Research on the Yunnan Large-Leaf Tea Tree Disease Detection Model Based on the Improved YOLOv10 Network and UAV Remote Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
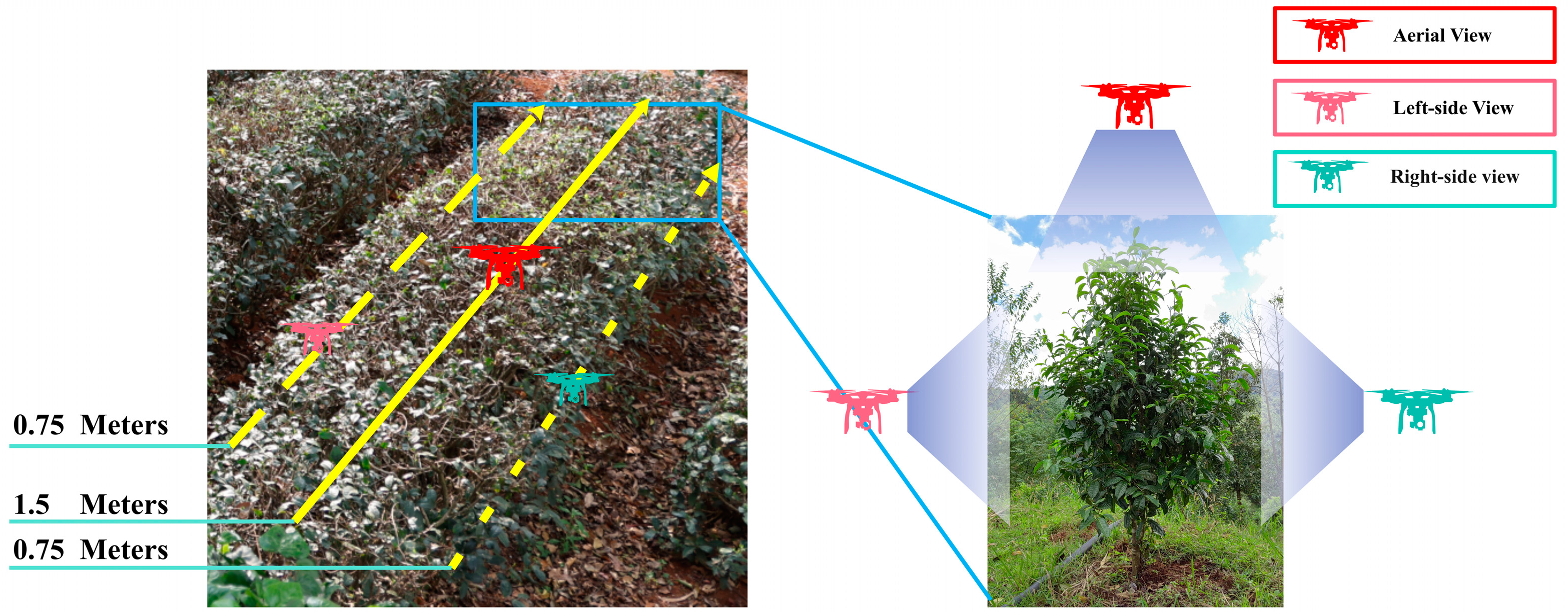
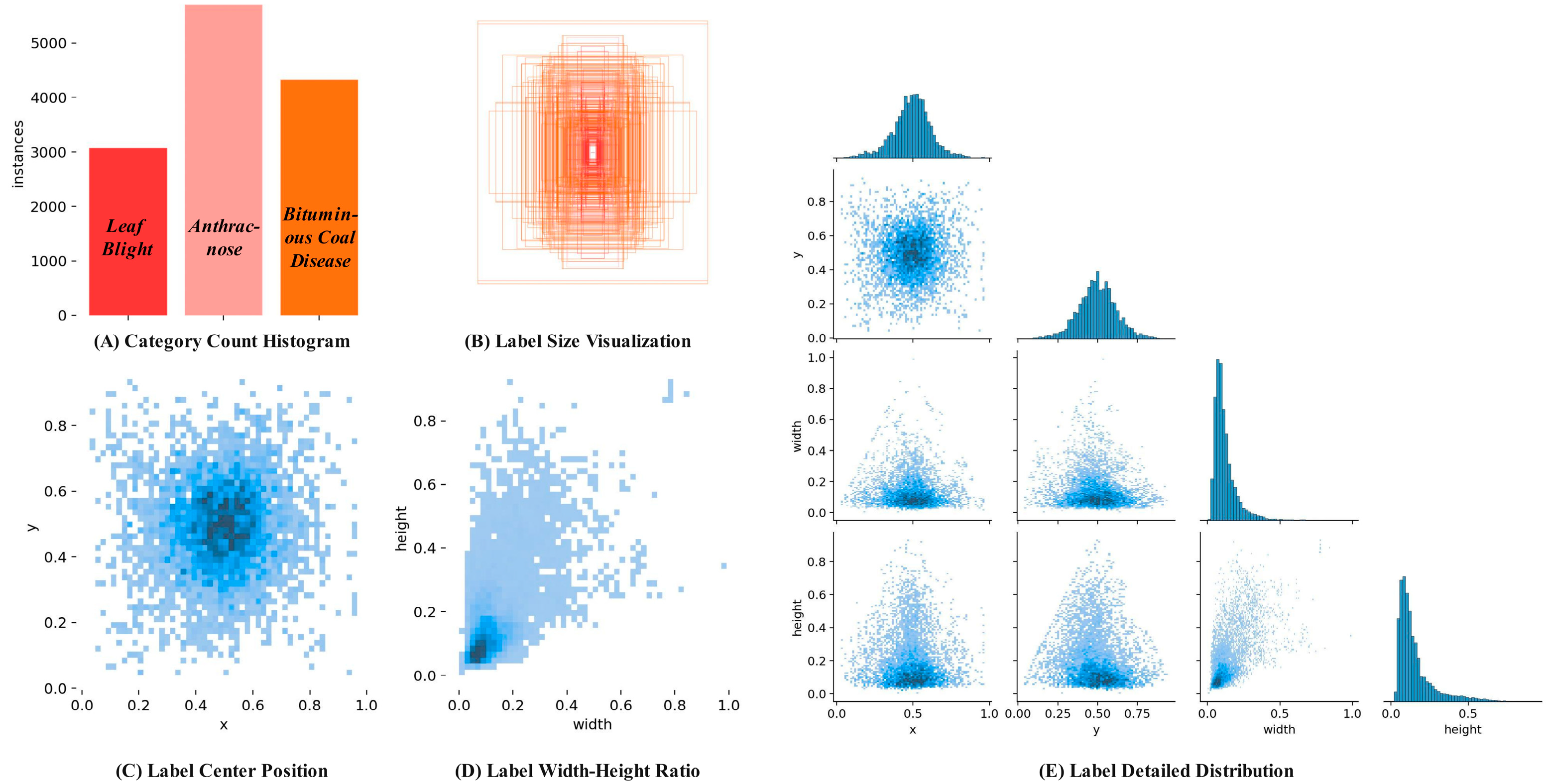
2.1. Dataset Construction
2.2. YOLOv10 Network Improvement
2.2.1. Bounding Box Regression Loss Optimization
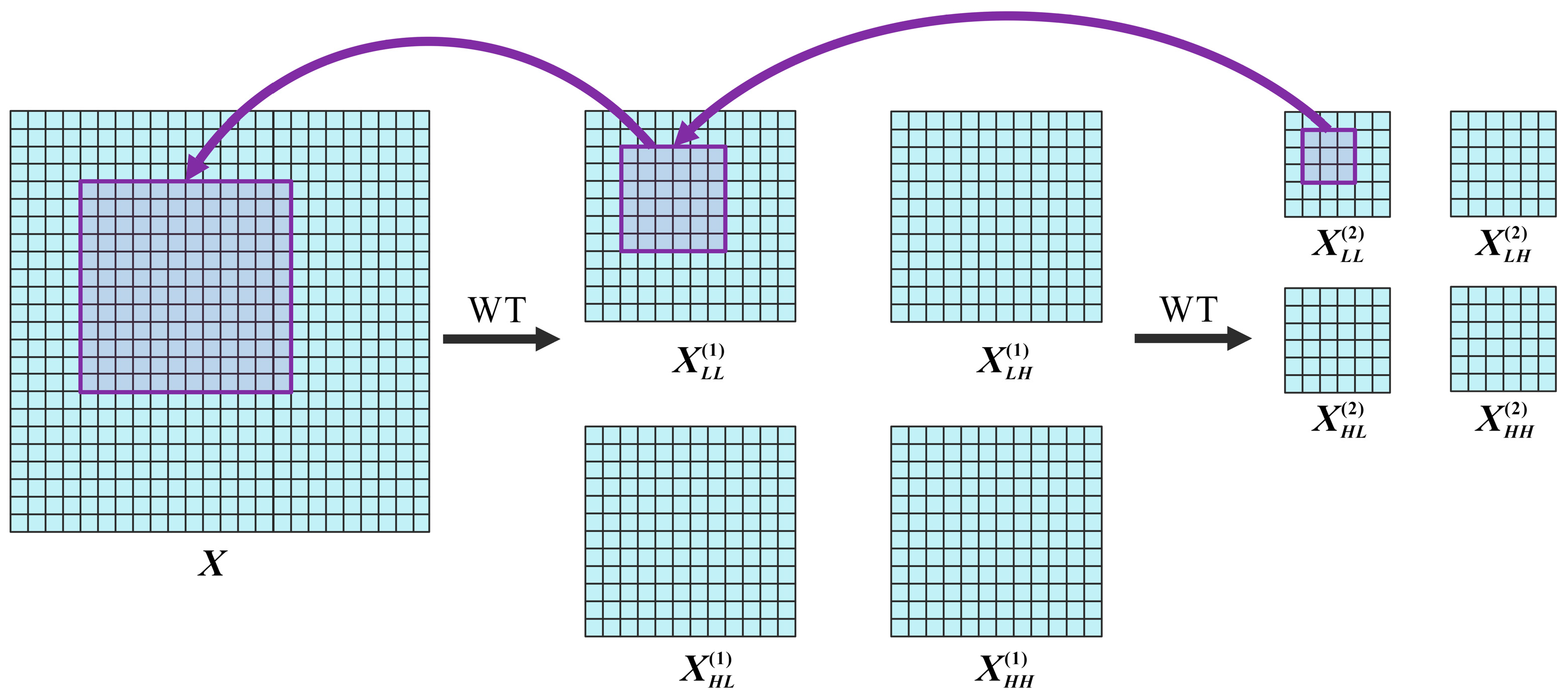
2.2.2. Wavelet Transform Conv Optimization
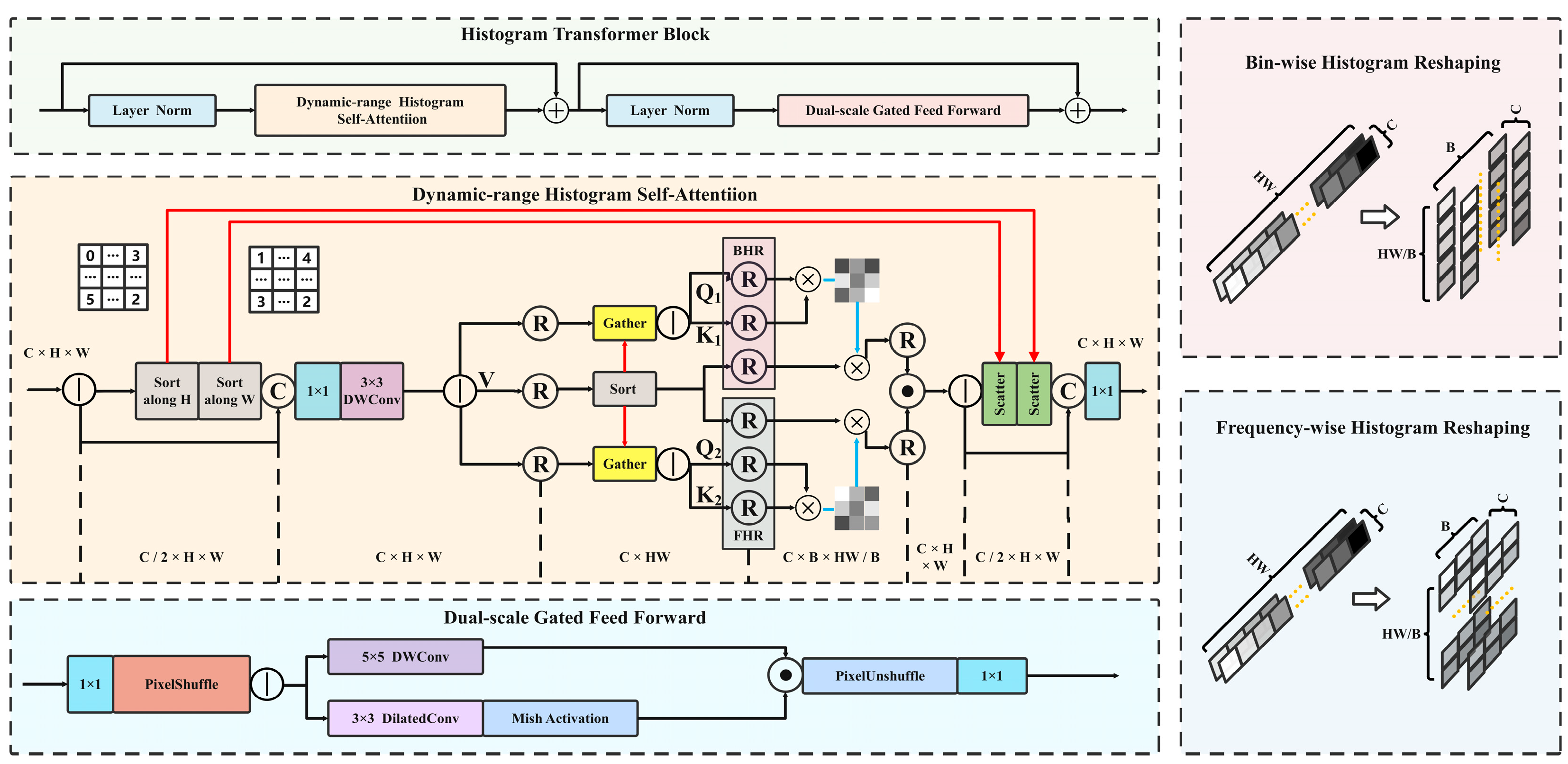
2.2.3. Histogram Transformer Optimization
2.3. Model Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
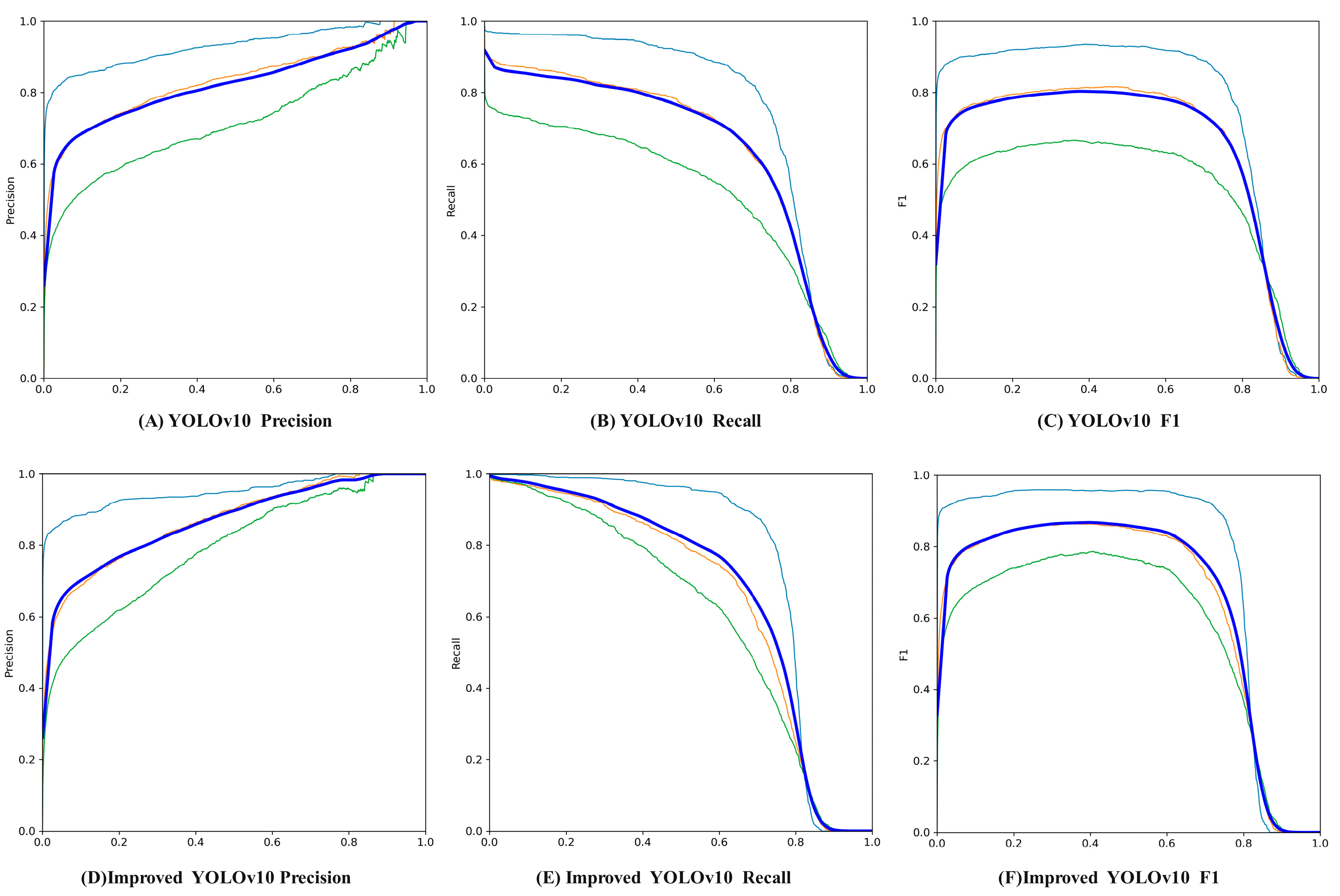
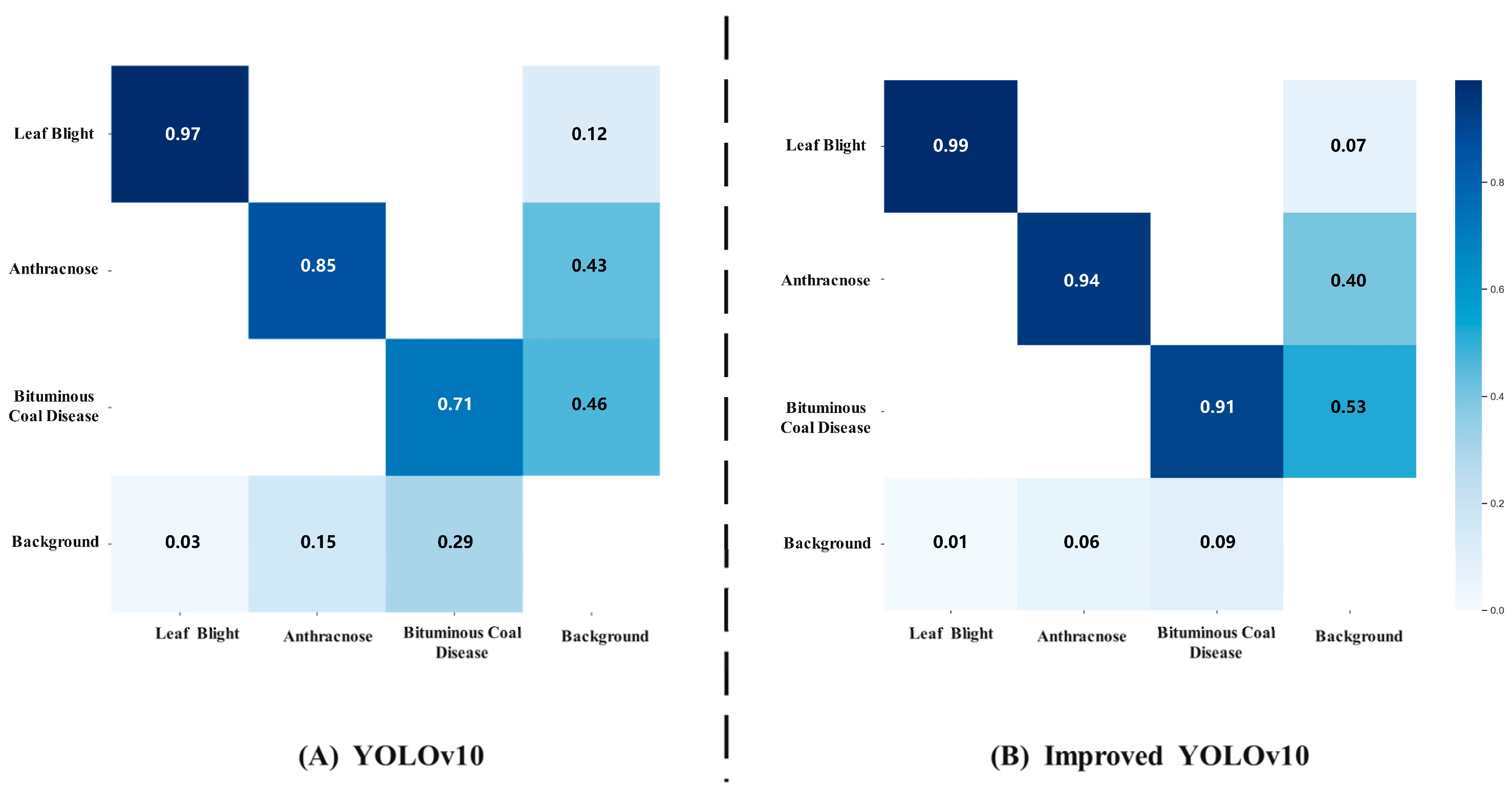
3.1. Model Result Analysis
3.2. Ablation Study
3.3. Model Comparison Experiments
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Regarding the model loss function, under the One-to-Many Head, the improved YOLOv10 exhibits Box Loss, Cls Loss, and DFL Loss values of 1.16, 0.66, and 1.24, respectively, which represent reductions of 15.94%, 13.16%, and 8.82% compared to the original network values of 1.38, 0.76, and 1.36. Under the One-to-One Head, the Box Loss, Cls Loss, and DFL Loss are 1.23, 0.65, and 1.23, respectively, corresponding to reductions of 14.58%, 17.72%, and 8.89% relative to the original YOLOv10 network values of 1.44, 0.79, and 1.35.
- (2)
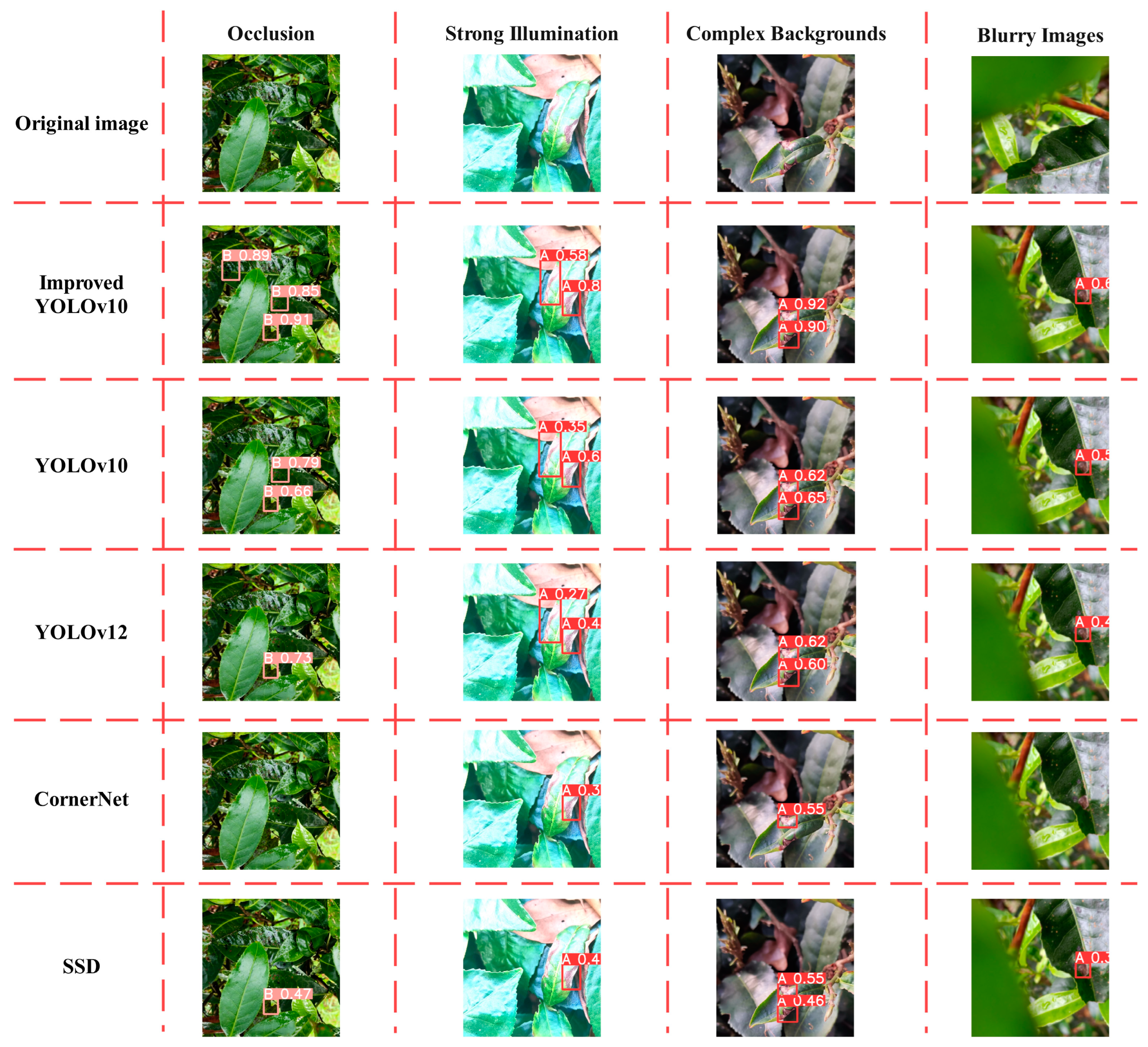
- In terms of detection performance, compared with YOLOv10, YOLOv12, CornerNet, and SSD, the improved YOLOv10 achieves increases in precision of 3.40%, 9.22%, 16.25%, and 13.51%, respectively; recall increases of 10.05%, 12.05%, 18.59%, and 17.53%; F1 score increases of 6.75%, 10.62%, 17.40%, and 15.51%; and mAP increases of 11.95%, 12.59%, 20.31%, and 18.04%, respectively. In the confusion matrix, compared with the original YOLOv10 network, the improved YOLOv10 shows an increase in detection accuracy of anthracnose by 6%, bacterial coil disease by 20%, and leaf blight by 2%. The improved YOLOv10 network not only exhibits excellent adaptability in addressing issues such as blurry images, complex backgrounds, strong illumination, and occlusion in disease detection, but also achieves high levels of precision and recall, thereby laying a solid technological foundation for precision agriculture and intelligent decision-making.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, S.; Lee, S. Efficient Data Augmentation Methods for Crop Disease Recognition in Sustainable Environmental Systems. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Shen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Tian, P.; Qian, Y. Deep migration learning-based recognition of diseases and insect pests in Yunnan tea under complex environments. Plant Methods 2024, 20, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yang, H.; Bao, X.; Hussain, M.; Bao, Q.; Zeng, Z.; Xiao, C.; Zhou, L.; Qin, X. Brevibacillus brevis HNCS-1: A biocontrol bacterium against tea plant diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1198747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Liang, R.; Wang, D. A novel lightweight model for tea disease classification based on feature reuse and channel focus attention mechanism. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2025, 61, 101940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Shao, G.; Yang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Gao, Q.; Li, T. Detection Model of Tea Disease Severity under Low Light Intensity Based on YOLOv8 and EnlightenGAN. Plants 2024, 13, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Bai, D.; Xu, R.; Lin, H. TSBA-YOLO: An improved tea diseases detection model based on attention mechanisms and feature fusion. Forests 2023, 14, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Xie, L.; Huang, Q. Inception convolutional vision transformers for plant disease identification. Internet Things 2023, 21, 100650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, S.; Jain, R.; Marwaha, S.; Arora, A.; Haque, M.A.; Dheeraj, A.; Singh, V.K. Deep transfer learning model for disease identification in wheat crop. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 75, 102068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Wang, L.; Xie, Q.; Gao, R.; Su, Z.; Li, Y. A novel deep learning method for maize disease identification based on small sample-size and complex background datasets. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 75, 102011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yuan, W.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Yang, F.; Wang, B. YOLOv8n-WSE-Pest: A Lightweight Deep Learning Model Based on YOLOv8n for Pest Identification in Tea Gardens. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Uhlen, A.K.; Aamot, H.U.; Dieseth, J.A.; Shafiee, S. Integrating UAV-based multispectral remote sensing and machine learning for detection and classification of chocolate spot disease in faba bean. Crop Sci. 2025, 65, e21454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, A.; Ma, X.; Wang, C.; Lin, Z. Dense small object detection algorithm for unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing images in complex backgrounds. Digit. Signal Process. 2025, 158, 104938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, S.; Zong, M.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Duan, C.; Peng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, J.; Lin, C.; Feng, Y.; et al. The effects of the soil environment on soil organic carbon in tea plantations in Xishuangbanna, southwestern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 297, 106951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Bai, X.; Gouda, M.; Hu, H.; Yang, N.; He, Y.; Feng, X. Transfer learning for plant disease detection model based on low-altitude UAV remote sensing. Precis. Agric. 2025, 26, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Hou, W.; Liu, L.; He, Y.; Wang, Y. Improving long-tailed pest classification using diffusion model-based data augmentation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 234, 110244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünalan, S.; Günay, O.; Akkurt, I.; Gunoglu, K.; Tekin, H.O. A comparative study on breast cancer classification with stratified shuffle split and K-fold cross validation via ensembled machine learning. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2024, 17, 101080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J. Yolov10: Real-time end-to-end object detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 107984–108011. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Liao, L.; Xie, X.; Yuan, H. SCoralDet: Efficient real-time underwater soft coral detection with YOLO. Ecol. Inform. 2025, 85, 102937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, P.; Chen, F. Sctracker: Multi-object tracking with shape and confidence constraints. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 24, 3123–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, W.; Wang, L.; Tao, X.; Yin, Y.; Chen, D. HawkEye Conv-Driven YOLOv10 with Advanced Feature Pyramid Networks for Small Object Detection in UAV Imagery. Drones 2024, 8, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finder, S.E.; Amoyal, R.; Treister, E.; Freifeld, O. Wavelet convolutions for large receptive fields. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 363–380. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Ren, W.; Gao, X.; Wang, R.; Cao, X. Restoring Images in Adverse Weather Conditions via Histogram Transformer; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 111–129. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, S.; Lin, Y.; Lin, G.; Su, P.; Huang, S.; Meng, X.; Liu, P.; Yan, J. Real-time detection and counting of wheat spikes based on improved YOLOv10. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Lan, L.; Xu, J.; Sun, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Hu, J.; Wang, B. Smart Agricultural Pest Detection Using I-YOLOv10-SC: An Improved Object Detection Framework. Agronomy 2025, 15, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.K.; Dehuri, S.; Sarma, P.K.D. Analysis of machine learning approaches for predictive modeling in heart disease detection systems. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2025, 106, 107723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Xia, Y.; Wang, H.; Jin, R.; Wang, C.; Fan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B. Detection of small foreign objects in Pu-erh sun-dried green tea: An enhanced YOLOv8 neural network model based on deep learning. Food Control 2025, 168, 110890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Chen, J.; Lv, B.; Peng, L. Lightweight marine biodetection model based on improved YOLOv10. Alex. Eng. J. 2025, 119, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| ID | From | Params | Module | Arguments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | −1 | 464 | Conv | [3, 16, 3, 2] |
| 1 | −1 | 4672 | Conv | [16, 32, 3, 2] |
| 2 | −1 | 5216 | WTConv | [32, 32] |
| 3 | −1 | 18,560 | Conv | [32, 64, 3, 2] |
| 4 | −1 | 20,864 | WTConv | [64, 64] |
| 5 | −1 | 73,984 | Conv | [64, 128, 3, 2] |
| 6 | −1 | 41,728 | WTConv | [128, 128] |
| 7 | −1 | 295,424 | Conv | [128, 256, 3, 2] |
| 8 | −1 | 41,728 | WTConv | [256, 256] |
| 9 | −1 | 164,608 | SPPF | [256, 256, 5] |
| 10 | −1 | 249,728 | PSA | [256, 256] |
| 11 | −1 | 0 | Upsample | [None, 2, ‘nearest’] |
| 12 | [−1, 6] | 0 | Concat | [1] |
| 13 | −1 | 148,224 | C2f | [None, 2, ‘nearest’] |
| 14 | −1 | 0 | Upsample | [1] |
| 15 | [−1, 4] | 0 | Concat | [192, 64, 1] |
| 16 | −1 | 37,248 | C2f | [64] |
| 17 | −1 | 59,540 | Histogram Transformer | [64, 64, 3, 2] |
| 18 | −1 | 36,992 | Conv | [1] |
| 19 | [−1, 13] | 0 | Concat | [192, 128, 1] |
| 20 | −1 | 123,648 | C2f | [128, 128, 3, 2] |
| 21 | −1 | 147,712 | Conv | [1] |
| 22 | [−1, 10] | 0 | Concat | [384, 256, 1] |
| 23 | −1 | 493,056 | C2f | [1] |
| 24 | [17, 20, 23] | 862,888 | v10Detect | [4, [64, 128, 256]] |
| Model | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP (%) | Layers | Parameters | Gradients |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv10 | 81.98 | 78.03 | 80.97 | 402 | 2,497,778 | 2,497,762 |
| YOLOv10 + W | 80.33 | 81.75 | 84.93 | 323 | 2,766,354 | 2,744,834 |
| YOLOv10 + H | 80.49 | 82.47 | 85.67 | 369 | 3,431,302 | 3,431,286 |
| YOLOv10 + L | 80.87 | 81.35 | 85.21 | 402 | 2,497,778 | 2,497,762 |
| YOLOv10 + W + H | 82.97 | 84.88 | 89.48 | 339 | 2,825,894 | 2,804,374 |
| YOLOv10 + W + L | 81.03 | 83.57 | 87.33 | 323 | 2,766,354 | 2,744,834 |
| YOLOv10 + H + L | 83.85 | 86.37 | 90.16 | 369 | 3,431,302 | 3,431,286 |
| YOLOv10 + W + H + L | 85.38 | 88.08 | 92.92 | 339 | 2,825,894 | 2,804,374 |
| Model | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) | mAP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Improved YOLOv10 | 85.38 | 88.08 | 86.71 | 92.92 |
| YOLOv10 | 81.98 | 78.03 | 79.96 | 80.97 |
| YOLOv12 | 76.16 | 76.03 | 76.09 | 80.33 |
| CornerNet | 69.13 | 69.49 | 69.31 | 72.61 |
| SSD | 71.87 | 70.55 | 71.20 | 74.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B. Research on the Yunnan Large-Leaf Tea Tree Disease Detection Model Based on the Improved YOLOv10 Network and UAV Remote Sensing. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5301. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105301
Guo X, Yang C, Wang Z, Zhang J, Zhang S, Wang B. Research on the Yunnan Large-Leaf Tea Tree Disease Detection Model Based on the Improved YOLOv10 Network and UAV Remote Sensing. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(10):5301. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105301
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xiaoxue, Chunhua Yang, Zejun Wang, Jie Zhang, Shihao Zhang, and Baijuan Wang. 2025. "Research on the Yunnan Large-Leaf Tea Tree Disease Detection Model Based on the Improved YOLOv10 Network and UAV Remote Sensing" Applied Sciences 15, no. 10: 5301. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105301
APA StyleGuo, X., Yang, C., Wang, Z., Zhang, J., Zhang, S., & Wang, B. (2025). Research on the Yunnan Large-Leaf Tea Tree Disease Detection Model Based on the Improved YOLOv10 Network and UAV Remote Sensing. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5301. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105301







