Relationship Between Refractive Error, Visual Acuity, and Postural Stability in Elite Football Players
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Visual Acuity and Refractive Error Measurement
2.2. Postural Stability Assessment Using the Cyber-Sabots™ Platform
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Results
3.2. Analysis of Correlations Between Visual Parameters and Postural Stability
4. Discussion
4.1. Correlations Between Visual Parameters and Postural Stability
4.2. Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ivanenko, Y.; Gurfinkel, V.S. Human Postural Control. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floessel, P.; Hammerschmidt, F.; Koltermann, J.J.; Foerster, J.; Beck, H.; Disch, A.C.; Datzmann, T. Comparison of Measurements for Recording Postural Control in Standing and Seated Position in Healthy Individuals. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2024, 9, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillard, T. Plasticity of the Postural Function to Sport and/or Motor Experience. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 72, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luk, J.K.H.; Chan, T.Y.; Chan, D.K.Y. Falls Prevention in the Elderly: Translating Evidence into Practice. Hong Kong Med. J. 2015, 21, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncada, L.V.V.; Mire, L.G. Preventing Falls in Older Persons. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 96, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghiasi-Noughaby, A.; Amiri, P.; Kearney, R.E.; Mohebbi, A. Identification of the Human Postural Sway Response to Visual Inputs. In Proceedings of the 2024 46th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 July 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghapour, M.; Affenzeller, N.; Peham, C.; Lutonsky, C.; Tichy, A.; Bockstahler, B. Effect of Vision and Surface Slope on Postural Sway in Healthy Adults: A Prospective Cohort Study. Life 2024, 14, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.I.; Yu, D.-S.; Kim, S.-Y. Effect of Optical Correction by Fully Corrected Glasses on Postural Stability. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, B.-Y.; Cho, H.G.; Yu, D.-S.; Kim, S.-Y. Uncorrected Low Hyperopia in Young Subjects Induces Postural Instability Even in Those with Clear Visual Acuity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.-S.; Kim, S.-Y. Changes in Postural Control Ability after Wearing Corrective Glasses for Distance in Older Adults and Their Causes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J. Effects of Vision and Cognitive Load on Anticipatory and Compensatory Postural Control. Human. Mov. Sci. 2019, 64, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, S.; Aruin, A.S. Static and Dynamic Visual Cues in Feed-Forward Postural Control. Exp. Brain Res. 2013, 224, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohapatra, S.; Krishnan, V.; Aruin, A.S. The Effect of Decreased Visual Acuity on Control of Posture. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, S.C.; Bazett-Jones, D.M.; Joshi, M.N.; Earl-Boehm, J.E.; James, C.R. The Relationship Among Foot Posture, Core and Lower Extremity Muscle Function, and Postural Stability. J. Athl. Train. 2014, 49, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viseux, F.J.F. The Sensory Role of the Sole of the Foot: Review and Update on Clinical Perspectives. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2020, 50, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menz, H.B.; Dufour, A.B.; Riskowski, J.L.; Hillstrom, H.J.; Hannan, M.T. Foot Posture, Foot Function and Low Back Pain: The Framingham Foot Study. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 2275–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol, F.; Forghany, S.; Hosseini, S.M.; Taheri, A.; Menz, H.B. Structural and Functional Foot and Ankle Characteristics Associated with Falls in Older People. Gait Posture 2021, 88, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, W.G.; Ivanenko, Y.P.; Gurfinkel, V.S. Foot Anatomy Specialization for Postural Sensation and Control. J. Neurophysiol. 2012, 107, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillard, T. Relationship Between Sport Expertise and Postural Skills. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, V.; Chiaramello, E.; Canavese, L.; Bredariol, C.; Knaflitz, M. Postural Sway in Volleyball Players. Human. Mov. Sci. 2013, 32, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadczak, Ł.; Grygorowicz, M.; Wieczorek, A.; Śliwowski, R. Analysis of Static Balance Performance and Dynamic Postural Priority According to Playing Position in Elite Soccer Players. Gait Posture 2019, 74, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pau, M.; Arippa, F.; Leban, B.; Corona, F.; Ibba, G.; Todde, F.; Scorcu, M. Relationship between Static and Dynamic Balance Abilities in Italian Professional and Youth League Soccer Players. Phys. Ther. Sport. 2015, 16, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annino, G.; Manzi, V.; Alashram, A.R.; Romagnoli, C.; Coniglio, M.; Lamouchideli, N.; Perrone, M.A.; Limongi, D.; Padua, E. COVID-19 as a Potential Cause of Muscle Injuries in Professional Italian Serie A Soccer Players: A Retrospective Observational Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marotta, N.; de Sire, A.; Gimigliano, A.; Demeco, A.; Moggio, L.; Vescio, A.; Iona, T.; Ammendolia, A. Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on the Epidemiology of Soccer Muscle Injuries in Italian Serie A Professional Football Players. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 2022, 62, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A Flexible Statistical Power Analysis Program for the Social, Behavioral, and Biomedical Sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibos, L.N.; Wheeler, W.; Horner, D. Power Vectors: An Application of Fourier Analysis to the Description and Statistical Analysis of Refractive Error. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1997, 74, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AFP Standards 85/2000; Posturology Platform Standard; Normes 85. AFP Association Française de Posturologie: Paris, France, 1985.
- Altman, D.G.; Bland, J.M. Statistics Notes Variables and Parameters. BMJ 1999, 318, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, G. Likert Scales, Levels of Measurement and the “Laws” of Statistics. Adv. Health Sci. Educ. Theory Pract. 2010, 15, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grech, V.; Calleja, N. WASP (Write a Scientific Paper): Parametric vs. Non-Parametric Tests. Early Human. Development 2018, 123, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, J.; Fernandes, P. Static and Dynamic Visual Acuity and Refractive Errors in Elite Football Players. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2019, 102, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, J.; Jorge, J.P. Relationship between Dynamic Visual Acuity and Static Visual Acuity, Refractive Error, and Binocular Vision in Elite Soccer Players. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2024, 107, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, J.; Diaz-Rey, A.; Lira, M. Prevalence of Binocular Vision Dysfunctions in Professional Football Players. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2021, 105, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algaba-Del-Castillo, J.; Castro-Méndez, A.; Pérez-Belloso, A.J.; Garrido-Barragán, J.G.; Aguilar Sánchez, A.; Coheña-Jiménez, M. Pilot Study: The Relationship between Foot Posture and Movement Quality in Non-Professional Male Football Players. Life 2023, 13, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, P.D.S.S.; Kanas, M.; Wajchenberg, M. Sagittal Balance in Professional Brazilian Football Players. Spine Surg. Relat. Res. 2023, 7, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degache, F.; Goy, Y.; Vat, S.; Haba Rubio, J.; Contal, O.; Heinzer, R. Sleep-Disordered Breathing and Daytime Postural Stability. Thorax 2016, 71, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mangalam, M.; Kelty-Stephen, D.G. Hypothetical Control of Postural Sway. J. R. Soc. Interface 2021, 18, 20200951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodworth, A.; Kratzer, A.; Saavedra, S. Influence of Visual Biofeedback and Inherent Stability on Trunk Postural Control. Gait Posture 2020, 80, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, M.; Day, T.A.; Strzalkowski, N.D.J. Standing Balance Responses and Habituation to Sinusoidal Optic Flow Virtual Reality Perturbations. Exp. Brain Res. 2025, 243, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.; Burnfield, J. Gait Analysis: Normal and Pathological Function, 2nd ed.; Slack Incorporated: Thorofare, NJ, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-55642-766-4. [Google Scholar]
- Haddad, M. Motor Asymmetry in Football: Implications for Muscular Power, Balance, and Injury Prevention. Symmetry 2024, 16, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreeva, A.; Melnikov, A.; Skvortsov, D.; Akhmerova, K.; Vavaev, A.; Golov, A.; Draugelite, V.; Nikolaev, R.; Chechelnickaia, S.; Zhuk, D.; et al. Postural Stability in Athletes: The Role of Sport Direction. Gait Posture 2021, 89, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigsby, K.; Mangine, R.E.; Clark, J.F.; Rauch, J.T.; Bixenmann, B.; Susaret, A.W.; Hasselfeld, K.A.; Colosimo, A.J. Effects of Postural Control Manipulation on Visuomotor Training Performance: Comparative Data in Healthy Athletes. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2014, 9, 436–446. [Google Scholar]
- Chaari, F.; Boyas, S.; Sahli, S.; Fendri, T.; Harrabi, M.A.; Rebai, H.; Rahmani, A. Postural Balance Asymmetry and Subsequent Noncontact Lower Extremity Musculoskeletal Injuries among Tunisian Soccer Players with Groin Pain: A Prospective Case Control Study. Gait Posture 2022, 98, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murnaghan, C.D.; Horslen, B.C.; Inglis, J.T.; Carpenter, M.G. Exploratory Behavior during Stance Persists with Visual Feedback. Neuroscience 2011, 195, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mean ± SD | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Years) | 22.20 ± 3.50 | ||
| Visual acuity (LogMAR) | Right Eye | −0.01 ± 0.10 | |
| Left Eye | −0.02 ± 0.10 | ||
| Both Eyes | −0.03 ± 0.09 | ||
| Difference right/left eye | 0.01± 0.04 | ||
| Refractive error (D) | Right eye | M | 0.06 ± 0.44 |
| J0 | 0.07 ± 0.24 | ||
| J45 | −0.04 ± 0.15 | ||
| Anisometropia | 0.29 ± 0.31 | ||
| Anisoastigmatism | J0 | 0.11 ± 0.15 | |
| J45 | 0.10 ± 0.18 | ||
| Ametropia (%) | Myopia: | 5.90 | |
| Emmetropia: | 79.40 | ||
| Hyperopia: | 14.70 | ||
| Mean ± SD | ||
|---|---|---|
| Mean CoP position | Xmean (mm) | −1.18 ± 10.09 |
| Ymean (mm) | 43.42 ± 19.67 | |
| DistMean (mm) | 6.74 ± 2.13 | |
| Area and amplitude of sway | Surface (mm2) | 300.55 ± 157.07 |
| Length (mm) | 889.10 ± 270.52 | |
| LengthX (mm) | 729.77 ± 262.81 | |
| LengthY (mm) | 377.95 ± 93.63 | |
| Velocity and variability of CoP | VarV (mm2/s2) | 115.24 ± 56.46 |
| VFY (mm/s) | −5.00 ± 10.00 | |
| Frequency and spectral analysis | AN02X (%) | 27.35 ± 9.89 |
| AN02Y (%) | 27.63 ± 8.19 | |
| Load distribution and asymmetry | LF (%) | 0.28 ± 0.07 |
| LR (%) | 0.24 ± 0.09 | |
| RF (%) | 0.30 ± 0.07 | |
| RR (%) | 0.18 ± 0.07 | |
| LFOOT (%) | 0.51 ± 0.05 | |
| RFOOT (%) | 0.48 ± 0.05 | |
| Posterior (%) | 0.42 ± 0.13 | |
| Anterior (%) | 0.58 ± 0.13 | |
| APR (%) | −16.50 ± 25.19 | |
| LRR (%) | 3.07 ± 9.53 | |
| FeetP (°) | 4.20 ± 6.5 | |
| IntCorLR | 0.76 ± 0.15 | |
| Stability and postural stability | LFS | 1.75 ± 0.50 |
| IVV (PA) | −0.01 ± 0.16 | |
| Dependence vision | QRBG(Surf) (%) | 125.00 ± 97.80 |
| QRBVV (%) | 122.36 ± 43.83 |
| Visual Acuity Right Eye | Binocular Visual Acuity | M | J0 | J45 | Anisometropia | Ametropia | Anisoastigmatism J0 | Anisoastigmatism J45 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
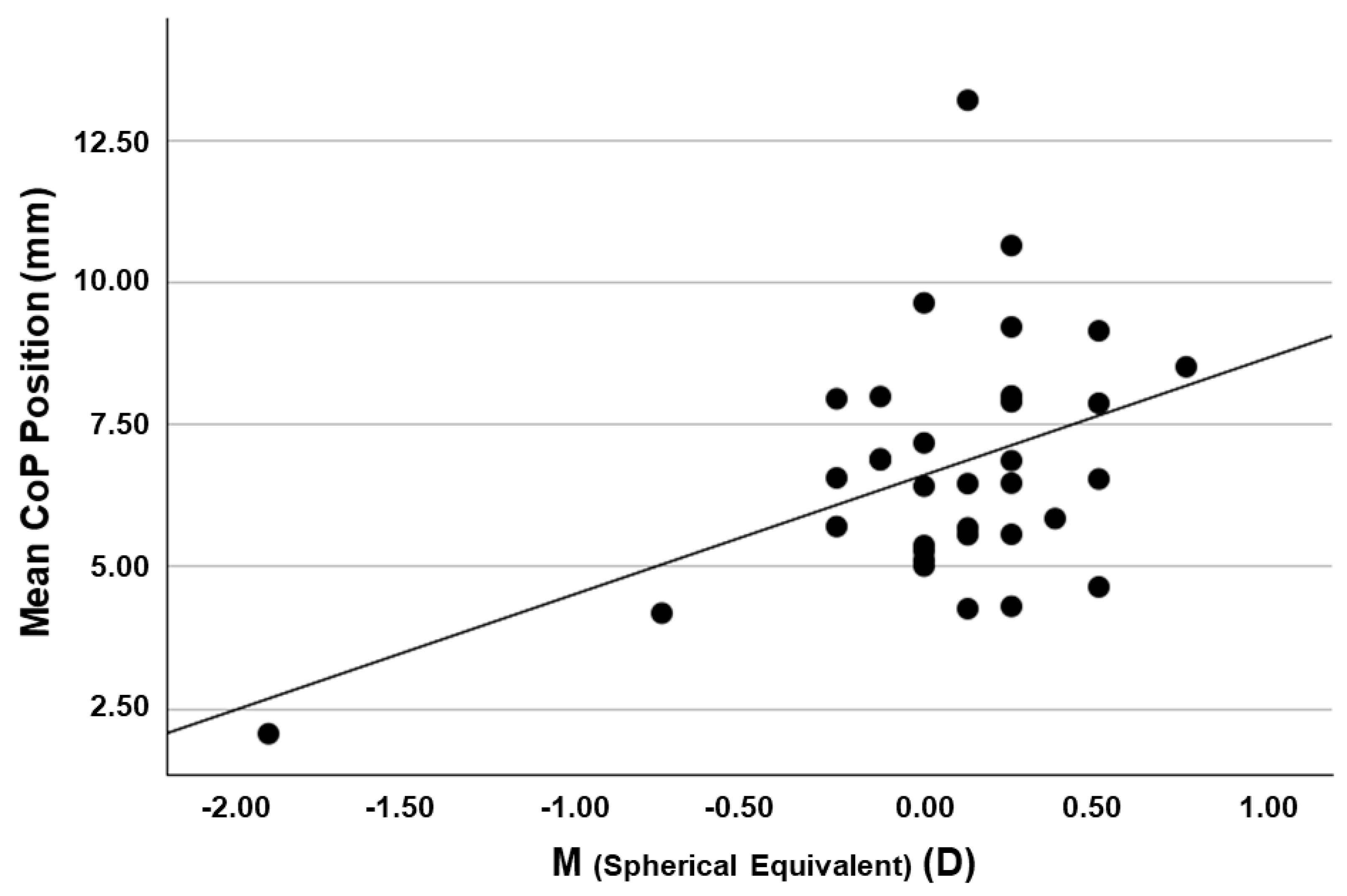
| Mean CoP position | DistMean | r | −0.318 [−0.592, 0.023] | −0.352 [−0.616, −0.015] | 0.437 [0.116, 0.676] | 0.412 [0.086, 0.659] | −0.343 [−0.610, −0.005] | 0.325 [−0.014, 0.598] | −0.502 [−0.718, −0.197] | ||
| p-value | 0.033 | 0.020 | 0.005 | 0.008 | 0.024 | 0.030 | 0.001 | ||||
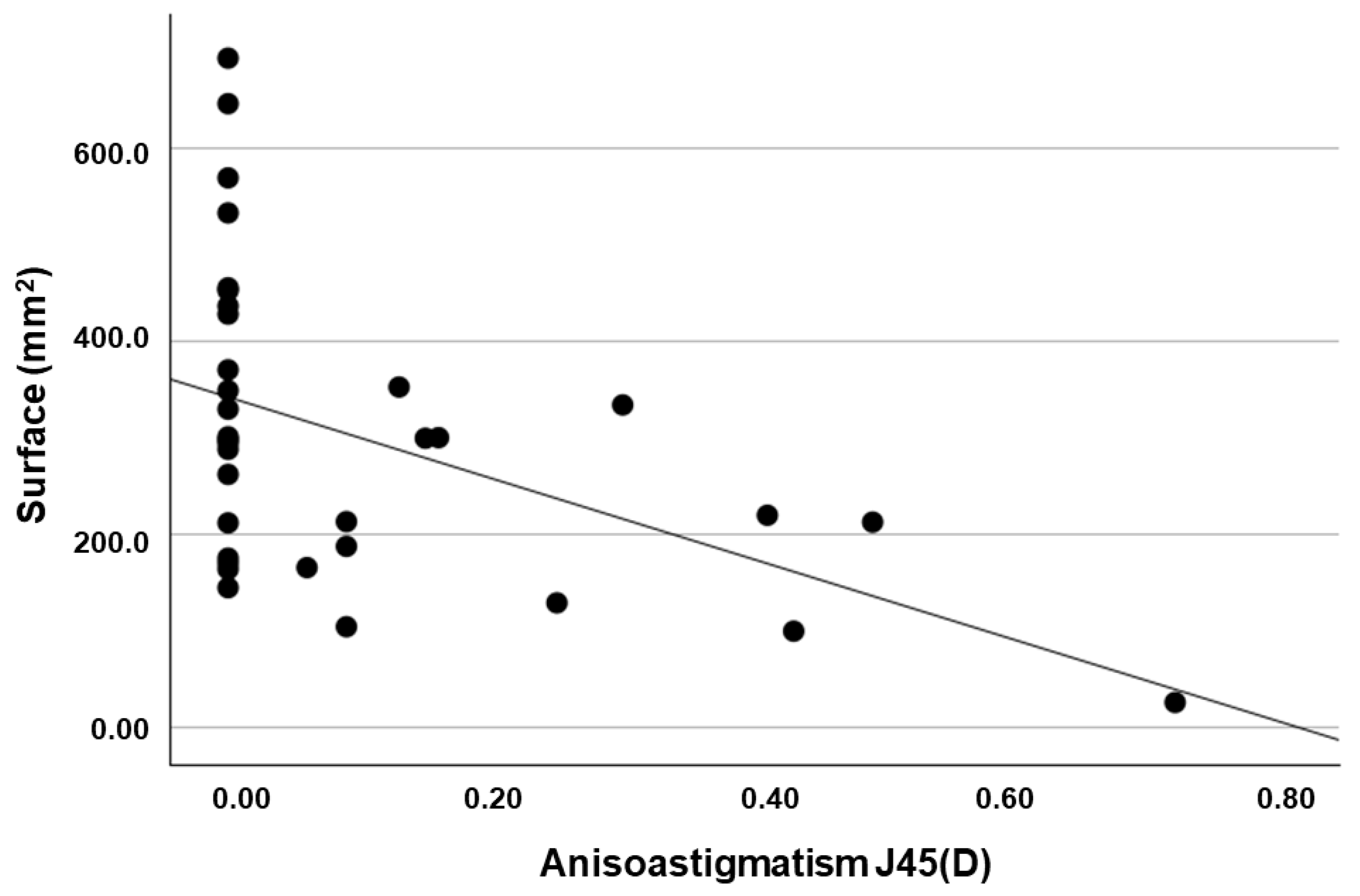
| Area and amplitude of sway | Surface | r | −0.326 [−0.598, 0.014] | −0.367 [−0.627, −0.032] | 0.329 [−0.010, 0.601] | 0.343 [0.006, 0.611] | −0.306 [−0.583, 0.036] | −0.471 [−0.697, −0.157] | |||
| p-value | 0.030 | 0.016 | 0.029 | 0.024 | 0.039 | 0.002 | |||||
| Length | r | −0.289 [−0.571, 0.055] | −0.370 [−0.629, −0.036] | 0.328 [−0.011, 0.600] | −0.363 [−0.624, −0.028] | ||||||
| p-value | 0.048 | 0.016 | 0.029 | 0.017 | |||||||
| LengthX | r | −0.350 [−0.615, −0.013] | 0.317 [−0.023, 0.592] | −0.352 [−0.616, −0.015] | |||||||
| p-value | 0.021 | 0.034 | 0.021 | ||||||||
| LengthY | r | −0.343 [−0.610, −0.005] | 0.324 [−0.015, 0.597] | −0.421 [−0.664, −0.096] | −0.291 [−0.572, 0.053] | −0.372 [−0.630, −0.038] | |||||
| p-value | 0.024 | 0.031 | 0.007 | 0.047 | 0.015 | ||||||
| Stability and Postural stability | LFS | r | −0.392 [−0.644, −0.062] | ||||||||
| p-value | 0.011 | ||||||||||
| Frequency and spectral analysis | AN02X | r | 0.297 [−0.045, 0.578] | ||||||||
| p-value | 0.044 | ||||||||||
| AN02Y | r | −0.289 [−0.571, 0.055] | |||||||||
| p-value | 0.049 | ||||||||||
| Load distribution and asymmetry | LF | r | 0.329 [−0.010, 0.601] | ||||||||
| p-value | 0.029 | ||||||||||
| RR | r | 0.311 [−0.030, 0.588] | |||||||||
| p-value | 0.036 | ||||||||||
| FeetP | r | −0.316 [−0.591, 0.025] | −0.374 [−0.632, −0.041] | ||||||||
| p-value | 0.034 | 0.015 | |||||||||
| LFOOT | r | −0.309 [−0.585, 0.033] | |||||||||
| p-value | 0.038 | ||||||||||
| RFOOT | r | 0.309 [−0.032, 0.586] | |||||||||
| p-value | 0.037 | ||||||||||
| LRR | r | −0.309 [−0.585, 0.033] | |||||||||
| p-value | 0.038 | ||||||||||
| Dependence Vision | QRBG (Surf) | r | −0.347 [−0.613, −0.010] | −0.338 [−0.606, 0.001] | −0.307 [−0.584, 0.035] | 0.361 [0.027, 0.624] | |||||
| p-value | 0.022 | 0.025 | 0.038 | 0.018 | |||||||
| QRBVV | r | −0.307 [−0.584, 0.035] | |||||||||
| p-value | 0.039 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, M.; Fuste, R.; Gene-Morales, J.; Gené-Sampedro, A.; Jorge, J. Relationship Between Refractive Error, Visual Acuity, and Postural Stability in Elite Football Players. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5437. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105437
Oliveira M, Fuste R, Gene-Morales J, Gené-Sampedro A, Jorge J. Relationship Between Refractive Error, Visual Acuity, and Postural Stability in Elite Football Players. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(10):5437. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105437
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Miguel, Rui Fuste, Javier Gene-Morales, Andrés Gené-Sampedro, and Jorge Jorge. 2025. "Relationship Between Refractive Error, Visual Acuity, and Postural Stability in Elite Football Players" Applied Sciences 15, no. 10: 5437. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105437
APA StyleOliveira, M., Fuste, R., Gene-Morales, J., Gené-Sampedro, A., & Jorge, J. (2025). Relationship Between Refractive Error, Visual Acuity, and Postural Stability in Elite Football Players. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5437. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105437








