Phlorotannins Isolated from Eisenia bicyclis and Lactobacillus casei Ameliorate Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice through the AhR Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of Phlorotannin-Rich Fractions from E. bicyclis
2.2. LC-MS Analysis
2.3. Fermentation with Lactic Acid Bacteria
2.4. Cell Culture and In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Assessment
2.5. Animal Experimental Design
2.6. Histopathological Analysis
2.7. ELISA Analysis
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) and qPCR Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. LC-MS Analysis of EB Extracts
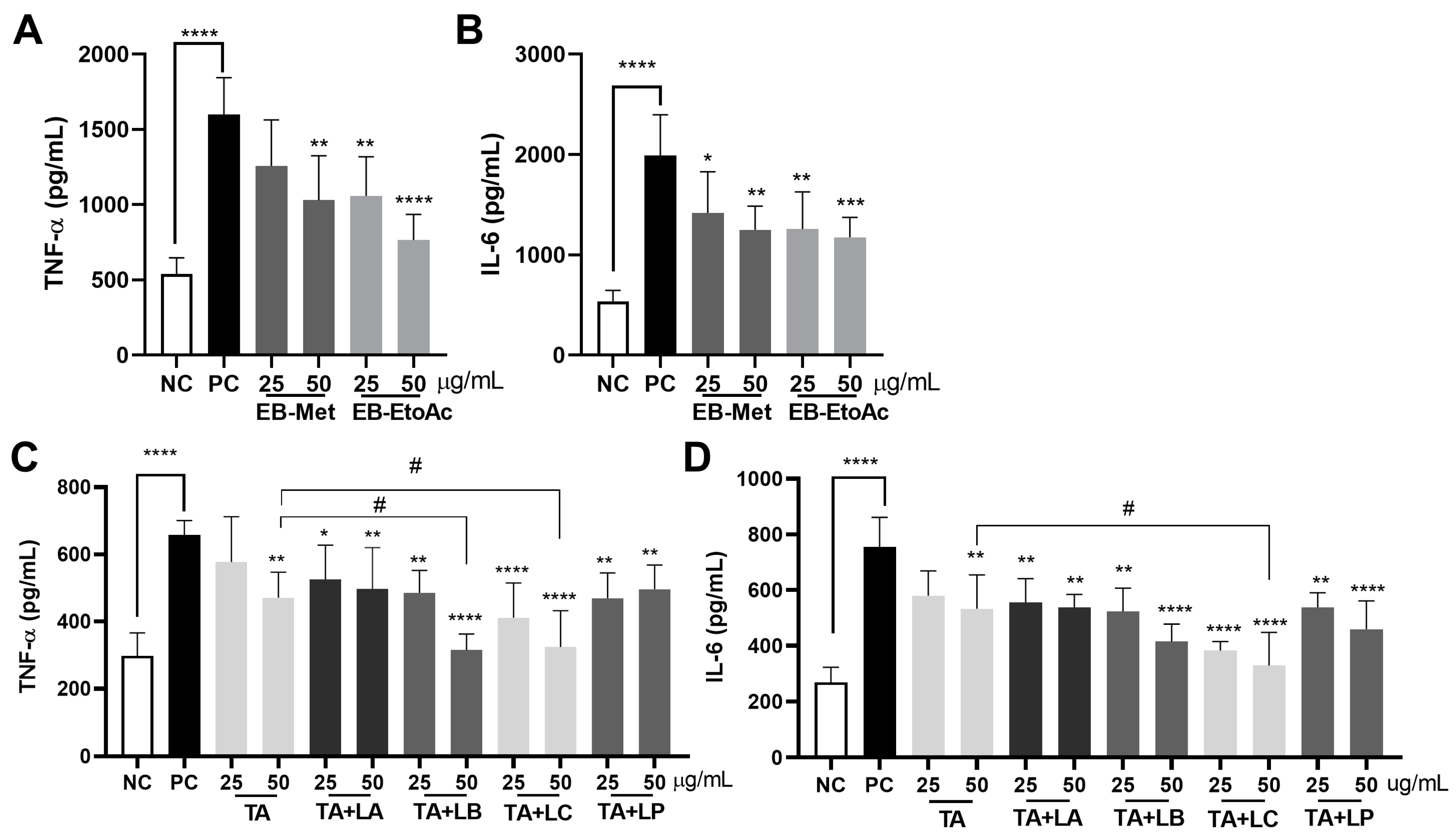
3.2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Phlorotannins Isolated from E. bicyclis and Fermented Phlorotannins with Lactic Acid Bacteria Species
3.3. Effects of TA and LC on Body Weight, DAI Index, Colon Length, Spleen Weight, and Histological Score in DSS-Treated Mice
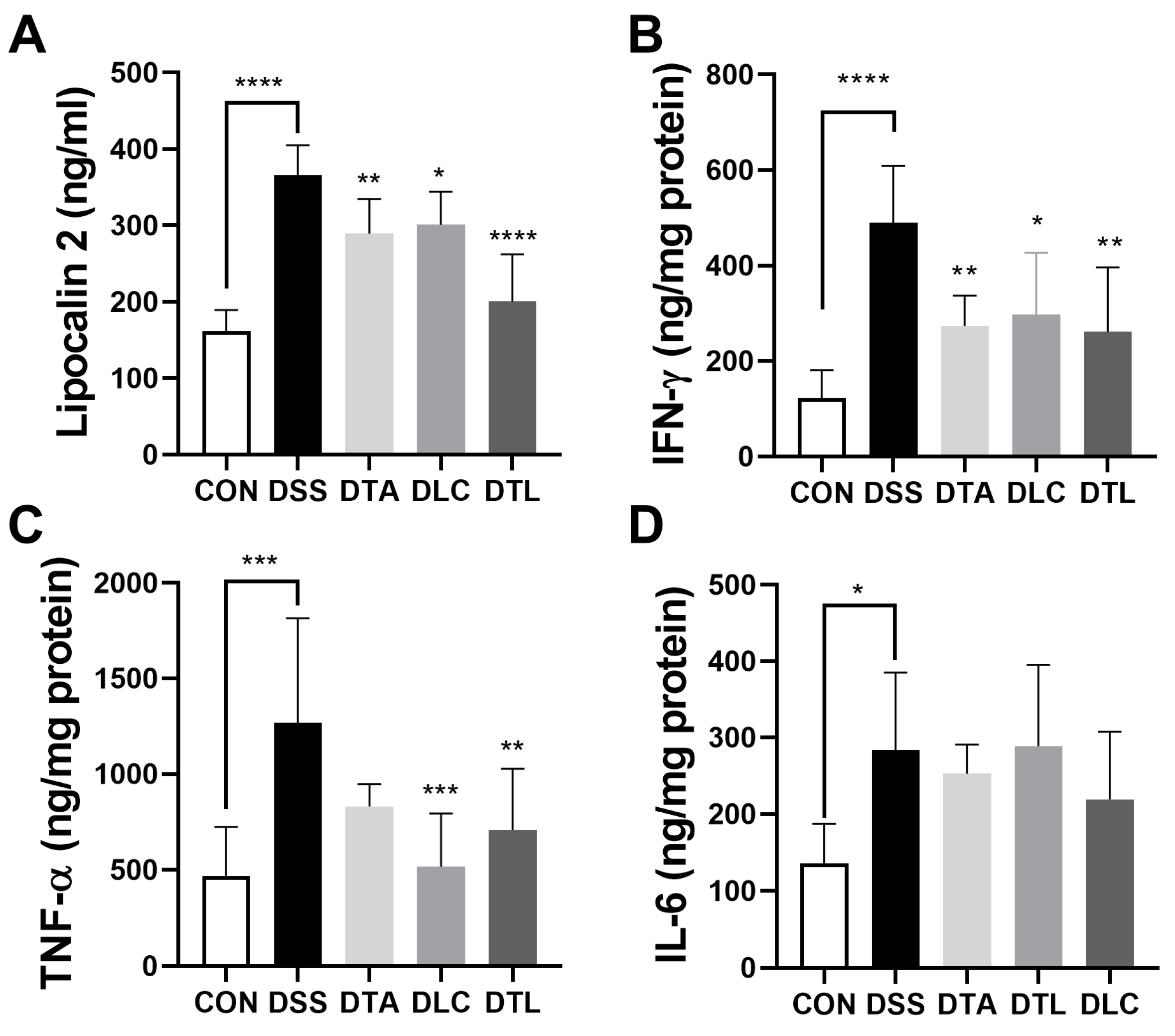
3.4. Effects of TA and LC on Inflammation Markers in DSS-Treated Mice
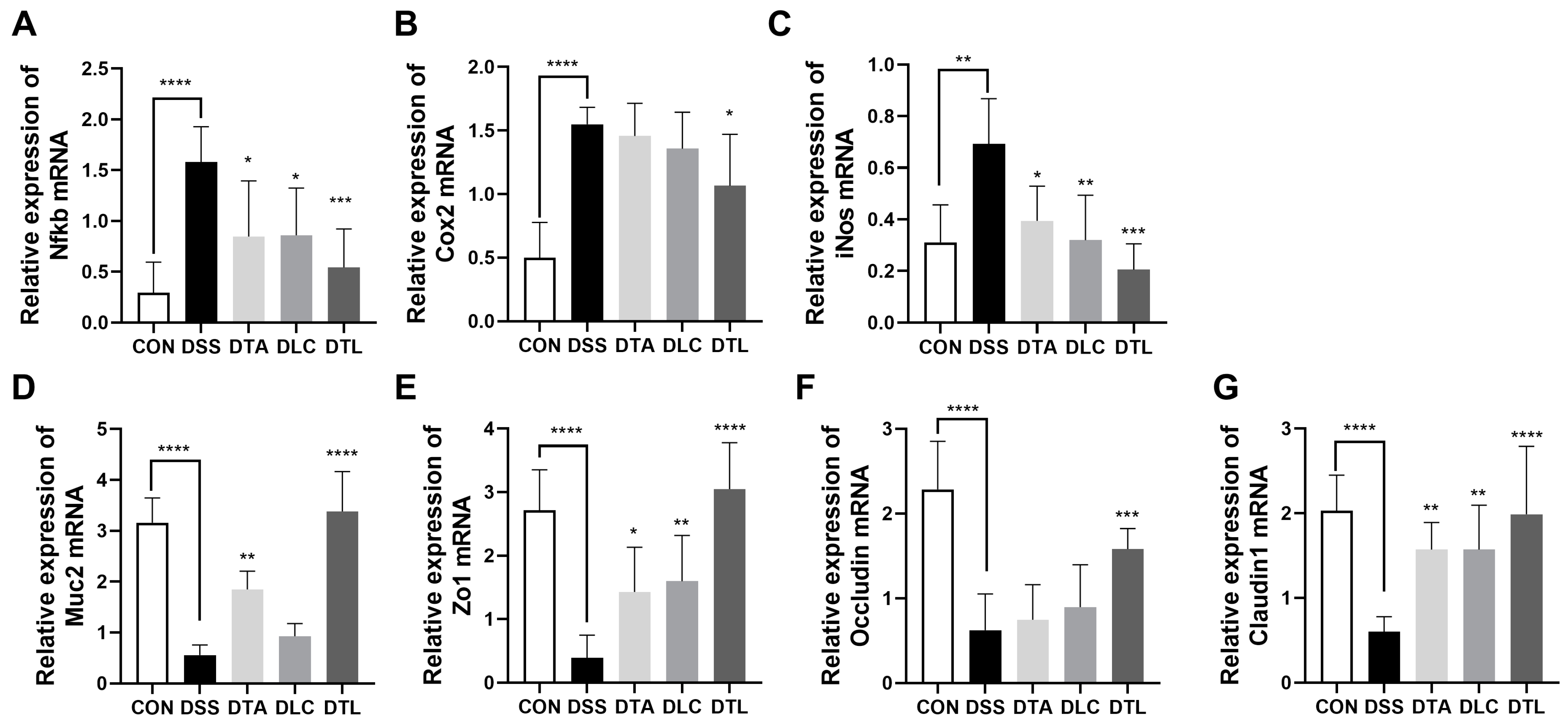
3.5. Effects of TA and LC on mRNA Expressions of Inflammatory Markers and Tight Junctions in DSS-Treated Mice
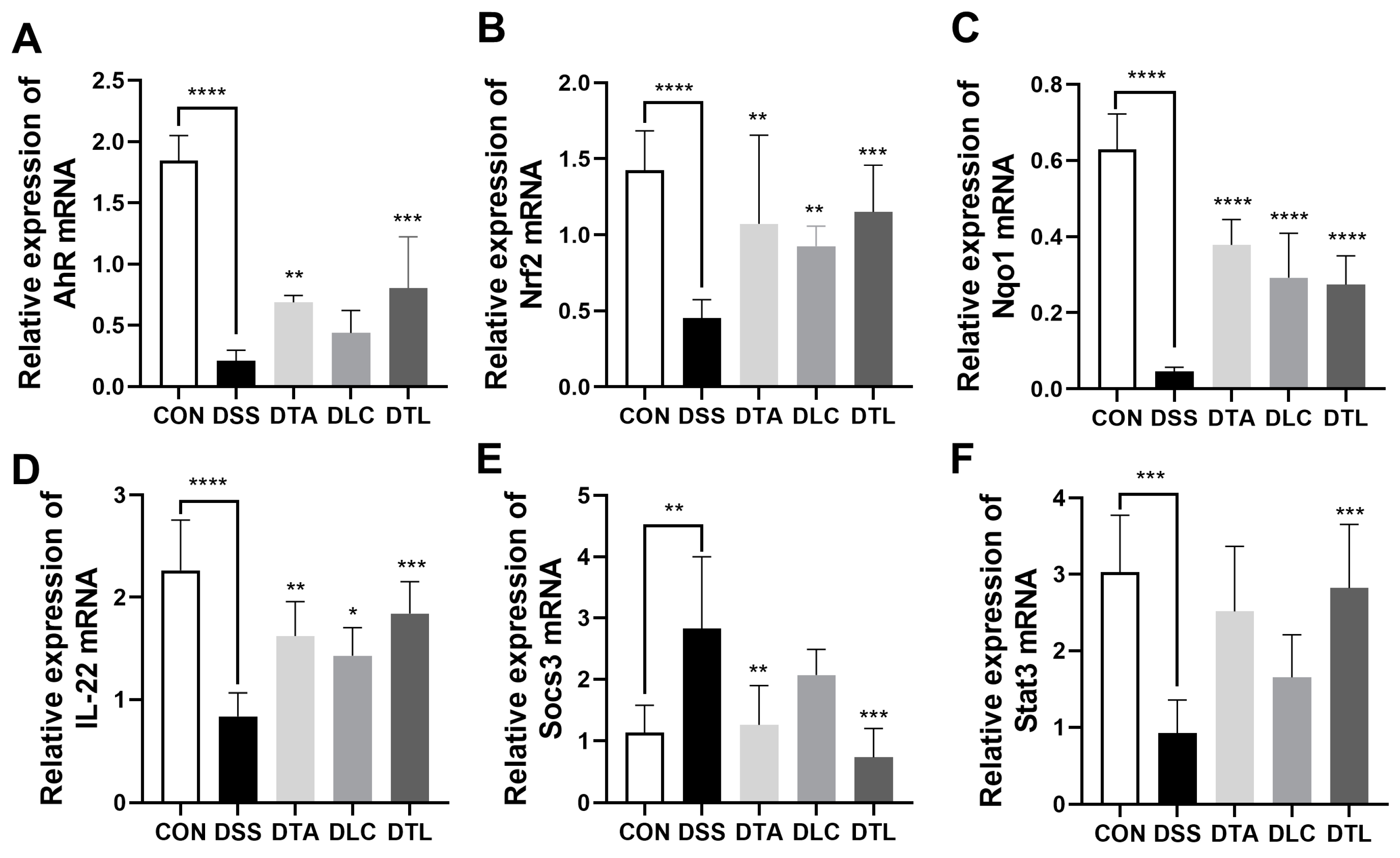
3.6. Effects of TA and LC on the AhR Pathway in DSS-Treated Mice
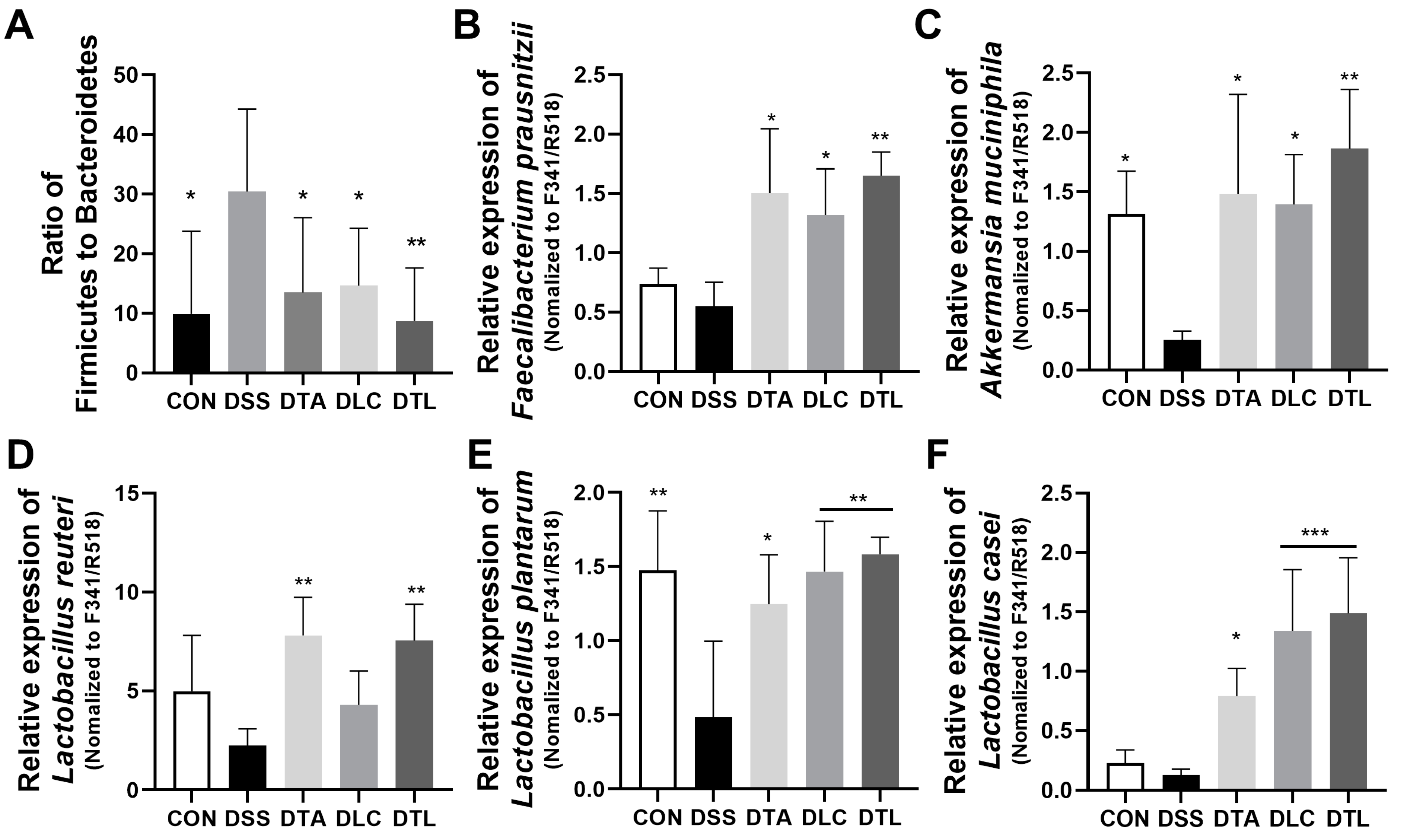
3.7. Effects of TA and LC on the Fecal Microbiota Composition in DSS-Treated Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seyedian, S.S.; Nokhostin, F.; Malamir, M.D. A review of the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment methods of inflammatory bowel disease. J. Med. Life 2019, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Ullah, N.; Zha, L.; Bai, Y.; Khan, A.; Zhao, T.; Che, T.; Zhang, C. Alteration of gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Cause or consequence? IBD treatment targeting the gut microbiome. Pathogens 2019, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatiya-Aphiradee, N.; Chatuphonprasert, W.; Jarukamjorn, K. Immune response and inflammatory pathway of ulcerative colitis. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 30, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- K Ko, J.; K Auyeung, K. Inflammatory bowel disease: Etiology, pathogenesis and current therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 1082–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Sebastian, S.A.; Parmar, M.P.; Ghadge, N.; Padda, I.; Keshta, A.S.; Minhaz, N.; Patel, A. Factors influencing the quality of life in inflammatory bowel disease: A comprehensive review. Dis. Mon. 2023, 70, 101672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, A.C.; Kane, S.V.; Khan, K.J.; Achkar, J.-P.; Talley, N.J.; Marshall, J.K.; Moayyedi, P. Efficacy of 5-aminosalicylates in Crohn’s disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, M.T.H.; Bangoura, I.; Kang, J.-Y.; Cho, J.Y.; Joo, J.; Choi, Y.S.; Hwang, D.S.; Hong, Y.-K. Comparison of Ecklonia cava, Ecklonia stolonifera and Eisenia bicyclis for phlorotannin extraction. J. Environ. Biol. 2014, 35, 713. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, T.; Nagayama, K.; Uchida, K.; Tanaka, R. Antioxidant activity of phlorotannins isolated from the brown alga Eisenia bicyclis. Fish. Sci. 1996, 62, 923–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Wei, S.; Hu, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, J. Protective Effect and Mechanisms of Eckol on Chronic Ulcerative Colitis Induced by Dextran Sulfate Sodium in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.V.; Kim, S.-K. Potential pharmacological applications of polyphenolic derivatives from marine brown algae. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 32, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, X.; Luo, C.; Alarifi, S.; Yang, H. Dieckol alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis via inhibition of inflammatory pathway and activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Environ. Toxicol. 2021, 36, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, P.; Yadav, S.; Strain, C.R.; Allsopp, P.J.; McSorley, E.M.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Prebiotics from seaweeds: An ocean of opportunity? Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Yang, W.; Li, L.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ni, H.; Jiang, Z.; Zheng, M. In vitro fermentation of seaweed polysaccharides and tea polyphenol blends by human intestinal flora and their effects on intestinal inflammation. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 1133–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Lactobacillus ruminis alleviates DSS-induced colitis by inflammatory cytokines and gut microbiota modulation. Foods 2021, 10, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabashsum, Z.; Peng, M.; Bernhardt, C.; Patel, P.; Carrion, M.; Biswas, D. Synbiotic-like effect of linoleic acid overproducing Lactobacillus casei with berry phenolic extracts against pathogenesis of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, G.; Ji, Y.; Anegboonlap, P.; Hotchkiss, S.; Gill, C.; Yaqoob, P.; Spencer, J.P.; Rowland, I. Gastrointestinal modifications and bioavailability of brown seaweed phlorotannins and effects on inflammatory markers. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 1240–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Abukhalil, M.H. Antiinflammatory natural products from marine algae. In Inflammation and Natural Products; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 175–203. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Christman, L.M.; Li, R.; Gu, L. Synergic interactions between polyphenols and gut microbiota in mitigating inflammatory bowel diseases. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4878–4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Zhang, S.; Han, S.; Qiu, B.; Lu, Y.; Huang, W.; Li, F.; Chen, D.; Berglund, B.; Xiao, H. The role of dihydroresveratrol in enhancing the synergistic effect of Ligilactobacillus salivarius Li01 and resveratrol in ameliorating colitis in mice. Research 2022, 2022, 9863845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fan, C.; Zhao, Z.; Zhai, Z.; Hao, Y. Anti-inflammatory effect of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis A6 on DSS-induced colitis in mice. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 2063–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Heller, J.J.; Guo, X.; Zong-ming, E.C.; Fish, K.; Fu, Y.-X.; Zhou, L. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates gut immunity through modulation of innate lymphoid cells. Immunity 2012, 36, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Li, L.; Yu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, G.; Li, X.; Xiao, W.; Xu, P. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation modulates intestinal epithelial barrier function by maintaining tight junction integrity. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neavin, D.R.; Liu, D.; Ray, B.; Weinshilboum, R.M. The role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) in immune and inflammatory diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xie, X.; Li, Y.; Xie, X.; Huang, S.; Pan, S.; Zou, Y.; Pan, Z.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J. Quercetin ameliorates ulcerative colitis by activating aryl hydrocarbon receptor to improve intestinal barrier integrity. Phytother. Res. 2023, 38, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, C.G.; Ávila-Gálvez, M.Á.; Lian, Y.; Moura-Alves, P.; Dos Santos, C.N. Targeting the aryl hydrocarbon receptor by gut phenolic metabolites: A strategy towards gut inflammation. Redox Biol. 2023, 61, 102622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumoto, S.; Toshimitsu, T.; Matsuoka, S.; Maruyama, A.; Oh-oka, K.; Takamura, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Ishimaru, K.; Fujii-Kuriyama, Y.; Ikegami, S. Identification of a probiotic bacteria-derived activator of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor that inhibits colitis. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2014, 92, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, A.; Lajili, S.; Elkaibi, M.A.; Ben Salem, Y.; Abdelhamid, A.; Muller, C.D.; Majdoub, H.; Kraiem, J.; Bouraoui, A. Optimized extraction, preliminary characterization and evaluation of the in vitro anticancer activity of phlorotannin-rich fraction from the brown seaweed, Cystoseira sedoides. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2019, 28, 892–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyton, A.; Pezoa-Conte, R.; Barriga, A.; Buschmann, A.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Mikkola, J.-P.; Lienqueo, M. Identification and efficient extraction method of phlorotannins from the brown seaweed Macrocystis pyrifera using an orthogonal experimental design. Algal Res. 2016, 16, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steevensz, A.J.; MacKinnon, S.L.; Hankinson, R.; Craft, C.; Connan, S.; Stengel, D.B.; Melanson, J.E. Profiling phlorotannins in brown macroalgae by liquid chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. 2012, 23, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-M.; Kim, H.-Y.; Jang, J.-T.; Hong, S. Preventive Effect of Ecklonia cava Extract on DSS-Induced Colitis by Elevating Intestinal Barrier Function and Improving Pathogenic Inflammation. Molecules 2023, 28, 8099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassaing, B.; Aitken, J.D.; Malleshappa, M.; Vijay-Kumar, M. Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2014, 104, 15.25.11–15.25.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perše, M.; Cerar, A. Dextran sodium sulphate colitis mouse model: Traps and tricks. Biomed Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 718617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, P.; Chen, W.; Chen, G. Ferroptosis mediated DSS-induced ulcerative colitis associated with Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Immunol. Lett. 2020, 225, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Gao, X.; Nie, L.; Xie, J.; Dai, T.; Shi, C.; Tao, L.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Sheng, J. Astragalin attenuates dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced acute experimental colitis by alleviating gut microbiota dysbiosis and inhibiting NF-κB activation in mice. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, Y.; Wang, Q.; Park, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, H. Sargassum horneri Extract Ameliorates DSS-Induced Colitis through Modulation of mTOR Axis and Intestinal Microbiota. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erben, U.; Loddenkemper, C.; Doerfel, K.; Spieckermann, S.; Haller, D.; Heimesaat, M.M.; Zeitz, M.; Siegmund, B.; Kühl, A.A. A guide to histomorphological evaluation of intestinal inflammation in mouse models. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 4557. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, C. Antioxidant functions of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 7943495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catarino, M.D.; Silva, A.M.; Mateus, N.; Cardoso, S.M. Optimization of phlorotannins extraction from Fucus vesiculosus and evaluation of their potential to prevent metabolic disorders. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, L.R.; Paul, P.T.; Anas, K.; Tejpal, C.; Chatterjee, N.; Anupama, T.; Mathew, S.; Ravishankar, C. Phlorotannins–bioactivity and extraction perspectives. J. Appl. Phycol. 2022, 34, 2173–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-M.; Kim, S.-K. Effect of phloroglucinol on oxidative stress and inflammation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2925–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Coman, M.M.; Guo, Y.; Hotchkiss, S.; Gill, C.; Yaqoob, P.; Spencer, J.P.; Rowland, I. Effect of simulated gastrointestinal digestion and fermentation on polyphenolic content and bioactivity of brown seaweed phlorotannin-rich extracts. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1700223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Wu, M.; Wang, Q.; Peng, X.; Wen, H.; McKinstry, W.J.; Chen, Q. Crystal structure of tannase from Lactobacillus plantarum. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 2737–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowiak, P.; Śliżewska, K. Effects of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on human health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.-J.; Ma, A.-H.; Qin, Y.-H. Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in inflammatory bowel disease: Insights from gut microbiota. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1279172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Jeong, G.-J.; Khan, M.S.A.; Tabassum, N.; Kim, Y.-M. Seaweed-Derived phlorotannins: A review of multiple biological roles and action mechanisms. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Choi, C.-G.; Kim, J.-I.; Kim, H.-R. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Hexane Fraction from Eisenia bicyclis on Lipopolysaccharides-Treated RAW 264.7 Cells. Fish Aquat. Sci. 2021, 54, 152–161. [Google Scholar]
- Manzella, C.; Singhal, M.; Alrefai, W.A.; Saksena, S.; Dudeja, P.K.; Gill, R.K. Serotonin is an endogenous regulator of intestinal CYP1A1 via AhR. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Ji, P.; Hua, Y.; Wei, Y. Huang-lian-jie-du decoction ameliorates acute ulcerative colitis in mice via regulating NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling pathways and enhancing intestinal barrier function. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Huo, X.; Gao, L.; Zhang, J.; Ni, H.; Cao, L. NF-κB and Nrf2 pathways contribute to the protective effect of Licochalcone A on dextran sulphate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickert, G.; Neufert, C.; Leppkes, M.; Zheng, Y.; Wittkopf, N.; Warntjen, M.; Lehr, H.-A.; Hirth, S.; Weigmann, B.; Wirtz, S. STAT3 links IL-22 signaling in intestinal epithelial cells to mucosal wound healing. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, K.; Ogawa, A.; Mizoguchi, E.; Shimomura, Y.; Andoh, A.; Bhan, A.K.; Blumberg, R.S.; Xavier, R.J.; Mizoguchi, A. IL-22 ameliorates intestinal inflammation in a mouse model of ulcerative colitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; de Haar, C.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; van der Woude, C.J. SOCS3 in immune regulation of inflammatory bowel disease and inflammatory bowel disease-related cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012, 23, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Tian, H.; Tian, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Wang, X. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor/IL-22/Stat3 signaling pathway is involved in the modulation of intestinal mucosa antimicrobial molecules by commensal microbiota in mice. Innate Immun. 2018, 24, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, A. Activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in Alzheimer’s disease: Role of tryptophan metabolites generated by gut host-microbiota. J. Mol. Med. 2023, 101, 201–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleaga, C.; García, M.; Solé, A.; Ciudad, C.J.; Izquierdo-Pulido, M.; Noé, V. CYP1A1 is overexpressed upon incubation of breast cancer cells with a polyphenolic cocoa extract. Eur. J. Nutr. 2012, 51, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-Y.; Wang, X.-J.; Su, Y.-I.; Wang, Q.; Huang, S.-W.; Pan, Z.-F.; Chen, Y.-P.; Liang, J.-J.; Zhang, M.-L.; Xie, X.-Q. Baicalein ameliorates ulcerative colitis by improving intestinal epithelial barrier via AhR/IL-22 pathway in ILC3s. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 1495–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, S.; Zhang, M.; Su, Y.; Pan, Z.; Liang, J.; Xie, X.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhou, L. Gegen Qinlian decoction activates AhR/IL-22 to repair intestinal barrier by modulating gut microbiota-related tryptophan metabolism in ulcerative colitis mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 302, 115919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Bodduluri, S.R.; Baby, B.V.; Hegde, B.; Kotla, N.G.; Hiwale, A.A.; Saiyed, T.; Patel, P.; Vijay-Kumar, M. Enhancement of the gut barrier integrity by a microbial metabolite through the Nrf2 pathway. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qi, Y.; Zheng, H. Dietary polyphenol, gut microbiota, and health benefits. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Gao, R.; Yan, X.; Huang, L.; Qin, H. Probiotics improve gut microbiota dysbiosis in obese mice fed a high-fat or high-sucrose diet. Nutrition 2019, 60, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoensiddhi, S.; Conlon, M.A.; Vuaran, M.S.; Franco, C.M.; Zhang, W. Polysaccharide and phlorotannin-enriched extracts of the brown seaweed Ecklonia radiata influence human gut microbiota and fermentation in vitro. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 2407–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y.; Pan, M.; Zhao, G. Effects of Phlorotannins from Sargassum on In Vitro Rumen Fermentation, Microbiota and Fatty Acid Profile. Animals 2023, 13, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leylabadlo, H.E.; Ghotaslou, R.; Feizabadi, M.M.; Farajnia, S.; Moaddab, S.Y.; Ganbarov, K.; Khodadadi, E.; Tanomand, A.; Sheykhsaran, E.; Yousefi, B. The critical role of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in human health: An overview. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ji, X.; Lu, G.; Zhang, F. The potential of Akkermansia muciniphila in inflammatory bowel disease. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 5785–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Peng, K.; Xiao, S.; Long, Y.; Yu, Q. The role of Lactobacillus in inflammatory bowel disease: From actualities to prospects. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, D.K.; Mohan, K.; Zhang, S.; Ganesan, A.R. Dieckol: A brown algal phlorotannin with biological potential. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 111988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, G.; Yang, Y.; Song, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lai, P.; Wang, S.; Ai, L. Lactobacillus plantarum AR113 alleviates DSS-induced colitis by regulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway and gut microbiota composition. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 67, 103854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sadi, R.; Nighot, P.; Nighot, M.; Haque, M.; Rawat, M.; Ma, T.Y. Lactobacillus acidophilus induces a strain-specific and toll-like receptor 2–dependent enhancement of intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier and protection against intestinal inflammation. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negara, B.F.S.P.; Sohn, J.H.; Kim, J.-S.; Choi, J.-S. Effects of phlorotannins on organisms: Focus on the safety, toxicity, and availability of phlorotannins. Foods 2021, 10, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.A.; Jin, S.E.; Ahn, B.R.; Lee, C.M.; Choi, J.S. Anti-inflammatory activity of edible brown alga Eisenia bicyclis and its constituents fucosterol and phlorotannins in LPS-stimulated RAW264. 7 macrophages. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 59, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, R.; Hemaiswarya, S.; Arunkumar, K.; Mathiyazhagan, N.; Kandasamy, S.; Arun, A.; Ramasamy, P. Efficacy of Eisenia bicyclis phlorotannins in the treatment of diabetes and reducing inflammation. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chu, J.S.; Fix, J.A. Colon-specific drug delivery: New approaches and in vitro/in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 235, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Shrestha, N.; Préat, V.; Beloqui, A. An overview of in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo models for studying the transport of drugs across intestinal barriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 175, 113795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Guo, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Wang, J. Eckol protects against acute experimental colitis in mice: Possible involvement of Reg3g. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 73, 104088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, M.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Han, J.K.; Kim, J.; Yang, H.; Yoon, M.; Kim, J.; Kang, S.W.; Cho, S. Phlorotannin supplement decreases wake after sleep onset in adults with self-reported sleep disturbance: A randomized, controlled, double-blind clinical and polysomnographic study. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Incà, R.; Barollo, M.; Scarpa, M.; Grillo, A.R.; Brun, P.; Vettorato, M.G.; Castagliuolo, I.; Sturniolo, G.C. Rectal administration of Lactobacillus casei DG modifies flora composition and Toll-like receptor expression in colonic mucosa of patients with mild ulcerative colitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
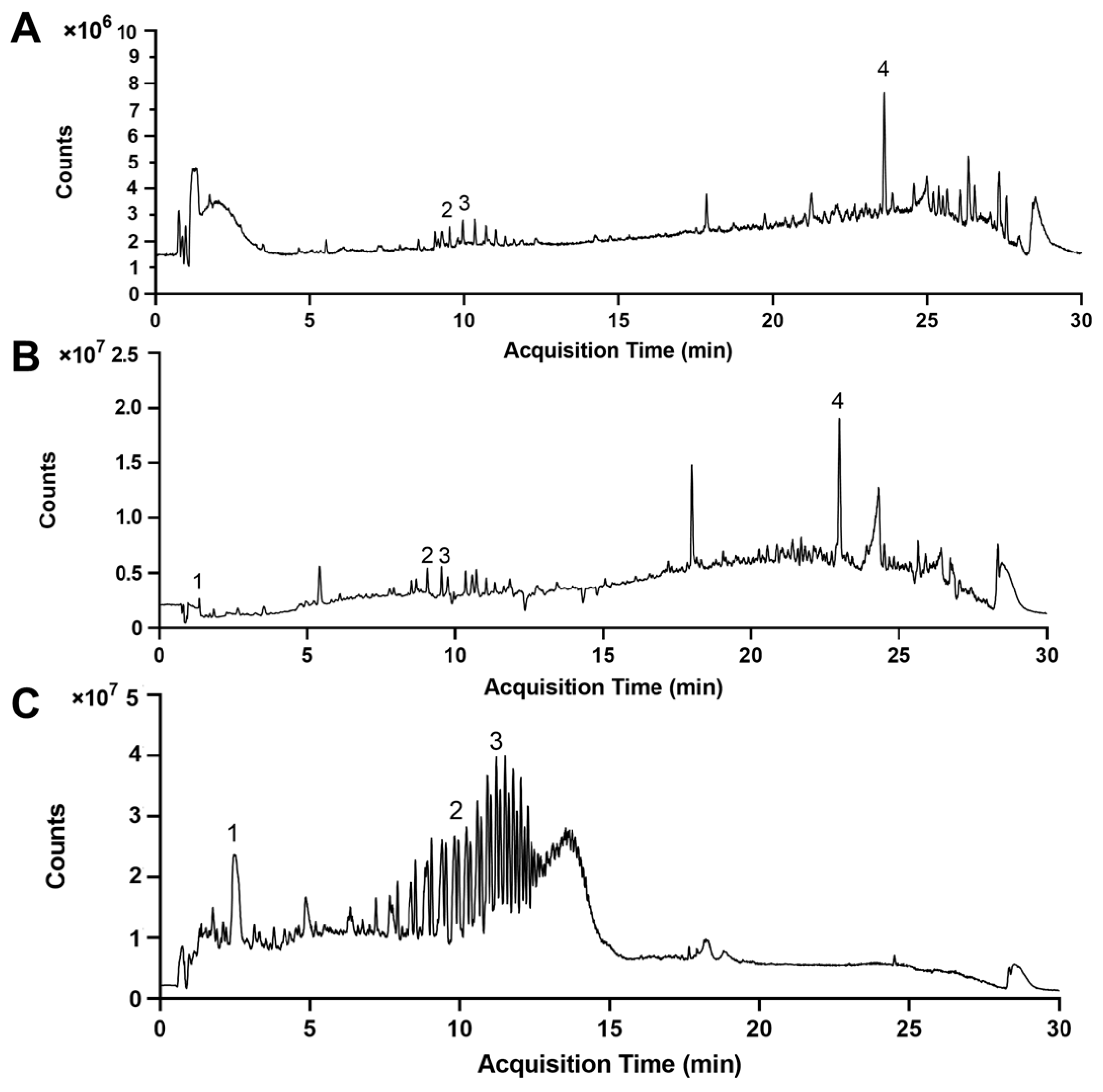

| Peak | Compound Name | Molecular Formula | [M + H]+ | Fragment Ion (m/z) | EB-Met | EB-EtOAc | Fermented EB-EtOAC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (min) | Content * | Time (min) | Content * | Time (min) | Content * | |||||
| 1 | Phloroglucinol | C6H6O3 | 127.0389 | 127.0401, 127.0393, 128.0392 | - | - | 2.177 | 3.605 | 2.47 | 237.385 |
| 2 | 7-Phloroeckol | C24H16O12 | 497.0703 | 498.0741, 499.0761, 499.0765 | 9.051 | 3.005 | 9.058 | 12.980 | 9.059 | 54.654 |
| 3 | Phlorofucofuroeckol A | C30H18O14 | 603.0763 | 604.0787, 605.0809 | 9.754 | 5.216 | 10.355 | 18.240 | 9.835 | 92.306 |
| 4 | Dieckol | C36H22O18 | 743.42 | 743.0865, 744.0898, 745.0923 | 22.98 | 37.275 | 22.985 | 89.707 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Go, Y.G.; Wang, Q.; Park, J.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, H. Phlorotannins Isolated from Eisenia bicyclis and Lactobacillus casei Ameliorate Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice through the AhR Pathway. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072835
Go YG, Wang Q, Park J, Lee H-J, Kim H. Phlorotannins Isolated from Eisenia bicyclis and Lactobacillus casei Ameliorate Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice through the AhR Pathway. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(7):2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072835
Chicago/Turabian StyleGo, Yeon Gyeong, Qunzhe Wang, Jumin Park, Hae-Jeung Lee, and Hyemee Kim. 2024. "Phlorotannins Isolated from Eisenia bicyclis and Lactobacillus casei Ameliorate Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice through the AhR Pathway" Applied Sciences 14, no. 7: 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072835
APA StyleGo, Y. G., Wang, Q., Park, J., Lee, H.-J., & Kim, H. (2024). Phlorotannins Isolated from Eisenia bicyclis and Lactobacillus casei Ameliorate Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice through the AhR Pathway. Applied Sciences, 14(7), 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072835







