Synthesis of a Multi-Template Molecular Imprinted Bulk Polymer for the Adsorption of Non-Steroidal Inflammatory and Antiretroviral Drugs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemical Reagents
2.2. Characterization Techniques
2.3. Synthesis of Polymers
2.4. Template Removal
2.5. Grinding and Sieving Process of the Polymers
2.6. Batch Optimizations and Adsorptions Studies
2.6.1. Selectivity Experiments
2.6.2. Swelling Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
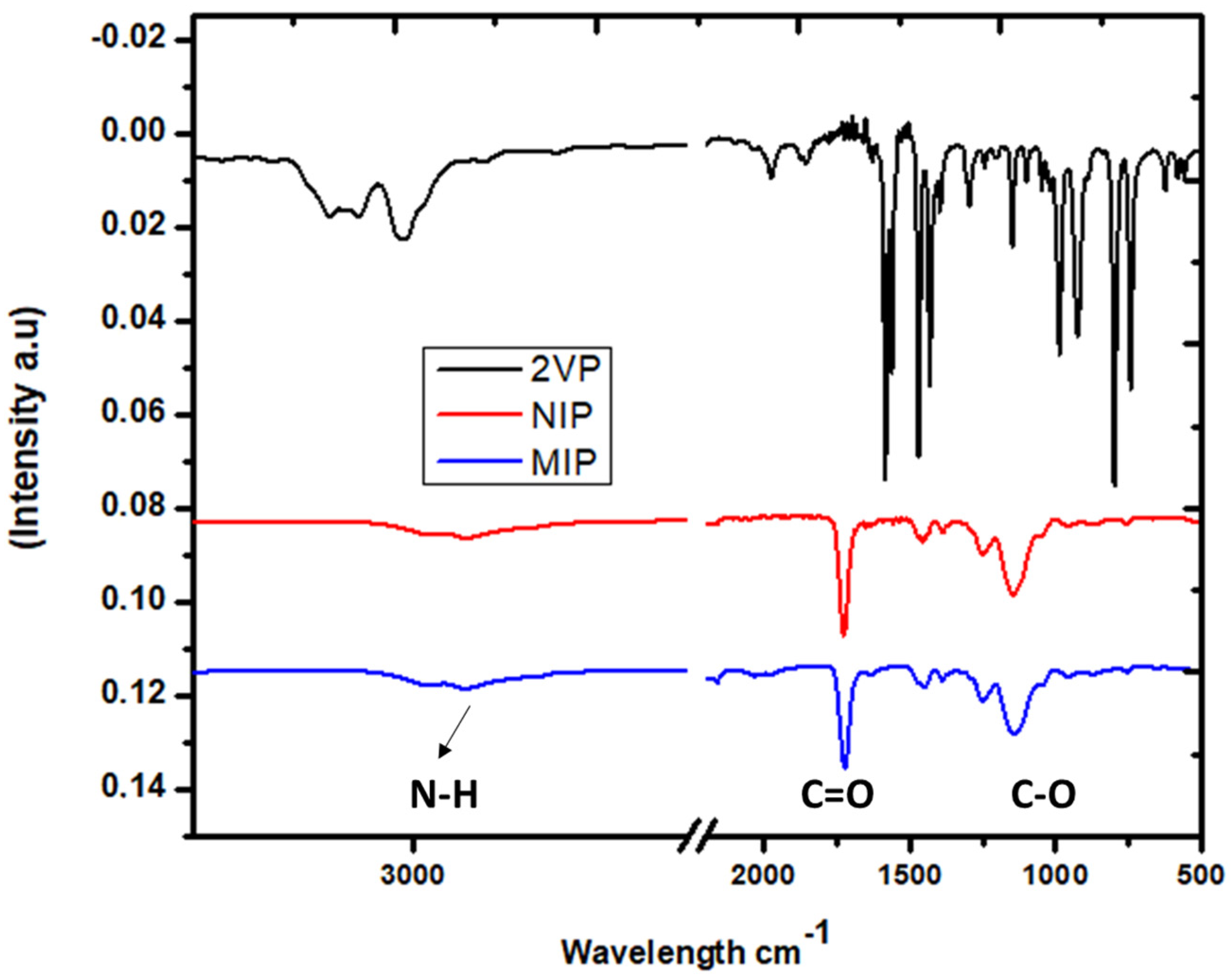
3.1. Surface Chemistry
3.2. Morphology Analysis
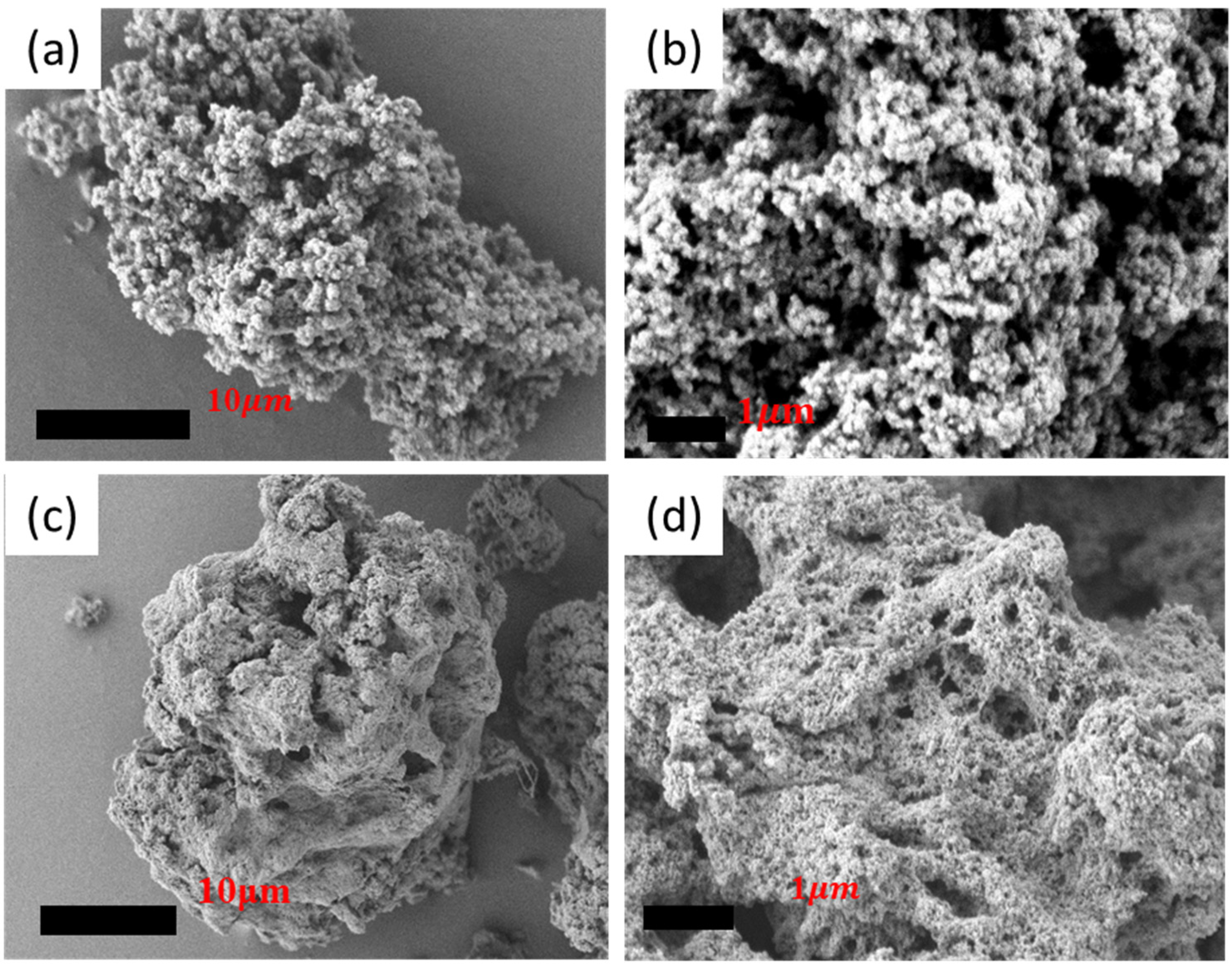
3.2.1. SEM
3.2.2. Brunauer, Emmett, and Teller (BET) Analysis
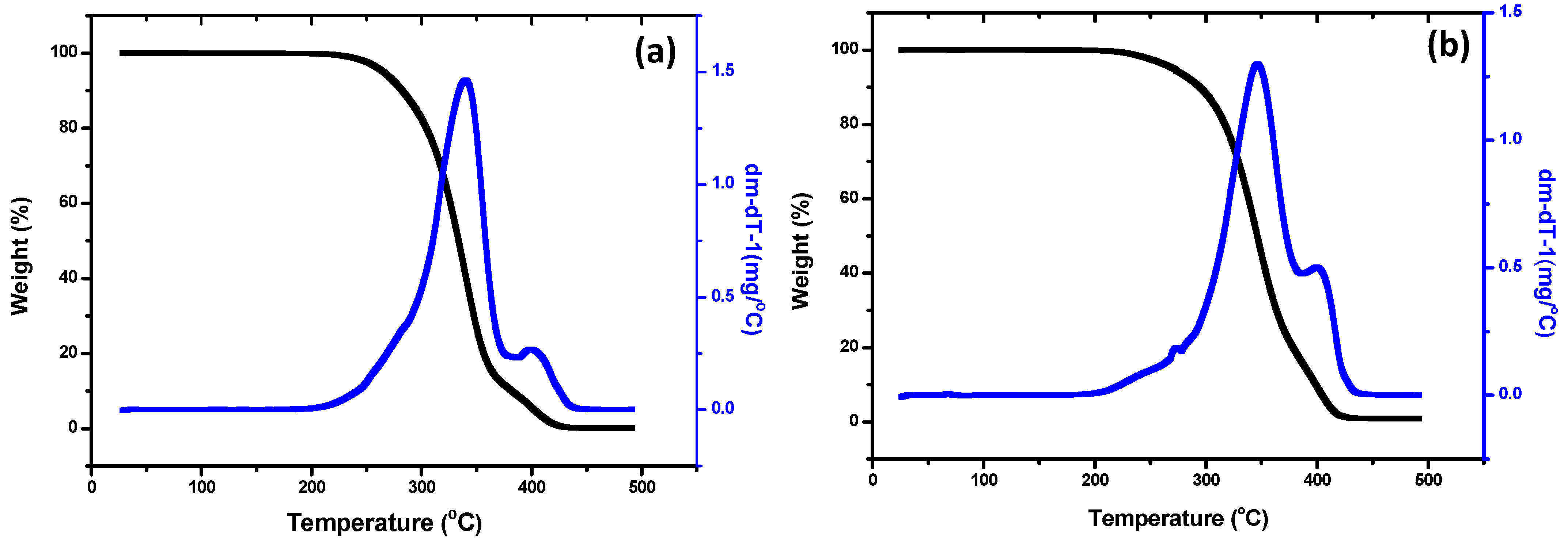
3.2.3. Thermal Properties
3.3. Adsorption Studies
3.3.1. Effects of pH
3.3.2. Effects of Polymer Mass
3.3.3. Effects of Initial Concentration
3.3.4. Effects of Contact Time
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics
3.4.1. Adsorption Isotherms
3.4.2. Kinetic Modelling
3.5. Swelling Behaviour
3.6. Selectivity Studies
3.7. Comparative Adsorbent Data
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patel, M.; Kumar, R.; Kishor, K.; Mlsna, T.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D. Pharmaceuticals of emerging concern in aquatic systems: Chemistry, occurrence, effects, and removal methods. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3510–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebele, A.J.; Oluseyi, T.; Drage, D.S.; Harrad, S.; Abdallah, M.A.-E. Occurrence, seasonal variation and human exposure to pharmaceuticals and personal care products in surface water, groundwater and drinking water in Lagos State, Nigeria. Emerg. Contam. 2020, 6, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bian, Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Du, R.Z.; Li, M.; Tan, Y.; Feng, X.-S. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in the environment: Recent updates on the occurrence, fate, hazards and removal technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahammad, N.A.; Ahmad, M.A.; Hameed, B.H.; Din, A.T.M. A mini review of recent progress in the removal of emerging contaminants from pharmaceutical waste using various adsorbents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 124459–124473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couto, C.F.; Lange, L.C.; Amaral, M.C.S. Occurrence, fate and removal of pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) in water and wastewater treatment plants—A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K’oreje, K.O.; Vergeynst, L.; Ombaka, D.; De Wispelaere, P.; Okoth, M.; Van Langenhove, H.; Demeestere, K. Occurrence patterns of pharmaceutical residues in wastewater, surface water and groundwater of Nairobi and Kisumu city, Kenya. Chemosphere 2016, 149, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- K’oreje, K.O.; Okoth, M.; Van Langenhove, H.; Demeestere, K. Occurrence and treatment of contaminants of emerging concern in the African aquatic environment: Literature review and a look ahead. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 254, 109752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.I.; Ayati, A.; Farghali, M.; Krivoshapkin, P.; Tanhaei, B.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Krivoshapkina, E.; Taheri, P.; Tracey, C.; Al-Fatesh, A.; et al. Advanced Adsorbents for Ibuprofen Removal from Aquatic Environments: A Review; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; Volume 22, no. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abafe, O.A.; Späth, J.; Fick, J.; Jansson, S.; Buckley, C.; Stark, A.; Pietruschka, B.; Martincigh, B.S. LC-MS/MS determination of antiretroviral drugs in influents and effluents from wastewater treatment plants in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ncube, S.; Madikizela, L.M.; Chimuka, L.; Nindi, M.M. Environmental fate and ecotoxicological effects of antiretrovirals: A current global status and future perspectives. Water Res. 2018, 145, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasonga, T.K.; Coetzee, M.A.A.; Kamika, I.; Ngole-Jeme, V.M.; Momba, M.N.B. Endocrine-disruptive chemicals as contaminants of emerging concern in wastewater and surface water: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, E.; Petrie, B.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Wolfaardt, G.M. The fate of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs), endocrine disrupting contaminants (EDCs), metabolites and illicit drugs in a WWTW and environmental waters. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigonya, S.; Mokhothu, T.H.; Mokhena, T.C.; Makhanya, T.R. Mitigation of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory and Antiretroviral Drugs as Environmental Pollutants by Adsorption Using Nanomaterials as Viable Solution—A Critical Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupp, Í.N.; Filho, A.V.; Arim, A.L.; Muniz, A.R.C.; da Rosa, G.S. Ibuprofen Adsorption onto Olive Pomace Activated Carbon. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2023, 46, 2395–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, J.; Hernández, L.; González, J.L.; Salazar-González, R.; Calzadilla, W.; Guerrero, L.; Escalona, N.; Huiliñir, C. Removal of Ibuprofen and Diclofenac in Batch Nitrifying Reactors: Effect of Natural Zeolite on the Process. Water 2023, 15, 2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, A.A.H. Preparation of molecularly imprinted silica particles with amino functionality for chiral separation of (±)-naproxen. Chirality 2023, 35, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouzidi, M.; Sellaoui, L.; Mohamed, M.; Franco, D.S.P.; Erto, A.; Badawi, M. A comprehensive study on paracetamol and ibuprofen adsorption onto biomass-derived activated carbon through experimental and theoretical assessments. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 376, 121457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popaliya, M.; Mishra, A. Modified zeolite as an adsorbent for dyes, drugs, and heavy metal removal: A review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 12919–12936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xiao, J.; Chen, L.; Ren, B.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y. A study of the optimal diffusion distance of ibuprofen through the synthesis of different sizes of mesoporous silica. J. Solid State Chem. 2023, 321, 123911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkika, D.A.; Tolkou, A.K.; A Lambropoulou, D.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Kokkinos, P.; Kalavrouziotis, I.K.; Kyzas, G.Z. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) as environmental separation tools. RSC Appl. Polym. 2024, 2, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilvenyte, G.; Ratautaite, V.; Boguzaite, R.; Ramanavicius, A.; Viter, R.; Ramanavicius, S. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for the Determination of Cancer Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Saldaña, V.; Castro-García, C.; Rodríguez-Maese, R.; Leal-Quezada, L.O. Advances in the extraction methods for the environmental analysis of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 169, 117409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, Y.; Beckett, L.E.; Sadula, S.; Vargheese, V.; Korley, L.S.T.J.; Vlachos, D.G. Bio-based molecular imprinted polymers for separation and purification of chlorogenic acid extracted from food waste. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 327, 124857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, F.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, Y.; Ren, X. Synthesis of a novel cross-linker doubles as a functional monomer for preparing a water compatible molecularly imprinted polymer. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 9483–9489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunngu, S.S.; Madikizela, L.M.; Chimuka, L.; Mdluli, P.S. Synthesis and application of a molecularly imprinted polymer in the solid-phase extraction of ketoprofen from wastewater. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2017, 20, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmandoust, M.; Soylak, M.; Erk, N. Innovative molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for the nanomolar detection of Tenofovir as an anti-HIV drug. Talanta 2023, 253, 123991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanah, A.N.; Susanti, I. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Pharmaceutical Impurities: Design and Synthesis Methods. Polymers 2023, 15, 3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bognár, Z.; Kozma, J.; Kovács, N.; Gyurcsányi, R.E. Novel functional monomer for the electrochemical synthesis of highly affine epitope-imprinted polymers. Electroanalysis 2023, 35, e202300025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigonya, S.; Chibuzor, S.; Phumlani, O.; Mdluli, S.; Hendrica, T. Method optimisation and application based on solid phase extraction of non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antiretroviral drugs, and a lipid regulator from coastal areas of Durban, South Africa. SN Appl. Sci. 2022, 4, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkosi, S.M.; Mahlambi, P.N.; Chimuka, L. Synthesis, characterisation and optimisation of bulk molecularly imprinted polymers from nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. S. Afr. J. Chem. 2022, 76, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madikizela, L.M.; Chimuka, L. Determination of ibuprofen, naproxen and diclofenac in aqueous samples using a multi-template molecularly imprinted polymer as selective adsorbent for solid-phase extraction. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 128, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qwane, S.N.; Mdluli, P.S.; Madikizela, L.M. Synthesis, Characterization and Application of a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer in Selective Adsorption of Abacavir from Polluted Water. S. Afr. J. Chem. 2020, 73, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madikizela, L.M.; Chimuka, L. Synthesis, adsorption and selectivity studies of a polymer imprinted with naproxen, ibuprofen and diclofenac. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4029–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbhele, Z.E.; Ncube, S.; Madikizela, L.M. Synthesis of a molecularly imprinted polymer and its application in selective extraction of fenoprofen from wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 36724–36735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orimi, S.M.H.; Khavarpour, M.; Kazemi, S. Removal of bisphenol a from water solution using molecularly imprinted nanopolymers: Isotherm and kinetic studies. J. Water Environ. Nanotechnol. 2020, 5, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tian, L.; Ren, R.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y. Constructing hollow ZIF-8/CDs@MIPs fluorescent sensor from Osmanthus leaves to specifically recognize bovine hemoglobin. Spectrochim. Acta—Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 287, 122121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zidarič, T.; Majer, D.; Maver, T.; Finšgar, M.; Maver, U. The development of an electropolymerized, molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) sensor for insulin determination using single-drop analysis. Analyst 2023, 148, 1102–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikiti, P.; Msagati, T.A.M.; Mamba, B.B.; Mishra, A.K. Synthesis and characterization of molecularly imprinted polymers for the remediation of PCBs and dioxins in aqueous environments. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madikizela, L.M.; Mdluli, P.S.; Chimuka, L. Experimental and theoretical study of molecular interactions between 2-vinyl pyridine and acidic pharmaceuticals used as multi-template molecules in molecularly imprinted polymer. React. Funct. Polym. 2016, 103, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, Y.; Ersan, G.; Vergili, I.; Gönder, Z.B.; Yilmaz, G.; Dizge, N.; Aydiner, C. The treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater using in a submerged membrane bioreactor under different sludge retention times. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 442, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Zenab, S.; Garcia, H.; Danquah, M.K.; Imanova, G. Recent advances in graphene-based nano-membranes for desalination. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 483, 149108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, K.; Qi, M.; Li, S.; Xu, G.; Wei, J.; He, X. Preparation of protein molecular-imprinted polysiloxane membrane using calcium alginate film as matrix and its application for cell culture. Polymers 2018, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negarestani, M.; Mollahosseini, A.; Farimaniraad, H.; Ghiasinejad, H.; Shayesteh, H.; Kheradmand, A. Efficient removal of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ibuprofen by polypyrrole-functionalized magnetic zeolite from aqueous solution: Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 435–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghal, H.H.; Nebsen, M.; El-Sayed, M.M.H. Eco-friendly Biopolymer/Activated Charcoal Magnetic Nanocomposites with Enhanced Stability and Adsorption Properties for Water Treatment Applications. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 31, 5338–5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.Y.; Seo, Y.D. Sorption of halogenated phenols and pharmaceuticals to biochar: Affecting factors and mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummadi, K.K.; Luo, S.; He, S. Adsorption of methylene blue dye from the aqueous solution via bio-adsorption in the inverse fluidized-bed adsorption column using the torrefied rice husk. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak, M.; Cegłowski, M.; Kurczewska, J. Hybrid chitosan/molecularly imprinted polymer hydrogel beads doped with iron for selective ibuprofen adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
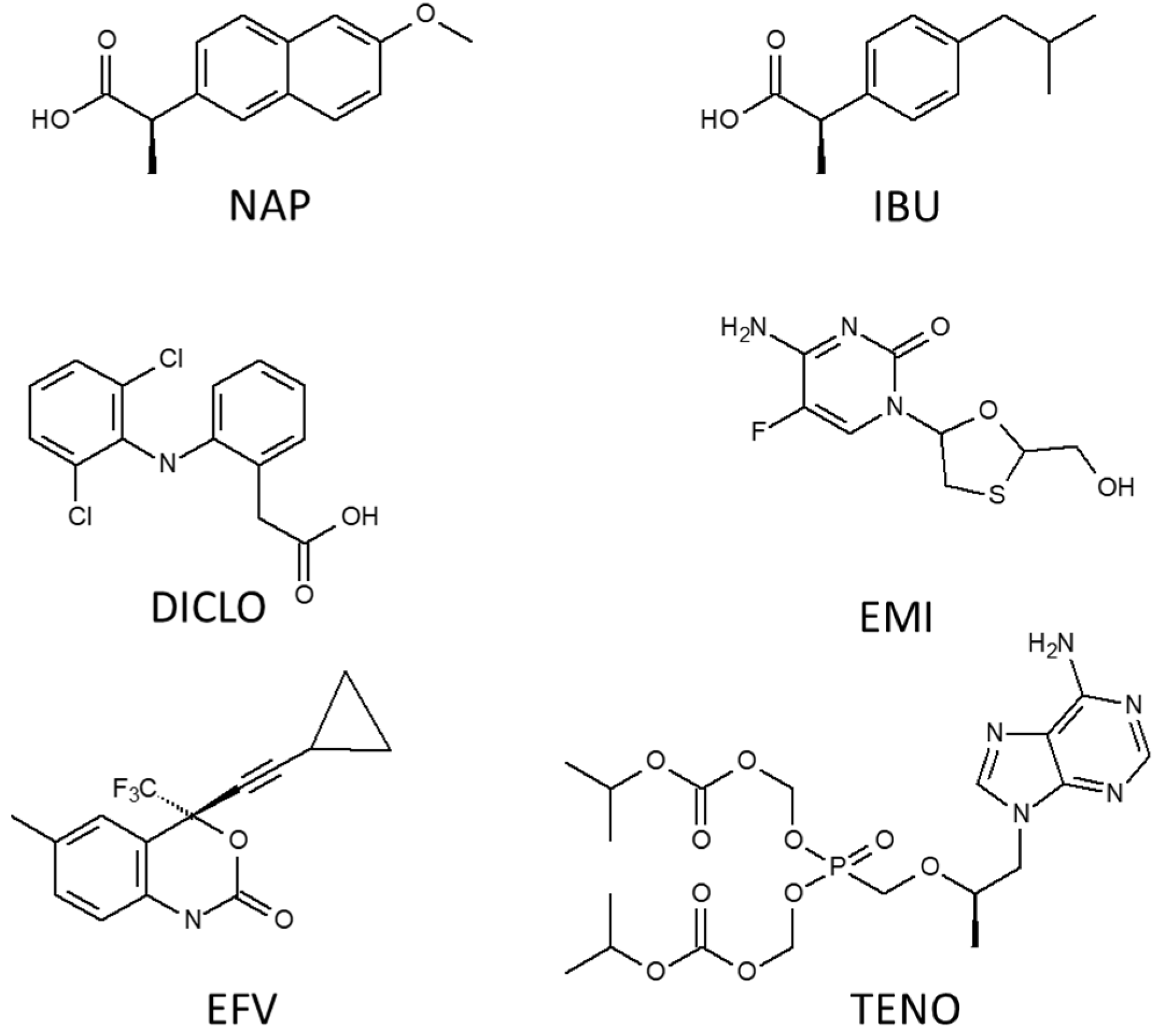





| Compounds | Formula | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Water Solubility (mg/L) | pKa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emtricitabine | C8H10FN3O3S | 247.25 | 1.12 × 106 | 2.65 |
| Tenofovir disoproxil | C19H30N5O10P | 287.21 | 13400 | 3.8 |
| Naproxen | C14H14O3 | 230.26 | 15.9 | 4.2 |
| Diclofenac | C14H11Cl2NO2 | 296.15 | 4.52 | 4.0 |
| Ibuprofen | C13H18O2 | 206.29 | 21 | 4.4 |
| Efavirenz | C14H9ClF3NO2 | 315.68 | 0.093 | 10.2 |
| Polymer | Surface Area (m2g−1) | Total Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (Å) | Total Area in Pores (m2g−1) | Average Particle Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIP | 425 | 0.345 | 44.2 | 258 | 14.1 |
| NIP | 347 | 0.393 | 45.3 | 201 | 17.3 |
| Polymer | Langmuir Isotherm (Equation (6)) | Freundlich Isotherm (Equation (5)) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | R2 | Intercept | 1/n | R2 | ||
| MIP | Emtricitabine | 0.6124 | −0.1977 | 1.1968 | 0.6943 | 0.9869 |
| Tenofovir disoproxil | 0.9709 | −0.7240 | 0.302 | 5.3002 | 0.9150 | |
| Naproxen | 0.6227 | −0.0942 | 2.487 | 0.8050 | 0.8139 | |
| Diclofenac | 0.8222 | 0.6402 | 0.7003 | 4.3672 | 0.9311 | |
| Ibuprofen | 0.9840 | −1.4099 | 16.359 | 0.0389 | 0.7001 | |
| Efavirenz | 0.8525 | −1.2718 | 1.5028 | 0.0535 | 0.9313 | |
| NIP | Emtricitabine | 0.8854 | 1.1022 | 0.5594 | 15.929 | 0.9951 |
| Tenofovir disoproxil | 0.7598 | 1.0834 | 0.7247 | 12.117 | 0.7425 | |
| Naproxen | 0.9856 | 0.277 | 0.4303 | 1.8958 | 0.9683 | |
| Diclofenac | 0.9592 | 0.6221 | 0.6456 | 4.1889 | 0.9840 | |
| Ibuprofen | 0.9585 | 0.0919 | 0.4199 | 1.2356 | 0.6853 | |
| Efavirenz | 0.8784 | 0.8577 | 0.7603 | 7.2061 | 0.9812 | |
| Polymer | Compounds | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | R2 | K2 (mg·g−1 min−1) | Qe (mg·g−1) | ||
| MIP | Emtricitabine | 0.86 | 1.00 | 2.75 | 0.90 |
| Tenofovir disoproxil | 0.61 | 1.00 | 3.47 | 0.83 | |
| Naproxen | 0.50 | 0.90 | 3.19 | 0.06 | |
| Diclofenac | 0.88 | 1.00 | 1.16 | 0.83 | |
| Ibuprofen | 0.86 | 0.83 | 0.07 | 0.07 | |
| Efavirenz | 0.86 | 1.00 | 2.07 | 0.13 | |
| NIP | Emtricitabine | 0.84 | 0.98 | 0.56 | 0.92 |
| Tenofovir disoproxil | 0.90 | 1.00 | 0.73 | 3.58 | |
| Naproxen | 0.75 | 0.99 | 0.43 | 2.91 | |
| Diclofenac | 0.63 | 1.00 | 0.65 | 3.75 | |
| Ibuprofen | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.42 | 0.10 | |
| Efavirenz | 0.84 | 0.92 | 0.76 | 0.92 | |
| Templates | Kd MIP (mg·g−1) | Kd NIP (mg·g−1) | K (MIP) | K (NIP) | K’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emtricitabine | 1.78 | 1.65 | 1.16 | 1.06 | 1.08 |
| Tenofovir disoproxil | 1.78 | 1.77 | 1.44 | 1.44 | 1.00 |
| Naproxen | 1.77 | 1.76 | 1.14 | 1.14 | 1.00 |
| Diclofenac | 1.79 | 1.78 | 1.15 | 1.14 | 1.00 |
| Ibuprofen | 1.68 | 1.59 | 1.09 | 1.02 | 1.06 |
| Efavirenz | 1.81 | 1.74 | 1.17 | 1.12 | 1.05 |
| Acetaminophen | 1.56 | 1.55 | - | - | - |
| Adsorbent | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Selectivity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sol—gel | 28.38 | - | [42] |
| Raw zeolite | 0.83 | - | [43] |
| Activated carbon | 90.9 | - | [44] |
| Biosolid biochar | 10.70 | - | [45] |
| Graphene oxide nanoplatelet | 38 | - | [46] |
| MIP (NSAIDs) | 1.230–1.249 | 1.12–2.4 | [30] |
| MIP(ARV) | 5.98 | 4.4 | [32] |
| Chitosan MIP | 79.41 | - | [47] |
| Bulk polymerization (MIP) | 0.92–3.92 | 1.68–1.81 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sigonya, S.; Mokhena, T.C.; Mayer, P.M.; Mdluli, P.S.; Makhanya, T.R.; Mokhothu, T.H. Synthesis of a Multi-Template Molecular Imprinted Bulk Polymer for the Adsorption of Non-Steroidal Inflammatory and Antiretroviral Drugs. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3320. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14083320
Sigonya S, Mokhena TC, Mayer PM, Mdluli PS, Makhanya TR, Mokhothu TH. Synthesis of a Multi-Template Molecular Imprinted Bulk Polymer for the Adsorption of Non-Steroidal Inflammatory and Antiretroviral Drugs. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(8):3320. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14083320
Chicago/Turabian StyleSigonya, Sisonke, Teboho Clement Mokhena, Paul Micheal Mayer, Phumlane Selby Mdluli, Talent Raymond Makhanya, and Thabang Hendrica Mokhothu. 2024. "Synthesis of a Multi-Template Molecular Imprinted Bulk Polymer for the Adsorption of Non-Steroidal Inflammatory and Antiretroviral Drugs" Applied Sciences 14, no. 8: 3320. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14083320
APA StyleSigonya, S., Mokhena, T. C., Mayer, P. M., Mdluli, P. S., Makhanya, T. R., & Mokhothu, T. H. (2024). Synthesis of a Multi-Template Molecular Imprinted Bulk Polymer for the Adsorption of Non-Steroidal Inflammatory and Antiretroviral Drugs. Applied Sciences, 14(8), 3320. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14083320








