Self-Selected Comfortable Foot Position in Upright Standing: Correlation with Anthropometric Measurements and Comparison to Standardized Foot Position During Stabilometric Exam—An Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
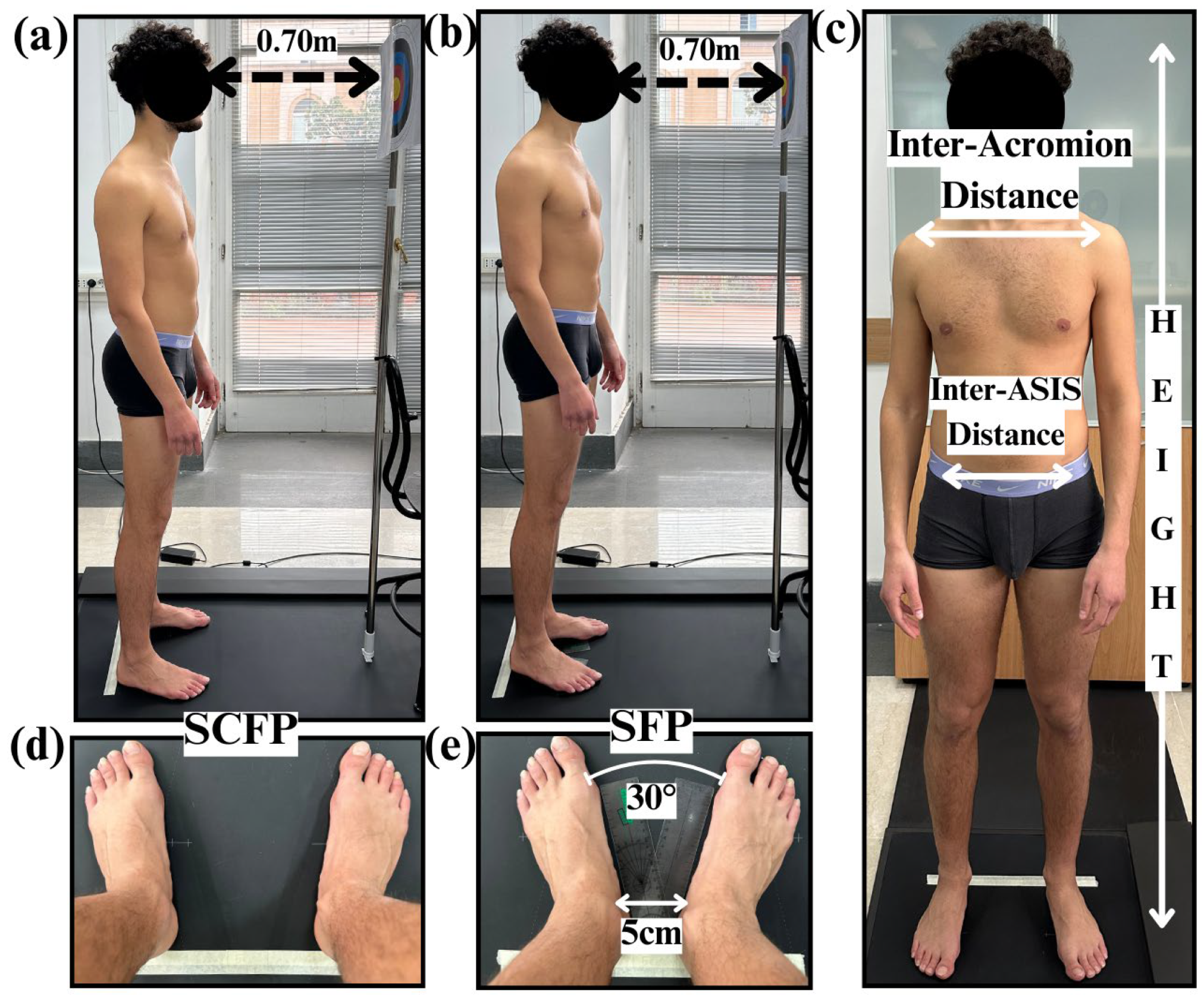
2.1. Subject Population
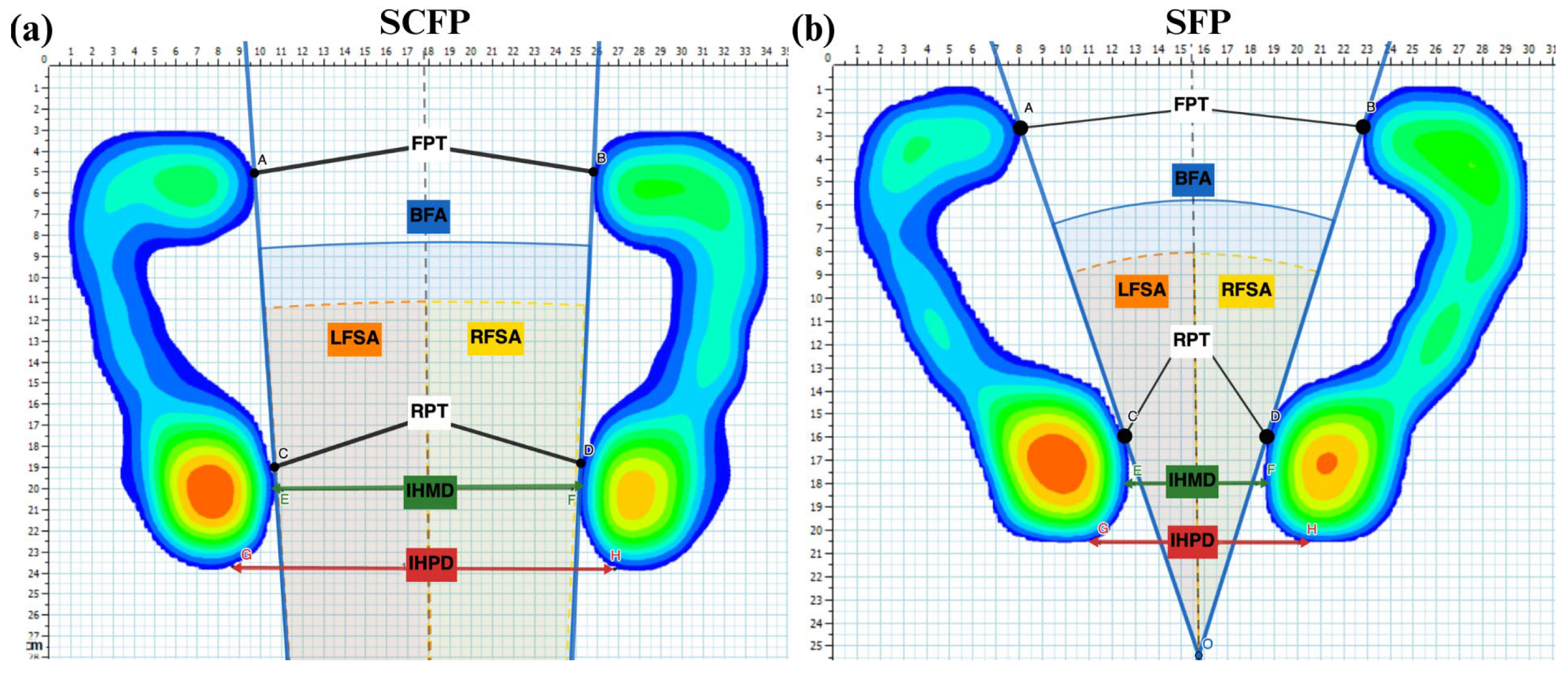
2.2. Experimental Protocol
2.3. Data Acquisition and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Correlation Between Anthropometric and Between-Feet Measurements in SCFP
3.2. Inter-Subject Comparison Between SCFP and SFP for Between-Feet Measurements (BFMs)
3.3. Intra-Subject (Inter-Trial) Variability of Stabilometric and Plantar Pressure Parameters in SCFP and SFP
3.4. The Effect of the Foot Positions (SCFP and SFP) on CVs
3.5. The Effect of Different Foot Positions (SCFP and SFP) on Stabilometric and Plantar Pressure Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiari, L.; Rocchi, L.; Cappello, A. Stabilometric parameters are affected by anthropometry and foot placement. Clin. Biomech. 2002, 17, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanenko, Y.; Gurfinkel, V.S. Human Postural Control. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horak, F.B. Postural orientation and equilibrium: What do we need to know about neural control of balance to prevent falls? Age Ageing 2006, 35 (Suppl. 2), ii7–ii11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massion, J. Postural control system. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1994, 4, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Blasiis, P.; Fullin, A.; De Girolamo, C.I.; Amata, O.; Caravaggi, P.; Caravelli, S.; Mosca, M.; Lucariello, A. Posture and vision: How different distances of viewing target affect postural stability and plantar pressure parameters in healthy population. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakusaki, K. Functional Neuroanatomy for Posture and Gait Control. J. Mov. Disord. 2017, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Blasiis, P.; Caravaggi, P.; Fullin, A.; Leardini, A.; Lucariello, A.; Perna, A.; Guerra, G.; De Luca, A. Postural stability and plantar pressure parameters in healthy subjects: Variability, correlation analysis and differences under open and closed eye conditions. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1198120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffa, S.; Perna, A.; Candela, G.; Cattolico, A.; Sellitto, C.; De Blasiis, P.; Guerra, G.; Tafuri, D.; Lucariello, A. Effects of Hoverboard on Balance in Young Soccer Athletes. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2020, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuthill, J.C.; Azim, E. Proprioception. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R194–R203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, S.; Immink, M.; Thewlis, D. Assessing Proprioception: A Systematic Review of Possibilities. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2015, 29, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravelli, S.; Bragonzoni, L.; Vocale, E.; Barone, G.; Vara, G.; Di Paolo, S.; Zinno, R.; Pinelli, E.; De Girolamo, C.I.; De Blasiis, P.; et al. Proprioception and Balance Control in Ankle Osteoarthritis and after Total Ankle Replacement: A Prospective Assessment. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goble, D.J.; Coxon, J.P.; Van Impe, A.; Geurts, M.; Van Hecke, W.; Sunaert, S.; Wenderoth, N.; Swinnen, S.P. The neural basis of central proprioceptive processing in older versus younger adults: An important sensory role for right putamen. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2012, 33, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Blasiis, P.; Fullin, A.; Caravaggi, P.; Lus, G.; Melone, M.A.; Sampaolo, S.; DE Luca, A.; Lucariello, A. Long-term effects of asymmetrical posture in boxing assessed by baropodometry. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2022, 62, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdikhani, M.; Khalaj, N.; Chung, T.Y.; Mazlan, M. The effect of feet position on standing balance in patients with diabetes. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2014, 228, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlroy, W.E.; Maki, B.E. Preferred placement of the feet during quiet stance: Development of a standardized foot placement for balance testing. Clin. Biomech. 1997, 12, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Ishikawa, K.; Aoki, M.; Mizuta, K.; Ito, Y.; Asai, M.; Shojaku, H.; Yamanaka, T.; Fujimoto, C.; Murofushi, T.; et al. Japanese standard for clinical stabilometry assessment: Current status and future directions. Auris Nasus Larynx 2018, 45, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, R.L.; Price, N.A.; MacLeod, D.A. The influence of foot position on standing balance. J. Biomech. 1987, 20, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouzat, A.; Dabonneville, M.; Bertrand, P. The effect of feet position on orthostatic posture in a female sample group. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 365, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoppa, F. Clinical Stabilometry Standardization: Feet Position in the Static Stabilometric Assessment of Postural Stability. Acta Med. Mediterr. 2017, 33, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantola, J.; Nardone, A.; Tacchini, E.; Schieppati, M. Human stance stability improves with the repetition of the task: Effect of foot position and visual condition. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 228, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hue, O.; Simoneau, M.; Marcotte, J.; Berrigan, F.; Doré, J.; Marceau, P.; Marceau, S.; Tremblay, A.; Teasdale, N. Body weight is a strong predictor of postural stability. Gait Posture 2007, 26, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Rubio, P.R.; Bagur-Calafat, C.; López-de-Celis, C.; Bueno-Gracía, E.; Cabanas-Valdés, R.; Herrera-Pedroviejo, E.; Girabent-Farrés, M. Validity and Reliability of the Satel 40 Hz Stabilometric Force Platform for Measuring Quiet Stance and Dynamic Standing Balance in Healthy Subjects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quialheiro, A.; Maestri, T.; Zimermann, T.A.; Ziemann, R.M.d.S.; Silvestre, M.V.; Maio, J.M.B.; Xavier, A.J.; Villeneuve, P.; Salgado, A.S.I.; Viseux, F.J.F.; et al. Stabilometric analysis as a cognitive function predictor in adults over the age of 50: A cross-sectional study conducted in a Memory Clinic. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2021, 27, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, H.S.; Lüdtke, D.D.; César de Oliveira Araújo, J.; Cidral-Filho, F.J.; Inoue Salgado, A.S.; Viseux, F.; Martins, D.F. Effects of core strengthening on balance in university judo athletes. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2019, 23, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoula, Z.; Lê, T.-T. Effects of distance and gaze position on postural stability in young and old subjects. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 173, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munafo, J.; Curry, C.; Wade, M.G.; Stoffregen, T.A. The distance of visual targets affects the spatial magnitude and multifractal scaling of standing body sway in younger and older adults. Exp. Brain Res. 2016, 234, 2721–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullin, A.; Caravaggi, P.; Picerno, P.; Mosca, M.; Caravelli, S.; De Luca, A.; Lucariello, A.; De Blasiis, P. Variability of Postural Stability and Plantar Pressure Parameters in Healthy Subjects Evaluated by a Novel Pressure Plate. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosário, J.L.P. A review of the utilization of baropodometry in postural assessment. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2014, 18, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoppa, F.; Capra, R.; Gallamini, M.; Shiffer, R. Clinical stabilometry standardization: Basic definitions—Acquisition interval—Sampling frequency. Gait Posture 2013, 37, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhe, A.; Fejer, R.; Walker, B. The test-retest reliability of centre of pressure measures in bipedal static task conditions—A systematic review of the literature. Gait Posture 2010, 32, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, K.R.; Myer, G.D.; Smith, R.L.; Byrnes, R.N.; Dopirak, S.E.; Hewett, T.E. Use of an overhead goal alters vertical jump performance and biomechanics. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2005, 19, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohenwarter, M.; Jones, K. Ways of linking geometry and algebra: The case of GeoGebra. Proc. Br. Soc. Res. Learn. Math. 2007, 27, 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- R: The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Hébert-Losier, K.; Murray, L. Reliability of centre of pressure, plantar pressure, and plantar-flexion isometric strength measures: A systematic review. Gait Posture 2020, 75, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennig, E.M.; Sterzing, T. Sensitivity mapping of the human foot: Thresholds at 30 skin locations. Foot Ankle Int. 2009, 30, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| BFMs Mean ± SD (Min; Max) Or Median (25th–75th Percentiles) | AMs Mean ± SD (min; max) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height [cm] | Inter-Acromion Distance [cm] | Inter-ASIS Distance [cm] | ||
| 172.1 ± 7.6 (160; 183) | 34.5 ± 2.7 (29.0; 39.0) | 24.8 ± 2.6 (20.5; 29.5) | ||
| Pearson Correlation Coefficient R (p-Value) [95% Confidence Interval] | ||||
| BFA [Deg] | 12.2 (6.8; 16.4) | 0.369 (0.100) [−0.075; 0.691] | 0.373 (0.095) [−0.070; 0.693] | 0.281 (0.218) [−0.172; 0.635] |
| IHMD [cm] | 15.1 ± 2.9 (8.0; 22.5) | 0.266 (0.244) [−0.187; 0.626] | 0.128 (0.581) [−0.322; 0.530] | 0.415 (0.061) [−0.020; 0.718] |
| IHPD [cm] | 19.6 ± 3.1 (12.2; 26.9) | 0.238 (0.296) [−0.215; 0.608] | 0.110 (0.634) [−0.337; 0.517] | 0.273 (0.096) [−0.070; 0.693] |
| BFMs | Feet Placement Condition | p-Value | |
SCFP | SFP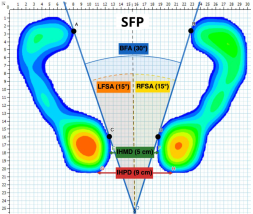 | ||
| Mean ± SD (Min; Max) or Median (25th–75th Percentiles) | Standardized Value | ||
| BFA [Deg] | 12.2 (6.8; 16.4) | 30 | <0.001 * |
| IHMD [cm] | 15.1 ± 2.9 (8.0; 22.5) | 5 | <0.001 * |
| IHPD [cm] | 19.1 ± 3.1 (12.2; 26.9) | 9 | <0.001 * |
| Coefficient of Variation (CV) | LS | SCFP (A) | SFP (B) | SCFP vs. SFP (A vs. B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (25th–75th Percentiles) | p-Value | |||
| Load Tf [%] | l | 1.4 (1.1; 1.9) | 2.1 (1.0; 3.6) | 0.035 (B) |
| r | 1.0 (0.9; 1.7) | 1.8 (1.0; 2.6) | 0.041 (B) | |
| Load Rf [%] | l | 3.0 (2.3; 4.3) | 6.8 (2.5; 10.9) | 0.004 (B) |
| r | 2.70 (2.2; 3.6) | 4.8 (3.8; 7.8) | 0.006 (B) | |
| Load Mf [%] | l | 7.8 (4.2; 15.0) | 14.4 (7.9; 28.2) | 0.032 (B) |
| r | 4.5 (2.2; 17.0) | 16.5 (6.6; 28.7) | 0.001 (B) | |
| Load Ff [%] | l | 3.0 (1.8; 4.94) | 6.7 (4.2; 10.6) | <0.001 (B) |
| r | 1.9 (1.5; 3.4) | 4.7 (2.9; 5.8) | 0.002 (B) | |
| Pmean Tf [KPa] | l | 4.1 (2.5; 5.0) | 5.8 (3.0; 11.3) | 0.041 (B) |
| r | 3.7 (2.8; 5.2) | 5.4 (3.2; 11.1) | 0.010 (B) | |
| Pmean Rf [KPa] | l | 4.9 (2.4; 8.2) | 8.1 (3.1; 15.2) | 0.027 (B) |
| r | 4.8 (3.0; 6.5) | 7.8 (4.3; 12.9) | 0.006 (B) | |
| Pmean Mf [KPa] | l | 4.7 (3.7; 7.9) | 10.9 (6.9; 16.7) | 0.002 (B) |
| r | 5.1 (3.8; 8.4) | 12.2 (8.1; 18.1) | 0.002 (B) | |
| Pmean Ff [KPa] | l | 3.2 (2.2; 3.9) | 6.9 (4.0; 8.9) | <0.001 (B) |
| r | 2.8 (2.0; 5.3) | 4.3 (3.1; 10.0) | 0.052 | |
| Pmax Tf [KPa] | l | 5.5 (3.5; 7.8) | 5.9 (4.2; 10.1) | 0.089 |
| r | 5.7 (3.1; 7.6) | 5.8 (3.1; 12.9) | 0.160 | |
| Pmax Rf [KPa] | l | 5.5 (3.5; 7.8) | 5.9 (4.2; 10.1) | 0.089 |
| r | 5.7 (3.1; 7.6) | 5.8 (3.1; 12.9) | 0.160 | |
| Pmax Mf [KPa] | l | 6.5 (5.7; 9.5) | 11.8 (6.1; 17.4) | 0.016 (B) |
| r | 5.8 (4.6; 14.2) | 15.1 (7.5; 19.8) | 0.035 (B) | |
| Pmax Ff [KPa] | l | 3.5 (1.9; 5.4) | 9.3 (6.9; 11.3) | 0.001 (B) |
| r | 4.1 (2.9; 7.3) | 6.5 (5.2; 10.5) | 0.027 (B) | |
| FCA [cm2] | l | 3.3 (2.3; 4.8) | 6.5 (2.4; 11.6) | 0.002 (B) |
| r | 3.1 (2.4; 4.7) | 5.4 (2.1; 8.2) | 0.025 (B) | |
| AI [%] | l | 8.3 (4.1; 14.9) | 13.9 (7.8; 28.6) | 0.032 (B) |
| r | 4.5 (3.2; 17.8) | 16.3 (6.7; 28.6) | 0.001 (B) | |
| CoPsa [mm2] | 42.8 (26.7; 58.1) | 54.1 (36.0; 67.7) | 0.060 | |
| CP speed [mm/s] | 11.5 (8.2; 17.6) | 15.4 (10.0; 25.4) | 0.129 | |
| LSF [mm−1] | 35.4 (30.4; 55.8) | 50.8 (39.7; 70.8) | 0.060 | |
| Plantar Pressure and Stabilometric Parameter | LS | SCFP (A) | SFP (B) | SCFP vs. SFP (A vs. B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (25th–75th Percentiles) | p-Value | |||
| Load Tf [%] | l | 46.1 (44.8; 47.8) | 46.6 (44.8; 48.5) | 0.217 |
| r | 53.9 (52.2; 55.2) | 53.4 (51.5; 55.2) | 0.217 | |
| Load Rf [%] | l | 46.9 (45.0; 50.0) | 48.2 (46.6; 51.4) | 0.099 |
| r | 42.7 (39.0; 46.1) | 43.7 (41.2; 45.9) | 0.131 | |
| Load Mf [%] | l | 11.3 (4.8; 14.4) | 11.9 (4.2; 16.9) | 0.455 |
| r | 13.3 (5.9; 18.9) | 12.4 (4.1; 18.4) | 0.332 | |
| Load Ff [%] | l | 41.7 (38.7; 48.3) | 39.9 (35.6; 45.9) | 0.017 (A) |
| r | 44.0 (40.1; 47.5) | 43.9 (38.8; 47.8) | 0.181 | |
| Pmean Tf [KPa] | l | 37.4 (33.7; 42.6) | 38.9 (33.4; 44.5) | 0.027 (B) |
| r | 38.0 (34.3; 42.1) | 39.2 (35.3; 43.6) | 0.205 | |
| Pmean Rf [KPa] | l | 50.4 (44.6; 57.1) | 51.6 (45.2; 58.9) | 0.305 |
| r | 49.6 (43.0; 57.8) | 51.3 (46.5; 56.5) | 0.274 | |
| Pmean Mf [KPa] | l | 21.9 (17.9; 26.8) | 23.1 (19.9; 25.3) | 0.027 (B) |
| r | 21.5 (18.4; 24.2) | 22.4 (20.4; 24.4) | 0.181 | |
| Pmean Ff [KPa] | l | 25.7 (22.1; 27.8) | 26.5 (23.5; 29.8) | 0.339 |
| r | 31.2 (30.3; 33.8) | 31.5 (28.0; 33.8) | 0.322 | |
| Pmax Tf [KPa] | l | 93.0 (80.7; 102.0) | 91.9 (81.7; 106.0) | 0.681 |
| r | 91.3 (73.3; 106.7) | 92.0 (84.0; 102.3) | 0.896 | |
| Pmax Rf [KPa] | l | 93.0 (80.7; 102.0) | 91.9 (81.7; 106.0) | 0.681 |
| r | 91.2 (72.7; 106.7) | 92.0 (84.0; 102.3) | 0.896 | |
| Pmax Mf [KPa] | l | 39.4 (30.7; 50.3) | 42.1 (30.7; 53.0) | 0.044 (B) |
| r | 39.9 (27.7; 50.3) | 41.5 (32.7; 53.7) | 0.198 | |
| Pmax Ff [KPa] | l | 42.9 (36.3; 48.3) | 44.1 (35.0; 54.3) | 0.339 |
| r | 53.9 (49.7; 57.7) | 56.2 (49.0; 60.3) | 0.054 | |
| FCA [mm2] | l | 94.4 (82.0; 108.6) | 91.9 (77.7; 104.0) | 0.149 |
| r | 108.3 (90.7; 127.7) | 103.3 (91.3; 121.6) | 0.032 (A) | |
| AI [%] | l | 11.3 (4.8; 14.4) | 11.9 (4.2; 16.9) | 0.394 |
| r | 13.3 (5.9; 19.1) | 12.5 (4.1; 18.4) | 0.289 | |
| CoPsa [mm2] | 38.1 (28.8; 47.9) | 38.2 (26.1; 51.0) | 0.931 | |
| CP speed [mm/s] | 4.8 (4.2; 5.2) | 4.4 (3.5; 4.2) | 0.001 (A) | |
| LSF [mm−1] | 4.7 (4.2; 7.7) | 4.7 (2.6; 6.3) | 0.085 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Blasiis, P.; De Girolamo, C.I.; Fullin, A.; Caravaggi, P.; Tirelli, A.; Arpaia, P.; Leardini, A.; De Luca, A. Self-Selected Comfortable Foot Position in Upright Standing: Correlation with Anthropometric Measurements and Comparison to Standardized Foot Position During Stabilometric Exam—An Observational Study. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5417. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105417
De Blasiis P, De Girolamo CI, Fullin A, Caravaggi P, Tirelli A, Arpaia P, Leardini A, De Luca A. Self-Selected Comfortable Foot Position in Upright Standing: Correlation with Anthropometric Measurements and Comparison to Standardized Foot Position During Stabilometric Exam—An Observational Study. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(10):5417. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105417
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Blasiis, Paolo, Ciro Ivan De Girolamo, Allegra Fullin, Paolo Caravaggi, Assunta Tirelli, Pasquale Arpaia, Alberto Leardini, and Antonio De Luca. 2025. "Self-Selected Comfortable Foot Position in Upright Standing: Correlation with Anthropometric Measurements and Comparison to Standardized Foot Position During Stabilometric Exam—An Observational Study" Applied Sciences 15, no. 10: 5417. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105417
APA StyleDe Blasiis, P., De Girolamo, C. I., Fullin, A., Caravaggi, P., Tirelli, A., Arpaia, P., Leardini, A., & De Luca, A. (2025). Self-Selected Comfortable Foot Position in Upright Standing: Correlation with Anthropometric Measurements and Comparison to Standardized Foot Position During Stabilometric Exam—An Observational Study. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5417. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105417










