Salp Swarm Algorithm Optimized A* Algorithm and Improved B-Spline Interpolation in Path Planning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Path Planning Algorithm
2.1. The A* Algorithm
2.2. Improvement of the A* Algorithm
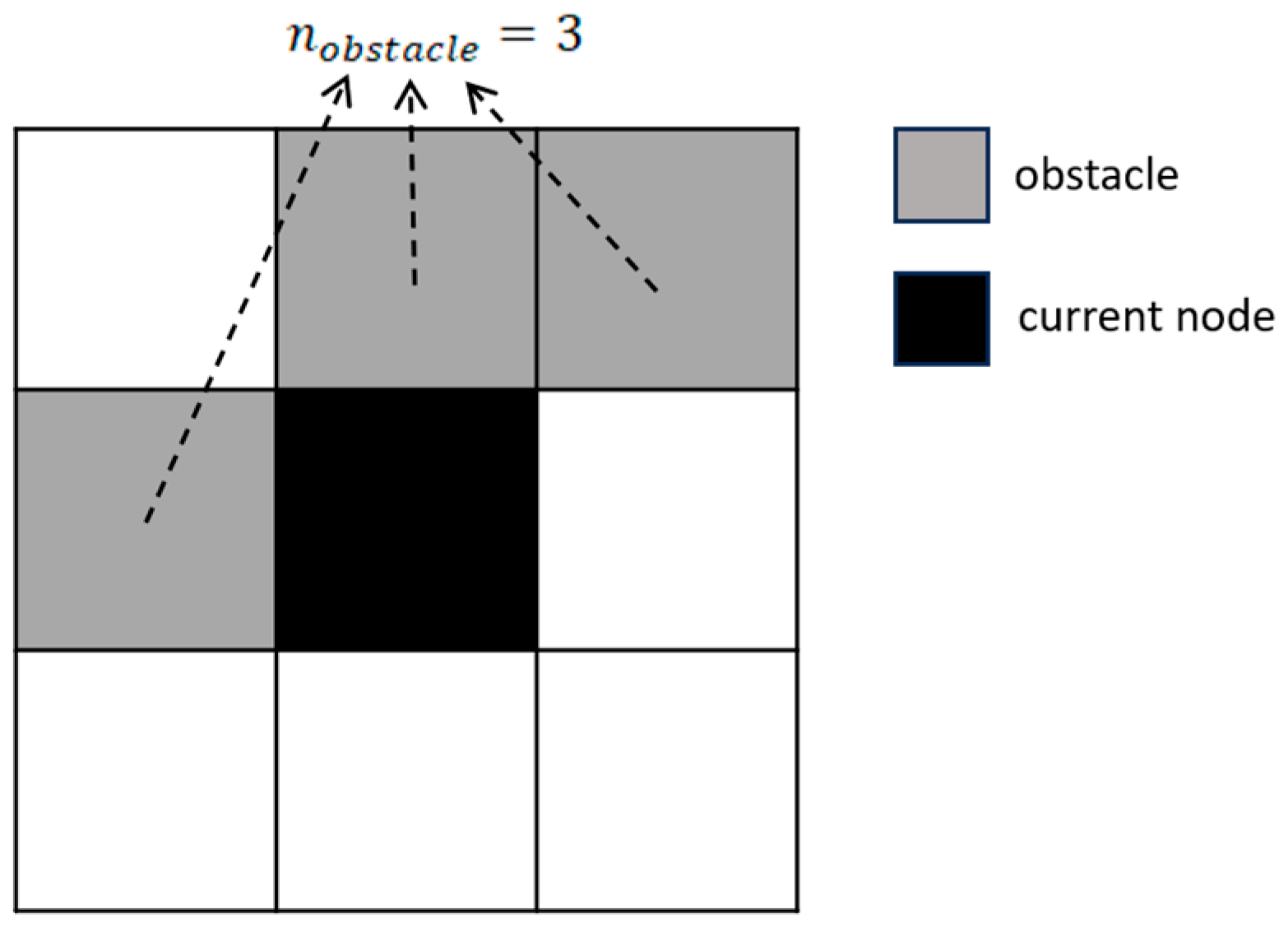
2.2.1. Determining the Variables Included in
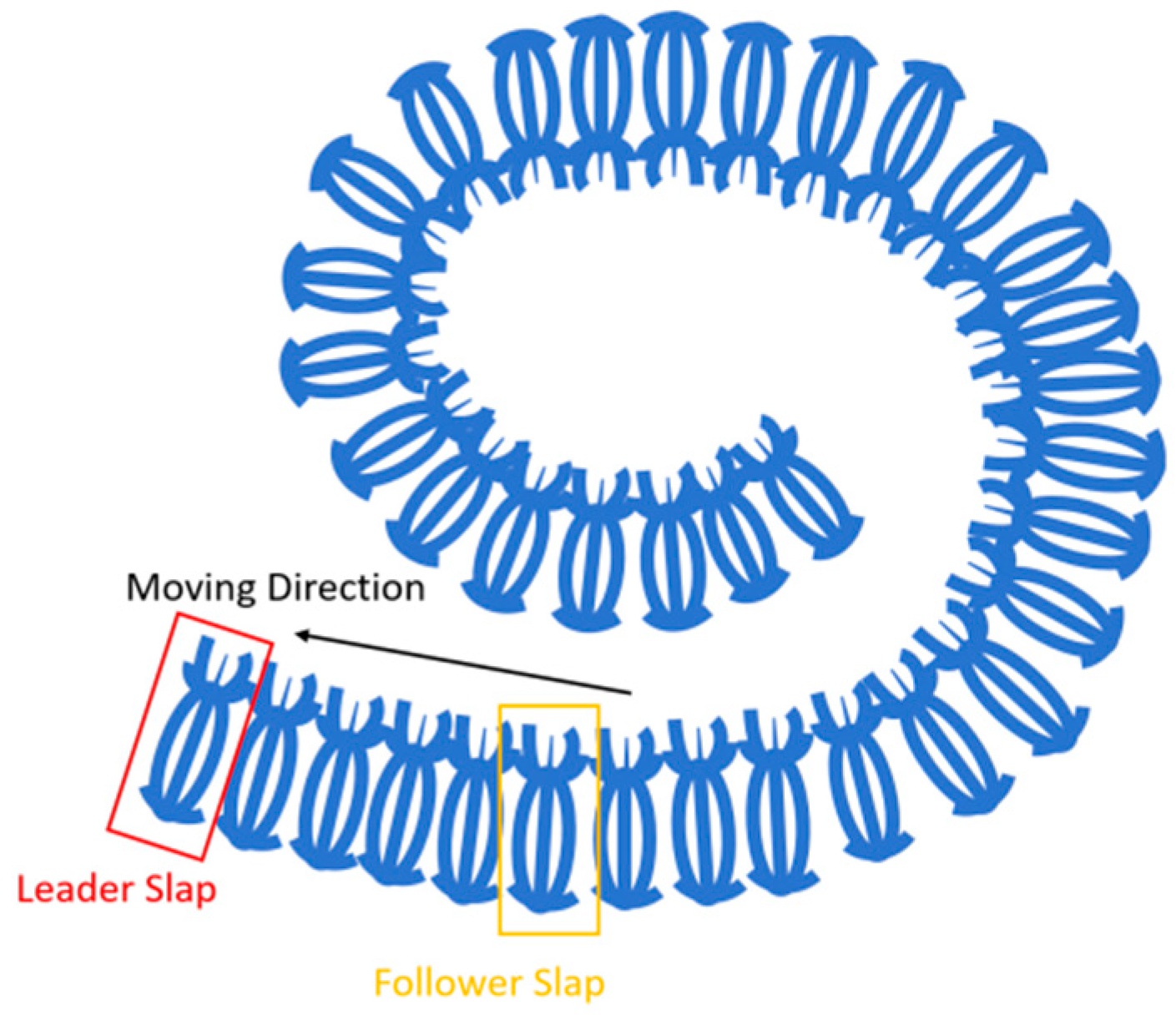
2.2.2. Optimization Using the SSA
| Algorithm 1: Improved A* Algorithm with the SSA Optimization |
| Input: Grid map , start point , end point , weight bounds , population size , maximum iterations Output: Optimal path , visited nodes list , optimal weight 1: BEGIN: 2: Initialization: Define 8-neighborhood direction set Initialize SSA population Initialize optimal weight Initialize optimal fitness Initialize iteration counter 3://SSA Optimization Process: 4: While : 5: For each 6: If 7: 8: Else: 9: 10: Clip to 11: 12: If 13: 14: 15: 16: Record current optimal fitness 17: 18: //A* Path Search:Use optimal weight Ω∗ to execute A* algorithm: 19: Initialize open list , parent map , cost map , and visited nodes list 20: While is not empty: 22: Pop 23: If 24: 25: Return 26: Add to 27: For each 28: 29: If is out of bounds or 30: Continue 31: if 32: 33: If 34: 35: 36: 37: 38: Push into 39: Return 40: END |
3. Path Smoothing Algorithm
3.1. B-Spline Interpolation Curve
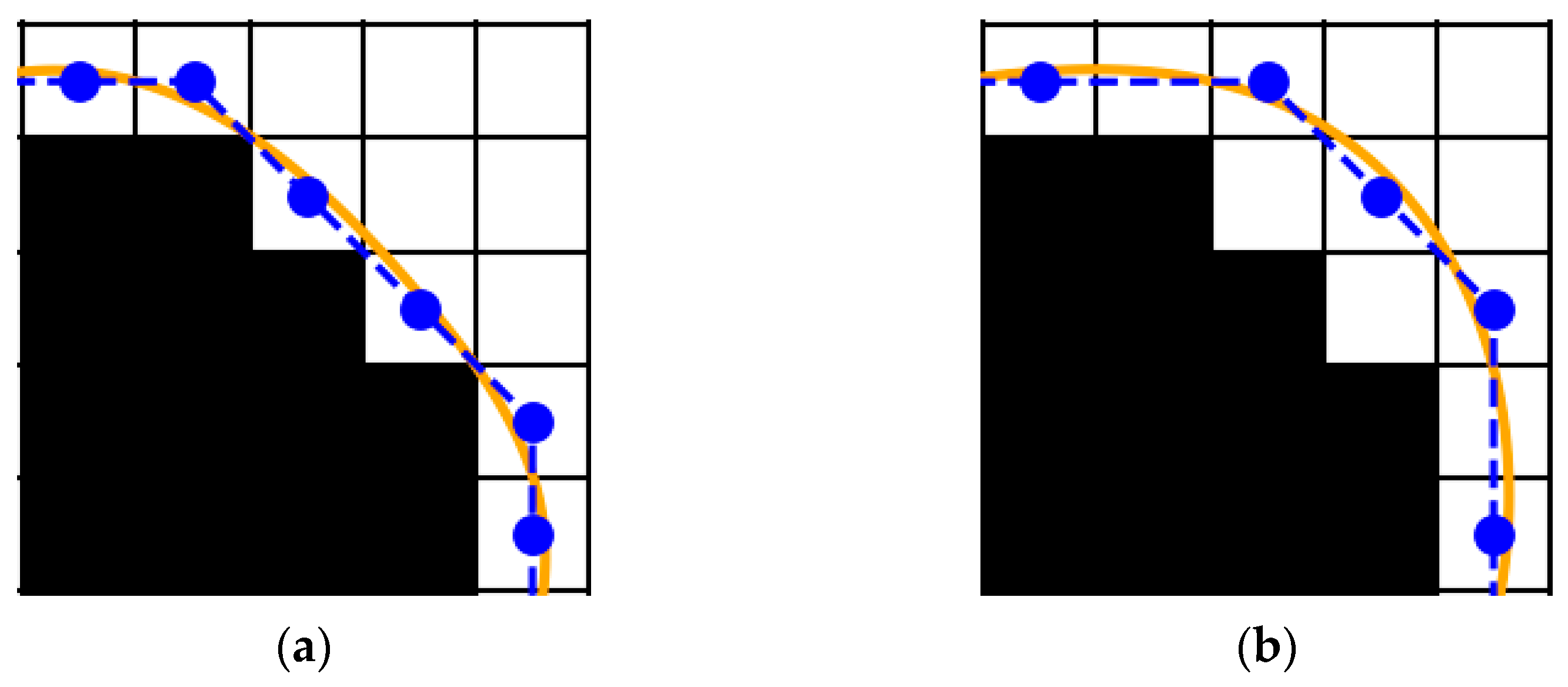
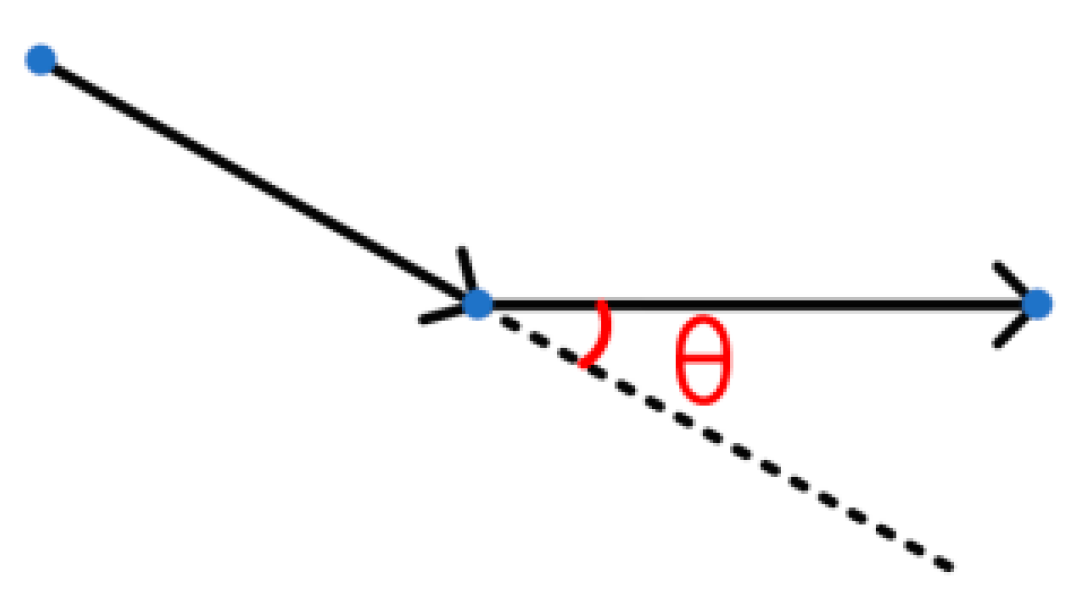
3.2. Control Point Adjustment
| Algorithm 2: Corner Avoidance Strategy |
| Input: Grid map , original path Output: Optimized path 1: BEGIN: 2: Initialize 3: 4: while do 5: 6: 7: if and then // Diagonal move 8: 9: 10: if then 11: if then 12: // Mark nodes for removal 13: if then 14: // Insert intermediate point C 15: // Skip the new point 16: else if then 17: // Insert intermediate point D 18: 19: end if 20: continue // Re-check current index 21: end if 22: end if 23: 24: end while 25: // Remove marked nodes 26: for in do 27: if and then 28: remove from 29: end if 30: end for 31: return 32: END |
| Algorithm 3: Path Obstacle Avoidance with Grid Map |
| Input: Optimized path ; Grid map ; Distance threshold ; Parameters Output: Final control point path 1: BEGIN: 2: Initialize as empty list 3: for in do 4: if or then 5: append to 6: continue 7: end if 8: Initialize 9: for each obstacle in do 10: 11: if then 12: 13: 14: 15: 16: end if 17: end for 18: if then 19: 20: 21: else 22: 23: end if 24: append to 25: end for 26: return 27: END |
4. Experimental Simulation
4.1. Path Planning Algorithm Simulation Experiment
4.1.1. Parameters for Path Planning Simulation
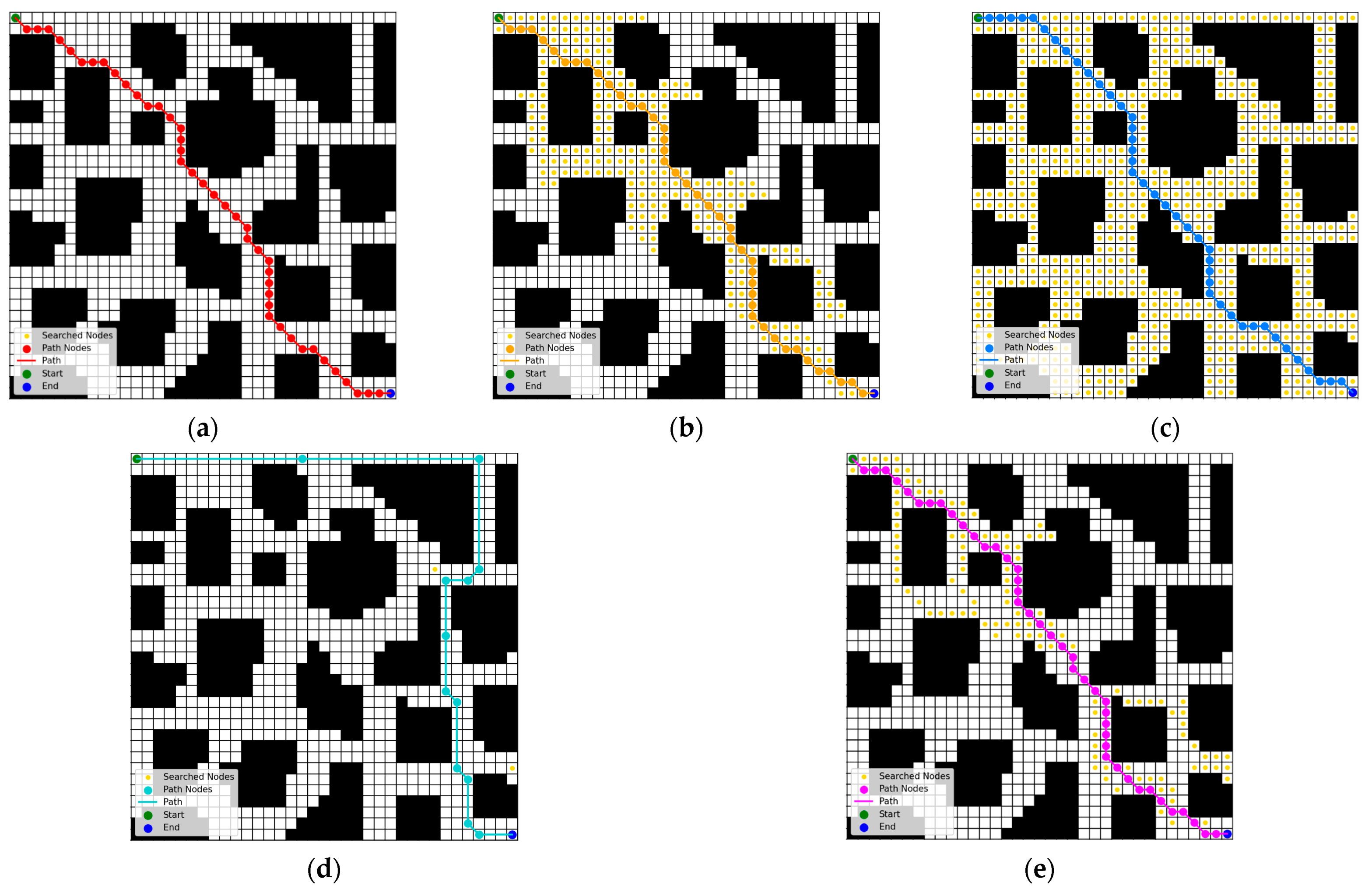
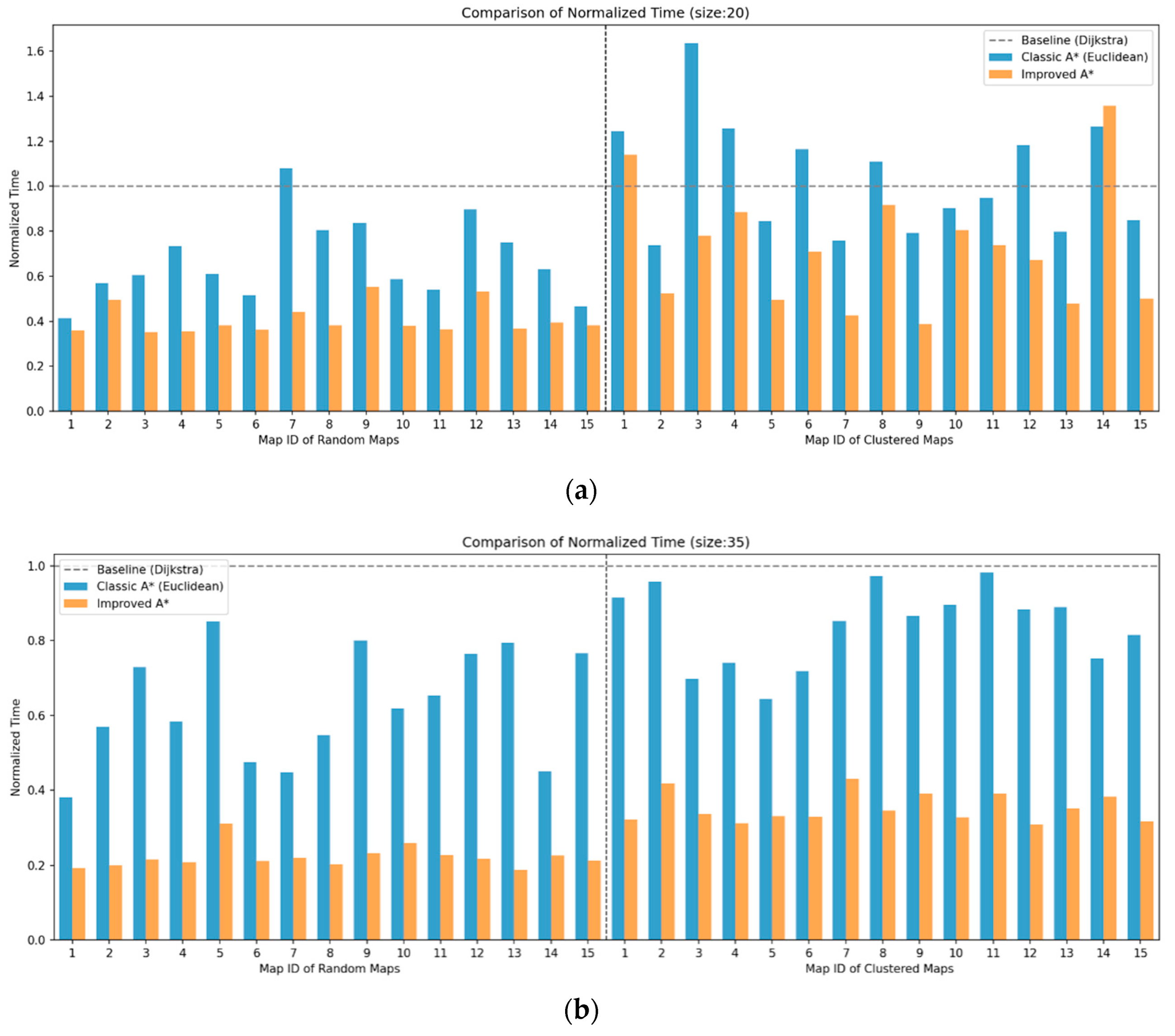
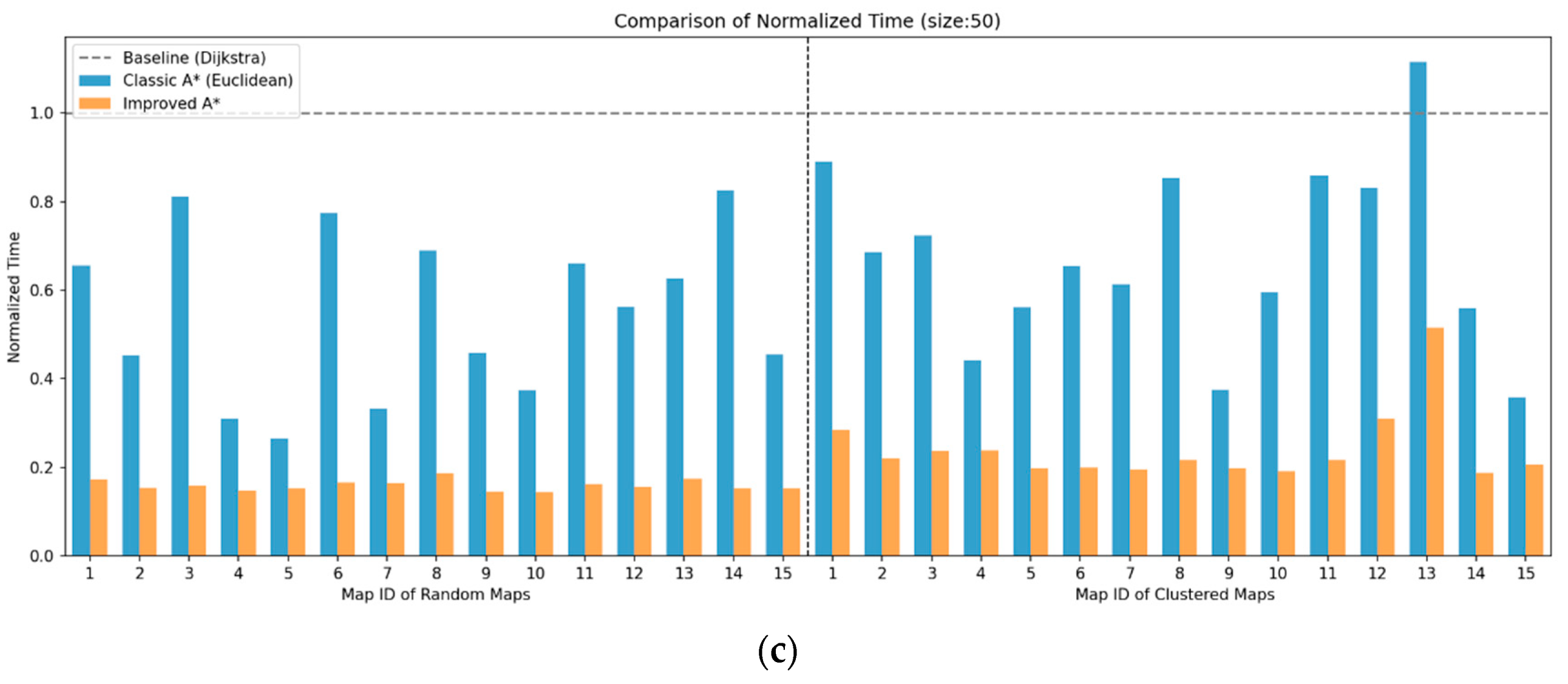
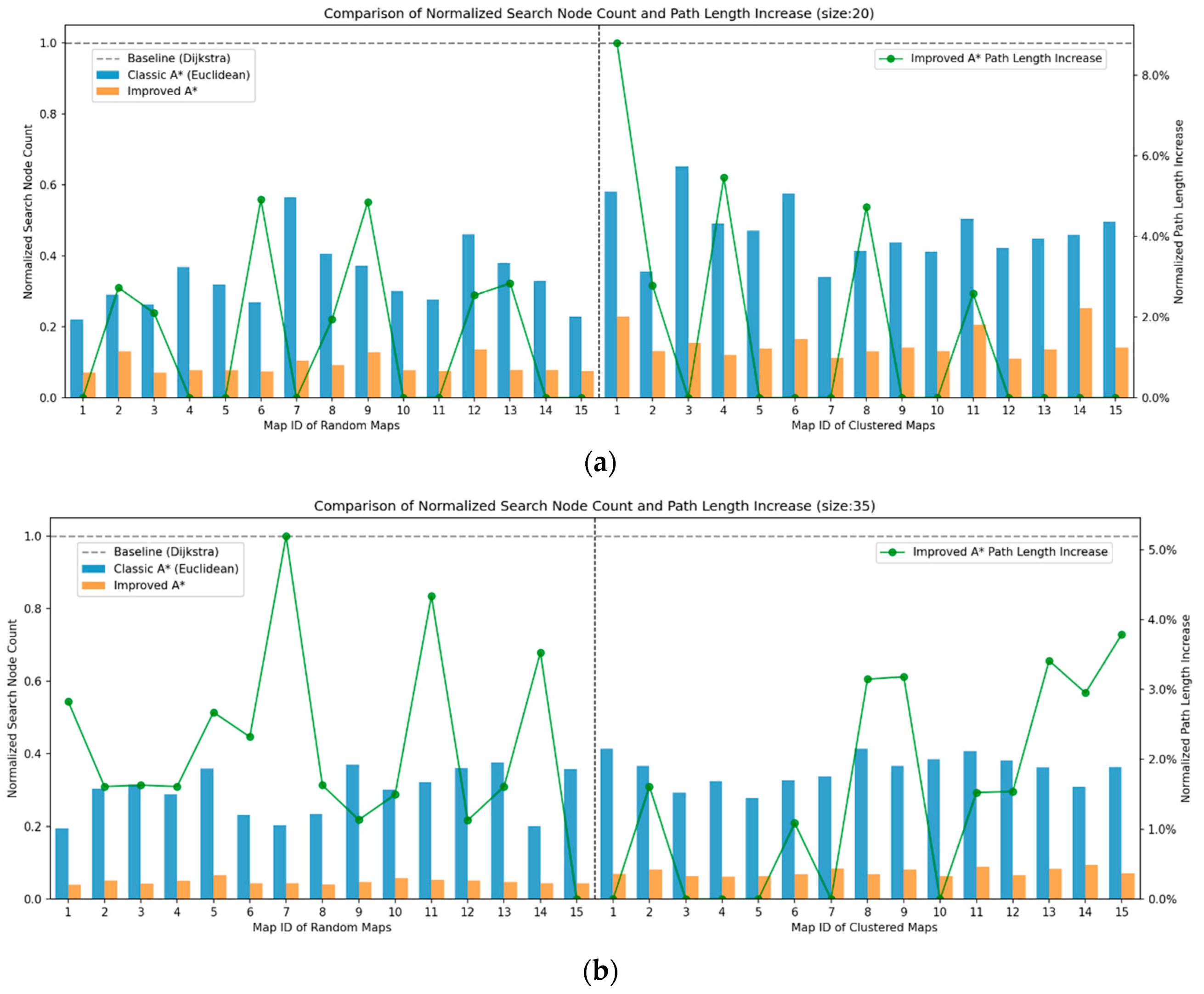
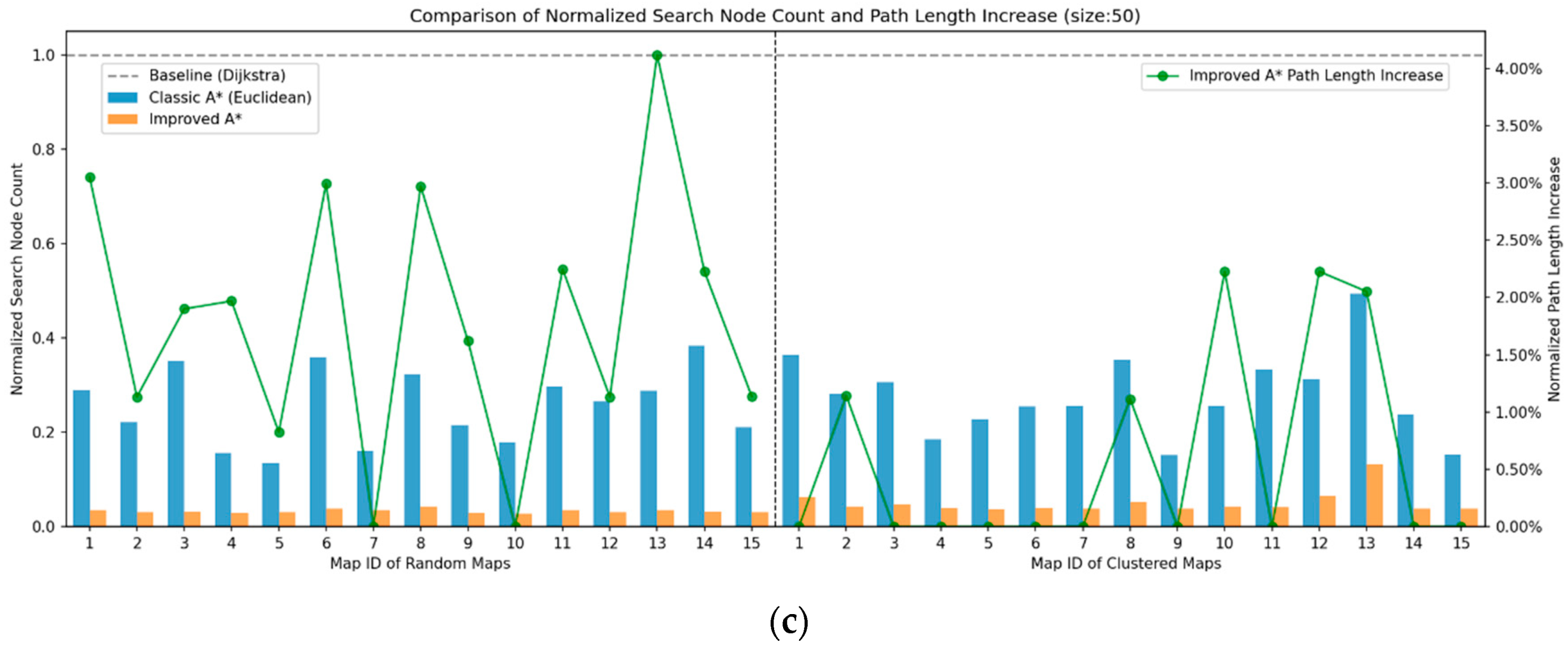
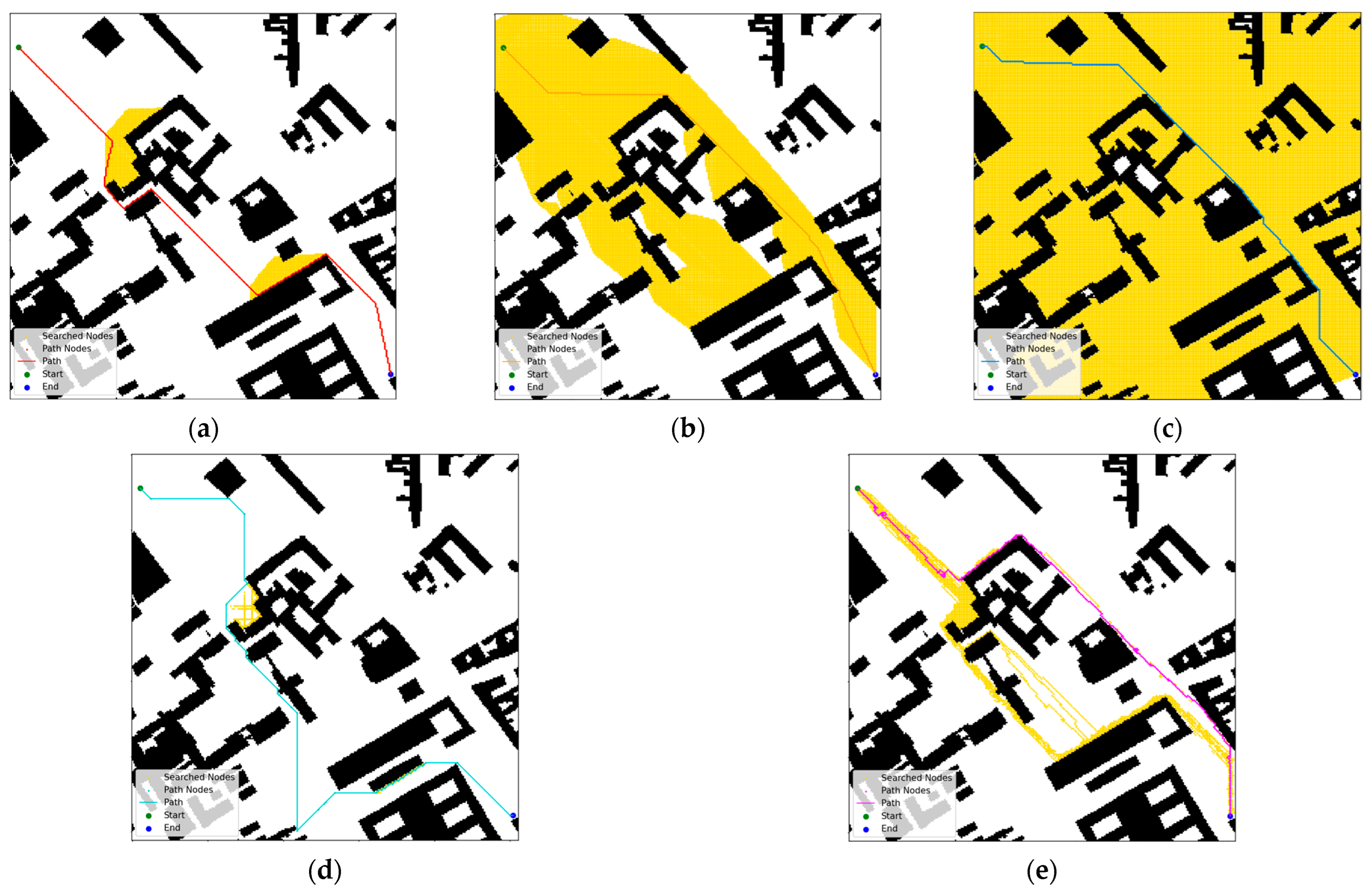
4.1.2. Results and Analysis of Path Planning Simulation Experiment
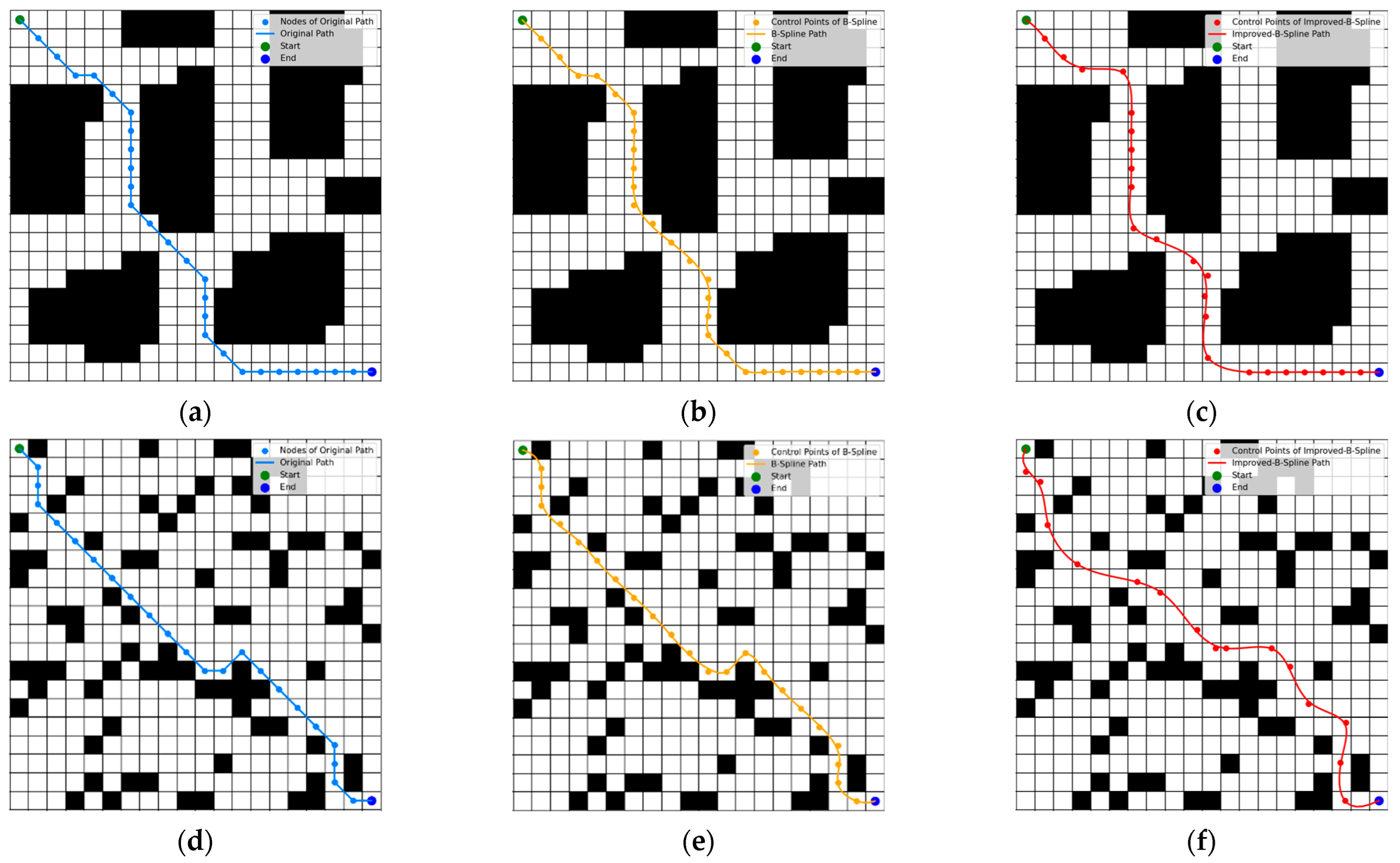
4.2. Path Smoothing Algorithm Simulation Experiment
4.2.1. Parameters for the Path Smoothing Algorithm Simulation Experiment
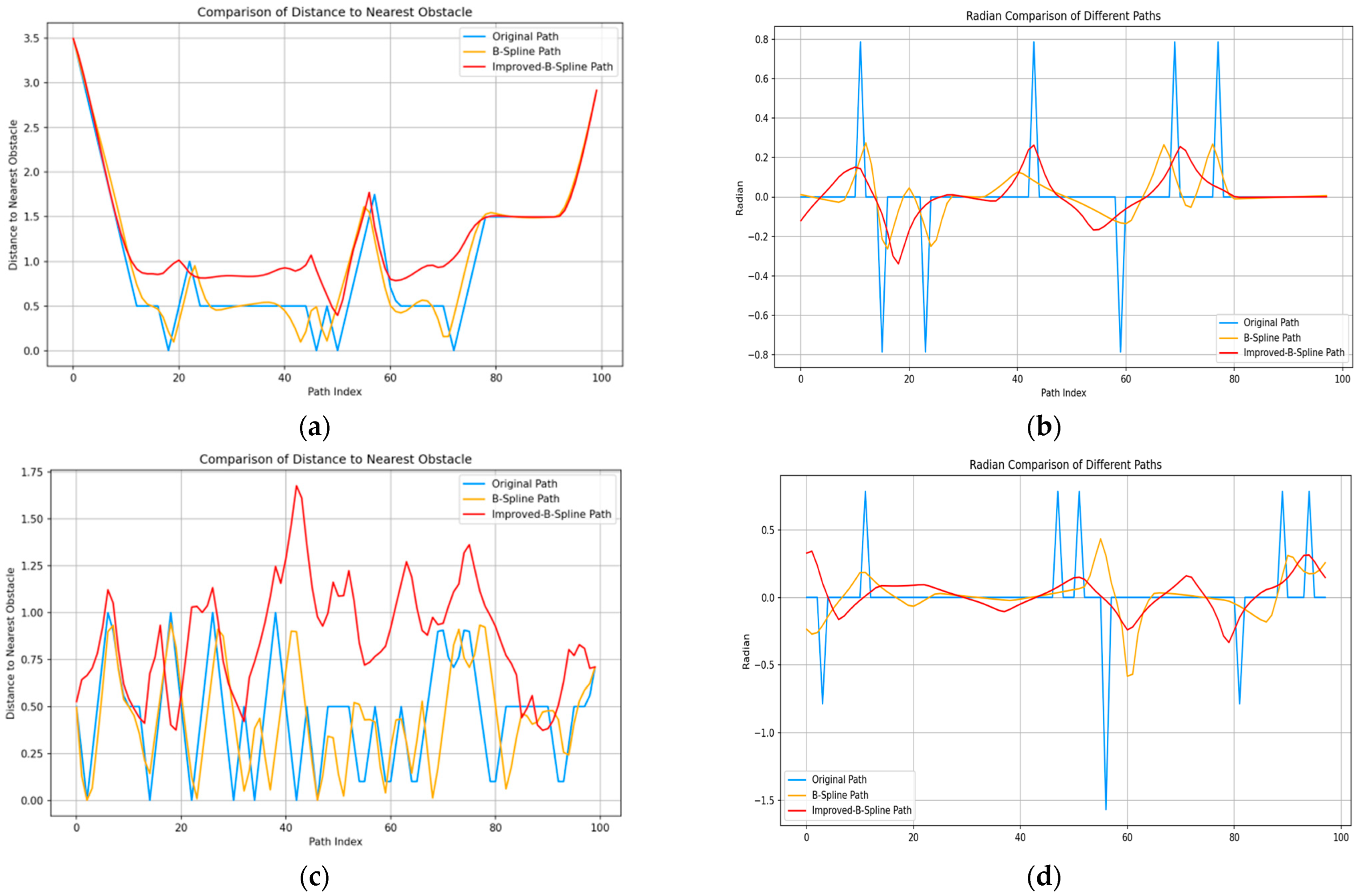
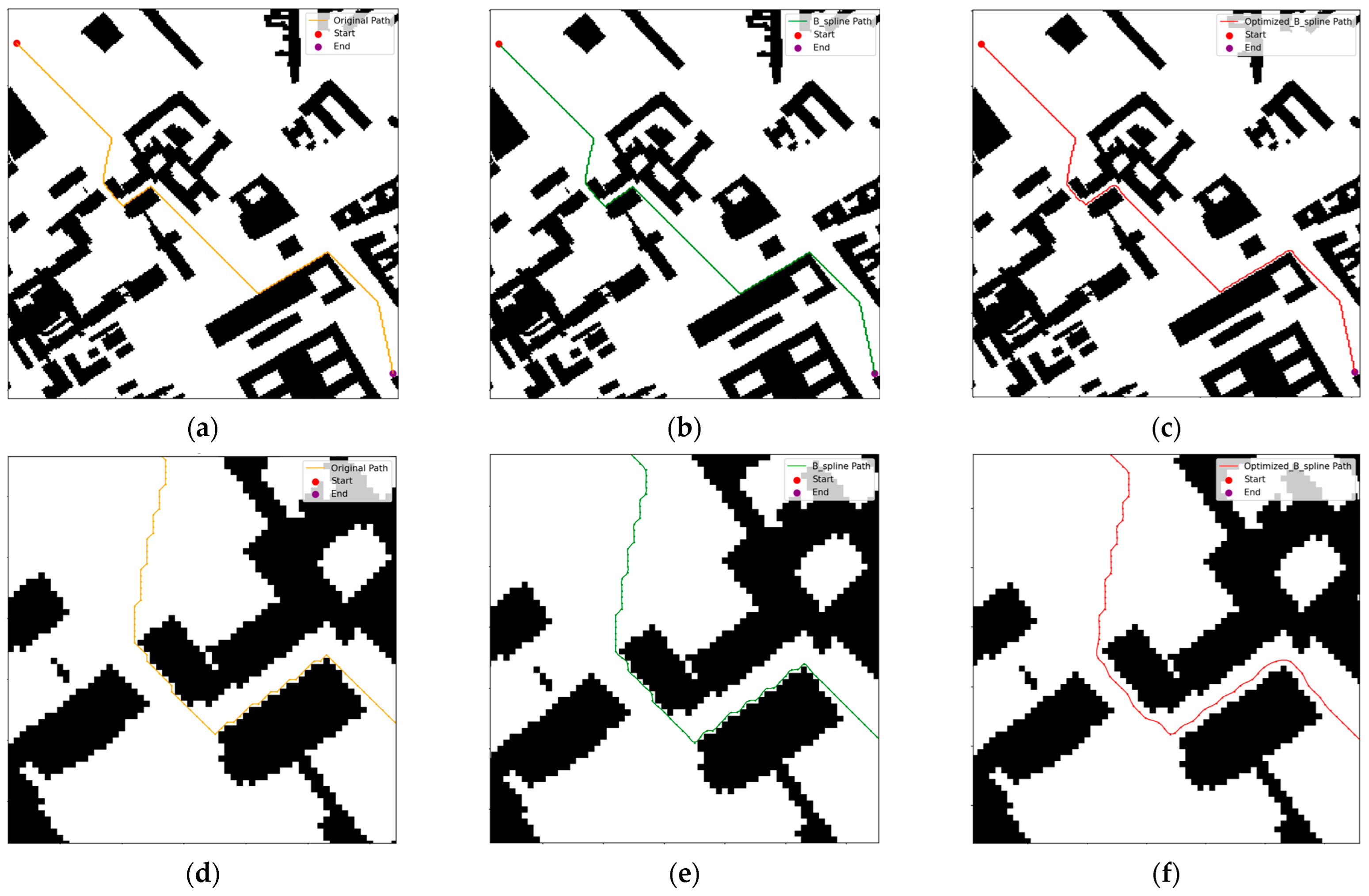
4.2.2. Results and Analysis of the Path Smoothing Algorithm Simulation Experiment
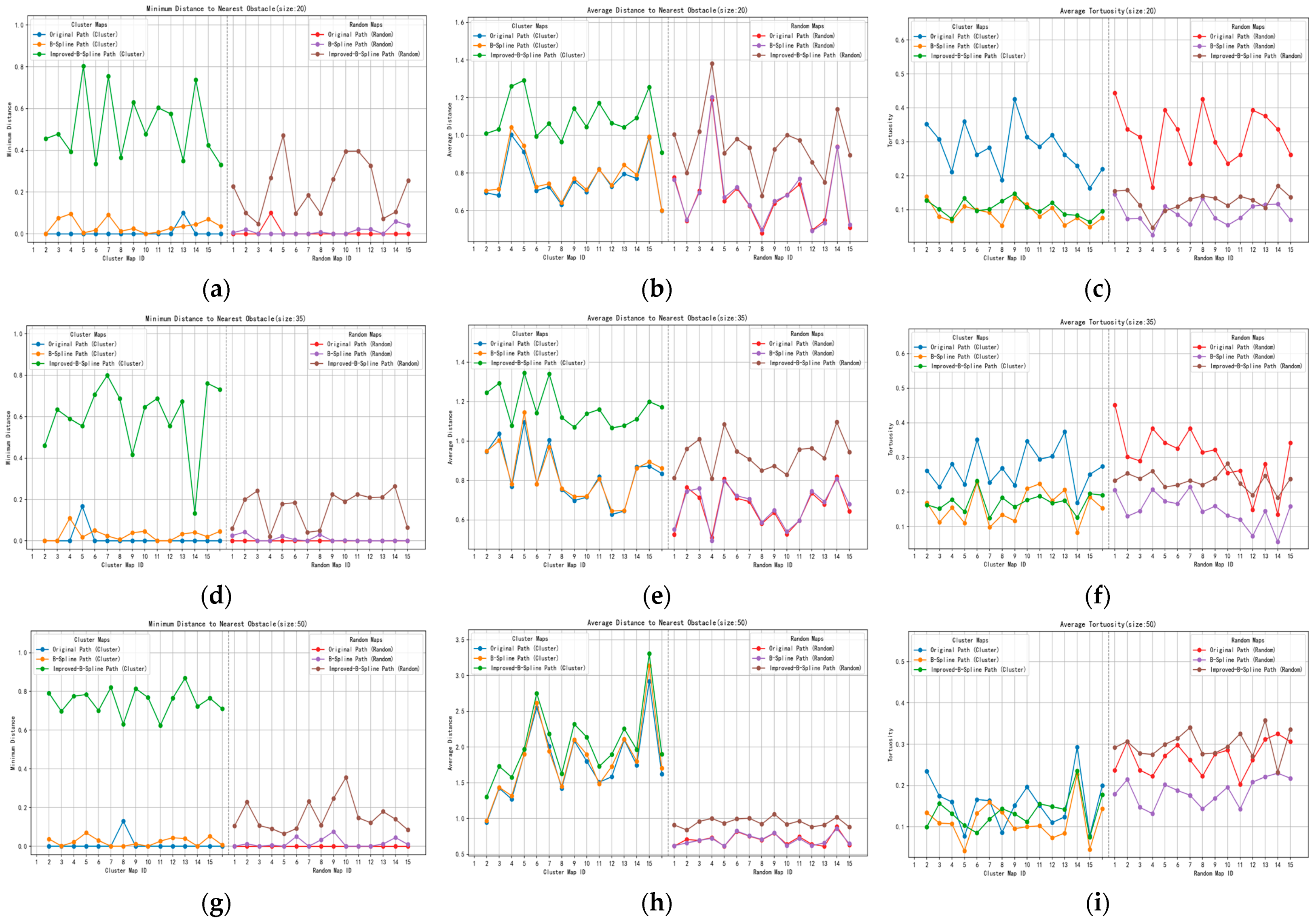
4.3. Benchmark Tests
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hassan, M.U.; Ullah, M.; Iqbal, J. Towards Autonomy in Agriculture: Design and Prototyping of a Robotic Vehicle with Seed Selector. In Proceedings of the 2016 2nd International Conference on Robotics and Artificial Intelligence (ICRAI), Rawalpindi, Pakistan, 1–2 November 2016; pp. 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, P. Path Planning Techniques for Mobile Robots: Review and Prospect. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 227, 120254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, L.M.; Boccardo, D.R.; Machado, R.C.; Miyazawa, F.K.; de Sá, V.G.P.; Szwarcfiter, J.L. Dijkstra graphs. Discret. Appl. Math. 2017, 261, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Lin, H.; Ouyang, J.; Huang, D. Combined Improved A* and Greedy Algorithm for Path Planning of Multi-Objective Mobile Robot. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, S.; Gao, Y.; Wang, P.; Schonfeld, P.; Zou, Y.; He, Q. 3D Constrained Hybrid A*: Improved Vehicle Path Planning Algorithm for Cost-Effective Road Alignment Design. Autom. Constr. 2024, 166, 105645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Fan, K.; Sun, W. Density Gradient-RRT: An Improved Rapidly Exploring Random Tree Algorithm for UAV Path Planning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 252, 124121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Chen, H.; Pohovey, J.; Driggs-Campbell, K. Neural Informed RRT*: Learning-based Path Planning with Point Cloud State Representations under Admissible Ellipsoidal Constraints. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.14595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worring, A.; Mayer, B.E.; Hamacher, K. Genetic Algorithm Niching by (Quasi-)infinite Memory. In Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference (GECCO ’21), Lille, France, 10–14 July 2021; pp. 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.; López, N.; Rodríguez, I. A Full Process Algebraic Representation of Ant Colony Optimization. Inf. Sci. 2024, 658, 120025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, Z.; Zou, C. Generational Exclusion Particle Swarm Optimization with Central Aggregation Mechanism. In Advances in Swarm Intelligence; Tan, Y., Shi, Y., Niu, B., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 13344, p. 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; An, Y.; Huang, Q.L.; Cui, Y.H.; Hu, H.S. Dynamic Path Planning of Mobile Robots Using Adaptive Dynamic Programming. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 235, 121112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Q.; Xu, X.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y. Research Progress of Nature-Inspired Metaheuristic Algorithms in Mobile Robot Path Planning. Electronics 2023, 12, 3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, A.; Markdahl, J. Swarm Bug Algorithms for Path Generation in Unknown Environments. In Proceedings of the 2023 62nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Singapore, 13–15 December 2023; pp. 6958–6965. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Cui, Y. An Autonomous Navigation Method for Orchard Rows Based on a Combination of an Improved A* Algorithm and SVR. Precis. Agric. 2024, 25, 429–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Huang, X.; Cui, J.; Liu, C.; Xiao, W. Modified adaptive ant colony optimization algorithm and its application for solving path planning of mobile robot. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 215, 119410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Duan, H.; Huo, M.; Wu, H. Enhancing the Heuristic Function of Improved A Algorithm for UAV Robotic Arm Path Planning Using Dynamic Pigeon-Inspired Optimization. In Advances in Guidance, Navigation and Control: ICGNC 2024; Yan, L., Duan, H., Deng, Y., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2025; Volume 1343, p. 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Peng, L.; Zhu, F. Path Planning for Mobile Robots Based on JPS and Improved A* Algorithm. J. Front. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2021, 15, 2233–2240. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Chen, C.; Shen, J.; Liu, G.; Xu, F. A Self-adaptive Neighborhood Search A-star Algorithm for Mobile Robots Global Path Planning. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2025, 123, 110018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Fang, X. ESSAWOA: Enhanced Whale Optimization Algorithm Integrated with Salp Swarm Algorithm for Global Optimization. Eng. Comput. 2022, 38 (Suppl. S1), 797–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmamoun, Z.; Khlie, K.; Bektemyssova, G.; Dehghani, M.; Gherabi, Y. Bobcat Optimization Algorithm: An Effective Bio-Inspired Metaheuristic Algorithm for Solving Supply Chain Optimization Problems. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmamoun, Z.; Khlie, K.; Dehghani, M.; Gherabi, Y. WOA: Wombat Optimization Algorithm for Solving Supply Chain Optimization Problems. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, H.; You, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, F. The Hybrid Path Planning Algorithm Based on Improved A* and Artificial Potential Field for Unmanned Surface Vehicle Formations. Ocean Eng. 2021, 223, 108709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Wang, Z.; Zou, L. An Improved PSO Algorithm for Smooth Path Planning of Mobile Robots Using Continuous High-degree Bezier Curve. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 100, 106960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Sun, P.; Ding, W.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y. Gradient-based Autonomous Obstacle Avoidance Trajectory Planning for B-spline UAVs. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P.E.; Nilsson, N.J.; Raphael, B. A Formal Basis for the Heuristic Determination of Minimum Cost Paths. IEEE Trans. Syst. Sci. Cybern. 1968, 4, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualigah, L.; Shehab, M.; Alshinwan, M.; Alabool, H. Salp Swarm Algorithm: A Comprehensive Survey. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 11195–11215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Gandomi, A.H.; Mirjalili, S.Z.; Saremi, S.; Faris, H.; Mirjalili, S.M. Salp Swarm Algorithm: A bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2017, 114, 163–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nautiyal, B.; Prakash, R.; Vimal, V.; Liang, G.; Chen, H. Improved Salp Swarm Algorithm with Mutation Schemes for Solving Global Optimization and Engineering Problems. Eng. Comput. 2022, 38, 3927–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhao, D.; Fan, T.; Long, F.; Fang, C.; Long, Y. Autonomous Underwater Vehicle Path Planning Based on Improved Salp Swarm Algorithm. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlShabi, M.A.; Ballous, K.; Nassif, A.B.; Bettayeb, M.; Obaideen, K.; Gadsden, S.A. Path Planning for a UGV using Salp Swarm Algorithm. In Proceedings of the Autonomous Systems: Sensors, Processing, and Security for Ground, Air, Sea, and Space Vehicles and Infrastructure, National Harbor, MD, USA, 21–26 April 2024; Volume 13052. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S. Control Point Reduction for Lofted B-spline Surface Interpolation Based on Serial Closed Contours. Comput. Appl. Math. 2023, 42, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter Name | Value or Range |
|---|---|
| [0.5, 2] | |
| [0.5, 2] | |
| [0.1, 1] | |
| Population Size | 10 |
| Number of Iterations | 100 |
| Map ID | Algorithm | Cluster Maps | Random Maps | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SN | Length | Time (ms) | SN | Length | Time (ms) | ||
| 1 | SSA-A* | 44 | 53.36 | 1.41 | 39 | 51.25 | 0.78 |
| A* | 261 | 53.36 | 4.01 | 191 | 49.84 | 1.54 | |
| Dijkstra | 631 | 53.36 | 4.38 | 979 | 49.84 | 4.05 | |
| JPS-A* | 16 | 71.66 | 1.01 | 30 | 62.14 | 0.62 | |
| ACO | 235 | 54.18 | 24.15 | 234 | 50.43 | 26.55 | |
| 2 | SSA-A* | 53 | 52.43 | 1.82 | 50 | 52.43 | 0.92 |
| A* | 239 | 51.6 | 4.17 | 297 | 51.60 | 2.64 | |
| Dijkstra | 651 | 51.6 | 4.35 | 982 | 51.60 | 4.63 | |
| JPS-A* | 23 | 62.38 | 1.51 | 29 | 60.97 | 0.9 | |
| ACO | 248 | 51.6 | 31.31 | 190 | 54.43 | 23.33 | |
| 3 | SSA-A* | 41 | 51.6 | 1.38 | 41 | 51.84 | 0.99 |
| A* | 187 | 51.6 | 2.86 | 309 | 51.01 | 3.34 | |
| Dijkstra | 641 | 51.6 | 4.1 | 981 | 51.01 | 4.58 | |
| JPS-A* | 26 | 58.63 | 1.47 | 27 | 62.14 | 0.85 | |
| ACO | 191 | 52.43 | 28.24 | 206 | 53.25 | 24.77 | |
| 4 | SSA-A* | 40 | 51.01 | 1.42 | 48 | 52.43 | 0.97 |
| A* | 209 | 51.01 | 3.37 | 278 | 51.60 | 2.72 | |
| Dijkstra | 644 | 51.01 | 4.55 | 967 | 51.60 | 4.66 | |
| JPS-A* | 21 | 66.63 | 1.45 | 30 | 61.56 | 0.79 | |
| ACO | 233 | 51.6 | 31.85 | 235 | 55.50 | 25.22 | |
| 5 | SSA-A* | 41 | 51.01 | 1.41 | 55 | 53.60 | 1.19 |
| A* | 178 | 51.01 | 2.75 | 338 | 52.77 | 3.25 | |
| Dijkstra | 643 | 51.01 | 4.27 | 940 | 52.77 | 3.82 | |
| JPS-A* | 36 | 61.8 | 2.38 | 37 | 61.80 | 0.69 | |
| ACO | 205 | 52.43 | 31.69 | 137 | 58.08 | 12.26 | |
| 6 | SSA-A* | 45 | 53.94 | 1.47 | 43 | 51.60 | 0.84 |
| A* | 214 | 53.36 | 3.21 | 229 | 50.43 | 1.89 | |
| Dijkstra | 654 | 53.36 | 4.47 | 989 | 50.43 | 3.98 | |
| JPS-A* | 21 | 59.21 | 1.52 | 25 | 61.56 | 0.66 | |
| ACO | 295 | 54.77 | 33.05 | 170 | 50.43 | 29.83 | |
| 7 | SSA-A* | 52 | 51.01 | 1.77 | 43 | 52.43 | 0.86 |
| A* | 207 | 51.01 | 3.51 | 201 | 49.84 | 1.75 | |
| Dijkstra | 612 | 51.01 | 4.12 | 993 | 49.84 | 3.91 | |
| JPS-A* | 20 | 70.38 | 1.58 | 30 | 62.97 | 0.77 | |
| ACO | 251 | 51.84 | 24.81 | 168 | 51.25 | 29.35 | |
| 8 | SSA-A* | 43 | 54.43 | 1.54 | 40 | 51.25 | 0.81 |
| A* | 260 | 52.77 | 4.34 | 230 | 50.43 | 2.19 | |
| Dijkstra | 629 | 52.77 | 4.46 | 983 | 50.43 | 4 | |
| JPS-A* | 19 | 63.31 | 1.45 | 24 | 62.73 | 0.64 | |
| ACO | 242 | 56.43 | 34.47 | 230 | 61.74 | 24.88 | |
| 9 | SSA-A* | 52 | 53.84 | 1.72 | 46 | 52.77 | 0.88 |
| A* | 234 | 52.18 | 3.8 | 364 | 52.18 | 3.04 | |
| Dijkstra | 639 | 52.18 | 4.39 | 983 | 52.18 | 3.8 | |
| JPS-A* | 15 | 58.63 | 1.05 | 26 | 62.14 | 0.69 | |
| ACO | 292 | 60.08 | 36.16 | 202 | 57.84 | 28.28 | |
| 10 | SSA-A* | 42 | 52.18 | 1.45 | 58 | 56.43 | 0.99 |
| A* | 251 | 52.18 | 3.96 | 300 | 55.60 | 2.37 | |
| Dijkstra | 653 | 52.18 | 4.42 | 995 | 55.60 | 3.83 | |
| JPS-A* | 17 | 62.73 | 1.38 | 89 | 80.63 | 2.26 | |
| ACO | 220 | 52.18 | 31.52 | 273 | 60.67 | 29.63 | |
| 11 | SSA-A* | 52 | 55.36 | 1.53 | 53 | 53.84 | 0.89 |
| A* | 239 | 54.53 | 3.84 | 319 | 51.60 | 2.55 | |
| Dijkstra | 586 | 54.53 | 3.91 | 994 | 51.60 | 3.9 | |
| JPS-A* | 19 | 60.04 | 1.29 | 35 | 60.63 | 0.88 | |
| ACO | 177 | 56.18 | 35.74 | 233 | 53.84 | 25.41 | |
| 12 | SSA-A* | 44 | 54.18 | 1.41 | 51 | 52.18 | 0.85 |
| A* | 251 | 53.36 | 4.02 | 353 | 51.60 | 2.99 | |
| Dijkstra | 657 | 53.36 | 4.55 | 977 | 51.60 | 3.91 | |
| JPS-A* | 17 | 69.21 | 1.38 | 43 | 63.56 | 1.23 | |
| ACO | 192 | 55.01 | 36.54 | 242 | 54.18 | 24.47 | |
| 13 | SSA-A* | 52 | 53.36 | 1.47 | 45 | 52.43 | 0.83 |
| A* | 227 | 51.6 | 3.72 | 362 | 51.60 | 3.51 | |
| Dijkstra | 627 | 51.6 | 4.18 | 965 | 51.60 | 4.42 | |
| JPS-A* | 23 | 67.31 | 1.49 | 30 | 62.14 | 0.83 | |
| ACO | 169 | 53.84 | 33.62 | 239 | 54.67 | 26.32 | |
| 14 | SSA-A* | 57 | 57.94 | 1.67 | 43 | 51.60 | 1.03 |
| A* | 188 | 56.28 | 3.28 | 194 | 49.84 | 2.05 | |
| Dijkstra | 609 | 56.28 | 4.36 | 971 | 49.84 | 4.55 | |
| JPS-A* | 19 | 62.63 | 2.5 | 25 | 58.63 | 0.74 | |
| ACO | 171 | 58.77 | 36.19 | 187 | 52.08 | 26.83 | |
| 15 | SSA-A* | 45 | 54.77 | 1.5 | 43 | 51.60 | 0.98 |
| A* | 229 | 52.77 | 3.86 | 346 | 51.60 | 3.53 | |
| Dijkstra | 630 | 52.77 | 4.73 | 968 | 51.60 | 4.61 | |
| JPS-A* | 20 | 68.63 | 2 | 26 | 60.97 | 0.74 | |
| ACO | 189 | 57.6 | 32.46 | 251 | 52.43 | 25.72 | |
| Map Size | 20 | 35 | 50 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Map Type | Cluster Map | Random Map | Cluster Map | Random Map | Cluster Map | Random Map | |
| Average Time Reduction in SSA-A* | vs. A* (%) | 30.79% | 36.56% | 57.45% | 63.09% | 62.82% | 67.75% |
| vs. Dijkstra (%) | 27.89% | 59.35% | 64.69% | 77.85% | 75.94% | 84.12% | |
| vs. ACO (%) | 95.57% | 96.92% | 95.16% | 96.16% | 95.04% | 97.61% | |
| Average Searched Nodes Reduction in SSA-A* | vs. A* (%) | 67.17% | 72.52% | 78.87% | 83.08% | 81.86% | 86.10% |
| vs. Dijkstra (%) | 84.64% | 91.01% | 92.58% | 95.19% | 95.00% | 96.73% | |
| vs. ACO (%) | 64.32% | 71.83% | 78.03% | 77.43% | 79.37% | 82.75% | |
| Average Distance Increase in SSA-A* vs. A* (%) | 1.62% | 1.46% | 1.48% | 2.18% | 0.58% | 1.82% | |
| Average Distance Reduction in SSA-A* | vs. JPS-A* (%) | 14.85% | 18.93% | 22.24% | 22.33% | 15.00% | 21.96% |
| vs. ACO (%) | 4.45% | 4.72% | 2.17% | 3.76% | 5.41% | 5.00% | |
| Parameter Name | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| Smoothing Factor () | 0.1 |
| Number of Interpolation Points | 100 |
| Map ID | Algorithm | Cluster Maps | Random Maps | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD | AD | AT | MD | AD | AT | ||
| 1 | A | 0.0000 | 0.6945 | 0.3521 | 0.0000 | 0.7765 | 0.4439 |
| B | 0.0000 | 0.7063 | 0.1387 | 0.0060 | 0.7638 | 0.1452 | |
| C | 0.4564 | 1.0097 | 0.1270 | 0.2277 | 1.0051 | 0.1549 | |
| 2 | A | 0.0000 | 0.6809 | 0.3073 | 0.0000 | 0.5451 | 0.3366 |
| B | 0.0752 | 0.7149 | 0.0792 | 0.0213 | 0.5507 | 0.0732 | |
| C | 0.4781 | 1.0321 | 0.1014 | 0.1000 | 0.7996 | 0.1575 | |
| 3 | A | 0.0000 | 1.0024 | 0.2115 | 0.0000 | 0.7057 | 0.3142 |
| B | 0.0961 | 1.0423 | 0.0668 | 0.0000 | 0.6960 | 0.0746 | |
| C | 0.3939 | 1.2601 | 0.0730 | 0.0480 | 1.0206 | 0.1132 | |
| 4 | A | 0.0000 | 0.9127 | 0.3600 | 0.1000 | 1.1887 | 0.1653 |
| B | 0.0046 | 0.9452 | 0.1102 | 0.0000 | 1.2021 | 0.0252 | |
| C | 0.8040 | 1.2919 | 0.1340 | 0.2677 | 1.3819 | 0.0469 | |
| 5 | A | 0.0000 | 0.7055 | 0.2618 | 0.0000 | 0.6499 | 0.3927 |
| B | 0.0183 | 0.7269 | 0.0994 | 0.0000 | 0.6707 | 0.1102 | |
| C | 0.3346 | 0.9950 | 0.0964 | 0.4718 | 0.9050 | 0.0967 | |
| 6 | A | 0.0000 | 0.7267 | 0.2827 | 0.0000 | 0.7176 | 0.3366 |
| B | 0.0919 | 0.7426 | 0.0915 | 0.0000 | 0.7250 | 0.0857 | |
| C | 0.7542 | 1.0624 | 0.1014 | 0.0975 | 0.9804 | 0.1088 | |
| 7 | A | 0.0000 | 0.6324 | 0.1870 | 0.0000 | 0.6256 | 0.2356 |
| B | 0.0127 | 0.6415 | 0.0532 | 0.0000 | 0.6289 | 0.0569 | |
| C | 0.3643 | 0.9650 | 0.1250 | 0.1845 | 0.9347 | 0.1308 | |
| 8 | A | 0.0000 | 0.7558 | 0.4254 | 0.0000 | 0.4808 | 0.4254 |
| B | 0.0260 | 0.7715 | 0.1350 | 0.0084 | 0.4984 | 0.1336 | |
| C | 0.6290 | 1.1425 | 0.1471 | 0.0974 | 0.6789 | 0.1402 | |
| 9 | A | 0.0000 | 0.6990 | 0.3142 | 0.0000 | 0.6392 | 0.2992 |
| B | 0.0000 | 0.7113 | 0.1155 | 0.0000 | 0.6500 | 0.0748 | |
| C | 0.4775 | 1.0443 | 0.1069 | 0.2611 | 0.9248 | 0.1339 | |
| 10 | A | 0.0000 | 0.8205 | 0.2856 | 0.0000 | 0.6837 | 0.2356 |
| B | 0.0084 | 0.8199 | 0.0793 | 0.0000 | 0.6818 | 0.0546 | |
| C | 0.6038 | 1.1713 | 0.0950 | 0.3946 | 1.0015 | 0.1122 | |
| 11 | A | 0.0000 | 0.7276 | 0.3200 | 0.0000 | 0.7396 | 0.2618 |
| B | 0.0277 | 0.7350 | 0.1053 | 0.0227 | 0.7692 | 0.0760 | |
| C | 0.5741 | 1.0648 | 0.1206 | 0.3956 | 0.9740 | 0.1391 | |
| 12 | A | 0.1000 | 0.7944 | 0.2618 | 0.0000 | 0.4960 | 0.3927 |
| B | 0.0359 | 0.8430 | 0.0541 | 0.0221 | 0.4932 | 0.1104 | |
| C | 0.3501 | 1.0428 | 0.0859 | 0.3259 | 0.8577 | 0.1283 | |
| 13 | A | 0.0000 | 0.7710 | 0.2291 | 0.0000 | 0.5484 | 0.3756 |
| B | 0.0458 | 0.7907 | 0.0758 | 0.0000 | 0.5329 | 0.1150 | |
| C | 0.7377 | 1.0929 | 0.0833 | 0.0731 | 0.7502 | 0.1057 | |
| 14 | A | 0.0000 | 0.9868 | 0.1636 | 0.0000 | 0.9388 | 0.3366 |
| B | 0.0702 | 0.9931 | 0.0487 | 0.0606 | 0.9384 | 0.1163 | |
| C | 0.4245 | 1.2563 | 0.0641 | 0.1057 | 1.1389 | 0.1701 | |
| 15 | A | 0.0000 | 0.5984 | 0.2199 | 0.0000 | 0.5090 | 0.2618 |
| B | 0.0365 | 0.6015 | 0.0754 | 0.0419 | 0.5247 | 0.0702 | |
| C | 0.3309 | 0.9086 | 0.0961 | 0.2562 | 0.8942 | 0.1368 | |
| Algorithm | Comparison to A* (100%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Searched-Nodes (%) | Length (%) | Time (%) | |
| SSA-A* | 4.39 | 104.83 | 6.31 |
| Dijkstra | 320.17 | 100.00 | 94.08 |
| A*-JPS | 0.70 | 130.75 | 325.38 |
| ACO | 12.04 | 132.65 | 210.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, H.; Shang, T.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, L. Salp Swarm Algorithm Optimized A* Algorithm and Improved B-Spline Interpolation in Path Planning. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5583. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105583
Zhou H, Shang T, Wang Y, Zuo L. Salp Swarm Algorithm Optimized A* Algorithm and Improved B-Spline Interpolation in Path Planning. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(10):5583. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105583
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Hang, Tianning Shang, Yongchuan Wang, and Long Zuo. 2025. "Salp Swarm Algorithm Optimized A* Algorithm and Improved B-Spline Interpolation in Path Planning" Applied Sciences 15, no. 10: 5583. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105583
APA StyleZhou, H., Shang, T., Wang, Y., & Zuo, L. (2025). Salp Swarm Algorithm Optimized A* Algorithm and Improved B-Spline Interpolation in Path Planning. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5583. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105583





