Effect of Sample Presentation on the Classification of Black Soldier Fly Larvae Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
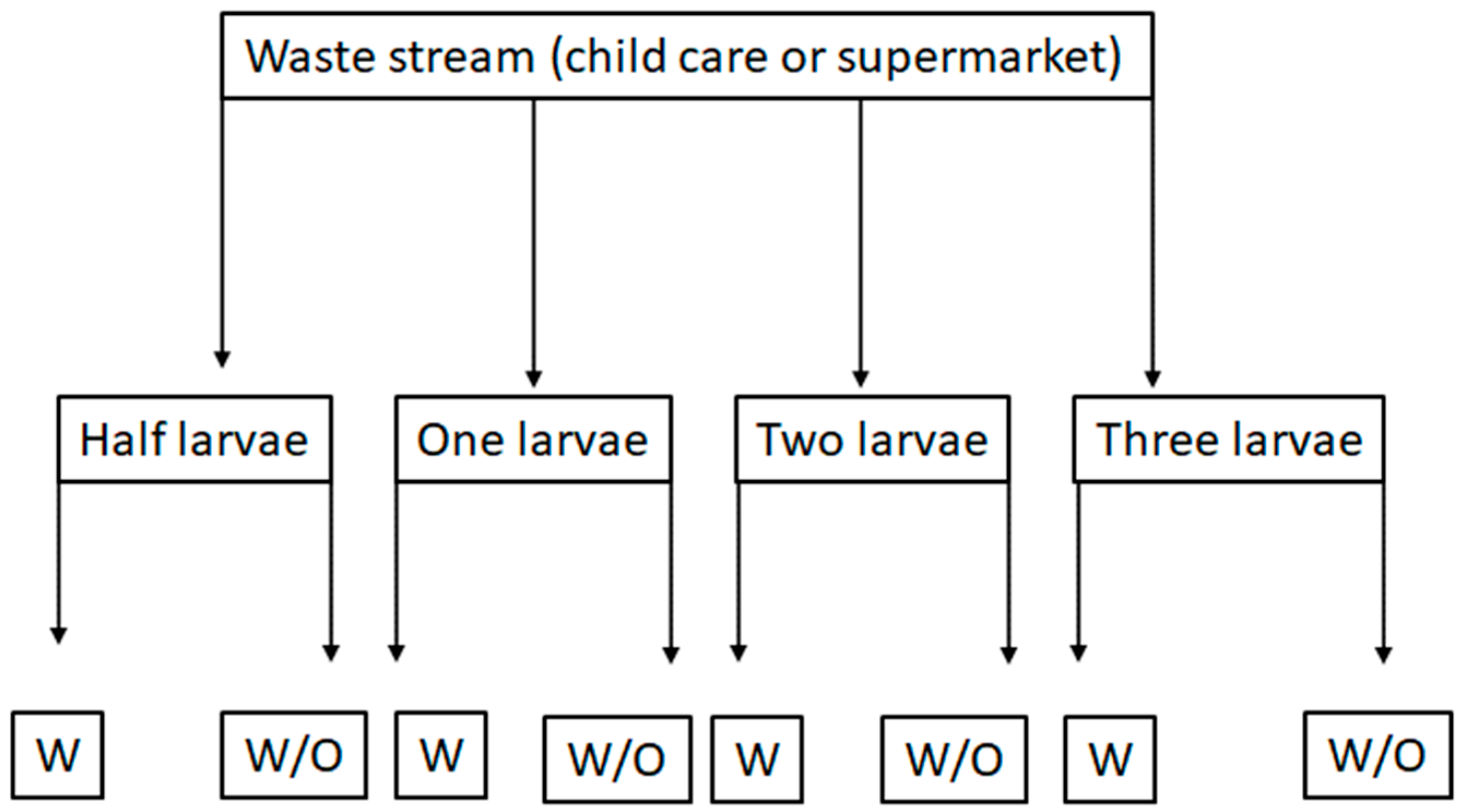
2. Materials and Methods
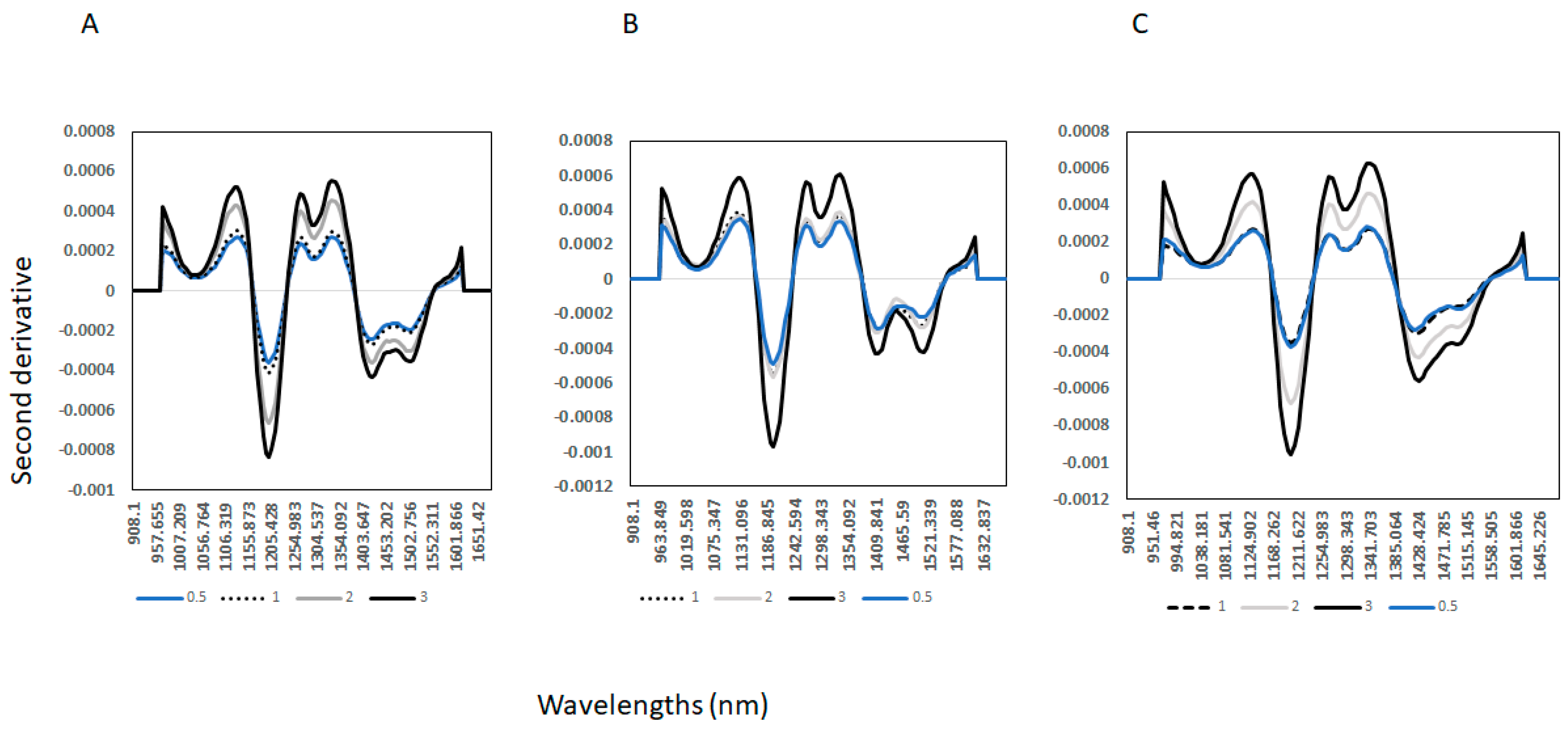
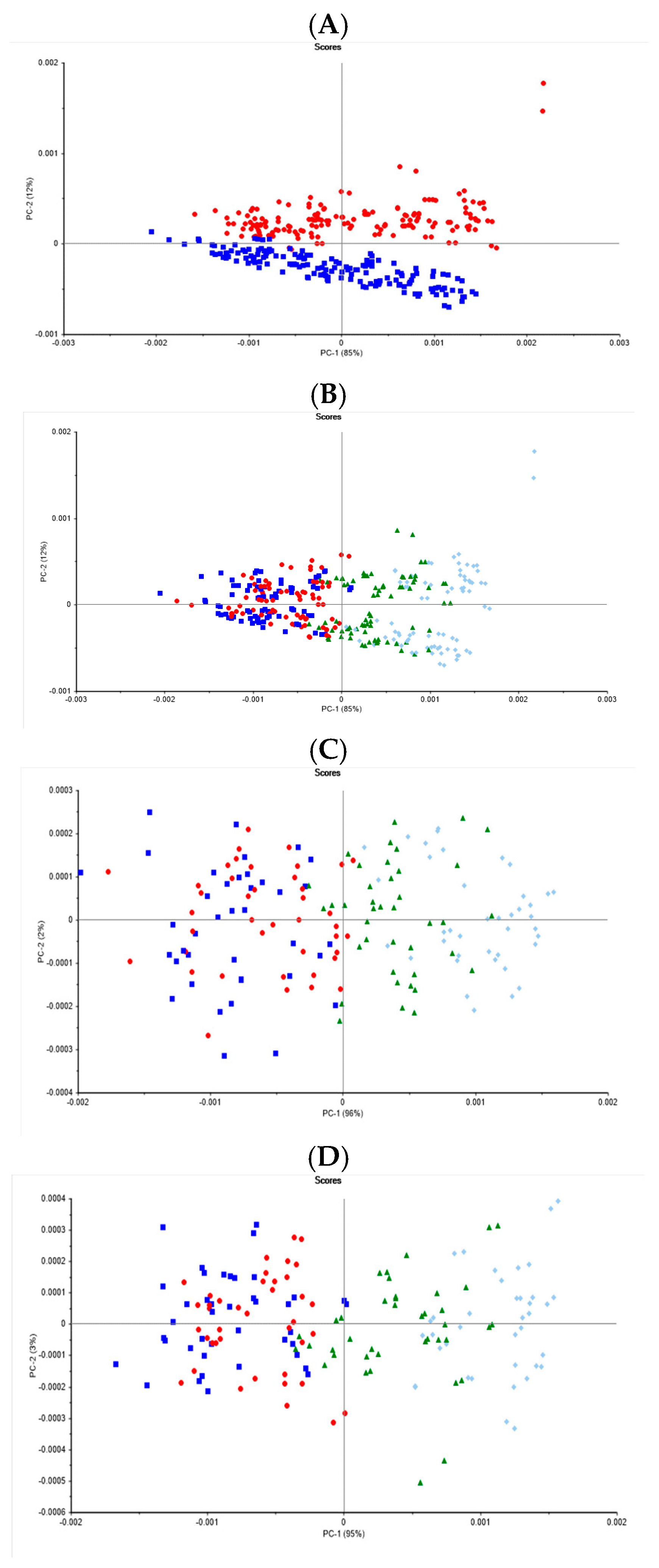
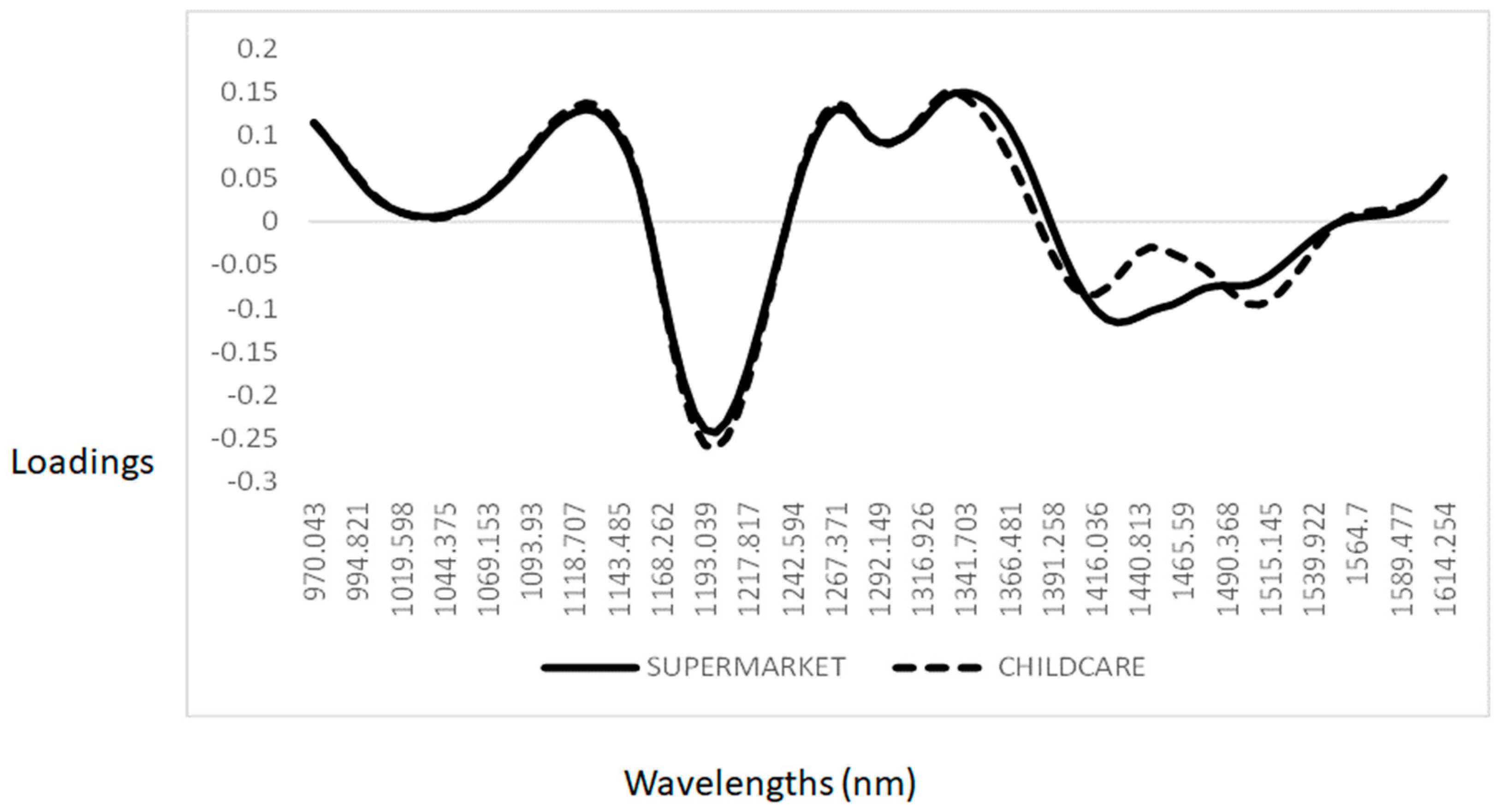
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alagappan, S.; Hoffman, L.C.; Mantilla, S.M.O.; Mikkelsen, D.; James, P.; Yarger, O.; Cozzolino, D. Near Infrared Spectroscopy as a Traceability Tool to Monitor Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) Intended as Animal Feed. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenta, S.; Garrigues, S.; de la Guardia, M. Green analytical chemistry. TRAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 276, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, L.C.; Zhang, S.; Alagappan, S.; Wills, V.; Yarger, O.; Cozzolino, D. Monitoring Compositional Changes in Black Soldier Fly Larvae (BSFL) Sourced from Different Waste Stream Diets Using Attenuated Total Reflectance Mid Infrared Spectroscopy and Chemometrics. Molecules 2022, 27, 7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira Dos Santos, C.A.; Lopo, M.; Pascoa’, R.N.M.J.; Lopes, J.A. A review on the applications of portable near-infrared spectrometers in the agro-food industry. Appl. Spectrosc. 2013, 67, 1215–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beć, K.B.; Grabska, J.; Huck, C.W. Principles and Applications of Miniaturized Near-Infrared (NIR) Spectrometers. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beć, K.B.; Grabska, J.; Huck, C.W. Miniaturized NIR Spectroscopy in Food Analysis and Quality Control: Promises, Challenges, and Perspectives. Foods 2022, 11, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kademi, H.I.; Ulusoy, B.H.; Hecer, C. Applications of miniaturized and portable near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) for inspection and control of meat and meat products. Food Rev. Int. 2019, 35, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giussani, B.; Gorla, G.; Riu, J. Analytical Chemistry Strategies in the Use of Miniaturised NIR Instruments: An Overview. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 14, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorla, G.; Taborelli, P.; Alamprese, C.; Grassi, S.; Giussani, B. On the Importance of Investigating Data Structure in Miniaturized NIR Spectroscopy Measurements of Food: The Case Study of Sugar. Foods 2023, 12, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorla, G.; Taborelli, P.; Ahmed, H.J.; Alamprese, C.; Grassi, S.; Boqué, R.; Riu, J.; Giussani, B. Miniaturized NIR Spectrometers in a Nutshell: Shining Light over Sources of Variance. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thygesen, L.G.; Løkke, M.M.; Micklander, E.; Engelsen, S.B. Vibrational microspectroscopy of food. Raman vs. FT-IR. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 14, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.H.; He, H.J.; Sun, D.W. Su WH, He HJ, Sun DW: Nondestructive and rapid evaluation of staple foods quality by using spectroscopic techniques: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, T.M.P.; Stellari, A. Review: NIR spectroscopy as a suitable tool for the investigation of the horticultural field. Agronomy 2019, 9, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Marín, D.; Calero, L.; Fearn, T.; Torres, I.; Garrido-Varo, A.; Sánchez, M.-T. A system using in situ NIRS sensors for the detection of product failing to meet quality standards and the prediction of optimal postharvest shelf-life in the case of oranges kept in cold storage. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 147, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, P.; O’Donnell, C.; Fagan, C. Benefits and Challenges of Adopting PAT for the Food Industry. In Process Analytical Technology for the Food Industry; O’Donnell, C., Fagan, C., Cullen, P., Eds.; Food Engineering Series; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hitzmann, B.; Hauselmann, R.; Niemoeller, A.; Sangi, D.; Traenkle, J.; Glassey, J. Process analytical technologies in food industry –challenges and benefits: A status report and recommendations. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 10, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Cullen, J.M. Food traceability: A generic theoretical framework. Food Control 2021, 123, 107848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, I.; Cowe, I. Sample preparation. In Near Infrared Spectroscopy in Agriculture; Roberts, C.A., Workman, J., Reeves, J.B., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2004; pp. 75–115. [Google Scholar]
- Cozzolino, D. Sample presentation, sources of error and future perspectives on the application of vibrational spectroscopy in the wine industry. J. Sci Food Agric. 2014, 95, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzolino, D. The sample, the spectra, and the maths—The critical pillars in the development of robust and sound vibrational spectroscopy applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobasa, E.M.; Phan, A.D.T.; Manolis, C.; Netzel, M.; Smyth, H.; Cozzolino, D.; Sultanbawa, Y. Effect of sample presentation on the near infrared spectra of wild harvest Kakadu plum fruits (Terminalia ferdinandiana). Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 111, 103560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobasa, E.M.; Netzel, M.E.; Cozzolino, D.; Phan, A.D.T.; Sultanbawa, Y. Measurement of total soluble solids and moisture in puree and dry powder of Kakadu plum (Terminalia ferdinandiana) samples using hand-held near infrared spectroscopy. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2021, 29, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertinetto, C.G.; Schoot, M.; Dingemans, M.; Meeuwsen, W.; Buydens, L.M.; Jansen, J.J. Influence of measurement procedure on the use of a handheld NIR spectrophotometer. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega-Castellote, M.; Pérez-Marín, D.; Torres, I.; Sánchez, M.-T. Non-destructive determination of fatty acid composition of in-shell and shelled almonds using handheld NIRS sensors. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 174, 111459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, M.; Rurik, M.; Drees, A.; Bigdowski, K.; Kohlbacher, O.; Fischer, M. Comparison of different sample preparation techniques for NIR screening and their influence on the geographical origin determination of almonds (Prunus dulcis MILL.). Food Control 2020, 115, 107302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewe, V.; Navarro-Cerrillo, R.M.; García-Olmo, J.; Riccioli, C.; Sanchez-Cuesta, R. Discriminant analysis of Mediterranean pine nuts (Pinus pinea L.) from Chilean plantations by near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS). Food Control. 2017, 73, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Dowell, F.E.; Lacey, R.E. Single Wheat Kernel Size Effects on Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectra and Color Classification. Cereal Chem. 1999, 76, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cruz-Tirado, J.P.; Silva dos Santos Vieira, M.; Amigo, J.M.; Siche, R.; Fernandes Barbin, D. Prediction of protein and lipid content in black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) larvae flour using portable NIR spectrometers and chemometrics. Food Control 2023, 153, 109969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Tirado, J.; Amigo, J.M.; Barbin, D.F. Determination of protein content in single black fly soldier (Hermetia illucens L.) larvae by near infrared hyperspectral imaging (NIR-HSI) and chemometrics. Food Control 2023, 143, 109266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumo, M.; Osuga, I.M.; Khamis, F.M.; Tanga, C.M.; Fiaboe, K.K.M.; Subramanian, S.; Ekesi, S.; van Huis, A.; Borgemeister, C. The nutritive value of black soldier fly larvae reared on common organic waste streams in Kenya. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohn, Z.; Latty, T.; Abbas, A. Understanding dietary carbohydrates in black soldier fly larvae treatment of organic waste in the circular economy. Waste Manag. 2022, 137, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Diener, S.; Zurbrügg, C.; Mathys, A. Decomposition of biowaste macronutrients, microbes, and chemicals in black soldier fly larval treatment: A review. Waste Manag. 2018, 82, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saviztky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinnan, A.; van denBerg, F.; Engelsen, S.B. Review of the most common pre-processing techniques for near-infrared spectra. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1201–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau, S.; Cozzolino, D.; Clark, C.J. Contributions of Fourier-transform mid infrared (FT-MIR) spectroscopy to the study of fruit and vegetables: A review. Post. Biol. Technol. 2019, 148, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Mallet, Y.; Walczak, B.; Penninckx, W.; Massart., D.L.; Heuerding, S.; Erni, F. Comparison of regularized discriminant analysis linear discriminant analysis and quadratic discriminant analysis applied to NIR data Author links open overlay panel. Anal. Chim. Acta 1996, 329, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Paliwal, K.K. Linear discriminant analysis for the small sample size problem: An overview. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cyber. 2015, 6, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteki, M.; Shahsavari, Z.; Simal-Gandara, J. Use of spectroscopic methods in combination with linear discriminant analysis for authentication of food products. Food Control 2018, 91, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workman, J.; Weyer, L. Practical Guide to Interpret Near-Infrared Spectroscopy; CRC Press Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Riu, J.; Vega, A.; Boqué, R.; Giussani, B. Exploring the Analytical Complexities in Insect Powder Analysis Using Miniaturized NIR Spectroscopy. Foods 2022, 11, 3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Number of Larvae | Supermarket | Childcare | %CC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 L | Supermarket | 38 | 2 | 93 |
| Childcare | 3 | 37 | ||
| 1 L | Supermarket | 40 | 0 | 100 |
| Childcare | 0 | 49 | ||
| 2 L | Supermarket | 40 | 0 | 100 |
| Childcare | 0 | 40 | ||
| 3 L | Supermarket | 40 | 0 | 100 |
| Childcare | 0 | 40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanchez, C.M.; Alagappan, S.; Hoffman, L.; Yarger, O.; Cozzolino, D. Effect of Sample Presentation on the Classification of Black Soldier Fly Larvae Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3841. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093841
Sanchez CM, Alagappan S, Hoffman L, Yarger O, Cozzolino D. Effect of Sample Presentation on the Classification of Black Soldier Fly Larvae Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(9):3841. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093841
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanchez, C. Mendez, S. Alagappan, L. Hoffman, O. Yarger, and D. Cozzolino. 2024. "Effect of Sample Presentation on the Classification of Black Soldier Fly Larvae Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy" Applied Sciences 14, no. 9: 3841. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093841
APA StyleSanchez, C. M., Alagappan, S., Hoffman, L., Yarger, O., & Cozzolino, D. (2024). Effect of Sample Presentation on the Classification of Black Soldier Fly Larvae Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Applied Sciences, 14(9), 3841. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093841









