. Res. 2023, 69, 6757–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Nguyen, T.-M.; Xie, L. Ultra-wideband aided fast localization and mapping system. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 1602–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurić, A.; Kendeš, F.; Marković, I.; Petrović, I. A Comparison of Graph Optimization Approaches for Pose Estimation in SLAM. In Proceedings of the 2021 44th International Convention on Information, Communication and Electronic Technology (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 24–28 May 2021; pp. 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, B.; Pahlavan, K. Modeling of the TOA-based distance measurement error using UWB indoor radio measurements. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2006, 10, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, P.; Wang, B.; Lai, J.; Bai, S.; Liu, M.; Yu, W. A factor graph optimization method for high-precision IMU-based navigation system. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 9509712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubović, D.; Erić, M.; Vukmirović, N.; Orlić, V. High-Resolution Sea Surface Target Detection Using Bi-Frequency High-Frequency Surface Wave Radar. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubović, D.; Erić, M.; Vukmirović, N. High-Resolution Azimuth Detection of Targets in HFSWRs Under Strong Interference. In Proceedings of the 2024 11th International Conference on Electrical, Electronic and Computing Engineering (IcETRAN), Nis, Serbia, 3–6 June 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Localization Algorithm | Error Metrics | Error Magnitude (m) |
|---|---|---|
| UWB | RMSE | 0.4212 |
| MAX | 0.9297 | |
| VIO | RMSE | 0.3052 |
| MAX | 0.7778 | |
| UWB/IMU | RMSE | 0.2722 |
| MAX | 0.7515 | |
| Proposed Algorithm | RMSE | 0.1361 |
| MAX | 0.3073 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, Z.; Luo, H.; Gao, X.; Liu, P. Fusion-Based Localization System Integrating UWB, IMU, and Vision. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6501. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126501
Deng Z, Luo H, Gao X, Liu P. Fusion-Based Localization System Integrating UWB, IMU, and Vision. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6501. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126501
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Zhongliang, Haiming Luo, Xiangchuan Gao, and Peijia Liu. 2025. "Fusion-Based Localization System Integrating UWB, IMU, and Vision" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6501. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126501
APA StyleDeng, Z., Luo, H., Gao, X., & Liu, P. (2025). Fusion-Based Localization System Integrating UWB, IMU, and Vision. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6501. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126501






