Abstract
To address the issue of missed detection for small-scale occluded pedestrians in dense scenes, this paper proposes an improved YOLOv8 detection algorithm named Dense-YOLOv8. Firstly, to resolve the difficulty of extracting features from small-scale pedestrians in dense environments, a backbone network enhanced with deformable convolution and dynamic convolution is adopted to improve feature extraction capabilities. Simultaneously, a multi-scale linear spatial attention module is designed to amplify features of visible parts of occluded pedestrians while suppressing interference from complex backgrounds. Secondly, a small-scale pedestrian detection head is introduced in the neck of the YOLOv8 network to enhance detection performance for diminutive pedestrians. Finally, to improve training efficiency, a novel weighted loss function named DFL-SIoU is developed to accelerate model convergence. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm achieves superior performance on two challenging dense pedestrian datasets, CrowdHuman and WiderPerson, significantly enhancing detection capabilities in dense scenarios. Comparative evaluations with other state-of-the-art pedestrian detection models further confirm the strong competitiveness of the proposed model.
1. Introduction
Pedestrian detection is a prominent research topic in computer vision, focusing on accurately identifying pedestrians and determining their locations. As a fundamental technology, pedestrian detection algorithms have been extensively adopted in both academic research and industrial applications. Current technical challenges primarily lie in occlusion and scale variation issues in dense scenarios. In crowded environments, pedestrian targets often exhibit small scale and heavy mutual occlusion, posing substantial detection challenges. Key difficulties include:
- (a)
- Occluded pedestrians exhibit sparse or blurred features, hindering effective feature extraction by neural networks.
- (b)
- Overcrowding leads to reduced individual target resolution, increasing missed-detection rates.
- (c)
- Complex background features in dense scenes impair accurate classification and localization, causing false positives.
To address occlusion challenges, Li Qi et al. [1] proposed partitioning pedestrian proposals using prior ratios and extracting region-specific features to recover occluded local features through body structure information. Zhang [2] developed FC-Net, a feature learning method that emphasizes visible pedestrian features while suppressing occluded regions through a novel self-activation mechanism. Liu Yi et al. [3] enhanced Faster R-CNN [4] with UAST-RCNN, improving global receptive fields, feature sample quality, and multi-scale training to boost occlusion handling.
Zhang et al. [5] introduced a variational Bayesian autoencoder-based algorithm that models dense proposals as latent variables, enhancing a conventional detector into a variational pedestrian detection framework. Chu et al. [6] observed persistent missed detection of small-scale pedestrians despite dense proposal predictions. For scale variation issues, Hong et al. [7] enhanced multi-scale feature optimization by highlighting scale-specific features and enabling cross-layer feature sharing between deep and shallow networks. Huang et al. [8] proposed a feature alignment pyramid network for dense image prediction, aligning upsampled features with local features via learned pixel offsets. While YOLOv8 [9,10] (2023) achieves real-time performance with high accuracy, current deep learning methods still struggle with missed detection and false alarms in dense pedestrian scenarios. Existing feature fusion and reconstruction approaches show limited performance gains in noisy, crowded environments.
To overcome these limitations, this paper proposes an enhanced YOLOv8-based algorithm focusing on multi-scale occluded feature enhancement and localization capability improvement. Key contributions include the following.
- (1)
- We designed a C2f_D2CN module to address the challenge of extracting small-scale pedestrian features in dense scenarios. This module enhances feature extraction capability by incorporating a backbone network improved with deformable convolution and dynamic convolution. Additionally, a multi-scale linear spatial attention module was designed to enhance the visible features of occluded pedestrians while suppressing interference from complex backgrounds.
- (2)
- We integrated a small-scale pedestrian detection head into the neck of the YOLOv8 network, effectively improving the detection accuracy of small-scale pedestrians in dense scenarios. Additionally, to improve training efficiency, we designed a novel loss function named DFL-SIoU, which enhances model convergence and achieves better bounding box regression performance.
- (3)
- We conducted experiments on two challenging dense pedestrian datasets, CrowdHuman and WiderPerson, and the detection accuracy showed significant improvement compared to most existing methods.
This work advances dense pedestrian detection by systematically addressing feature extraction, scale sensitivity, and localization precision in complex real-world scenarios.
2. Related Work
2.1. Pedestrian Detection
Pedestrian detection algorithms based on deep learning can be categorized into two-stage and single-stage approaches. Two-stage detection algorithms are candidate box-based methods, with representative examples including Fast R-CNN [11], Faster R-CNN [4], and SA-Fast R-CNN [12]. Compared to two-stage methods, which often suffer from slower inference speeds, typical single-stage detectors such as the single-shot multibox detector (SSD) [13] and YOLO can simultaneously perform object localization and classification, resulting in faster runtimes and greater advantages in practical applications. Although the SSD algorithm improves detection efficiency and enhances adaptability to multi-scale objects, its accuracy is somewhat limited. Lin et al. [14] introduced a new loss function, focal loss, to address class imbalance issues during training and utilize feature pyramid networks and anchor boxes to extract multi-scale features and locate objects. Building on SSD, Dong et al. [15] adopted cross-layer feature adaptive fusion to make the extracted features more directional, thereby improving pedestrian detection accuracy. Redmon et al. [16] proposed YOLO, a single-stage object detection algorithm that uses a single neural network to predict both object classes and locations, achieving high speed while maintaining high accuracy. With the evolution of pedestrian detection, models such as YOLOv2 [17] and YOLOv3 [18] were successively developed. In 2020, Glen J. Braden introduced YOLOv5, an advancement built upon YOLOv4 [19] offering improved speed, accuracy, and deployment flexibility. Additionally, in September 2022, the visual AI department of Meituan released YOLOv6 [20] on ArXiv, providing a range of models with varying sizes for industrial applications. In July 2022, Glen J. Braden published YOLOv7 [21], achieving the best results in both speed and accuracy. In 2023, Ultralytics released YOLOv8 [10], achieving higher precision and speed compared to previous versions. YOLOv9 [22] integrates advancements grounded in the information bottleneck principle and invertible function design, significantly improving information transmission and computational efficiency. YOLOv10 [23] further enhanced consistency and implemented NMS-free dual-task training, focusing on both efficiency and accuracy improvements. In 2024, Ultralytics proposed YOLOv11 [24], further enhancing detection accuracy and usability, making it an excellent choice for tasks such as object detection and tracking, pedestrian detection, instance segmentation, image classification, and pose estimation.
2.2. Dense Pedestrian Detection
In densely populated scenes, occlusions among pedestrians frequently result in the loss of critical target information, causing missed detections. Small pedestrian targets typically suffer from low resolution, making feature extraction more challenging. To address these issues, Fu et al. [25] proposed an improved YOLOv5s-DC algorithm based on YOLOv5s, which employs two different types of convolutions to decouple the YOLO head, thereby enhancing the focus on regression and classification tasks. Hong et al. [7] enhanced multi-scale feature optimization by highlighting scale-specific features and enabling cross-layer feature sharing between deep and shallow networks. Huang et al. [8] proposed a feature-aligned pyramid network for dense image prediction, aligning upsampled features with local features through learned pixel offsets. Xu et al. [26] introduced beta R-CNN, which models the relationship between full-body and visible bounding boxes using a beta representation for pedestrian targets, and proposed beta NMS to better distinguish highly overlapping pedestrians in dense scenes. Wang et al. [27] proposed DeFCN, a fully convolutional one-stage object detector based on FCOS, which achieves end-to-end detection in dense scenes without requiring post-processing like NMS. Li et al. [28] proposed GR-YOLO, an extension of YOLOv8, which enhances feature extraction capabilities and reconstructs the network’s neck by employing an aggregation–distribution mechanism to promote more efficient information exchange. Dong et al. [29] proposed HCA-YOLO, which enhances the optimized YOLOv8 baseline by introducing the HCA module to increase the model’s focus on non-salient objects. Li et al. [30] proposed a novel dense pedestrian detection algorithm called LEI-YOLO. By embedding a large kernel perception (LKP) module into the backbone network, the model captures global information on occluded targets, enabling more comprehensive feature representation. An et al. [31] introduced GC-YOLOv9, an improved version of YOLOv9 that replaces CBS layers with ghost convolution to reduce the number of model parameters and computational complexity while enhancing detection performance.
3. Methodology
In dense scenes, pedestrians are typically small, occluded, and appear in varying poses and lighting conditions, leading to common detection failures such as false positives and missed detections. These failures stem from two major limitations: (1) limited spatial adaptability—standard convolutional backbones struggle to capture deformable and irregular pedestrian shapes, especially in occluded scenarios, due to their fixed geometric receptive fields; and (2) inefficient small-object feature fusion—shallow features often lack semantic richness, while deeper features lack spatial detail, making it difficult to localize small objects in cluttered environments. To mitigate these challenges, we propose an enhanced dense pedestrian detection model based on YOLOv8, which integrates multi-scale feature fusion and linear spatial attention mechanisms, with the architecture illustrated in Figure 1. The original C2f module is replaced with a C2f-DP2N (deformable pyramid convolution network) module. By stacking multiple deformable convolution layers, this design expands the network’s receptive field and captures richer multi-scale pedestrian features, particularly critical for resolving small-scale target extraction in crowded scenes. A multi-scale linear spatial attention (MLSA) module is introduced to dynamically enhance visible features of occluded pedestrians while suppressing background interference. This module prioritizes discriminative spatial regions across scales, improving robustness in complex environments. A dedicated 160 × 160 small-target detection head is added to amplify sensitivity to diminutive pedestrians, addressing the prevalent issue of missed detections for low-resolution targets in dense scenarios. A novel loss is proposed to accelerate model convergence and refine bounding box regression. This hybrid loss combines the advantages of distribution-aware focal loss and adaptive IoU metrics, ensuring precise localization under occlusion and scale variation.
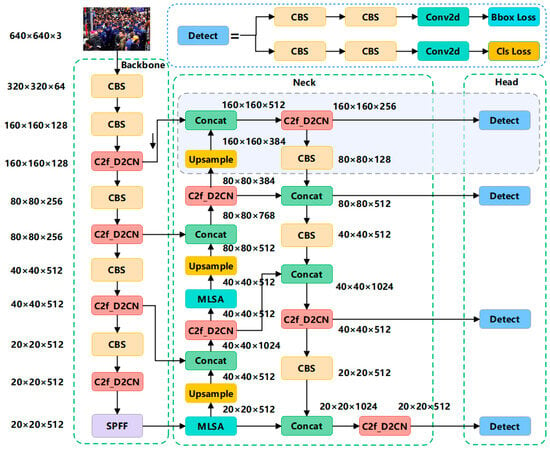
Figure 1.
Network architecture diagram. In the backbone component, C2f-D2CN module is proposed to replace the original C2f module. In the neck layer, a multi-scale linear spatial attention (MLS_Attention) module is designed to enhance the visible features of occluded pedestrians while suppressing interference from complex backgrounds. In the head layer, a small-scale pedestrian detection layer with a 160 × 160 feature map is added to enhance the model’s ability to detect small-scale pedestrians.
3.1. C2f-D2CN Module
To enhance pedestrian detection, we designed the C2f_DPCN module using deep deformable convolution [32] and dynamic convolution [33] to improve the extraction of pedestrian features at different scales. By introducing deformable convolution and dynamic convolution into the C2f, the model can capture richer feature representations, enhancing its ability to analyze images and improve computational efficiency, which strengthens the extraction of pedestrian features at different scales.
The proposed C2f_D2CN module innovatively integrates deformable convolution and dynamic convolution into the C2f module and introduces a branch-stacking structure along with skip connections. This not only enhances multi-scale receptive field aggregation but also maintains computational efficiency, making it more suitable for dense pedestrian detection tasks.
As illustrated in Figure 2, the C2f_D2CN module initially employs a 1 × 1 convolution to adjust the number of channels of the feature maps. Subsequently, a split operation is utilized to partition the features, effectively replacing the conventional 1 × 1 convolution. By stacking multiple deformable convolution and dynamic convolution modules, the network significantly expands its receptive field. Furthermore, the incorporation of an increased number of skip connections enhances the richness of the gradient flow, thereby facilitating the extraction of more diverse and multi-scale pedestrian features.
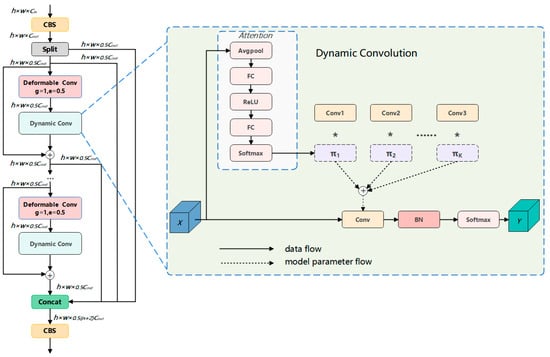
Figure 2.
Structure of C2f-D2CN, the symbol * represents multiplication operation.
For a standard convolutional layer, the parameter count is , whereas for dynamic convolution, the number of parameters is . The calculation of FLOPs includes the computation of coefficient generation and the dynamic weight fusion. However, the coefficient generator employs dimensionality-reduced operations, its computational cost is quite low, and thus its overhead can be ignored compared to the entire convolution operation. The total FLOPs of dynamic convolution do not significantly increase compared to the standard convolution layer. This design enables the C2f-D2CN module to retain the efficient feature processing capabilities of the C2f module while leveraging the adaptability of dynamic convolution to maintain stable model performance and reduce computational burden. Consequently, the model’s performance in detecting pedestrians in dense environments is substantially improved.
3.2. Multi-Scale Linear Spatial Attention Module
The multi-scale linear spatial attention module structure mainly consists of a multistage backbone network. It employs the ReLU linear attention mechanism to capture global contextual information and enhances local information processing capability through a spatial information module. The model adopts multi-scale learning by aggregating multi-scale information of Q, K, and V to improve its multi-scale feature extraction ability.
As illustrated in Figure 3, the input generates Q, K, and V through a linear layer. Q incorporates spatial information and enters the ReLU linear attention module. K passes through a 3 × 3 convolution before entering the ReLU linear attention module. V goes through a 5 × 5 convolution before entering the ReLU linear attention module. Since different convolutional kernel sizes are used, the receptive fields vary accordingly. Finally, the outputs from the three ReLU linear attention modules are concatenated. Then, a deformable convolution (Dconv) layer is applied to reduce the channel dimension back to its original shape.

Figure 3.
Structure of the multi-scale linear spatial attention module.
Given the input , the generalized formulation of softmax attention is expressed as:
where:
, and are learnable linear projection matrices. represents the i-th row of matrix O. is defined in Equation (5). Equation (1) transforms into the original softmax attention.
In addition to using the similarity function, other similar functions can also be used. We introduce linear attention [34] to achieve a global receptive field, rather than using the more complex softmax-based attention mechanism [35]. In ReLU linear attention, the similarity function is defined as follows:
ReLU linear attention is about 4 times faster than softmax attention under similar computations and exhibits better performance in terms of latency. Using Equation (6), Equation (1) can be rewritten as:
Then, by leveraging the associativity of matrix multiplication, both computational complexity and memory usage can be reduced from quadratic to linear.
As shown in Equation (8), the expressions and ( only require computation once. These values can then be reused for each query, resulting in a computational cost of O(n) and memory usage of O(n).
Although the ReLU linear attention network outperforms the softmax attention network in computational complexity and hardware latency, it tends to produce diffused attention maps, which compromise its efficiency in capturing local information. We incorporate a spatial information module to enhance the ReLU linear attention network, embedding spatial information into Q to better capture local details.
In this work, we use a spatial information extraction network to process the features after linear transformation. First, is passed through a channel-based global max pooling (GMP) and global average pooling (GAP) to obtain two feature maps of size [. These two feature maps are then concatenated along the channel axis and used as the input to a convolution operation f. After the convolution reduces the number of channels, the resulting features are passed through a sigmoid function to obtain features that carry spatial information. Finally, the spatial information features are multiplied element-wise by , enabling the features to incorporate spatial information. This helps ensure that the target can still be correctly detected even when parts of its features are missing. The specific formulation of the spatial information features is shown in Equation (9).
By incorporating spatial information, the model enhances its ability to capture local features more effectively, thus improving accuracy in tasks that require precise localization. Through the effective integration of multi-scale linear attention and spatial positional information, the feature learning network can comprehensively extract salient pedestrian features, thereby mitigating the adverse effects of information loss caused by pedestrian occlusion in dense scenes.
3.3. Add Small-Target Detection Head
After feature fusion, the detection layers of YOLOv8 output three feature maps with sizes of 80 × 80, 40 × 40, and 20 × 20, which are used to detect objects larger than 8 × 8, 16 × 16, and 32 × 32 pixels, respectively. Shallow feature maps with larger dimensions and smaller receptive fields contain more local details and positional information, making them suitable for detecting small objects. Conversely, deeper feature maps with smaller dimensions and larger receptive fields encode more complex semantic information, but lack distinct local details, making them more appropriate for detecting larger targets.
However, real-world dense pedestrian detection scenarios often contain numerous small-scale pedestrians with pixel sizes below 8 × 8 that are densely distributed. If the original algorithm continues to be used for detection, significant loss of small-target feature information will occur, leading to false positives and missed detections. To address these issues, this paper improves the original network architecture by adding a small-target detection layer with a 160 × 160 feature map in the prediction head. This small-target detection layer can effectively extract features of pedestrians smaller than 8 × 8 pixels, thereby improving the model’s detection capability for small-scale pedestrians.
3.4. DFL-SIoU Loss Function
Dense pedestrian detection constitutes a single-category detection task, where the network’s localization capability should be particularly strengthened during the classification and localization stages. Therefore, we employed a combined regression loss consisting of distributed focal loss (DFL) [36] and an improved CIoU [37] to enhance model convergence and achieve superior bounding box prediction performance.
DFL uses the distances from a point to the four edges of the bounding box as regression targets. Since real targets typically distribute near annotation positions, DFL explicitly increases the probabilities of the two nearest anchor points and (where ≤ ≤ ) to the ground truth label y, enabling the network to rapidly converge to values near the true label y. The mathematical definition of DFL is expressed as:
where , and can guarantee the estimated return target wireless close tag .
While DFL calculates loss by regressing anchor boxes toward annotated boxes, it cannot explicitly determine the containment relationship between anchors and ground truth boxes. To address this limitation, we introduced an enhanced CIoU loss to compute overlap loss between ground truth and anchor boxes, combining it with DFL to form the final bounding box regression loss. The formal definition of CIoU is presented in Equations (11)–(13):
where IoU denotes the intersection-over-union ratio and and represent the center points of the predicted box and ground truth box, respectively. Additionally, indicates the Euclidean distance between these centers, denotes the diagonal length of the minimum bounding rectangle enclosing both boxes, and and correspond to the width and height of the predicted box and ground truth box, respectively.
Our analysis reveals two critical issues in the current formulation. In Equation (12), only reflects the difference in aspect ratios rather than capturing the actual proportional relationships between predicted/ground truth widths ( and ) or heights ( and ). The partial derivatives exhibit contradictory behavior: . Consequently, if one variable (either or ) increases, the other decreases. This unstable gradient behavior may lead to gradient explosion, particularly when detecting small-scale targets.
Therefore, the CIoU loss may optimize similarity in an irrational manner, hindering the model from effectively reducing the actual discrepancies between and . To address these two limitations, this paper proposes a more stable loss function named SIoU, formally defined in Equations (14) and (15):
where and represent the width and height of the minimum enclosing rectangle covering both the predicted and ground truth bounding boxes, is an offset added to prevent the case where = 0, and other parameters retain the same definitions as in CIoU. Additionally, squaring each term enhances the convergence speed of the loss function. Similarly, we analyze the gradients of with respect to and , as shown in Equations (16) and (17).
The analysis demonstrates that this gradient function effectively avoids gradient explosion issues caused by small targets. The final regression loss combining the two abovementioned losses is formulated as:
The weighting coefficients and are determined based on the regression loss weight settings of YOLOv8. Since high IoU values are critical for accurate target localization and detection, they require greater weight. Conversely, DFL tends to cause overfitting during model training, which adversely affects the model’s generalization capability, thus necessitating less weight. Through experimental analysis, we set = 0.2 and = 0.8. The combined regression loss enhances the model’s training efficiency.
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Datasets
To comprehensively validate the effectiveness of the improved algorithm, we conducted experiments using two public dense pedestrian detection datasets: CrowdHuman [38] and WiderPerson [39].
The CrowdHuman dataset is a large-scale human detection benchmark containing 24,370 high-resolution images (15,000 training, 4370 validations, and 5000 test images). It includes approximately 470,000 pedestrian instances, averaging 23 instances per image, with extensive multi-scale targets and occluded objects across diverse environments and complex poses. Each pedestrian instance is annotated with three bounding boxes: head box, visible-region box, and full-body box. Our experiments used the most challenging full-body annotations. As shown in Figure 4, the dataset contains images with significant challenges, including crowd density, occlusions, and scale variations.

Figure 4.
The CrowdHuman dataset.
The WiderPerson dataset is a widely used benchmark for human detection in real-world complex scenarios. It contains 13,382 images selected from diverse environments, comprising approximately 400,000 pedestrian instances with varying occlusion levels. The dataset features complex occlusion scenarios, dense crowds, and diverse human poses, as shown in Figure 5. While it originally included five categories (pedestrians, cyclists, crowds, etc.), this study exclusively used the pedestrian category for experimentation.

Figure 5.
The WiderPerson dataset.
4.2. Experimental Environment and Implementation Details
This study employed Python 3.9 with PyTorch 1.11, running with Nvidia GeForce RTX 4090 GPU acceleration. Table 1 shows the hardware and implementation details.

Table 1.
Hardware and implementation details.
The input images underwent random preprocessing through operations including color space distortion, image flipping, and scaling, and we did not use any pre-training techniques.
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
For the CrowdHuman dataset, we used average precision (AP), recall, log-average miss rate (denoted MR−2), floating-point operations per second (FLOPS), and frames per second (FPS) for performance evaluation. For the WiderPerson dataset, the evaluation was conducted using the official metric AP and MR−2. AP represents the average detection accuracy for all images belonging to a specific category, and a higher value indicates better detection performance. Recall measures how many positive samples are correctly predicted, reflecting the network’s ability to detect positive samples, and a higher value is better. MR−2 is derived by plotting a curve with FPPI on the horizontal axis and log (MR) on the vertical axis [40]. Nine FPPI values are uniformly sampled within the range [0.01,1], and the corresponding logarithmic miss rate values were calculated. The average of these values was then computed, and an exponential transformation applied to express it as a percentage, representing the miss rate (MR−2). Lower MR−2 values indicate superior detector performance. The formulas for precision (P), recall (R), and average precision (AP) are as follows:
where TP represents the number of true-positive detections, FP denotes the number of false positives (background regions incorrectly identified as targets), FN indicates the number of false negatives (actual targets misclassified as background) and n represents the total number of images belonging to a certain class.
MR−2 is an evaluation metric optimized for pedestrian detection tasks, particularly suitable for small-target detection in dense scenarios. The calculation formula is:
where FPPIi denotes the FPPI value at the i-th sampling point within the interval [10−2,100] (i.e., FPPI ranging from 0.01 to 1) sampled at logarithmic intervals of 100.25. N represents the total number of sampling points.
4.4. Ablation Experiment
4.4.1. Module Ablation Experiment
To evaluate the effectiveness of each module, ablation studies were conducted on the CrowdHuman dataset. By sequentially adding each module and comparing evaluation metrics before and after their integration, we comprehensively assessed the performance of network components. All ablation experiments were performed by training models on the CrowdHuman training set and validating them on the validation set. The results in Table 2 clearly demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, showing significant improvements in AP and MR−2.

Table 2.
Module validation: ablation experiment results on module validation AP (%) and MR−2%. Baseline (ResNet50) refers to replacing the CSPDarknet backbone of YOLOv8-L with ResNet50, MLA represents the multi-scale line attention, MLSA represents the multi-scale line spatial attention module, and SPDH refers to the small-scale pedestrian detection head.
In our experiments, we adopted YOLOv8-L as the baseline algorithm and conducted ablation studies by incrementally integrating proposed modules. To validate the effectiveness of the original backbone, we replaced the CSPDarknet backbone of YOLOv8-L with ResNet50, referred to as “Baseline (ResNet50)”. This modification resulted in a decrease in performance, with AP dropping from 87.7% to 87.2%, MR−2 increasing from 42.9% to 43.6%, FLOPs rising from 165.2 to 177.9, and FPS dropping from 59.7 to 52.7. These results indicate that CSPDarknet is more suitable than ResNet50 for the YOLOv8 architecture in terms of detection accuracy and efficiency, especially in dense pedestrian scenarios. Compared to ResNet, CSPDarkNet has lower computational complexity and fewer parameters, enabling faster training and inference speeds. Consequently, all subsequent ablation studies were carried out on the official YOLOv8-L implementation. Replacing the original C2f module in YOLOv8 with the C2f-D2CN module significantly improved both average precision (AP) and miss rate (MR−2). The C2f-D2CN module enhances the network’s receptive field through stacked deformable convolution modules while reducing parameters, leveraging skip connections to extract richer multi-scale pedestrian features.
Further incorporating the multi-scale linear attention module (MLSAM) increased AP by 1.8% and reduced MR−2 by 1.4%, validating its effectiveness. The MLAM captures global contextual information through line attention mechanisms and strengthens local feature processing via spatial enhancement, mitigating missed or false detections across scales.
Adding the small-target detection head (SPDH) improved AP by 1.6% and MR−2 by 0.8%. Subsequent integration of DFL-SIoU further boosted AP by 1.0% and reduced MR−2 by 1.2%. These ablation experiments collectively demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed components. Compared to the baseline, our final algorithm achieved a 5.6% AP gain and 4.2% MR−2 reduction, substantially enhancing detection capability in dense scenarios.
4.4.2. Ablation Experiment on C2f_D2CN
To verify the effectiveness of the deformable convolution and dynamic convolution in the C2f_D2CN module, we conducted experiments on the CrowdHuman dataset. The experimental results in Table 3 clearly demonstrate the improvement in both accuracy and efficiency brought by the C2f_D2CN module. With the addition of deformable convolution and dynamic convolution, the FLOPs only slightly increased, while the AP improved by 1.5% and the MR−2 decreased by 1.1%. This proves that our proposed module can effectively enhance detection accuracy while maintaining computational efficiency.

Table 3.
Ablation study of the C2f_D2CN module on the CrowdHuman dataset.
4.4.3. Ablation Experiment on Attention Mechanisms
To validate the impact of different attention mechanisms on model performance, ablation experiments were conducted on various attention types, with results shown in Table 4. The first row represents the baseline without any attention mechanism. The second and third rows indicate the addition of SE attention and CBAM attention, respectively. The fourth row incorporates CA attention, the fifth row adds EMA attention, and the sixth row integrates the proposed multi-scale linear spatial attention (MLSA). The results demonstrate that compared to mainstream attention mechanisms (SE, CBAM, CA, EMA), the proposed multi-scale linear spatial attention significantly enhances detection accuracy. Relative to the baseline without attention, multi-scale linear spatial attention improved AP by 1.8%, increased recall by 2.0%, and reduced MR−2 by 1.9%. SE attention showed limited improvements because it focuses solely on channel-wise interdependencies while ignoring spatial features. CBAM attention, though leveraging large-kernel convolutions for spatial feature extraction, fails to address long-range dependencies. In contrast, the proposed multi-scale linear spatial attention effectively balances spatial-channel interactions and long-range dependency modeling, substantially boosting overall performance.

Table 4.
Ablation experiment results for attention mechanisms (%).
4.4.4. Ablation Experiment on Loss Function
To validate the proposed DFL-SIoU loss function, we compared its performance against several mainstream loss functions in dense pedestrian detection, with experimental results presented in Table 5. The results demonstrate that our DFL-SIoU achieves superior performance across all evaluation metrics. Specifically, the proposed loss function holistically addresses the characteristics of small-scale pedestrians in dense scenarios by mitigating gradient explosion issues while accelerating convergence.

Table 5.
Ablation experiment results for loss function.
We visualized the training process of the loss function. As shown in Figure 6, the proposed DFL-SIOU does not suffer from gradient explosion in dense scenarios due to small pedestrian targets or occlusion. Moreover, it converges faster and its prediction results are closer to the ground truth.
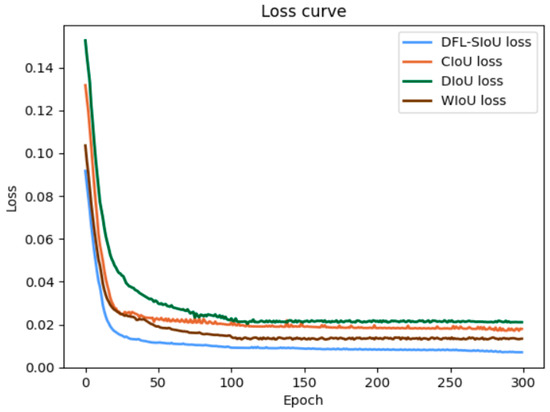
Figure 6.
The loss curve during training on the CrowdHuman dataset.
4.4.5. Ablation Experiment on Parameters
To investigate the impact of weighting coefficients and on model performance, parameter analysis experiments were conducted on the CrowdHuman dataset. As shown in Table 6, the detection performance is optimal when the weights are set to = 0.2 and , meaning the model achieves the best fitting performance with DFL weighted at 0.2 and SIOU at 0.8. The experiments indicate that high IoU values are critical for accurate target localization and detection, thus requiring greater weight. Conversely, DFL tends to cause overfitting during training, which degrades the model’s generalization capability, necessitating a less weight.

Table 6.
Analysis of parameters and .
4.5. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
To validate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm, comparative experiments were performed on various subsets of the CrowdHuman dataset, using AP, recall, and MR−2 as evaluation metrics. The results are summarized in Table 7.

Table 7.
Comparison of miss rate with existing methods on CrowdHuman (AP, recall, and MR−2%).
The CrowdHuman dataset, known for its complexity and diversity, poses significant challenges to pedestrian detection in dense and crowded scenes, testing the generalization capabilities of detection algorithms. Our method achieved satisfactory results, effectively demonstrating the robustness and generalization ability of the algorithm in dense environments. As shown in Table 7, the proposed model achieved an MR−2 of 38.7% on the CrowdHuman dataset, effectively detecting pedestrians in crowded scenes. This performance is attributed to the method’s focus on addressing feature loss caused by pedestrian occlusion in crowded environments. By leveraging contextual information to capture potential effective features and incorporating spatial location information of the targets, the detector improves its ability to locate pedestrians. Furthermore, the combination of visual attention and pose information enhances the robustness of visual representations. The proposed model also achieves optimal performance on AP and suboptimal on recall metrics, with experimental results confirming its strong effectiveness.
We conducted a comparison of different YOLO versions and RF-DETR on the CrowdHuman dataset, showcasing performance metrics including average precision (AP), MR−2%, and FLOPS. As shown in Table 8, Dense-YOLOv8-M (ours) outperformed other models in terms of AP, achieving a score of 92.7, which is significantly higher than YOLOv7 (86.8) and comparable to RF-DETR-B (92.8). Furthermore, Dense-YOLOv8-M maintained a favorable trade-off in terms of MR−2 at 39.6%, outperforming both YOLOv9-M (42.7%) and YOLOv10-M (42.1%), while offering better efficiency in GFLOPS (82.1).

Table 8.
Comparison of different YOLO versions and RF-DETRon CrowdHuman (AP% and MR−2% and GFLOPS).
Additionally, Dense-YOLOv8-L (ours) achieved an impressive AP of 93.3, which surpasses several advanced models, including YOLOE-v11-L [64], YOLOv10-L (90.1), and YOLOv11-L (91.0). Its MR−2 was also competitive, at 38.7%, demonstrating effective performance in dense pedestrian detection. Despite having a slightly higher GFLOPS of 169.3 compared to Dense-YOLOv8-M, the model’s higher AP and lower MR−2 underscore its superior detection capability in complex scenarios. These results highlight the effectiveness of the Dense-YOLOv8 models in enhancing pedestrian detection performance while maintaining computational efficiency, especially in dense scenes.
To validate the generalization capability of the proposed model, experiments were conducted on the WiderPerson dataset using the evaluation metrics AP and MR−2, with results presented in Table 9. The proposed model achieved state-of-the-art performance in both AP and MR−2 on the WiderPerson dataset, demonstrating its strong generalization capability.

Table 9.
Comparison of AP and MR−2 with existing methods on WiderPerson (%).
4.6. Visualization
We compared the improved model with the baseline network in terms of visual effects. Figure 7 and Figure 8 present partial visualization results of validation images from the WiderPerson dataset and the CityPersons [72] dataset, respectively. The first row displays the detection results of the baseline model (YOLOv8-L), where red bounding boxes indicate pedestrians detected by the baseline model. The second row presents the detection results of the state-of-the-art model (LEI-YOLO), where red bounding boxes indicate pedestrians detected by the baseline model, green bounding boxes denote pedestrians missed by the baseline but detected by the LEI-YOLO model, and blue bounding boxes indicate pedestrians incorrectly detected by the baseline model, but correctly identified by the LEI-YOLO model. The third row shows the detection results of our proposed model: red bounding boxes represent pedestrians detected by both our model and the baseline model, green bounding boxes denote pedestrians missed by the baseline, but detected by our model, yellow bounding boxes denote pedestrians missed by LEI-YOLO, but detected by our model, and blue bounding boxes indicate pedestrians incorrectly detected by the baseline model, but correctly identified by our proposed model. The improved model demonstrates significant improvement in detecting dense pedestrians, showing fewer missed detections and false positives compared to the original model.

Figure 7.
The visualization results of different models on WiderPerson.

Figure 8.
The visualization results of different models on CityPersons.
5. Conclusions
This paper presents an enhanced pedestrian detection algorithm based on YOLOv8, specifically designed to address the challenges posed by multi-scale occlusions in densely populated scenes. The proposed method incorporates the C2f-D2CN module, which leverages deformable and dynamic convolutions to improve the network’s capacity for multi-scale feature representation. Additionally, a multi-scale linear spatial attention mechanism is introduced to selectively emphasize the visible regions of occluded pedestrians while suppressing noise from complex backgrounds. The integration of a dedicated detection head for small-scale pedestrians further improves the model’s sensitivity to subtle visual cues. During training, the combination of DFL loss with an improved CIoU loss function enhanced both the convergence rate and the precision of bounding box regression. Extensive experiments conducted on the CrowdHuman and WiderPerson datasets demonstrate that the proposed algorithm achieves substantial improvements over baseline methods in terms of detection accuracy and robustness under challenging conditions. Despite these advancements, the algorithm still encounters issues such as missed detections and false positives, particularly in scenarios with severe occlusion. Future research will focus on further refining the network architecture, improving detection performance and inference efficiency in extremely dense environments, and extending the applicability of the method to a broader range of real-world pedestrian detection tasks.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.G., T.L. and M.L.; methodology, H.G., L.W. and M.L.; software, S.H., T.L. and M.L.; validation, H.G., L.W. and M.L.; formal analysis, S.H., T.L. and M.L.; data curation, H.G., S.H., T.L. and M.L.; writing—original draft preparation, H.G., L.W., S.H. and T.L.; visualization, H.G., S.H. and M.L.; supervision S.H., T.L. and M.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants 62276118 and 61772244).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.H. Pedestrian detection and tracking algorithm based on occlusion-aware. Transducer Microsyst. Technol. 2023, 42, 126–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q. Feature calibration network for occluded pedestrian detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 23, 4151–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, C.Y.; Li, G.Y.; Pan, Y.H. UAST-RCNN: Object detection algorithm for blocking pedestrians. J. Electron. Meas. Instrum. 2022, 36, 168–175. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; He, H.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; See, J.; Lin, W. Variational pedestrian detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 11622–11631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Zheng, A.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J. Detection in crowded scenes: One proposal, multiple predictions. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 12214–12223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Li, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, L. SSPNet: Scale selection pyramid network for tiny person detection from UAV images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Lu, Z.; Cheng, R.; He, C. FaPN: Feature-aligned pyramid network for dense image prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terven, J.; Cordova-Esparza, D.M.; Romero-Gonzalez, J.A. A Comprehensive Review of YOLO Architectures in Computer Vision: From YOLOv1 to YOLOv8 and YOLO-NAS. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2023, 5, 1680–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Qiu, J. Ultralytics YOLOv8, 2023. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/v8.0.6 (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, X.; Shen, S.; Xu, T.; Feng, J.; Yan, S. Scale-aware fast R-CNN for pedestrian detection. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2017, 20, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part I 14. pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K. Focal loss for dense object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Luo, X. Research on a Pedestrian Detection Algorithm Based on Improved SSD Network. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1802, 032073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7263–7271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Weng, K.; Geng, Y.; Li, L.; Ke, Z.; Li, Q.; Cheng, M.; Nie, W. YOLOv6: A single-stage object detection framework for industrial applications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.02976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Yeh, I.-H.; Mark Liao, H.-Y. Yolov9: Learning what you want to learn using programmable gradient information. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J. Yolov10: Real-time end-to-end object detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 107984–108011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G.; Qiu, J. Ultralytics YOLO11, 2024. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Fu, P.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H. Answer sheet layout analysis based on YOLOv5s-DC and MSER. Vis. Comput. 2024, 40, 6111–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, B.; Yuan, Y.; Dang, A. Beta r-cnn: Looking into pedestrian detection from another perspective. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 33, 19953–19963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, L.; Li, Z.; Sun, H.; Sun, J.; Zheng, N. End-to-end object detection with fully convolutional network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 15849–15858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Bai, X.; Shen, X.; Xin, P.; Tian, J.; Chai, T.; Wang, Z. Dense pedestrian detection based on GR-YOLO. Sensors 2024, 24, 4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, L. HCA-YOLO: A non-salient object detection method based on hierarchical attention mechanism. Clust. Comput. 2024, 27, 9663–9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Hu, L. Towards real-time accurate dense pedestrian detection via large-kernel perception module and multi-level feature fusion. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2025, 22, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Zhang, X.; Sun, M.; Wang, G. GC-YOLOv9: Innovative smart city traffic monitoring solution. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 106, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Dai, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, D.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Z. Dynamic convolution: Attention over convolution kernels. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 11030–11039. [Google Scholar]
- Katharopoulos, A.; Vyas, A.; Pappas, N.; Fleuret, F. Transformers are rnns: Fast autoregressive transformers with linear attention. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Online, 13–18 July 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inform. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Wu, L.; Chen, S.; Hu, X.; Li, J.; Tang, J.; Yang, J. Generalized focal loss: Learning qualified and distributed bounding boxes for dense object detection. Adv. Neural Inform. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 21002–21012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Zhao, Z.; Li, B.; Xiao, T.; Yu, G.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J. CrowdHuman: A Benchmark for Detecting Human in a Crowd. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.00123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xie, Y.; Wan, J.; Xia, H.; Li, S.Z.; Guo, G. Widerperson: A diverse dataset for dense pedestrian detection in the wild. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2019, 22, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollar, P.; Wojek, C.; Schiele, B.; Perona, P. Pedestrian detection: An evaluation of the state of the art. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 34, 743–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, D.; He, S.; Zhang, G.; Luo, M.; Guo, H.; Zhan, J.; Huang, Z. Efficient multi-scale attention module with cross-spatial learning. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Tan, T. Focal and efficient IOU loss for accurate bounding box regression. Neurocomputing 2022, 506, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanjia, T.; Yuhang, C.; Zewei, X.; Rong, Y. Wise-IoU: Bounding Box Regression Loss with Dynamic Focusing Mechanism. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.10051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodla, N.; Singh, B.; Chellappa, R.; Davis, L.S. Soft-NMS--improving object detection with one line of code. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 5561–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y. Adaptive nms: Refining pedestrian detection in a crowd. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 6459–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, J.; Wei, Y. Relation networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3588–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, D. Receptive field block net for accurate and fast object detection. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-h.; Wang, X.-q.; Wang, D.; Duan, B.-g.; Rui, T. Object detection in crowded scenes via joint prediction. Def. Technol. 2023, 21, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, M.; Yuan, J. Self-mimic learning for small-scale pedestrian detection. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Online, 12–16 October 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Su, W.; Lu, L.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Dai, J. Deformable detr: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.04159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, Y.; Kong, T.; Xu, C.; Zhan, W.; Luo, P. Sparse R-CNN: An End-to-End Framework for Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 15650–15664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qi, X.; Sun, J. Progressive end-to-end object detection in crowded scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ci, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Tang, S.; Bai, L.; Zhu, F.; Zhao, R.; Yu, F.; Qi, D.; Ouyang, W. Unihcp: A unified model for human-centric perceptions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 17840–17852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Ouyang, W. OTP-NMS: Toward Optimal Threshold Prediction of NMS for Crowded Pedestrian Detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 3176–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Liu, K.; Shakeel, M.S.; Wang, H.; Kang, W. DDAD: Detachable Crowd Density Estimation Assisted Pedestrian Detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 1867–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wei, M.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X. An Anchor-Free Dual-Branch Approach for Real-Time Metro Passenger Detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 3428635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Huang, G.; Zhong, G.; Yuan, X.; Tan, Z.; Lu, Z.; Pun, C. Triangular Chain Closed-Loop Detection Network for Dense Pedestrian Detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 5003714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Gaikov, G.; Rybalchenko, D.; Chigorin, A.; Laptev, I.; Zagoruyko, S. PairDETR: Joint Detection and Association of Human Bodies and Faces. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, S. Non-Maximum Suppression Guided Label Assignment for Object Detection in Crowd Scenes. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. Yoloe: Real-time seeing anything. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.07465. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Jie, Z.; Huang, X.; Xu, R.; Yoshie, O. Ps-rcnn: Detecting secondary human instances in a crowd via primary object suppression. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), London, UK, 6–10 July 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukhovich, D.; Sofiiuk, K.; Galeev, D.; Barinova, O.; Konushin, A. Iterdet: Iterative scheme for object detection in crowded environments. In Proceedings of the Structural, syntactic, and statistical pattern recognition: Joint IAPR international workshops, s+ SSPR 2020, Padua, Italy,, 21–22 January 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; He, N.; Zhang, R.; Yan, K.; Yu, H. Multi-scale feature balance enhancement network for pedestrian detection. Multimed. Syst. 2022, 28, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ge, Z.; Jie, Z.; Yoshie, O. Nms by representative region: Towards crowded pedestrian detection by proposal pairing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 10750–10759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.; Zhang, S.; Xing, J.; Lei, Z. Pedhunter: Occlusion robust pedestrian detector in crowded scenes. In Proceedings of the 2020 AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, C. Double Mask R-CNN for Pedestrian Detection in a Crowd. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 4012252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhuo, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. Cascade transformer decoder based occluded pedestrian detection with dynamic deformable convolution and Gaussian projection channel attention mechanism. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 25, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Benenson, R.; Schiele, B. Citypersons: A diverse dataset for pedestrian detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3213–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).