How Pseudomonas nitroreducens Passivates Cadmium to Inhibit Plant Uptake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cd-Tolerant Strain
2.2. Soil and Houttuynia Cordata
2.3. Identification of Strain
2.4. Biosorption
2.5. Pot Tests
2.6. Statistical Assays
3. Results and Discussions
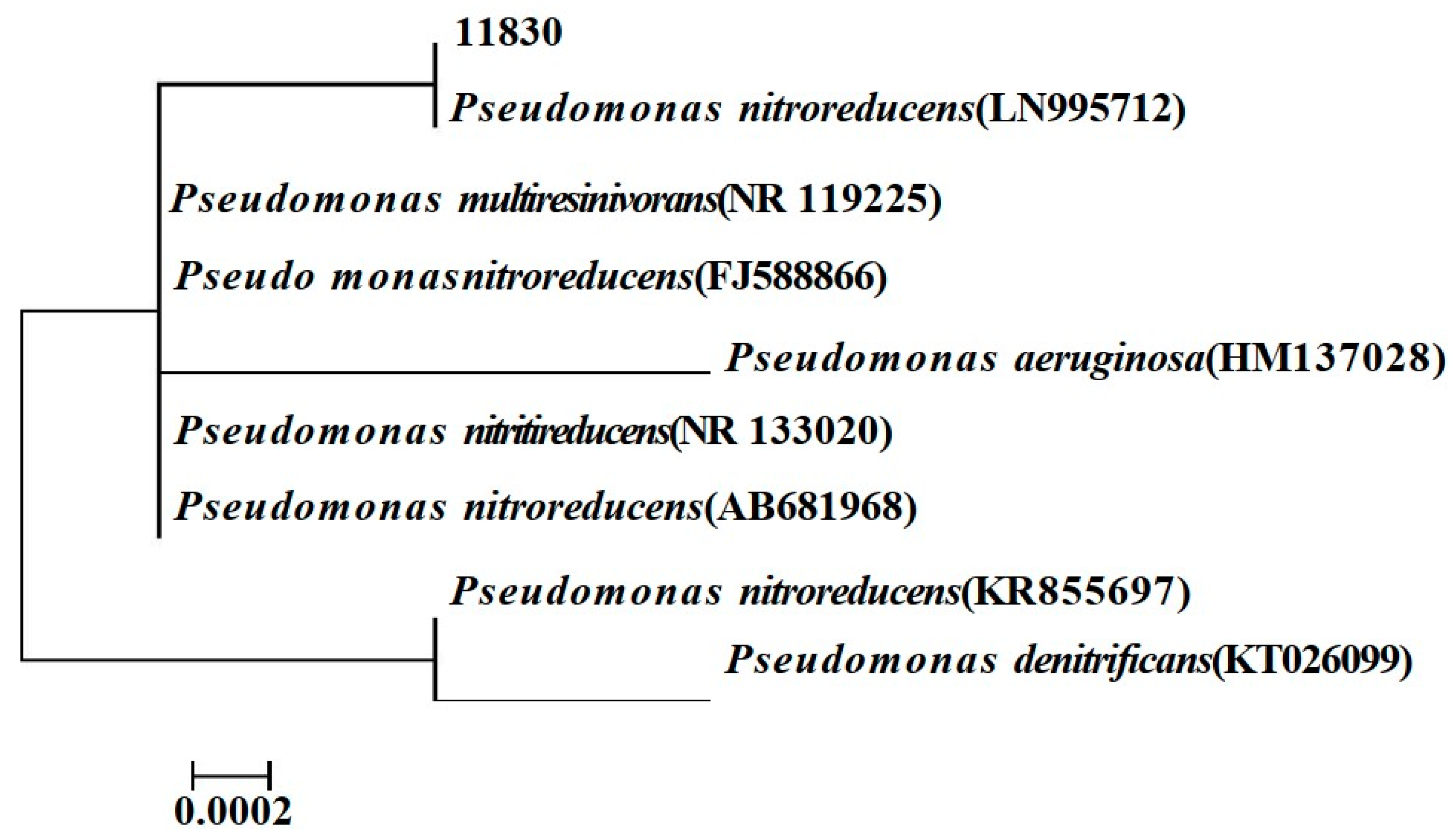
3.1. Identification of 11830
3.2. Biosorption Isotherms
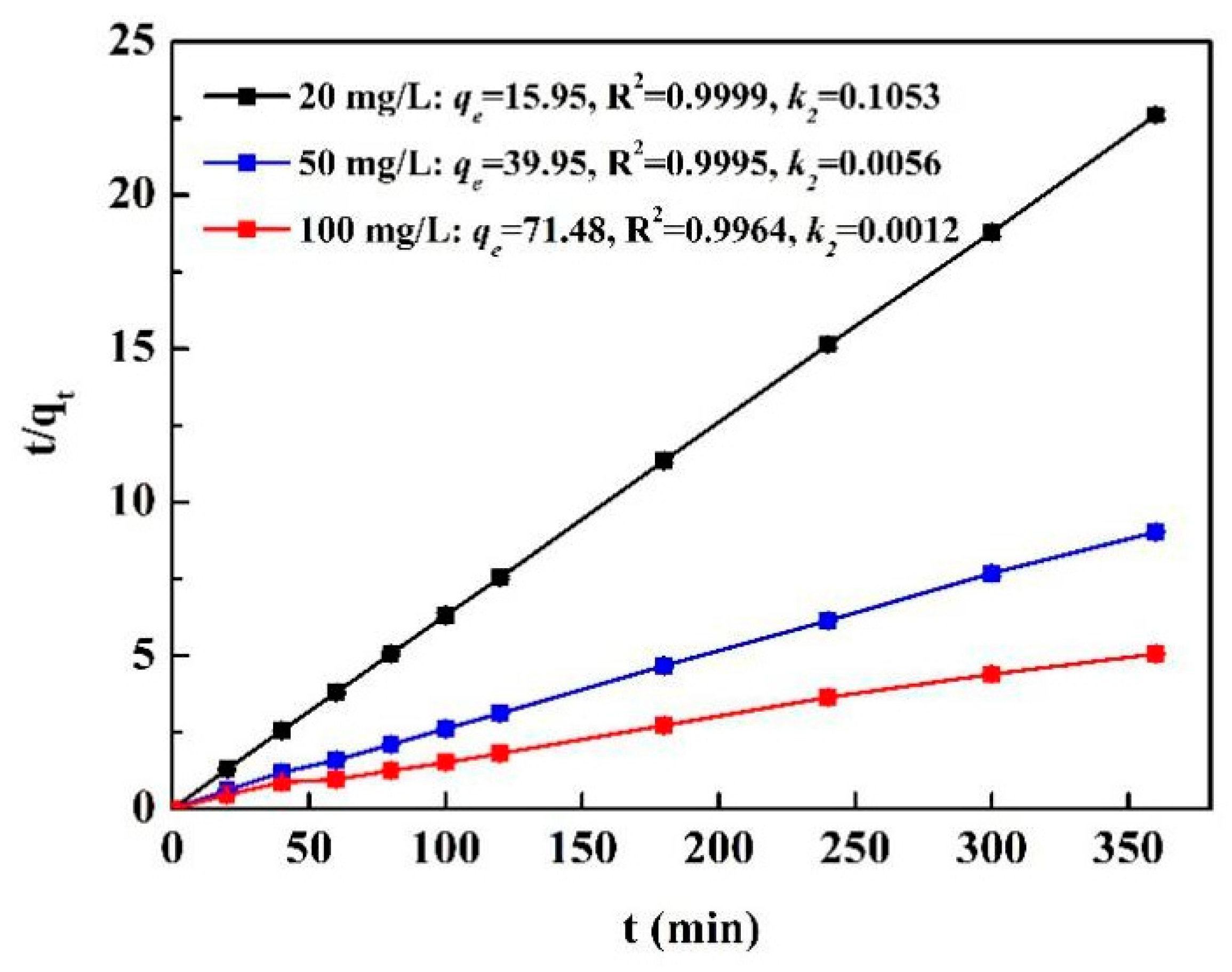
3.3. Kinetics of the Biosorption Process
- qt and qe (mg/g) are the biosorption capacities at time and equilibrium, respectively.
- t is the reaction time (min).
- k1 and k2 are the adsorption rate constant of the first- and second-order equation, respectively.
3.4. Mechanism of Cd Biosorption on 11830
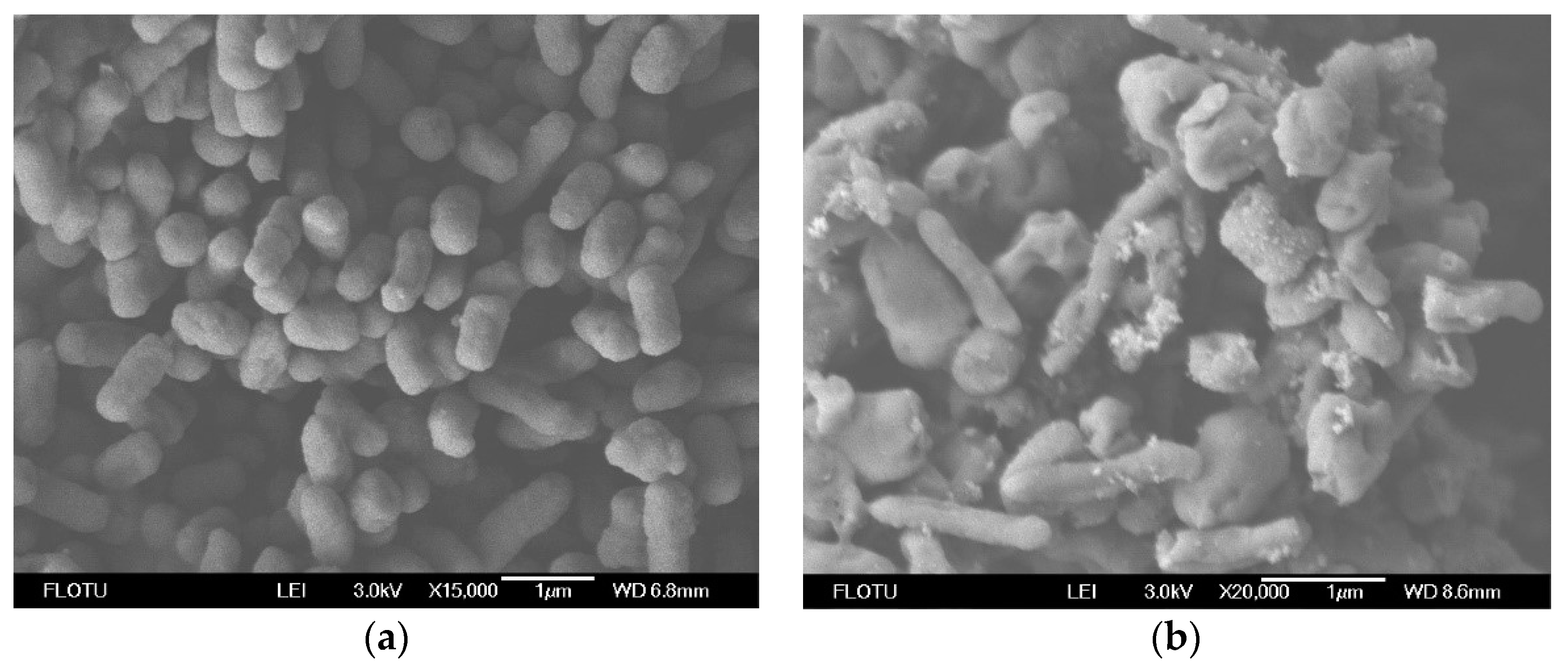
3.4.1. SEM Analysis
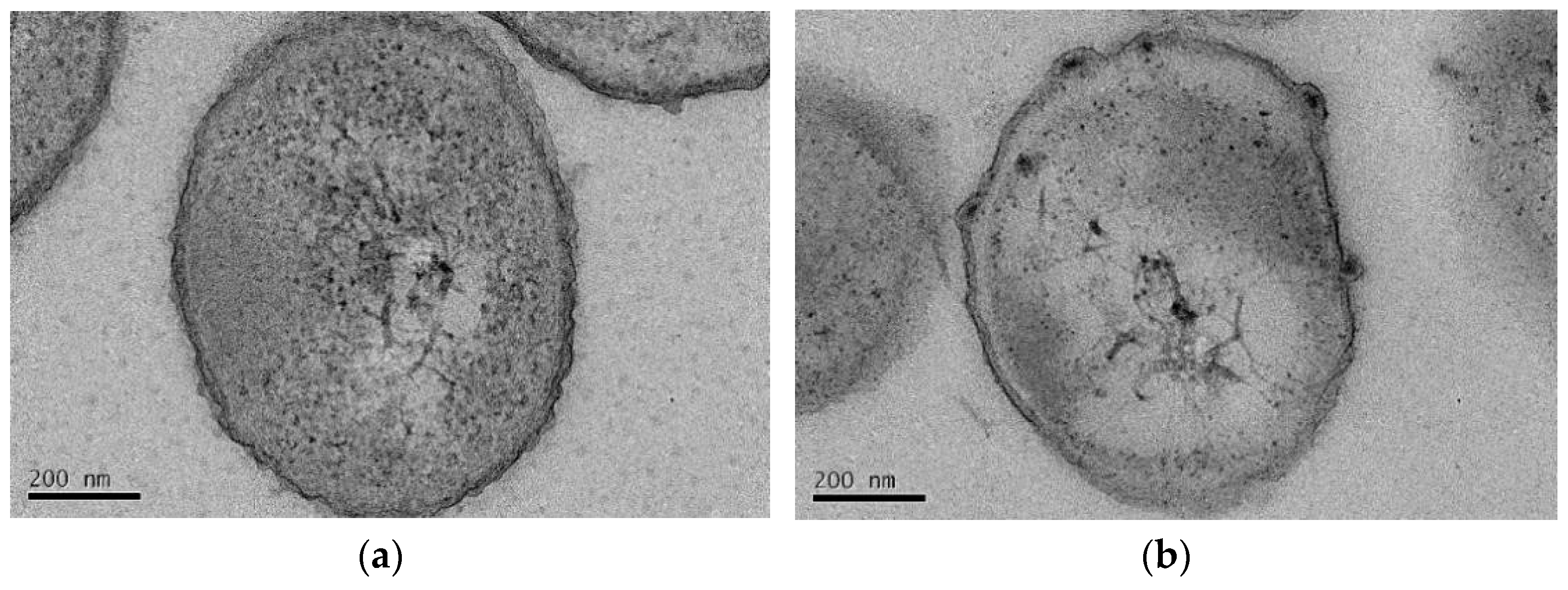
3.4.2. TEM and EDS Analysis
3.4.3. Protein Differential Analysis
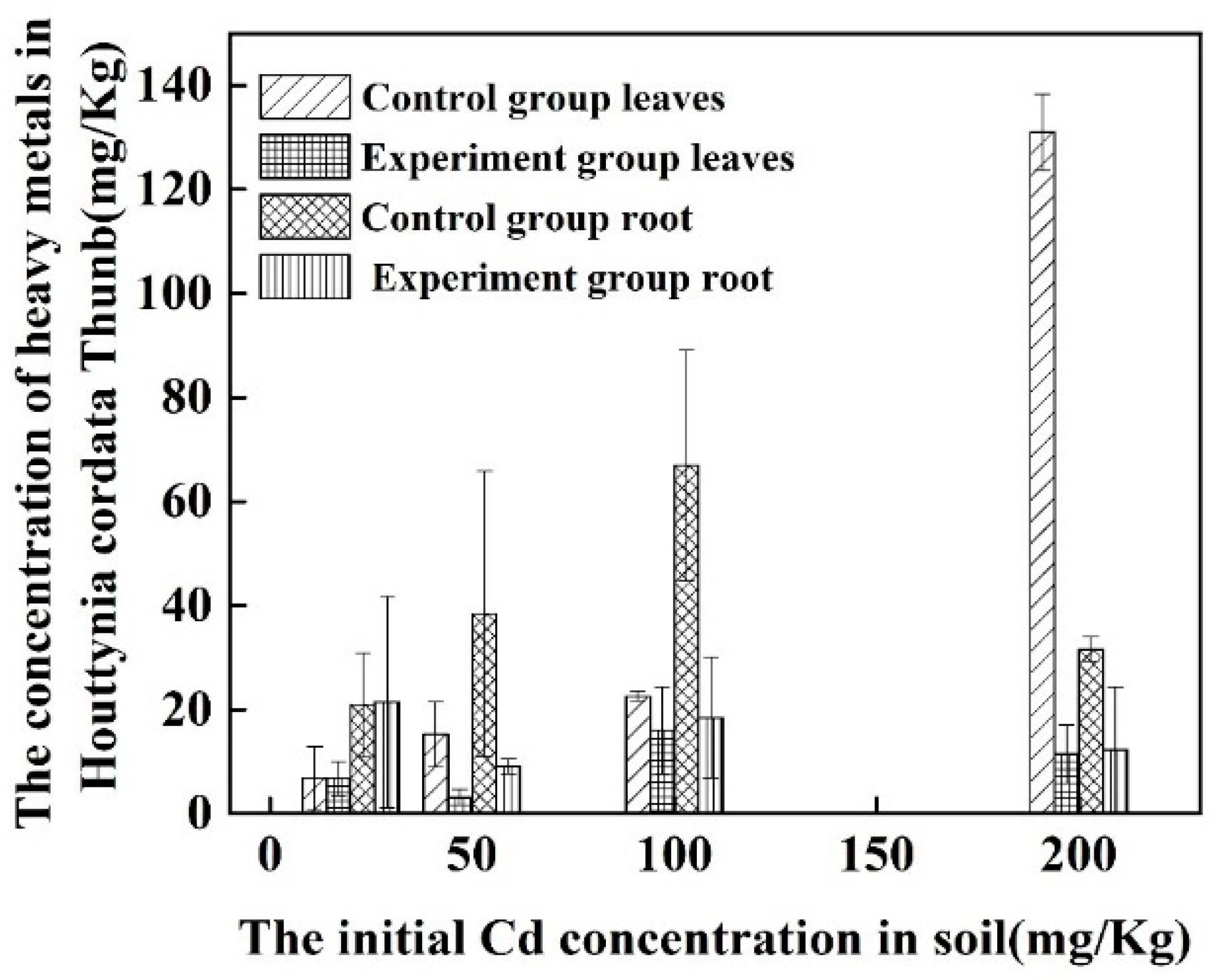
3.5. Pot Tests of 11830 on Biosorption of Cd
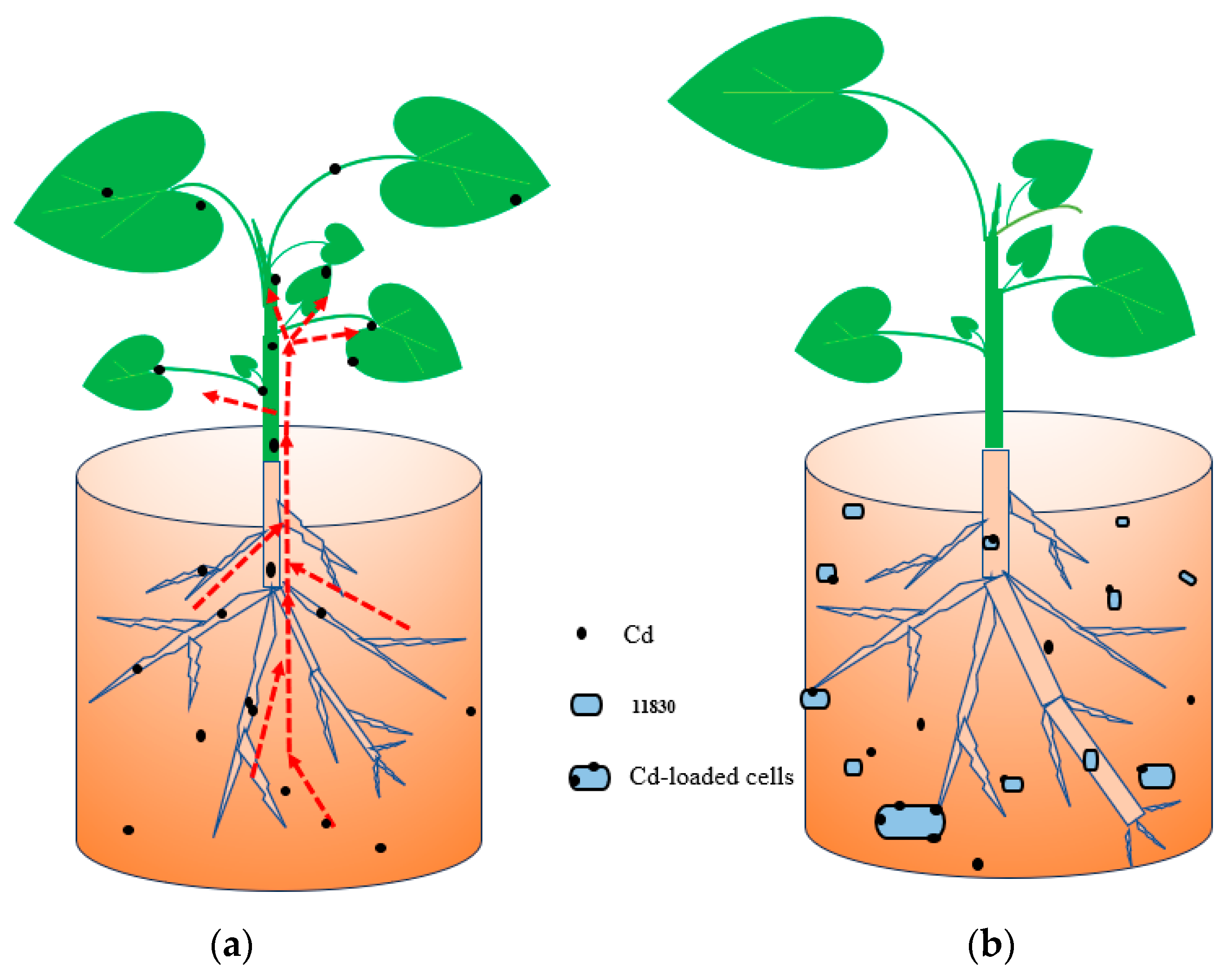
3.6. 11830 Passivation Cadmium to Inhibit Adsorption of H. cordata
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Cd | Cadmium |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscope |
| EDS | Energy-dispersive spectroscopy |
| H. cordata | Houttuynia cordata Thunb |
| T | Temperature |
| ICP-AES | Inductively Coupled Plasma–Atomic Emission Spectrometry |
| ICP-MS | Inductively Coupled Plasma–Mass Spectrometry |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PAGE | Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
References
- Hossain, Z.; Huq, F. Studies on the interaction between Cd2+ ions and nucleobases and nucleotides. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2002, 90, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyder, O.; Chung, M.; Cosgrove, D.; Herman, J.M.; Li, Z.P.; Firoozmand, A.; Gurakar, A.; Koteish, A.; Pawlik, T.M. Cadmium Exposure and Liver Disease among US Adults. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2013, 17, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.J.; Han, S.H. Blood Cadmium Is Associated with Osteoporosis in Obese Males but Not in Non-Obese Males: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008–2011. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 12144–12157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.Y.; Cho, S.H.; Lim, Y.H.; Seo, J.C.; Hong, Y.C. Effects of environmental cadmium exposure on liver function in adults. Occup. Environ. Med. 2013, 70, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.F.; Wu, Y.N. Adverse effects of low dose exposures to cadmium below renal damage level should be emphasized for human health effect studies. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2016, 50, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.R.; He, S.B.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhang, W.; Lu, D.N. Bioadsorption and biostabilization of cadmium by Enterobacter cloacae TU. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.X.; Tang, J.X.; Yin, H.Q.; Liu, X.D.; Jiang, P.; Liu, H.W. Isolation, identification and cadmium adsorption of a high cadmium-resistant Paecilomyces lilacinus. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 6525–6533. [Google Scholar]
- Polak-Berecka, M.; Boguta, P.; Ciesla, J.; Bieganowski, A.; Skrzypek, T.; Czernecki, T.; Wasko, A. Studies on the removal of Cd ions by gastrointestinal lactobacilli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 3415–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marwan, H.; Nassar, D.; Shtaya, M. Heavy metals accumulation in soil and uptake by barley (Hordeum vulgare) irrigated with contaminated water. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4121. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, K.B.; Jensen, P.E.; Ottosen, L.M.; Lejon, T. An optimised method for electrodialytic removal of heavy metals from harbour sediments. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 173, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pedersen, K.B.; Lejon, T.; Ottosen, L.M.; Jensen, P.E. Screening of variable importance for optimizing electrodialytic remediation of heavy metals from polluted harbour sediments. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 2364–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.C.; Yang, J.S.; Jeon, E.K.; Baek, K. Enhanced-electrokinetic extraction of heavy metals from dredged harbor sediment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 9912–9921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Fu, Y.Q.; Hu, M.Q.; Wang, S.Q.; Liu, Z.G. Highly efficient SnS-decorated Bi2O3 nanosheets for simultaneous electrochemical detection and removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II). J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 856, 113744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motlochová, M.; Slovák, V.; Pliingrová, E.; Lidin, S.; Subrt, J. Highly-efficient removal of Pb(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) from water by novel lithium, sodium and potassium titanate reusable microrods. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 3694–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mignardi, S.; Corami, A.; Ferrini, V. Evaluation of the effectiveness of phosphate treatment for the remediation of mine waste soils contaminated with Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadasa, K.; Yellaiah, G.; Nagabhushanam, M. Optical and transport properties of Cd0.8Zn0.2S:Cu compounds prepared by modified chemical co-precipitation method. Optik 2014, 125, 6602–6608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, R.K.; Jain, S.K.; Khatri, P.K. Iminodiacetic acid functionalized cation exchange resin for adsorptive removal of Cr(VI), Cd(II), Ni(II) and Pb(II) from their aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 1508–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koiodynska, D.; Krukowska-Bak, J.; Kazmierczak-Razna, J.; Pietrzak, R. Uptake of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by sorbents obtained from the spent ion exchange resins. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 244, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selatnia, A.; Boukazoula, A.; Kechid, N.; Bakhti, M.Z.; Chergui, A. Biosorption of Fe3+ from aqueous solution by a bacterial dead Streptomyces rimosus biomass. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, C.; Wilhelmi, B.; Duncan, J.R.; Burgess, J.E. Biosorption of precious metals. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, G.; Pandey, S.; Ray, A.K.; Kumar, R. Bioremediation of Heavy Metals by a Novel Bacterial Strain Enterobacter cloacae and Its Antioxidant Enzyme Activity, Flocculant Production, and Protein Expression in Presence of Lead, Cadmium, and Nickel. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.H.; Wu, W.; Lu, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Rao, W.H.; Guan, X. Biosorption and extraction of europium by Bacillus thuringiensis strain. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2017, 75, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Viraraghavan, T. Mechanism of biosorption of heavy metals by Mucor rouxii. Eng. Life Sci. 2008, 8, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Q.; Sun, X.X.; Shen, Y.P.; Chang, C.; Guo, E.H.; La, G.X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.Z. Tolerance and Removal Mechanisms of Heavy Metals by Fungus Pleurotus ostreatus HAAS. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.F.; Yin, W.K.; Chang, Z.Y.; Lundholm, N.; Jiang, Z.M. Biosorption capacity and kinetics of cadmium(II) on live and dead Chlorella vulgaris. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edris, G.; Alhamed, Y.; Alzahrani, A. Biosorption of Cadmium and Lead from Aqueous Solutions by Chlorella vulgaris Biomass: Equilibrium and Kinetic Study. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2014, 39, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, P.; Padmavathy, V.; Dhingra, S.C. Kinetics of biosorption of cadmium on Baker’s yeast. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 89, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goksungur, Y.; Uren, S.; Guvenc, U. Biosorption of cadmium and lead ions by ethanol treated waste baker’s yeast biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.Q.; Huang, W.W.; Dong, J.J.; Zhu, Q.F.; Lu, D.N.; Liu, Y.M. Study on the Removal of Cd(II) by Pseudomonas nitroreducens: Biosorption Characteristics and Mechanism. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.K.; Zhu, Q.F.; Dong, X.Z.; Huang, W.W.; Du, C.Y.; Lu, D.N. How Serratia marcescens HB-4 absorbs cadmium and its implication on phytoremediation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 185, 109723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argun, M.E.; Dursun, S.; Ozdemir, C.; Karatas, M. Heavy metal adsorption by modified oak sawdust: Thermodynamics and kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, B.H.; Ahmad, A.A.; Aziz, N. Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics of acid dye adsorption on activated palm ash. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 133, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The Adsorption of Gases on Plane Surfaces of Glass, Mica and Platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Concerning adsorption in solutions. Z. Fur Phys. Chem.-Stochiom. Verwandtschaftslehre 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, J.H.; Hassan, S.H.A.; Oh, S.E. Comparative study of biosorption of Zn2+ by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Bacillus cereus. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2010, 64, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzba, S. Biosorption of nickel (II) and zinc (II) from aqueous solutions by the biomass of yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2017, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Dang, Z.; Guo, C.L.; Lu, G.N.; Gu, R.R.; Liu, H.J.; Zhang, H. Biosorption of Cd(II) by live and dead cells of Bacillus cereus RC-1 isolated from cadmium-contaminated soil. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 107, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njikam, E.; Schiewer, S. Optimization and kinetic modeling of cadmium desorption from citrus peels: A process for biosorbent regeneration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 213–214, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dai, Y.; Tao, Q.Q.; Gao, Z.; Xu, L. Ultrahigh efficient and selective adsorption of U(VI) with amino acids-modified magnetic chitosan biosorbents: Performance and mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 214, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lamb, D.; Paneerselvam, P.; Choppala, G.; Bolan, N.; Chung, J.W. Role of organic amendments on enhanced bioremediation of heavy metal(loid) contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 549–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chibuike, G.U.; Obiora, S.C. Heavy metal polluted soils: Effect on plants and bioremediation methods. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2014, 2014, 752708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, M.W.; Miller, C.D.; Dimkpa, C.O.; Anderson, A.J.; McLean, J.E. Defining the surface adsorption and internalization of copper and cadmium in a soil bacterium, Pseudomonas putida. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.B.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, B.P.; Mohamad, O.; Wei, G.H. Bioaccumulation characterization of zinc and cadmium by Streptomyces zinciresistens, a novel actinomycete. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 77, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambuckersberhin, F.; Remacle, J. Cadmium Sequestration in Cells of 2 Strains of Alcaligenes-Eutrophus. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1990, 73, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uraguchi, S.; Kamiya, T.; Clemens, S.; Fujiwara, T. Characterization of OsLCT1, a cadmium transporter from indica rice (Oryza sativa). Physiol. Plant. 2014, 151, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.; Yao, S.Y.; Chen, D.G.; Zhang, L.L. Research progress on the mechanisms of cadmium transport. Chem. Life 2018, 38, 483–490. [Google Scholar]
- Kayser, A.; Wenger, K.; Keller, A.; Attinger, W.; Felix, H.R.; Gupta, S.K.; Schulin, R. Enhancement of phytoextraction of Zn, Cd, and Cu from calcareous Soil: The use of NTA and sulfur amendments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 1778–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, W.; Hou, L. Notice of Retraction: The Cadmium Accumulation Ability of Huttuynia cordata Enhanced by Microorganisms in Soil. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Wuhan, China, 10–12 May 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Lin, H.; Dong, Y.B.; He, Y.H. Effects of cropping patterns of four plants on the phytoremediation of vanadium-containing synthetic wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 115, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, S.T.; He, X.L.; Xie, M.H.; Cai, M.Z.; Zhu, Y.X.; Du, S.T. A promising product: Abscisic acid-producing bacterial agents for restricting cadmium enrichment in field vegetable crops. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, F.; Fu, T.L.; He, G.D.; Tian, W.J.; Wen, J.C.; Yang, M.F.; Wei, X.L.; He, Y.; He, T.B. Different composites inhibit Cd accumulation in grains under the rice-oilseed rape rotation mode of karst area: A field study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 256, 114884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
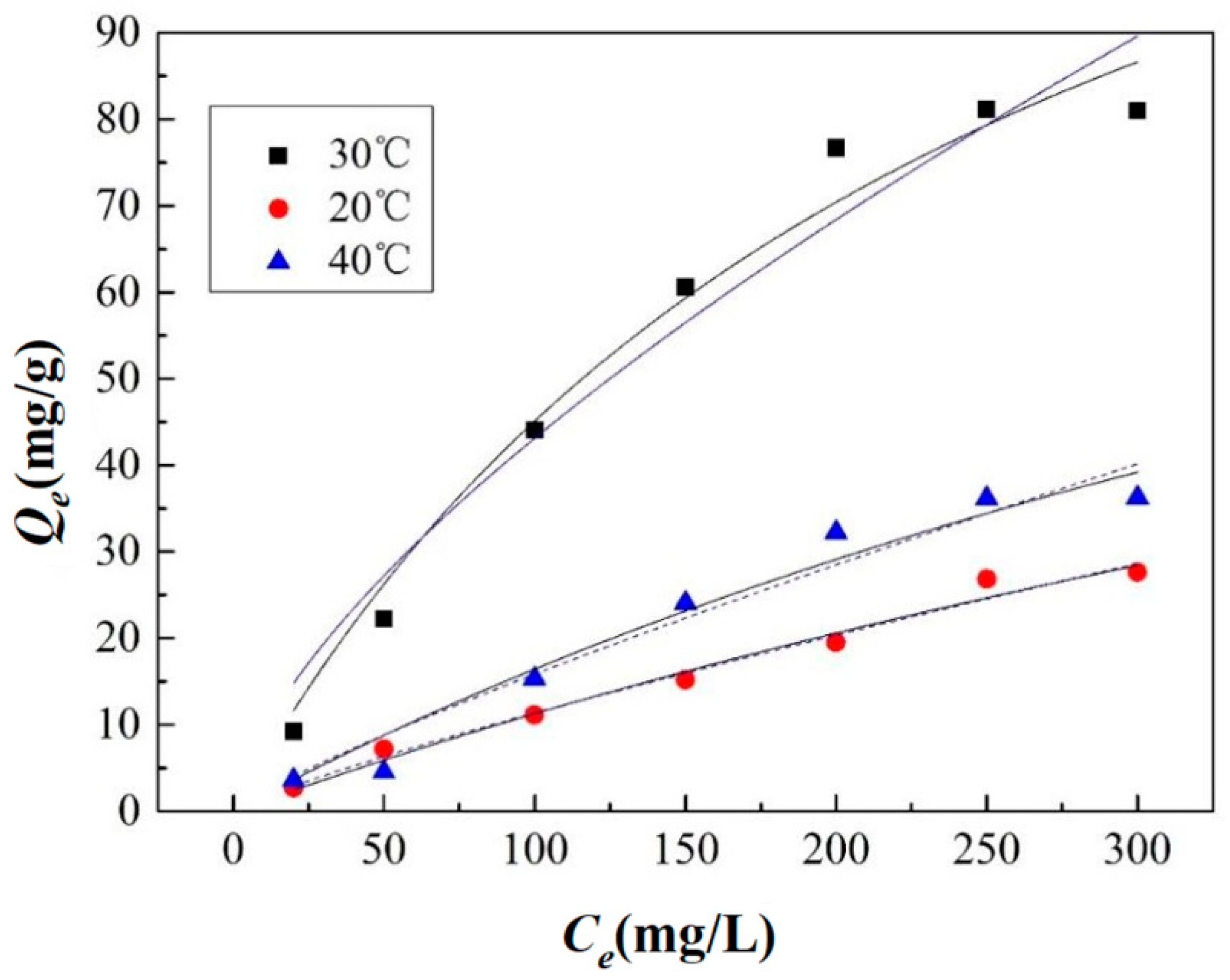


| T (°C) | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax (mg/g) | b | R2 | n | K | R2 | |
| 20 | 118.32 | 0.001 | 0.980 | 1.188 | 0.235 | 0.981 |
| 30 | 160.51 | 0.004 | 0.977 | 1.503 | 2.012 | 0.949 |
| 40 | 127.86 | 0.001 | 0.959 | 1.181 | 0.321 | 0.946 |
| MW [KDa] | Description | Amino Acid Sequence Coverage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | Experiment | ||
| 9.3 | Interferon-induced transmembrane protein | 0 | 16.3 |
| 15.1 | Acyl-CoA thioesterase | 0 | 17.42 |
| 15.5 | Blue light-and temperature-regulated antirepressor YcgF | 0 | 6.94 |
| 15.7 | Lipocalin | 0 | 7.41 |
| 15.9 | Aerotaxis sensor receptor protein | 0 | 11.27 |
| 16.7 | CAMP-binding protein | 0 | 5.1 |
| 17.1 | Exclusion suppressor | 0 | 7.74 |
| 18.6 | 18 k peptidoglycan-associated outer membrane lipoprotein | 0 | 47.67 |
| 22.4 | Aerotaxis receptor | 0 | 5.57 |
| 23.6 | 2-octaprenyl-3-methyl-6-methoxy-1,4-benzoquinol hydroxylase | 0 | 6.91 |
| 24.5 | Glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase | 0 | 4.78 |
| 27.9 | Zinc import ATP-binding protein ZnuC | 0 | 9.96 |
| 28.2 | Zn-dependent protease with chaperone function | 0 | 23.51 |
| 29.3 | Bacterial transcriptional regulator family protein | 0 | 5.22 |
| 31.6 | 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate 2,3-dioxygenase | 0 | 5.32 |
| 38.1 | 23S rRNA (guanosine-2′-O-)-methyltransferase RlmB | 0 | 6.38 |
| 39.5 | Metallo-beta-lactamase family protein | 0 | 4.46 |
| 42.8 | C4-type zinc finger protein | 0 | 19.32 |
| 42.9 | 2-octaprenyl-6-methoxyphenyl hydroxylase | 0 | 5.72 |
| 44.8 | Outer membrane efflux protein | 0 | 32.13 |
| 47.9 | Trigger factor | 0 | 31.32 |
| 49.2 | 2,4-diaminobutyrate 4-transaminase | 0 | 15.22 |
| 61.0 | Bacterial leucyl aminopeptidase | 0 | 10.37 |
| 62.9 | Arsenic ABC transporter ATPase | 0 | 4.08 |
| 64.0 | Bacterial extracellular solute-binding family protein | 0 | 12.65 |
| 67.3 | BipA GTPase | 0 | 14.5 |
| 72.8 | Metal-transporting P-type ATPase transmembrane protein | 0 | 1.42 |
| 79.6 | Zinc-regulated outer membrane | 0 | 50.75 |
| 82.5 | Catecholate siderophore receptor Fiu | 0 | 17.18 |
| 88.0 | Aerobic respiration control sensor protein | 0 | 1.54 |
| 116.3 | Heavy metal efflux pump, cobalt-zinc-cadmium | 0 | 4.39 |
| 175.9 | Alpha-2-macroglobulin | 0 | 25.71 |
| 18.8 | Adenosylcobinamide kinase | 10.98 | 0 |
| 33.6 | 2-nitropropane dioxygenase | 17.3 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Fang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, D. How Pseudomonas nitroreducens Passivates Cadmium to Inhibit Plant Uptake. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072857
Chen Y, Yu Y, Fang X, Zhou Y, Lu D. How Pseudomonas nitroreducens Passivates Cadmium to Inhibit Plant Uptake. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(7):2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072857
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yakui, Yongquan Yu, Xiaoyu Fang, Yinhuan Zhou, and Diannan Lu. 2024. "How Pseudomonas nitroreducens Passivates Cadmium to Inhibit Plant Uptake" Applied Sciences 14, no. 7: 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072857
APA StyleChen, Y., Yu, Y., Fang, X., Zhou, Y., & Lu, D. (2024). How Pseudomonas nitroreducens Passivates Cadmium to Inhibit Plant Uptake. Applied Sciences, 14(7), 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072857








