Curiosity-Driven Camouflaged Object Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We introduce the idea of curiosity into the COS task and propose a novel Curiosity-Driven network (CDNet) to obtain more information from unknown areas, thereby facilitating accurate segmentation of camouflaged objects.
- The fusion bridge module (FBM) is meticulously designed to effectively fuse the features extracted by CNN and Transformer by using the idea of curiosity to obtain complete information.
- The curiosity-refinement module (CRM) is proposed to gradually discover and reduce the curiosity of camouflaged objects, and iteratively improve the initial segmentation to distinguish intricate details, thereby enhancing accuracy in segmentation results.
- Extensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that our proposed CDNet outperforms 28 state-of-the-art methods on three widely adopted benchmark datasets, establishing its superior performance.
2. Related Work
2.1. Camouflaged Object Segmentation
2.2. Dual-Branch Architecture
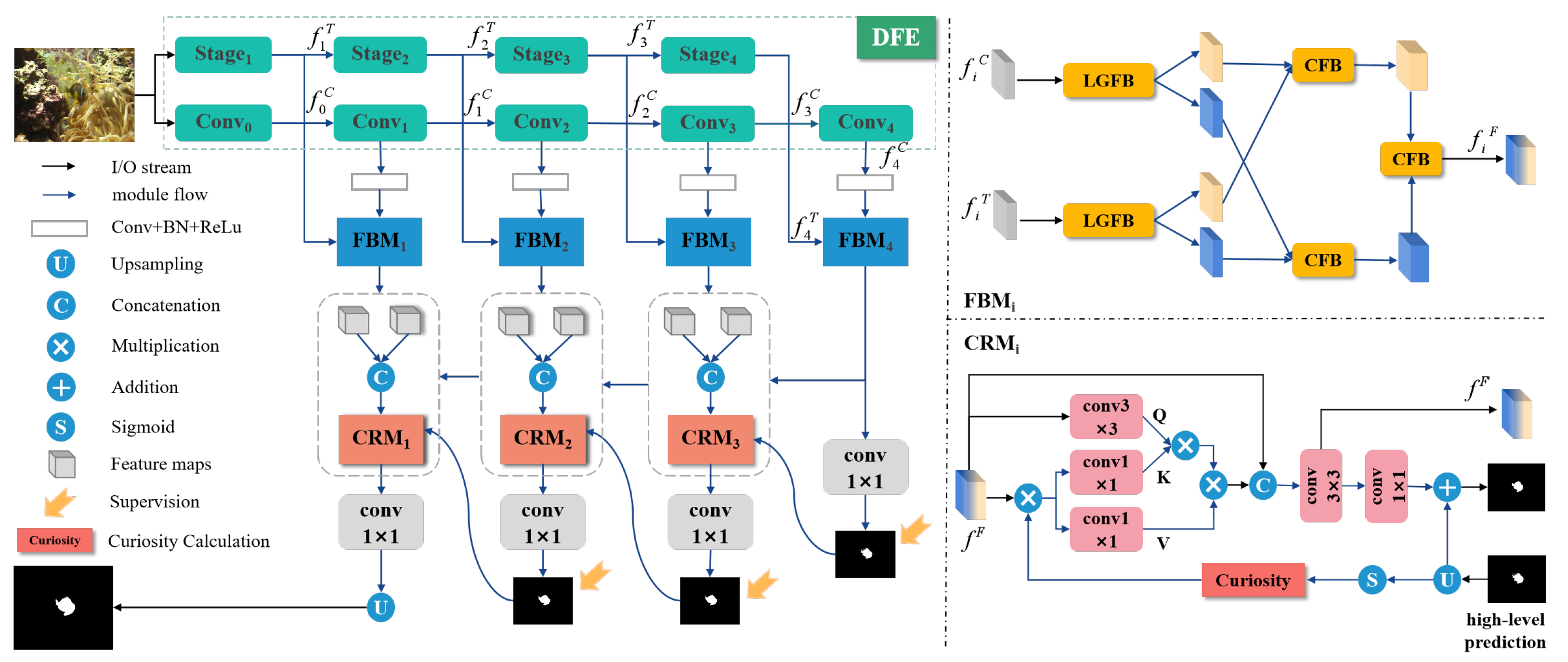
3. Methodology
3.1. Overview
3.2. Dual-Branch Feature Encoder
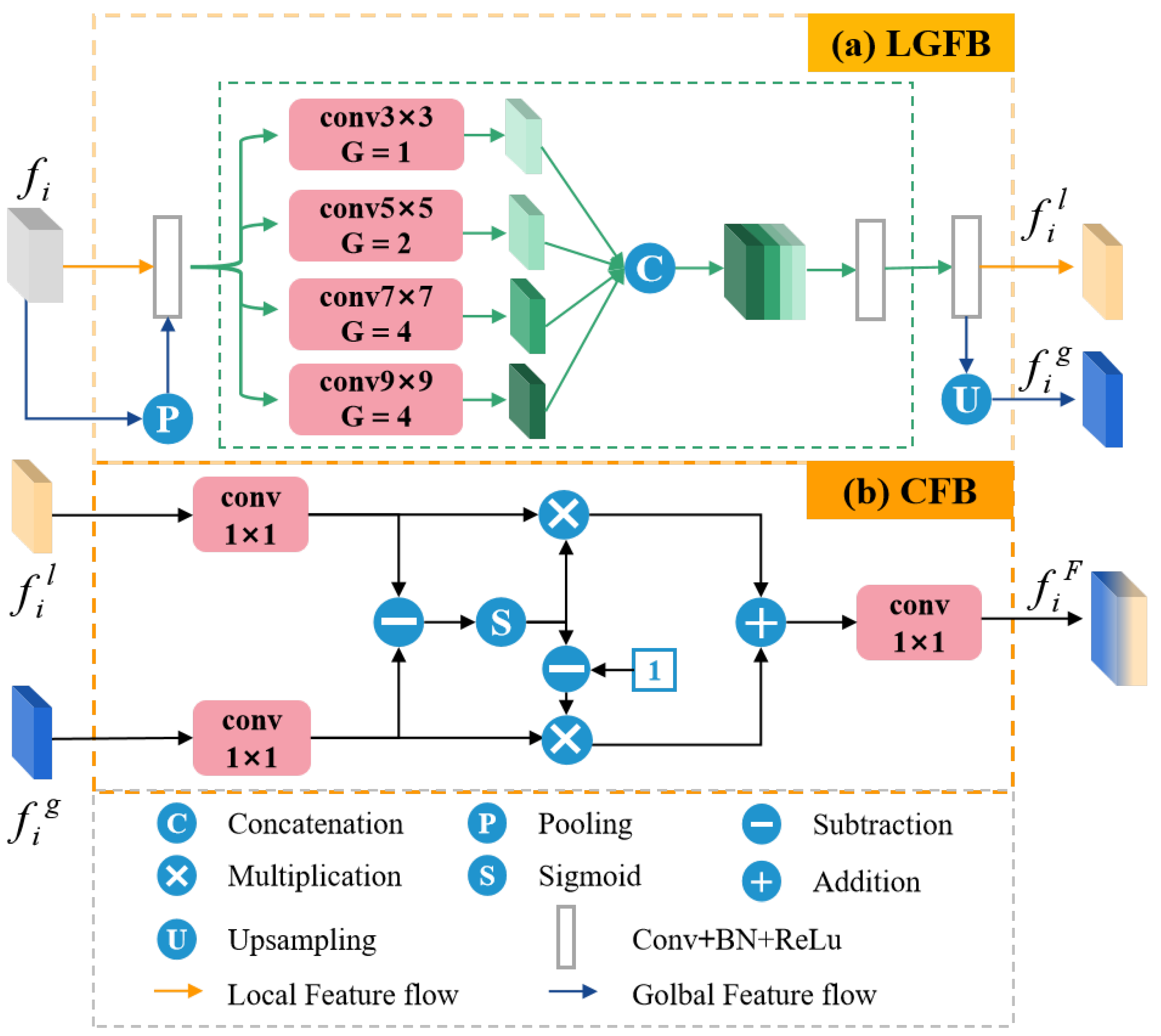
3.3. Fusion Bridge Module
3.4. Curiosity-Refinement Module
3.5. Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Comparison with State-of-the-Arts
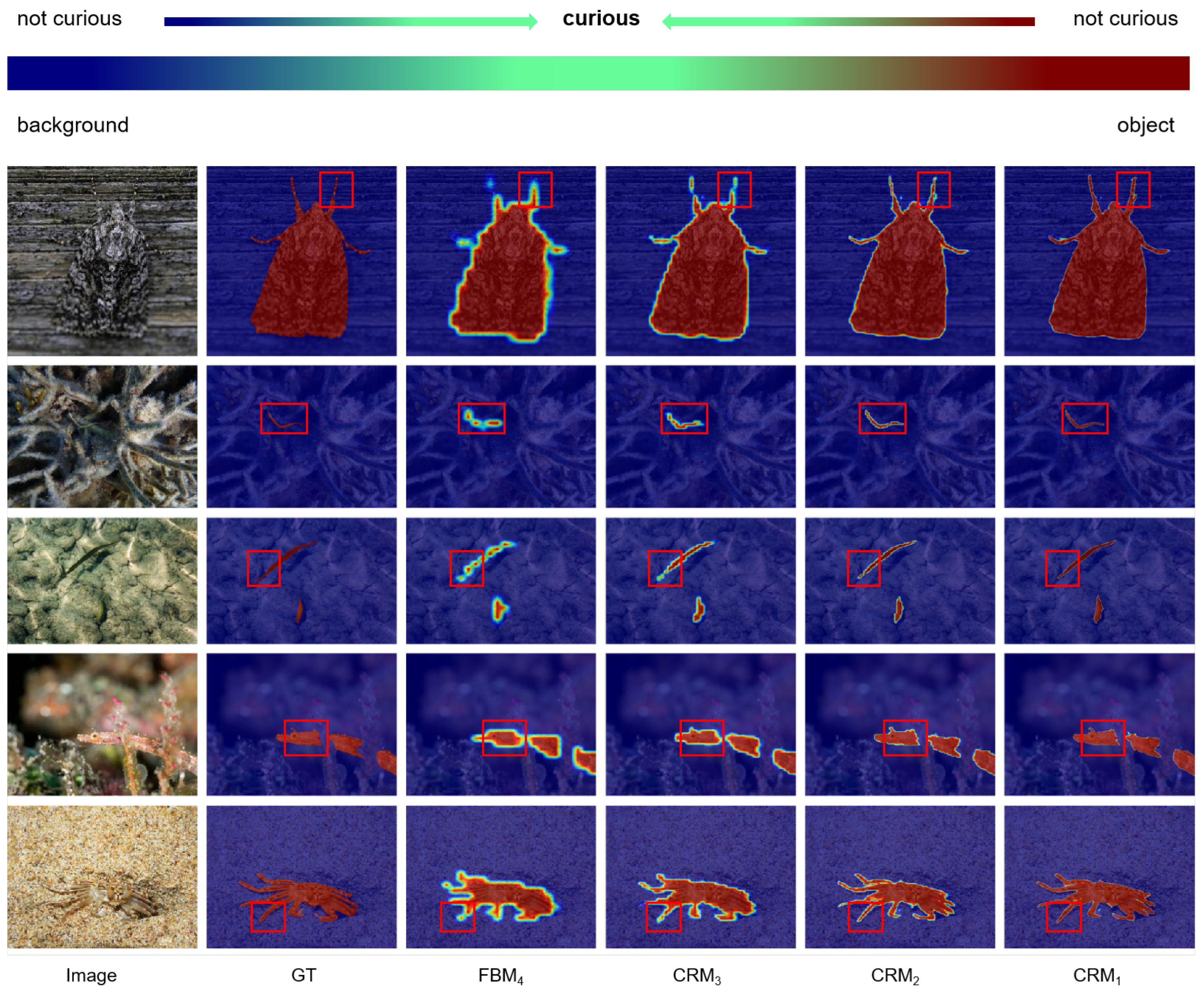
4.3. Ablation Study
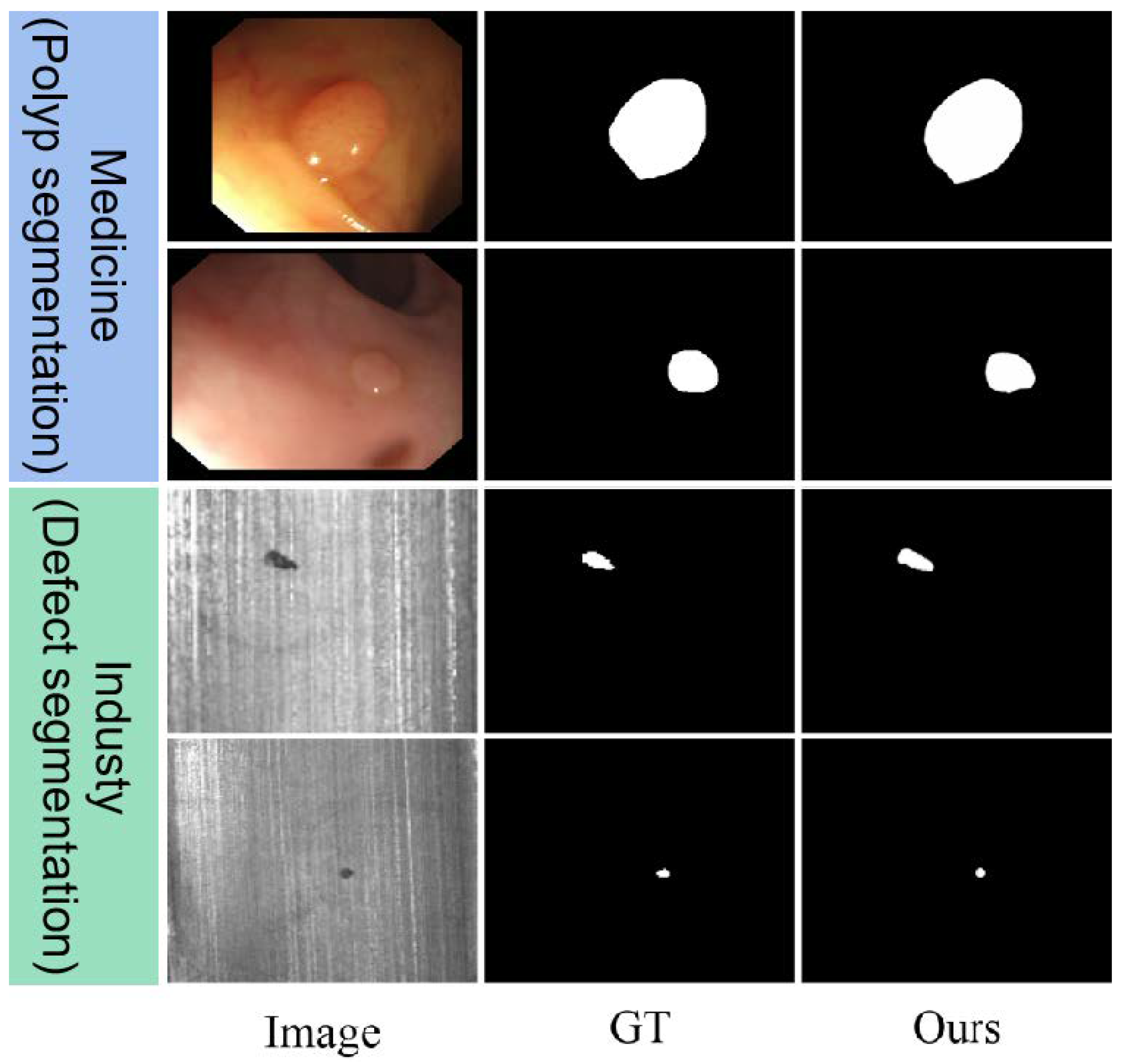
4.4. Extension Applications
4.5. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, D.P.; Ji, G.P.; Xu, P.; Cheng, M.M.; Sakaridis, C.; Van Gool, L. Advances in deep concealed scene understanding. Vis. Intell. 2023, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Qian, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhang, L.; Luo, Q.; Bi, Z.; Zhang, W. MugenNet: A Novel Combined Convolution Neural Network and Transformer Network with Application in Colonic Polyp Image Segmentation. Sensors 2024, 24, 7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Qiao, X. An Edge-Enhanced Network for Polyp Segmentation. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, N.K.; Jha, D.; Bagci, U.; Ali, S. TGANet: Text-guided attention for improved polyp segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2022: 25th International Conference, Singapore, 18–22 September 2022; Proceedings, Part III. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.P.; Ji, G.P.; Zhou, T.; Chen, G.; Fu, H.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. Pranet: Parallel reverse attention network for polyp segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2020: 23rd International Conference, Lima, Peru, 4–8 October 2020; Proceedings, Part VI 23. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Shi, H.; Hu, Y.; Yu, Z. Enhancing Anomaly Detection Models for Industrial Applications through SVM-Based False Positive Classification. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Lim, J.; Lee, H. The Amalgamation of the Object Detection and Semantic Segmentation for Steel Surface Defect Detection. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Deng, X.; Jiang, P.; Wan, S.; Guo, Y. Crossfuser: Multi-modal feature fusion for end-to-end autonomous driving under unseen weather conditions. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 14378–14392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Prabhakaran, B. Facilitating fashion camouflage art. In Proceedings of the 21st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Barcelona, Spain, 21–25 October 2013; pp. 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, N.; Green, S.; Troscianko, J.; Tregenza, T.; Stevens, M. Background matching and disruptive coloration as habitat-specific strategies for camouflage. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, T.W. Quantifying camouflage and conspicuousness using visual salience. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 1883–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Cui, G.; Song, W. Camouflage texture evaluation using saliency map. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Internet Multimedia Computing and Service, Huangshan, China, 17–18 August 2013; pp. 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, P.; Xu, X. Study on the camouflaged target detection method based on 3D convexity. Mod. Appl. Sci. 2011, 5, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Han, Y.; Hou, W.; Li, J. Detection of the mobile object with camouflage color under dynamic background based on optical flow. Procedia Eng. 2011, 15, 2201–2205. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.P.; Ji, G.P.; Sun, G.; Cheng, M.M.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. Camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2777–2787. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dai, Y.; Li, A.; Liu, B.; Barnes, N.; Fan, D.P. Simultaneously localize, segment and rank the camouflaged objects. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 11591–11601. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.N.; Nguyen, T.V.; Nie, Z.; Tran, M.T.; Sugimoto, A. Anabranch network for camouflaged object segmentation. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2019, 184, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.P.; Ji, G.P.; Cheng, M.M.; Shao, L. Concealed Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 6024–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, C.; Xiang, T.Z. Boundary-guided camouflaged object detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.00794. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Liu, S.J.; Sun, Y.J.; Ji, G.P.; Wu, Y.F.; Zhou, T. Camouflaged object detection via context-aware cross-level fusion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 6981–6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Ji, G.P.; Wei, Z.; Yang, X.; Wei, X.; Fan, D.P. Camouflaged object segmentation with distraction mining. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 8772–8781. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, X. Camouflaged object detection with feature decomposition and edge reconstruction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 22046–22055. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, F.; Song, Y. Camouflaged object segmentation with transformer. In Proceedings of the Cognitive Systems and Information Processing: 6th International Conference, ICCSIP 2021, Suzhou, China, 20–21 November 2021; Revised Selected Papers 6. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 225–237. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Wu, W. Boosting camouflaged object detection with dual-task interactive transformer. In Proceedings of the 2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–25 August 2022; pp. 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Wang, S.; Qin, X.; Dai, H.; Ren, W.; Tai, Y.; Wang, C.; Shao, L. High-resolution iterative feedback network for camouflaged object detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.11624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Dai, H.; Xiang, T.Z.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.X.; Qin, J.; Xiong, H. Feature shrinkage pyramid for camouflaged object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 5557–5566. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xiang, T.Z.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H. Zoom in and out: A mixed-scale triplet network for camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2160–2170. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Bai, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Lin, Z.; Timofte, R.; Van Gool, L. Cddfuse: Correlation-driven dual-branch feature decomposition for multi-modality image fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 5906–5916. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Gao, C.; Wang, J.; Yu, G.; Shen, C.; Sang, N. Bisenet v2: Bilateral network with guided aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 3051–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Cui, Q.; Wei, X.S.; Chen, Z.M. Bbn: Bilateral-branch network with cumulative learning for long-tailed visual recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9719–9728. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pyramid vision transformer: A versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 568–578. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Wang, S.; Huang, Q. F3Net: Fusion, feedback and focus for salient object detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 12321–12328. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.P.; Cheng, M.M.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Borji, A. Structure-measure: A new way to evaluate foreground maps. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4548–4557. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.P.; Ji, G.P.; Qin, X.; Cheng, M.M. Cognitive vision inspired object segmentation metric and loss function. Sci. Sin. Inf. 2021, 6, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Margolin, R.; Zelnik-Manor, L.; Tal, A. How to evaluate foreground maps? In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Perazzi, F.; Krähenbühl, P.; Pritch, Y.; Hornung, A. Saliency filters: Contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 733–740. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, C.; Tian, Y. Selectivity or invariance: Boundary-aware salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3799–3808. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J. Inferring camouflaged objects by texture-aware interactive guidance network. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 3599–3607. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Zhang, J.; Lv, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, T.; Dai, Y. Uncertainty-aware joint salient object and camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 10071–10081. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Q.; Li, X.; Yang, F.; Chen, C.; Cheng, H.; Fan, D.P. Mutual graph learning for camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 12997–13007. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Zhai, Q.; Li, X.; Huang, R.; Luo, A.; Cheng, H.; Fan, D.P. Uncertainty-guided transformer reasoning for camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 4146–4155. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, K.; Bi, H.; Liu, Z.; Yang, L. Camouflaged object detection via neighbor connection and hierarchical information transfer. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2022, 221, 103450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.P.; Zhu, L.; Zhuge, M.; Fu, K. Fast camouflaged object detection via edge-based reversible re-calibration network. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 123, 108414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, C.; Bi, H. TPRNet: Camouflaged object detection via transformer-induced progressive refinement network. Vis. Comput. 2022, 39, 4593–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, C.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. Feature Aggregation and Propagation Network for Camouflaged Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 7036–7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Li, P.; Xie, H.; Yan, X.; Liang, D.; Chen, D.; Wei, M.; Qin, J. I can find you! Boundary-guided separated attention network for camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Pomona, CA, USA, 24–28 October 2022; Volume 36, pp. 3608–3616. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Barnes, N. Modeling aleatoric uncertainty for camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 1445–1454. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Xu, S.; Piao, Y.; Shi, D.; Lin, S.; Lu, H. Preynet: Preying on camouflaged objects. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 5323–5332. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Q.; Yao, S.; Liu, Y.; Fan, X.; Liu, R.; Luo, Z. Segment, magnify and reiterate: Detecting camouflaged objects the hard way. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 4713–4722. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Li, B.; Tang, L.; Kuang, S.; Wu, S.; Ding, S. Detecting camouflaged object in frequency domain. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 4504–4513. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, G.P.; Fan, D.P.; Chou, Y.C.; Dai, D.; Liniger, A.; Van Gool, L. Deep gradient learning for efficient camouflaged object detection. Mach. Intell. Res. 2023, 20, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

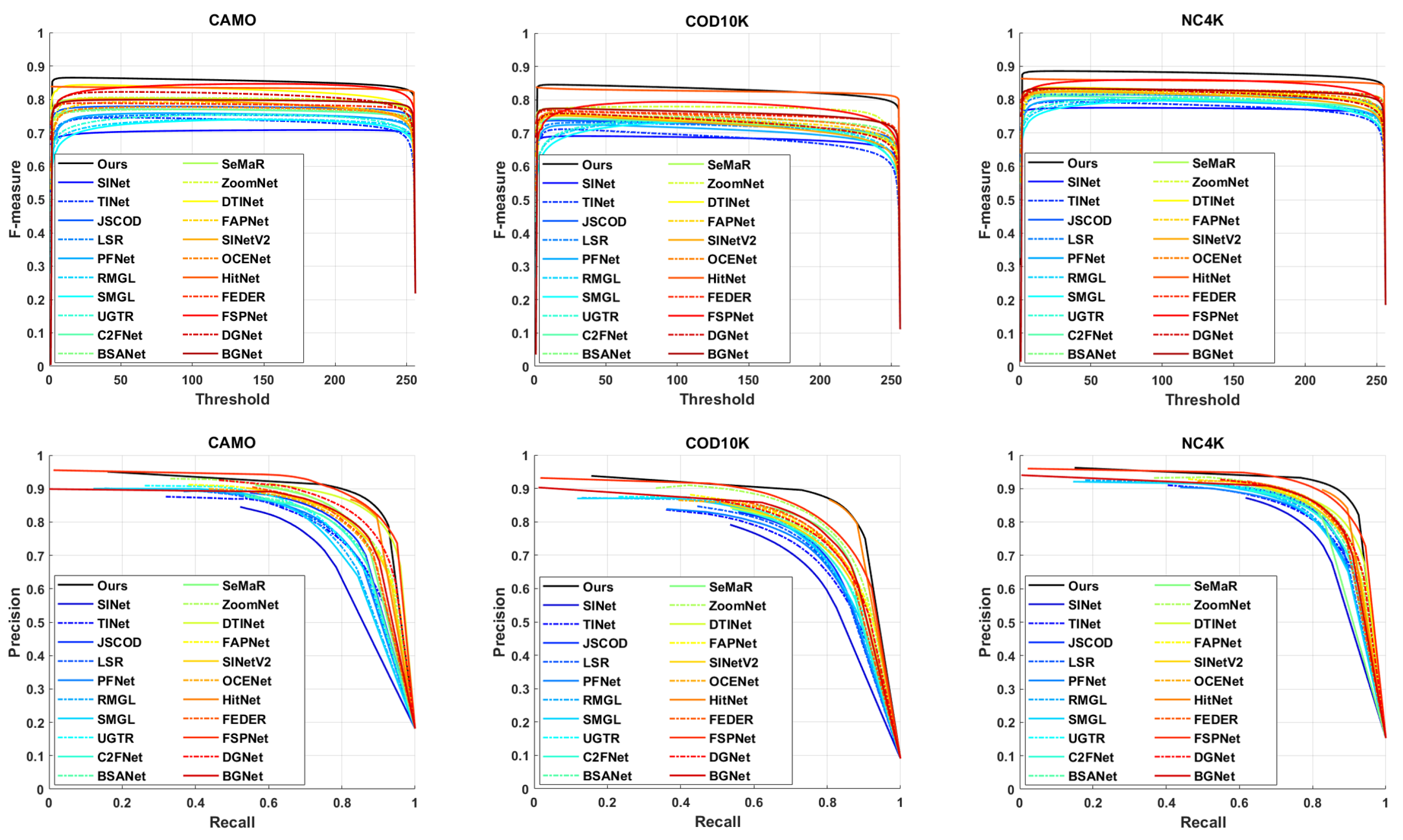

| Methods | CAMO-Test{250 Images} | COD10K-Test{2026 Images} | NC4K{4121 Images} | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN-Based Method | ||||||||||||
| SINet | 0.751 | 0.771 | 0.606 | 0.100 | 0.771 | 0.806 | 0.551 | 0.051 | 0.808 | 0.871 | 0.769 | 0.058 |
| C2FNet | 0.796 | 0.865 | 0.719 | 0.080 | 0.813 | 0.886 | 0.686 | 0.036 | 0.838 | 0.901 | 0.762 | 0.049 |
| TINet | 0.781 | 0.847 | 0.678 | 0.087 | 0.793 | 0.848 | 0.635 | 0.042 | 0.829 | 0.882 | 0.734 | 0.055 |
| JSCOD | 0.800 | 0.872 | 0.728 | 0.073 | 0.809 | 0.882 | 0.684 | 0.035 | 0.842 | 0.906 | 0.771 | 0.047 |
| PFNet | 0.782 | 0.852 | 0.695 | 0.085 | 0.800 | 0.868 | 0.660 | 0.040 | 0.829 | 0.887 | 0.745 | 0.053 |
| LSR | 0.793 | 0.826 | 0.725 | 0.085 | 0.793 | 0.868 | 0.658 | 0.041 | 0.839 | 0.883 | 0.779 | 0.053 |
| R-MGL | 0.775 | 0.848 | 0.673 | 0.088 | 0.814 | 0.865 | 0.666 | 0.035 | 0.833 | 0.890 | 0.740 | 0.052 |
| S-MGL | 0.772 | 0.850 | 0.664 | 0.089 | 0.811 | 0.851 | 0.655 | 0.037 | 0.829 | 0.885 | 0.731 | 0.055 |
| UGTR | 0.785 | 0.859 | 0.686 | 0.086 | 0.818 | 0.850 | 0.667 | 0.035 | 0.839 | 0.886 | 0.746 | 0.052 |
| NCHIT | 0.784 | 0.841 | 0.652 | 0.088 | 0.792 | 0.794 | 0.591 | 0.046 | 0.830 | 0.872 | 0.710 | 0.058 |
| ERRNet | 0.779 | 0.855 | 0.679 | 0.085 | 0.786 | 0.845 | 0.630 | 0.043 | 0.827 | 0.892 | 0.737 | 0.054 |
| TPRNet | 0.814 | 0.870 | 0.781 | 0.076 | 0.829 | 0.892 | 0.725 | 0.034 | 0.854 | 0.903 | 0.790 | 0.047 |
| FAPNet | 0.815 | 0.877 | 0.734 | 0.076 | 0.822 | 0.875 | 0.694 | 0.036 | 0.851 | 0.903 | 0.775 | 0.047 |
| BSANet | 0.794 | 0.866 | 0.717 | 0.079 | 0.818 | 0.894 | 0.699 | 0.034 | 0.841 | 0.906 | 0.771 | 0.048 |
| OCENet | 0.807 | 0.767 | 0.866 | 0.075 | 0.832 | 0.745 | 0.890 | 0.032 | 0.857 | 0.817 | 0.899 | 0.044 |
| PreyNet | 0.790 | 0.856 | 0.708 | 0.077 | 0.813 | 0.894 | 0.697 | 0.034 | 0.834 | 0.899 | 0.763 | 0.050 |
| SINetV2 | 0.820 | 0.882 | 0.743 | 0.070 | 0.815 | 0.887 | 0.680 | 0.037 | 0.847 | 0.903 | 0.769 | 0.048 |
| BGNet | 0.812 | 0.870 | 0.749 | 0.073 | 0.831 | 0.901 | 0.722 | 0.033 | 0.851 | 0.907 | 0.788 | 0.044 |
| SeMaR | 0.815 | 0.881 | 0.753 | 0.071 | 0.833 | 0.893 | 0.724 | 0.034 | 0.841 | 0.905 | 0.781 | 0.046 |
| FDNet | 0.841 | 0.901 | 0.775 | 0.063 | 0.840 | 0.906 | 0.729 | 0.030 | 0.834 | 0.895 | 0.750 | 0.052 |
| ZoomNet | 0.820 | 0.883 | 0.752 | 0.066 | 0.838 | 0.893 | 0.729 | 0.029 | 0.853 | 0.907 | 0.784 | 0.043 |
| DGNet-S | 0.826 | 0.896 | 0.754 | 0.063 | 0.810 | 0.869 | 0.672 | 0.036 | 0.845 | 0.902 | 0.764 | 0.047 |
| DGNet | 0.839 | 0.906 | 0.769 | 0.057 | 0.822 | 0.879 | 0.693 | 0.033 | 0.857 | 0.910 | 0.784 | 0.042 |
| FEDER | 0.807 | 0.873 | 0.785 | 0.069 | 0.823 | 0.900 | 0.740 | 0.032 | 0.846 | 0.905 | 0.817 | 0.045 |
| Transformer-Based Method | ||||||||||||
| COS-T | 0.813 | 0.896 | 0.776 | 0.060 | 0.790 | 0.901 | 0.693 | 0.035 | 0.825 | 0.881 | 0.730 | 0.055 |
| DTINet | 0.857 | 0.912 | 0.796 | 0.050 | 0.824 | 0.893 | 0.695 | 0.034 | 0.863 | 0.915 | 0.792 | 0.041 |
| HitNet | 0.844 | 0.902 | 0.801 | 0.057 | 0.868 | 0.932 | 0.798 | 0.024 | 0.870 | 0.921 | 0.825 | 0.039 |
| FSPNet | 0.856 | 0.899 | 0.799 | 0.050 | 0.851 | 0.895 | 0.735 | 0.026 | 0.879 | 0.915 | 0.816 | 0.035 |
| Ours | 0.870 | 0.924 | 0.828 | 0.047 | 0.879 | 0.938 | 0.806 | 0.021 | 0.893 | 0.940 | 0.854 | 0.030 |
| Model | Method | CAMO-Test{250 Images} | COD10K-Test{2026 Images} | NC4K{4121 Images} | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | B1 | 0.784 | 0.802 | 0.701 | 0.069 | 0.793 | 0.808 | 0.651 | 0.048 | 0.801 | 0.873 | 0.758 | 0.052 |
| (b) | B2 | 0.832 | 0.887 | 0.784 | 0.057 | 0.847 | 0.874 | 0.716 | 0.035 | 0.853 | 0.901 | 0.779 | 0.042 |
| (c) | B1+B2+FBM | 0.865 | 0.917 | 0.822 | 0.052 | 0.871 | 0.927 | 0.793 | 0.024 | 0.885 | 0.929 | 0.848 | 0.032 |
| (d) | B1+CRM C | 0.831 | 0.887 | 0.769 | 0.060 | 0.811 | 0.869 | 0.718 | 0.041 | 0.841 | 0.902 | 0.784 | 0.049 |
| (e) | B1+CRM | 0.836 | 0.891 | 0.751 | 0.058 | 0.818 | 0.884 | 0.724 | 0.039 | 0.847 | 0.908 | 0.788 | 0.048 |
| (f) | B2+CRM C | 0.861 | 0.911 | 0.815 | 0.054 | 0.865 | 0.917 | 0.785 | 0.030 | 0.883 | 0.921 | 0.839 | 0.035 |
| (g) | B2+CRM | 0.865 | 0.916 | 0.819 | 0.052 | 0.869 | 0.921 | 0.789 | 0.023 | 0.891 | 0.929 | 0.845 | 0.031 |
| (h) | B1+B2+FBM+CRM C | 0.867 | 0.921 | 0.824 | 0.048 | 0.874 | 0.931 | 0.799 | 0.022 | 0.887 | 0.932 | 0.848 | 0.031 |
| (i) | Ours | 0.869 | 0.924 | 0.826 | 0.047 | 0.876 | 0.936 | 0.806 | 0.021 | 0.891 | 0.938 | 0.851 | 0.030 |
| Methods | Medicine{CVC-300 Dataset} | Industry{CDS2K Dataset} | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DGNet | 0.827 | 0.852 | 0.706 | 0.035 | 0.822 | 0.851 | 0.731 | 0.028 |
| FEDER | 0.835 | 0.863 | 0.719 | 0.034 | 0.828 | 0.863 | 0.740 | 0.028 |
| HitNet | 0.844 | 0.869 | 0.724 | 0.032 | 0.849 | 0.893 | 0.759 | 0.026 |
| FSPNet | 0.841 | 0.866 | 0.726 | 0.032 | 0.847 | 0.882 | 0.755 | 0.026 |
| Ours | 0.846 | 0.873 | 0.739 | 0.034 | 0.851 | 0.895 | 0.763 | 0.025 |
| Methods | MACs | Para. | COD10K-Test{2026 Images} | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGNet | 58.45 G | 79.85 M | 0.831 | 0.901 | 0.722 | 0.033 |
| ZoomNet | 95.5 G | 23.38 M | 0.838 | 0.893 | 0.729 | 0.029 |
| DTINet | 144.68 G | 266.33 M | 0.824 | 0.893 | 0.695 | 0.034 |
| HitNet | 55.95 G | 25.73 M | 0.868 | 0.932 | 0.798 | 0.024 |
| PopNet | 154.88 G | 188.05 M | 0.851 | 0.91 | 0.757 | 0.028 |
| Ours | 38.36 G | 59.34 M | 0.878 | 0.938 | 0.806 | 0.021 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, M.; Sun, M.; Wang, Z. Curiosity-Driven Camouflaged Object Segmentation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010173
Pang M, Sun M, Wang Z. Curiosity-Driven Camouflaged Object Segmentation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(1):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010173
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Mengyin, Meijun Sun, and Zheng Wang. 2025. "Curiosity-Driven Camouflaged Object Segmentation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 1: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010173
APA StylePang, M., Sun, M., & Wang, Z. (2025). Curiosity-Driven Camouflaged Object Segmentation. Applied Sciences, 15(1), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010173







