Abstract
Given the cervical spinal cord’s role in locomotor and rhythmic upper limb tasks, its neuromodulation has emerged as an important area of study for understanding human spinal rhythmogenesis. We previously demonstrated that, under unloading conditions, arm muscle vibrostimulation can elicit non-voluntary upper limb oscillations. In this study, we investigated the effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) of the motor cortex during both voluntary and non-voluntary (vibration-induced) rhythmic arm movements. We analyzed motor-evoked potentials, mean arm muscle activity, and kinematic parameters of arm movements, including cycle duration and shoulder and elbow joint angular oscillations. Motor-evoked potentials in proximal arm muscles were significantly modulated during both movement types. Notably, low-frequency TMS markedly enhanced non-voluntary arm oscillations, whereas its effect on voluntary movements was statistically non-significant. This differential response is likely due to the absence of characteristic supraspinal influences in sensory-induced spinal activation during non-voluntary movements. These findings align with previous evidence showing that supraspinal pathways facilitate rhythmogenesis in the lower limbs, and they now extend this concept to the upper limbs. Overall, our results suggest that therapies aimed at modulating cervical central pattern generators may benefit from the active engagement of supraspinal motor circuits.
1. Introduction
Locomotion in mammals, including humans, is largely based on the activity of neural circuits located in the spinal cord (central pattern generators, CPGs) [1,2]. Although it has been shown that neural networks that determine the pattern of muscle activity and interlimb coordination are located in the spinal cord [3], supraspinal centers are an important and necessary element of locomotion control in mammals. There is evidence that the motor centers of the brain, and, in particular, the motor cortex, play a significant role during walking in humans [4,5,6], as well as in rhythmic arm movements associated with stepping [7]. The human spinal cord’s lumbosacral and cervical regions are both capable of rhythmogenesis [8]. Depending on the conditions of movement organization, such as when the limbs are unloaded in a horizontal gravity-neutral body position, external, non-invasive influences like muscle vibration [9], tonic electrical stimulation of the peripheral nerves [10], direct electromagnetic stimulation of the spinal circuitry [11], or transcutaneous or epidural electrical stimulation [12,13,14] can activate the generators of rhythmic lower and upper limb movements.
Concerning the motor centers of the brain, transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) can be used to study the excitability of motor cortex neurons and their influences on spinal networks [7,15,16,17]. TMS of the motor cortex causes short-latency motor responses (motor-evoked potentials, MEPs) in target muscles mediated by the pyramidal tract [18]. The magnitude of the MEP in the muscle is also affected by its EMG activity at the time of stimulus application. The ratio of the MEP to the background muscle activity is larger during a motor act with a significant amount of motor cortex participation than during actions when the cortex is less involved [19]. The MEPs during non-voluntary locomotor-like leg movements induced by muscle vibration are smaller than the MEPs during voluntary cyclic leg movements, suggesting a lower involvement of the motor cortex in the former case [16]. Concerning the state of the cervical spinal cord, it is less clear whether similar supraspinal impacts vary depending on the type (voluntary or evoked) of rhythmic movements of the upper limbs. It should also be mentioned that the motor cortex may control the arm movements to a greater extent than the lower limbs [20,21].
In this study, we examined the effects of TMS of the motor cortex during non-voluntary (vibration-induced) arm oscillations and also compared them with those during voluntary rhythmic arm movements. A number of studies have investigated the effect of arm muscle vibration on corticospinal excitability by examining MEPs in different arm muscles [22,23,24,25,26], different postures [27], or with partial weight unloading [28], although they have mainly been conducted in the sitting or standing position and did not specifically address the rhythmogenesis of the cervical spinal cord. Rhythmic arm muscle activation is an inherent part of numerous human locomotor activities (walking, running, swimming, cycling, crawling, skiing, etc.), and additional interest in investigating cervical spinal cord activation is due to the fact that it shares spinal control mechanisms with lower limb rhythmogenesis and arm–leg coordination [29,30,31], which may also have clinical implications. Therefore, apart from examining MEPs, the impact of supraspinal inputs might be significant when it comes to entraining and activating the spinal CPG networks.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
A total of 13 healthy volunteers (11 males and 2 females), aged 20–68 years and without any known neurological or motor disorders, participated in the experiments. Three of these individuals had also taken part in a previous study [8] and were preselected based on their demonstrated ability to exhibit non-voluntary rhythmic upper limb movements entrained by arm muscle vibration. All other participants were enrolled for the first time. The experiments were performed according to the procedures of the Ethics Committee of the Institute for Information Transmission Problems (protocol n.14/11 on 7.02.2017) and in conformity with the Declaration of Helsinki for experiments on humans. All subjects were informed about the research procedures and gave their written consent to participate in the experiments.
2.2. Experimental Setup
The experimental setup used to elicit and record the non-voluntary cyclic upper limb movements was similar to what we reported in our previous studies [8]. To minimize the effects of gravity and external resistance, the subjects lay on their right side with their upper limbs hanging out, in a setup that allowed them to perform arm movements in the horizontal plane in a gravity-neutral position [32] (Figure 1A). The gravity-neutral position greatly facilitates the effect of neurostimulation in eliciting rhythmic movements by activating the spinal pattern generation circuitry [9,10,11]. The subject was relaxed when lying down, and the suspended limb entered an equilibrium position. In order to limit rotation and tilt during limb movements, the trunk was fastened between two rests that were placed on the breast and back of the trunk. The head was resting on a pillow, while the remaining limbs were lying still. The participants were instructed to relax and refrain from interfering with any movements that might be brought on by stimulation.
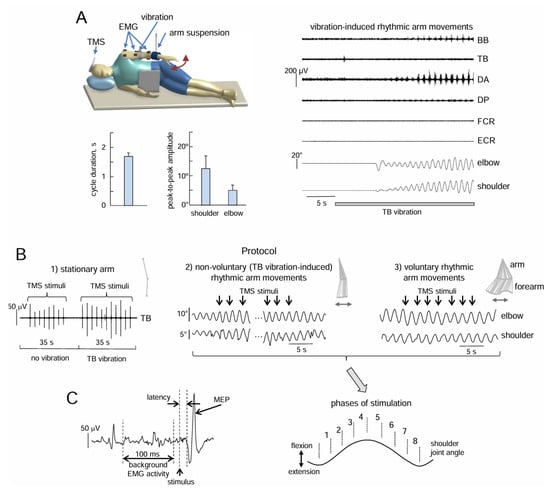
Figure 1.
Experimental setup and protocol. (A) The subject lay on her/his right side on a couch with the left upper limb suspended in the horizontal (gravity-neutral) position in order to evoke non-voluntary arm oscillations in the horizontal plane by TB vibrostimulation. An example of non-voluntary rhythmic arm movements is shown on the right panel, while the bottom left panels display the characteristics of movements in subjects exhibiting non-voluntary arm oscillations (cycle duration, and shoulder and elbow joint angular oscillations, mean + SE). BB, biceps brachii; TB, triceps brachii; DA, deltoideus anterior; DP, deltoideus posterior; FCR, flexor carpi radialis; ECR, extensor carpi radialis. (B) Experimental protocols. Protocol 1 (left panel): the effect of TB vibration on MEPs elicited by low-frequency TMS in muscles of the stationary arm. Protocol 2 (middle panel): the effect of low-frequency TMS during non-voluntary arm oscillations. Protocol 3 (right panel): the effect of TMS during voluntary arm oscillations. The top inserts display stick diagrams of upper limb oscillations. (C) An example of MEP (its latency, amplitude, and the preceding background EMG activity were evaluated) and phases of TMS during arm oscillations.
2.3. Stimulation Technique
Two types of stimulation were applied: muscle vibration (to evoke non-voluntary movements) and TMS of the motor cortex (to examine motor responses).
Muscle vibrostimulation. Continuous vibration (60 Hz sinusoid, ∼0.8 mm amplitude) of m. triceps brachii (TB) was produced by a small DC motor DMP-3-N1-01 placed in a cylindrical box (3 cm diameter, 7 cm length) with an attached eccentric weight. We selected this muscle based on previous observations that vibrostimulation of the TB muscle’s proprioceptors could entice non-voluntary arm movements [32,33]. Though other afferent signals may also be elicited, muscle vibration primarily stimulates Ia muscle spindle afferents [34]. A rubber belt was used to secure the vibrator over the TB muscle’s belly.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation. Using a figure-8 magnetic coil (diameter of inner wings: 10 cm) connected to the “Mag-2” stimulator (Schwarzer, Germany, maximum output 2.1 T, 200 s stimulus duration), TMS was administered to the right primary motor cortex, which corresponds to the arm representation. The coil was positioned tangentially to the scalp, with the handle pointed posterior-laterally at ∼30° to the midline, and the induced current in the cortex flowed from posterior to anterior over the motor strip. The coil was positioned to best elicit responses from the majority of arm muscles in the stationary suspended arm, approximately 2 cm ahead and 2–3 cm to the right of the vertex. The stimulation intensity (usually 50–55% of the stimulator’s maximal output) was adjusted to produce motor-evoked potentials that were at least three times the background (noise level) EMG activity of muscles [16]. Although the intention was typically to elicit a response from at least four recorded muscles, in most situations, responses could be obtained from all of them. Following the identification and elicitation of these responses, the coil was fixed and kept there for the duration of the experiment.
2.4. Protocol
Three experimental paradigms were tested for different upper limb conditions (Figure 1B): stationary arm (Exp 1), non-voluntary rhythmic arm oscillations evoked by triceps brachii (TB) vibration (Exp 2), and voluntary rhythmic arm movements (Exp 3).
Exp 1. Under stationary conditions, TMS-induced MEPs were recorded in the proximal (biceps brachii, BB; triceps brachii, TB; deltoideus anterior, DA; deltoideus posterior, DP) and distal (flexor carpi radialis, FCR; extensor carpi radialis, ECR) muscles of the left arm. About ten stimuli without vibration and ten stimuli during TB vibration were applied to the stationary relaxed arm (Figure 1B). The stimuli were delivered with a frequency of 0.4 Hz. The duration of the trial was about 60 s. All 13 subjects participated in this experiment. In the 7 subjects in whom vibration induced rhythmic arm movements (see below), it was not possible to administer 10 TMS stimuli in one trial, because the vibration-evoked non-voluntary movements had begun. However, the latency interval for the onset of evoked rhythmic movements (Figure 1B) varied between participants and trials, ranging from a few seconds to tens of seconds (2–25 s) [8]. Therefore, after applying 10 stimuli without vibration, 2 to 5 stimuli were applied against a vibration background until the onset of movement. Samples with vibration were repeated until a total of ten stimuli against the background of vibration were recorded.
Exp 2 and Exp 3. In the second and third paradigms (Figure 1B), the motor cortex was stimulated when arm movements approached steady-state levels (constant frequency and amplitude). We recorded these steady-state oscillations for ~10 s, followed by 40–60 s of low-frequency TMS, and finally ~10–15 s without TMS. A computer program automatically defined the onset of the movement cycle (when the shoulder angle changed its direction) and was used to trigger the TMS stimuli in different phases of the cycle (Figure 1C) at a frequency of approximately 0.4 Hz (∼T = 2.5 s), and the first stimulation time was also chosen in a random manner across trials. Since the interstimulus interval was different and lower than the cycle duration of non-voluntary arm oscillations (∼1.7 s, see Results), the TMS stimuli were applied at different moments of the individual arm movement cycles within the trial. MEPs were recorded in the same 6 muscles as in Exp 1. The duration of each trial was 60–80 s. Six to ten trials in Exp 2 and six to ten trials in Exp 3 were recorded. The subjects were given a rest of 30–60 s between trials. Since the stimulation time was 40–60 s, an average of 10–18 stimuli per trial was applied.
First, we recorded the trials in Exp 1, followed by Exp 2 and finally Exp 3. The effects of muscle vibration are known to manifest in only a subset of subjects [9,32,35]. Exp 2 included 7 of the 13 subjects who participated in the previous experiment (Exp 1) and were prompted to move their upper limb in a rhythmic manner by TB vibration. In Exp 3, we recorded the same seven subjects as in Exp 2 in order to compare the effects of TMS during non-voluntary and voluntary arm movements.
2.5. Data Recording and Analysis
EMG activity was recorded from the six muscles on the upper limb (DA, DP, BB, TB, FCR, and ECR) using surface wireless bipolar electrodes (Delsys Trigno EMG system, Natick, MA, USA). EMGs were pre-amplified and filtered (bandwidth of 20–450 Hz). Angular displacements in the two upper limb joints (shoulder and elbow) were recorded using potentiometers attached laterally to each joint. The kinematic and EMG data were sampled at 1000 Hz.
General parameters of rhythmic arm movements included the following: cycle duration, angular joint oscillations, and mean EMG activity. The kinematic data were low-pass-filtered with a zero-lag 4th-order Butterworth filter (4 Hz cut-off), and cycle duration and amplitudes of angular motions in different joints were evaluated as the parameters averaged over 8–10 cycles. Raw EMG data were rectified, low-pass-filtered with a zero-lag 4th-order Butterworth filter (10 Hz cut-off), and time-interpolated over a time base of 100 points for individual arm movement cycles (max shoulder angle as the cycle’s onset), and the mean amplitude of EMG waveforms was computed for each cycle and averaged across cycles. To prevent potential flooding caused by muscle vibrostimulation, the signal was also filtered with a 6th-order Butterworth bandpass filter at the power supply (50 Hz) and vibration (60 Hz) frequencies. MEP intervals were excluded from the calculation of mean EMG activity in TMS cycles.
The MEP was measured by calculating the peak-to-peak amplitude of the EMG signal over the period from 10 to 40 ms following stimulation (Figure 1C left panel) and normalized to the maximum MEP (MEPmax) across all probes of non-voluntary and voluntary movement conditions. Only those MEPs that fulfilled the following criteria were considered: the average amplitude of the MEP was at least three times greater than the amplitude of the background activity of this muscle before the stimulus was applied. The background activity was calculated as the mean value of rectified EMG in the interval from 110 to 10 ms before the stimulus (Figure 1C). The MEP’s latency was measured when the EMG response exceeded three times the background EMG activity. The total number of MEPs we analyzed in each subject was on average 115 ± 17 (mean ± SD) per muscle during voluntary movements and 126 ± 20 during vibration-induced rhythmic arm movements. Since the MEP value is dependent on the phase of movement [16], we separated the arm movement cycle into eight equal intervals (Figure 1C right panel) and averaged the MEPs for each of the eight stimulation intervals.
2.6. Statistics
The mean values and standard errors of the mean were used as descriptive statistics of the characteristics of movement parameters that met the normal distribution criteria (Shapiro–Wilk’s W-test, p > 0.05). Paired t-tests were used to compare the cycle duration and the amplitude of angular movements with and without applying TMS. When the experimental data set did not meet the normal distribution criteria, non-parametric statistics were used. Descriptive statistics included medians, quartiles, and range of values. For paired comparisons of two conditions, the Wilcoxon matched pair test was used (effect size statistics: PSdep = n+/N, where n+ is the number of positive difference scores; N—number of pairs). For comparisons of MEPs in 8 movement cycle phases, the Kruskal–Wallis test with Holm Bonferroni correction for post hoc analysis was used. The level of statistical significance was set at 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. MEPs in Muscles of the Stationary Arm During Rest and During TB Vibration
Figure 2A illustrates an example of MEPs in different muscles of the stationary arm in one participant. MEPs were successfully elicited in most muscles in all subjects. Since the latencies were ~15–17 ms, we calculated the MEP amplitudes in the interval 10–40 ms following the stimulus. The background levels of EMG activity were not different between conditions (no vibration vs. TB vibration, paired t-test, p > 0.05 for each muscle pair, Figure 2B), likely because the arm was relaxed and the tonic vibratory reflex was not elicited in the vibrated (TB) and not-vibrated muscles (note also relatively low levels of background EMG values, ~2 μV, that could likely reflect noise in EMG recordings). Despite some variability across muscles and subjects (in part due to differences in skin impedance across muscles and subjects), there were no significant differences in the MEPs of most muscles between “no vibration” and “TB vibration” conditions (p > 0.05, Wilcoxon matched pair test), except for TB (p < 0.05) (Figure 2C).
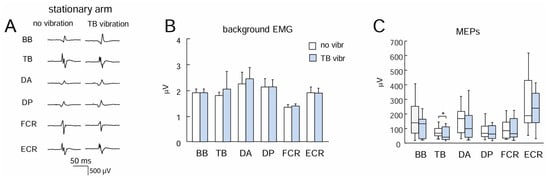
Figure 2.
Effect of TB vibration on motor response in different upper limb muscles during stationary conditions. (A) Examples of MEPs. (B,C) Background EMG activity and MEPs, respectively (mean + SE, n = 13 subjects). BB, biceps brachii; TB, triceps brachii; DA, deltoideus anterior; DP, deltoideus posterior; FCR, flexor carpi radialis; ECR, extensor carpi radialis. Asterisk (*) denotes significant differences.
3.2. Effects of Low-Frequency TMS on Non-Voluntary Arm Oscillations
In Exp 2, we applied low-frequency TMS during sustained non-voluntary rhythmic upper limb oscillations evoked by TB vibration. Only a fraction of subjects are known to exhibit the effects of muscle vibration; nevertheless, non-voluntary locomotor-related upper and lower limb movements have been documented in various studies using tonic sensory inputs to the spinal cord [9,11,32]. In our experiments, we observed non-voluntary vibration-induced rhythmic arm movements in 7 out of 13 participants. An example and the general characteristics of these movements are shown in Figure 1A. Typically, rhythmic movements started with a latency of several seconds and increased monotonically for 3–8 cycles until they reached a relatively constant amplitude of angular oscillations (1.5–3 s cycle duration, 5–30° amplitude in the shoulder joint, 3–20° in the elbow joint). Generally, the shoulder joint angle oscillations were larger in most subjects than the elbow joint angle oscillations and could be accompanied by EMG activity of the proximal upper limb muscles (Figure 1A).
TMS during non-voluntary arm oscillations evoked MEPs that were phase-modulated for the proximal upper limb muscles that were most active (Figure 3C). In particular, the Kruskal–Wallis test showed significant modulation for TB (p = 0.002), DP (p = 0.0001), and DA (p = 0.004) muscles. The Holm Bonferroni post hoc test revealed differences: for TB between phases 2 and 6; for DP between phase 1 and phases 5, 6, and 7, and also between phase 2 and phases 5, 6, and 7; for DA between phases 1 and 5, and also between phase 2 and phases 5 and 6, and between phases 3 and 5. For BB, FCR, and ECR, differences in MEPs across different movement phases were not significant (p > 0.05).
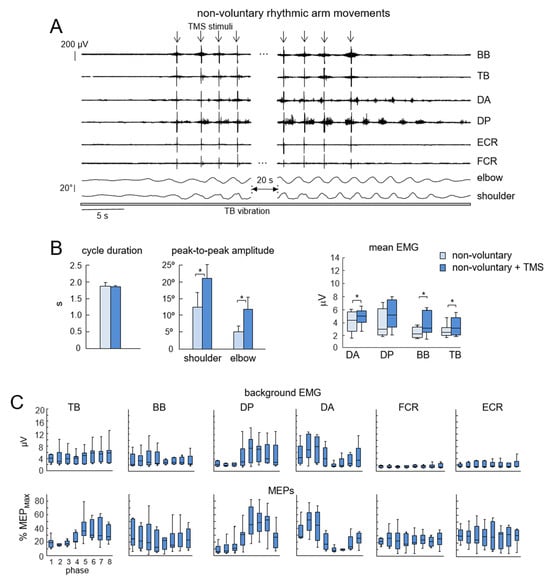
Figure 3.
Effect of low-frequency TMS of the motor cortex during vibration-induced non-voluntary upper limb oscillations. (A) Example of the facilitatory effect of TMS on non-voluntary arm oscillations (n = 7 subjects). Note an increase in elbow and shoulder joint angular oscillations following the onset of TMS and a decrease when stimulation ends. (B) Effect of TMS on kinematic and EMG parameters (mean + SE). Asterisks denote significant differences. (C) Background EMG activity (upper panels) and MEPs (lower panels) during different phases of the cycle. MEPs were expressed in percentage MEPmax after being normalized to the maximal MEP (MEPmax) of a particular muscle across all probes of non-voluntary and voluntary arm movement conditions and all stimulation phases. BB, biceps brachii; TB, triceps brachii; DA, deltoideus anterior; DP, deltoideus posterior; FCR, flexor carpi radialis; ECR, extensor carpi radialis.
Considerable changes were observed in the effect of low-frequency TMS on the manifestation of non-voluntary arm oscillations. While the cycle duration did not change significantly (p = 0.07, paired t-test), the amplitude of shoulder and elbow joint angular oscillations increased substantially in all subjects (p = 0.03 and p = 0.02, respectively, Figure 3B), including both the previously studied individuals (in [8]) and the new participants. The Wilcoxon matched pair test also showed increments in the mean activity of DA (p = 0.03, PD = 0.52), BB (p = 0.04, PD = 0.49), and TB (p = 0.02, PD = 0.54) during low-frequency TMS with respect to mean EMG activity before TMS (Figure 3B right panel). It is also worth noting that after cessation of TMS, the amplitude of oscillations and EMG activity gradually diminished to pre-TMS levels (Figure 3A).
3.3. Effects of Low-Frequency TMS on Voluntary Arm Oscillations
Similarly to non-voluntary movements, MEPs demonstrated considerable phase modulation for the majority of the most active proximal muscles during voluntary arm oscillations (Figure 4C). This was especially true for TB (p = 0.008, Kruskal–Wallis test), DP (p = 0.001), and DA (p = 0.002). For BB, FCR, and ECR, the significant differences were not found. However, the potentiation of arm movements was significantly less prominent (Figure 4). There were some increments in the mean EMG activity of DP (p = 0.03, Wilcoxon test) and TB (0.004) muscles (Figure 4B), although the increments in the amplitude of shoulder and elbow joint angle oscillations were minute and did not reach a significant level (p > 0.05, paired t-test, Figure 4B).
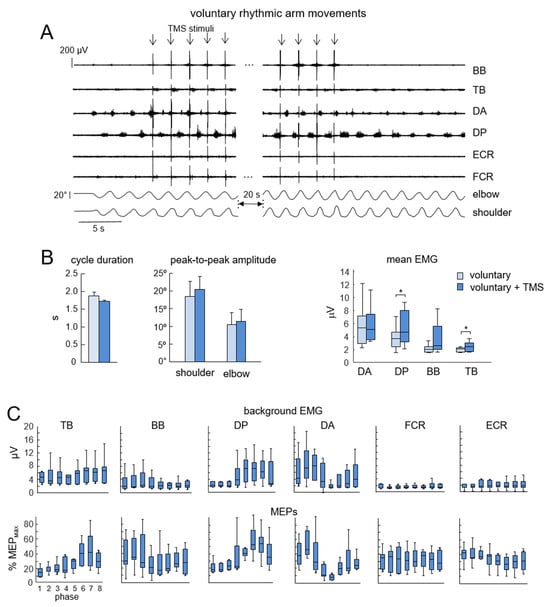
Figure 4.
Effect of low-frequency TMS of the motor cortex during voluntary upper limb oscillations. Same format as in Figure 3. (A) Example of the effect of TMS on voluntary arm oscillations (n = 7 subjects). (B) Effect of TMS on kinematic and EMG parameters (mean + SE). (C) Background EMG activity (upper panels) and MEPs (lower panels) during different phases of the cycle. Note a non-significant effect of TMS on arm oscillations (cf. Figure 3A,B with Figure 4A,B). BB, biceps brachii; TB, triceps brachii; DA, deltoideus anterior; DP, deltoideus posterior; FCR, flexor carpi radialis; ECR, extensor carpi radialis. Asterisks (*) denote significant differences.
4. Discussion
As evidenced by the notable facilitation of non-voluntary rhythmic movements (elicited by sensory stimulation) by low-frequency TMS of the motor cortex (Figure 3)—as opposed to its statistically non-significant effect on voluntary upper limb movements (Figure 4)—our results demonstrate that motor responses to TMS are not limited to short-latency motor-evoked potentials (Figure 2). Rather, these responses are also reflected in the magnitude of induced non-voluntary limb oscillations (Figure 3A,B).
This study has several limitations. For instance, non-voluntary upper limb oscillations were evoked in only ~50% of participants. This could be due to the fact that muscle vibration stimulates a relatively small number of sensory fibers entering the dorsal roots and/or to individual differences in the excitability of the spinal pattern generation circuitry. These individual differences are not only interesting in their own right but may also be critical for understanding behavioral variability and for developing personalized therapeutic approaches. In our previous work, we showed that individuals with a higher responsiveness of the pattern generation circuitry to tonic sensory input—both in the upper and lower limbs—tended to have larger H-reflexes [32]. In the present study, we were unable to evaluate the relationship between non-voluntary movements and TMS-evoked muscle responses due to the inability to reliably normalize and compare MEPs (and TMS intensity) across participants. Nonetheless, regardless of the exact mechanism behind the individual differences in the appearance of non-voluntary rhythmic arm movements, it is important to highlight that their facilitation by low-frequency TMS (Figure 3) was consistently observed in all participants who exhibited such oscillations. Another limitation is the lack of a sham-TMS or control-coil condition. Non-specific TMS effects on MEPs—such as auditory or somatosensory coactivation—cannot be fully excluded. However, our previous study showed that electrical stimulation of upper limb skin receptors did not evoke non-voluntary arm oscillations (in contrast to the prominent effect of peripheral nerve stimulation), suggesting limited contribution of such non-specific factors [33]. Notably, the effect of low-frequency TMS was primarily observed during non-voluntary (Figure 3B) rather than voluntary (Figure 4B) arm movements, despite identical stimulation intensity. This supports the interpretation that the observed effects are mainly due to TMS-induced modulation of spinal circuits rather than sensory coactivation.
The finding that motor cortex TMS significantly potentiated non-voluntary arm movements is of particular interest (Figure 3). This effect cannot be attributed solely to the direct “mechanical” influence of MEPs on muscle contraction, as stimuli were delivered at various phases of the movement cycle, and the timing of stimulation did not align with the natural movement period. Furthermore, the observed increases in arm oscillations were accompanied by heightened EMG activity in proximal muscles, which gradually declined after TMS cessation (Figure 3A,B). In contrast, the influence of TMS on voluntary hand movement parameters was considerably smaller, if present at all (Figure 4). This discrepancy may be due to non-voluntary arm movements being predominantly driven by spinal rather than central mechanisms, potentially lacking certain supraspinal influences involved in voluntary movement control.
It is plausible that the activation of corticospinal pathways by TMS is summated with ongoing activity in spinal neurons that constitute the spinal generator of rhythmic hand movements, thereby facilitating supraspinal modulation. This phenomenon bears resemblance to the effects observed during epidural electrical stimulation of the lumbosacral spinal cord, where a mixed pattern emerges—consisting of both short-latency spinal reflex responses and non-voluntary rhythmic flexor–extensor muscle activity, attributable to activation of spinal pattern generators [36]. Low-frequency TMS may induce long-lasting post-effects on spinal motoneurons and/or interneurons—possibly related to persistent inward currents, serotonergic modulation, or general network activation—which, in turn, contribute to the potentiation of non-voluntary rhythmic arm movements. Given that the same motoneurons and interneurons contribute to a wide range of possible movements, supraspinal motor commands not only activate specific motor pathways but also provide a “preparatory” command for spinal neurons and inhibit competing movement patterns, playing a vital role in motor control (“a lock with two keys” [37]). Since corticospinal excitation is mediated by polysynaptic pathways, and because TMS influences not only motoneurons but also spinal interneurons [38]—which are critical for pattern generation—such stimulation could significantly modulate the physiological state of spinal networks and contribute to the observed facilitation of non-voluntary rhythmic arm movements (Figure 3).
While phase-dependent MEPs suggest spinal involvement, we acknowledge that we did not directly measure interneuronal or CPG activity. As such, the observed enhancement of non-voluntary arm oscillations (Figure 3B) could alternatively reflect augmented sensory feedback or general corticospinal facilitation, rather than canonical CPG engagement. Although we propose that TMS effects summate with ongoing CPG activity, this alternative explanation cannot be ruled out and may well contribute to the observed movement potentiation. Importantly, whether or not targeted propriospinal interneurons (and motoneurons) are considered an integral component of cervical CPGs, they participate in shaping the rhythmic and patterned output of spinal networks. Their involvement aligns with our broader interpretation that supraspinal inputs—whether acting directly or via spinal interneurons—can modulate the excitability of spinal circuits.
In summary, low-frequency TMS significantly increased non-voluntary arm oscillations, whereas its effect on voluntary arm oscillations was much smaller (Figure 3 and Figure 4). These findings suggest that physiologically meaningful assessments of spinal cord neuromodulation and the individual physiological state of reflex pathways represent a promising area for further research. As with the lumbosacral spinal cord [16,39], our results support the notion that therapies targeting cervical CPGs could benefit from incorporating active engagement of supraspinal motor areas.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.A.S., V.A.S. and Y.I.; methodology, I.A.S., V.A.S., I.Y.D. and Y.I.; software, I.Y.D.; validation, I.A.S., G.C. and Y.I.; formal analysis, I.A.S., I.Y.D. and Y.I.; investigation, I.A.S., V.A.S. and I.Y.D.; data curation, I.Y.D.; writing—original draft preparation, I.A.S., G.C. and Y.I.; writing—review and editing, I.A.S., V.A.S., I.Y.D., G.C. and Y.I.; visualization, I.A.S., I.Y.D. and Y.I.; supervision, I.A.S. and Y.I.; project administration, I.A.S.; funding acquisition, I.A.S., G.C. and Y.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the State Task of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of Russian Federation (project FFNU-2025-0047), Italian Ministry of Health (Ricerca Corrente, IRCCS Fondazione Santa Lucia), and Italian University Ministry (#NEXTGENERATIONEU NGEU National Recovery and Resilience Plan NRRP, project MNESYS PE0000006—A Multiscale integrated approach to the study of the nervous system in health and disease DN. 1553 11.10.2022).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Institute for Information Transmission Problems (protocol n.14/11 on 7.02.2017).
Informed Consent Statement
Signed informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BB | Biceps brachii |
| CPG | Central pattern generator |
| DA | Deltoideus anterior |
| DP | Deltoideus posterior |
| ECR | Extensor carpi radialis |
| EMG | Electromyography |
| FCR | Flexor carpi radialis |
| MEP | Motor-evoked potential |
| TB | Triceps brachii |
| TMS | Transcranial magnetic stimulation |
References
- Kiehn, O. Decoding the Organization of Spinal Circuits That Control Locomotion. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillner, S.; El Manira, A. Current Principles of Motor Control, with Special Reference to Vertebrate Locomotion. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 100, 271–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlovsky, G.; Deliagina, T.; Grillner, S. Neuronal Control of Locomotion; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, N.T.; Butler, J.E.; Marchand-Pauvert, V.; Fisher, R.; Ledebt, A.; Pyndt, H.S.; Hansen, N.L.; Nielsen, J.B. Suppression of EMG Activity by Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Human Subjects during Walking. J. Physiol. 2001, 537, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capaday, C. The Special Nature of Human Walking and Its Neural Control. Trends Neurosci. 2002, 25, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.B. How We Walk: Central Control of Muscle Activity during Human Walking. Neuroscientist 2003, 9, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelemy, D.; Nielsen, J.B. Corticospinal Contribution to Arm Muscle Activity during Human Walking. J. Physiol. 2010, 588, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solopova, I.A.; Selionov, V.A.; Zhvansky, D.S.; Gurfinkel, V.S.; Ivanenko, Y. Human Cervical Spinal Cord Circuitry Activated by Tonic Input Can Generate Rhythmic Arm Movements. J. Neurophysiol. 2016, 115, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurfinkel, V.S.; Levik, Y.S.; Kazennikov, O.V.; Selionov, V.A. Locomotor-like Movements Evoked by Leg Muscle Vibration in Humans. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1998, 10, 1608–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selionov, V.A.; Ivanenko, Y.P.; Solopova, I.A.; Gurfinkel, V.S. Tonic Central and Sensory Stimuli Facilitate Involuntary Air-Stepping in Humans. J. Neurophysiol. 2009, 101, 2847–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gerasimenko, Y.; Gorodnichev, R.; Machueva, E.; Pivovarova, E.; Semyenov, D.; Savochin, A.; Roy, R.R.; Edgerton, V.R. Novel and Direct Access to the Human Locomotor Spinal Circuitry. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 3700–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapkova, E.Y. Spinal Locomotor Capabality Revealed by Electrical Stimulation of the Lumbar Enlargement in Paraplegic Patients. In Progress in Motor Control; Latash, M., Levin, M., Eds.; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2004; pp. 253–289. Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Gerasimenko, Y.; Gorodnichev, R.; Moshonkina, T.; Sayenko, D.; Gad, P.; Reggie Edgerton, V. Transcutaneous Electrical Spinal-Cord Stimulation in Humans. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 58, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minassian, K.; Hofstoetter, U.S.; Dzeladini, F.; Guertin, P.A.; Ijspeert, A. The Human Central Pattern Generator for Locomotion. Neuroscientist 2017, 23, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solopova, I.A.; Kazennikov, O.V.; Deniskina, N.B.; Levik, Y.S.; Ivanenko, Y.P. Postural Instability Enhances Motor Responses to Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Humans. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 337, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solopova, I.A.; Selionov, V.A.; Kazennikov, O.V.; Ivanenko, Y.P. Effects of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation during Voluntary and Non-Voluntary Stepping Movements in Humans. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 579, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, T.H.; Willerslev-Olsen, M.; Conway, B.A.; Nielsen, J.B. The Motor Cortex Drives the Muscles during Walking in Human Subjects. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 2443–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.; Swayne, O.B.; Vandermeeren, Y.; Camus, M.; Dimyan, M.A.; Harris-Love, M.; Perez, M.A.; Ragert, P.; Rothwell, J.C.; Cohen, L.G. Contribution of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation to the Understanding of Cortical Mechanisms Involved in Motor Control. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 325–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemon, R.N.; Johansson, R.S.; Westling, G. Corticospinal Control during Reach, Grasp, and Precision Lift in Man. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 6145–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffner, R.; Masterton, B. Variation in Form of the Pyramidal Tract and Its Relationship to Digital Dexterity. Brain Behav. Evol. 1975, 12, 161–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, R.; Lemon, R. Corticospinal Function and Voluntary Movement, Monographs of the Physiological Society; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bertolasi, L.; Priori, A.; Tinazzi, M.; Bertasi, V.; Rothwell, J.C. Inhibitory Action of Forearm Flexor Muscle Afferents on Corticospinal Outputs to Antagonist Muscles in Humans. J. Physiol. 1998, 511 Pt 3, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossev, A.; Siggelkow, S.; Schubert, M.; Wohlfarth, K.; Dengler, R. Muscle Vibration: Different Effects on Transcranial Magnetic and Electrical Stimulation. Muscle Nerve 1999, 22, 946–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, K.; Rothwell, J.C. Differential Effect of Muscle Vibration on Intracortical Inhibitory Circuits in Humans. J. Physiol. 2003, 551, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkranz, K.; Rothwell, J.C. The Effect of Sensory Input and Attention on the Sensorimotor Organization of the Hand Area of the Human Motor Cortex. J. Physiol. 2004, 561, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancheva, K.; Schrader, C.; Christova, L.; Dengler, R.; Kossev, A.R. The Effect of Muscle Vibration on Short Latency Intracortical Inhibition in Humans. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 114, 2073–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantak, S.S.; Wittenberg, G.F.; Liao, W.-W.; Magder, L.S.; Rogers, M.W.; Waller, S.M. Posture-Related Modulations in Motor Cortical Excitability of the Proximal and Distal Arm Muscles. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 533, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runnalls, K.D.; Anson, G.; Wolf, S.L.; Byblow, W.D. Partial Weight Support Differentially Affects Corticomotor Excitability across Muscles of the Upper Limb. Physiol. Rep. 2014, 2, e12183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaad, F.; Levin, O.; Meyns, P.; Drijkoningen, D.; Swinnen, S.P.; Duysens, J. Arm Sway Holds Sway: Locomotor-like Modulation of Leg Reflexes When Arms Swing in Alternation. Neuroscience 2014, 258, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehr, E.P.; Barss, T.S.; Dragert, K.; Frigon, A.; Vasudevan, E.V.; Haridas, C.; Hundza, S.; Kaupp, C.; Klarner, T.; Klimstra, M.; et al. Neuromechanical Interactions between the Limbs during Human Locomotion: An Evolutionary Perspective with Translation to Rehabilitation. Exp. Brain Res. 2016, 234, 3059–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigon, A. The Neural Control of Interlimb Coordination during Mammalian Locomotion. J. Neurophysiol. 2017, 117, 2224–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solopova, I.A.; Selionov, V.A.; Blinov, E.O.; Dolinskaya, I.Y.; Zhvansky, D.S.; Lacquaniti, F.; Ivanenko, Y. Higher Responsiveness of Pattern Generation Circuitry to Sensory Stimulation in Healthy Humans Is Associated with a Larger Hoffmann Reflex. Biology 2022, 11, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solopova, I.A.; Zhvansky, D.S.; Selionov, V.A.; Ivanenko, Y. Synergistic Influences of Sensory and Central Stimuli on Non-Voluntary Rhythmic Arm Movements. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2019, 64, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roll, J.P.; Vedel, J.P.; Ribot, E. Alteration of Proprioceptive Messages Induced by Tendon Vibration in Man: A Microneurographic Study. Exp. Brain Res. 1989, 76, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, G.M.; McCloskey, D.I.; Matthews, P.B. Proprioceptive Illusions Induced by Muscle Vibration: Contribution by Muscle Spindles to Perception? Science 1972, 175, 1382–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapkova, E.Y.; Schomburg, E.D. Two Types of Motor Modulation Underlying Human Stepping Evoked by Spinal Cord Electrical Stimulation (SCES). Acta Physiol. Pharmacol. Bulg. 2001, 26, 155–157. [Google Scholar]
- Gurfinkel, V.S.; Ivanenko, Y.P.; Levik, Y.S.; Kazennikov, O.V.; Selionov, V.A. The Neural Control of Posture and Locomotion: A Lock with Two Keys. In Motor Control Today and Tomorrow; Gantchev, G.N., Mori, S., Massion, J., Eds.; Academic Publishing House: Sofia, Bulgaria, 1999; pp. 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- York, D.H. Review of Descending Motor Pathways Involved with Transcranial Stimulation. Neurosurgery 1987, 20, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorach, H.; Galvez, A.; Spagnolo, V.; Martel, F.; Karakas, S.; Intering, N.; Vat, M.; Faivre, O.; Harte, C.; Komi, S.; et al. Walking Naturally after Spinal Cord Injury Using a Brain-Spine Interface. Nature 2023, 618, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).