Material Composition Testing Related to Measurement Instrument Enclosure Design and Safety
Abstract
1. Introduction
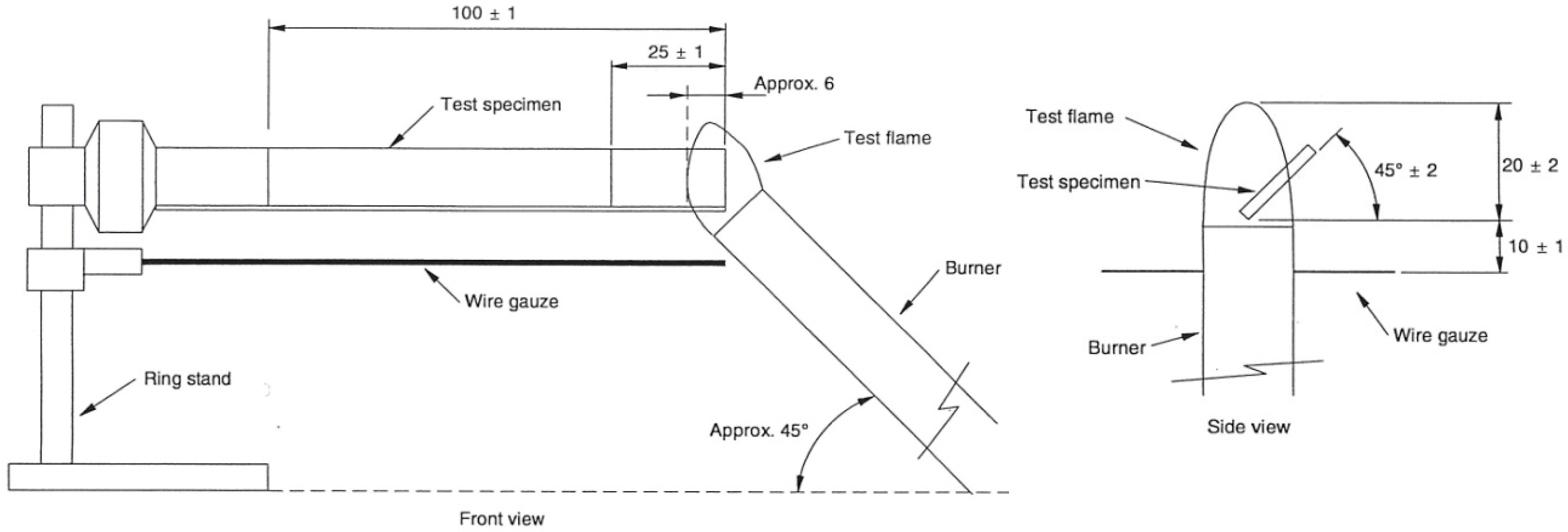
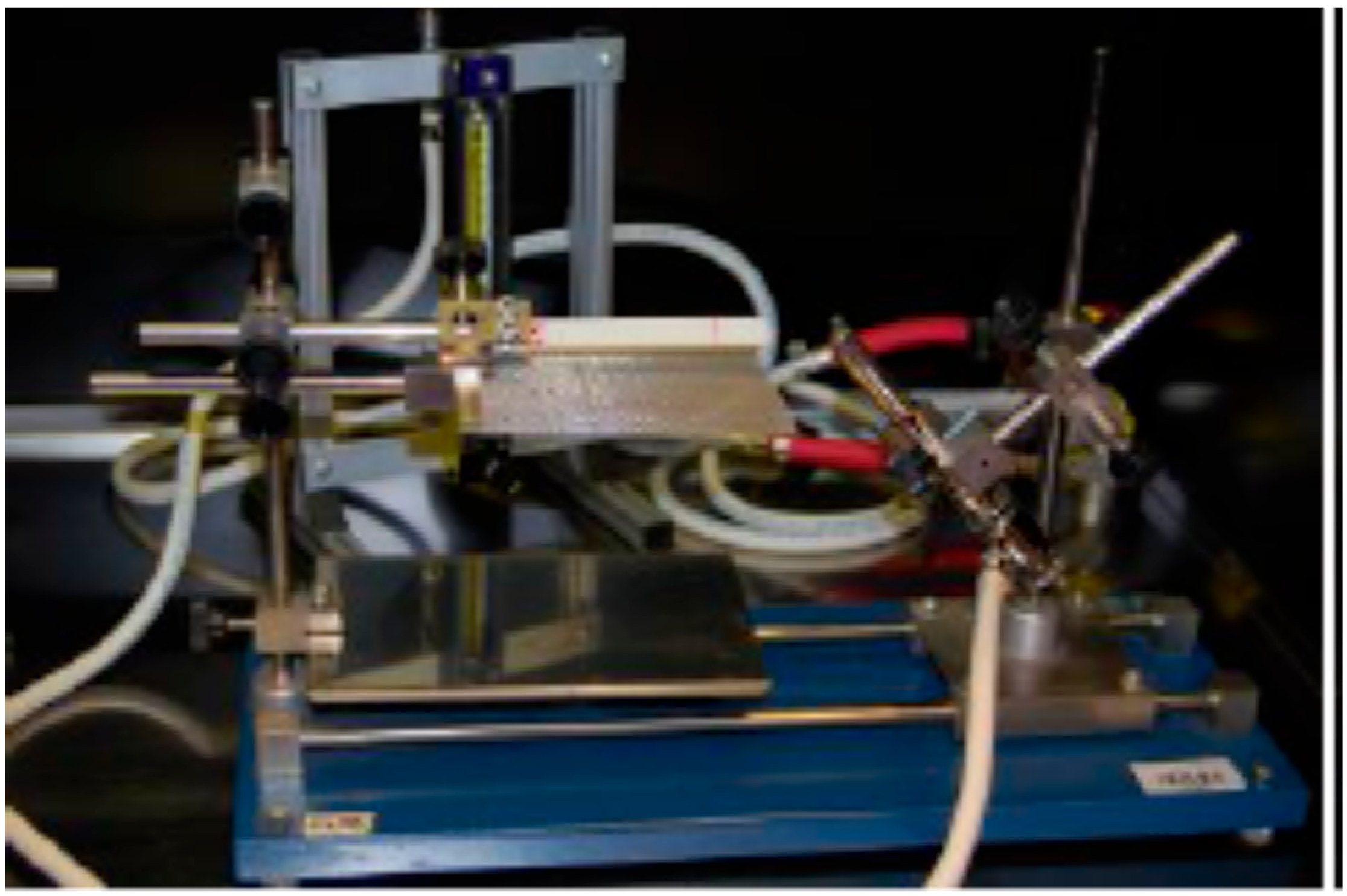
2. Testing Method
- Laboratory fume hood/chamber: Volume of 0.5 m3, with dark walls and recorded light levels below 20 lx, equipped with an exhaust fan (switched off during the test) and a positive closing damper.
- Laboratory burner compliant with IEC 60695-11-4 standard.
- Specimen holder with clamps to securely position the test specimen.
- Timing device with a resolution of at least 0.5 s.
- Measuring scale graduated in millimeters.
- Wire gauze (20 mesh), compliant with standards.
- Conditioning chamber-maintaining conditions of 23 ± 2 °C and 50 ± 5% relative humidity (RH).
Materials Classification Criteria
- HB classification: (a) The material does not visibly burn after the removal of the ignition source. (b) If burning continues, the flame front does not pass the 100 mm mark. (c) If the flame front passes the 100 mm mark, the linear burning rate must not exceed 40 mm/min for thicknesses between 3.0 mm and 13.0 mm or 75 mm/min for thicknesses below 3.0 mm. (d) If the linear burning rate does not exceed 40 mm/min at a thickness of 3.0 mm ± 0.2 mm, the material is automatically accepted down to a minimum thickness of 1.5 mm.
- HB40 classification: (a) The material does not visibly burn after the removal of the ignition source. (b) If burning continues, the flame front must not pass the 100 mm mark. (c) If the flame front passes the 100 mm mark, the linear burning rate must not exceed 40 mm/min.
- HB75 classification: (a) The linear burning rate of the material must not exceed 75 mm/min if the flame front passes the 100 mm mark.
3. Results
3.1. Tested Materials
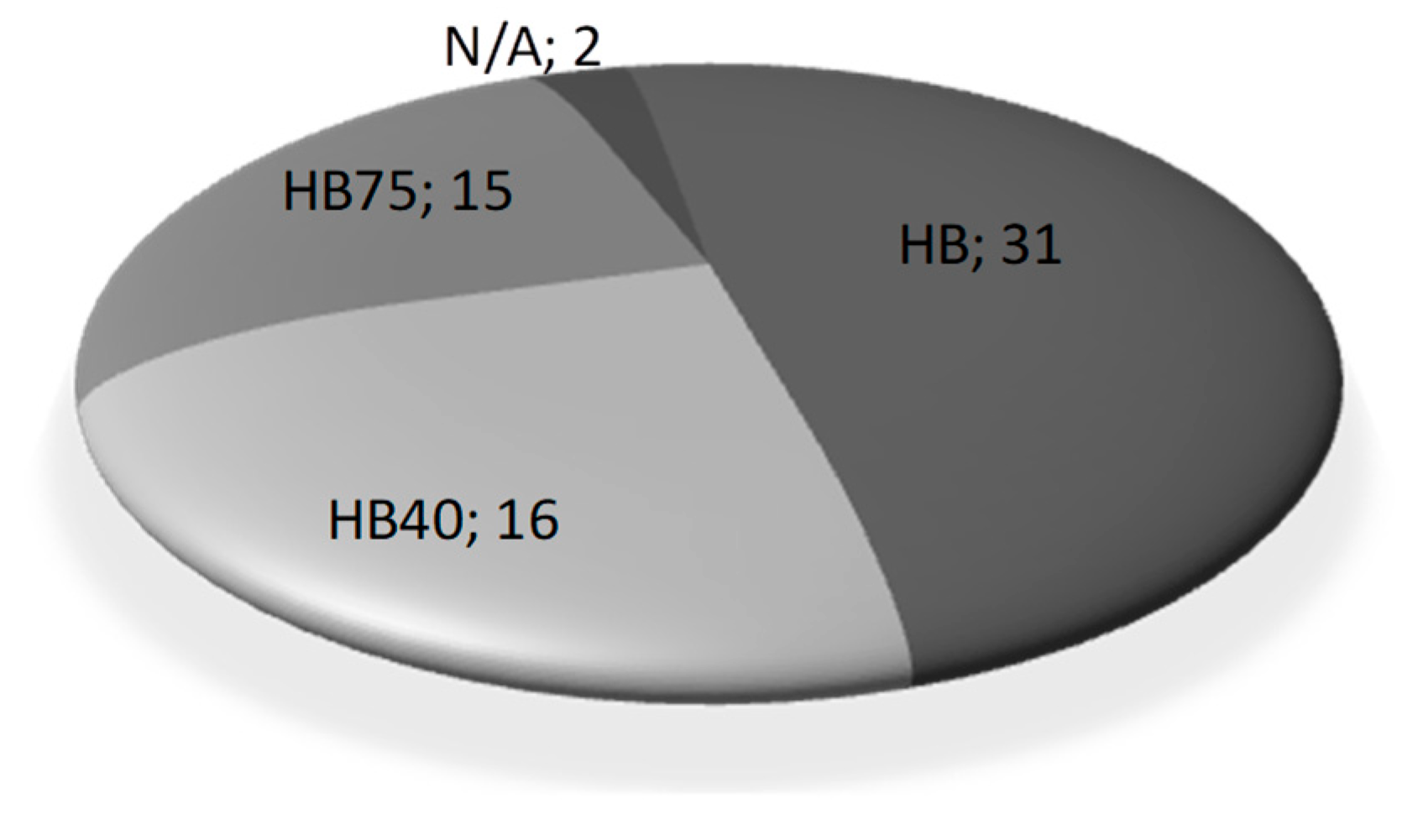
3.2. Classification of Test Samples by Burning Categories
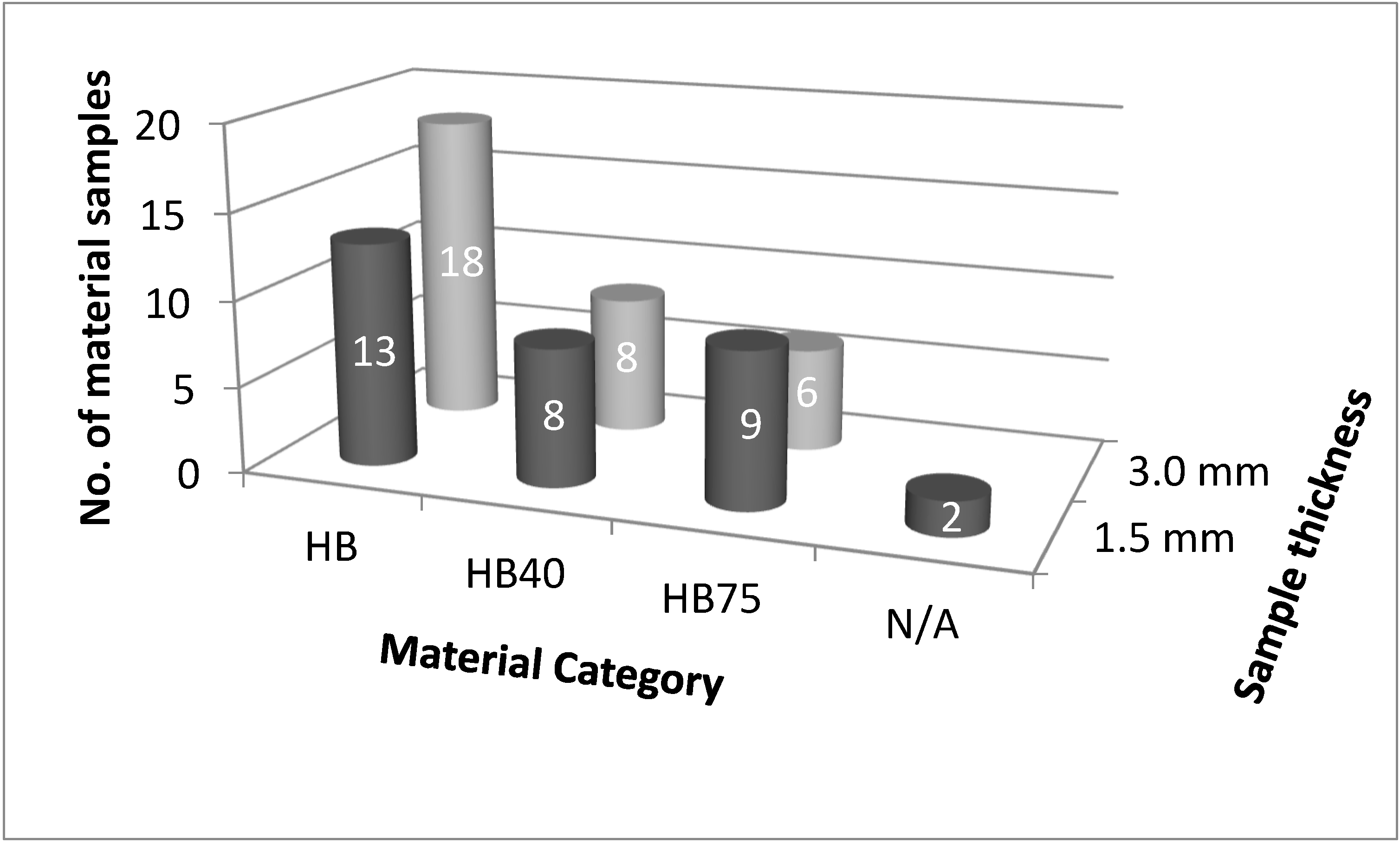
3.3. Classification of Test Samples by Category and Thickness
3.4. Classification of Test Samples by Material Mixture
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Minor changes in composition, such as pigments and fillers, significantly affected the flammability classification (HB, HB40, HB75) in several material groups.
- Seven material groups showed consistent classification across all tested variations, suggesting potential for reducing redundant testing.
- Sample thickness had less influence than expected; thinner samples did not always show a worse performance.
- Manufacturers can leverage these findings to optimize material selection, streamline safety certification, and reduce testing costs by focusing on “equivalent” additive systems.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Parliament and Council Directive 2004/22/EC on Measuring Instruments (MID). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32004L0022 (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Conformity Assessment of Products for Consumers: Electrical Products, Products Intended for Children, Textile and Apparel, and General Consumer Safety Comparative Study, Klaus Ziegler, Yao Xiaojing Robert Huigen. Available online: https://expertdirectory.s-ge.com/data/files/Comparative%20Study%20on%20CA%20for%20Consumer%20Products%20v2.1%20Final%20Draft.pdf#:~:text=%E2%80%A2%20Constitute%20no%20unreasonable%20threat,by%20the%20applicable%20legislation%2C%20unless (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Patel, P.; Hull, T.R.; Moffatt, C. PEEK polymer flammability and the inadequacy of the UL-94 classification. Fire Mater. 2012, 36, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 60695-11-10:2013; Fire Hazard Testing—Part 11-10: Test Flames—50 W Horizontal and Vertical Flame Test Methods. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. Available online: https://webstore.iec.ch/en/publication/2938 (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- IEC 60695-11-4:2011; Fire Hazard Testing—Part 11-4: Test Flames—1 kW Nominal Premixed Flame—Apparatus, Confirmatory Test Arrangement and Guidance. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- Simionescu, T.M.; Minea, A.A.; Reis, P.N.B.D. Fire Properties of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene Enhanced with Organic Montmorillonite and Exolit Fire Retardant. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shi, W.; Mai, Y.; Liao, B. Effect of Thermal Conductive Fillers on the Flame Retardancy, Thermal Conductivity, and Thermal Behavior of Flame-Retardant and Thermal Conductive Polyamide 6. Materials 2019, 12, 4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbot’Ko, S.; Naumov, I.; Vol’Nyi, O.; Alifanov, E. The Effect of Pigments on the Flammability Characteristics of a Rubber Compound Based on Methylvinylsiloxane Rubber. Int. Polym. Sci. Technol. 2018, 44, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razak, J.A.; Akil, H.M.; Ong, H. Effect of Inorganic Fillers on the Flammability Behavior of Polypropylene Composites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2007, 20, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrenga, P.; Vandlíčková, M.; Konárik, M. Experimental Investigation of Fire—Technical Characteristics of Selected Flame Retardants for the Protection of Wooden Structures. Coatings 2025, 15, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eizaguirre-Iribar, A.; Olano-Azkune, X.; Renaux, T.; Huet, V.; Izabel, D. Fire Safety of Steel Envelope Systems with Bio-Based Insulation: Evaluation of Smoldering Phenomenon. Fire 2025, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maake, T.; Asante, J.K.O.; Mhike, W.; Mwakikunga, B. Fire-Retardant Wood Polymer Composite to Be Used as Building Material Focusing on Informal and Formal Dwellings. Fire 2025, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, F.; Simion, A.; Anghel, I.; Sandu, M.; Banyai, D. Enhancing Fire Safety: Real-Scale Experimental Analysis of Fire Dynamics and Façade Performance. Fire 2023, 6, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, D. Fire Resistance of an Assembled Integrated Enclosure Panel System. Buildings 2022, 12, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czel, G.; Sycheva, A.; Janovszky, D. Effect of different fillers on thermal conductivity, tribological properties of Polyamide 6. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
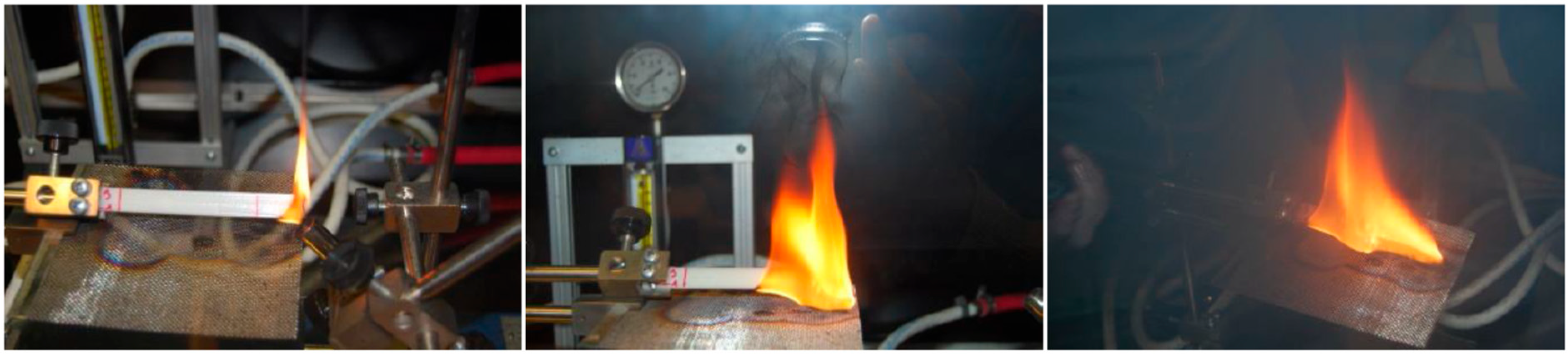


| Ref. No. | Material (Provided by Metrel-SLO, Slovenia) | |
|---|---|---|
| materials | 81001531 | ABS Terluran GP 22 |
| 81001295 | ABS 100-x01 natur | |
| 81001482 | PC Makrolon 6557 | |
| 81001443 | ABS VAMBSAB 0023 | |
| 81002009 | TPE Megol I A 65 SV/P | |
| 81001810 | TPU Elastollane S 90 A 15000 | |
| 81000936 | PA6 Bergamid B 70 UF dark grey VN 5371 CF | |
| 81000935 | PA6 Bergamid B 70 UF blue VN 537o CF | |
| 10223024 | PA66 Ultramid A3K black | |
| 10238024 | PA66 Ultramind A3X2G5 black 23187 | |
| 81000264 | PA66 Ultramind A3k natur | |
| 81000863 | PC makrolon 2805 | |
| 81001893 | PC Lexan DMX 1435 | |
| 81000917 | PP Hostancom M2 U01 natur | |
| 81000918 | PP Novolen 2300 K natur | |
| 81000853 | ABS Novodur P2H AT grey (RAL 7012) | |
| 81000851 | Plastic PC Makrolon 2607 | |
| additions | 81001532 | Pigment EUROCOLOR A92936 RAL 7021 4% |
| 81000577 | HOSTATRON-SYSTEM P1935 | |
| 81001483 | Pigment EUROCOLOR-GRIGIO A90917 RAL 7001 2% | |
| 81001119 | MASTERBACH 58-BU-20 blue for TPU | |
| 81001135 | MASTERBATCH 1031-BU-50 for polyamide, blue | |
| 81001134 | MASTERBATCH 1-RD-72 ZA POLIAMID for polyamide, red | |
| 81000267 | Green colour 232-GN-50 for POLIAMID | |
| 81001315 | MASTERBATCH UN2319-ORANGE | |
| 81000916 | MASTERBATCH 77-GY-50 grey PE/PP |
| Basic Material Group | Mixture Mark (Sample No._Thickness) | Material Combination (Base Material + Additive(s)) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | S1_1.5 | 81001531 |
| S1_3 | 81001531 | |
| S2_1.5 | 81001531 + 81001532—4% | |
| S2_3 | 81001531 + 81001532—4% | |
| S3_1.5 | 81001531 + 81000577—2% | |
| S3_3 | 81001531 + 81000577—2% | |
| S4_1.5 | 81001531 + 81000577—2% + 81001532—4% | |
| S4_3 | 81001531 + 81000577—2% + 81001532—4% | |
| S5_1.5 | 81001531 + 81001483—2% | |
| S5_3 | 81001531 + 81001483—2% | |
| 2 | S6_1.5 | 81001295 |
| S6_3 | 81001295 | |
| S7_1.5 | 81001295 + 81001119—2% | |
| S7_3 | 81001295 + 81001119—2% | |
| 3 | S8_1.5 | 81001482 |
| S8_3 | 81001482 | |
| S9_1.5 | 81001482 + 81001483—2% | |
| S9_3 | 81001482 + 81001483—2% | |
| 4 | S10_1.5 | 81001443 |
| S10_3 | 81001443 | |
| 5 | S11_1.5 | 81002009 |
| S11_3 | 81002009 | |
| S12_1.5 | 81002009 + 81001119—2% | |
| S12_3 | 81002009 + 81001119—2% | |
| 6 | S13_1.5 | 81001810 |
| S13_3 | 81001810 | |
| S14_1.5 | 81001810 + 81001119—2% | |
| S14_3 | 81001810 + 81001119—2% | |
| 7 | S15_1.5 | 81000936 |
| S15_3 | 81000936 | |
| 8 | S16_1.5 | 81000935 |
| S16_3 | 81000935 | |
| 9 | S17_1.5 | 10223024 |
| S17_3 | 10223024 | |
| 10 | S18_1.5 | 10238024 |
| S18_3 | 10238024 | |
| 11 | S19_1.5 | 81000264 |
| S19_3 | 81000264 | |
| S20_1.5 | 81000264 + 81001135—2% | |
| S20_3 | 81000264 + 81001135—2% | |
| S21_1.5 | 81000264 + 81001483—2% | |
| S21_3 | 81000264 + 81001483—2% | |
| S22_1.5 | 81000264 + 81001134—2% | |
| S22_3 | 81000264 + 81001134—2% | |
| S23_1.5 | 81000264 + 81000267—2% | |
| S23_3 | 81000264 + 81000267—2% | |
| 12 | S24_1.5 | 81000863 |
| S24_3 | 81000863 | |
| S25_1.5 | 81000863 + 81001315—2% | |
| S25_3 | 81000863 + 81001315—2% | |
| 13 | S26_1.5 | 81001893 |
| S26_3 | 81001893 | |
| 14 | S27_1.5 | 81000917 |
| S27_3 | 81000917 | |
| S28_1.5 | 81000917—48% + 81000918—48% + 81000916—2% + 81000577—2% | |
| S28_3 | 81000917—48% + 81000918—48% + 81000916—2% + 81000577—2% | |
| 15 | S29_1.5 | 81000918 |
| S29_3 | 81000918 | |
| 16 | S30_1.5 | 81000853 |
| S30_3 | 81000853 | |
| 17 | S31_1.5 | 81000851 |
| S31_3 | 81000851 | |
| S32_1.5 | 81000851 + 81001315—2% | |
| S32_3 | 81000851 + 81001315—2% |
| Material Category HB | Material Category HB40 | Material Category HB75 | Cannot Be Categorized |
|---|---|---|---|
| S8_1.5 | S2_3 | S1_3 | S1_1.5 |
| S8_3 | S7_3 | S2_1.5 | S3_1.5 |
| S9_1.5 | S11_3 | S3_3 | |
| S9_3 | S12_1.5 | S4_1.5 | |
| S10_1.5 | S12_3 | S4_3 | |
| S10_3 | S13_1.5 | S5_1.5 | |
| S13_3 | S20_1.5 | S5_3 | |
| S14_3 | S23_1.5 | S6_1.5 | |
| S15_1.5 | S23_3 | S6_3 | |
| S15_3 | S24_1.5 | S7_1.5 | |
| S16_1.5 | S26_1.5 | S11_1.5 | |
| S16_3 | S27_1.5 | S14_1.5 | |
| S17_1.5 | S27_3 | S28_1.5 | |
| S17_3 | S28_3 | S30_1.5 | |
| S18_1.5 | S29_1.5 | S30_3 | |
| S18_3 | S29_3 | ||
| S19_1.5 | |||
| S19_3 | |||
| S20_3 | |||
| S21_1.5 | |||
| S21_3 | |||
| S22_1.5 | |||
| S22_3 | |||
| S24_3 | |||
| S25_1.5 | |||
| S25_3 | |||
| S26_3 | |||
| S31_1.5 | |||
| S31_3 | |||
| S32_1.5 | |||
| S32_3 |
| Material Thickness | Material CategoryHB | Material CategoryHB40 | Material CategoryHB75 | Cannot Be Categorized |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 mm | S8_1.5 | S12_1.5 | S2_1.5 | S1_1.5 |
| S9_1.5 | S13_1.5 | S4_1.5 | S3_1.5 | |
| S10_1.5 | S20_1.5 | S5_1.5 | ||
| S15_1.5 | S23_1.5 | S6_1.5 | ||
| S16_1.5 | S24_1.5 | S7_1.5 | ||
| S17_1.5 | S26_1.5 | S11_1.5 | ||
| S18_1.5 | S27_1.5 | S14_1.5 | ||
| S19_1.5 | S29_1.5 | S28_1.5 | ||
| S21_1.5 | S30_1.5 | |||
| S22_1.5 | ||||
| S25_1.5 | ||||
| S31_1.5 | ||||
| S32_1.5 | ||||
| 3.0 mm | S8_3 | S2_3 | S1_3 | |
| S9_3 | S7_3 | S3_3 | ||
| S10_3 | S11_3 | S4_3 | ||
| S13_3 | S12_3 | S5_3 | ||
| S14_3 | S23_3 | S6_3 | ||
| S15_3 | S27_3 | S30_3 | ||
| S16_3 | S28_3 | |||
| S17_3 | S29_3 | |||
| S18_3 | ||||
| S19_3 | ||||
| S20_3 | ||||
| S21_3 | ||||
| S22_3 | ||||
| S24_3 | ||||
| S25_3 | ||||
| S26_3 | ||||
| S31_3 | ||||
| S32_3 |
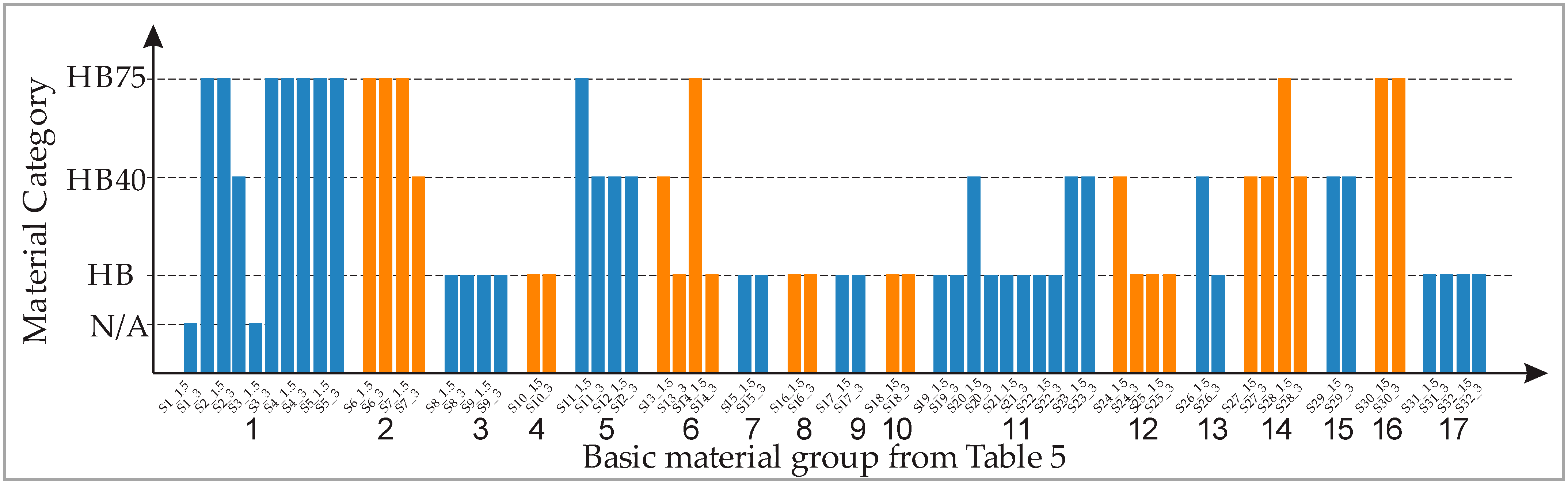
| Basic Material Group | Mixture Mark | Material Combination | Material Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | S1_1.5 | 81001531 | Cannot be categorized |
| S1_3 | 81001531 | HB75 | |
| S2_1.5 | 81001531 + 81001532—4% | HB75 | |
| S2_3 | 81001531 + 81001532—4% | HB40 | |
| S3_1.5 | 81001531 + 81000577—2% | Cannot be categorized | |
| S3_3 | 81001531 + 81000577—2% | HB75 | |
| S4_1.5 | 81001531 + 81000577—2% + 81001532—4% | HB75 | |
| S4_3 | 81001531 + 81000577—2% + 81001532—4% | HB75 | |
| S5_1.5 | 81001531 + 81001483—2% | HB75 | |
| S5_3 | 81001531 + 81001483—2% | HB75 | |
| 2 | S6_1.5 | 81001295 | HB75 |
| S6_3 | 81001295 | HB75 | |
| S7_1.5 | 81001295 + 81001119—2% | HB75 | |
| S7_3 | 81001295 + 81001119—2% | HB40 | |
| 3 | S8_1.5 | 81001482 | HB |
| S8_3 | 81001482 | HB | |
| S9_1.5 | 81001482 + 81001483—2% | HB | |
| S9_3 | 81001482 + 81001483—2% | HB | |
| 4 | S10_1.5 | 81001443 | HB |
| S10_3 | 81001443 | HB | |
| 5 | S11_1.5 | 81002009 | HB75 |
| S11_3 | 81002009 | HB40 | |
| S12_1.5 | 81002009 + 81001119—2% | HB40 | |
| S12_3 | 81002009 + 81001119—2% | HB40 | |
| 6 | S13_1.5 | 81001810 | HB40 |
| S13_3 | 81001810 | HB | |
| S14_1.5 | 81001810 + 81001119—2% | HB75 | |
| S14_3 | 81001810 + 81001119—2% | HB | |
| 7 | S15_1.5 | 81000936 | HB |
| S15_3 | 81000936 | HB | |
| 8 | S16_1.5 | 81000935 | HB |
| S16_3 | 81000935 | HB | |
| 9 | S17_1.5 | 10223024 | HB |
| S17_3 | 10223024 | HB | |
| 10 | S18_1.5 | 10238024 | HB |
| S18_3 | 10238024 | HB | |
| 11 | S19_1.5 | 81000264 | HB |
| S19_3 | 81000264 | HB | |
| S20_1.5 | 81000264 + 81001135—2% | HB40 | |
| S20_3 | 81000264 + 81001135—2% | HB | |
| S21_1.5 | 81000264 + 81001483—2% | HB | |
| S21_3 | 81000264 + 81001483—2% | HB | |
| S22_1.5 | 81000264 + 81001134—2% | HB | |
| S22_3 | 81000264 + 81001134—2% | HB | |
| S23_1.5 | 81000264 + 81000267—2% | HB40 | |
| S23_3 | 81000264 + 81000267—2% | HB40 | |
| 12 | S24_1.5 | 81000863 | HB40 |
| S24_3 | 81000863 | HB | |
| S25_1.5 | 81000863 + 81001315—2% | HB | |
| S25_3 | 81000863 + 81001315—2% | HB | |
| 13 | S26_1.5 | 81001893 | HB40 |
| S26_3 | 81001893 | HB | |
| 14 | S27_1.5 | 81000917 | HB40 |
| S27_3 | 81000917 | HB40 | |
| S28_1.5 | 81000917—48% + 81000918—48% + 81000916—2% + 81000577—2% | HB75 | |
| S28_3 | 81000917—48% + 81000918—48% + 81000916—2% + 81000577—2% | HB40 | |
| 15 | S29_1.5 | 81000918 | HB40 |
| S29_3 | 81000918 | HB40 | |
| 16 | S30_1.5 | 81000853 | HB75 |
| S30_3 | 81000853 | HB75 | |
| 17 | S31_1.5 | 81000851 | HB |
| S31_3 | 81000851 | HB | |
| S32_1.5 | 81000851 + 81001315—2% | HB | |
| S32_3 | 81000851 + 81001315—2% | HB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beges, G.; Hudoklin, D. Material Composition Testing Related to Measurement Instrument Enclosure Design and Safety. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5480. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105480
Beges G, Hudoklin D. Material Composition Testing Related to Measurement Instrument Enclosure Design and Safety. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(10):5480. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105480
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeges, Gaber, and Domen Hudoklin. 2025. "Material Composition Testing Related to Measurement Instrument Enclosure Design and Safety" Applied Sciences 15, no. 10: 5480. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105480
APA StyleBeges, G., & Hudoklin, D. (2025). Material Composition Testing Related to Measurement Instrument Enclosure Design and Safety. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5480. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105480






