Effects of Coal Mining Subsidence on Loess Slope Morphology and Soil Erosion in the Middle Reaches of the Yellow River
Abstract
1. Introduction
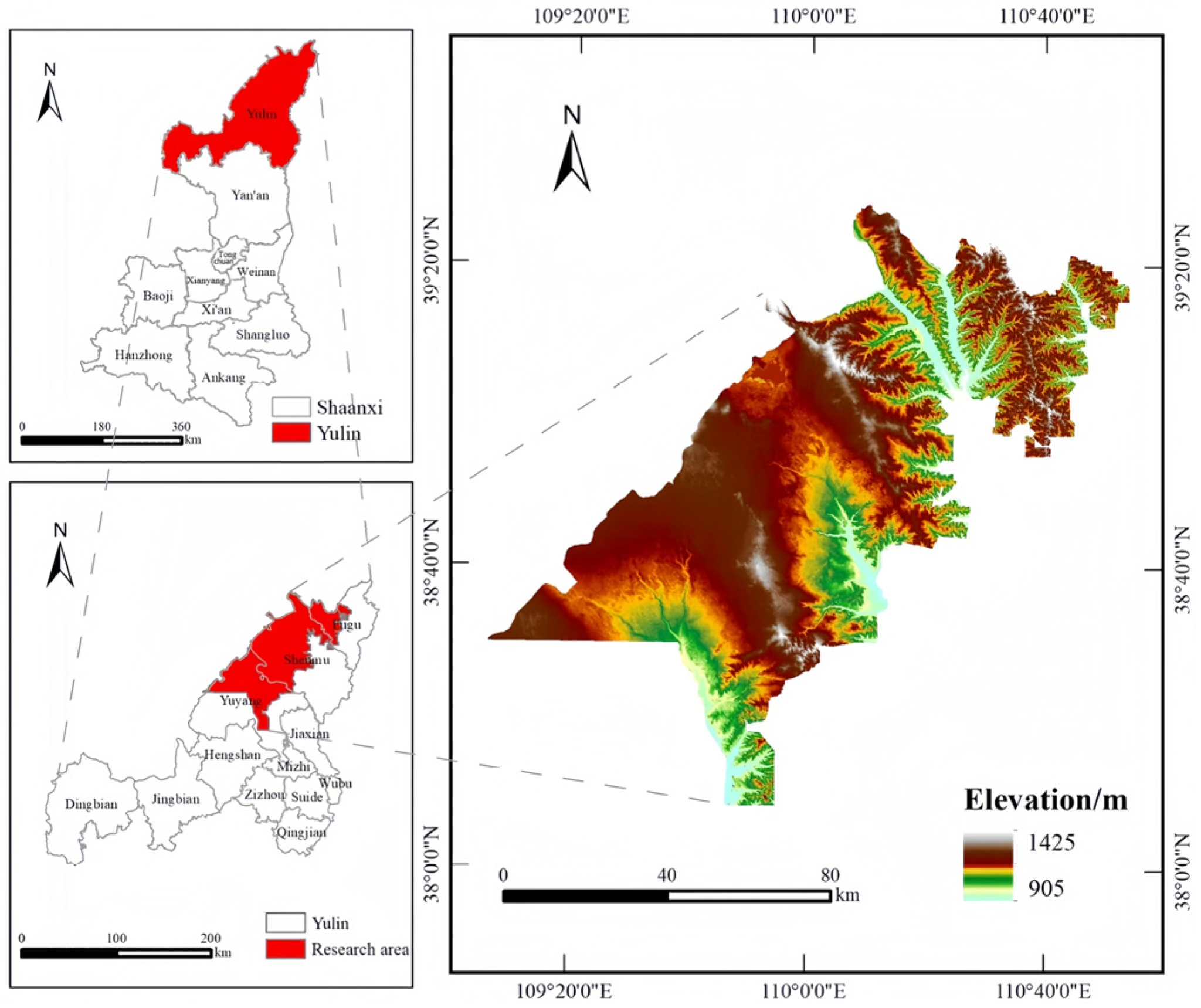
2. Overview of the Study Area
3. Research Method and Process
3.1. Numerical Model Construction and Experiment
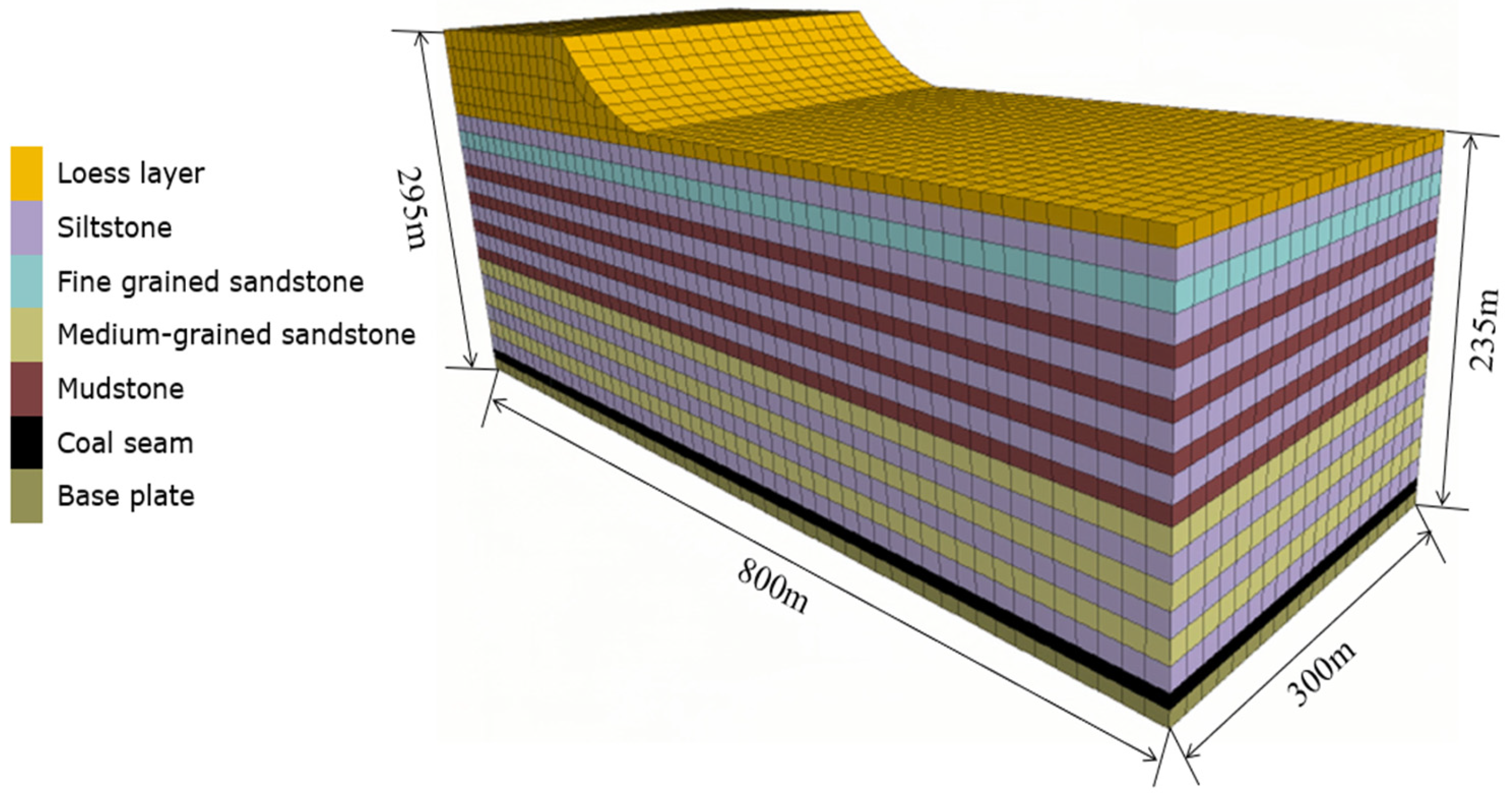
3.1.1. Model Framework
3.1.2. Model Type Division
3.1.3. Simulation Test Process
3.2. Calculation and Data Processing Method
3.2.1. Calculation of Morphological Parameters of Subsidence Slope
3.2.2. Calculation of Soil Erosion Modulus
4. Results
4.1. The Influence of Coal Mining Subsidence on the Slope of Loess Slope
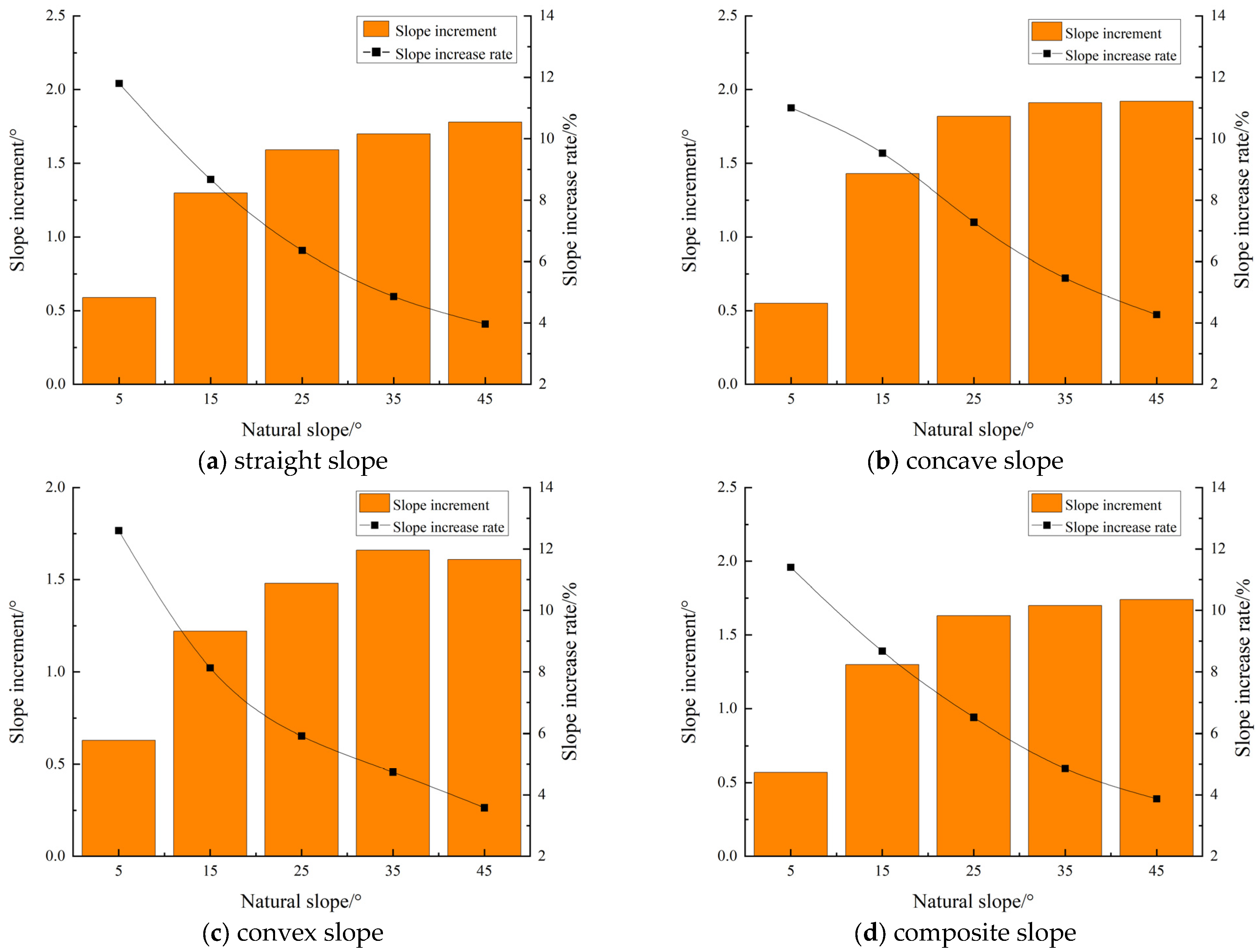
4.1.1. Slope Variation Characteristics of Subsidence Slope Under the Same Natural Slope Shape
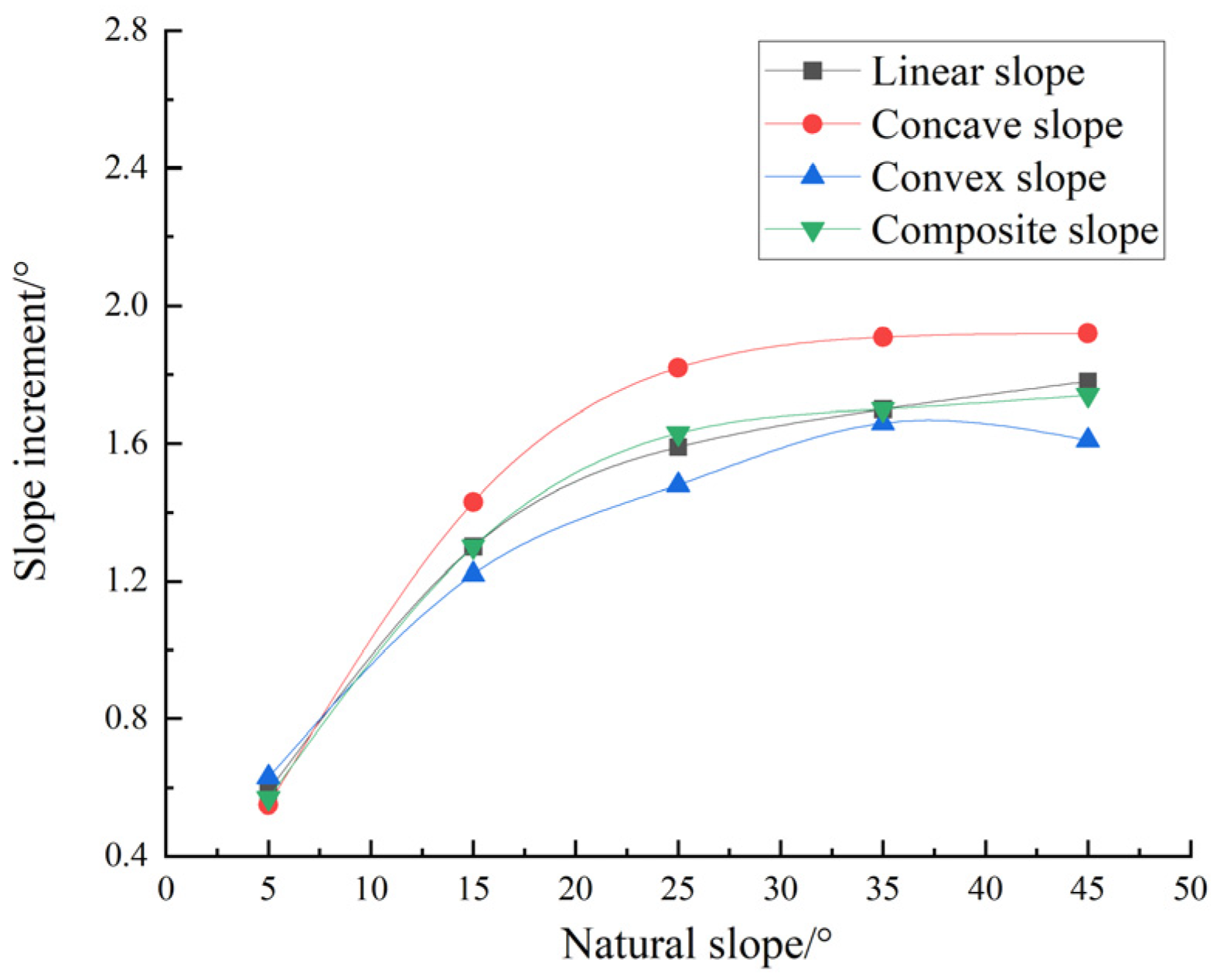
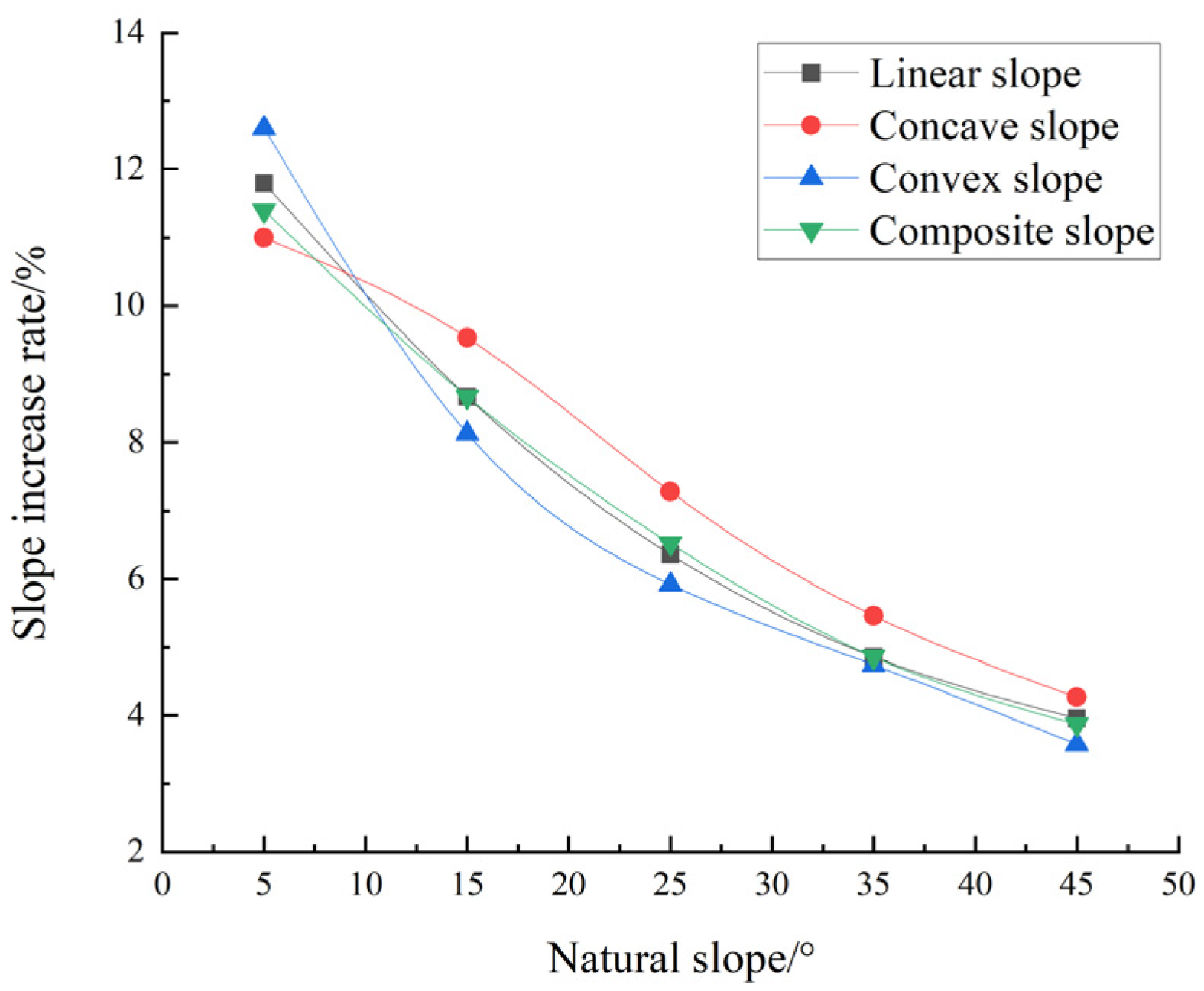
4.1.2. Slope Variation Characteristics of Subsidence Slope Under the Same Natural Slope
4.2. The Influence of Coal Mining Subsidence on Slope Length of Loess Slope
4.2.1. The Variation Characteristics of Slope Length of Subsidence Slope Under the Same Natural Slope Shape
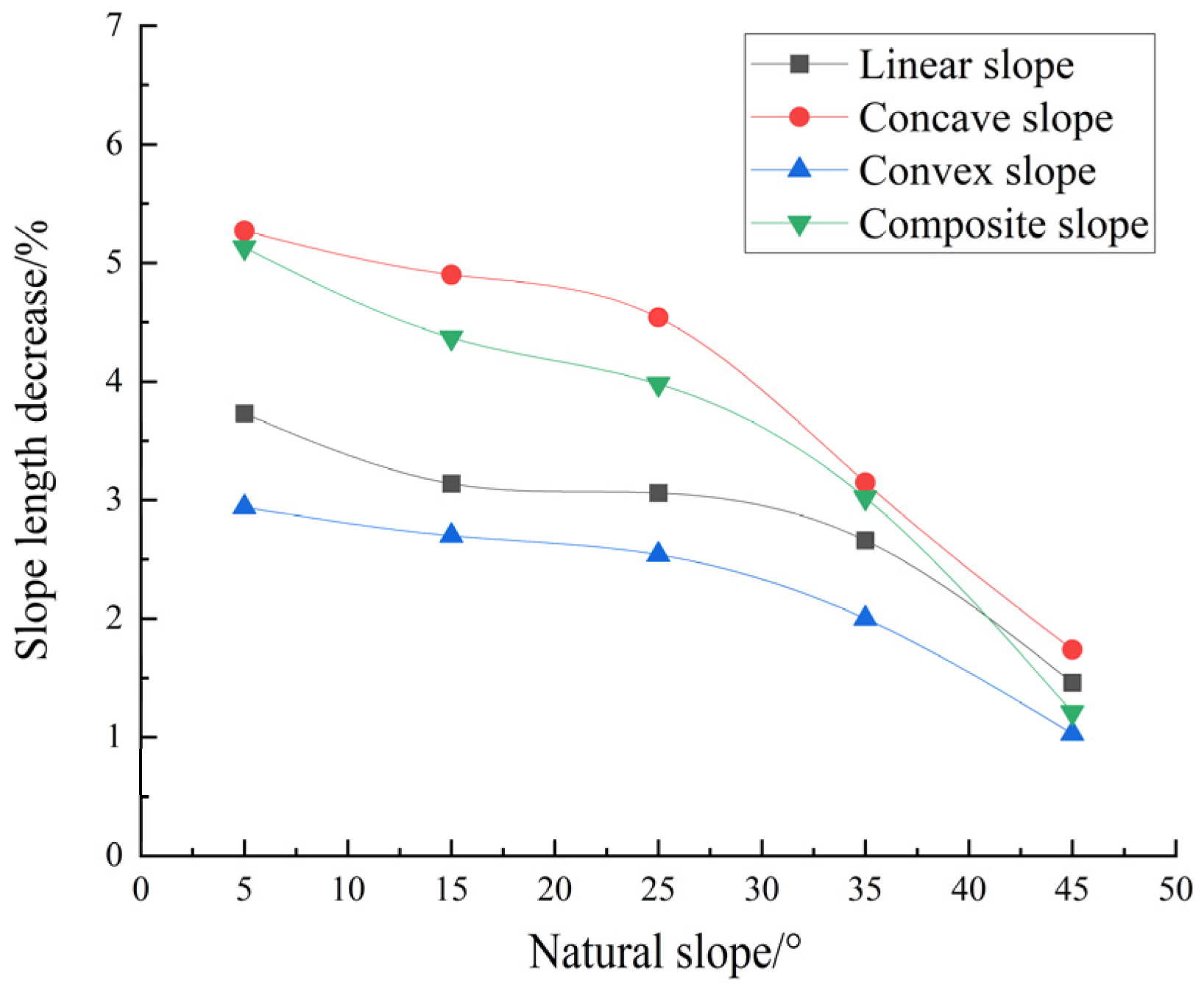
4.2.2. The Variation Characteristics of Slope Length of Subsidence Slope Under the Same Natural Slope
4.3. Analysis of Soil Erosion Effect of Slope Deformation
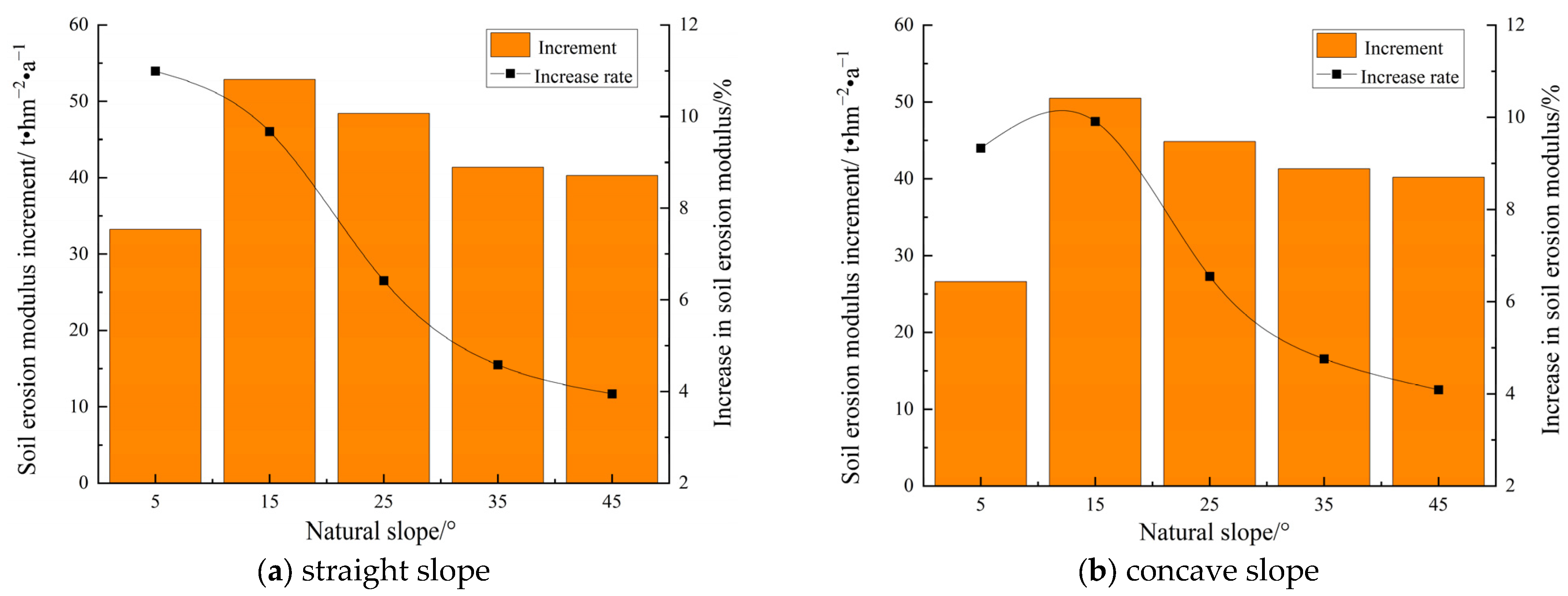
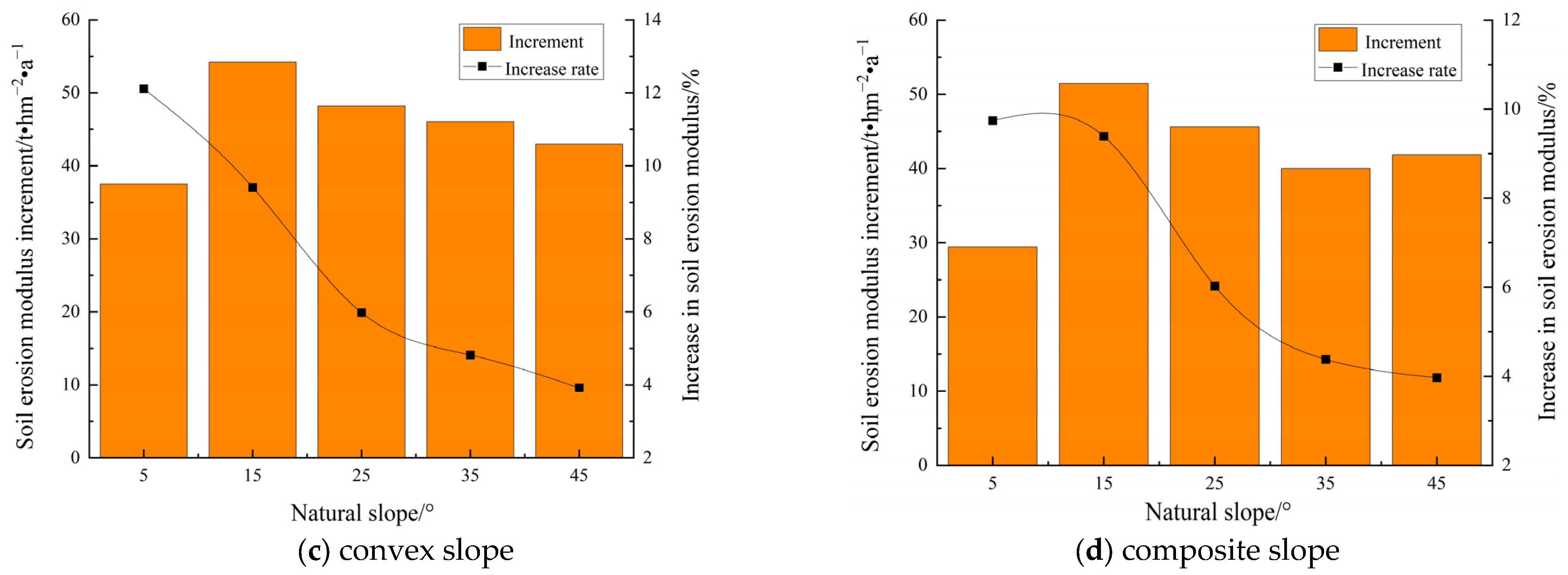
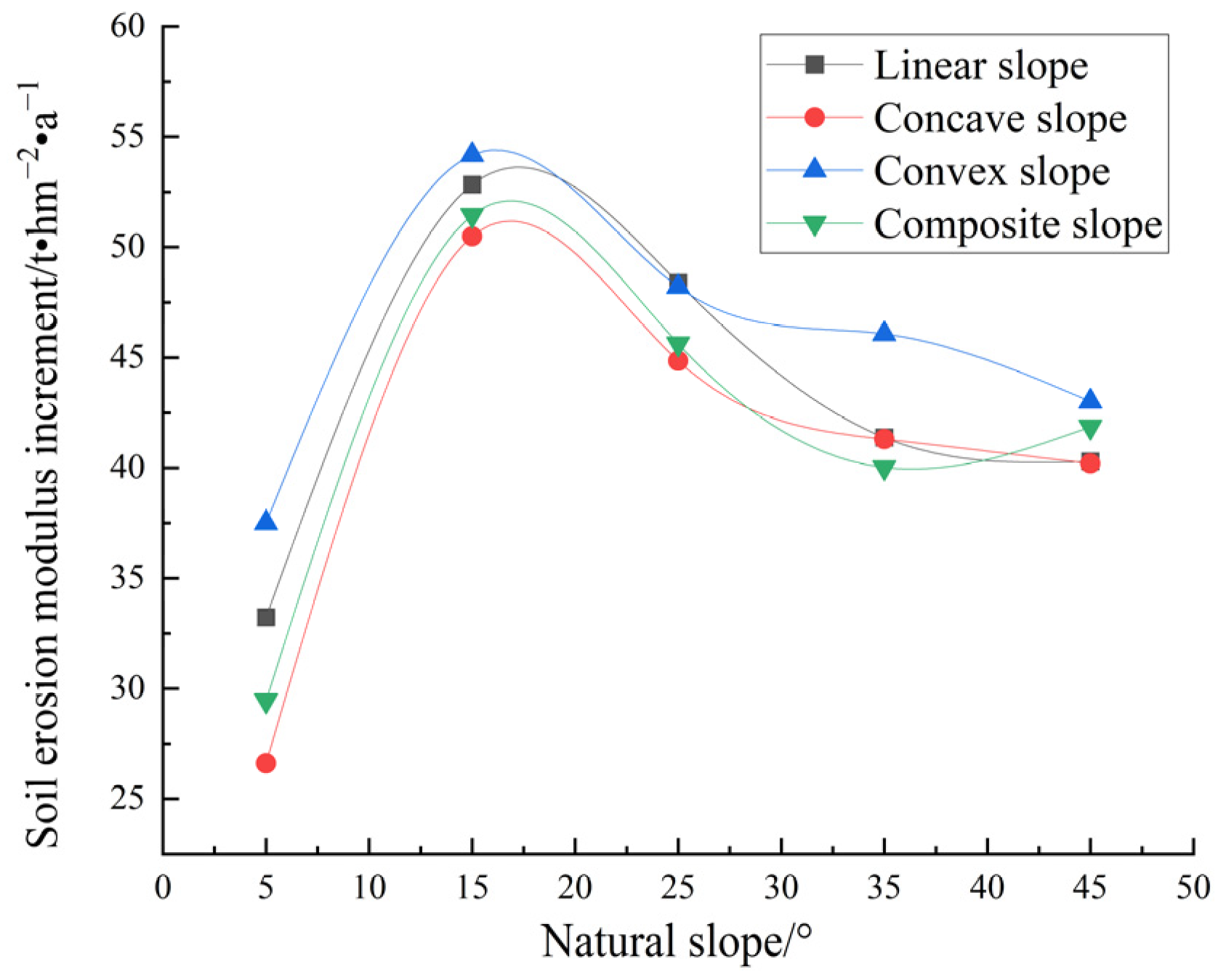
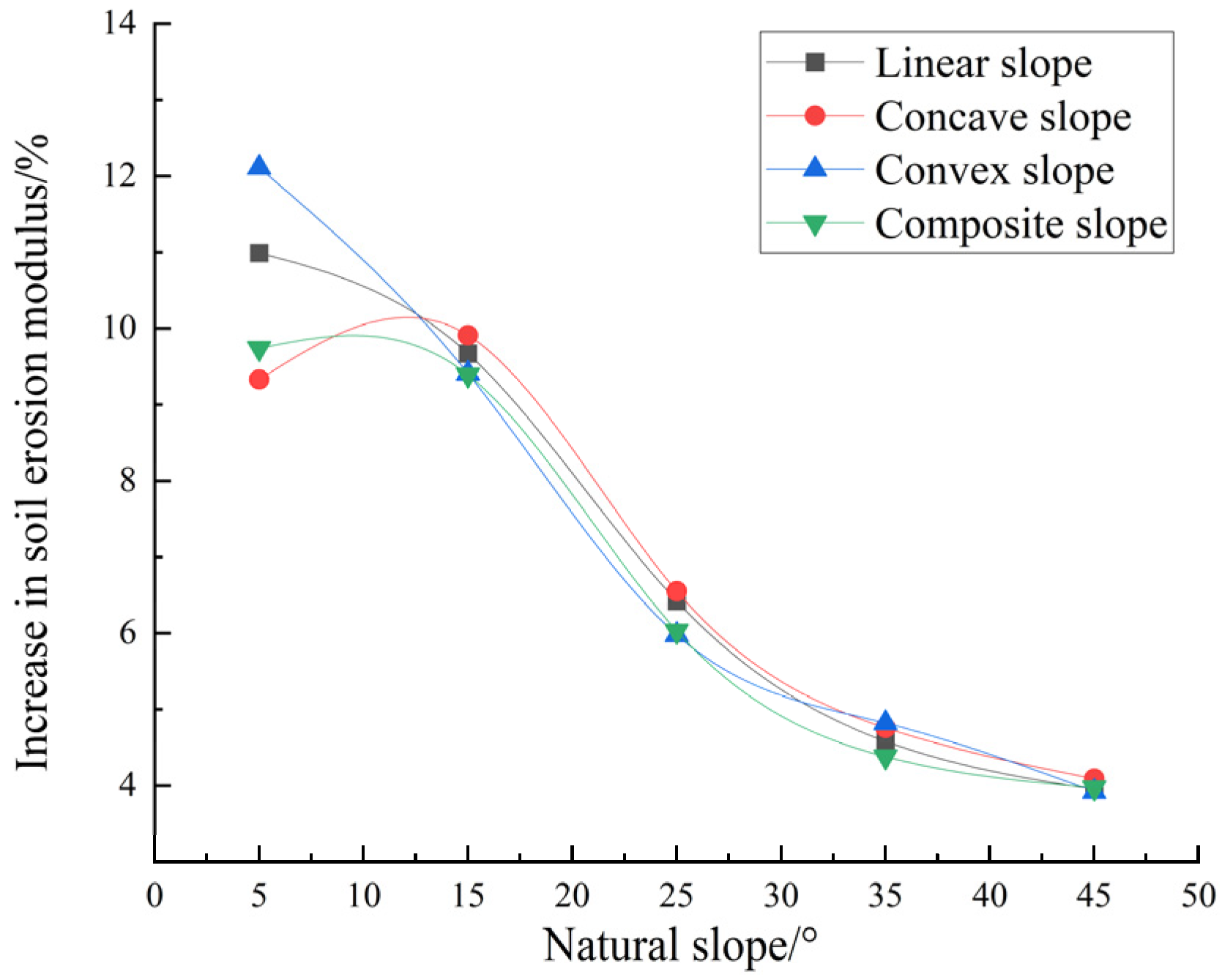
4.3.1. Soil Erosion Effect Under Annual Erosion Rainfall Scale
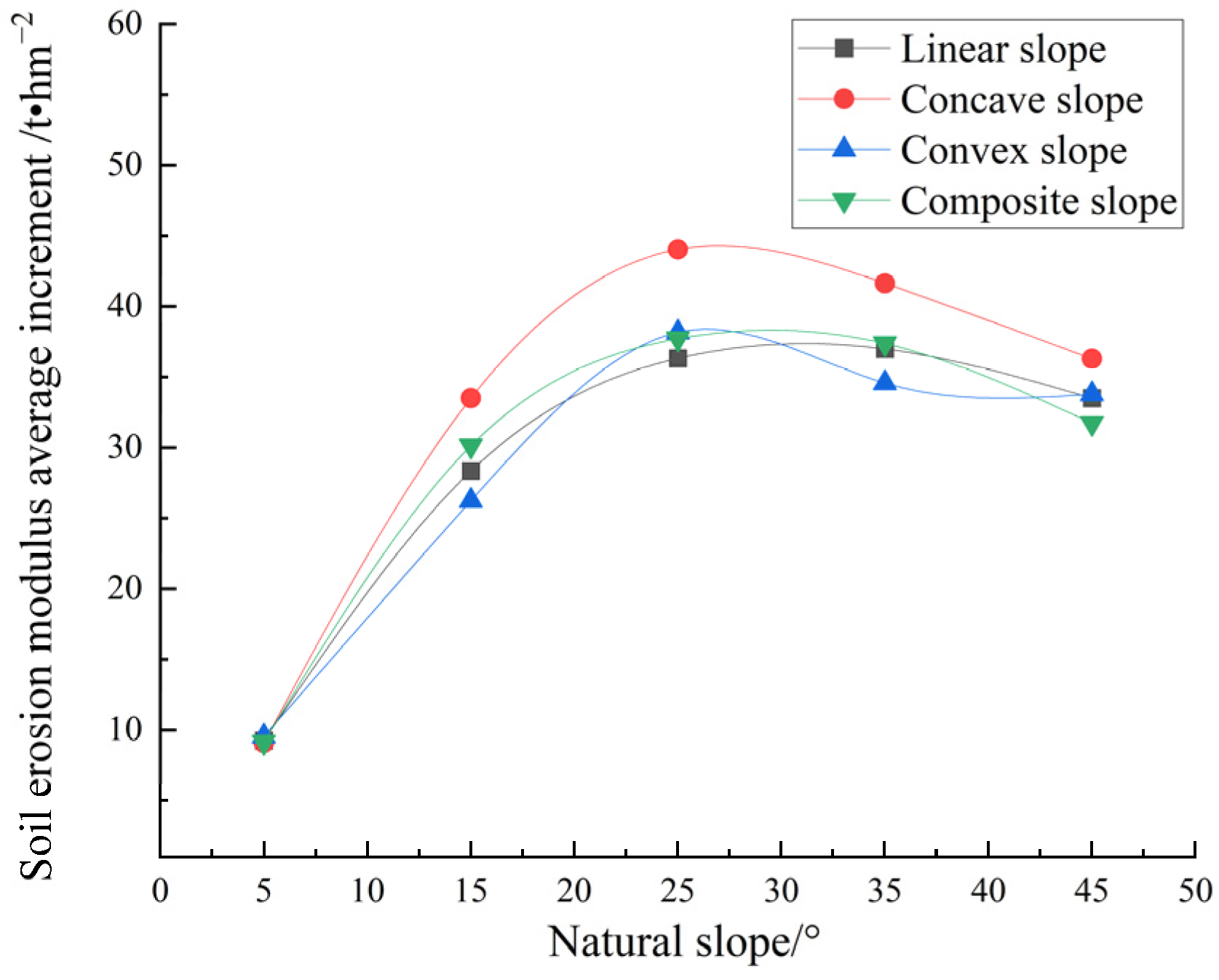
4.3.2. Soil Erosion Effect Under Typical Field Erosion Rainfall Scale
5. Discussion
5.1. Effects of Slope Gradient on Stability and Deformation of Loess Slope
5.2. Influence of Slope Shape on the Stability and Deformation Characteristics of Loess Slopes
5.3. Influence of Coal Mining Subsidence on Soil Erosion
6. Conclusions
7. Recommendations and Future Actions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huo, C.; Liu, T.; Fan, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, C. Study on national coal resources exploration and exploitation layout under carbon neutrality and emission peak settings. Geol. Rev. 2022, 68, 938–944. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. 2024 National Economic and Social Development Statistical Bulletin. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/xxgk/sjfb/zxfb2020/202502/t20250228_1958817.html (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Xie, H.; Ren, S.; Xie, Y.; Jiao, X. Development opportunities of the coal industry towards the goal of carbon neutrality. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 2197–2211. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Song, S.; Liu, L.; Gu, L.; Wei, J. Change of coal energy status and green and low-carbon development under the “dual carbon” goal. J. China Coal Soc. 2023, 48, 2599–2612. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Bi, Y. Strategic consideration and core technology about environmental ecological restoration in coal mine areas in the Yellow River basin of China. J. China Coal Soc. 2020, 45, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q. One line and one game of chess boost the high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Technol. Ind. China 2023, 4, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wei, J.; Song, S.; Wang, S.; Sun, T. Influence of thick sandstone on development of overburden mining fissures in northern Shaanxi coal mining area of Yellow River Basin and suggestions on water-preserved coal mining. Coal Geol. Explor. 2022, 50, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Sun, T.; Zheng, B.; Niu, R.; Ruan, H.; Cheng, X. Effect of coal mining subsidence on loess slope morphology and soil erosion in loess gully region of Northern Shaanxi. Coal Sci. Technol. 2023, 51, 422–435. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Sun, X. River Basin Green Quality Development and Its Environmental Law Guarantee—Reflections from the “Yellow River Basin Development Conference”. J. Henan Univ. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2022, 62, 35–41+153. [Google Scholar]
- Outline of the Yellow River Basin Ecological Protection and High-Quality Development Plan. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2021/content_5647346.htm (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Song, S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Analysis and numerical simulation on the influence of the overlying strata’s rock-soil ratio on the mining subsidence. China Coal 2015, 41, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, X. Field tests on deformation property of self-weight collapsible loess with large thickness. Int. J. Geomech. 2014, 14, 04014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Wang, C.; Guo, J.; Liu, J. Law of movement of discontinuous deformation of strata and ground with a thick loess layer and thin bedrock in long wall mining. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewnik, M.; Skiba, M.; Szymański, W.; Żyła, M. Mineral composition vs. soil forming processes in loess soils—A case study from Kraków (Southern Poland). Catena 2014, 119, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Qiao, D.; Zhang, J. Influence of Collapsible Loess Layer on Mining Subsidence in Loess Covered Mining Area. Coal Eng. 2015, 47, 88–90+94. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Huang, H.; Liu, D.; Hui, X. Study on permeability and collapsibility characteristics of sandy loess in northern Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, X.A.; Li, L.C.; Hong, B.; Yao, W.; Lei, H.N.; Zhang, C. Characterization of the collapsible mechanisms of Malan loess on the Chinese Loess Plateau and their effects on eroded loess landforms. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2020, 26, 2541–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Vanapalli, S.; Li, T. Review of collapse triggering mechanism of collapsible soils due to wetting. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2016, 8, 256–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalley, I.J.; Marković, S.B. Loessification and hydroconsolidation: There is a connection. Catena 2014, 117, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Feng, Z.; Sun, T.; Zheng, B.; Wei, J. Loess slope deformation and soil erosion effect in coal mining subsidence area of northern Shaanxi. J. Xi’an Univ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 43, 301–311. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, W.; Yuan, Z. Effect of underground coal mining on slope morphology and erosion. Coal Eng. 2020, 52, 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Guo, Y.; Yang, K. Routinized Studying Mode on Land Surface Movement and Deformation Law of Mining Subsidence in Coal Mine. Coal Sci. Technol. 2014, 42, 252–255. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Wu, D.; Ma, L. Numerical Simulation and Verification of Goaf Morphology Evolution and Surface Subsidence in a Mine. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 144, 106918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Long, J.; Hu, H.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Li, J. Study on Influence of Coal Mining under Ancient Building on Deformation Disturbance of Overlying Accumulation Layer on Slope. Coal Sci. Technol. 2024, 52, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Steiner, J.; Zheng, F.; Gowda, P. Impact of rainfall pattern on interrill erosion process. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 1833–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babur, E.; Uslu, Ö.S.; Battaglia, M.L.; Diatta, A.; Fahad, S.; Datta, R.; Zafar-ul-Hye, M.; Hussain, G.S.; Danish, S. Studying soil erosion by evaluating changes in physico-chemical properties of soils under different land-use types. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2021, 20, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Luukkanen, O.; Tokola, T.; Nieminen, J. Effect of vegetation cover on soil erosion in a mountainous watershed. Catena 2008, 75, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diyabalanage, S.; Samarakoon, K.K.; Adikari, S.B.; Hewawasam, T. Impact of soil and water conservation measures on soil erosion rate and sediment yields in a tropical watershed in the Central Highlands of Sri Lanka. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 79, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wei, J.; Song, S.; Sun, Q.; Yang, T. Experiment and numerical simulation of overburden and surface damage law in shallow coal seam mining under the gully. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 207. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Du, L.; Song, S. Influence of mining ground fissures on soil erodibility in Northern Shaanxi coal mining area of Yellow River Basin. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 3027–3038. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Jin, D.; Li, Z.; Shen, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Xu, F.; Wang, Q. Analysis of overlying aquifer water inrush above mining seam in Yushen mining area. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 523–533. [Google Scholar]
- Lokhande, R.D.; Murthy, V.M.S.R.; Singh, K.B.; Verma, C.P.; Verma, A.K. Numerical Modeling of Pot-Hole Subsidence Due to Shallow Underground Coal Mining in Structurally Disturbed Ground. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. D 2018, 99, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.; Yadav, A.; Singh, P.S.G.; Sharma, S.K. Numerical Modeling Study of the Geo-mechanical Response of Strata in Longwall Operations with Particular Reference to Indian Geo-mining Conditions. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2019, 53, 1827–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Song, S.; Cheng, X.; Niu, R.; Cheng, X.; Ruan, H.; Li, G. The influence of coal mining subsidence on the movement and deformation of loess slope in the loess gully area of Northern Shaanxi. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1273389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Du, H.D.; Liu, N. Influence of Coal Mining Subsidence on Surface Slope Morphology and Its Soil and Water Loss Effect in Typical Coal Mining Areas in the Middle Reaches of the Yellow River; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Guo, S.; Li, Z.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, X. Sampling survey of water erosion in China. Soil Water Conserv. China 2013, 10, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.Y.; Zhang, K.L.; Xie, Y. An empirical soil loss equation. In Proceedings of ISCO Pot; Tsinghua Press: Beijing, China, 2022; pp. 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, R.; Qi, F.; Liu, X.; Niu, Y.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Yuan, L.; Yang, S.; et al. The CSLE Model Based Soil Erosion Prediction: Comparisons of Sampling Density and Extrapolation Method at the County Level. Catena 2018, 165, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budeba, M.D.; Joubert, J.W.; Webber-Youngman, R.; Shafiee, S. Predicting the Efficiency of a Surface Coal Mine for Competitiveness. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2017, 31, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Ma, N. Temporal and Spatial Dynamic Analysis of Soil Erosion in Shendong Mining Area. Yellow River 2022, 44, 124–127. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Su, J.; Sang, Y.Z.; Zhang, W.J.; Wang, Q. Spatial and temporal characteristics of rainfall erosivity in Shaanxi Province. Arid Land Geogr. 2014, 37, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall-Erosion Losses from Cropland East of the Rocky Mountains: Guide for Selection of Practices for Soil and Water Conservation; Agricultural Research Service, US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1965.
- Song, S.; Wang, S.; Sun, T. Variation of soil erodibility on loess slope under various subsidence years in coal mining subsidence area located in Northern Shaanxi. Coal Sci. Technol. 2022, 50, 289–299. [Google Scholar]
- Desmet, P.J.J.; Govers, G. A GIS procedure for automatically calculating the USLE LS factor on topographically complex landscape units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- McCool, D.K.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A. Slope length and steepness factors (LS). In Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); United States Government Printing: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; pp. 101–141. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Risse, L.M. Slope gradient effects on soil loss for steep slopes. Trans. ASAE 1994, 37, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Ding, S.; Shi, Z.; Huang, L.; Zhang, G. Study of applying USLE and geographical information system IDRISI to predict soil erosion in small watershed. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 2000, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, X.; Liu, B. Analysis of Erosion Environment and Dynamic Mechanism of Gentle Slope Cultivated Land; Shaanxi Science Press: Xi’an, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kokutse, N.K.; Temgoua, A.G.T.; Kavazović, Z. Slope stability and vegetation: Conceptual and numerical investigation of mechanical effects. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 86, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, C.; Xiao, P. A demonstration project for detailed geo-hazard survey in the Baota district, Yan’an. Northwest Geol 2007, 40, 29–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. The variation law of stability factor of loess slopes with different slopes. Soil Water Conserv. China 2020, 08, 42–43. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, O.; Morgan, J.K.; Aharonov, E.; Dugan, B. Controls on the size and geometry of landslides: Insights from discrete element numerical simulations. Geomorphology 2014, 220, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Cui, P.; Regmi, A.D.; Hu, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. The effects of slope length and slope gradient on the size distributions of loess slides: Field observations and simulations. Geomorphology 2018, 300, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, B.; Gao, Y.; Yang, B.; Li, L.; Kong, W. Analysis of terrain change characteristics and disaster causing points under mining disturbance in western mountainous area. Metal Mine 2021, 7, 172–178. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Tian, F.; Ao, J. Effect of mining subsidence on soil erosion in mountainous area of the Loess Plateau. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 228–235. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Ma, S.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X. Influence of topographic and geomorphic conditions on the dynamic response of slope acceleration. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2019, 36, 98. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.W. Stability Analysis of Concave and Convex Slopes Under Earthquake Action. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.H. Evaluating the effect of slope curvature on slope stability by a numerical analysis. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2013, 60, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J. Identification of topographic settings conducive to landsliding from DEM in Nelson County, Virginia, USA. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1993, 18, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-J.; Lin, R.-J.; Zheng, Z.-J.; Wang, J.-R.; Sun, J.-L. Characteristic analysis of soil and water loss in typical small watersheds of the Middle Yellow River based on RUSLE model. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 35, 200–208. [Google Scholar]
- Farhan, Y.; Zreqat, D.; Nawaysa, S. Assessing the influence of physical factors on spatial soil erosion risk in northern Jordan. J. Am. Sci. 2014, 10, 9–29. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Quan, X.; Shi, H.; He, J.; Cai, Q.; Sun, L. Erosion process and spatial distribution characteristics of erosion-deposition on the loess slope. J. Shaanxi Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2021, 49, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Jin, P.; Jiang, X.; Lin, L.; Kou, X.; Xu, Z.; Lin, B.; Fang, Z. Model construction and verification of vegetation cover and management factor in southern red soil region of China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Jin, H.; Gao, Z.; He, Y.; Zhang, W.; Song, X.; Zhang, R. Analysis of the influencing factors of soil erosion in Qilong Bay. Water Saving Irrig. 2023, 8, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Yu, X.; Cai, Q.; Sun, L.; Fang, H.; Jia, G.; He, J. Erosion process of loess slope and influencing factors in the loess hilly-gully region, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 2886–2894. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D. Benefits of runoff and sediment reductions of different soil and water conservation measures in Mentougou area of Beijing City. Bull. Soil. Water Conserv. 2015, 35, 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. A review of the design and operation of runoff and soil loss plots. Catena 2016, 145, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Gao, H.; Song, J.; Li, H. Influence of slope length on soil erosion in yellow sloping farmland of karst. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 25, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Li, A.; Liu, G.; Shi, Y. Assessment of soil erosion in rolling hilly region of Northeast China using Chinese Soil Loss Equation (CSLE) model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 49–56. [Google Scholar]




| Model Types | Slope Shape | Natural Slope/(°) | Natural Slope Length/(m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | straight slope | 5 | 688.45 |
| A2 | 15 | 231.82 | |
| A3 | 25 | 141.97 | |
| A4 | 35 | 104.61 | |
| A5 | 45 | 84.85 | |
| B1 | concave slope | 5 | 613.05 |
| B2 | 15 | 201.40 | |
| B3 | 25 | 117.15 | |
| B4 | 35 | 96.14 | |
| B5 | 45 | 78.88 | |
| C1 | convex slope | 5 | 722.56 |
| C2 | 15 | 257.37 | |
| C3 | 25 | 162.34 | |
| C4 | 35 | 116.97 | |
| C5 | 45 | 98.15 | |
| D1 | composite slope | 5 | 688.78 |
| D2 | 15 | 233.27 | |
| D3 | 25 | 143.33 | |
| D4 | 35 | 106.57 | |
| D5 | 45 | 90.51 |
| Lithologic Characters | Elastic Modulus/(MPa) | Tensile Strength/(MPa) | Volumetric Weight/(KN·m−3) | The Angle of Internal Friction/(°) | Poisson Ratio | Cohesive Forces/(MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loess layer | 107.0 | 0.20 | 18.60 | 37.2 | 0.30 | 0.60 |
| Fine-grained sandstone | 3270 | 3.79 | 24.11 | 40.0 | 0.28 | 0.15 |
| Mudstone | 3450 | 2.20 | 24.30 | 37.0 | 0.36 | 1.16 |
| Medium-grained sandstone | 4720 | 1.20 | 25.28 | 37.0 | 0.38 | 4.06 |
| Siltstone | 4430 | 1.31 | 24.50 | 40.0 | 0.44 | 3.20 |
| Coal seam | 2570 | 0.24 | 13.60 | 38.5 | 0.36 | 0.61 |
| Base plate | 4720 | 1.86 | 23.81 | 37.7 | 0.35 | 3.60 |
| Rain Fall /(mm) | Rainfall Intensity /(mm·h−1) | Raindrop Kinetic Energy /(J·m−2) | Quantization of S, L, and Ms | Correlation Index R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16.6 | 12.73 | 255.64 | 0.970 | |
| 26.9 | 122.28 | 766.11 | 0.997 | |
| 39.7 | 14.44 | 634.80 | 0.990 |
| Slope Shape | Natural Slope/° | Slope After Mining | Slope Length After Mining | Under the Scale of Annual Erosion Rainfall | Soil Erosion Modulus Under Typical Field Erosion Rainfall Scale | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16.6 mm | 26.9 mm | 39.7 mm | |||||||||||
| Variable Quantity /° | Rate of Change /% | Variable Quantity /m | Rate of Change /% | Variable Quantity /t·hm−2·a−1 | Rate of Change /% | Variable Quantity /t·hm−2 | Rate of Change /% | Variable Quantity /t·hm−2 | Rate of Change /% | Variable Quantity /t·hm−2 | Rate of Change /% | ||
| straight | 5 | 0.59 | 11.80 | 25.67 | 3.73 | 33.23 | 10.99 | 1.93 | 9.64 | 22.93 | 12.12 | 2.89 | 10.61 |
| 15 | 1.30 | 8.67 | 7.29 | 3.14 | 52.84 | 9.67 | 5.24 | 8.24 | 71.62 | 10.36 | 8.18 | 9.07 | |
| 25 | 1.59 | 6.36 | 4.35 | 3.06 | 48.39 | 6.42 | 6.46 | 5.80 | 92.37 | 7.06 | 10.17 | 6.27 | |
| 35 | 1.70 | 4.86 | 2.78 | 2.66 | 41.38 | 4.58 | 6.47 | 4.14 | 94.34 | 4.93 | 10.19 | 4.43 | |
| 45 | 1.78 | 3.96 | 1.24 | 1.46 | 40.30 | 3.95 | 5.58 | 2.85 | 85.96 | 3.48 | 8.99 | 3.09 | |
| concave | 5 | 0.55 | 11.00 | 32.31 | 5.27 | 26.62 | 9.33 | 1.98 | 9.58 | 22.39 | 11.62 | 2.89 | 10.34 |
| 15 | 1.43 | 9.53 | 9.87 | 4.90 | 50.49 | 9.91 | 6.44 | 9.73 | 84.28 | 11.93 | 9.82 | 10.56 | |
| 25 | 1.82 | 7.28 | 5.32 | 4.54 | 44.85 | 6.55 | 8.20 | 6.97 | 111.38 | 8.26 | 12.55 | 7.43 | |
| 35 | 1.91 | 5.46 | 3.03 | 3.15 | 41.30 | 4.76 | 7.41 | 4.63 | 105.93 | 5.46 | 11.54 | 4.93 | |
| 45 | 1.92 | 4.27 | 1.37 | 1.74 | 40.20 | 4.09 | 6.15 | 3.08 | 92.94 | 3.72 | 9.81 | 3.32 | |
| convex | 5 | 0.63 | 12.60 | 21.28 | 2.94 | 37.50 | 12.11 | 1.95 | 9.87 | 23.74 | 12.64 | 2.96 | 10.98 |
| 15 | 1.22 | 8.13 | 6.94 | 2.70 | 54.19 | 9.41 | 4.76 | 7.72 | 66.47 | 9.77 | 7.53 | 8.53 | |
| 25 | 1.48 | 5.92 | 4.13 | 2.54 | 48.20 | 5.98 | 6.54 | 6.10 | 97.41 | 7.60 | 10.52 | 6.69 | |
| 35 | 1.66 | 4.74 | 2.34 | 2.00 | 46.07 | 4.82 | 5.83 | 3.86 | 88.52 | 4.71 | 9.39 | 4.18 | |
| 45 | 1.61 | 3.58 | 1.01 | 1.03 | 43.01 | 3.92 | 5.38 | 2.87 | 87.07 | 3.61 | 8.91 | 3.16 | |
| composite | 5 | 0.57 | 11.40 | 35.34 | 5.13 | 29.45 | 9.74 | 1.96 | 9.78 | 22.57 | 11.93 | 2.88 | 10.59 |
| 15 | 1.30 | 8.67 | 10.20 | 4.37 | 51.45 | 9.39 | 5.68 | 8.94 | 75.95 | 11.00 | 8.76 | 9.73 | |
| 25 | 1.63 | 6.52 | 5.70 | 3.98 | 45.62 | 6.03 | 6.85 | 6.16 | 95.66 | 7.32 | 10.64 | 6.58 | |
| 35 | 1.70 | 4.86 | 3.21 | 3.02 | 40.02 | 4.38 | 6.60 | 4.25 | 95.20 | 4.99 | 10.34 | 4.51 | |
| 45 | 1.74 | 3.87 | 1.10 | 1.21 | 41.86 | 3.97 | 5.19 | 2.70 | 81.57 | 3.34 | 8.46 | 2.95 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, S.; Niu, R.; Yang, S.; Cheng, X.; Ruan, H.; Chen, B.; Li, Y.; Tang, L. Effects of Coal Mining Subsidence on Loess Slope Morphology and Soil Erosion in the Middle Reaches of the Yellow River. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5684. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105684
Song S, Niu R, Yang S, Cheng X, Ruan H, Chen B, Li Y, Tang L. Effects of Coal Mining Subsidence on Loess Slope Morphology and Soil Erosion in the Middle Reaches of the Yellow River. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(10):5684. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105684
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Shijie, Ruilin Niu, Shuai Yang, Xing Cheng, Hao Ruan, Baodeng Chen, Yuanhong Li, and Lijun Tang. 2025. "Effects of Coal Mining Subsidence on Loess Slope Morphology and Soil Erosion in the Middle Reaches of the Yellow River" Applied Sciences 15, no. 10: 5684. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105684
APA StyleSong, S., Niu, R., Yang, S., Cheng, X., Ruan, H., Chen, B., Li, Y., & Tang, L. (2025). Effects of Coal Mining Subsidence on Loess Slope Morphology and Soil Erosion in the Middle Reaches of the Yellow River. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5684. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105684






