Recent Web Platforms for Multi-Omics Integration Unlocking Biological Complexity
Abstract
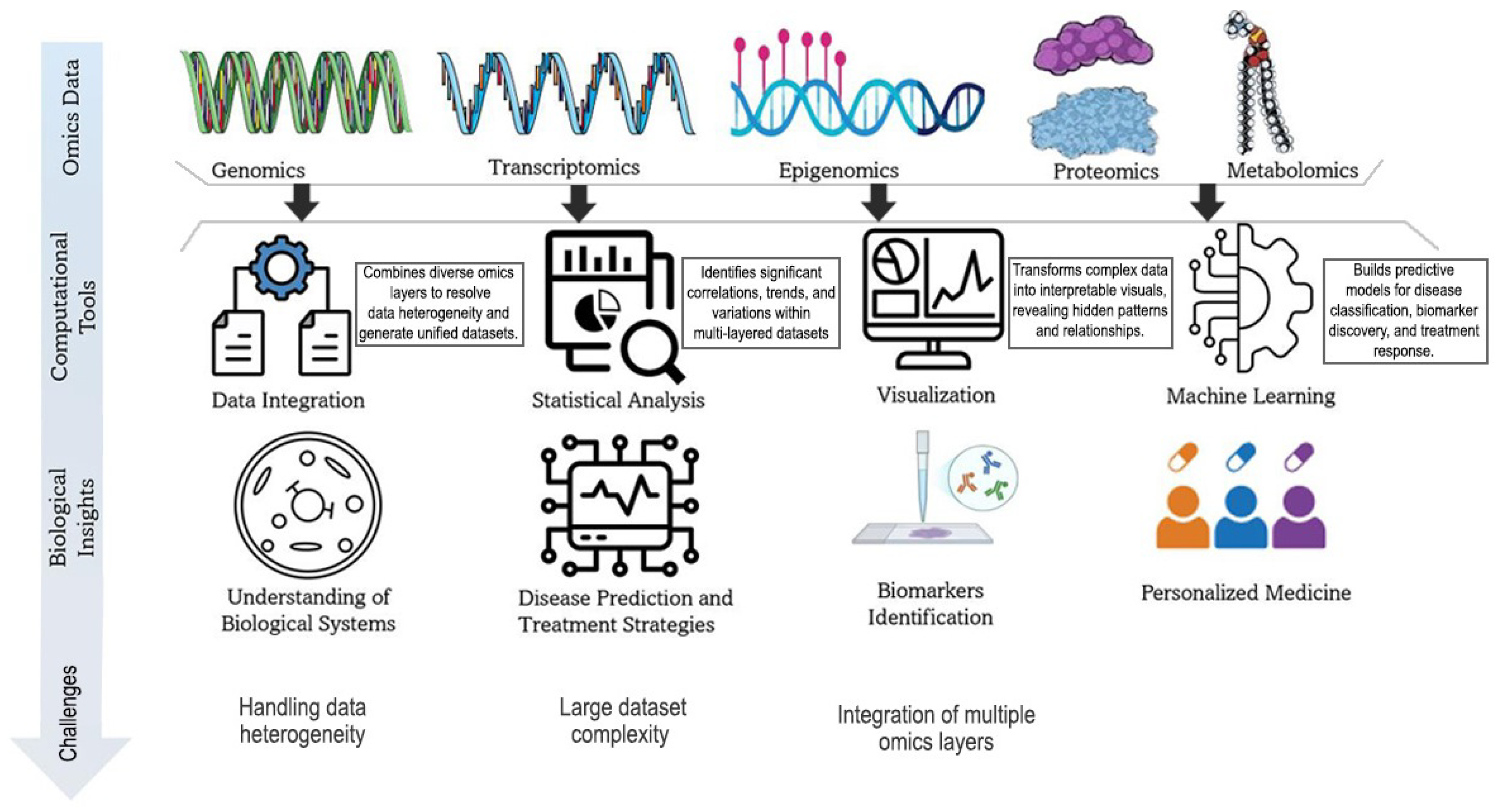
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Platforms for Disease-Specific Research and Drug Discovery
2.1.1. AlzGPS: A Platform for Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Using Multi-Omics
2.1.2. PALMO: A Tool for Longitudinal Multi-Omics Analysis Across Diverse Diseases
2.1.3. Aging Bank: A Specialized Platform for Aging and Age-Related Disease Research
2.1.4. iODA: A Cancer-Focused Platform for Multi-Omics Pathway Analysis
2.1.5. Summary and Comparative Insights
2.2. Platforms for Multi-Omics Visualization and Pathway Exploration
2.2.1. multiSLIDE: A Real-Time Visualization Tool for Transcriptomics and Proteomics Pathways
2.2.2. MVP: A Multi-Omics Visualization Platform Supporting Genomics to Metabolomics
2.2.3. VDJView: A Specialized Platform for Immune Repertoire Analysis Through VDJ Recombination Visualization
2.2.4. ProteomicsDB: A Platform Dedicated to Large-Scale Protein Expression and Interaction Data
2.2.5. PaintOmics 3: A Web-Based Pathway-Centric Tool for Multi-Omics Visualization
2.2.6. Argonaut: A Collaborative Multi-Omics Platform with Real-Time Statistical and Interactive Visualization Tools
2.2.7. Summary and Comparative Insights
2.3. Platforms for High-Throughput and Spatial Multi-Omics Integration
2.3.1. SM-Omics: Automating High-Performance Spatial Transcriptomics and Proteomics Data Analysis
2.3.2. OmicsSuite: A GUI-Based High-Throughput Multi-Omics Integration Platform
2.3.3. Single-Platform Multi-Omic Profiling: Concurrent Proteomics and Metabolomics Integration
2.3.4. CHOmics: Optimizing CHO Cells for Biopharmaceutical Production Through Multi-Omics Integration
2.3.5. Majorbio Cloud: A Cloud-Based Suite for Large-Scale Multi-Omics Research
2.3.6. Summary and Comparative Insights
2.4. Platforms for Clinical Decision-Making and Personalized Medicine
2.4.1. GraphOmics: A Network-Based Approach to Multi-Omics Data for Disease Biomarker Identification
2.4.2. OmicsAnalyst: A User-Friendly Web Platform for Clinical and Personalized Medicine Research
2.4.3. OmicsNet 2.0: A Platform for Network Visualization and Multi-Omics Interaction Mapping
2.4.4. Summary and Comparative Insights
| Platform/Paper | Programming Languages/Tools | Processes/Analysis Performed |
|---|---|---|
| AlzGPS [14] | Django, HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Cytoscape.js, NetworkX | Network-based drug repurposing, AD-related gene and protein network analysis, Mechanism of action (MOA) analysis, Network proximity analysis |
| PALMO [15] | R, Python, ArchR, Seurat, variancePartition | Variance Decomposition Analysis (VDA), Coefficient of Variation Profiling (CVP), Stability Pattern Evaluation (SPECT), Outlier Detection Analysis (ODA), Time Course Analysis (TCA) |
| Aging Bank [16] | Web-based platform using tools like Differential Expression Analyzer, Co-Expression Network, Functional Annotation Analyzer | Multi-omics data integration, differential expression analysis, co-expression network analysis, functional annotation, cancer-aging associations |
| iODA [17] | Java, R, MACS, PeakAnalyzer, Perl | Differential gene/mRNA expression analysis, pathway enrichment analysis, ChIP-Seq data analysis, cross-level omics consistency analysis |
| multiSLIDE [18] | Java (backend), Python (computation), Angular (frontend), MongoDB, SVG (visualization) | Heatmap visualization of multi-omics data, pathway and GO term-based queries, hierarchical clustering, network visualization of inter-omics relationships, differential expression analysis, FDR control |
| MVP [19] | HTML, JavaScript, CSS, SQLite, IGV.js, Lorikeet | Proteogenomics data integration, visualization of peptides, MS/MS spectra visualization, protein-genome alignment, variant annotation analysis |
| VDJView [20] | R, Shiny, dplyr, Seurat, tcR, Rcircos | Gene expression and clonotype analysis, clustering, dimensionality reduction (PCA, t-SNE, UMAP), pseudo-time analysis, immune receptor gene analysis |
| ProteomicsDB [21] | SAP HANA (database), JavaScript, R, Docker, Prosit (deep learning), Python | Mass spectrometry-based proteomics, transcriptomics-proteomics integration, drug sensitivity prediction, protein-protein interaction analysis, missing value imputation, biochemical assay analysis |
| PaintOmics 3 [22] | Python, R, MongoDB, JavaScript, HTML5 | Pathway enrichment, multi-layer feature matching, network analysis, interactive visualization, KEGG-based pathway mapping, heatmaps, trend analysis, integration of regulatory data |
| Argonaut [23] | Docker, HTML, JavaScript (D3.js), MySQL, PHP, Bootstrap, Angular | Real-time statistical analysis, interactive data visualization (e.g., volcano plots, PCA, GO enrichment), batch control, missing value imputation, outlier analysis, secure data sharing |
| SM-Omics [24] | Python, Image registration tools (SpoTteR) | High-throughput spatial transcriptomics, multiplex protein detection, image registration |
| OmicsSuite [25] | Java, R, Shiny, JavaFX, BioJava, Bioconductor | Multi-omics integration, differential expression analysis, PPI network construction, enrichment analysis, single-cell RNA-Seq, spatial transcriptomics workflows |
| Single-Platform Multi-Omic Profiling system [26] | LC-MS, nLC-MS, computational workflows for proteomics and metabolomics integration | Simultaneous proteomics and metabolomics data acquisition, network-based integrative framework, sample preparation techniques, high-sensitivity analysis, pathway and network analysis, mass spectrometry optimization |
| CHOmics [27] | PHP, R, JavaScript, Limma, Subread, Voom, KEGG pathways | RNA-Seq processing, Differential expression (DE) analysis, PCA, pathway enrichment, meta-analysis, visualization of gene expression and pathway diagrams across multiple omics |
| Majorbio Cloud [28] | Django, HTML, CSS, JavaScript, MongoDB, Ceph, MySQL, D3 | One-stop multi-omics data integration, gene expression analysis, gene set and structure analysis, metagenomics, differential expression analysis, taxonomic and functional analysis, correlation, model predictive analysis, visualization through Sanger-Charts, interactive analysis reports, and cloud storage. |
| GraphOmics [29] | Python, JavaScript, Django, Plotly, D3, SQLite, Neo4j | Horizontal omics integration using Reactome pathways, differential expression analysis, PCA, pathway enrichment analysis, interactive clustering, heatmaps, gene ontology analysis, multi-omics integration, linked data exploration across tables |
| OmicsAnalyst [30] | Java, R, JavaServer Faces (JSF), PrimeFaces, sigma.js, three.js | Correlation network analysis, cluster heatmap analysis, dimension reduction analysis, multi-view clustering, interactive 2D/3D visual analytics, PCA, DIABLO, feature correlation, enrichment analysis |
| OmicsNet 2.0 [31] | Python, R, JavaScript, Rcpp, Cytoscape, Rgraphviz | Multi-omics network creation, SNP and peak annotation, microbiome interaction network analysis, 2D and 3D network visualization, random walk with restart algorithm for disease gene prediction, network refinement using graph algorithms (PCSF), enrichment analysis |
| Platform/Paper | Genome | Transcriptome | Proteome | Metabolome | Epigenome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlzGPS [14] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| PALMO [15] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Aging Bank [16] | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| iODA [17] | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| multiSLIDE [18] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| MVP [19] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| VDJView [20] | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| ProteomicsDB [21] | No | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| PaintOmics 3 [22] | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Argonaut [23] | No | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| SM-Omics [24] | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| OmicsSuite [25] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Single-Platform Multi-Omic Profiling system [26] | No | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| CHOmics [27] | No | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Majorbio Cloud [28] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| GraphOmics [29] | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| OmicsAnalyst [30] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| OmicsNet 2.0 [31] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
3. Discussion
3.1. Case Studies in Multi-Omics Platforms
3.1.1. Clinical Research Applications
3.1.2. Disease-Specific Insights
3.1.3. Emerging Applications
3.2. Limitations of Current Platforms
3.3. Essential Improvements for Future Platforms
4. Future Directions: AI and ML Tools in Multi-Omics Platforms
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chakraborty, S.; Sharma, G.; Karmakar, S.; Banerjee, S. Multi-OMICS approaches in cancer biology: New era in cancer therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-(Bba)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, J.; Nussinov, R.; Zhang, Y.C.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, Z.K. Computational network biology: Data, models, and applications. Phys. Rep. 2020, 846, 1–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, A.J.; Mentzer, A.; Knight, J.C. Host genetics and infectious disease: New tools, insights and translational opportunities. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shema, E.; Bernstein, B.E.; Buenrostro, J.D. Single-cell and single-molecule epigenomics to uncover genome regulation at unprecedented resolution. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krassowski, M.; Das, V.; Sahu, S.K.; Misra, B.B. State of the field in multi-omics research: From computational needs to data mining and sharing. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 610798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W. Survey on multi-omics, and multi-omics data analysis, integration and application. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2023, 19, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysoy, A.; Bai, Z.; Satija, R.; Fan, R. The technological landscape and applications of single-cell multi-omics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 695–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agamah, F.E.; Bayjanov, J.R.; Niehues, A.; Njoku, K.F.; Skelton, M.; Mazandu, G.K.; Ederveen, T.H.A.; Mulder, N.; Chimusa, E.R.; Hoen, P.A. Computational approaches for network-based integrative multi-omics analysis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 967205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greener, J.G.; Kandathil, S.M.; Moffat, L.; Jones, D.T. A guide to machine learning for biologists. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 23, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Eckhardt, C.M.; Baccarelli, A.A. Molecular mechanisms of environmental exposures and human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reel, P.S.; Reel, S.; Pearson, E.; Trucco, E.; Jefferson, E. Using machine learning approaches for multi-omics data analysis: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 49, 107739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, J.M.; Luke, J.J.; Guglietta, S.; Krieg, C. High throughput multi-omics approaches for clinical trial evaluation and drug discovery. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 590742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graw, S.; Chappell, K.; Washam, C.L.; Gies, A.; Bird, J.; Robeson, M.S.; Byrum, S.D. Multi-omics data integration considerations and study design for biological systems and disease. Mol. Omics 2021, 17, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Fang, J.; Bekris, L.M.; Kim, Y.H.; Pieper, A.A.; Leverenz, J.B.; Cummings, J.; Cheng, F. AlzGPS: A genome-wide positioning systems platform to catalyze multi-omics for Alzheimer’s drug discovery. Alzheimer’S Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasaikar, S.V.; Savage, A.K.; Gong, Q.; Swanson, E.; Talla, A.; Lord, C.; Heubeck, A.T.; Reading, J.; Graybuck, L.T.; Meijer, P.; et al. A comprehensive platform for analyzing longitudinal multi-omics data. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Shang, S.; Guo, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, H.; Sun, Y.; Gan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Ning, S.; et al. AgingBank: A manually curated knowledgebase and high-throughput analysis platform that provides experimentally supported multi-omics data relevant to aging in multiple species. Briefings Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbac438. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Qi, X.; Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, B. iODA: An integrated tool for analysis of cancer pathway consistency from heterogeneous multi-omics data. J. Biomed. Inform. 2020, 112, 103605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Datta, A.; Choi, H. MultiSLIDE is a web server for exploring connected elements of biological pathways in multi-omics data. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGowan, T.; Johnson, J.E.; Kumar, P.; Sajulga, R.; Mehta, S.; Jagtap, P.D.; Griffin, T.J. Multi-omics Visualization Platform: An extensible Galaxy plug-in for multi-omics data visualization and exploration. GigaScience 2020, 9, giaa025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samir, J.; Rizzetto, S.; Gupta, M.; Luciani, F. Exploring and analysing single cell multi-omics data with VDJView. BMC Med. Genom. 2020, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaras, P.; Schmidt, T.; Frejno, M.; Gessulat, S.; Reinecke, M.; Jarzab, A.; Zecha, J.; Mergner, J.; Giansanti, P.; Ehrlich, H.C.; et al. ProteomicsDB: A multi-omics and multi-organism resource for life science research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D1153–D1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-de-Diego, R.; Tarazona, S.; Martínez-Mira, C.; Balzano-Nogueira, L.; Furió-Tarí, P.; Pappas, G.J., Jr.; Conesa, A. PaintOmics 3: A web resource for the pathway analysis and visualization of multi-omics data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W503–W509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brademan, D.R.; Miller, I.J.; Kwiecien, N.W.; Pagliarini, D.J.; Westphall, M.S.; Coon, J.J.; Shishkova, E. Argonaut: A web platform for collaborative multi-omic data visualization and exploration. Patterns 2020, 1, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickovic, S.; Lötstedt, B.; Klughammer, J.; Mages, S.; Segerstolpe, Å.; Rozenblatt-Rosen, O.; Regev, A. SM-Omics is an automated platform for high-throughput spatial multi-omics. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, B.B.; Dong, W.; Gu, Y.X.; Han, Z.F.; Luo, X.; Ke, C.H.; You, W.W. OmicsSuite: A customized and pipelined suite for analysis and visualization of multi-omics big data. HOrticulture Res. 2023, 10, uhad195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, B.C.; Mousavi, F.; Emili, A. Single-platform ‘multi-omic’profiling: Unified mass spectrometry and computational workflows for integrative proteomics–metabolomics analysis. Mol. Omics 2018, 14, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Yalamanchili, H.B.; Zhang, X.; Lewis, N.E.; Alves, C.S.; Groot, J.; Arnsdorf, J.; Bjørn, S.P.; Wulff, T.; Voldborg, B.G.; et al. CHOmics: A web-based tool for multi-omics data analysis and interactive visualization in CHO cell lines. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1008498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, G.; Shi, C.; Liu, L.; Guo, Q.; Han, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Gao, H.; et al. Majorbio Cloud: A one-stop, comprehensive bioinformatic platform for multiomics analyses. IMeta 2022, 1, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandy, J.; Daly, R. TGraphOmics: An interactive platform to explore and integrate multi-omics data. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Ewald, J.; Xia, J. OmicsAnalyst: A comprehensive web-based platform for visual analytics of multi-omics data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W476–W482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Pang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Ewald, J.; Xia, J. OmicsNet 2.0: A web-based platform for multi-omics integration and network visual analytics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W527–W533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Zhang, S.; Poleksic, A.; Xie, L. Heterogeneous multi-layered network model for omics data integration and analysis. Front. Genet. 2020, 10, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arıkan, M.; Muth, T. Integrated multi-omics analyses of microbial communities: A review of the current state and future directions. Mol. Omics 2023, 19, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldoseri, A.; Al-Khalifa, K.N.; Hamouda, A.M. Re-thinking data strategy and integration for artificial intelligence: Concepts, opportunities, and challenges. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.; Batista, T.; Cavalcante, E.; Souza, A.; Lopes, F.; Cacho, N. A platform for integrating heterogeneous data and developing smart city applications. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2022, 128, 552–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althati, C.; Tomar, M.; Shanmugam, L. Enhancing Data Integration and Management: The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Modern Data Platforms. J. Artif. Intell. Gen. Sci. (JAIGS) 2024, 2, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z. Multi-omics strategies for personalized and predictive medicine: Past, current, and future translational opportunities. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2022, 6, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segun-Falade, O.D.; Osundare, O.S.; Kedi, W.E.; Okeleke, P.A.; Ijomah, T.I.; Abdul-Azeez, O.Y. Developing cross-platform software applications to enhance compatibility across devices and systems. Comput. Sci. Res. J. 2024, 5, 2040–2061. [Google Scholar]
- Torab-Miandoab, A.; Samad-Soltani, T.; Jodati, A.; Rezaei-Hachesu, P. Interoperability of heterogeneous health information systems: A systematic literature review. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2023, 23, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshisht, M.K. Machine learning and deep learning in synthetic biology: Key architectures, applications, and challenges. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 9921–9945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri, M.R. Integration of natural language processing, self-service platforms, predictive maintenance, and prescriptive analytics for cost reduction, personalization, and real-time insights customer service and operational efficiency. Int. J. Inf. Cybersecur. 2023, 7, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Koppad, S.; Gkoutos, G.V.; Acharjee, A. Cloud computing enabled big multi-omics data analytics. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2021, 15, 11779322211035921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papadaki, E.; Kakkos, I.; Vlamos, P.; Petropoulou, O.; Miloulis, S.T.; Palamas, S.; Vrahatis, A.G. Recent Web Platforms for Multi-Omics Integration Unlocking Biological Complexity. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010329
Papadaki E, Kakkos I, Vlamos P, Petropoulou O, Miloulis ST, Palamas S, Vrahatis AG. Recent Web Platforms for Multi-Omics Integration Unlocking Biological Complexity. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(1):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010329
Chicago/Turabian StylePapadaki, Eugenia, Ioannis Kakkos, Panagiotis Vlamos, Ourania Petropoulou, Stavros T. Miloulis, Stergios Palamas, and Aristidis G. Vrahatis. 2025. "Recent Web Platforms for Multi-Omics Integration Unlocking Biological Complexity" Applied Sciences 15, no. 1: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010329
APA StylePapadaki, E., Kakkos, I., Vlamos, P., Petropoulou, O., Miloulis, S. T., Palamas, S., & Vrahatis, A. G. (2025). Recent Web Platforms for Multi-Omics Integration Unlocking Biological Complexity. Applied Sciences, 15(1), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010329










