YOLO-AFR: An Improved YOLOv12-Based Model for Accurate and Real-Time Dangerous Driving Behavior Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
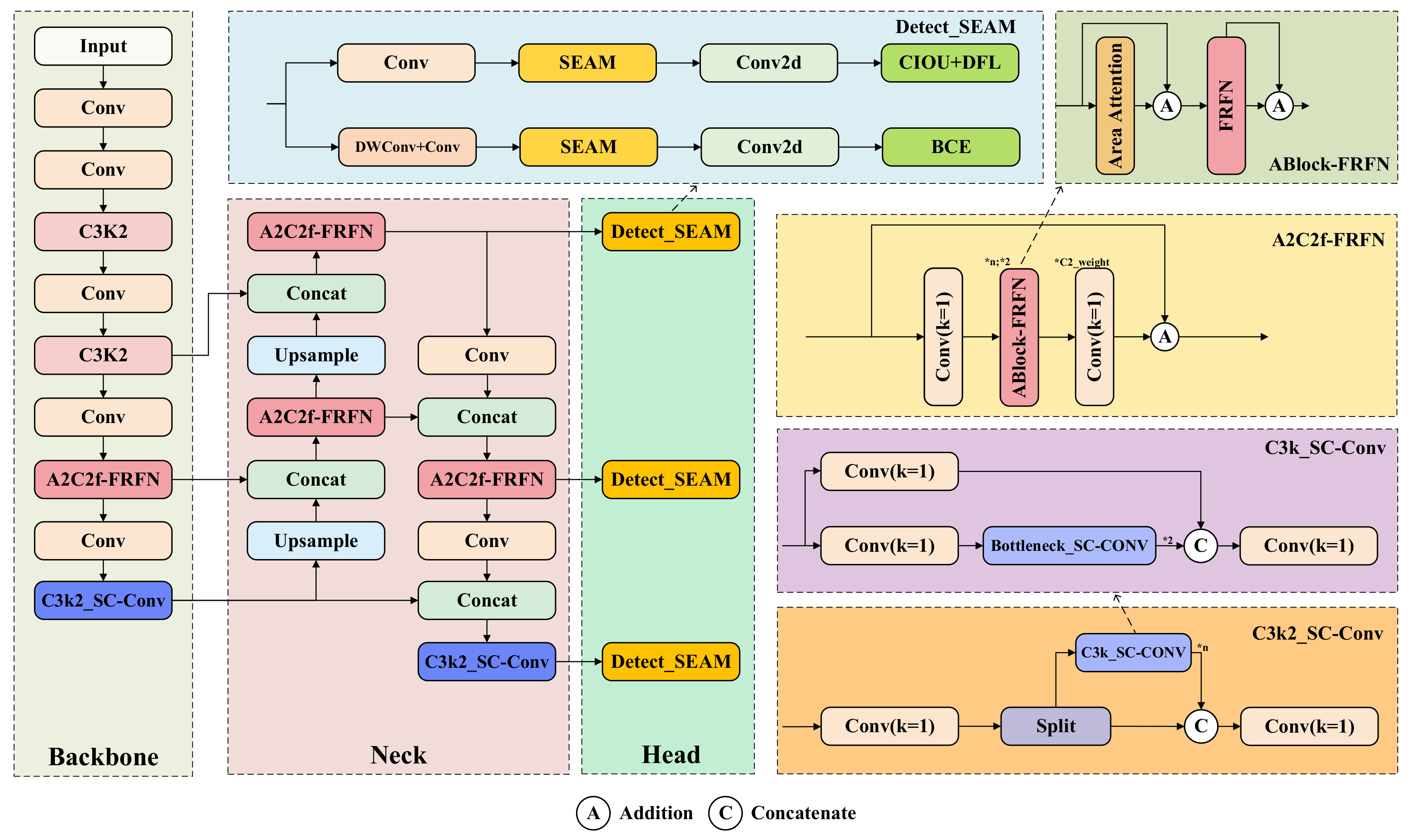
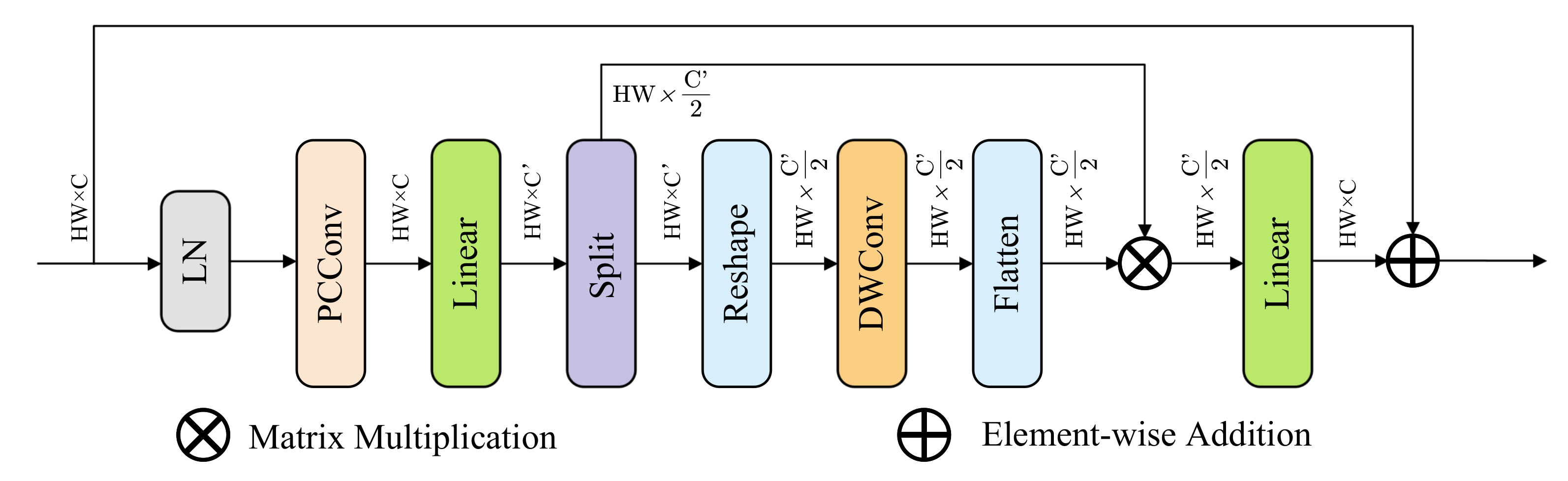
- We propose A2C2f-FRFN, an enhanced attention mechanism for the R-ELAN module in YOLOv12. This novel module integrates a Feature-Refinement Feedforward Network [19] (FRFN) to dynamically enhance spatial feature representations while suppressing redundancy, thereby improving the discriminative capacity for risky driving behaviors. This addresses the limitations of the original Area Attention by also considering channel-wise redundancy.
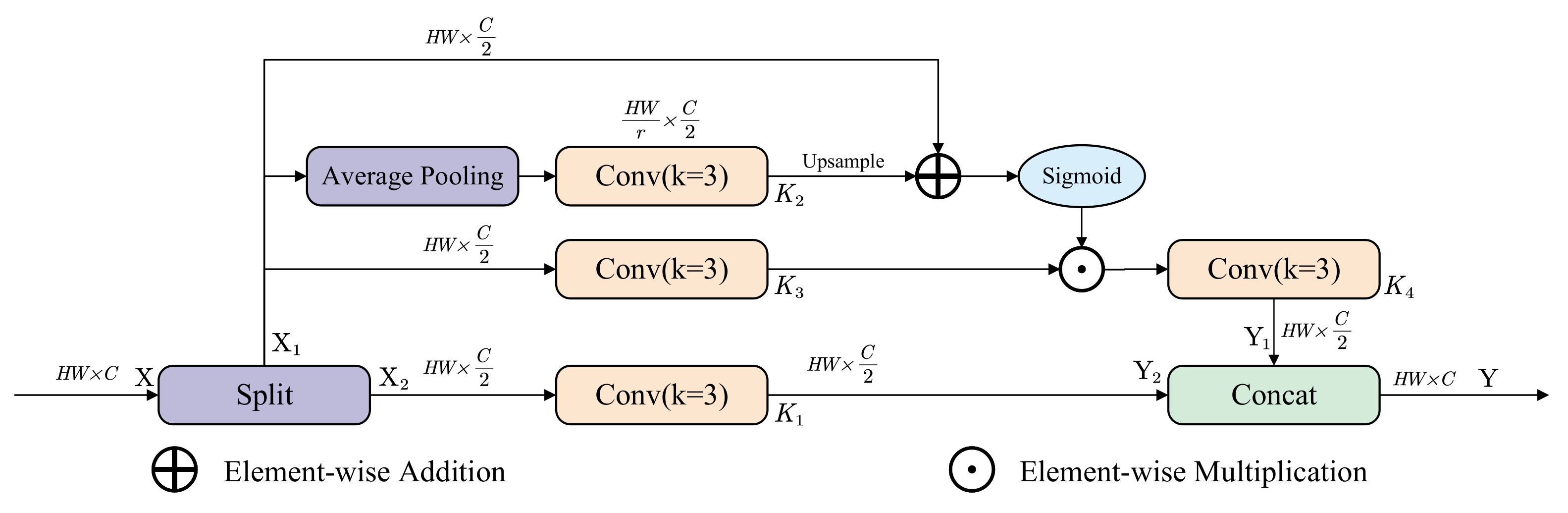
- We develop C3k2_SC-Conv structure within the backbone and neck of YOLOv12, introducing self-calibrated convolution [20] (SC-Conv). This integration broadens the receptive field and improves its ability to capture crucial contextual information for dangerous driving behavior detection without increasing computational costs. SC-Conv adaptively adjusts feature representations based on spatial and channel information, improving robustness.
- We develop Detect_SEAM by incorporating the Separated and Enhanced Attention Mechanism [21] (SEAM) into the Detect module of YOLOv12. This enhancement specifically addresses the challenges of dynamic occlusion and complex background interference common in driving scenarios. SEAM leverages depthwise separable convolution and cross-channel fusion to boost responses in unobstructed regions and compensate for occlusion-induced feature loss, improving the detection of occluded dangerous behaviors.
2. Related Works
2.1. Dangerous Driving Behavior Detection
2.2. YOLOv12 Object Detection Network
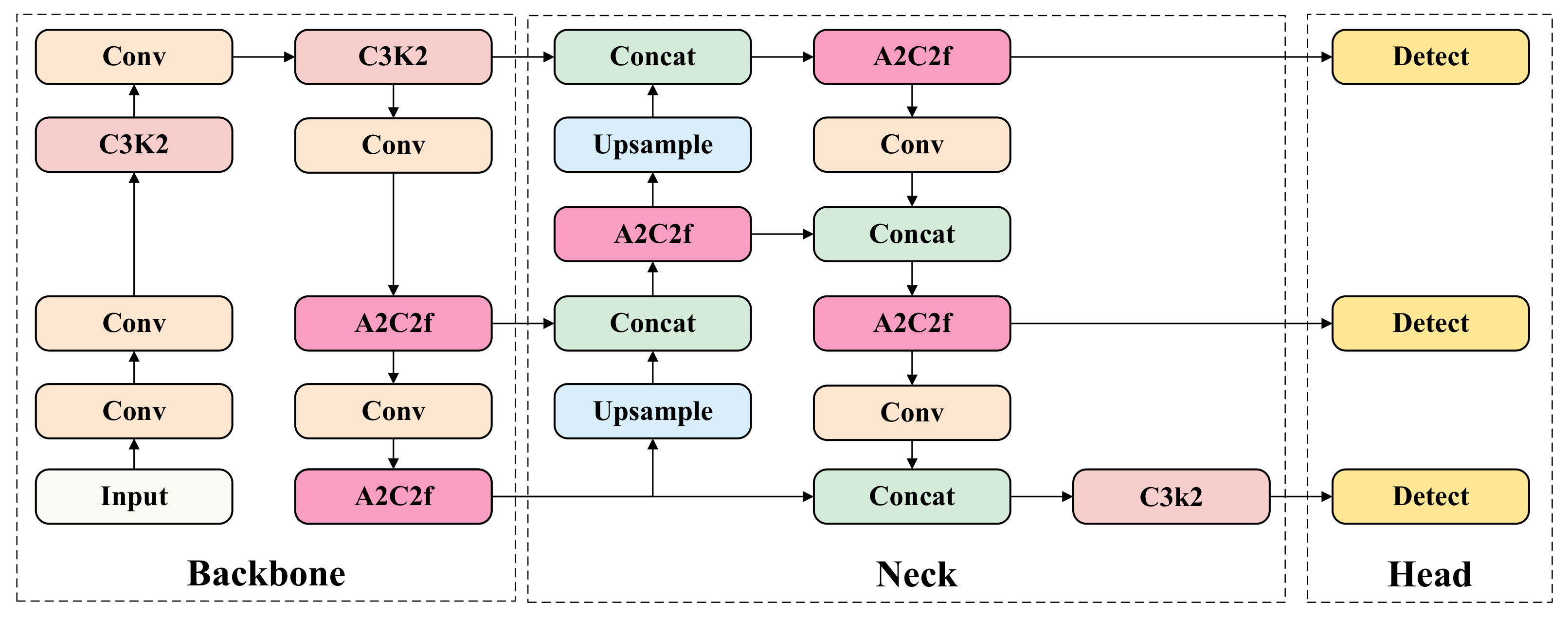
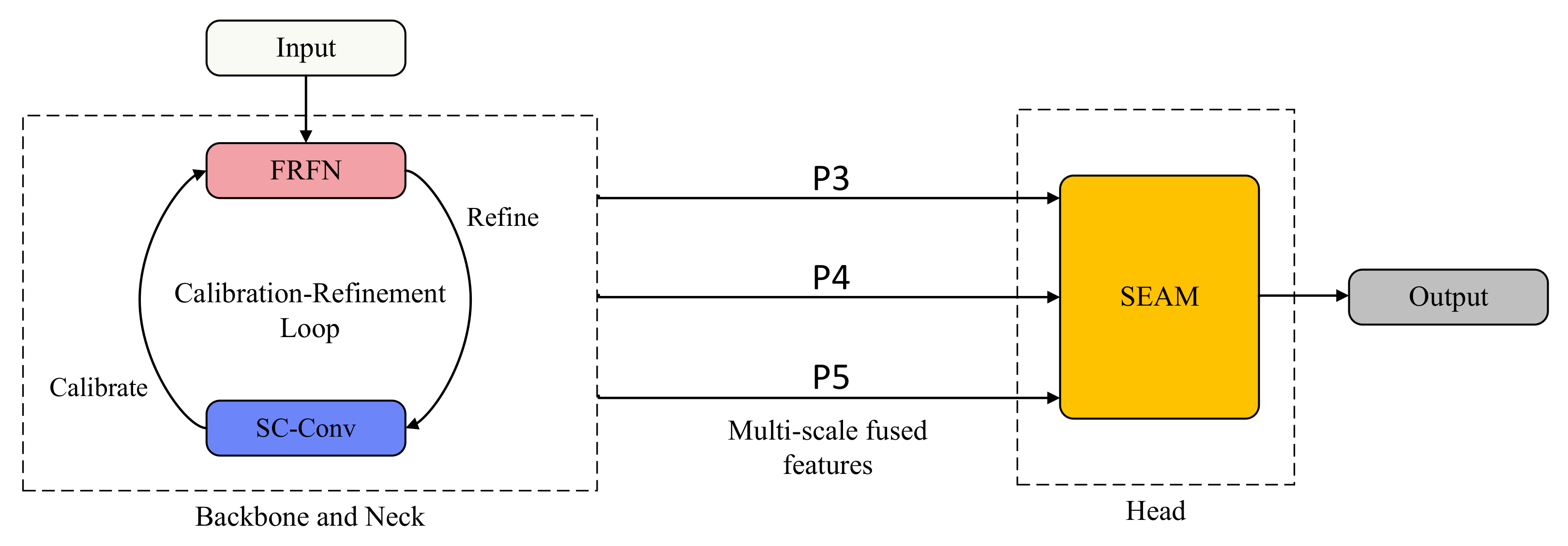
3. Methods
- The A2C2f-FRFN module incorporates the Feature-Refinement Feedback Network (FRFN) for adaptive feature refinement.
- The C3k2_SC-Conv structure utilizes self-calibrated convolution (SC-Conv) to enhance contextual modeling capability.
- The Detect_SEAM head employs the Separated and Enhanced Attention Mechanism (SEAM), designed to improve global contextual awareness.
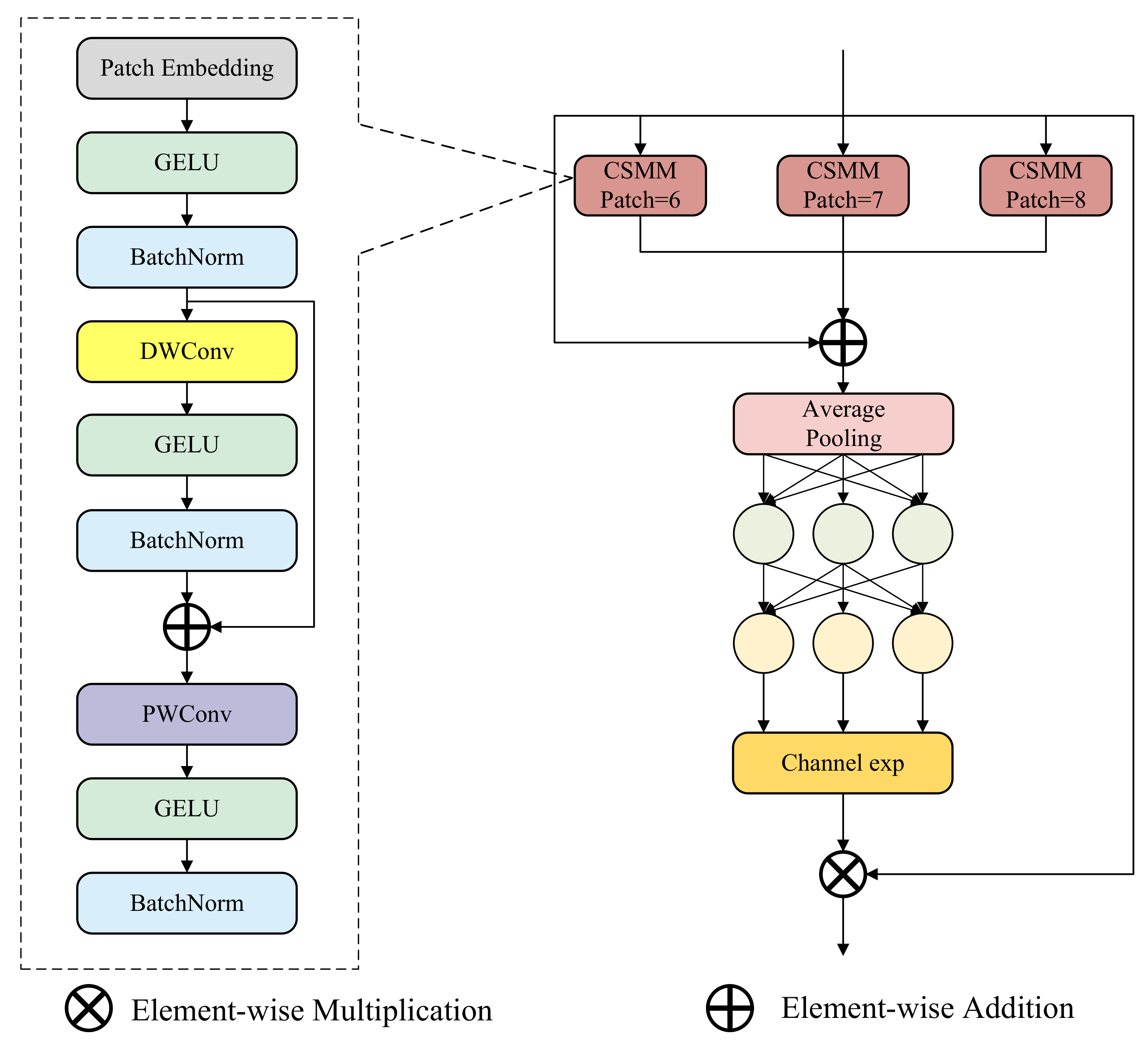
3.1. A2C2f-FRFN
3.1.1. Feature-Refinement Feedforward Network
3.1.2. Structure of A2C2f-FRFN
3.2. C3k2_SC-Conv
3.2.1. Self-Calibrated Convolutions
3.2.2. Architecture Development of C3k2_SC-Conv
3.3. Detect_SEAM
3.3.1. Separated and Enhancement Attention Module
3.3.2. Construction of Detect_SEAM
4. Experiments and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Dataset
4.2. Experimental Environment
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.4. Model Comparison Experiment
4.4.1. Comparison of Detection Accuracy Across Models
4.4.2. Comparison of Model Efficiency and Complexity
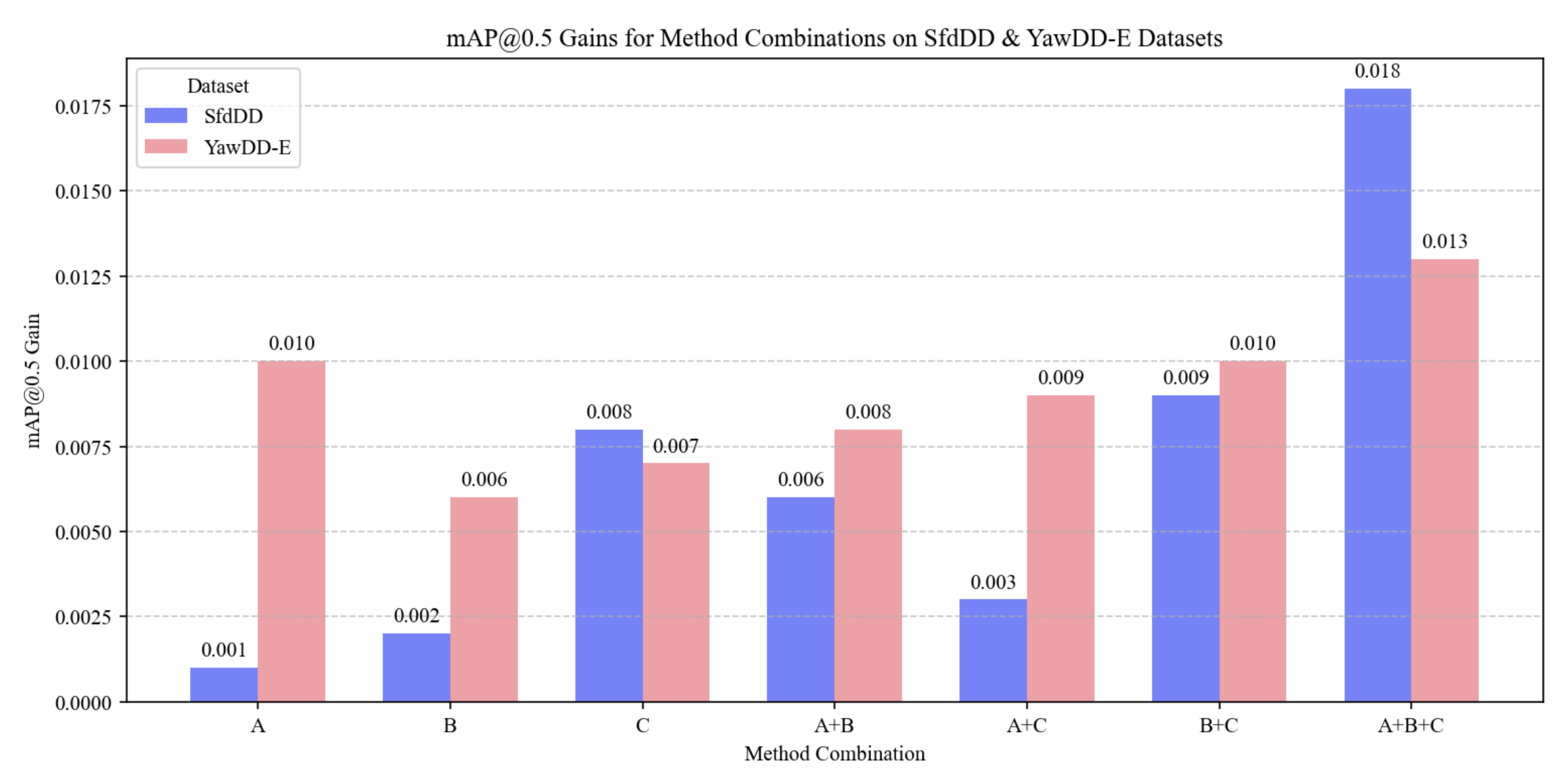
4.5. Ablation Experiment
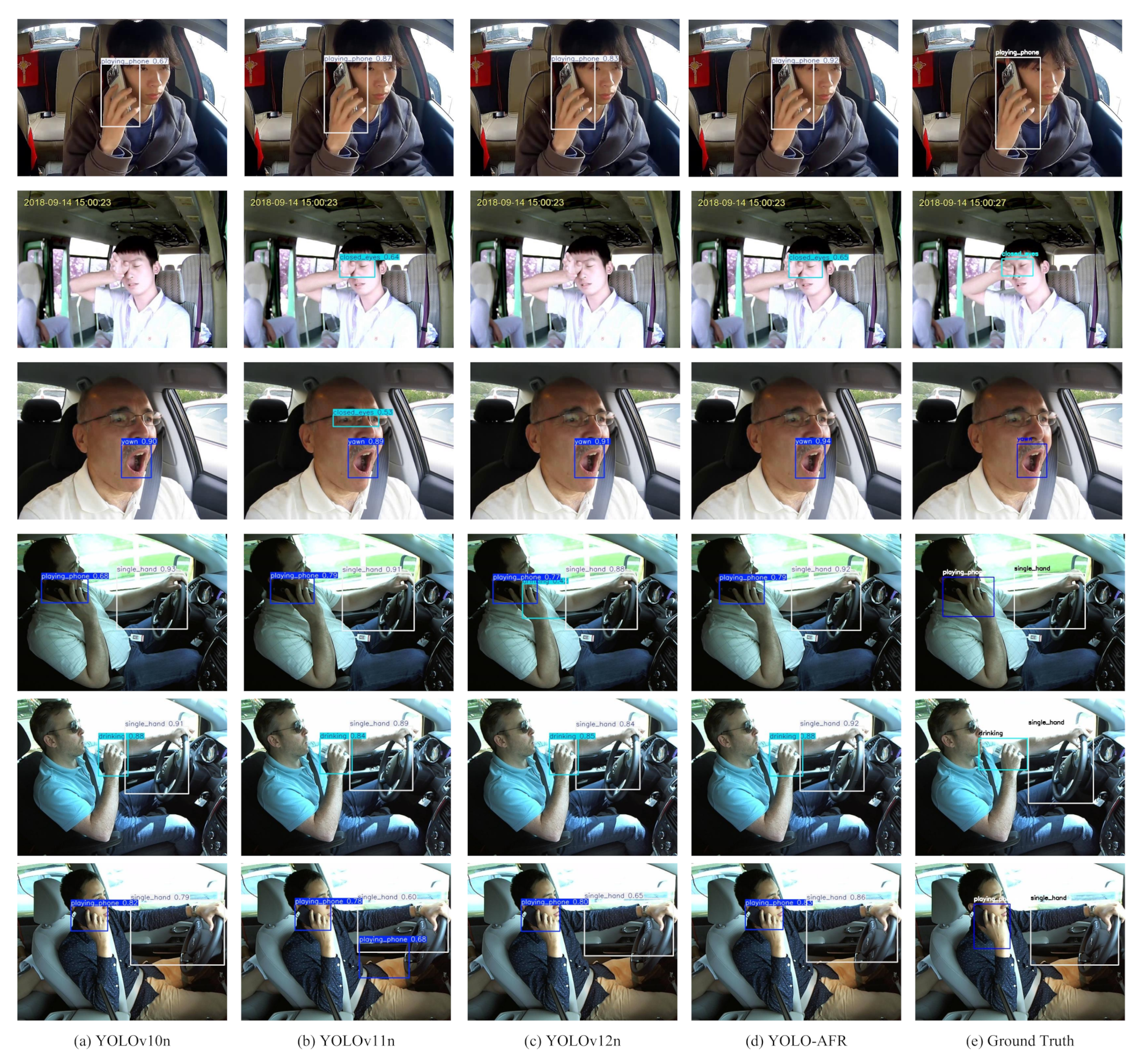
4.6. Visual Comparison of Detection Results
4.7. In-Car Deployment Test
5. Discussion
Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| YOLO-AFR | YOLO with Adaptive Feature Refinement |
| FRFN | Feature-Refinement Feedback Network |
| SC-Conv | Self-Calibrated Convolution |
| SEAM | Separated and Enhanced Attention Mechanism |
| R-ELAN | Residual Efficient Layer Aggregation Network |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| SSD | Single Shot MultiBox Detector |
| FPS | Frames Per Second |
| DBN | Deep Belief Network |
| A2C2f | Attention-based 2-Convolutional Layer with 2-Fused Connections |
| PConv | Partial Convolution |
| DWConv | Depthwise Separable Convolution |
| LN | Layer Normalization |
References
- Ahmed, S.K.; Mohammed, M.G.; Abdulqadir, S.O.; El-Kader, R.G.A.; El-Shall, N.A.; Chandran, D.; Rehman, M.E.U.; Dhama, K. Road traffic accidental injuries and deaths: A neglected global health issue. Health Sci. Rep. 2023, 6, e1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Kushwaha, V.; Agarwal, A.D.; Sandhu, S.S. Fatal road traffic accidents: Causes and factors responsible. J. Indian Acad. Forensic Med. 2016, 38, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, B.; Heaton, K.; Vance, D.E.; Stavrinos, D. The useful field of view assessment predicts simulated commercial motor vehicle driving safety. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2016, 17, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, J.; McDonald, M. Advanced Driver Assistance Systems from Autonomous to Cooperative Approach. Transp. Rev. 2008, 28, 659–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhong, Y.; He, W. Research Progress of Dangerous Driving Behavior Recognition Methods Based on Deep Learning. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhang, G.; Long, Y. Identification of dangerous driving state based on lightweight deep learning model. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 105, 108509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negash, N.M.; Yang, J. Driver Behavior Modeling Toward Autonomous Vehicles: Comprehensive Review. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 22788–22821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, N.J.; Shapiai, M.I.; Ghani, R.A.; Yassin, M.N.M.; Ibrahim, M.Z.; Wahid, N. Lane Detection in Autonomous Vehicles: A Systematic Review. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 3729–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.W.; Chen, H.M. Driver Behavior Monitoring and Warning With Dangerous Driving Detection Based on the Internet of Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 7232–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Zhu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Jiang, G.; He, A. A Deep-Learning-Based Scheme for Detecting Driver Cell-Phone Use. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 18580–18589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, T.C.; Lin, C.C.; Fan, C.P. Deep learning based driver smoking behavior detection for driving safety. J. Image Graph. 2020, 8, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, A.C.; Trieu, T.N.; Phan, T.C. Driver drowsiness detection and smart alerting using deep learning and IoT. Internet Things 2023, 22, 100705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Learned-Miller, E. Face Detection with the Faster R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2017), Washington, DC, USA, 30 May–3 June 2017; pp. 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehl, W.; Manhardt, F.; Tombari, F.; Ilic, S.; Navab, N. Ssd-6d: Making rgb-based 3d detection and 6d pose estimation great again. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1521–1529. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; Yu, C.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Z. YOLO8-FASG: A High-Accuracy Fish Identification Method for Underwater Robotic System. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 73354–73362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yin, H.; Rong, C.; Zhao, J.; Liang, X.; Li, R.; Mo, X. YOLO-MRS: An efficient deep learning-based maritime object detection method for unmanned surface vehicles. Appl. Ocean Res. 2024, 153, 104240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yu, C.; Qin, X.; An, X.; Zhao, J.; Chuai, W.; Liu, B. YOLO-SGC: A Dangerous Driving Behavior Detection Method With Multiscale Spatial-Channel Feature Aggregation. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 36044–36056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, D. CoP-YOLO: A Light-weight Dangerous Driving Behavior Detection Method. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Sensing, Measurement & Data Analytics in the Era of Artificial Intelligence (ICSMD), Huangshan, China, 31 October–3 November 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Chen, D.; Pan, J.; Shi, J.; Yang, J. Adapt or Perish: Adaptive Sparse Transformer with Attentive Feature Refinement for Image Restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 2952–2963. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.J.; Hou, Q.; Cheng, M.M.; Wang, C.; Feng, J. Improving Convolutional Networks With Self-Calibrated Convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Huang, H.; Chen, W.; Su, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. YOLO-FaceV2: A scale and occlusion aware face detector. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 155, 110714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomerleau, D. RALPH: Rapidly adapting lateral position handler. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Vehicles ’95. Symposium, Detroit, MI, USA, 25–26 September 1995; pp. 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromer, M.; Salb, D.; Walzer, T.; Madrid, N.M.; Seepold, R. ECG sensor for detection of driver’s drowsiness. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 159, 1938–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y. Real-time driver fatigue detection based on face alignment. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Digital Image Processing (ICDIP 2017), Hong Kong, China, 19–22 May 2017; Volume 10420, p. 1042003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich Feature Hierarchies for Accurate Object Detection and Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G.; Stoken, A.; Borovec, J.; Changyu, L.; Hogan, A.; Diaconu, L.; Poznanski, J.; Yu, L.; Rai, P.; Ferriday, R.; et al. ultralytics/yolov5: V3.0. Zenodo. 2020. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/3983579 (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Geng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, B.; Ke, Z.; Xu, X.; Chu, X. YOLOv6 v3.0: A Full-Scale Reloading. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.05586. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable Bag-of-Freebies Sets New State-of-the-Art for Real-Time Object Detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Sohan, M.; Sai Ram, T.; Rami Reddy, C.V. A Review on YOLOv8 and Its Advancements. In Proceedings of the Data Intelligence and Cognitive Informatics; Jacob, I.J., Piramuthu, S., Falkowski-Gilski, P., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 529–545. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv9: Learning What You Want to Learn Using Programmable Gradient Information. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.13616. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. YOLOv10: Real-Time End-to-End Object Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14458. [Google Scholar]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M. YOLOv11: An Overview of the Key Architectural Enhancements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17725. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Ye, Q.; Doermann, D. YOLOv12: Attention-Centric Real-Time Object Detectors. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.12524. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.N.; Ono, S.; Sugimoto, A.; Kawasaki, H. Attention R-CNN for Accident Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 19 October–13 November 2020; pp. 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Yang, J.; Meng, J. Driver’s Illegal Driving Behavior Detection with SSD Approach. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning (PRML), Chengdu, China, 16–18 July 2021; pp. 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amira, B.G.; Zoulikha, M.M.; Hector, P. Driver drowsiness detection and tracking based on YOLO with Haar cascades and ERNN. Int. J. Saf. Secur. Eng. 2021, 11, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trockman, A.; Kolter, J.Z. Patches Are All You Need? arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.09792. [Google Scholar]
- Abtahi, S.; Omidyeganeh, M.; Shirmohammadi, S.; Hariri, B. YawDD: Yawning Detection Dataset. 2020. Available online: https://ieee-dataport.org/open-access/yawdd-yawning-detection-dataset (accessed on 23 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- yunxizhineng. VOC-COCO Dataset. Available online: https://aistudio.baidu.com/datasetdetail/94583/0 (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Barcelona Autonomous University, Computer Vision Center. CVC11 DrivFace Dataset. Available online: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/dataset/378/drivface (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Montoya, A. State Farm Distracted Driver Detection. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/state-farm-distracted-driver-detection/data (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, A.; Kaimal, R.M.; Bijlani, K. Yaw Estimation Using Cylindrical and Ellipsoidal Face Models. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2014, 15, 2308–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, L.; Min, W.; Yang, X.; Xiong, X. Driver Yawning Detection Based on Subtle Facial Action Recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 23, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kır Savaş, B.; Becerikli, Y. Behavior-based driver fatigue detection system with deep belief network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 14053–14065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.T.; Lin, H.Y.; Chang, C.C. Driver Fatigue and Distracted Driving Detection Using Random Forest and Convolutional Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Yu, W.; Xiao, Z.; Havyarimana, V.; Regan, A.C.; Jiang, H.; Jiao, L. Two-Stream Spatial–Temporal Graph Convolutional Networks for Driver Drowsiness Detection. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 13821–13833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alameen, S.A.; Alhothali, A.M. A Lightweight Driver Drowsiness Detection System Using 3DCNN With LSTM. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2023, 44, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Ma, X.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, K.; Li, Y. Driver fatigue detection and human-machine cooperative decision-making for road scenarios. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 12487–12518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelnaga, Y.; Eraqi, H.M.; Moustafa, M.N. Real-time Distracted Driver Posture Classification. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1706.09498. [Google Scholar]
- Baheti, B.; Talbar, S.; Gajre, S. Towards Computationally Efficient and Realtime Distracted Driver Detection with MobileVGG Network. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2020, 5, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Qian, J.; Xin, Y.; Liu, B.; Dong, Y. Distracted Driver Detection Based on a CNN with Decreasing Filter Size. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 6922–6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, J.; Ren, T.; Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z. Learning Accurate, Speedy, Lightweight CNNs via Instance-Specific Multi-Teacher Knowledge Distillation for Distracted Driver Posture Identification. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 17922–17935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, E.; Liu, H.; Yang, Z.; Du, J.; Ge, Y. FedBiKD: Federated Bidirectional Knowledge Distillation for Distracted Driving Detection. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 11643–11654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Liu, Y. Improving real-time driver distraction detection via constrained attention mechanism. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 128, 107408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chillakuru, P.; Ananthajothi, K.; Divya, D. Three stage classification framework with ranking scheme for distracted driver detection using heuristic-assisted strategy. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 293, 111589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dataset | Closed Eyes | Yawn | Playing Phone | Drinking | Single Hand |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YawDD-E | 1177 | 1385 | 1269 | ~ | ~ |
| SfdDD | ~ | ~ | 1597 | 1700 | 3053 |
| Methods | mAP@0.5 | mAP@0.5:0.95 | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | 0.557 | 0.352 | 0.541 | 0.601 | 0.569 |
| SSD | 0.879 | 0.507 | 0.865 | 0.842 | 0.853 |
| YOLOv3-tiny | 0.935 | 0.698 | 0.884 | 0.864 | 0.874 |
| YOLOv5n | 0.934 | 0.706 | 0.892 | 0.869 | 0.880 |
| YOLOv6n | 0.950 | 0.734 | 0.895 | 0.891 | 0.893 |
| YOLOv7-tiny | 0.934 | 0.728 | 0.923 | 0.863 | 0.892 |
| YOLOv8n | 0.952 | 0.764 | 0.933 | 0.879 | 0.905 |
| YOLOv9-C | 0.962 | 0.772 | 0.945 | 0.890 | 0.917 |
| YOLO-SGC | 0.972 | 0.793 | 0.949 | 0.908 | 0.928 |
| YOLOv10n | 0.960 | 0.738 | 0.900 | 0.943 | 0.920 |
| YOLOv11n | 0.963 | 0.742 | 0.922 | 0.922 | 0.920 |
| YOLOv12n | 0.963 | 0.737 | 0.928 | 0.920 | 0.922 |
| YOLO-AFR | 0.976 | 0.763 | 0.936 | 0.947 | 0.940 |
| Methods | mAP@0.5 | mAP@0.5:0.95 | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | 0.663 | 0.512 | 0.661 | 0.666 | 0.663 |
| SSD | 0.933 | 0.551 | 0.937 | 0.942 | 0.939 |
| YOLOv3-tiny | 0.958 | 0.560 | 0.955 | 0.957 | 0.956 |
| YOLOv5n | 0.954 | 0.543 | 0.943 | 0.940 | 0.941 |
| YOLOv6n | 0.964 | 0.563 | 0.964 | 0.944 | 0.951 |
| YOLOv7-tiny | 0.968 | 0.548 | 0.967 | 0.968 | 0.967 |
| YOLOv8n | 0.970 | 0.586 | 0.958 | 0.962 | 0.960 |
| YOLOv9-C | 0.983 | 0.590 | 0.978 | 0.988 | 0.983 |
| YOLO-SGC | 0.980 | 0.596 | 0.976 | 0.982 | 0.979 |
| YOLOv10n | 0.966 | 0.586 | 0.947 | 0.953 | 0.950 |
| YOLOv11n | 0.972 | 0.590 | 0.961 | 0.961 | 0.961 |
| YOLOv12n | 0.971 | 0.575 | 0.950 | 0.960 | 0.954 |
| YOLO-AFR | 0.989 | 0.698 | 0.978 | 0.982 | 0.980 |
| Model | Narayanan et al. [45] | Yang et al. [46] | Kir et al. [47] | Dong et al. [48] | Bai et al. [49] | Alameen et al. [50] | Li et al. [51] | YOLO-SGC [17] | YOLO-AFR |
| mAP@0.5 | 0.818 | 0.834 | 0.880 | 0.910 | 0.934 | 0.960 | 0.944 | 0.972 | 0.976 |
| Model | Abouelnaga et al. [52] | Baheti et al. [53] | Qin et al. [54] | Li et al. [55] | Shang et al. [56] | Gao et al. [57] | Chillakuru et al. [58] | YOLO-SGC [17] | YOLO-AFR |
| mAP@0.5 | 0.937 | 0.952 | 0.956 | 0.949 | 0.946 | 0.935 | 0.976 | 0.980 | 0.989 |
| Metric | Group | N | Mean | SD | t-Test | Welch’s t-Test | Mean Diff. | Cohen’s d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP@0.5 | YOLO-SGC | 20 | 0.969 | 0.003 | T = −6.953 | T = −6.953 | 0.004 | 2.199 |
| YOLO-AFR | 20 | 0.973 | 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | |||
| Total | 40 | 0.971 | 0.003 |
| Metric | Group | N | Mean | SD | t-Test | Welch’s t-Test | Mean Diff. | Cohen’s d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP@0.5 | YOLO-SGC | 20 | 0.977 | 0.003 | T = 11.815 | T = 11.815 | 0.008 | 3.736 |
| YOLO-AFR | 20 | 0.985 | 0.002 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | |||
| Total | 40 | 0.981 | 0.005 |
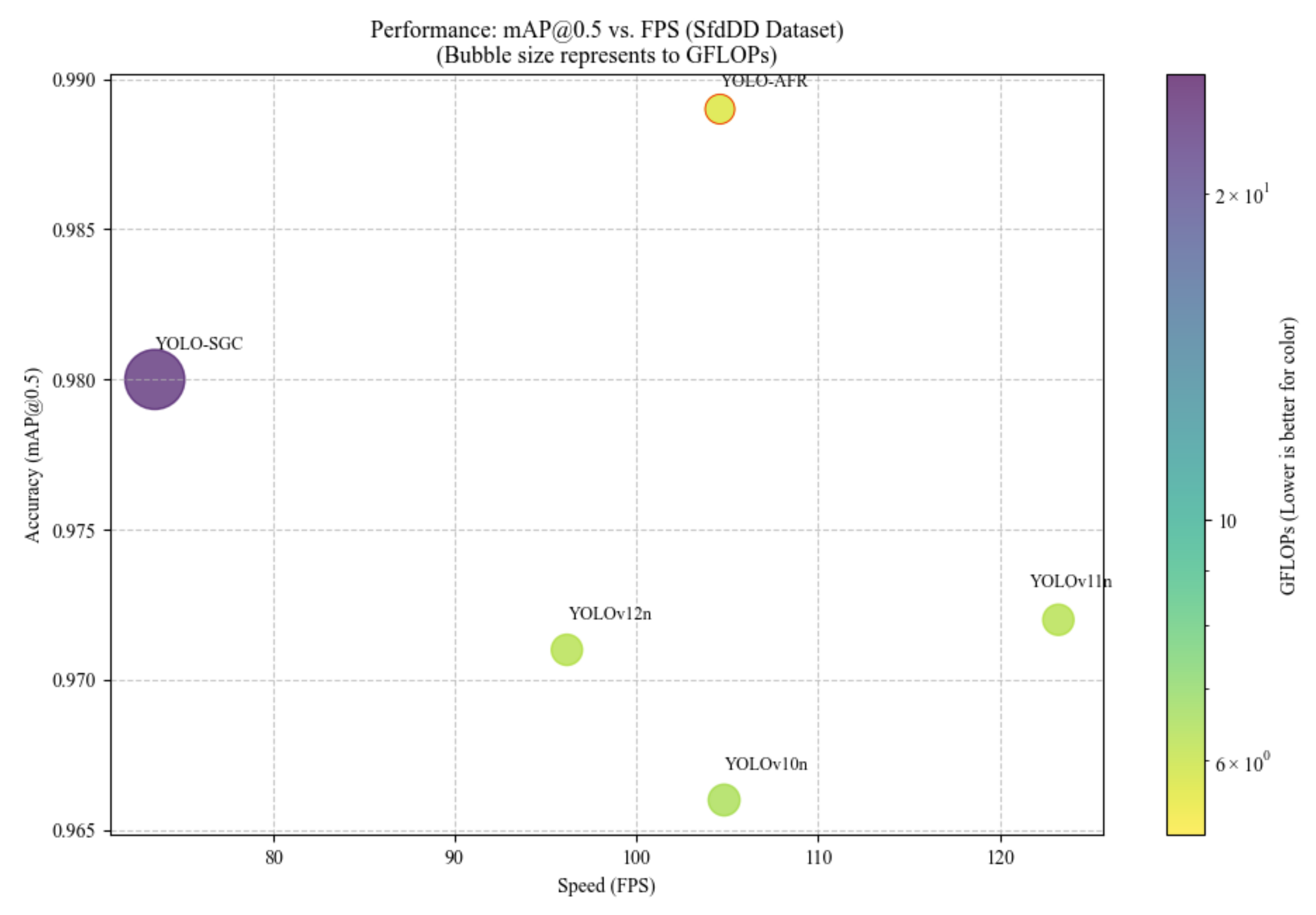
| Model | GFLOPs | Parameters (M) | Speed (ms) | FPS | Weight Size (MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLO-SGC | 23.4 | 8.832 | 13.61 | 73.50 | 5.2 |
| YOLOv10n | 6.5 | 2.266 | 9.54 | 104.82 | 5.5 |
| YOLOv11n | 6.3 | 2.583 | 8.12 | 123.21 | 5.2 |
| YOLOv12n | 6.3 | 2.557 | 10.40 | 96.17 | 5.3 |
| YOLO-AFR | 5.7 | 2.421 | 9.56 | 104.59 | 5.0 |
| Method | SEAM | FRFN | SC-Conv | Category | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | AP@0.5 | AP@0.5:0.95 | mAP@0.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | Playing phone | 0.933 | 0.936 | 0.934 | 0.963 | 0.464 | 0.971 | |||
| Drinking | 0.930 | 0.969 | 0.949 | 0.958 | 0.543 | |||||
| Single hand | 0.986 | 0.973 | 0.980 | 0.991 | 0.719 | |||||
| A | 🗸 | Playing phone | 0.916 | 0.936 | 0.926 | 0.940 | 0.574 | 0.972 | ||
| Drinking | 0.979 | 0.980 | 0.979 | 0.984 | 0.684 | |||||
| Single hand | 0.990 | 0.967 | 0.978 | 0.992 | 0.800 | |||||
| B | 🗸 | Playing phone | 0.926 | 0.927 | 0.927 | 0.949 | 0.596 | 0.973 | ||
| Drinking | 0.962 | 0.973 | 0.968 | 0.979 | 0.691 | |||||
| Single hand | 0.993 | 0.978 | 0.986 | 0.991 | 0.802 | |||||
| C | 🗸 | Playing phone | 0.956 | 0.959 | 0.957 | 0.965 | 0.571 | 0.979 | ||
| Drinking | 0.970 | 0.973 | 0.972 | 0.982 | 0.689 | |||||
| Single hand | 0.987 | 0.968 | 0.977 | 0.992 | 0.805 | |||||
| A + B | 🗸 | 🗸 | Playing phone | 0.947 | 0.960 | 0.954 | 0.968 | 0.595 | 0.977 | |
| Drinking | 0.957 | 0.973 | 0.965 | 0.971 | 0.677 | |||||
| Single hand | 0.994 | 0.967 | 0.980 | 0.992 | 0.797 | |||||
| A + C | 🗸 | 🗸 | Playing phone | 0.937 | 0.955 | 0.946 | 0.958 | 0.600 | 0.974 | |
| Drinking | 0.947 | 0.969 | 0.958 | 0.972 | 0.661 | |||||
| Single hand | 0.981 | 0.990 | 0.986 | 0.993 | 0.800 | |||||
| B + C | 🗸 | 🗸 | Playing phone | 0.953 | 0.951 | 0.952 | 0.965 | 0.575 | 0.980 | |
| Drinking | 0.967 | 0.966 | 0.966 | 0.980 | 0.683 | |||||
| Single hand | 0.984 | 0.971 | 0.977 | 0.991 | 0.811 | |||||
| A + B + C | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | Playing phone | 0.969 | 0.988 | 0.978 | 0.987 | 0.600 | 0.989 |
| Drinking | 0.979 | 0.984 | 0.982 | 0.988 | 0.695 | |||||
| Single hand | 0.985 | 0.972 | 0.978 | 0.990 | 0.799 |
| Method | SEAM | FRFN | SC-Conv | Category | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | AP@0.5 | AP@0.5:0.95 | mAP@0.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | Yawn | 0.877 | 0.977 | 0.924 | 0.975 | 0.809 | 0.963 | |||
| Closed eyes | 0.926 | 0.867 | 0.896 | 0.954 | 0.770 | |||||
| Playing phone | 0.982 | 0.916 | 0.948 | 0.961 | 0.632 | |||||
| A | 🗸 | Yawn | 0.868 | 0.971 | 0.917 | 0.975 | 0.819 | 0.973 | ||
| Closed eyes | 0.927 | 0.913 | 0.920 | 0.962 | 0.775 | |||||
| Playing phone | 0.955 | 0.951 | 0.953 | 0.981 | 0.667 | |||||
| B | 🗸 | Yawn | 0.836 | 0.994 | 0.908 | 0.977 | 0.809 | 0.969 | ||
| Closed eyes | 0.930 | 0.927 | 0.929 | 0.957 | 0.784 | |||||
| Playing phone | 0.956 | 0.944 | 0.950 | 0.973 | 0.657 | |||||
| C | 🗸 | Yawn | 0.904 | 0.966 | 0.934 | 0.977 | 0.826 | 0.970 | ||
| Closed eyes | 0.944 | 0.874 | 0.908 | 0.965 | 0.769 | |||||
| Playing phone | 0.977 | 0.895 | 0.934 | 0.969 | 0.636 | |||||
| A + B | 🗸 | 🗸 | Yawn | 0.882 | 0.986 | 0.931 | 0.977 | 0.823 | 0.971 | |
| Closed eyes | 0.917 | 0.911 | 0.914 | 0.962 | 0.775 | |||||
| Playing phone | 0.964 | 0.935 | 0.949 | 0.974 | 0.667 | |||||
| A + C | 🗸 | 🗸 | Yawn | 0.853 | 0.989 | 0.916 | 0.972 | 0.815 | 0.972 | |
| Closed eyes | 0.907 | 0.937 | 0.922 | 0.965 | 0.788 | |||||
| Playing phone | 0.939 | 0.967 | 0.953 | 0.977 | 0.678 | |||||
| B + C | 🗸 | 🗸 | Yawn | 0.865 | 0.989 | 0.923 | 0.978 | 0.820 | 0.973 | |
| Closed eyes | 0.926 | 0.909 | 0.917 | 0.962 | 0.780 | |||||
| Playing phone | 0.955 | 0.965 | 0.960 | 0.978 | 0.665 | |||||
| A + B + C | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | Yawn | 0.874 | 0.989 | 0.928 | 0.980 | 0.828 | 0.976 |
| Closed eyes | 0.953 | 0.887 | 0.919 | 0.961 | 0.797 | |||||
| Playing phone | 0.981 | 0.965 | 0.973 | 0.986 | 0.663 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, T.; Ning, B.; Xie, Y. YOLO-AFR: An Improved YOLOv12-Based Model for Accurate and Real-Time Dangerous Driving Behavior Detection. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6090. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116090
Ge T, Ning B, Xie Y. YOLO-AFR: An Improved YOLOv12-Based Model for Accurate and Real-Time Dangerous Driving Behavior Detection. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):6090. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116090
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Tianchen, Bo Ning, and Yiwu Xie. 2025. "YOLO-AFR: An Improved YOLOv12-Based Model for Accurate and Real-Time Dangerous Driving Behavior Detection" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 6090. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116090
APA StyleGe, T., Ning, B., & Xie, Y. (2025). YOLO-AFR: An Improved YOLOv12-Based Model for Accurate and Real-Time Dangerous Driving Behavior Detection. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 6090. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116090







