Robust Parameter Inversion and Subsidence Prediction for Probabilistic Integral Methods in Mining Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methodology
2.1. Principle of the Probability Integral Method
2.2. Robust Estimation Method
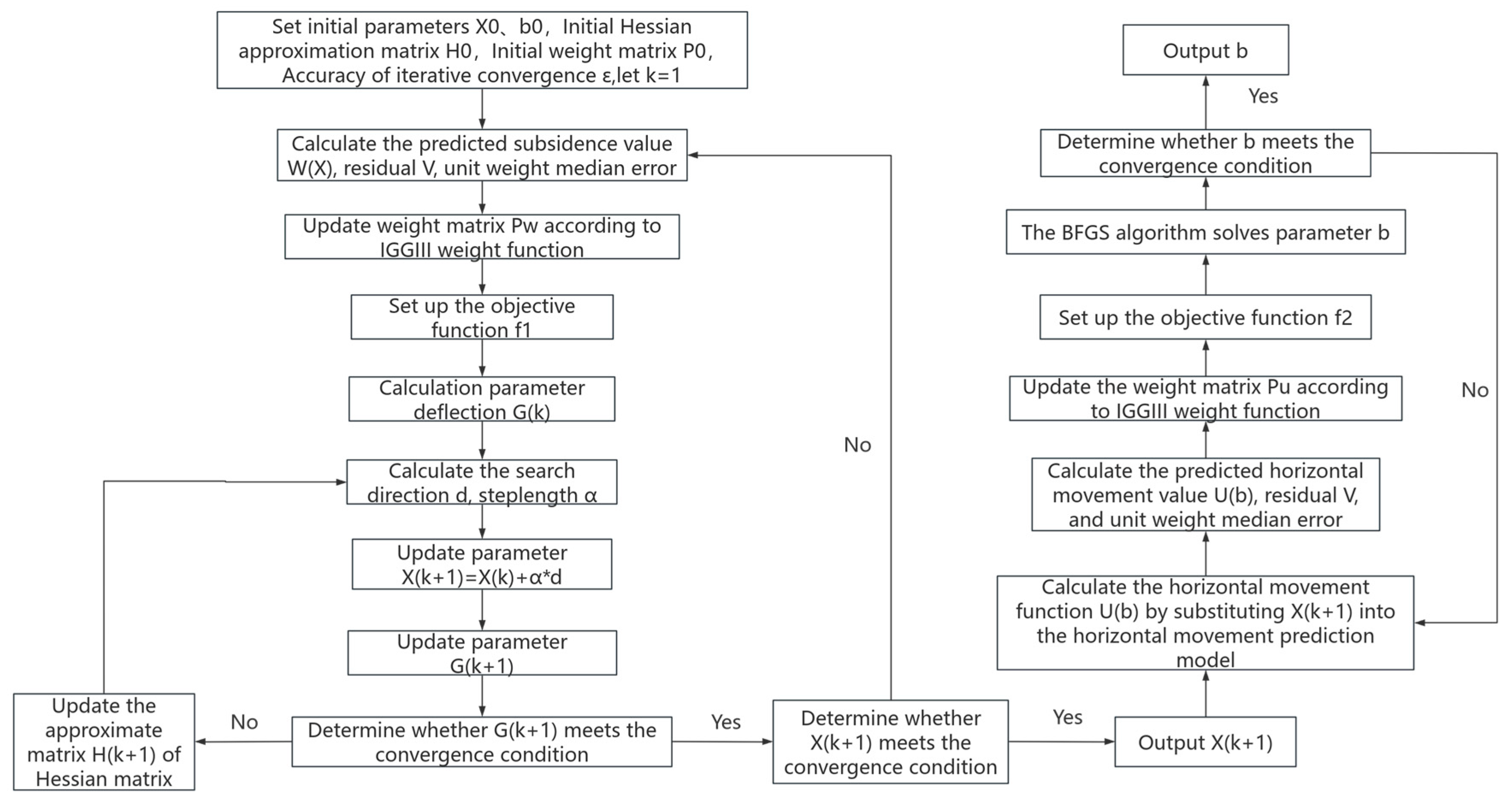
2.3. BFGS Parameter Inversion Algorithm
2.4. Robust BFGS Parameter Inversion Algorithm
3. Simulation Experiments and Statistical Analyses of Results
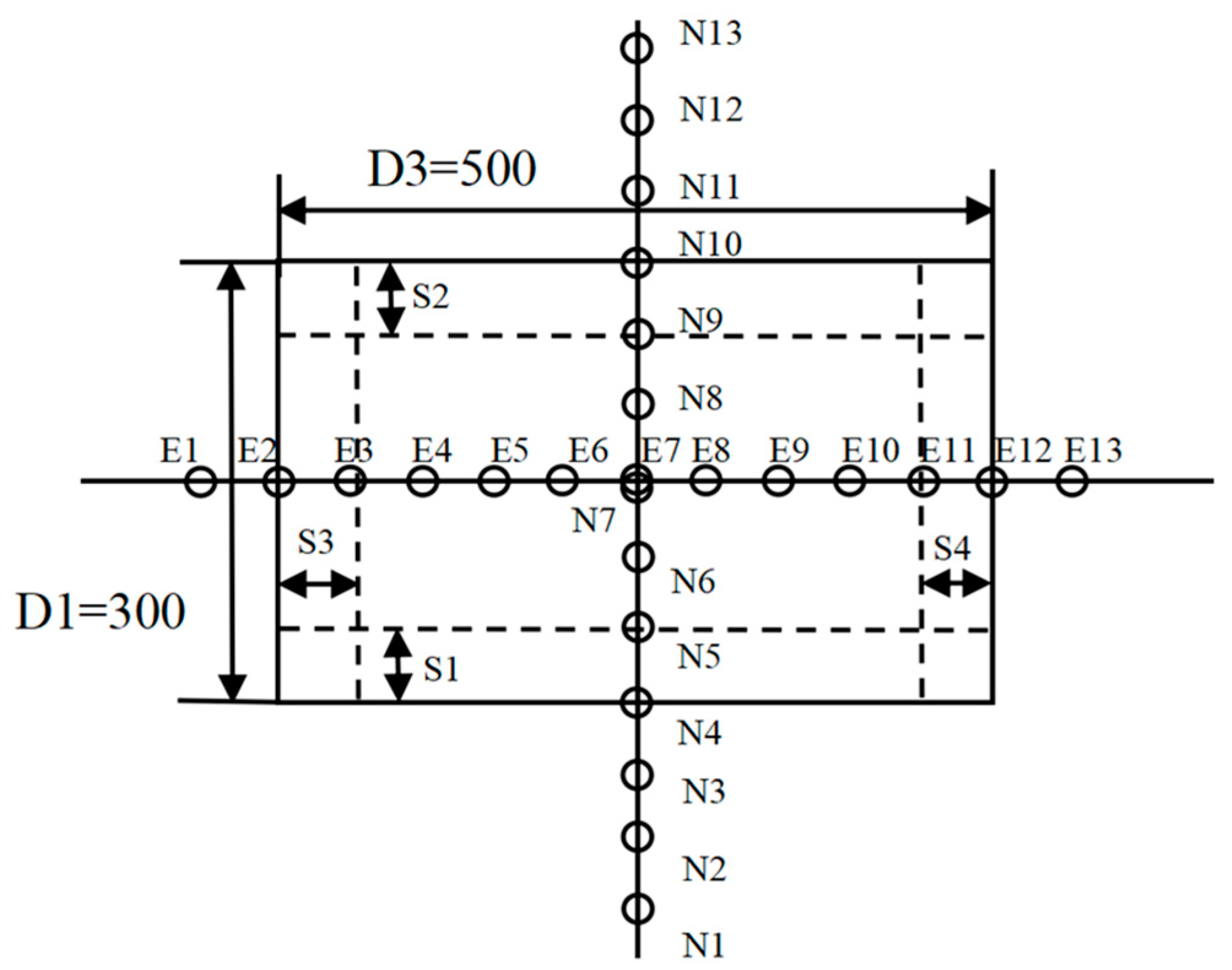
3.1. Design of Simulation Experimental Area and Experimental Data
3.2. Comparison of Commonly Used Robust Estimation Methods
3.3. Comparison of IGGIII-BFGS Algorithm with BFGS Algorithm
3.4. Comparison of IGGIII-BFGS Algorithm with PSO Algorithm
4. Engineering Examples and Results of Statistical Analyses
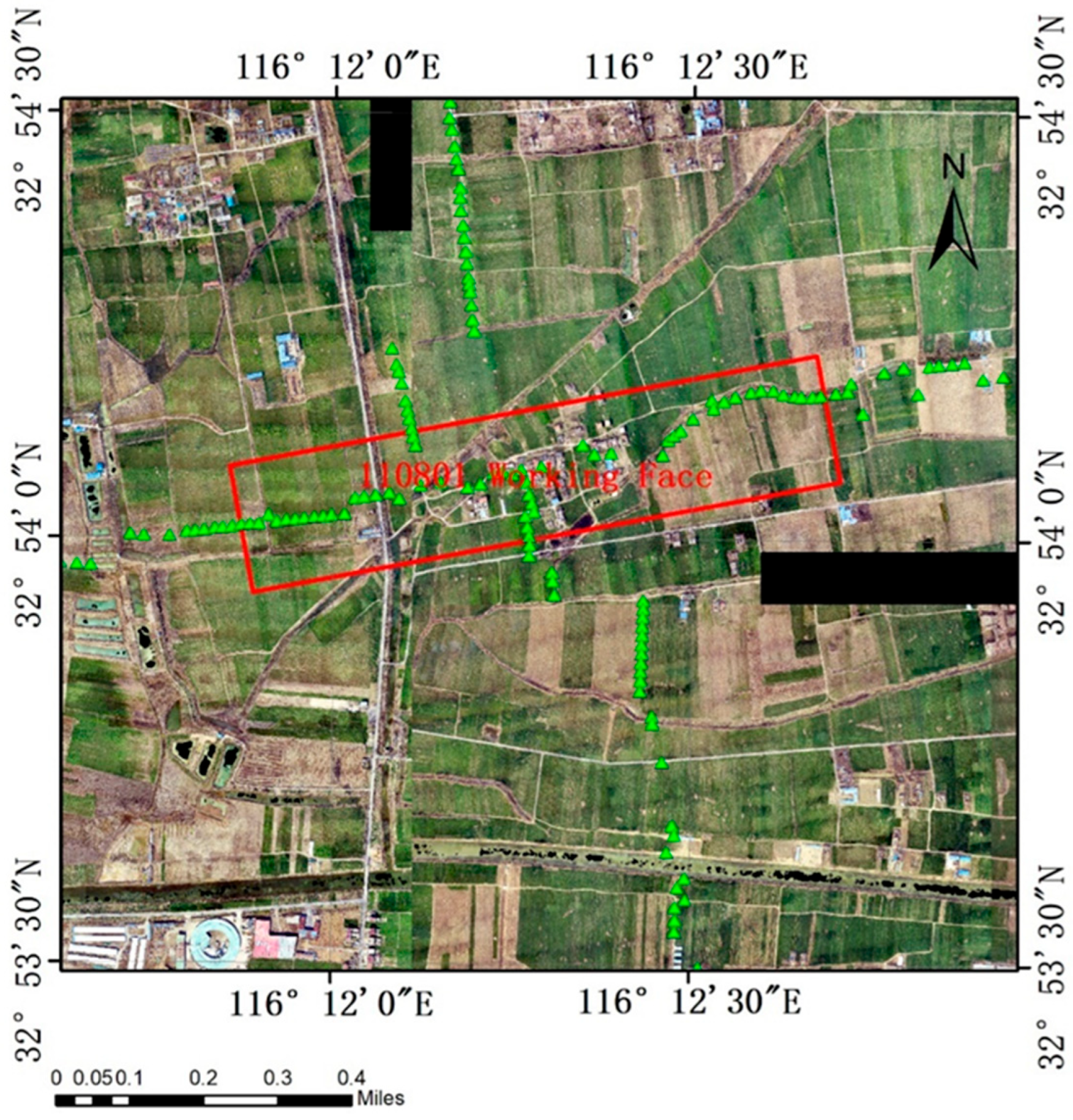
4.1. Overview of the Mining Area
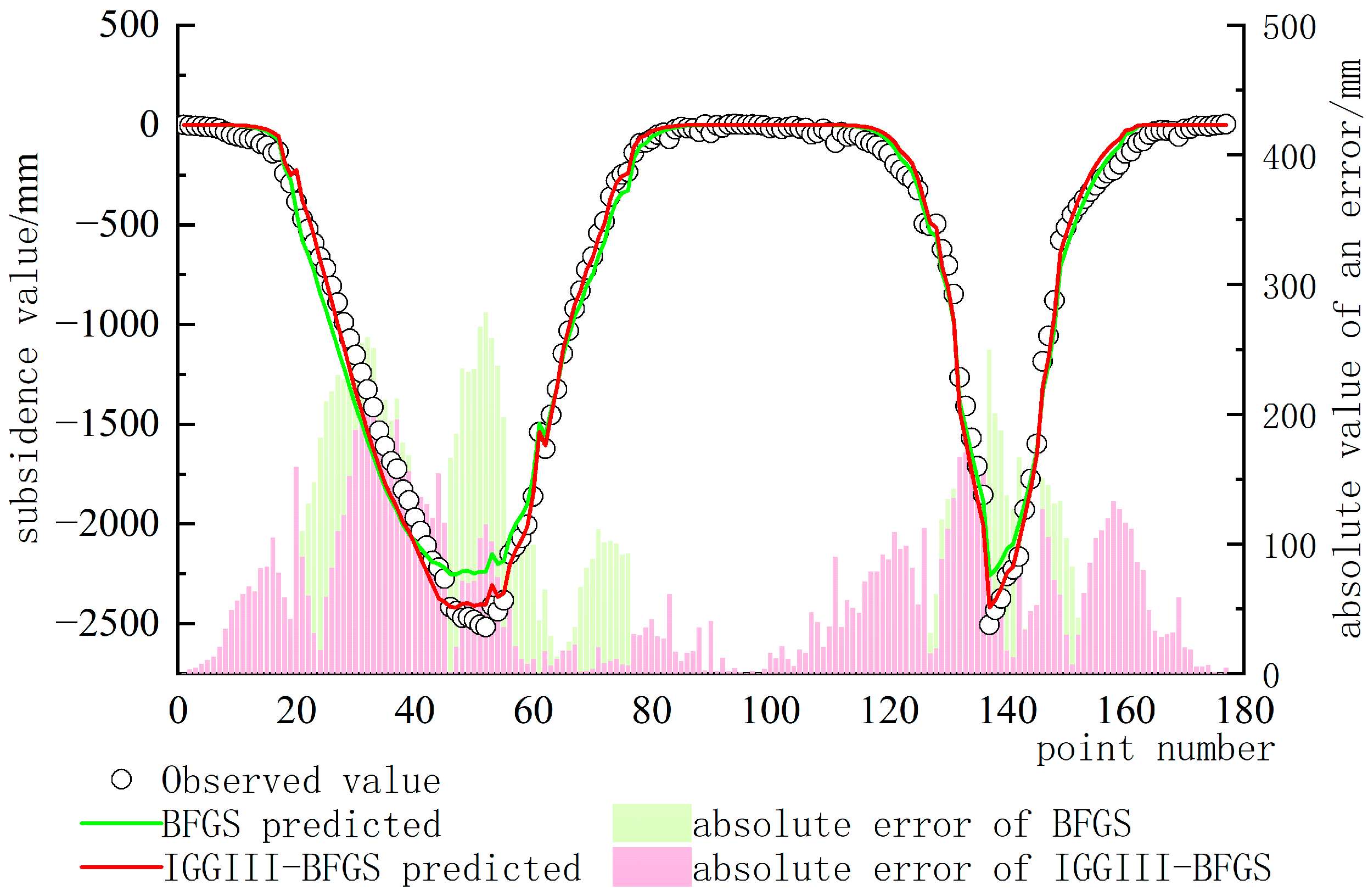
4.2. Results and Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Q.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Guo, Y.; Liang, Y. A Study on Historical Big Data Analysis of Surface Ecological Damage in the Coal Mining Area of Lvliang City Based on Two Mining Modes. Land 2024, 13, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, S.; Bai, L.; Cao, Y.; Yan, Z. Effects of Underground Mining on Soil–Vegetation System: A Case Study of Different Subsidence Areas. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2023, 9, 0122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Shen, Y. Influence analysis of between subsidence and structure evolution in overburden rock under mining. J. China Coal Soc. 2019, 44, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Guo, G.; Zha, J.; Wang, T.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Huo, W. A new method of regional mining subsidence control for sustainable development in coal areas. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Yu, L.; Bai, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zheng, C.; Huang, X.; He, J.; Zhou, H. Parameter design and effectiveness evaluation of wide strip mining of extra thick coal seams under dense buildings. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10037. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Ji, X.; Li, Y. Prediction of surface subsidence in Gequan coal mine based on probability integral and numerical simulation. Acad. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2024, 7, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Zheng, M.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Guo, G.; Su, Z.; Huo, W. Delineation of Backfill Mining Influence Range Based on Coal Mining Subsidence Principle and Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Lu, L.; Yao, Y. Method combining probability integration model and a small baseline subset for time series monitoring of mining subsidence. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Wang, Y. Research on robust estimation model of probability integral method parameters and its application. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sinica 2000, 29, 162–165+171. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, J. Calculation and analysis of surface subsidence prediction parameters. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2004, 21, 78–79+82. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, J.; Schaedler, W.; Borgatti, L.; Corsini, A.; Schanz, T. Inverse parameter identification technique using PSO algorithm applied to geotechnical modeling. J. Artif. Evol. Appl. 2008, 2008, 574613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Peng, D.; Tan, Z.; Deng, K. Study of probability integration method parameter inversion by the genetic algorithm. Inter-Natl. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2017, 27, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhao, S. Application of improved WOA-BP algorithm in parameter prediction of probability integral method. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2023, 48, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Qiao, B.; Yang, Y.; Guo, J. Research on parameter inversion of coal mining subsidence prediction model based on improved whale optimization algorithm. Energies 2024, 17, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.Q.; Le, T.T.T.; Nguyen, T.G.; Tran, D.T. Prediction of underground mining-induced subsidence: Artificial neural network based approach. Min. Miner. Depos. 2023, 17, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Cheng, P.; Wang, M.; Shao, Y.; Qi, L. Comparison study on the power of global optimization solvers for nonlinear system equations solving. Comput. Appl. Softw. 2022, 39, 1–10+24. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, B. BFGS method based inversion of parameters in probability integral model. J. China Coal Soc. 2019, 44, 3058–3068. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, H.; Kang, J.; Hu, J. Robust estimation of model parameters of the probability integral method based on CA-rPSO. Surv. Rev. 2022, 54, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J. A parameter inversion method for the probability integral method based on robust ridge estimation. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 11, 1330163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurpeissova, M.; Rysbekov, K.; Kenesbayeva, A.; Bekbassarov, Z.; Levin, E. Simulation of geodynamic processes. Eng. J. Satbayev Univ. 2021, 143, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y. Research on the key technologies of InSAR/GIS monitoring for illegalunderground mining in coal mining area. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2020, 53, 394. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Misa, R.; Li, P.; Yuan, X.; Sroka, A.; Jiang, Y. Summary and development of mining subsidence theory. Met. Mine 2019, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Lian, X.; Ge, L.; Liu, X.; Du, Z.; Yang, W.; Wu, Y.; Hu, H.; Cai, Y. Surface subsidence monitoring induced by underground coal mining by combining DInSAR and UAV photogrammetry. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moklyachuk, M. Minimax-robust estimation problems for stationary stochastic sequences. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.17917. [Google Scholar]
- Pensia, A.; Jog, V.; Loh, P.-L. Robust regression with covariate filtering: Heavy tails and adversarial contamination. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2024, 2024, 2392906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. An improved robust estimation method for gnss/sins under gnss-challenged environment. In Proceedings of the 2022 11th International Conference on Control, Automation and Information Sciences (ICCAIS), Hanoi, Vietnam, 21–24 November 2022; pp. 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wang, K.; Abel, D. Robust state and protection-level estimation within tightly coupled GNSS/INS navigation system. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q. Equivalent weight function and robust estimation method with adaptive criterion. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2017, 46, 911–916. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, T.; Xu, G. Application of Combining Methodof Outlier Detection and Robust Estimation to GPS Kinematic Relative Positioning. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2011, 36, 476–480. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; Yang, Y. Influence of stochastic model on the coordinate of Xi’an mobile SLR station determination. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2019, 44, 1765–1770. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, A.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jing, Y.; Ma, Y. A method of protection level reconstruction basedon robust estimation. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2021, 46, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Q.; Jiang, R.; Mokhtari, A. Non-asymptotic Global Convergence Rates of BFGS with Exact Line Search. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.01267. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Yang, C.; Wu, Q.; Wang, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Zhao, L. Improved Reconstruction Algorithm of Wireless Sensor Network Based on BFGS Quasi-Newton Method. Electronics 2023, 12, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
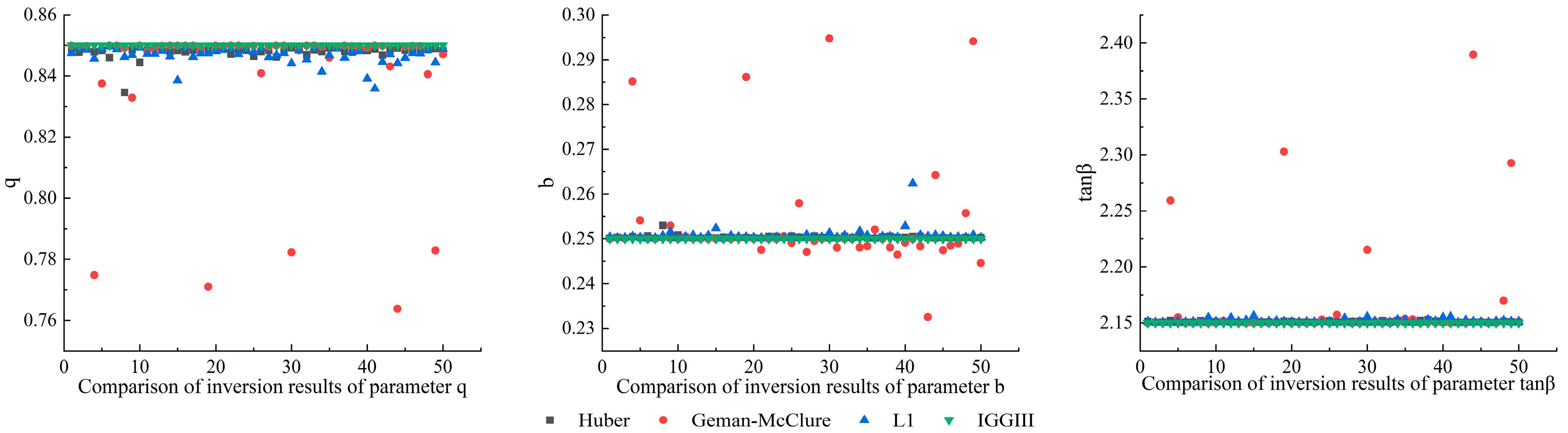
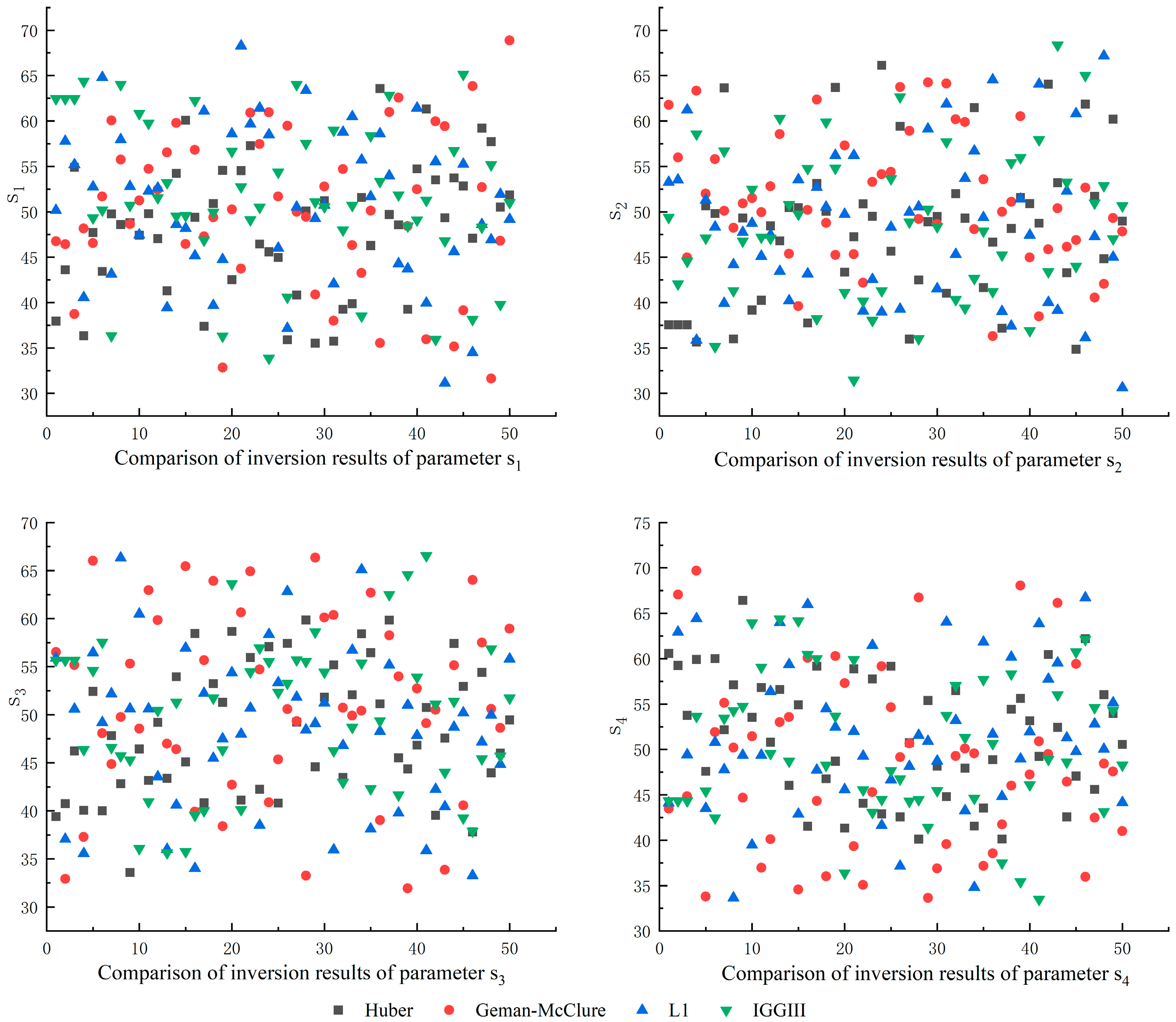
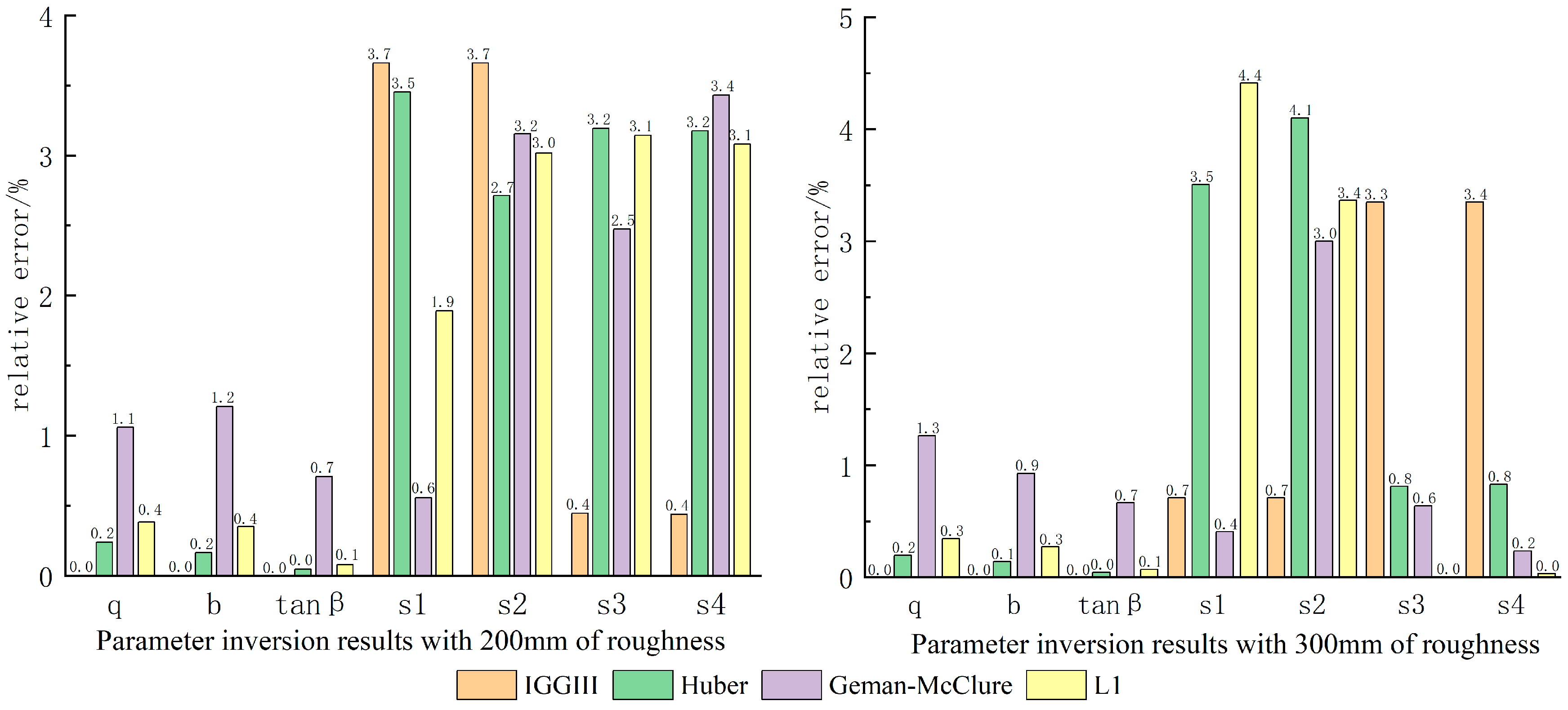
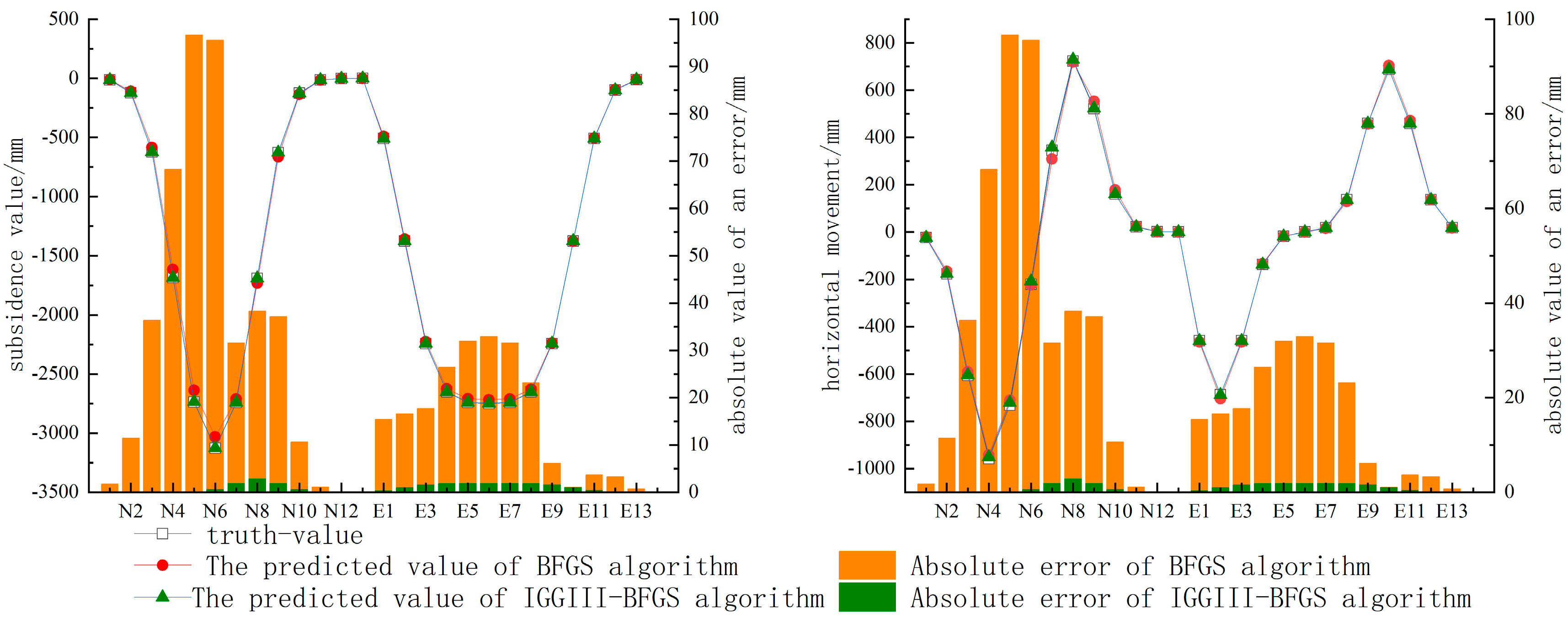
| Gross Error Number | Position of Gross Error | Parameter Name | q | b | tan β | s1 | s2 | s3 | s4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Truth Value | 0.85 | 0.25 | 2.15 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | ||
| 1 | Near the maximum subsidence value | BFGS | 0.832 | 0.255 | 2.168 | 50.654 | 47.160 | 51.804 | 47.709 |
| relative error | 2.13% | 1.90% | 0.84% | 1.31% | 5.68% | 3.61% | 4.58% | ||
| IGGIII-BFGS | 0.850 | 0.250 | 2.150 | 51.614 | 48.386 | 50.881 | 49.119 | ||
| relative error | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 3.23% | 3.23% | 1.76% | 1.76% | ||
| Near the inflection points | BFGS | 0.848 | 0.251 | 2.179 | 51.506 | 48.738 | 46.252 | 53.405 | |
| relative error | 0.28% | 0.35% | 1.35% | 3.01% | 2.52% | 7.50% | 6.81% | ||
| IGGIII-BFGS | 0.850 | 0.250 | 2.150 | 52.928 | 47.092 | 52.415 | 47.557 | ||
| relative error | 0.02% | 0.03% | 0.01% | 5.86% | 5.82% | 4.83% | 4.89% | ||
| Near the edges | BFGS | 0.849 | 0.250 | 2.155 | 49.722 | 50.237 | 50.537 | 49.577 | |
| relative error | 0.10% | 0.15% | 0.25% | 0.56% | 0.47% | 1.07% | 0.85% | ||
| IGGIII-BFGS | 0.850 | 0.250 | 2.150 | 49.209 | 50.789 | 48.670 | 51.330 | ||
| relative error | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 1.58% | 1.58% | 2.66% | 2.66% | ||
| 2 | Near the maximum subsidence value | BFGS | 0.815 | 0.259 | 2.181 | 48.649 | 46.716 | 53.040 | 46.067 |
| relative error | 4.11% | 3.60% | 1.45% | 2.70% | 6.57% | 6.08% | 7.87% | ||
| IGGIII-BFGS | 0.850 | 0.250 | 2.150 | 48.966 | 51.033 | 49.412 | 50.589 | ||
| relative error | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 2.07% | 2.07% | 1.18% | 1.18% | ||
| Near the inflection points | BFGS | 0.839 | 0.255 | 2.200 | 50.739 | 49.287 | 46.984 | 52.516 | |
| relative error | 1.29% | 1.87% | 2.30% | 1.48% | 1.43% | 6.03% | 5.03% | ||
| IGGIII-BFGS | 0.849 | 0.250 | 2.154 | 48.528 | 51.474 | 47.781 | 48.284 | ||
| relative error | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 2.94% | 2.95% | 4.44% | 3.43% | ||
| Near the edges | BFGS | 0.845 | 0.252 | 2.181 | 47.605 | 52.162 | 49.261 | 51.671 | |
| relative error | 0.55% | 0.86% | 1.44% | 4.79% | 4.32% | 1.48% | 3.34% | ||
| IGGIII-BFGS | 0.850 | 0.250 | 2.150 | 50.397 | 49.602 | 53.034 | 46.967 | ||
| relative error | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 1.58% | 1.58% | 2.66% | 2.66% |
| Parameter | PSO Algorithm | IGGIII-BFGS Algorithm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inversion Mean | Absolute Value of Error | Relative Error | Inversion Mean | Absolute Value of Error | Relative Error | |
| q | 0.812 | 0.038 | 4.53% | 0.850 | 0.000 | 0.00% |
| b | 0.259 | 0.009 | 3.54% | 0.250 | 0.000 | 0.02% |
| tan β | 2.224 | 0.074 | 3.42% | 2.150 | 0.000 | 0.00% |
| θ0 | 86.413 | 0.413 | 0.48% | 85.953 | 0.047 | 0.05% |
| s1 | 42.599 | 7.401 | 14.80% | 50.045 | 0.045 | 0.09% |
| s2 | 53.110 | 3.110 | 6.22% | 49.000 | 1.000 | 2.00% |
| s3 | 33.857 | 16.143 | 32.29% | 49.138 | 0.862 | 1.72% |
| s4 | 67.206 | 17.206 | 34.41% | 50.408 | 0.408 | 0.82% |
| Method | q | tan β | θ0 | s1 | s2 | s3 | s4 | RMSE/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BFGS | 1.530 | 1.665 | 93.825 | 5.023 | 0.235 | 62.479 | 59.481 | 109.482 |
| IGGIII-BFGS | 1.513 | 1.808 | 93.825 | 15.809 | 4.605 | 71.095 | 72.479 | 81.278 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, X.; Yang, R.; Zhu, M.; Duan, J.; Chi, S. Robust Parameter Inversion and Subsidence Prediction for Probabilistic Integral Methods in Mining Areas. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5849. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115849
Fang X, Yang R, Zhu M, Duan J, Chi S. Robust Parameter Inversion and Subsidence Prediction for Probabilistic Integral Methods in Mining Areas. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):5849. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115849
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Xinjian, Rui Yang, Mingfei Zhu, Jinling Duan, and Shenshen Chi. 2025. "Robust Parameter Inversion and Subsidence Prediction for Probabilistic Integral Methods in Mining Areas" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 5849. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115849
APA StyleFang, X., Yang, R., Zhu, M., Duan, J., & Chi, S. (2025). Robust Parameter Inversion and Subsidence Prediction for Probabilistic Integral Methods in Mining Areas. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 5849. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115849





