Parametric Analysis of Outrigger Systems for High-Rise Buildings with Different Geometric Shapes
Abstract
1. Introduction
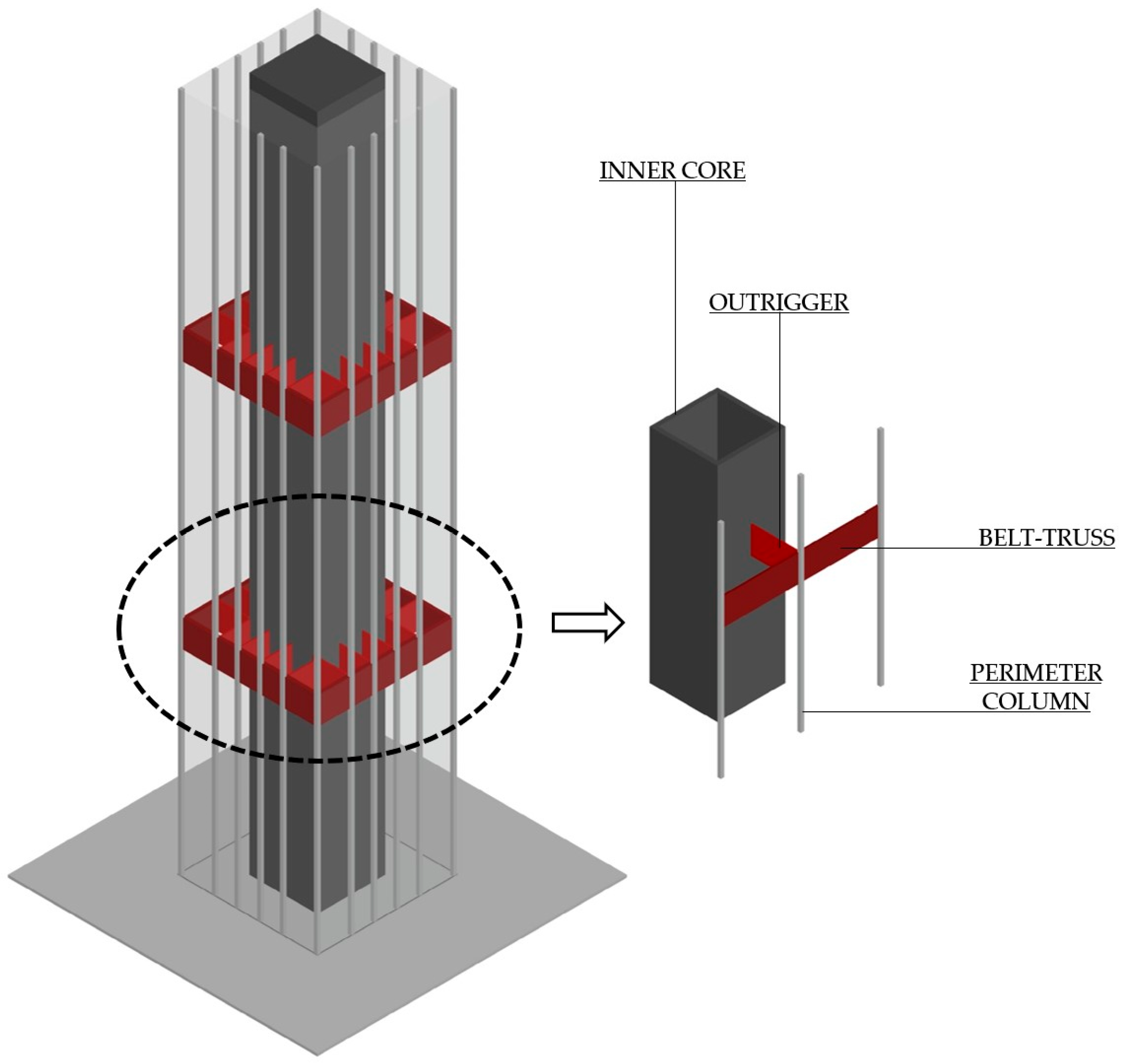
2. Simplified Approach for Outrigger Systems
2.1. Background
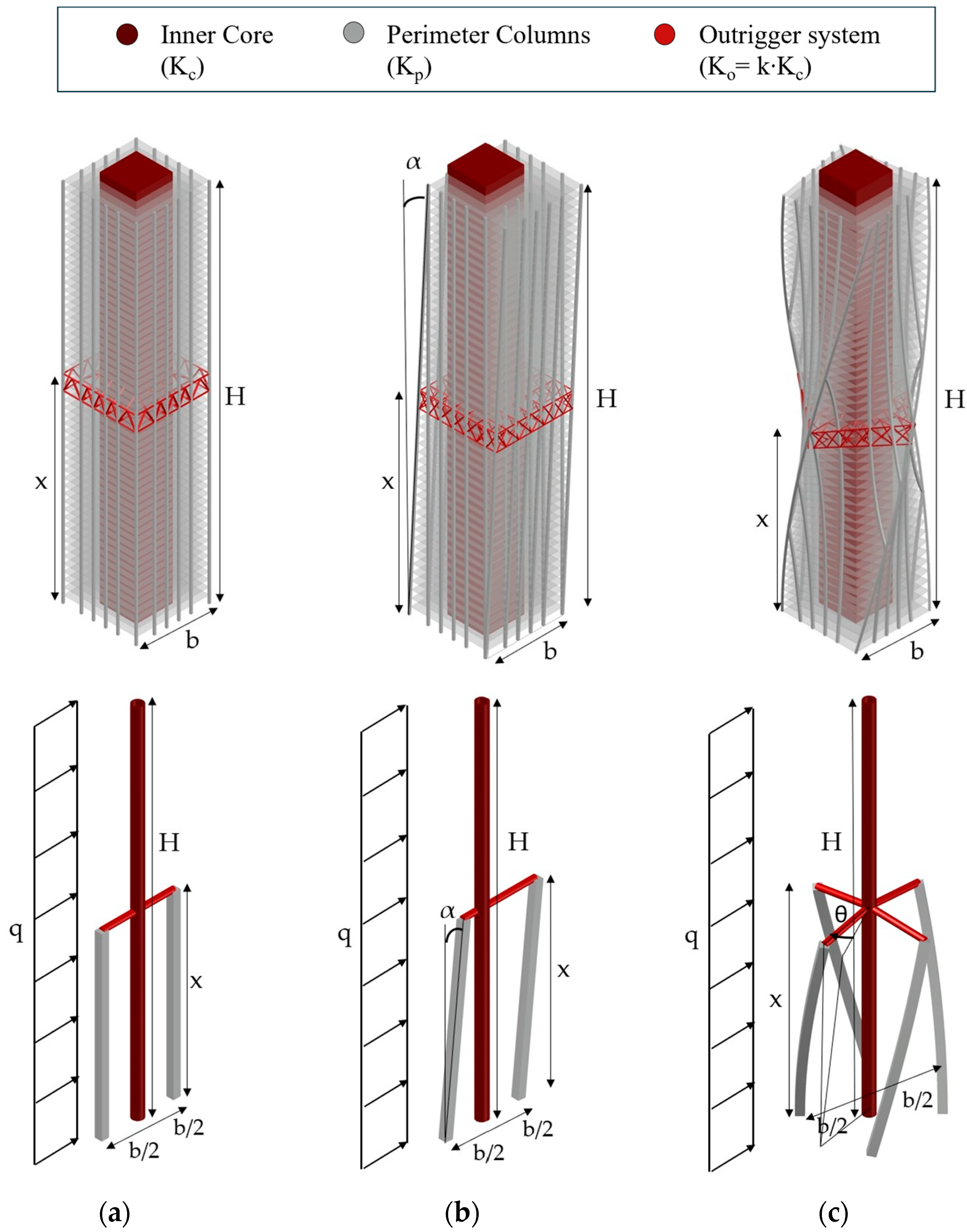
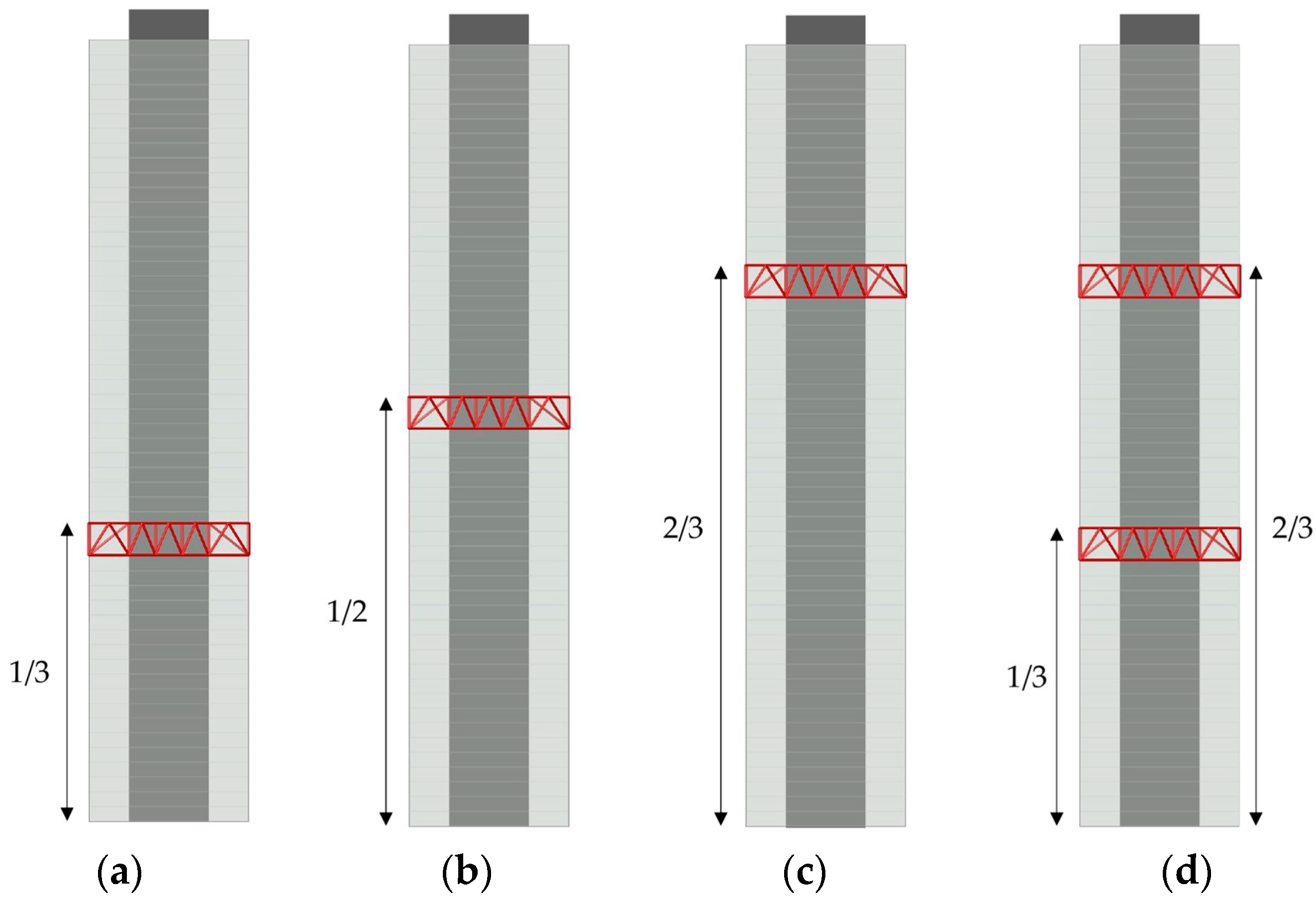
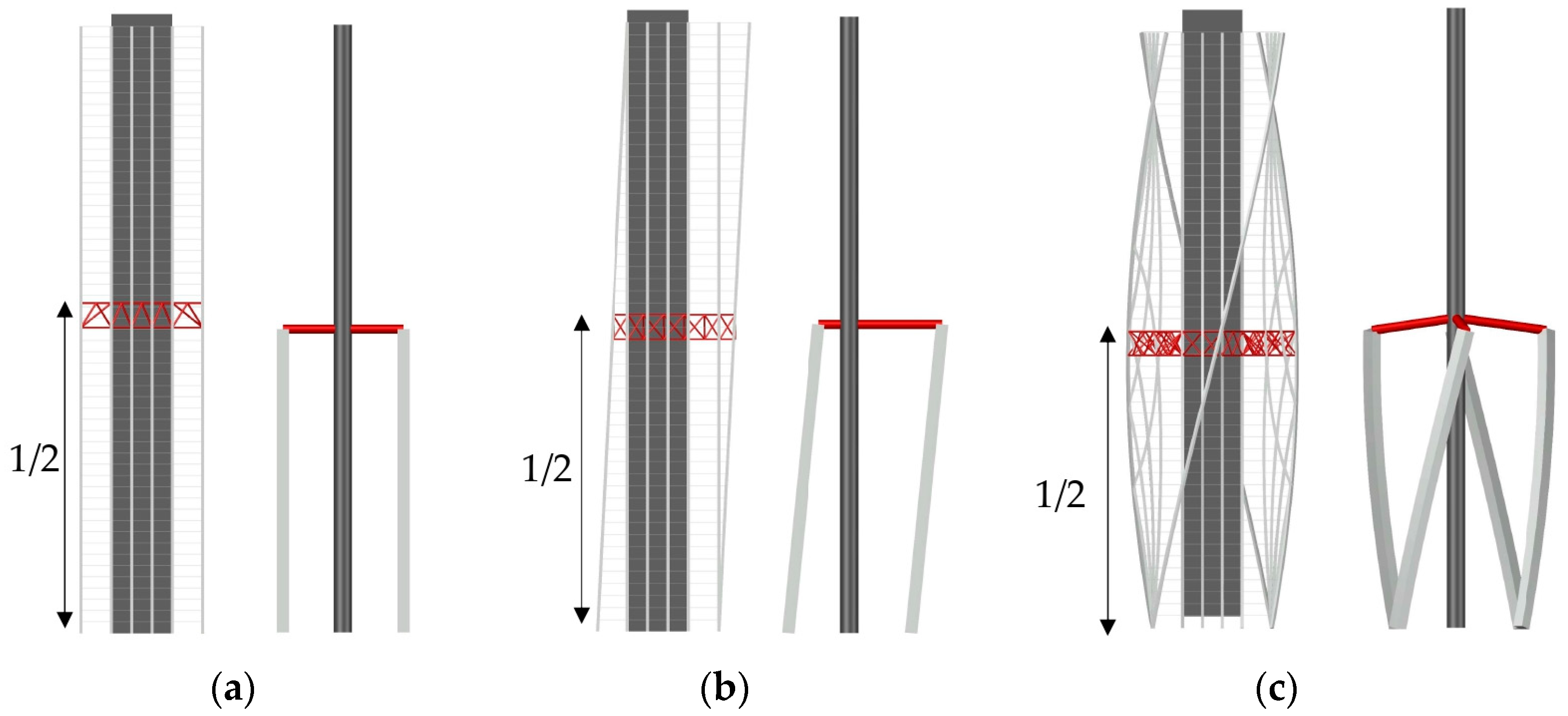
2.2. Parametrization of the Core–Column–Outrigger System
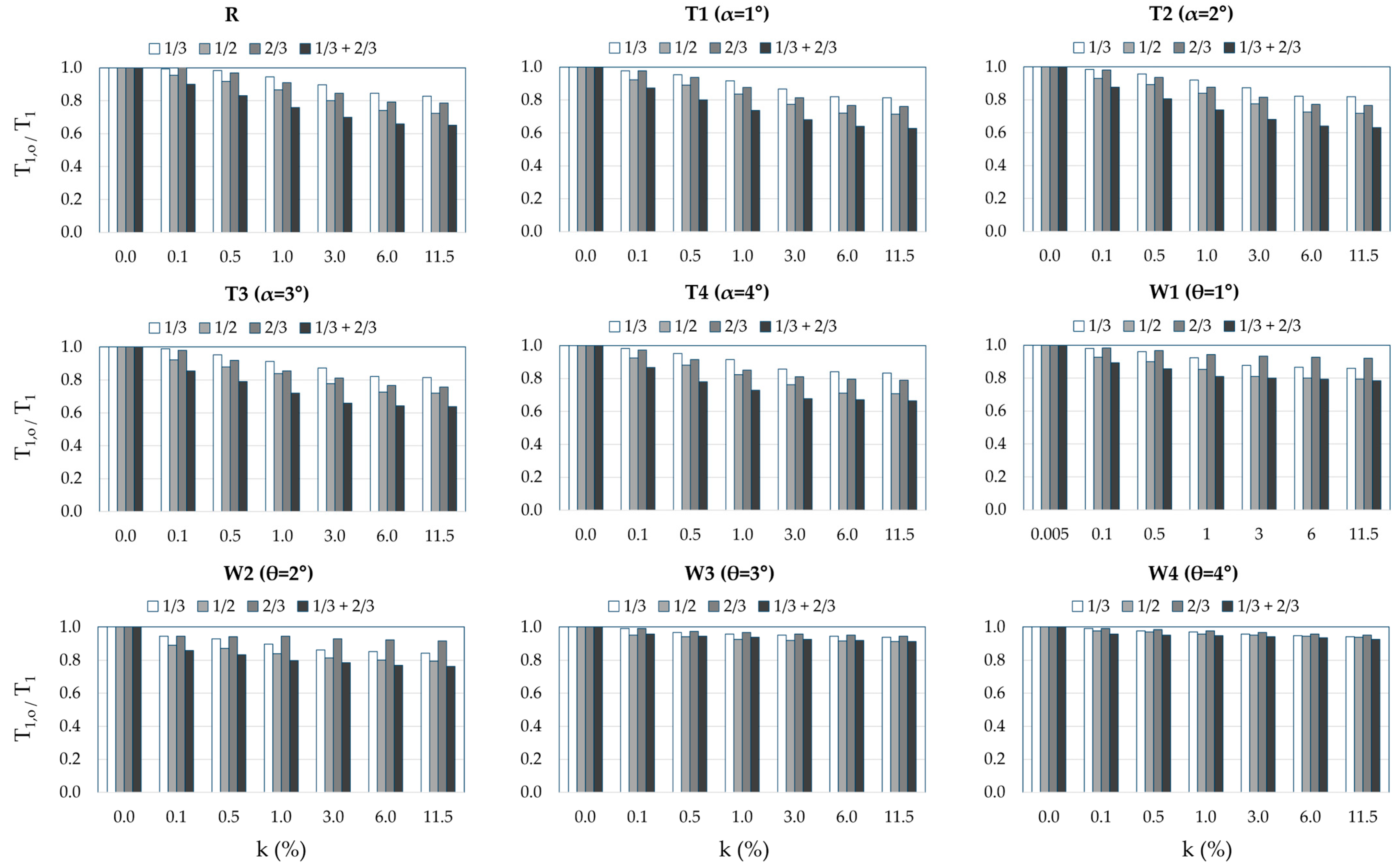
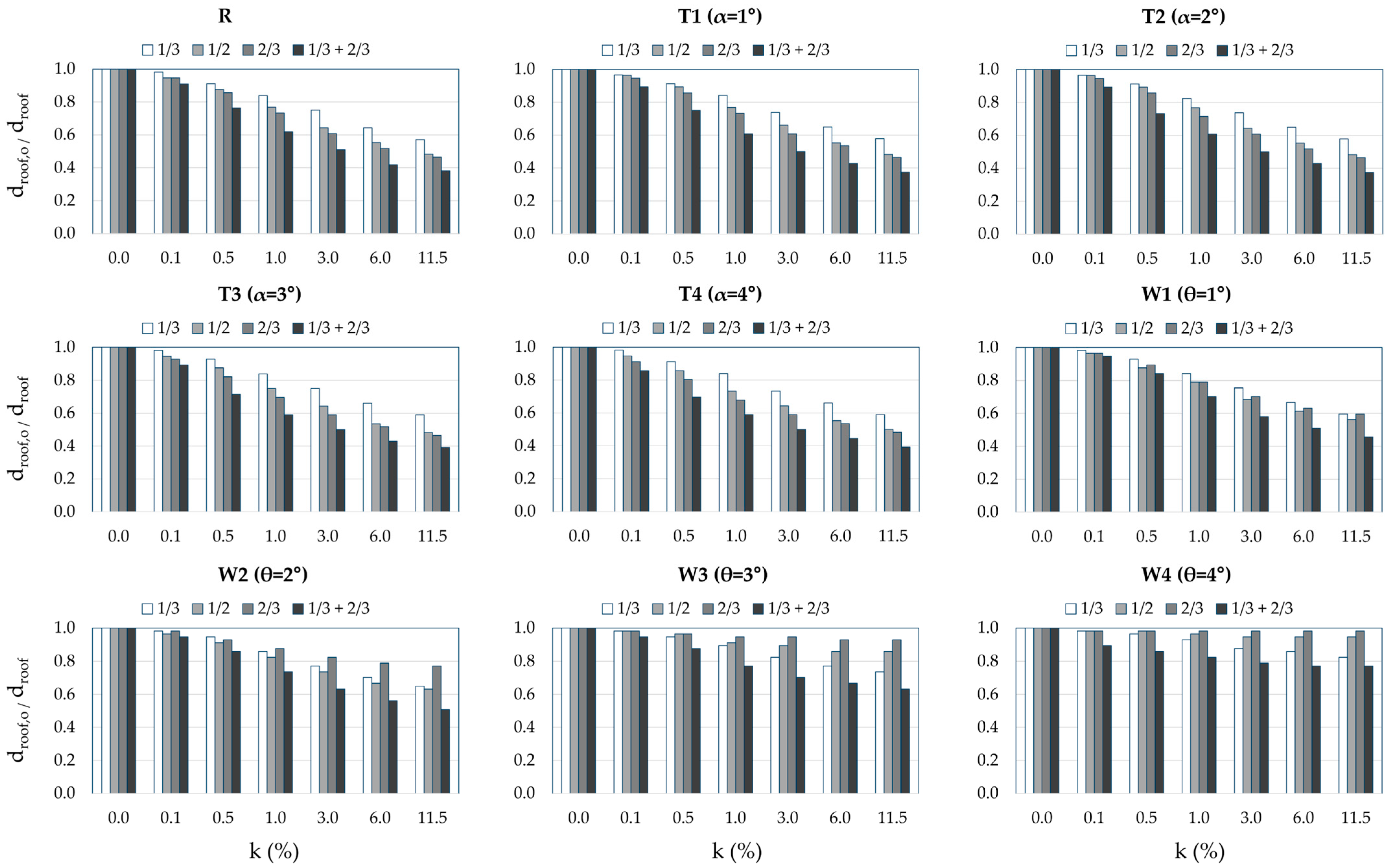
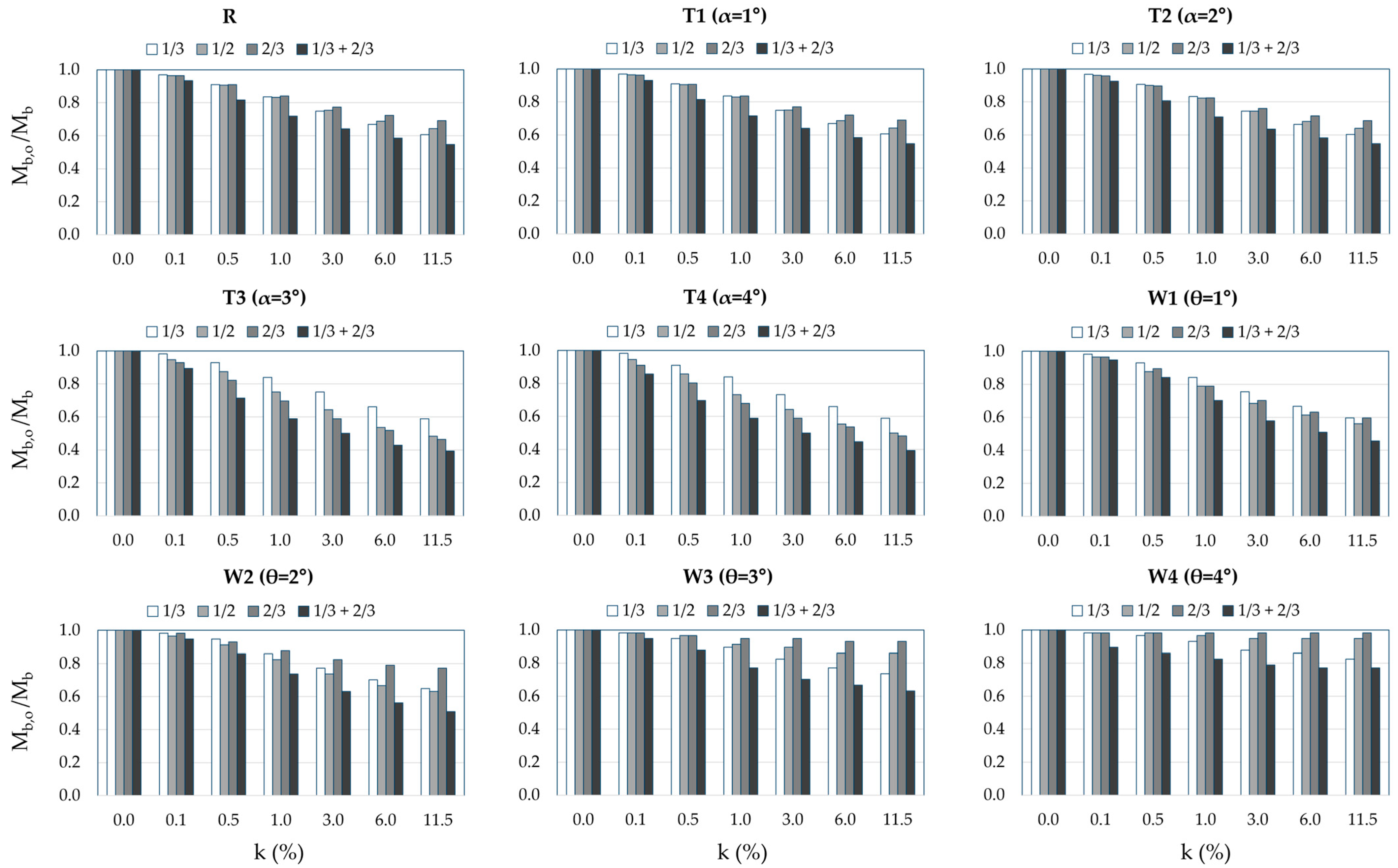
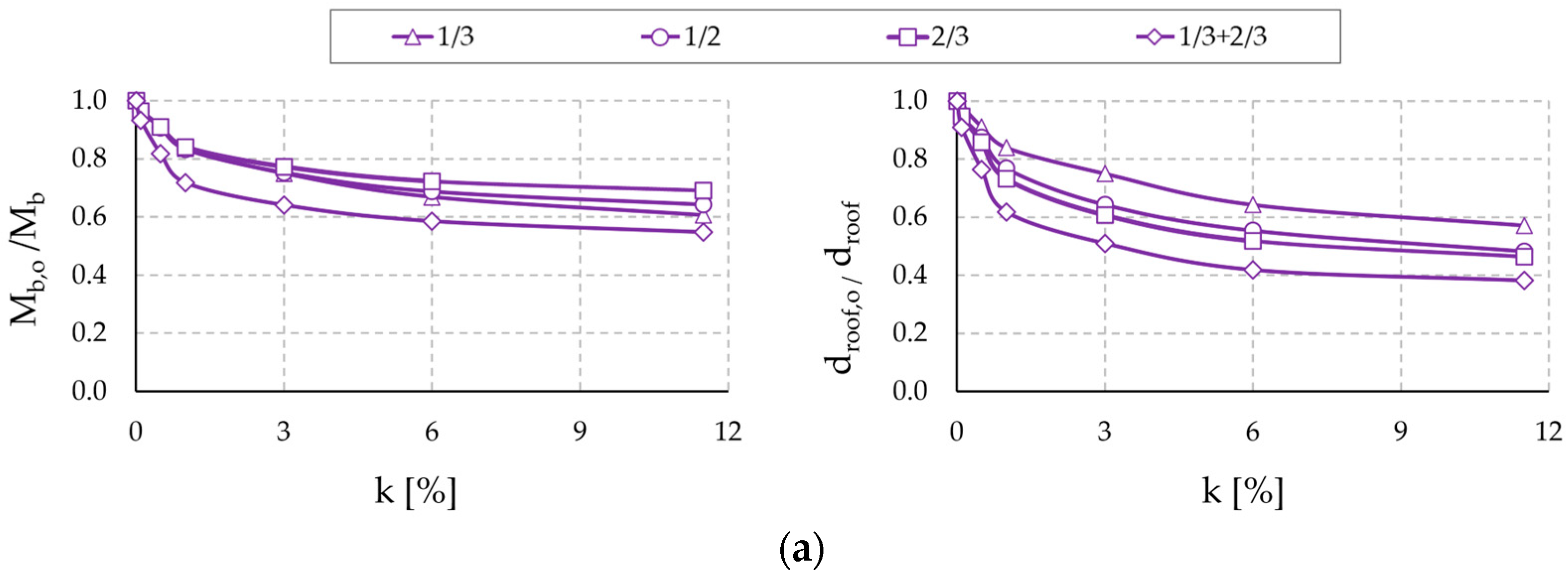
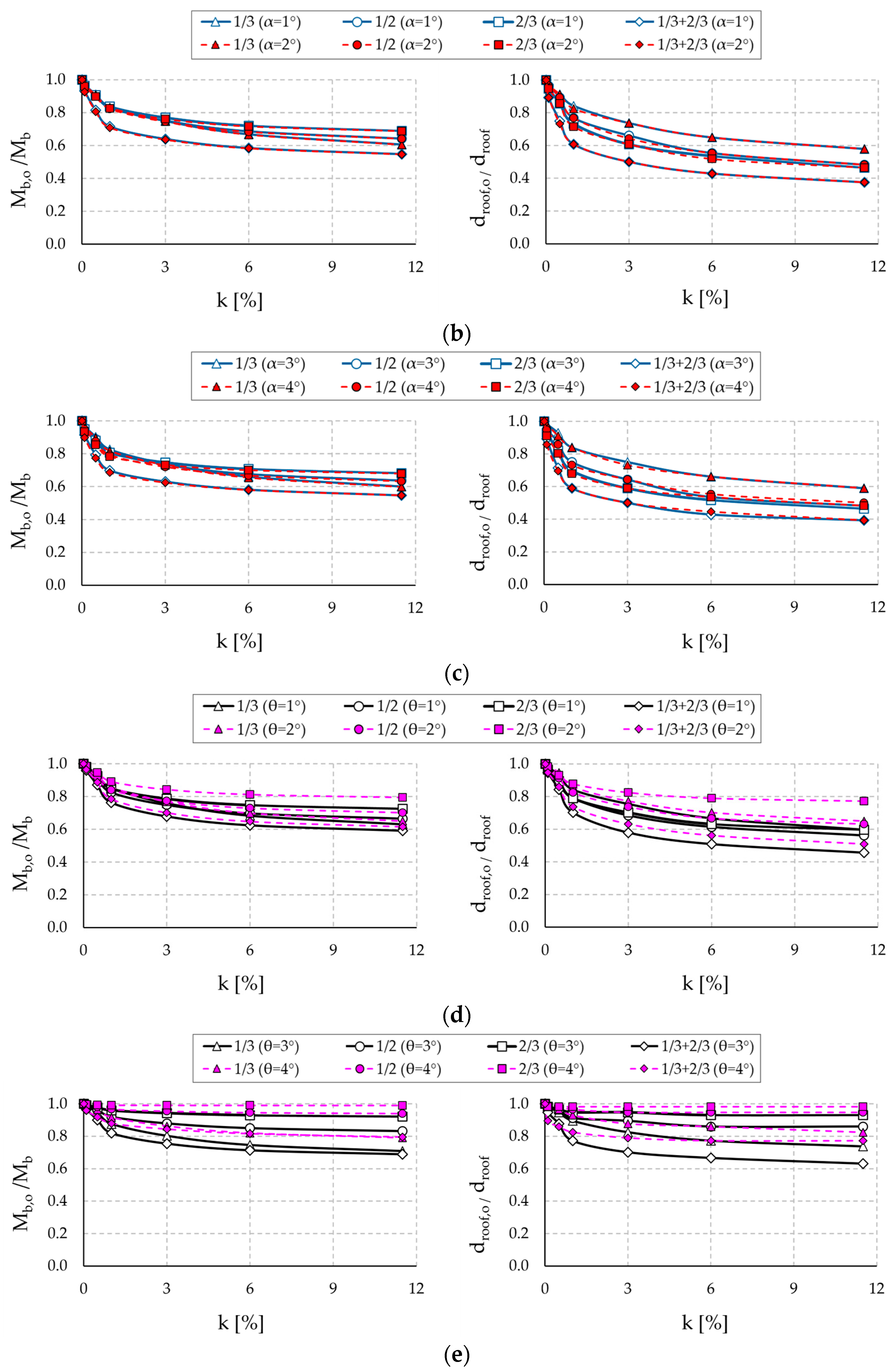
2.3. Results and Discussion
3. Refined Modeling for Outrigger Systems
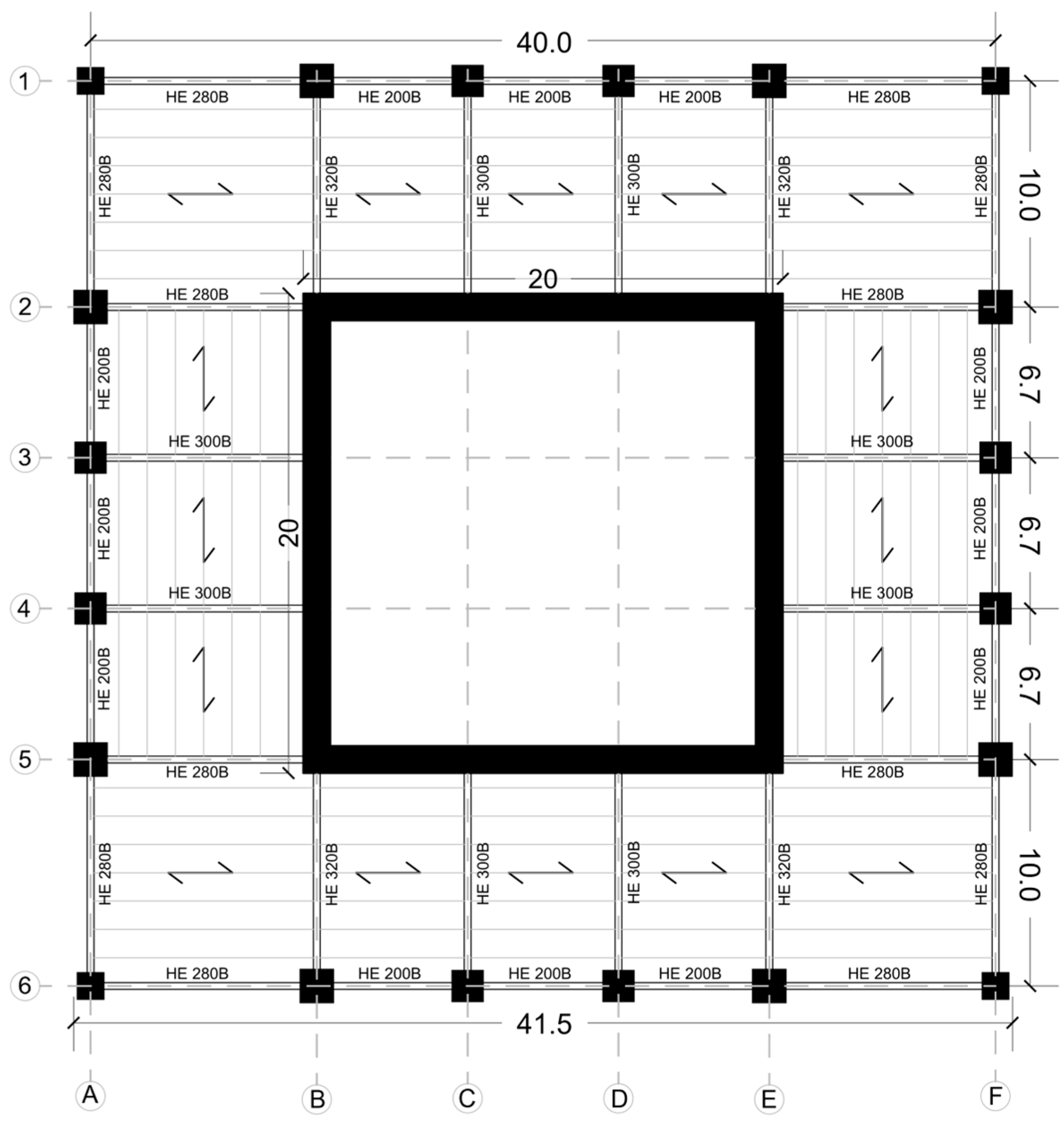
3.1. Model Description
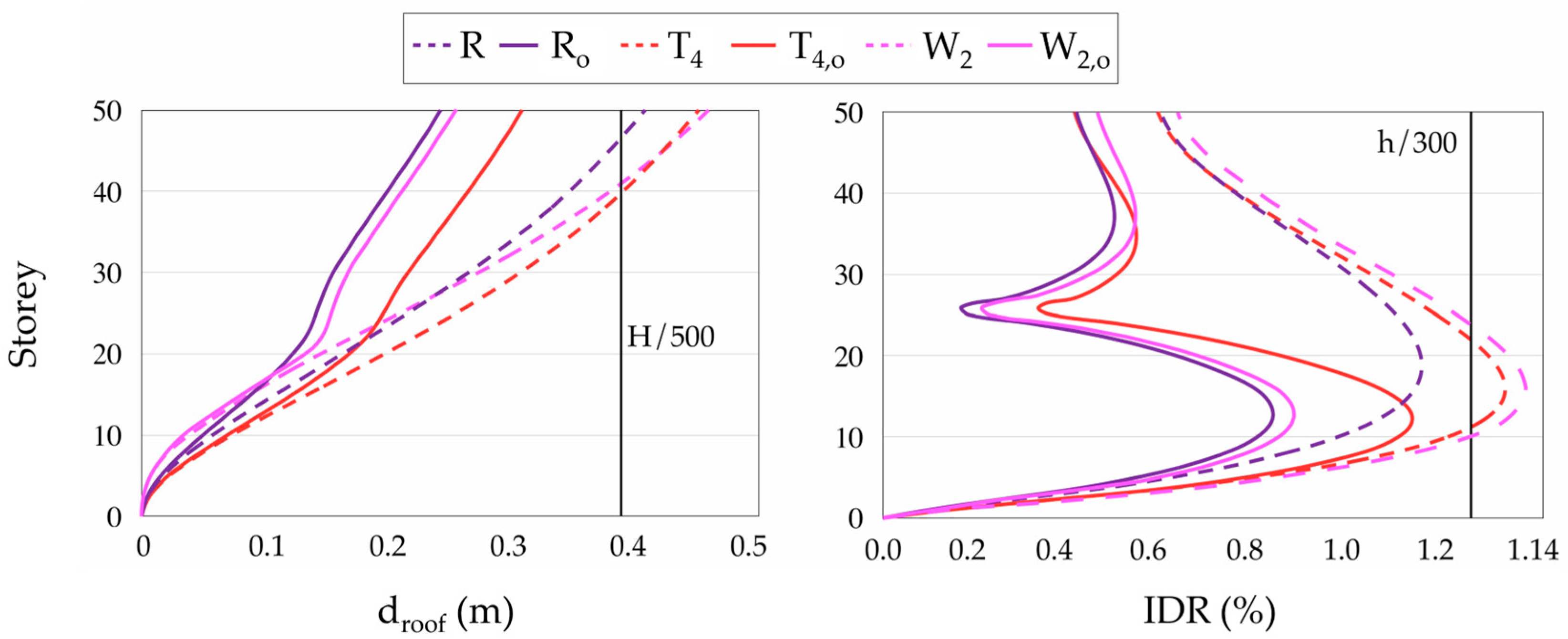
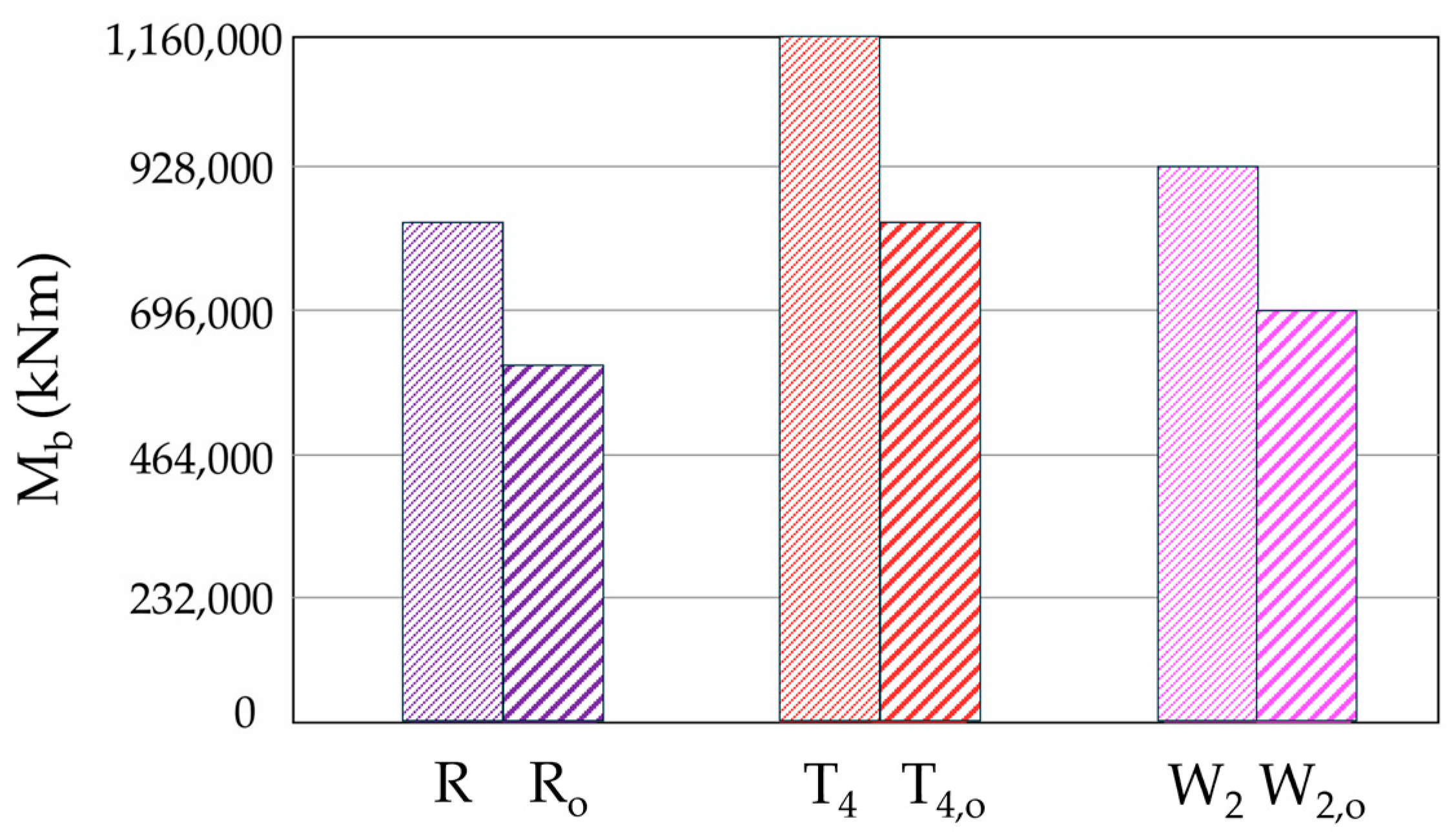
3.2. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kavyashree, B.G.; Patil, S.; Rao, V.S. Evolution of Outrigger Structural System: A State-of-the-Art Review. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 10313–10331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelucci, G.; Mollaioli, F.; Molle, M.; Paris, S. Performance assessment of timber high-rise buildings: Structural and technological considerations. Open Constr. Build. Technol. J. 2022, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, N.G.; Mhatre, P. Outrigger Structural System—A Review and Comparison of the Structural System. Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol. 2018, 64, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Luo, X.W.; Li, Q.S. Decision framework for optimal installation of outriggers in tall buildings. Autom. Constr. 2018, 93, 200–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikumar, S.; Jithma, T. Analytical Study of Tall Building with Outrigger System. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2020, 7, 3420–3423. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, K.S.; Connor, J.J.; Fernandez, J.E. Diagrid structural systems for tall buildings: Characteristics and methodology for preliminary design. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2007, 16, 205–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuori, G.M.; Mele, E.; Brandonisio, G.; De Luca, A. Geometrical patterns for diagrid buildings: Exploring alternative design strategies from the structural point of view. Eng. Struct. 2014, 71, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelucci, G.; Mollaioli, F. Voronoi-Like Grid Systems for Tall Buildings. Front. Built Environ. 2018, 4, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaramozzino, D.; Lacidogna, G.; Carpinteri, A. New Trends Towards Enhanced Structural Efficiency and Aesthetic Potential in Tall Buildings: The Case of Diagrids. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelucci, G.; Mollaioli, F.; Tardocchi, R. A new modular structural system for tall buildings based on tetrahedral configuration. Buildings 2020, 10, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stromberg, L.L.; Beghini, A.; Baker, W.F.; Paulino, G.H. Topology optimization for braced frames: Combining continuum and beam/column elements. Eng. Struct. 2012, 37, 106–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelucci, G.; Quaranta, G.; Mollaioli, F. Topology optimization of multi-story buildings under fully non-stationary stochastic seismic ground motion. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2022, 65, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Moon, K.S. Advances in structural systems for tall buildings: Emerging developments for contemporary urban giants. Building 2018, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanduri, P.M.B.R.K.; Suresh, B.; Hussain, I. Optimum Position of Outrigger System for High-Rise Reinforced Concrete Buildings Under Wind And Earthquake Loadings. Am. J. Eng. Res. 2013, 2, 76–89. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Moon, K.S. Structural Developments in Tall Buildings: Current Trends and Future Prospects. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2007, 50, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lame, A. Optimization of Outrigger Structures. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S. Optimum Locations of Outriggers in a Concrete Tall Building to Reduce Differential Axial Shortening. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2018, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanorkar, A.; Sukhdeve, S.; Denge, S.V.; Raut, S.P. Outrigger and Belt Truss System for Tall Building to Control Deflection: A Review. Glob. Res. Dev. J. Eng. 2016, 1, 6–15. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.C.; Kuang, J.S. Stiffened Coupled Shear Walls. J. Eng. Mech. 1989, 115, 247–267. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.C.; Kuang, J.S. Elastic Design Charts for Stiffened Coupled Shear Walls. J. Struct. Eng. 1989, 115, 689–703. [Google Scholar]
- Taranath, B.S. Structural Analysis and Design of Tall Buildings, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1988; p. 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranath, B.S. Steel, Concrete, and Composite Design of Tall Buildings, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997; p. 1024. [Google Scholar]
- McNabb, J.W. Drift Reduction Factors for Belted High-Rise Structures. Struct. Eng. 1975, 12, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, N.; Haritos, N.; Ngo, T.; Mendis, P. Behavior of Outrigger Beams in High Rise Buildings under Earthquake Loads. In Proceedings of the Australian Earthquake Engineering Society Conference, 18th Australian Earthquake Engineering Conference, Newcastle, Australia, 11–13 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gerasimidis, S.; Efthymiou, E.; Baniotopoulos, C.C. Optimum outrigger location of high-rise steel buildings for wind loading. In Proceedings of the 5th European & African Conference on Wind Engineering, Florence, Italy, 19–23 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, Y.K. Optimization of Outrigger Locations in Tall Buildings Subjected to Wind Loads. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Stafford Smith, B.; Coull, A. Tall Buildings Structures: Analysis and Design, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc: New York, NY, USA, 1991; p. 552. [Google Scholar]
- Boggs, P.C.; Gasparini, D.A. Lateral Stiffness of Core and Outrigger System. Struct. Eng. 1983, 20, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baygi, S.; Khazaee, A. The Optimal Number of Outriggers in a Structure Under Different Lateral Loadings. J. Inst. Eng. 2019, 100, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, R.; Arekar, V.; Patel, V.B. Analysis of outrigger numbers and locations with different bracing system. J. Emerg. Technol. Innov. Res. 2019, 6, 444–452. [Google Scholar]
- Fawzia, S.; Fatima, T. Optimum position of steel outrigger system for high-rise composite buildings subjected to wind loads. Adv. Steel Constr. 2015, 2, 134–153. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S.; Lee, H.L.; Lim, Y.J. Multi-objective optimization of dual-purpose outriggers in tall buildings to reduce lateral displacement and differential axial shortening. Eng. Struct. 2019, 189, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Tovar, A. Outrigger placement in tall buildings using topology optimization. Eng. Struct. 2014, 74, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z. Analysis of outrigger numbers and locations in outrigger braced structures using a multiobjective genetic algorithm. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2018, 27, e1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.R.; Li, Q.S. Structural performance of multi-outrigger braced tall buildings. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2003, 12, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaddad, W.; Halabi, Y.; Xu, H.; Lei, H. Outrigger and Belt-Truss System Design for High-Rise Buildings: A Comprehensive Review Part II—Guideline for Optimum Topology and Size Design. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 2589735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.S. Outrigger Systems for Structural Design of Complex-Shaped Tall Buildings. Int. J. High-Rise Build. 2016, 5, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.S. Comparative Evaluation of Structural Systems for Tilted Tall Buildings. Int. J. High-Rise Build. 2014, 3, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Taranath, B.S. Optimum Belt Truss Location for High-Rise Structures. Eng. J. 1974, 11, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford Smith, B.; Nwaka, I.O. Behavior of Multi-Outrigger Braced Tall Building Structures. Am. Concr. Inst. 1980, 63, 515–542. [Google Scholar]
- Stafford Smith, B.; Salim, I. Parameter Study of Outrigger-Braced Tall Building Structures. J. Struct. Div. 1981, 107, 2001–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenderkamp, J.C.D.; Bakker, M.C.M. Analysis of high-rise braced frames with outriggers. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2003, 12, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenderkamp, J.C.D. Second outrigger at optimum location on high-rise shear wall. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2008, 17, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, H. Simplified Analytical Model for Outrigger-Braced Structures Considering Transverse Shear Deformation. In Proceedings of the Seoul Conference, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2–3 December 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Bang, M.; Kim, J.Y. An analytical model for high-rise wall structures with outrigger. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2008, 16, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, D.; Lee, K.; Ahn, N. Geometric nonlinear analysis of tall building structures with outriggers. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2013, 22, 454–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhao, W.G.; Zhu, H.P.; Zhou, C.S. Safety analysis of optimal outriggers location in high-rise building structures. J. Zhejiang Univ. 2007, 8, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.K.L.; Wong, P.C.W.; Chandler, A.M. Application of Strut-and-tie method on outrigger braced core wall buildings. In Tall Buildings: From Engineering to Sustainability; World Scientific: Singapore, 2005; pp. 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahgozar, R.; Sharifi, Y. An approximate analysis of combined system of framed tube, shear core and belt truss in high-rise buildings. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2009, 18, 607–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekinejad, M.; Rahgozar, R. Free vibration analysis of tall buildings with outrigger-belt truss system. Earthq. Struct. 2011, 2, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.C.H. Seismic Design of Outrigger System for Tall Buildings. Ph.D. Thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Marabi, B.; Alih, S.C.; Feridmehr, I. Evaluation of the Efficiency of Single-Outrigger Structural Systems in Tall Buildings. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Wind & Earthquake Engineering, Putrajaya, Malaysia, 16–17 October 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranath, B.S. Wind and Earthquake Resistance Buildings: Structural Analysis and Design, 1st ed.; CRC Press LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2004; p. 912. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, J.C. Study of Outrigger Structural System for High Rise Building. Ph.D. Thesis, Nirma University Institute of Technology, Ahmedabad, India, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.L.; Chen, C.C. Outrigger system study for tall building structure with central core and square floor plate. In Proceedings of the CTBUH 8th World Congress, CTBUH 8th World Congress, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 3–5 March 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, K.; Wang, X. Parameter study of framed-tube structures with outriggers using genetic algorithm. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2018, 27, e1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissanka, N.A.C.C.; Fernando, A.M.; Gamage, J.C.P.H. Effectiveness of Various Outrigger Systems of Different Structural Materials for Lateral Load Resistance in Reinforced Concrete High-Rise Buildings. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Sustainable Built Environment, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 15–16 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sakr, T.A.; Hanaa, E.M. Elasto-Plastic Behavior of Outrigger Braced Walls. J. Am. Sci. 2012, 8, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Mulla, K.A.; Srinivas, B.N. A Study on Outrigger System in a Tall R.C Structure with Steel Bracing. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 551–557. [Google Scholar]
- Chambulwar, S.; Kadam, T.S.; Bhujbal, A.M.; Konde, P.P.; Alandkar, S.B. Comparative Study of RCCC Structure with and without Outrigger System. Int. J. Res. Eng. Sci. 2021, 9, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Marmar, A.; Zouia, S.; Ismail, S.; Hallik, A. Twisted Buildings: Concepts and approaches. Archit. Plan. J. 2021, 27, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sev, A.; Başarır, B. A recent trend in tall building design: Twisted forms. Now World Sci. Acad. 2011, 6, 1603–1619. [Google Scholar]
- Golasz-Szolomicka, H.; Szolomicki, J. Architectural and Structural Analysis of Selected Twisted Tall Buildings. In Proceedings of the 4th World Multidisciplinary Civil Engineering, Architecture, Urban Planning Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Kim, E.S.; Kang, D.E.; Kim, T. Seismic Performance Evaluation of Twisted Outrigger System. In Proceedings of the 15th National Conference on Wind & Earthquake Engineering, Lisboa, Portugal, 24–28 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, K.S. Studies on various structural system design options for twisted tall buildings and their performances. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2019, 23, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedeoğlu, I.O.; Calayir, Y. Effectiveness of outrigger and belt truss systems on the seismic behavior of high-rise buildings. J. Struct. Eng. Appl. Mech. 2020, 3, 180–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| k | Io | IR,T | IW |
|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (cm4) | (cm4) | (cm4) |
| 0.005 | 4.74 × 106 | 2.37 × 106 | 1.19 × 106 |
| 0.1 | 9.48 × 107 | 4.74 × 107 | 2.37 × 107 |
| 0.5 | 4.74 × 108 | 2.37 × 108 | 1.19 × 108 |
| 1.0 | 9.48 × 108 | 4.74 × 108 | 2.37 × 108 |
| 3.0 | 2.84 × 109 | 1.42 × 109 | 7.11 × 108 |
| 6.0 | 5.69 × 109 | 2.84 × 109 | 1.42 × 109 |
| 11.5 | 1.09 × 1010 | 5.45 × 109 | 2.73 × 109 |
| k (%) | x = 1/3 (s) | x = 1/2 (s) | x = 2/3 (s) | x = 1/3 and x = 2/3 (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.005 | 2.90 | 2.90 | 2.90 | 2.90 |
| 0.1 | 2.88 | 2.77 | 2.93 | 2.61 |
| 0.5 | 2.85 | 2.66 | 2.81 | 2.41 |
| 1.0 | 2.74 | 2.51 | 2.64 | 2.20 |
| 3.0 | 2.60 | 2.32 | 2.45 | 2.03 |
| 6.0 | 2.45 | 2.15 | 2.30 | 1.91 |
| 11.5 | 2.40 | 2.10 | 2.28 | 1.89 |
| k (%) | x = 1/3 (s) | x = 1/2 (s) | x = 2/3 (s) | x = 1/3 and x = 2/3 (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α = 1° | ||||
| 0.005 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| 0.1 | 2.93 | 2.77 | 2.93 | 2.62 |
| 0.5 | 2.86 | 2.67 | 2.81 | 2.40 |
| 1.0 | 2.75 | 2.51 | 2.63 | 2.21 |
| 3.0 | 2.60 | 2.32 | 2.44 | 2.04 |
| 6.0 | 2.46 | 2.16 | 2.30 | 1.92 |
| 11.5 | 2.44 | 2.14 | 2.28 | 1.88 |
| α = 2° | ||||
| 0.005 | 2.98 | 2.98 | 2.98 | 2.98 |
| 0.1 | 2.93 | 2.77 | 2.92 | 2.61 |
| 0.5 | 2.85 | 2.66 | 2.79 | 2.40 |
| 1.0 | 2.74 | 2.50 | 2.61 | 2.20 |
| 3.0 | 2.60 | 2.31 | 2.43 | 2.03 |
| 6.0 | 2.45 | 2.16 | 2.30 | 1.91 |
| 11.5 | 2.44 | 2.14 | 2.28 | 1.88 |
| α = 3° | ||||
| 0.005 | 2.96 | 2.96 | 2.96 | 2.96 |
| 0.1 | 2.93 | 2.73 | 2.90 | 2.53 |
| 0.5 | 2.82 | 2.60 | 2.72 | 2.34 |
| 1.0 | 2.70 | 2.48 | 2.53 | 2.13 |
| 3.0 | 2.58 | 2.30 | 2.40 | 1.95 |
| 6.0 | 2.43 | 2.15 | 2.27 | 1.90 |
| 11.5 | 2.41 | 2.13 | 2.24 | 1.89 |
| α = 4° | ||||
| 0.005 | 2.95 | 2.95 | 2.95 | 2.95 |
| 0.1 | 2.90 | 2.73 | 2.87 | 2.56 |
| 0.5 | 2.81 | 2.60 | 2.70 | 2.30 |
| 1.0 | 2.70 | 2.43 | 2.51 | 2.15 |
| 3.0 | 2.53 | 2.25 | 2.39 | 2.00 |
| 6.0 | 2.48 | 2.10 | 2.35 | 1.98 |
| 11.5 | 2.46 | 2.09 | 2.33 | 1.96 |
| k (%) | x = 1/3 (s) | x = 1/2 (s) | x = 2/3 (s) | x = 1/3 and x = 2/3 (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| θ = 1° | ||||
| 0.005 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| 0.1 | 2.94 | 2.78 | 2.95 | 2.68 |
| 0.5 | 2.88 | 2.70 | 2.90 | 2.57 |
| 1.0 | 2.77 | 2.56 | 2.83 | 2.43 |
| 3.0 | 2.63 | 2.43 | 2.80 | 2.40 |
| 6.0 | 2.60 | 2.40 | 2.78 | 2.38 |
| 11.5 | 2.58 | 2.38 | 2.76 | 2.35 |
| θ = 2° | ||||
| 0.005 | 3.12 | 3.12 | 3.12 | 3.12 |
| 0.1 | 2.95 | 2.78 | 2.95 | 2.68 |
| 0.5 | 2.90 | 2.72 | 2.94 | 2.60 |
| 1.0 | 2.80 | 2.62 | 2.95 | 2.49 |
| 3.0 | 2.69 | 2.54 | 2.90 | 2.45 |
| 6.0 | 2.66 | 2.50 | 2.88 | 2.40 |
| 11.5 | 2.63 | 2.48 | 2.86 | 2.38 |
| θ = 3° | ||||
| 0.005 | 3.13 | 3.13 | 3.13 | 3.13 |
| 0.1 | 3.10 | 2.98 | 3.10 | 3.00 |
| 0.5 | 3.03 | 2.95 | 3.05 | 2.96 |
| 1.0 | 3.00 | 2.90 | 3.03 | 2.94 |
| 3.0 | 2.98 | 2.88 | 3.00 | 2.90 |
| 6.0 | 2.96 | 2.87 | 2.98 | 2.88 |
| 11.5 | 2.94 | 2.86 | 2.96 | 2.86 |
| θ = 4° | ||||
| 0.005 | 3.13 | 3.13 | 3.13 | 3.13 |
| 0.1 | 3.10 | 3.06 | 3.10 | 3.00 |
| 0.5 | 3.06 | 3.04 | 3.08 | 2.98 |
| 1.0 | 3.04 | 3.00 | 3.06 | 2.97 |
| 3.0 | 3.00 | 2.98 | 3.03 | 2.95 |
| 6.0 | 2.97 | 2.96 | 3.00 | 2.93 |
| 11.5 | 2.95 | 2.94 | 2.98 | 2.90 |
| Refined Model’s Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Height (H) | 200 m |
| Story levels | 50 |
| Inter-story height | 4 m |
| Plan dimension | 40 × 40 m |
| Inner core dimension | 20 × 20 m |
| Primary resisting system | RC MRF and RC core shear walls |
| Secondary resisting system | Steel outrigger and belt-truss system |
| Outrigger location | ½ H = 100 m |
| Member | Dimension (m) | Material | Typology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slab thickness | 0.37 | RC C28/35 | Precast slab |
| Column | 1.5 × 1.5 | RC C50/60 | Rectangular section |
| Core thickness | 1.2 | RC C50/60 | Box section |
| Outrigger | 1.5 × 0.17 | Steel S450 | Hollow circular tube |
| Belt-truss | 1.0 × 0.12 | Steel S450 | Hollow circular tube |
| R | Ro | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | Period (s) | UX (%) | UY (%) | Period (s) | UX (%) | UY (%) |
| 1 | 4.98 | 67% | 3% | 3.77 | 66% | 9% |
| 2 | 4.98 | 70% | 70% | 3.77 | 75% | 75% |
| 3 | 3.55 | 70% | 70% | 3.19 | 75% | 75% |
| 4 | 1.35 | 78% | 75% | 1.32 | 82% | 77% |
| 5 | 1.35 | 83% | 83% | 1.32 | 84% | 84% |
| 6 | 1.14 | 83% | 83% | 1.07 | 84% | 84% |
| 7 | 0.65 | 83% | 83% | 0.57 | 84% | 84% |
| 8 | 0.62 | 88% | 83% | 0.49 | 89% | 84% |
| 9 | 0.62 | 88% | 88% | 0.49 | 89% | 89% |
| 10 | 0.43 | 88% | 88% | 0.42 | 89% | 89% |
| 11 | 0.35 | 91% | 88% | 0.35 | 91% | 89% |
| 12 | 0.35 | 91% | 91% | 0.35 | 92% | 92% |
| T4 | T4,o | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | Period (s) | UX (%) | UY (%) | Period (s) | UX (%) | UY (%) |
| 1 | 4.74 | 39% | 29% | 3.85 | 1% | 67% |
| 2 | 4.71 | 70% | 69% | 3.56 | 75% | 68% |
| 3 | 3.08 | 70% | 71% | 2.58 | 75% | 76% |
| 4 | 1.38 | 82% | 72% | 1.32 | 83% | 78% |
| 5 | 1.34 | 83% | 82% | 1.30 | 85% | 84% |
| 6 | 0.99 | 83% | 83% | 0.91 | 85% | 85% |
| 7 | 0.68 | 84% | 86% | 0.64 | 85% | 85% |
| 8 | 0.65 | 86% | 87% | 0.63 | 85% | 85% |
| 9 | 0.64 | 86% | 87% | 0.63 | 85% | 85% |
| 10 | 0.63 | 86% | 87% | 0.63 | 85% | 85% |
| 11 | 0.63 | 86% | 87% | 0.63 | 85% | 85% |
| 12 | 0.63 | 86% | 87% | 0.63 | 85% | 85% |
| W2 | W2,o | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | Period (s) | Sum UX (%) | Sum UY (%) | Period (s) | Sum UX (%) | Sum UY (%) |
| 1 | 4.70 | 63% | 4% | 3.70 | 60% | 10% |
| 2 | 4.66 | 67% | 67% | 3.67 | 71% | 71% |
| 3 | 2.38 | 67% | 68% | 2.23 | 71% | 72% |
| 4 | 1.38 | 82% | 68% | 1.33 | 84% | 72% |
| 5 | 1.33 | 83% | 83% | 1.29 | 84% | 84% |
| 6 | 1.03 | 83% | 83% | 1.03 | 84% | 84% |
| 7 | 1.03 | 83% | 83% | 1.03 | 84% | 84% |
| 8 | 1.01 | 83% | 83% | 1.00 | 84% | 84% |
| 9 | 0.99 | 83% | 83% | 0.97 | 84% | 84% |
| 10 | 0.96 | 83% | 83% | 0.96 | 84% | 84% |
| 11 | 0.91 | 83% | 83% | 0.91 | 84% | 84% |
| 12 | 0.89 | 83% | 83% | 0.89 | 84% | 84% |
| Model | Approach | Δdroof | ΔMb |
|---|---|---|---|
| R | Simplified | 40.2% | 27.9% |
| Refined | 40.4% | 28.2% | |
| T4 | Simplified | 29.8% | 24.9% |
| Refined | 31.7% | 20.4% | |
| W2 | Simplified | 40.2% | 30.6% |
| Refined | 44.3% | 25.0% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angelucci, G.; Cecca, E.; Mollaioli, F. Parametric Analysis of Outrigger Systems for High-Rise Buildings with Different Geometric Shapes. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5643. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105643
Angelucci G, Cecca E, Mollaioli F. Parametric Analysis of Outrigger Systems for High-Rise Buildings with Different Geometric Shapes. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(10):5643. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105643
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngelucci, Giulia, Edoardo Cecca, and Fabrizio Mollaioli. 2025. "Parametric Analysis of Outrigger Systems for High-Rise Buildings with Different Geometric Shapes" Applied Sciences 15, no. 10: 5643. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105643
APA StyleAngelucci, G., Cecca, E., & Mollaioli, F. (2025). Parametric Analysis of Outrigger Systems for High-Rise Buildings with Different Geometric Shapes. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5643. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105643







