Prediction of Consolidation Tumor Ratio on Planning CT Images of Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Radiotherapy Based on Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Cases
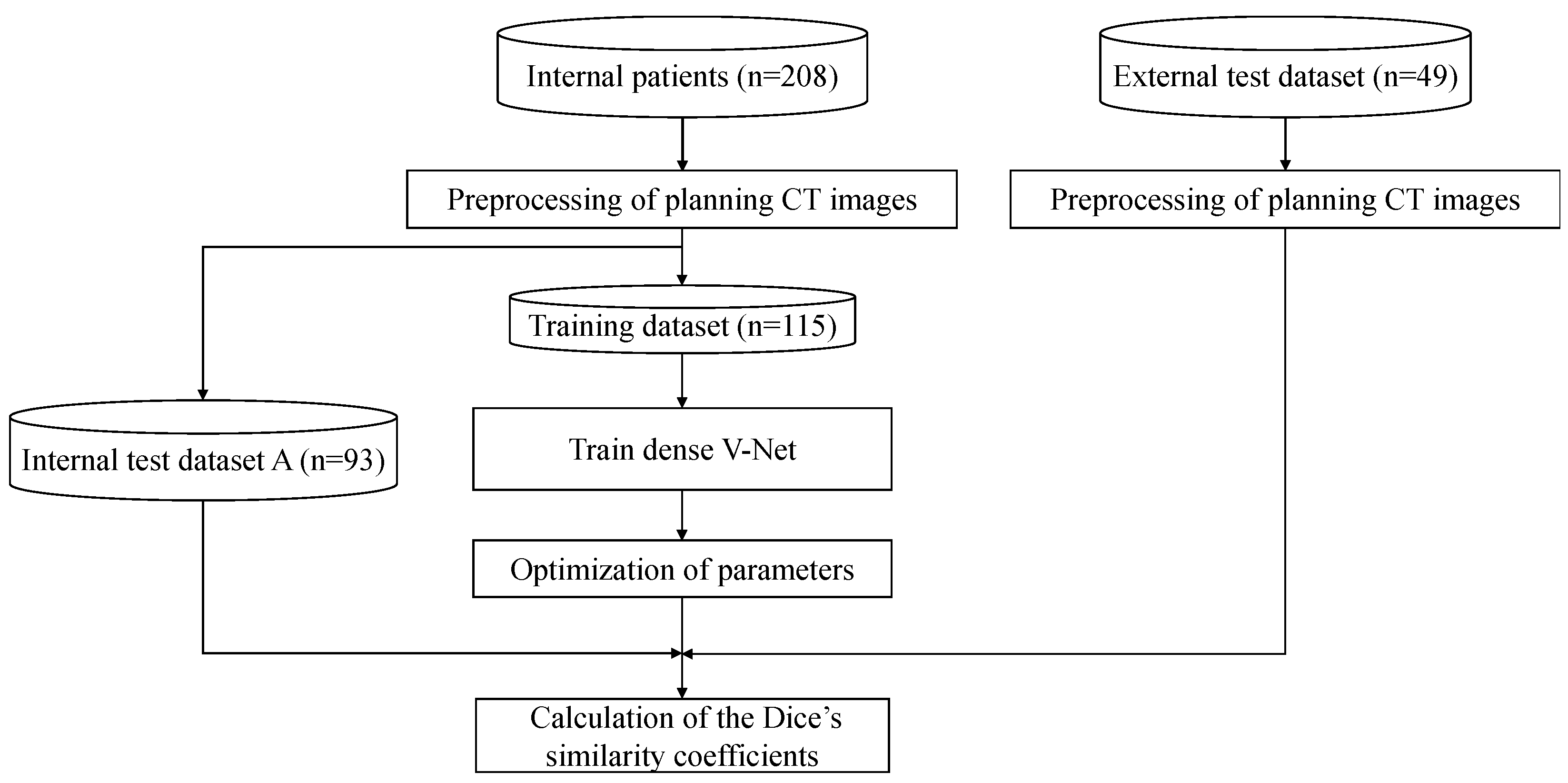
2.2. Overall Workflow
2.3. Preprocessing of Dataset
2.4. DLS Model
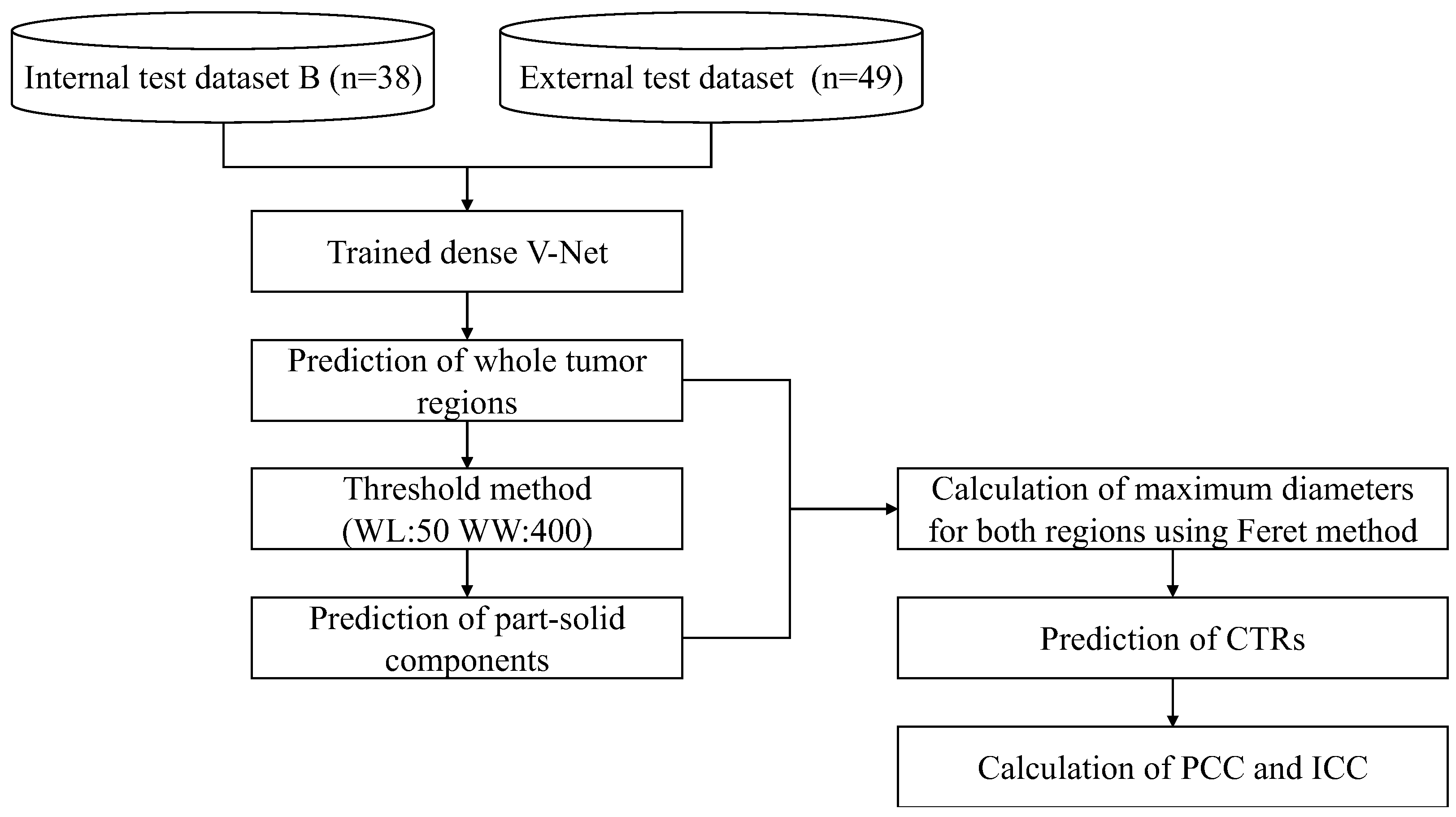
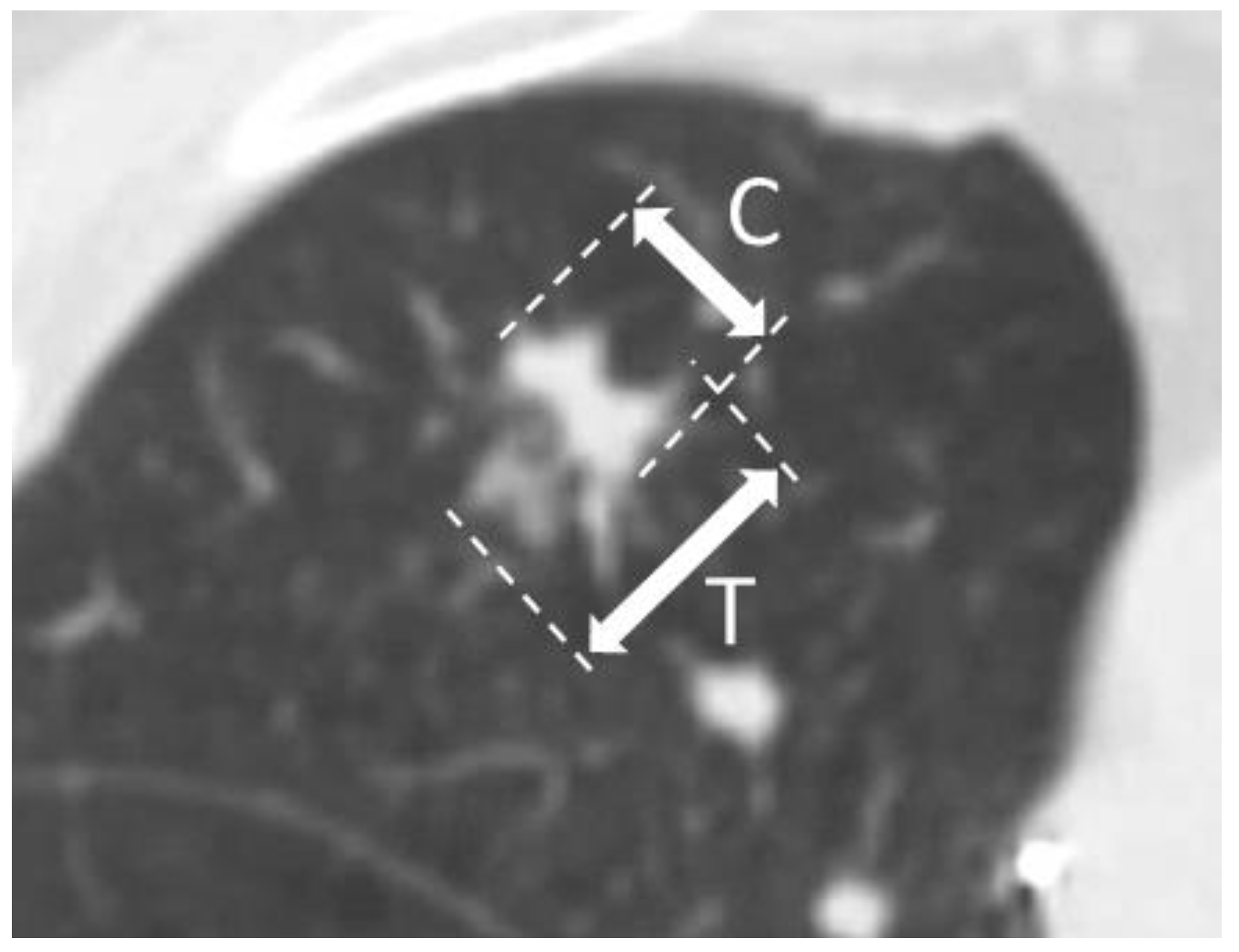
2.5. Prediction of CTR
2.6. Evaluation and Statistical Analysis
2.7. Implementation of Automated Prediction Approach of CTRs
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaw, V.R.; Byun, J.; Pettit, R.W.; Han, Y.; Hsiou, D.A.; Nordstrom, L.A.; Amos, C.I. A Comprehensive Analysis of Lung Cancer Highlighting Epidemiological Factors and Psychiatric Comorbidities from the All of Us Research Program. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horinouchi, H.; Kusumoto, M.; Yatabe, Y.; Aokage, K.; Watanabe, S.-I.; Ishikura, S. Lung Cancer in Japan. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Shimizu, S.; Onimaru, R.; Takeda, A.; Onishi, H.; Nagata, Y.; Kimura, T.; Karasawa, K.; Arimoto, T.; Hareyama, M.; et al. Clinical Outcomes of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Small Lung Lesions Clinically Diagnosed as Primary Lung Cancer on Radiologic Examination. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2009, 75, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, H.; Shirato, H.; Nagata, Y.; Hiraoka, M.; Fujino, M.; Gomi, K.; Karasawa, K.; Hayakawa, K.; Niibe, Y.; Takai, Y.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) for Operable Stage I Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Can SBRT Be Comparable to Surgery? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, 1352–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koike, T.; Koike, T.; Yamato, Y.; Yoshiya, K.; Toyabe, S.-I. Predictive Risk Factors for Mediastinal Lymph Node Metastasis in Clinical Stage IA Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badiyan, S.N.; Bierhals, A.J.; Olsen, J.R.; Creach, K.M.; A Garsa, A.; DeWees, T.; Bradley, J.D.; Robinson, C.G. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for the Treatment of Early-Stage Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma or Adenocarcnioma in Situ (Formerly Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma): A Patterns of Failure Analysis. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Koike, T.; Asakawa, T.; Kusumoto, M.; Asamura, H.; Nagai, K.; Tada, H.; Mitsudomi, T.; Tsuboi, M.; Shibata, T.; et al. A Prospective Radiological Study of Thin-Section Computed Tomography to Predict Pathological Noninvasiveness in Peripheral Clinical IA Lung Cancer (Japan Clinical Oncology Group 0201). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, Y.; Tagawa, T.; Kinoshita, F.; Haratake, N.; Takada, K.; Kohno, M.; Takenaka, T.; Kamitani, T.; Shimokawa, M.; Oda, Y.; et al. Relationship between Consolidation Tumor Ratio and Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Small-Sized Lung Adenocarcinoma. Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 2134–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.-J.; Tu, J.-H.; Chen, H.; Yan, R.-H.; Chen, R.-Q.; Chen, C.; You, C.-X.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Yu, S.-B.; Chen, S.-C. A Multi-Institutional Analysis of the Combined Effect of Micropapillary Component and Consolidation-to-Tumor Ratio >0.5 on the Prognosis of Pathological, Stage IA3, Lung Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 30, 5843–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurugai, Y.; Kozuka, T.; Ishizuka, N.; Oguchi, M. Relationship between the consolidation to maximum tumor diameter ratio and outcomes following stereotactic body radiotherapy for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer, 2016; 92, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, H.; Shioyama, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Shibamoto, Y.; Miyakawa, A.; Suzuki, G.; Nishimura, Y.; Sasaki, R.; Miyawaki, D.; Kuriyama, K.; et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy in patients with lung tumors composed of mainly ground-glass opacity. J. Radiat. Res. 2020, 61, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, J.; Yin, J.; Liang, J.; Zhan, C.; Jiang, W.; Lin, Z.; Xu, S.; Wang, Q. Prognostic Impact of Radiological Consolidation Tumor Ratio in Clinical Stage IA Pulmonary Ground Glass Opacities. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 616149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velazquez, E.R.; Aerts, H.J.; Gu, Y.; Goldgof, D.B.; De Ruysscher, D.; Dekker, A.; Korn, R.; Gillies, R.J.; Lambin, P. A Semiautomatic CT-Based Ensemble Segmentation of Lung Tumors: Comparison with Oncologists’ Delineations and with the Surgical Specimen. Radiother. Oncol. 2012, 105, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, L.; Hu, B.; Du, Z.; Cho, W.C.; Witharana, P.; Sun, H.; Ma, D.; Ye, M.; Chen, J.; et al. Deep learning-based solid component measuring enabled interpretable prediction of tumor invasiveness for lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2023, 186, 107392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.-M.; Li, J.-Q.; Dou, S.-H.; Li, H.-J.; Qiu, Z.-B.; Zhang, C.; Yang, X.-W.; Zhang, J.-T.; Qiu, X.-H.; Xie, H.-S.; et al. Lack of incremental value of three-dimensional measurement in assessing invasiveness for lung cancer. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2023, 64, ezad373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ma, H.; Yang, H.; Liu, B.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; et al. Prognostic impact of deep learning-based quantification in clinical stage 0-I lung adenocarcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 8542–8553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Arimura, H.; Nakano, R.; Yoshitake, T.; Shioyama, Y.; Yabuuchi, H. Automated Approach for Segmenting Gross Tumor Volumes for Lung Cancer Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Using CT-Based Dense V-Networks. J. Radiat. Res. 2021, 62, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Arimura, H.; Yoshitake, T.; Shioyama, Y.; Yabuuchi, H. Deep Learning Model Fusion Improves Lung Tumor Segmentation Accuracy across Variable Training-to-Test Dataset Ratios. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2023, 46, 1271–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Wee, L.; Rios Velazquez, E.; Leijenaar RT, H.; Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Carvalho, S.; Bussink, J.; Monshouwer, R.; Haibe-Kains, B.; et al. Data from NSCLC-Radiomics (Version 4) [Data Set]. The Cancer Imaging Archive; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertina, B.; Watson, M.; Holback, C.; Jarosz, R.; Kirk, S.; Lee, Y.; Rieger-Christ, K.; Lemmerman, J. The Cancer Genome Atlas Lung Adenocarcinoma Collection (TCGA-LUAD) (Version 4) [Data Set]. The Cancer Imaging Archive; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, S.; Lee, Y.; Kumar, P.; Filippini, J.; Albertina, B.; Watson, M.; Rieger-Christ, K.; Lemmerman, J. The Cancer Genome Atlas Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Collection (TCGA-LUSC) (Version 4) [Data Set]. The Cancer Imaging Archive; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikushima, K.; Arimura, H.; Jin, Z.; Yabu-Uchi, H.; Kuwazuru, J.; Shioyama, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Honda, H.; Sasaki, M. Computer-Assisted Framework for Machine-Learning-Based Delineation of GTV Regions on Datasets of Planning CT and PET/CT Images. J. Radiat. Res. 2017, 58, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, H.; Cunningham, J. The Physics of Radiology, 4th ed.; Charles C Thomas Publisher: Springfield, IL, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate Use and Interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, G.T.; Zheng, J.; Bucholtz, C.A. Shape-Based Interpolation. EEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 1992, 12, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, E.; Giganti, F.; Hu, Y.; Bonmati, E.; Bandula, S.; Gurusamy, K.; Davidson, B.; Pereira, S.P.; Clarkson, M.J.; Barratt, D.C. Automatic Multi-Organ Segmentation on Abdominal CT With Dense V-Networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1822–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedamonti, D. Comparison of non-linear activation functions for deep neural networks on MNIST classification task. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to Build a Bridge from a Population-Based to a More “Personalized” Approach to Cancer Staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, A.; Toss, M.S.; Parkin, M.A.; Sano, T.; Oyama, T.; Quinn, C.M.; O Ellis, I.; A Rakha, E. Nuclear Morphology in Breast Lesions: Refining Its Assessment to Improve Diagnostic Concordance. Histopathology 2022, 80, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitwood, D.H.; Eithun, M.; Munch, E.; Ophelders, T. Topological Mapper for 3D Volumetric Images. In Proceedings of the Mathematical Morphology and Its Applications to Signal and Image Processing, Saarbrücken, Germany, 8–10 July 2019; Burgeth, B., Kleefeld, A., Naegel, B., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the Amount of Ecologic Association Between Species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giavarina, D. Understanding Bland Altman Analysis. Biochem. Med. 2015, 25, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arrigo, G.; Leonardis, D.; Abd ElHafeez, S.; Fusaro, M.; Tripepi, G.; Roumeliotis, S. Methods to Analyse Time-to-Event Data: The Kaplan-Meier Survival Curve. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 2290120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, A.; Mittal, A.; Ricketts, D.; Rogers, B. Understanding survival analysis: Actuarial life tables and the Kaplan-Meier plot. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2019, 80, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroell, N. imea: A Python package for extracting 2D and 3D shape measurements from images. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkel, J.; Khalilzadeh, O.; Hintze, C.; Fabel, M.; Puderbach, M.; Eichinger, M.; Schlemmer, H.-P.; Thorn, M.; Heussel, C.; Thomas, M.; et al. Inter-Observer Reproducibility of Semi-Automatic Tumor Diameter Measurement and Volumetric Analysis in Patients with Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2013, 82, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, M.; Xu, B.; Pun, C.; Lu, F.-I.; Parra-Herran, C.; Nofech-Mozes, S.; Slodkowska, E. Breast Specimen Measurement Methodology and Its Potential Major Impact on Tumor Size. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2021, 29, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuvelmans, M.A.; Walter, J.E.; Vliegenthart, R.; van Ooijen, P.M.; De Bock, G.H.; de Koning, H.J.; Oudkerk, M. Disagreement of Diameter and Volume Measurements for Pulmonary Nodule Size Estimation in CT Lung Cancer Screening. Thorax 2018, 73, 779–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Li, G. Automated Lung Segmentation and Image Quality Assessment for Clinical 3D/4D Computed Tomography. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2014, 2, 1800110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanoon, M.A.; Zulkifley, M.A.; Zainuri, M.A.A.M.; Abdani, S.R. A Review of Deep Learning Techniques for Lung Cancer Screening and Diagnosis Based on CT Images. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecsey-Nagy, M.; Jermendy, Á.L.; Suhai, F.I.; Panajotu, A.; Csőre, J.; Borzsák, S.; Fontanini, D.M.; Kolossváry, M.; Vattay, B.; Boussoussou, M.; et al. Model-based adaptive filter for a dedicated cardiovascular CT scanner: Assessment of image noise, sharpness and quality. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 145, 110032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goceri, E. Medical image data augmentation: Techniques, comparisons and interpretations. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 12561–12605, Advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Ding, Y.; Qiu, R.; Wang, T.; Roper, J.; Fu, Y.; Shu, H.-K.; Mao, H.; Yang, X. Hippocampus substructure segmentation using morphological vision transformer learning. Phys. Med. Biol. 2023, 68, 235013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


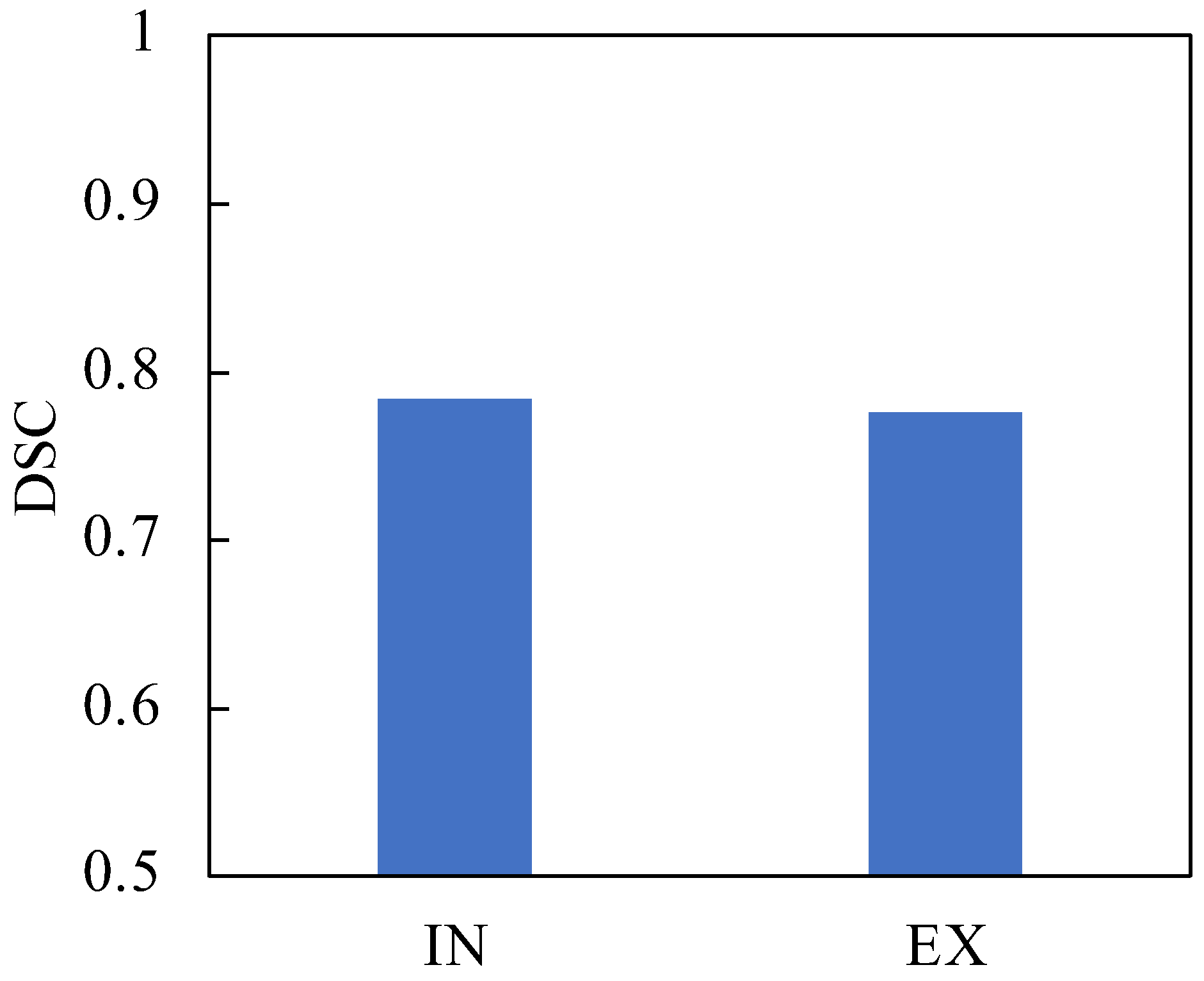
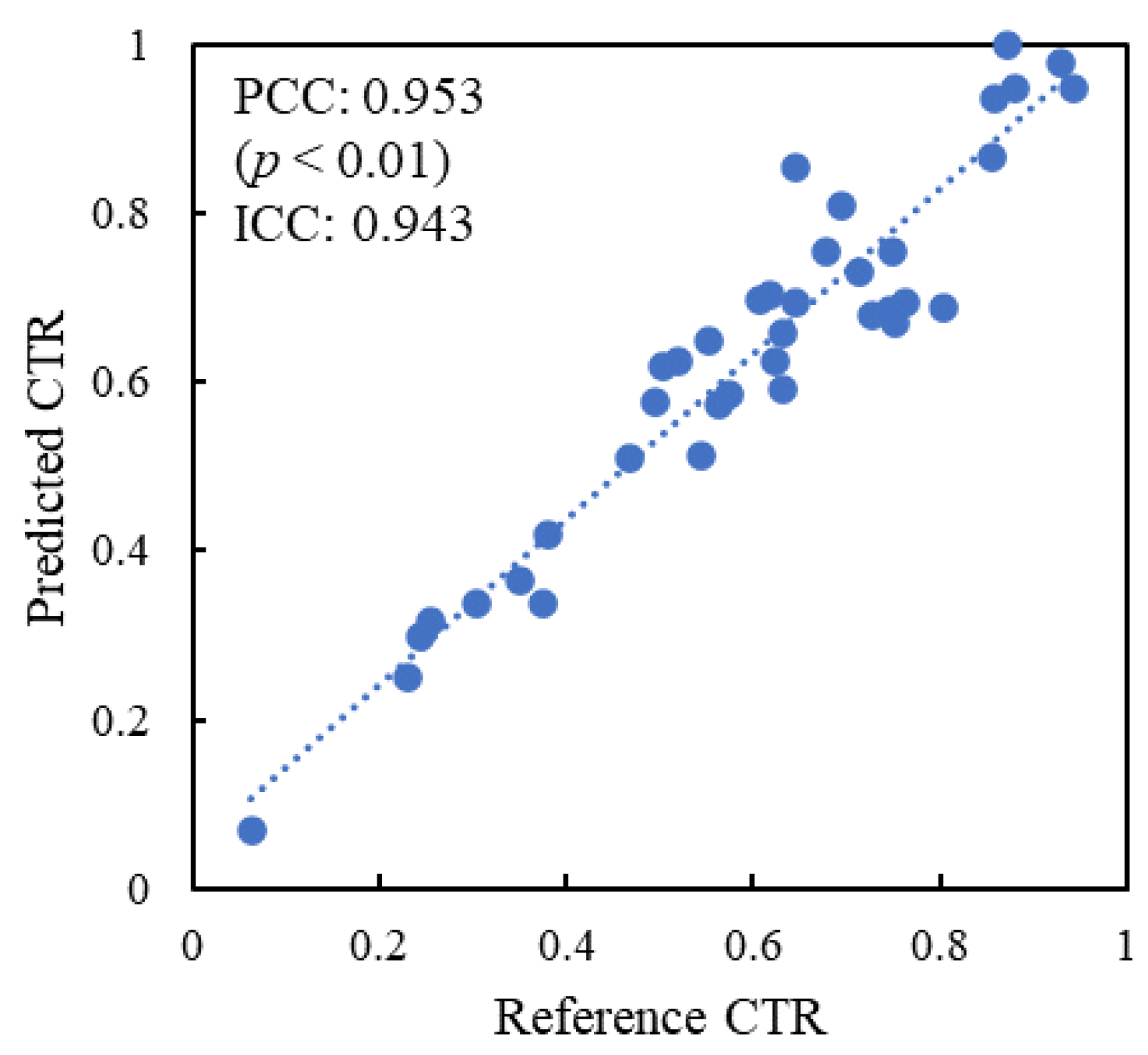
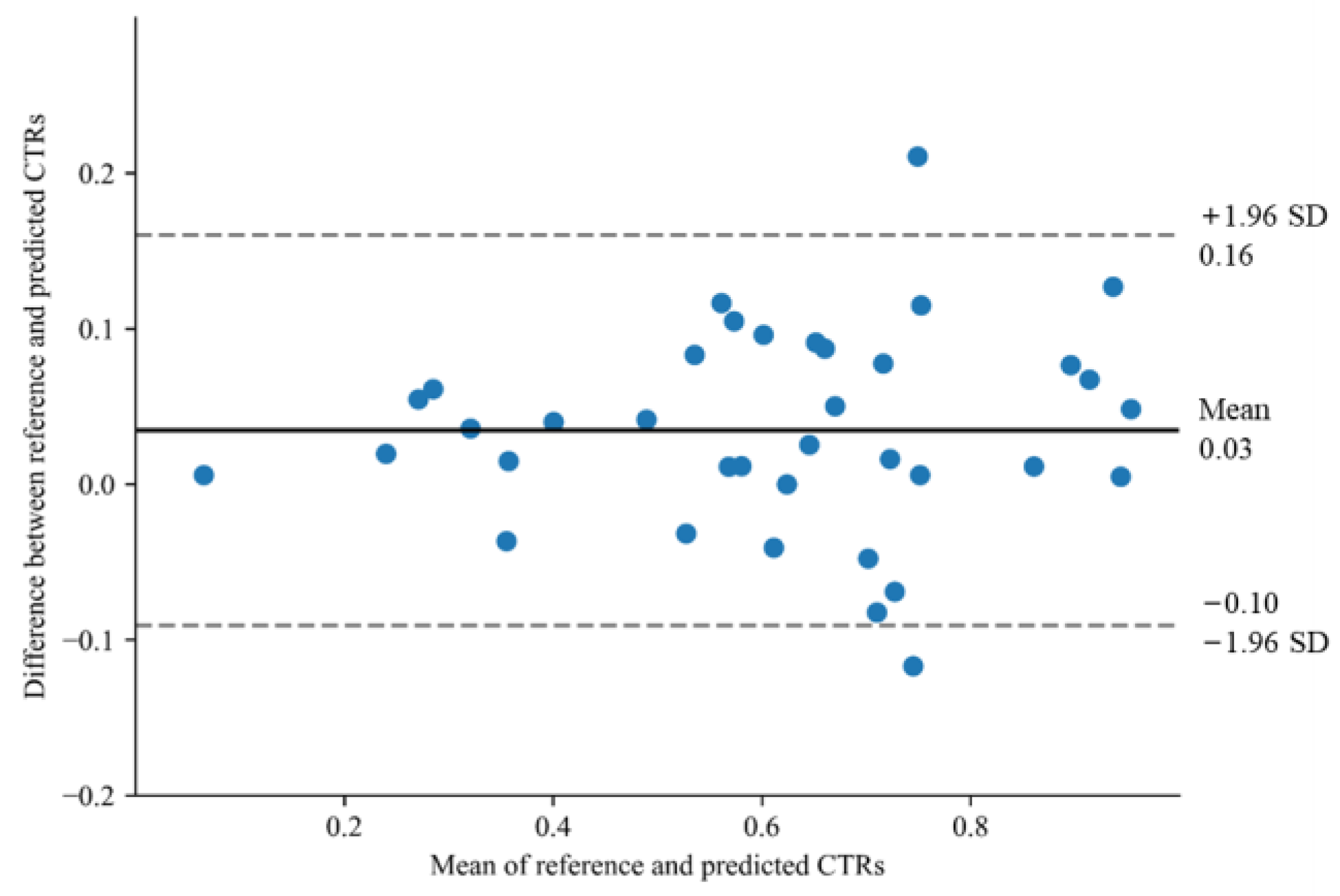

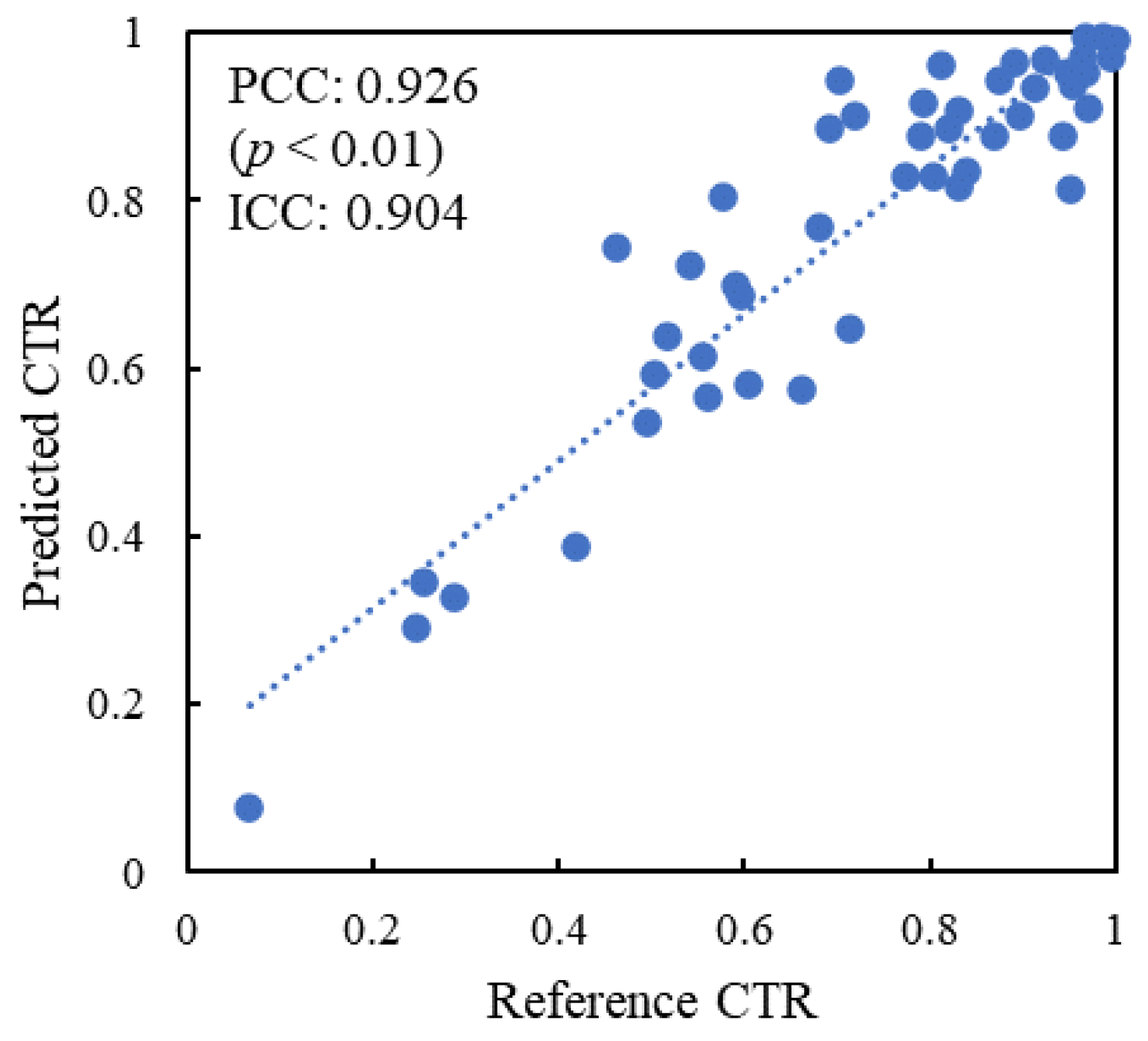
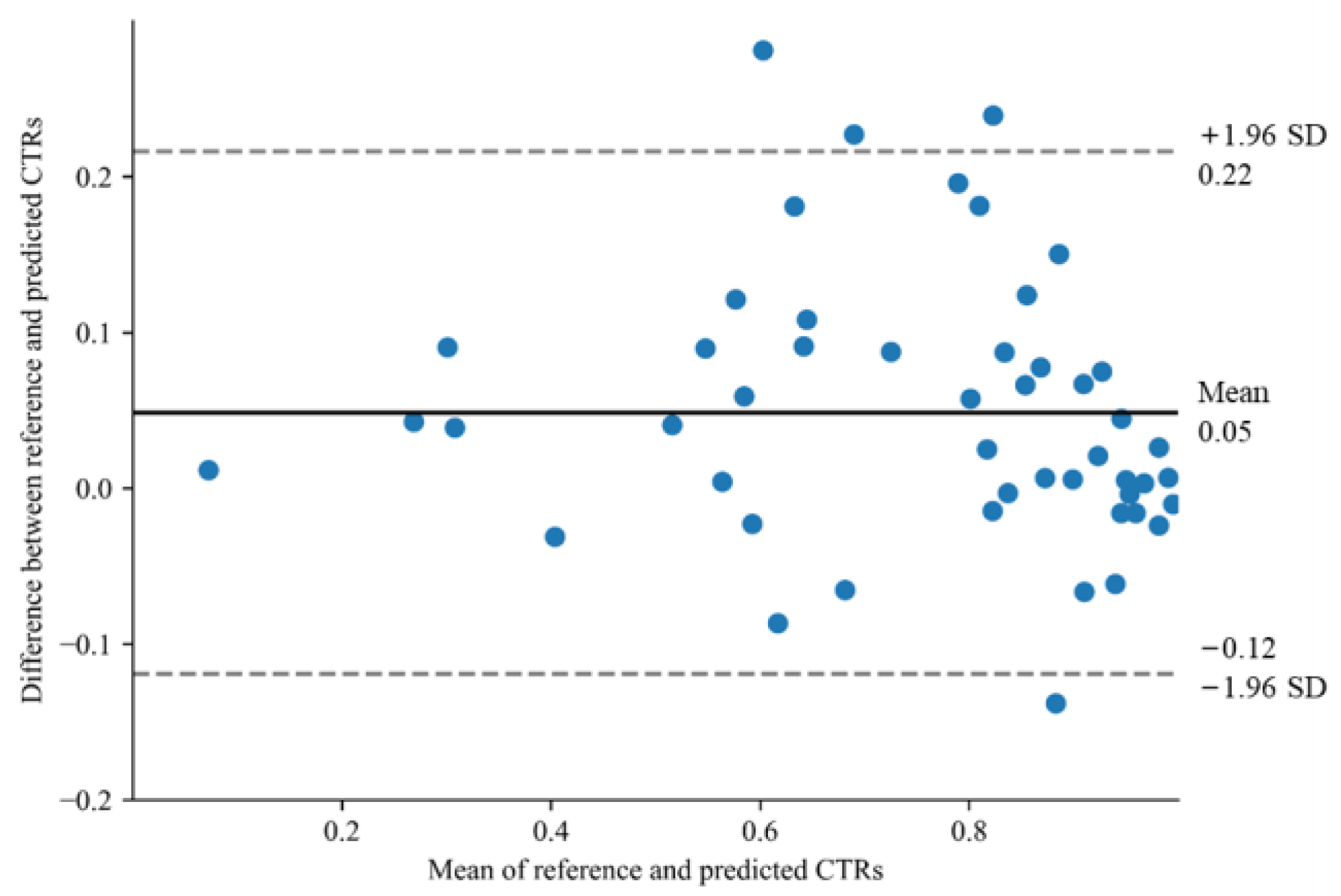
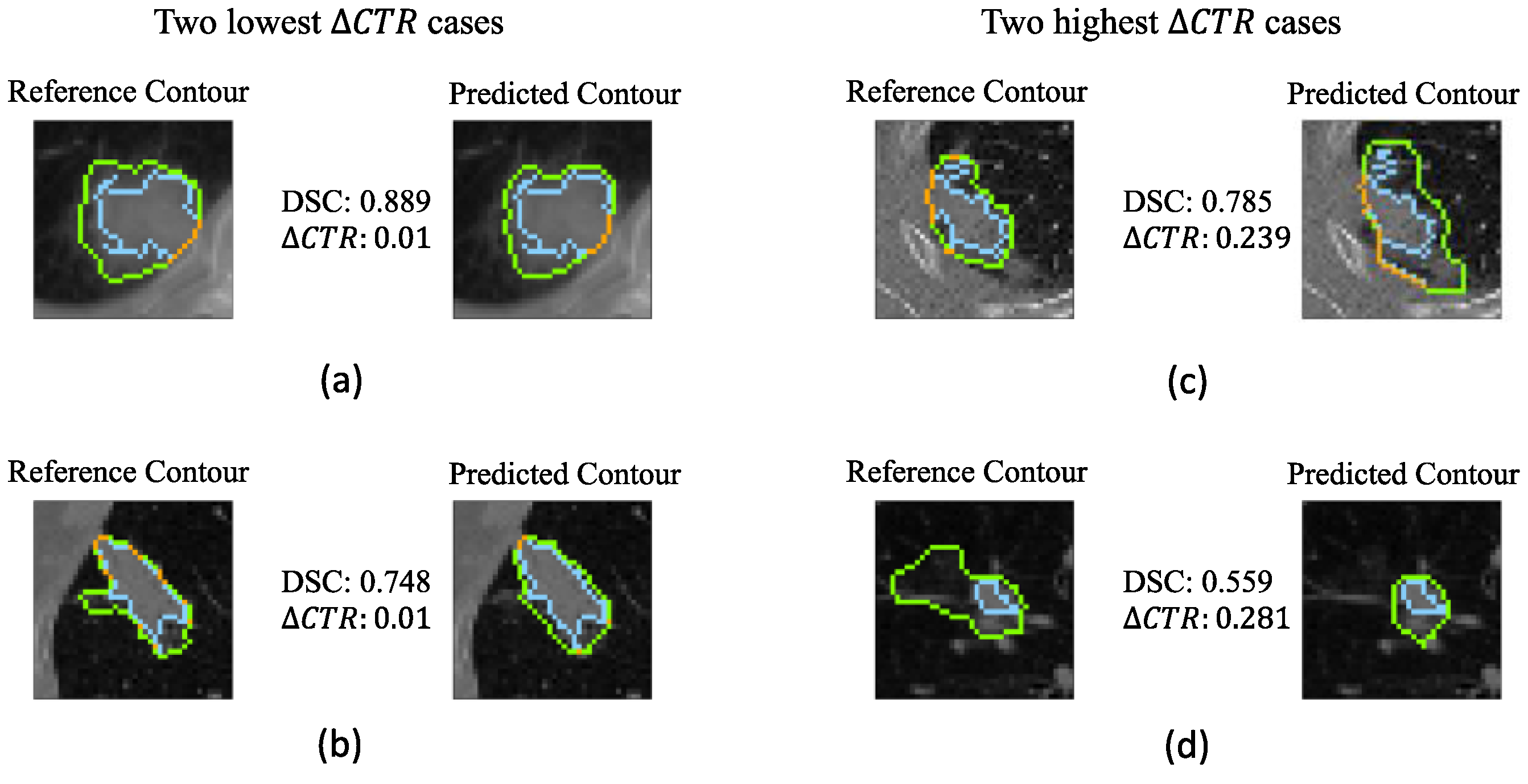
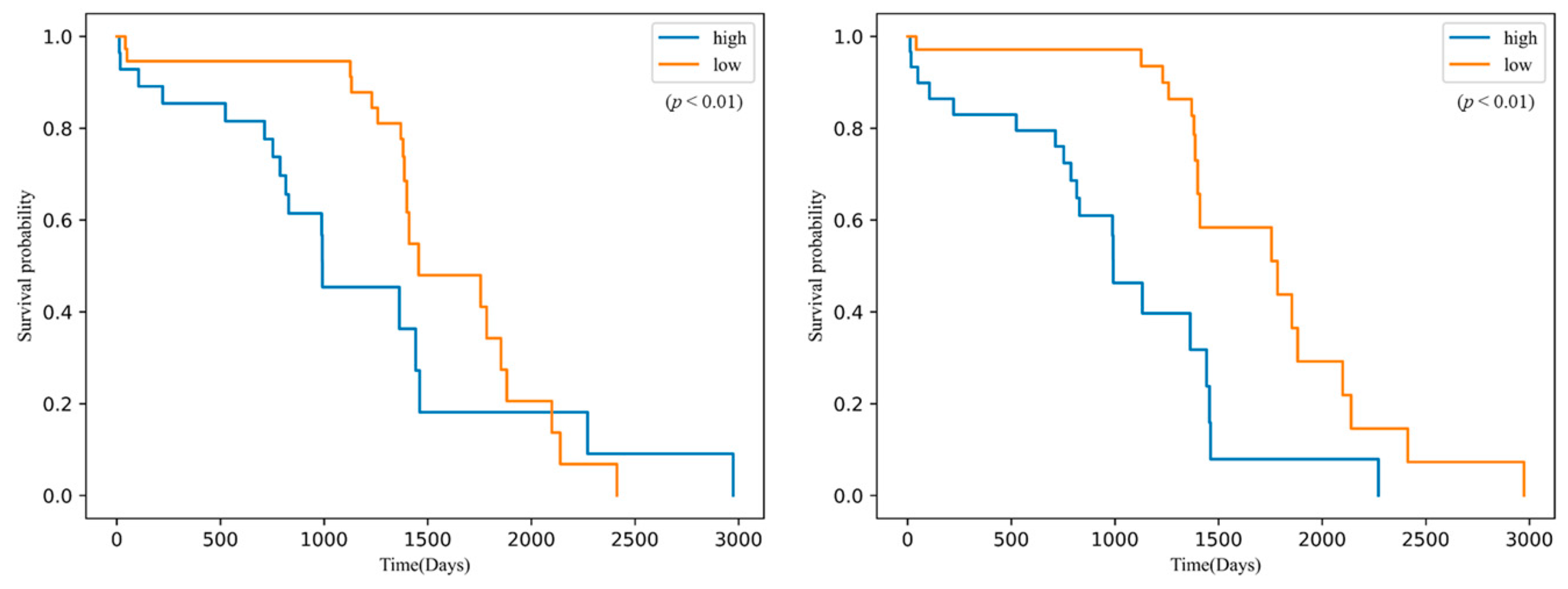
| Characteristics | Training Dataset (n = 115) | Internal Test Dataset A (n = 93) | External Test Dataset (n = 49) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Institution | Kyushu University Hospital | Kyushu University Hospital | TCIA * |
| Age (years) | 40–92 (median: 76) | 44–89 (median: 78) | 50–85 (median: 72) |
| Sex | |||
| Male | 69 | 61 | 24 |
| Female | 46 | 32 | 25 |
| Tumor type | |||
| Solid | 73 | 45 | 0 |
| Part-solid | 31 | 38 | 49 |
| Pure GGO | 11 | 10 | 0 |
| Matrix size | 512 × 512 | 512 × 512 | 512 × 512 |
| Number of slices | 103–235 | 103–225 | 38–515 |
| Pixel size (mm) | 0.78–0.98 | 0.78–0.98 | 0.55–0.98 |
| Slice thickness (mm) | 2.0 | 2.0, 3.2 | 0.63–5.0 |
| Characteristics | Internal Test Dataset B (n = 38) | External Test Dataset (n = 49) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 59–89 (median: 79.5) | 50–85 (median: 72) |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 22 | 24 |
| Female | 16 | 25 |
| Tumor type | ||
| Part-solid | 38 | 49 |
| Matrix size | 512 × 512 | 512 × 512 |
| Number of slices | 120–224 | 38–515 |
| Pixel size (mm) | 0.78–0.98 | 0.55–0.98 |
| Slice thickness (mm) | 2.0 | 0.625–5.0 |
| Histology | ||
| Adenocarcinoma | 17 | 39 |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 1 | 10 |
| Unknown | 20 | 0 |
| Time to progression | ||
| Unknown | 16 | 0 |
| Range (days) | 283–2329 (median: 920) | 12–2793 (median: 1014) |
| Maximum diameters of solid components (mm) * | 1.5–57.5 (median: 20.3) | 1.5–81.7 (median: 32.6) |
| Maximum diameters of whole tumors (mm) * | 10.5–67.3 (median: 32.3) | 21.4–81.7 (median: 42.4) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, Y.; Arimura, H.; Yoshitake, T.; Cui, Y.; Kodama, T.; Shioyama, Y.; Wirestam, R.; Yabuuchi, H. Prediction of Consolidation Tumor Ratio on Planning CT Images of Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Radiotherapy Based on Deep Learning. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14083275
Tong Y, Arimura H, Yoshitake T, Cui Y, Kodama T, Shioyama Y, Wirestam R, Yabuuchi H. Prediction of Consolidation Tumor Ratio on Planning CT Images of Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Radiotherapy Based on Deep Learning. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(8):3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14083275
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Yizhi, Hidetaka Arimura, Tadamasa Yoshitake, Yunhao Cui, Takumi Kodama, Yoshiyuki Shioyama, Ronnie Wirestam, and Hidetake Yabuuchi. 2024. "Prediction of Consolidation Tumor Ratio on Planning CT Images of Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Radiotherapy Based on Deep Learning" Applied Sciences 14, no. 8: 3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14083275
APA StyleTong, Y., Arimura, H., Yoshitake, T., Cui, Y., Kodama, T., Shioyama, Y., Wirestam, R., & Yabuuchi, H. (2024). Prediction of Consolidation Tumor Ratio on Planning CT Images of Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Radiotherapy Based on Deep Learning. Applied Sciences, 14(8), 3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14083275









