DeepGun: Deep Feature-Driven One-Class Classifier for Firearm Detection Using Visual Gun Features and Human Body Pose Estimation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work and Our Contributions
- Unsupervised Firearm Detection: We propose a fully unsupervised approach for detecting active firearms using a unified feature representation derived from a VAE and HPE. This method eliminates the need for prior labeling of anomalous samples with handgun and instead exploits averaged latent sample representations for improved accuracy.
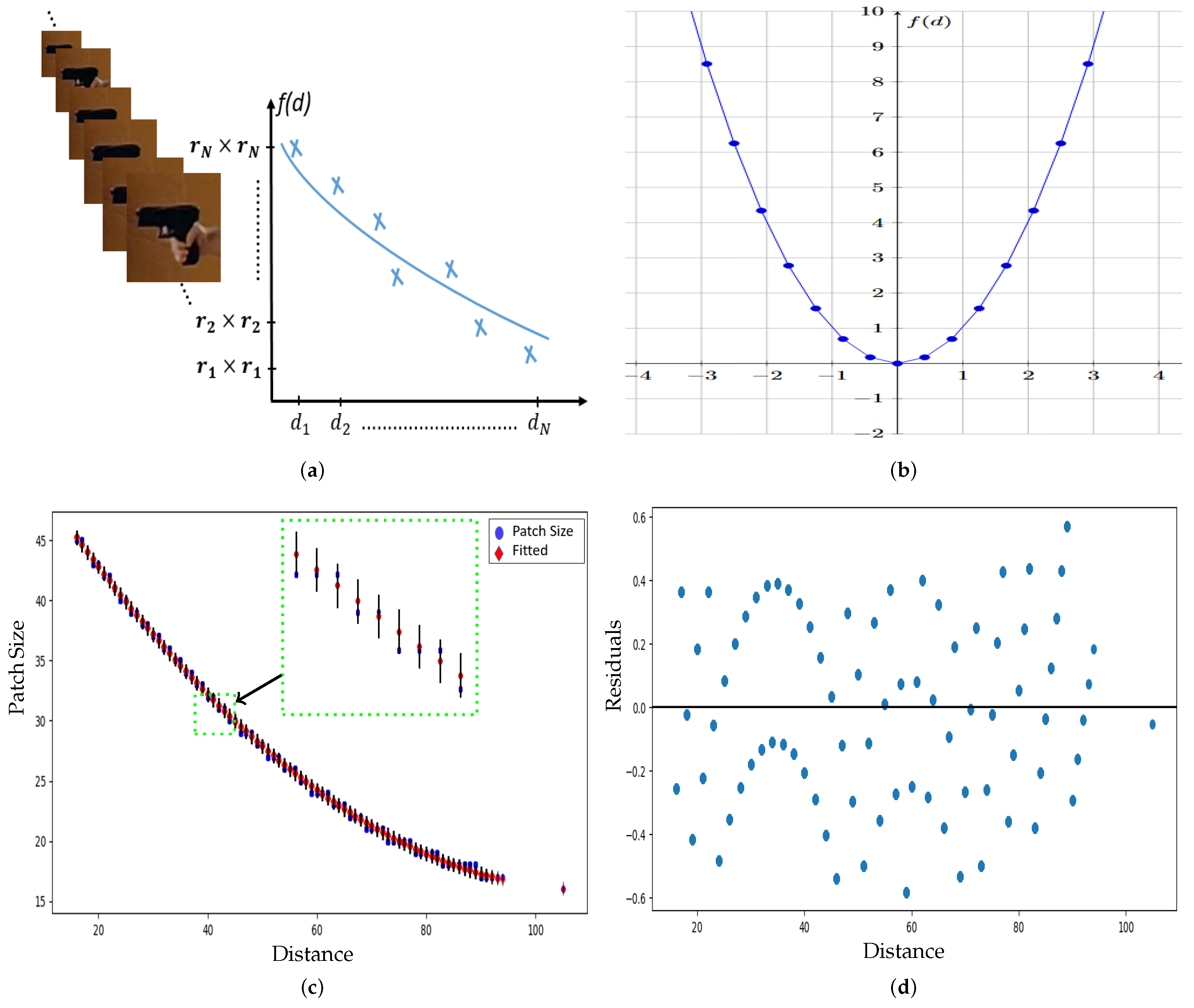
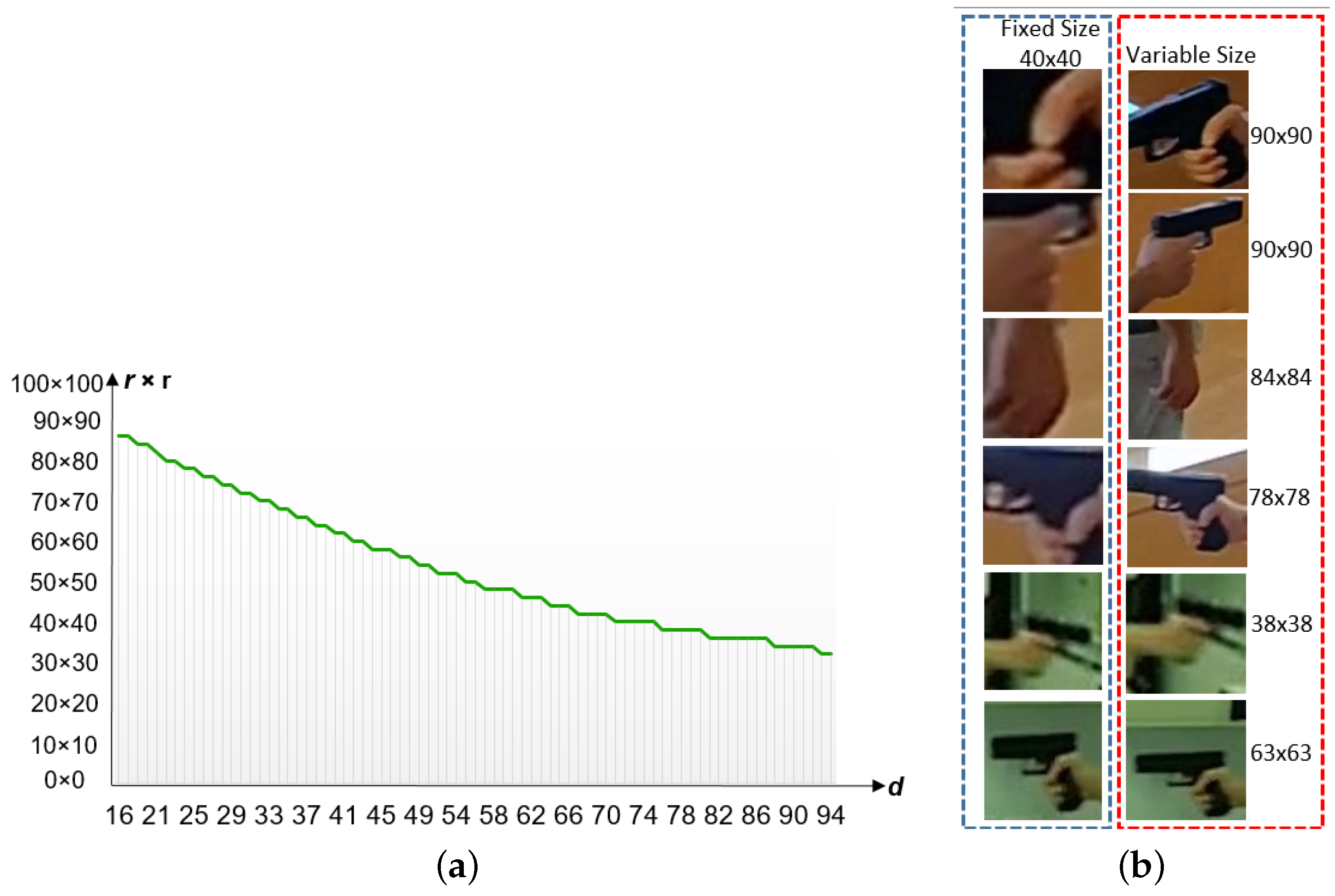
- Adaptive Patch Extraction: We introduce an automatic variable patch size extraction technique based on estimating the distance between the subject and the camera using HPE. This novel approach eliminates the need for cropping or oversizing patches extracted from visual gun instances in frames, ensuring robust and efficient feature extraction.
- Comprehensive Benchmark Evaluation: We conduct extensive experiments using the VISILAB, UCF-Crime and YouTube benchmark firearm datasets, evaluating the performance of various video action analysis models, feature extraction techniques, and state-of-the-art OCC methods for firearm detection.
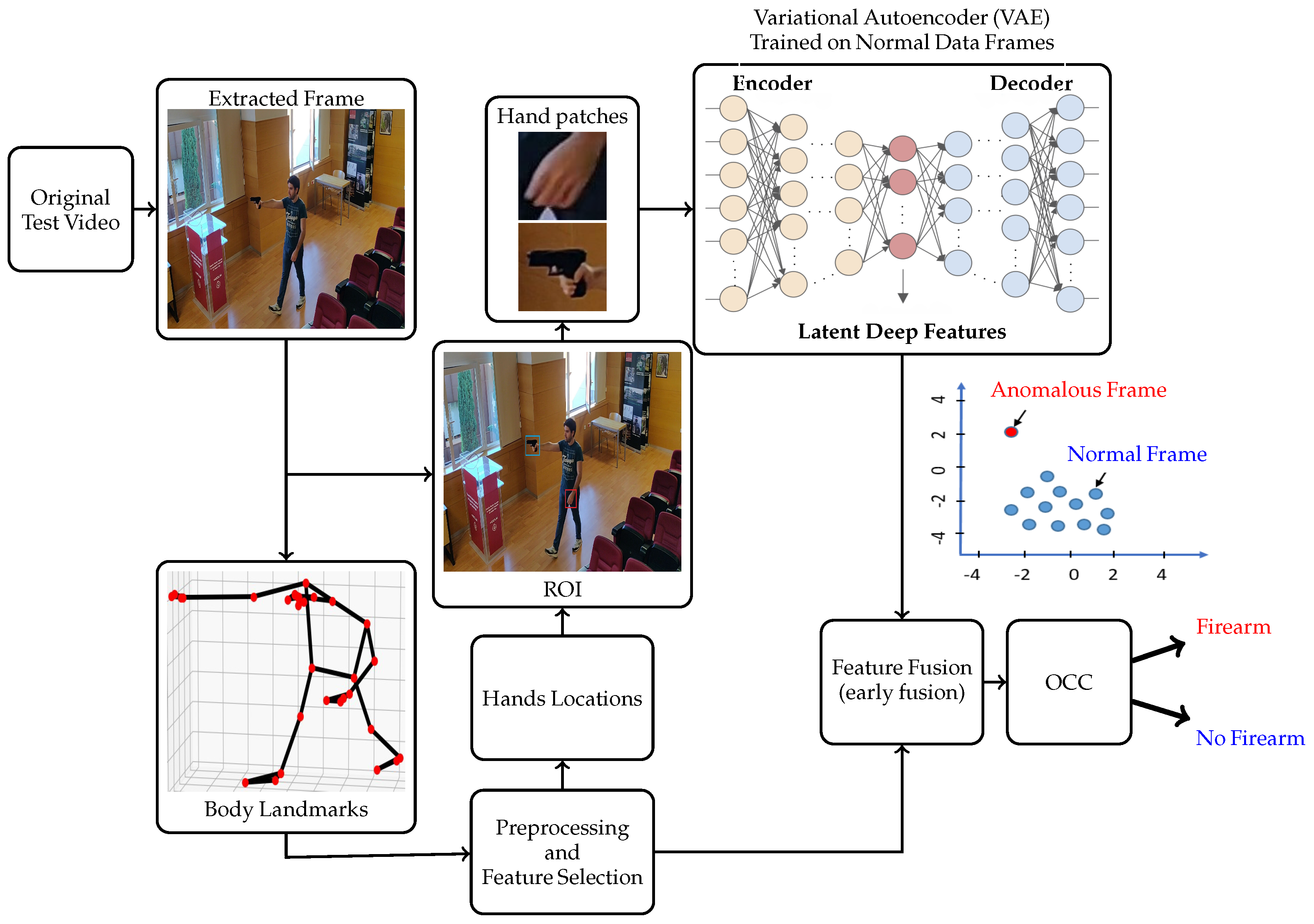
3. Proposed Algorithm
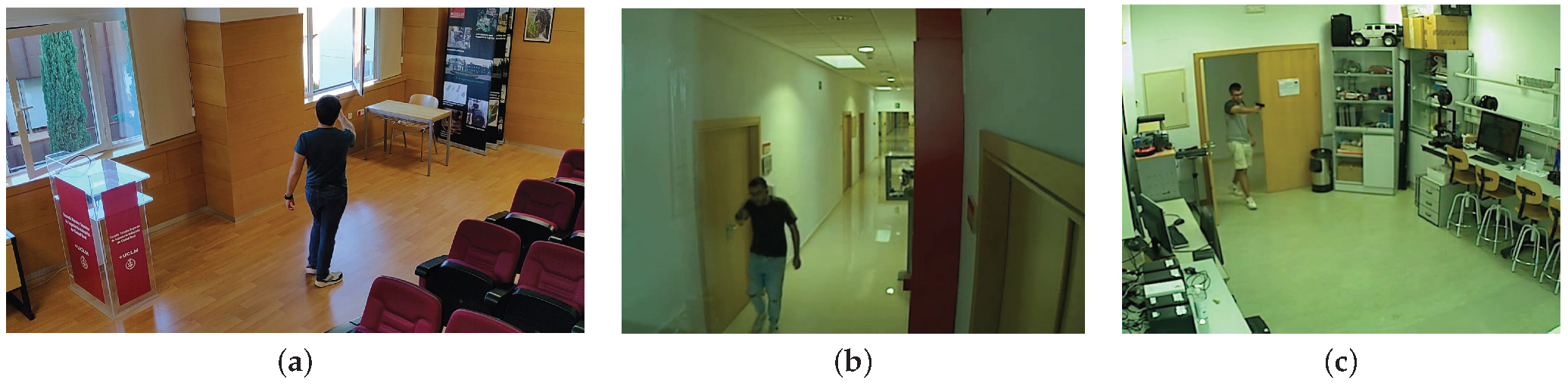
3.1. Firearm Dataset Used
3.2. Hand Patch Extraction Based on HPE
- Step-1: For each frame, compute the maximum confidence value of landmarks belong to left and right hand (i.e., wrist, pinky, index, and thumb landmarks).
- Step-2: Discard patches and landmarks if the computed confidence (computed in step-1) for both left and right hands is below . Frames that do not meet this threshold will be excluded from both the training and testing phases.
- Step-3: If one hand (left or right) is not visible, copy the landmark values and patches from the last frame for that hand. This reduces the waste of patches and body landmarks. Therefore, if the confidence for one hand is above the threshold, but the other hand’s confidence is below, the information for the invisible hand will be determined by the last frame for that invisible frame.
3.3. Variational Autoencoders (VAE)
3.4. Feature Fusion and Anomaly Detection
4. Experiments and Evaluation
4.1. Comparative Analysis with Other Firearm Detection and Action Recognition Frameworks
4.2. DeepGun vs. Deep Architectures as Feature Extractor
4.3. Cross-Validation Evaluation and Ablation Study
4.4. Failure Cases and the Potential for Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thakur, A.; Shrivastav, A.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, T.; Puri, K. Real-Time Weapon Detection Using YOLOv8 for Enhanced Safety. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.19862. [Google Scholar]
- Burnayev, Z.R.; Toibazarov, D.O.; Atanov, S.K.; Canbolat, H.; Seitbattalov, Z.Y.; Kassenov, D.D. Weapons Detection System Based on Edge Computing and Computer Vision. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2023, 14, 0140586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.; Oliveira, H.; Cunha, A. Systematic review on weapon detection in surveillance footage through deep learning. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2024, 51, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akshaya, P.; Reddy, P.B.; Panuganti, P.; Gurusai, P.; Subhahan, A. Automatic weapon detection using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Research Methodologies in Knowledge Management, Artificial Intelligence and Telecommunication Engineering (RMKMATE), Chennai, India, 1–2 November 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salido, J.; Lomas, V.; Ruiz-Santaquiteria, J.; Deniz, O. Automatic handgun detection with deep learning in video surveillance images. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gun Violence Archive. Available online: https://www.gunviolencearchive.org/reports/mass-shooting/year-2023 (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Ruiz-Santaquiteria, J.; Velasco-Mata, A.; Vallez, N.; Deniz, O.; Bueno, G. Improving handgun detection through a combination of visual features and body pose-based data. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 136, 109252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, J.D.; Ruiz-Santaquiteria, J.; Deniz, O.; Bueno, G. Concealed Weapon Detection Using Thermal Cameras. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmos, R.; Tabik, S.; Herrera, F. Automatic handgun detection alarm in videos using deep learning. Neurocomputing 2018, 275, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Gupta, N.; Sharma, P.K. A comprehensive study towards high-level approaches for weapon detection using classical machine learning and deep learning methods. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 212, 118698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Santaquiteria, J.; Muñoz, J.D.; Maigler, F.J.; Deniz, O.; Bueno, G. Firearm-related action recognition and object detection dataset for video surveillance systems. Data Brief 2024, 52, 110030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grega, M.; Matiolański, A.; Guzik, P.; Leszczuk, M. Automated Detection of Firearms and Knives in a CCTV Image. Sensors 2016, 16, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omnilert. Available online: https://www.omnilert.com/solutions/ai-gun-detection (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Pelco. Available online: https://www.pelco.com/blog/weapons-detection-systems (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Egiazarov, A.; Mavroeidis, V.; Zennaro, F.M.; Vishi, K. Firearm Detection and Segmentation Using an Ensemble of Semantic Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 European Intelligence and Security Informatics Conference (EISIC), Oulu, Finland, 26–27 November 2019; pp. 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, G.K.; Dhillon, A. A Handheld Gun Detection using Faster R-CNN Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Computer and Communication Technology, ICCCT-2017, New York, NY, USA, 24–26 November 2017; pp. 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearst, M.A.; Dumais, S.T.; Osuna, E.; Platt, J.; Scholkopf, B. Support vector machines. IEEE Intell. Syst. Their Appl. 1998, 13, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.C.; Amini, M.H.; Wu, Y. Accurate and Efficient Two-Stage Gun Detection in Video. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.06317. [Google Scholar]
- Kondratyuk, D.; Yuan, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tan, M.; Brown, M.; Gong, B. Movinets: Mobile video networks for efficient video recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 16020–16030. [Google Scholar]
- Wasim, S.T.; Khattak, M.U.; Naseer, M.; Khan, S.; Shah, M.; Khan, F.S. Video-FocalNets: Spatio-temporal focal modulation for video action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 13778–13789. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Wang, H.; Torresani, L.; Ray, J.; LeCun, Y.; Paluri, M. A closer look at spatiotemporal convolutions for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6450–6459. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, N.S.; Ogura, K.; Cosatto, E.; Ariyoshi, M. Real-time concealed weapon detection on 3D radar images for walk-through screening system. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023; pp. 673–681. [Google Scholar]
- Kaul, C.; Mitchell, K.J.; Kassem, K.; Tragakis, A.; Kapitany, V.; Starshynov, I.; Villa, F.; Murray-Smith, R.; Faccio, D. AI-Enabled Sensor Fusion of Time-of-Flight Imaging and mmWave for Concealed Metal Detection. Sensors 2024, 24, 5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, P.Y.; Kim, Y.G. Real-Time Abnormal Object Detection for Video Surveillance in Smart Cities. Sensors 2022, 22, 3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, Y.W.; Price, T.; Wei, Z.; Lu, X.; Rewkowski, N.; Chabra, R.; Qin, Z.; Kim, H.; Su, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Towards fully mobile 3D face, body, and environment capture using only head-worn cameras. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2018, 24, 2993–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Mata, A.; Ruiz-Santaquiteria, J.; Vallez, N.; Deniz, O. Using human pose information for handgun detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 17273–17286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.L.; Ong, L.Y.; Leow, M.C. Comparative Analysis of Skeleton-Based Human Pose Estimation. Future Internet 2022, 14, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, H.; Velastin, S.A.; Meza, I.; Fabregas, E.; Makris, D.; Farias, G. Fall Detection and Activity Recognition Using Human Skeleton Features. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 33532–33542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Amemiya, Y.; Sato, M. Skeleton-based visualization of poor body movements in a child’s gross-motor assessment using convolutional auto-encoder. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics (ICM), Kashiwa, Japan, 7–9 March 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, R.A.A.; de Oliveira, A.C.M.; de Almeida Ribeiro, P.R.; de Almeida Neto, A. Firearm detection using DETR with multiple self-coordinated neural networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 22013–22022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Santaquiteria, J.; Velasco-Mata, A.; Vallez, N.; Bueno, G.; Alvarez-Garcia, J.A.; Deniz, O. Handgun detection using combined human pose and weapon appearance. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 123815–123826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dever, J.; da Vitoria Lobo, N.; Shah, M. Automatic visual recognition of armed robbery. In Proceedings of the 2002 International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 11–15 August 2002; Volume 1, pp. 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darker, I.; Gale, A.; Ward, L.; Blechko, A. Can CCTV Reliably Detect Gun Crime? In Proceedings of the 2007 41st Annual IEEE International Carnahan Conference on Security Technology, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 8–11 October 2007; pp. 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazarevsky, V.; Grishchenko, I.; Raveendran, K.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, F.; Grundmann, M. BlazePose: On-device Real-time Body Pose tracking. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.10204. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Hidalgo, G.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.E.; Sheikh, Y. Openpose: Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultani, W.; Chen, C.; Shah, M. Real-world anomaly detection in surveillance videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6479–6488. [Google Scholar]
- Seliya, N.; Abdollah Zadeh, A.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A literature review on one-class classification and its potential applications in big data. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, L.; Vandermeulen, R.; Goernitz, N.; Deecke, L.; Siddiqui, S.A.; Binder, A.; Müller, E.; Kloft, M. Deep one-class classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; PMLR: Breckenridge, CO, USA, 2018; pp. 4393–4402. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.S.; Madden, M.G. One-class classification: Taxonomy of study and review of techniques. Knowl. Eng. Rev. 2014, 29, 345–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, P.; Nallapati, R.; Xiang, B. Ocgan: One-class novelty detection using gans with constrained latent representations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2898–2906. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Li, A.; Wen, X.; Chen, H.; Yang, P. Steel surface defect detection using GAN and one-class classifier. In Proceedings of the 2019 25th International Conference on Automation and Computing (ICAC), Lancaster, UK, 5–7 September 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Perera, P.; Patel, V.M. Learning deep features for one-class classification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 5450–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, A.; Kucheryavskiy, S. VAE-SIMCA—Data-driven method for building one class classifiers with variational autoencoders. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2025, 256, 105276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. An introduction to variational autoencoders. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 2019, 12, 307–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.; Raghunathan, A.; Jain, M.; Simhadri, H.V.; Jain, P. DROCC: Deep robust one-class classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020; PMLR: Breckenridge, CO, USA, 2020; pp. 3711–3721. [Google Scholar]
- MediaPipe ML Solutions in MediaPipe. Available online: https://chuoling.github.io/mediapipe/ (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Alsawadi, M.S.; Rio, M. Human Action Recognition using BlazePose Skeleton on Spatial Temporal Graph Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 9th International Conference on Information Technology, Computer, and Electrical Engineering (ICITACEE), Semarang, Indonesia, 25–26 August 2022; pp. 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Pei, Y.; Li, J. A comprehensive survey on design and application of autoencoder in deep learning. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 138, 110176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandram, D.; Taylor, G.W. Deep multimodal learning: A survey on recent advances and trends. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2017, 34, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.T.; Ting, K.M.; Zhou, Z.H. Isolation Forest. In Proceedings of the 2008 Eighth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Pisa, Italy, 15–19 December 2008; pp. 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal component analysis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, D.A. Gaussian mixture models. Encycl. Biom. 2009, 741, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseeuw, P.J.; van Driessen, K. A Fast Algorithm for the Minimum Covariance Determinant Estimator. Technometrics 1999, 41, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Zoph, B.; Vasudevan, V.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. Learning transferable architectures for scalable image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8697–8710. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Saul, L.K.; Weiss, Y.; Bottou, L. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 17: Proceedings of the 2004 Conference; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Vallez, N.; Velasco-Mata, A.; Deniz, O. Deep autoencoder for false positive reduction in handgun detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 5885–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Liu, C.; Long, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, G.; Cai, H. Multi-RoI Human Mesh Recovery with Camera Consistency and Contrastive Losses. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Springe: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; pp. 439–458. [Google Scholar]
- Akrami, H.; Joshi, A.A.; Li, J.; Aydöre, S.; Leahy, R.M. A robust variational autoencoder using beta divergence. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 238, 107886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tan, S.; Zhen, X.; Xu, S.; Zheng, F.; He, Z.; Shao, L. Deep 3D human pose estimation: A review. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2021, 210, 103225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



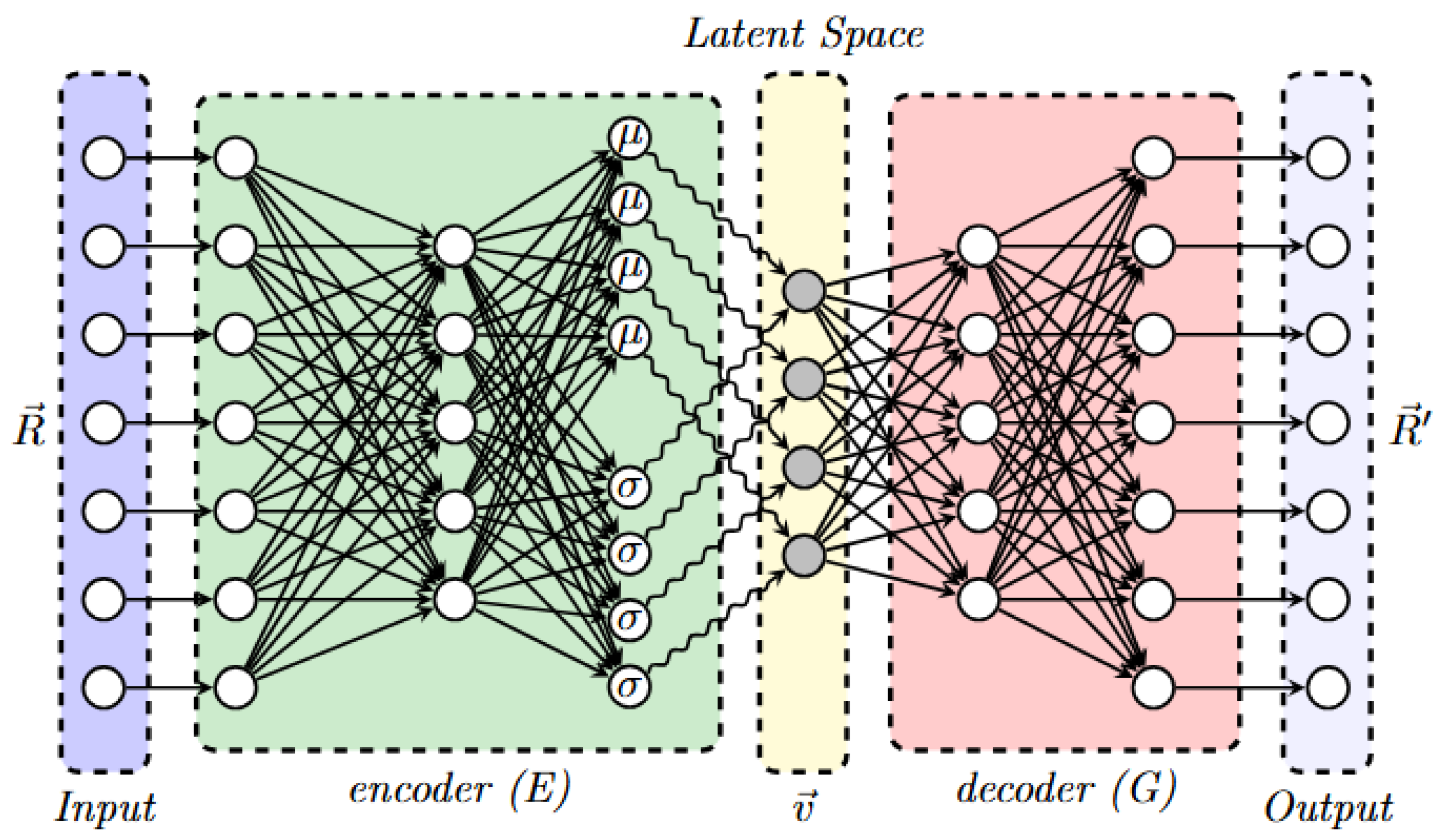
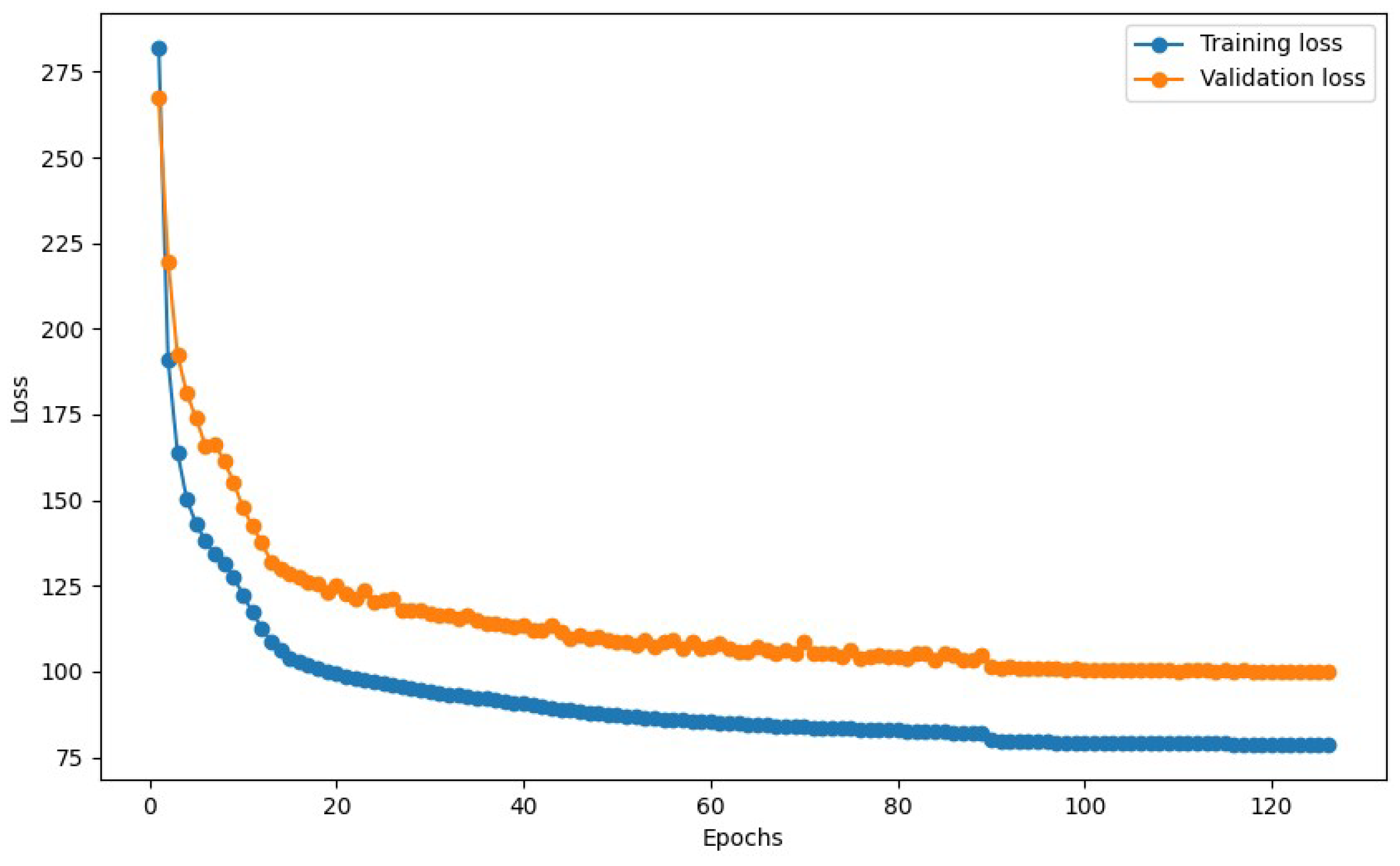
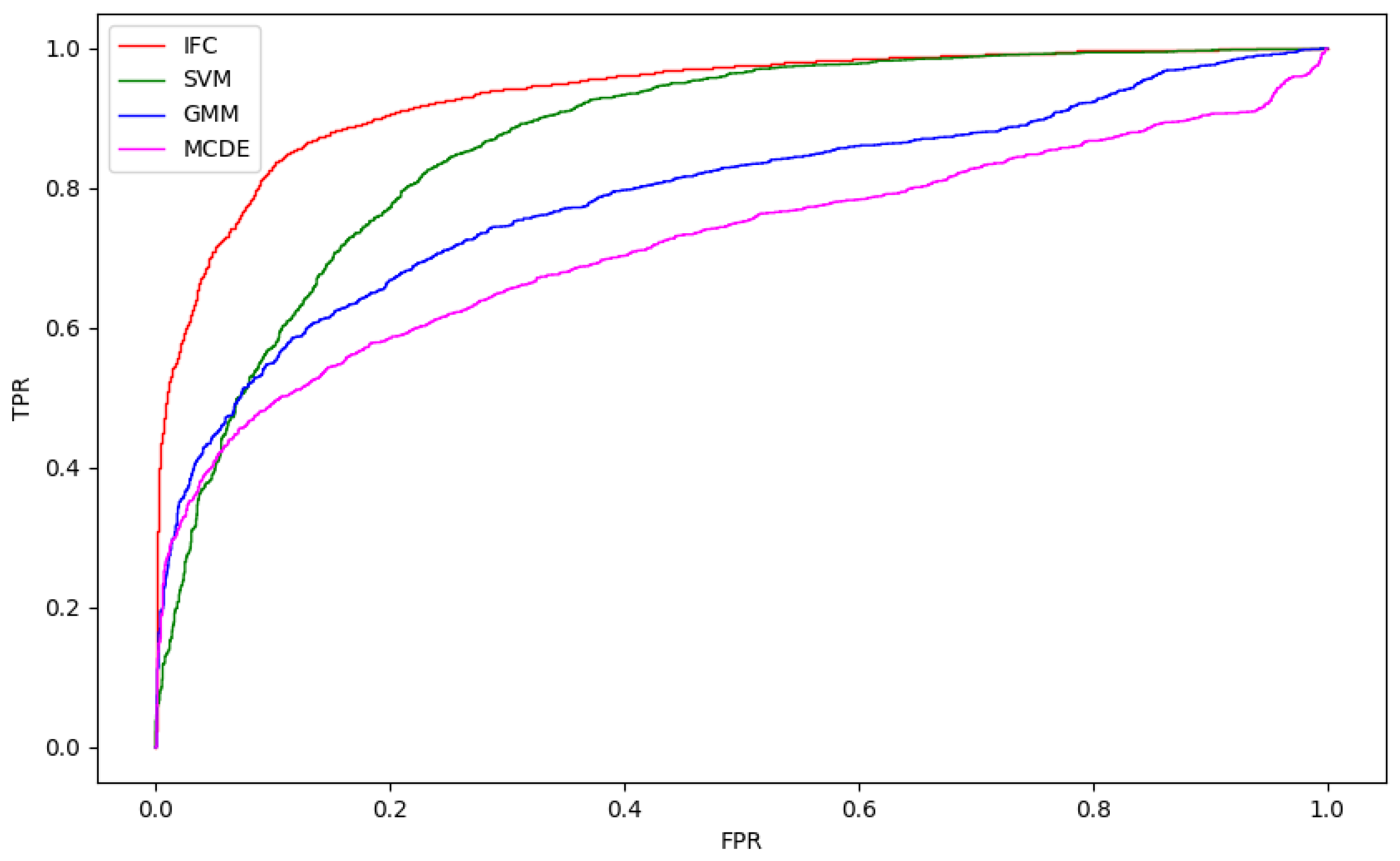

| Network Layer | Network Structure | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Encoder layer 1 | Fully Connected | 1024 | 512 |
| Encoder layer 2 | Fully Connected | 512 | 256 |
| Encoder layer 3 | Fully Connected | 256 | 128 |
| Encoder layer 4 | Fully Connected | 128 | 64 |
| Decoder layer 1 | Fully Connected | 64 | 128 |
| Decoder layer 2 | Fully Connected | 128 | 256 |
| Decoder layer 3 | Fully Connected | 256 | 512 |
| Decoder layer 4 | Fully Connected | 512 | 1024 |
| Method | ACC (VISILAB) | ACC (UCF-Firearm) | Model Specifications |
|---|---|---|---|
| DeepGun | 85.2 | 84.1 | VAE with KL loss and reconstruction loss, NN encoder with 4 blocks, 1D kernel, latent space 64,200 epochs, early stopping with patience 10, input patch size . |
| R-CNN [16] | 82.2 | 80.5 | VGG-16 pretrained on Imagenet database, mini-batch gradient descent with momentum, 50 epochs, early stopping with patience 10, input size . |
| TSGD [18] | 51.9 | 67.16 | YOLOv11 for gun detection, VGG trained on Imagenet and Transformer [60] combination for handling the temporal features in videos, 200 epochs, early stopping, input frame size . |
| Video-FocalNets [20] | 83.33 | 75 | Spatio-temporal focal modulation, 4 blocks with 2D depthwise followed by 1D pointwise convolution, 120 epochs, batch size 512. |
| Movinets [19] | 83.44 | 79.16 | Vision transformer, 5 blocks with 3D-CNN kernel, 240 epochs, batch size 1024. |
| 3D-CNNs [21] | 67.39 | 67.16 | Spatiotemporal 3D CNNs with 34 layers, 45 epochs, input size . |
| Method | ACC | Precision (P) | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|
| DeepGun | 85.2 | 95.3 | 96.4 |
| VAE-SIMCA [43] | 62.0 | 93.8 | 43.0 |
| TSGD [18] | 51.9 | 98.1 | 50.0 |
| Classifier | Metric | Nas-NetLarge | Dense-Net201 | VGG19 | Mobile-NetV2 | Res-Net50 | AE | DeepGun |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFC | 85.1 | 82.3 | 83.7 | 83.2 | 83.7 | 81.3 | 86.6 | |
| 83.4 | 80.9 | 82.2 | 81.9 | 82.6 | 79.3 | 85.2 | ||
| P | 90.1 | 87.2 | 89.8 | 88.2 | 87.7 | 87.2 | 95.3 | |
| R | 75.0 | 72.4 | 72.6 | 73.6 | 75.8 | 68.6 | 74.0 | |
| 80.1 | 76.9 | 78.9 | 78.1 | 78.6 | 75.5 | 83.5 | ||
| SVM | 62.1 | 68.6 | 69.4 | 66.0 | 64.8 | 53.5 | 79.2 | |
| 70.6 | 74.3 | 75.1 | 72.7 | 72.5 | 66.3 | 81.1 | ||
| P | 64.2 | 67.8 | 68.3 | 66.3 | 65.6 | 60.5 | 76.3 | |
| R | 93.0 | 92.2 | 93.6 | 92.2 | 94.2 | 94.8 | 90.2 | |
| 63.2 | 66.4 | 67.1 | 65.0 | 64.7 | 59.8 | 73.7 | ||
| MCDE | 61.0 | 61.0 | 61.1 | 61.2 | 62.3 | 61.0 | 77.7 | |
| 51.6 | 51.6 | 51.7 | 51.8 | 54.5 | 51.7 | 79.1 | ||
| P | 51.0 | 51.0 | 51.1 | 51.2 | 53.1 | 51.1 | 83.4 | |
| R | 76.0 | 75.8 | 76.0 | 76.2 | 75.4 | 75.8 | 72.8 | |
| 50.8 | 50.8 | 50.8 | 50.9 | 52.3 | 50.8 | 74.3 | ||
| GMM | 41.0 | 49.0 | 57.2 | 53.1 | 44.7 | 68.3 | 56.8 | |
| 47.8 | 49.4 | 52.3 | 52.0 | 47.8 | 65.7 | 52.0 | ||
| P | 47.1 | 49.3 | 51.8 | 51.9 | 47.2 | 63.4 | 51.6 | |
| R | 36.4 | 48.8 | 63.8 | 54.4 | 42.6 | 74.2 | 63.3 | |
| 48.9 | 49.7 | 51.1 | 51.0 | 48.8 | 59.9 | 51.0 |
| Classifier | Metric | Nas-NetLarge | Dense-Net201 | VGG19 | Mobile-NetV2 | Res-Net50 | AE | DeepGun |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFC | 68.4 | 62.2 | 45.6 | 69.4 | 44.7 | 46.4 | 65.0 | |
| 85.6 | 83.1 | 78.8 | 85.8 | 78.4 | 77.3 | 84.1 | ||
| P | 88.6 | 86.6 | 81.7 | 89.2 | 81.5 | 82.0 | 87.6 | |
| R | 92.6 | 91.8 | 92.3 | 92.9 | 92.3 | 89.5 | 92.0 | |
| 87.6 | 85.7 | 81.2 | 88.1 | 81.4 | 81.3 | 86.6 | ||
| SVM | 30.4 | 35.9 | 32.0 | 28.1 | 11.6 | 10.0 | 21.9 | |
| 75.0 | 75.9 | 75.0 | 74.4 | 71.3 | 65.4 | 73.1 | ||
| P | 78.4 | 79.5 | 78.7 | 78.0 | 75.3 | 73.6 | 76.9 | |
| R | 92.2 | 91.7 | 91.7 | 92.0 | 92.0 | 84.4 | 92.0 | |
| 78.2 | 79.1 | 78.4 | 77.8 | 75.5 | 73.9 | 76.8 | ||
| MCDE | 84.3 | 83.3 | 83.3 | 83.5 | 83.2 | 83.3 | 83.3 | |
| 74.4 | 72.0 | 72.0 | 72.2 | 71.9 | 72.1 | 72.0 | ||
| P | 77.3 | 75.6 | 75.7 | 75.5 | 75.5 | 75.7 | 75.7 | |
| R | 92.6 | 92.7 | 92.7 | 93.4 | 92.2 | 75.8 | 92.7 | |
| 77.2 | 75.5 | 75.6 | 75.5 | 75.5 | 75.7 | 75.7 | ||
| GMM | 24.1 | 37.3 | 18.4 | 33.4 | 37.9 | 38.0 | 18.3 | |
| 25.3 | 28.4 | 71.4 | 28.8 | 29.9 | 32.2 | 71.5 | ||
| P | 16.0 | 23.8 | 30.9 | 21.6 | 24.2 | 24.5 | 31.0 | |
| R | 48.3 | 86.9 | 13.0 | 72.6 | 87.2 | 84.7 | 13.0 | |
| 20.4 | 23.9 | 25.3 | 22.4 | 24.2 | 24.5 | 25.5 |
| Classifier | Metric | Nas-NetLarge | Dense-Net201 | VGG19 | Mobile-NetV2 | Res-Net50 | AE | DeepGun |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFC | 76.7 | 78.0 | 78.8 | 80.1 | 80.5 | 66.6 | 81.8 | |
| 84.7 | 85.5 | 85.8 | 86.8 | 86.8 | 68.7 | 87.6 | ||
| P | 88.2 | 89.3 | 90.2 | 90.4 | 91.4 | 95.7 | 92.1 | |
| R | 89.1 | 89.0 | 88.5 | 89.9 | 88.6 | 55.8 | 89.2 | |
| 86.0 | 86.9 | 87.5 | 88.1 | 88.7 | 83.1 | 89.4 | ||
| SVM | 75.0 | 74.7 | 76.7 | 75.5 | 78.5 | 49.4 | 84.7 | |
| 84.7 | 84.4 | 85.5 | 84.9 | 86.4 | 32.8 | 90.1 | ||
| P | 86.0 | 86.1 | 87.3 | 86.4 | 88.2 | 10.0 | 92.0 | |
| R | 92.2 | 91.6 | 91.7 | 92.0 | 92.0 | 10.0 | 93.3 | |
| 84.6 | 84.5 | 85.6 | 68.9 | 86.6 | 67.1 | 90.3 | ||
| MCDE | 76.9 | 79.4 | 79.5 | 78.3 | 79.7 | 80.0 | 79.6 | |
| 64.0 | 68.7 | 68.8 | 66.4 | 69.5 | 70.1 | 69.0 | ||
| P | 67.5 | 71.0 | 71.1 | 69.1 | 72.0 | 72.4 | 71.2 | |
| R | 89.4 | 90.1 | 90.0 | 90.4 | 89.2 | 89.4 | 90.1 | |
| 67.5 | 70.6 | 70.7 | 68.9 | 71.5 | 71.9 | 70.8 | ||
| GMM | 25.7 | 44.8 | 25.8 | 41.6 | 43.8 | 27.4 | 44.9 | |
| 61.7 | 33.3 | 66.5 | 33.3 | 34.1 | 65.4 | 33.4 | ||
| P | 35.6 | 30.6 | 47.8 | 29.2 | 30.4 | 44.4 | 30.8 | |
| R | 20.2 | 82.3 | 13.0 | 72.1 | 78.0 | 84.7 | 82.4 | |
| 33.4 | 31.1 | 35.5 | 30.2 | 30.9 | 35.1 | 31.2 |
| Classifier | Metric | Nas-NetLarge | Dense-Net201 | VGG19 | Mobile-NetV2 | Res-Net50 | AE | DeepGun |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFC | 83 ± 0.00 | 82 ± 0.01 | 83 ± 0.01 | 82 ± 0.02 | 85 ± 0.01 | 83 ± 0.01 | 85 ± 0.01 | |
| 82 ± 0.00 | 80 ± 0.01 | 82 ± 0.01 | 80 ± 0.02 | 83 ± 0.01 | 81 ± 0.01 | 83 ± 0.01 | ||
| P | 88 ± 0.01 | 86 ± 0.02 | 87 ± 0.01 | 85 ± 0.03 | 92 ± 0.02 | 89 ± 0.01 | 91 ± 0.01 | |
| R | 73 ± 0.01 | 73 ± 0.01 | 74 ± 0.01 | 74 ± 0.01 | 73 ± 0.00 | 71 ± 0.01 | 74 ± 0.01 | |
| 78 ± 0.01 | 76 ± 0.01 | 78 ± 0.01 | 76 ± 0.02 | 81 ± 0.01 | 77 ± 0.01 | 80 ± 0.01 | ||
| SVM | 68 ± 0.02 | 69 ± 0.01 | 70 ± 0.01 | 68 ± 0.01 | 71 ± 0.01 | 22 ± 0.05 | 69 ± 0.01 | |
| 74 ± 0.01 | 74 ± 0.01 | 75 ± 0.00 | 74 ± 0.01 | 76 ± 0.00 | 49 ± 0.03 | 74 ± 0.01 | ||
| P | 68 ± 0.01 | 68 ± 0.01 | 69 ± 0.00 | 67 ± 0.01 | 70 ± 0.00 | 49 ± 0.02 | 68 ± 0.01 | |
| R | 92 ± 0.01 | 92 ± 0.00 | 92 ± 0.00 | 92 ± 0.01 | 92 ± 0.00 | 83 ± 0.04 | 92 ± 0.01 | |
| 66 ± 0.01 | 67 ± 0.01 | 67 ± 0.00 | 66 ± 0.00 | 68 ± 0.00 | 50 ± 0.02 | 66 ± 0.01 | ||
| MCDE | 59 ± 0.00 | 66 ± 0.01 | 66 ± 0.01 | 59 ± 0.01 | 65 ± 0.01 | 64 ± 0.00 | 67 ± 0.01 | |
| 51 ± 0.01 | 62 ± 0.02 | 62 ± 0.02 | 47 ± 0.01 | 61 ± 0.02 | 59 ± 0.03 | 63 ± 0.03 | ||
| P | 50 ± 0.00 | 60 ± 0.02 | 60 ± 0.02 | 48 ± 0.01 | 59 ± 0.02 | 57 ± 0.02 | 61 ± 0.03 | |
| R | 72 ± 0.01 | 74 ± 0.01 | 74 ± 0.01 | 74 ± 0.01 | 73 ± 0.01 | 73 ± 0.01 | 73 ± 0.01 | |
| 50 ± 0.00 | 57 ± 0.01 | 57 ± 0.01 | 49 ± 0.00 | 56 ± 0.01 | 55 ± 0.02 | 58 ± 0.02 | ||
| GMM | 38 ± 0.23 | 44 ± 0.28 | 33 ± 0.28 | 46 ± 0.25 | 42 ± 0.28 | 65 ± 0.01 | 35 ± 0.27 | |
| 49±0.02 | 50 ± 0.01 | 50 ± 0.01 | 50 ± 0.02 | 49 ± 0.00 | 51 ± 0.02 | 50 ± 0.01 | ||
| P | 47 ± 0.04 | 49 ± 0.03 | 47 ± 0.04 | 48 ± 0.04 | 47 ± 0.03 | 51 ± 0.01 | 48 ± 0.03 | |
| R | 42 ± 0.39 | 58 ± 0.46 | 40 ± 0.44 | 48 ± 0.42 | 54 ± 0.43 | 89 ± 0.04 | 42 ± 0.45 | |
| 50 ± 0.01 | 50 ± 0.00 | 50 ± 0.00 | 50 ± 0.01 | 49 ± 0.00 | 51 ± 0.01 | 50 ± 0.00 |
| Metric | DeepGun-CNN | DeepGun-E2 | DeepGun-FPS | DeepGun |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 83.7 | 85.9 | 81.3 | 86.6 | |
| 82.6 | 84.3 | 79.3 | 85.2 | |
| P | 88.8 | 94.1 | 87.2 | 95.3 |
| R | 74.0 | 73.6 | 68.6 | 74.0 |
| 78.7 | 83.0 | 75.5 | 83.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, H.; Deniz, O.; Ruiz-Santaquiteria, J.; Muñoz, J.D.; Bueno, G. DeepGun: Deep Feature-Driven One-Class Classifier for Firearm Detection Using Visual Gun Features and Human Body Pose Estimation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5830. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115830
Singh H, Deniz O, Ruiz-Santaquiteria J, Muñoz JD, Bueno G. DeepGun: Deep Feature-Driven One-Class Classifier for Firearm Detection Using Visual Gun Features and Human Body Pose Estimation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):5830. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115830
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Harbinder, Oscar Deniz, Jesus Ruiz-Santaquiteria, Juan D. Muñoz, and Gloria Bueno. 2025. "DeepGun: Deep Feature-Driven One-Class Classifier for Firearm Detection Using Visual Gun Features and Human Body Pose Estimation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 5830. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115830
APA StyleSingh, H., Deniz, O., Ruiz-Santaquiteria, J., Muñoz, J. D., & Bueno, G. (2025). DeepGun: Deep Feature-Driven One-Class Classifier for Firearm Detection Using Visual Gun Features and Human Body Pose Estimation. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 5830. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115830









