Migration Behaviour of the Combined Pollutants of Cadmium and 2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-Hexabrominated Diphenyl Ether (BDE-153) in Amaranthus mangostanus L. and Their Toxicity to A. mangostanus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Experimental Design
2.1.1. Chemicals
2.1.2. Hydroponic Design
2.2. Cd Measurement
2.3. GC/MS Analysis
2.4. Determination of the Chlorophyll Content
2.5. In Vivo ROS Detection and Antioxidant Enzyme Analysis
2.5.1. Apical Plasma Membrane Integrity and Apical ·O2− Fluorescence Intensity
2.5.2. Antioxidant Enzymes
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
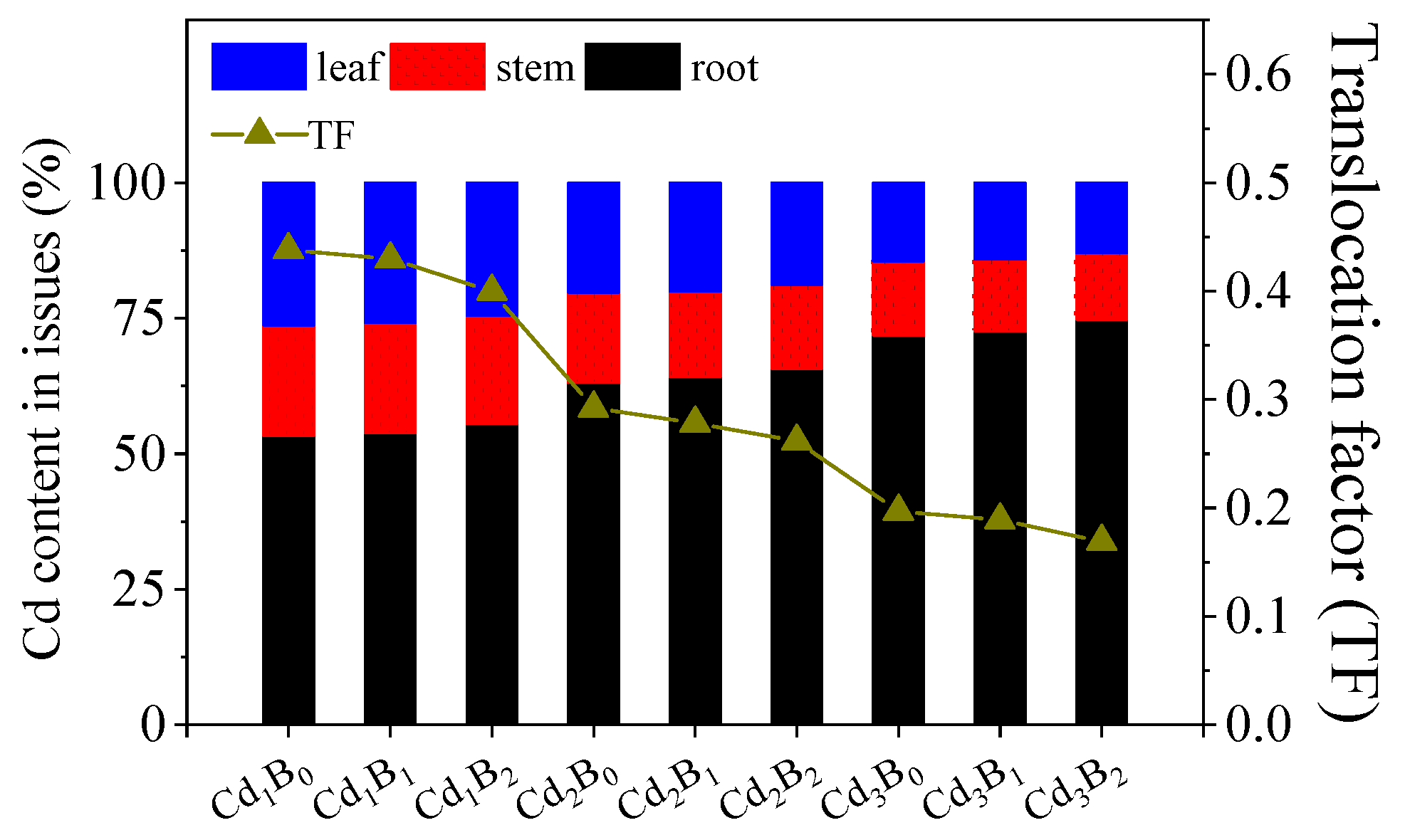
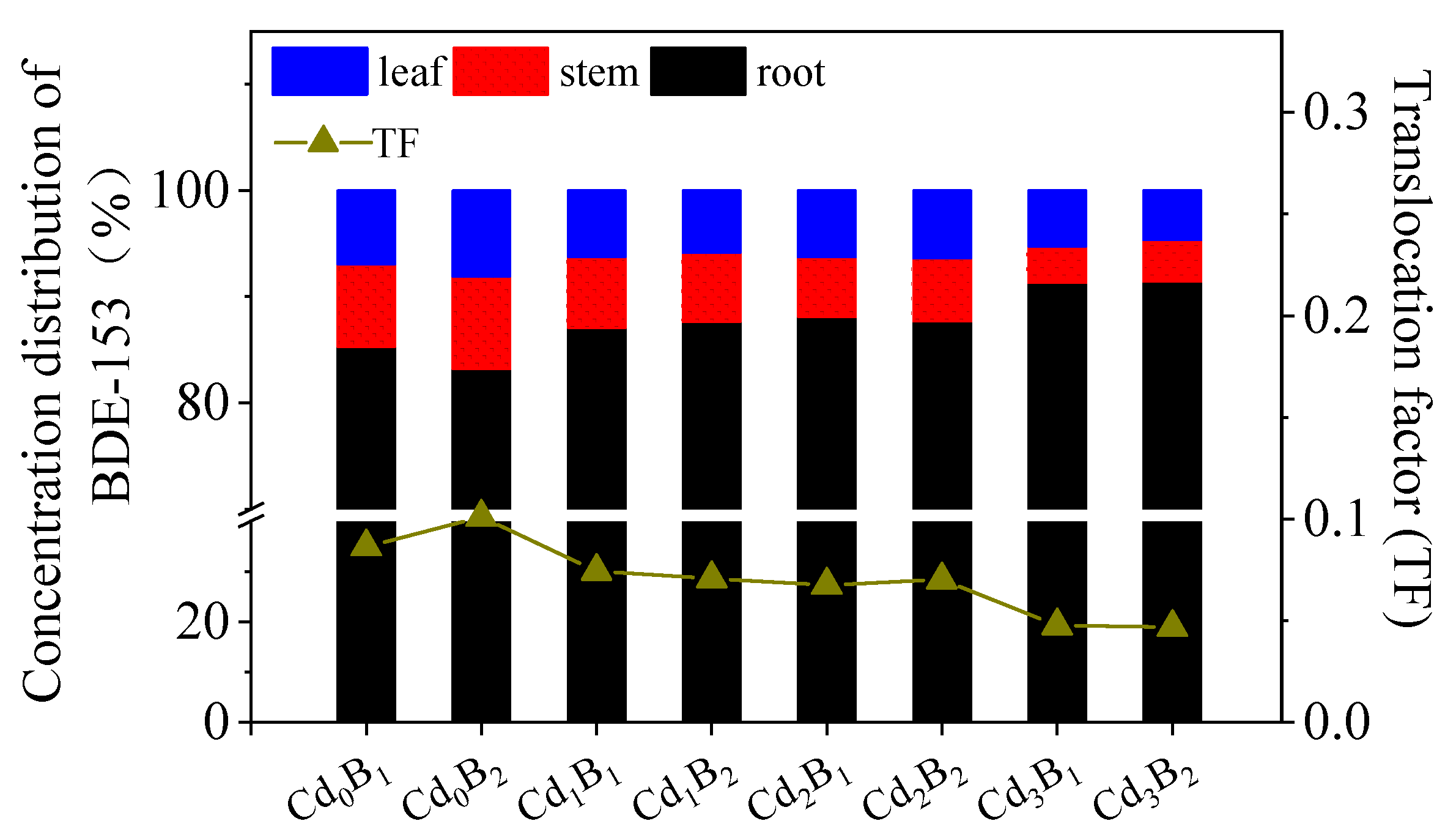
3.1. Accumulation and Transfer of the Combined Pollutants in Amaranth
3.1.1. Cd Content in the Roots, Stems, and Leaves of Amaranth Affected by BDE-153
3.1.2. BDE-153 Content in the Amaranth as Affected by Cd
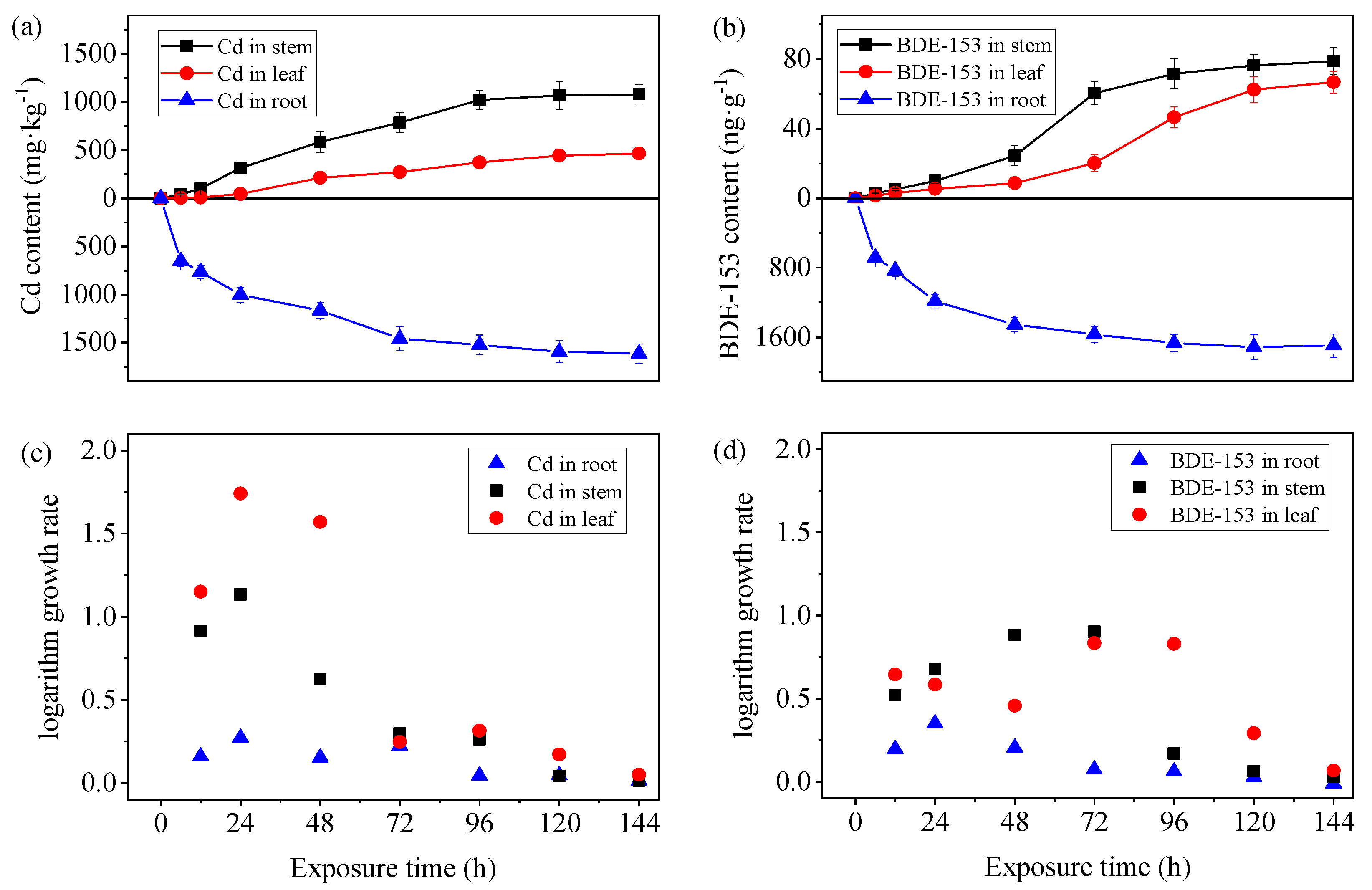
3.2. Variation in Kinetics of Pollutant Uptake by Amaranth
3.3. Amaranth Biomass Affected by the Combined Pollutants of Cd and BDE-153
3.4. Chlorophyll Content Affected by the Combined Pollutants of Cd and BDE-153
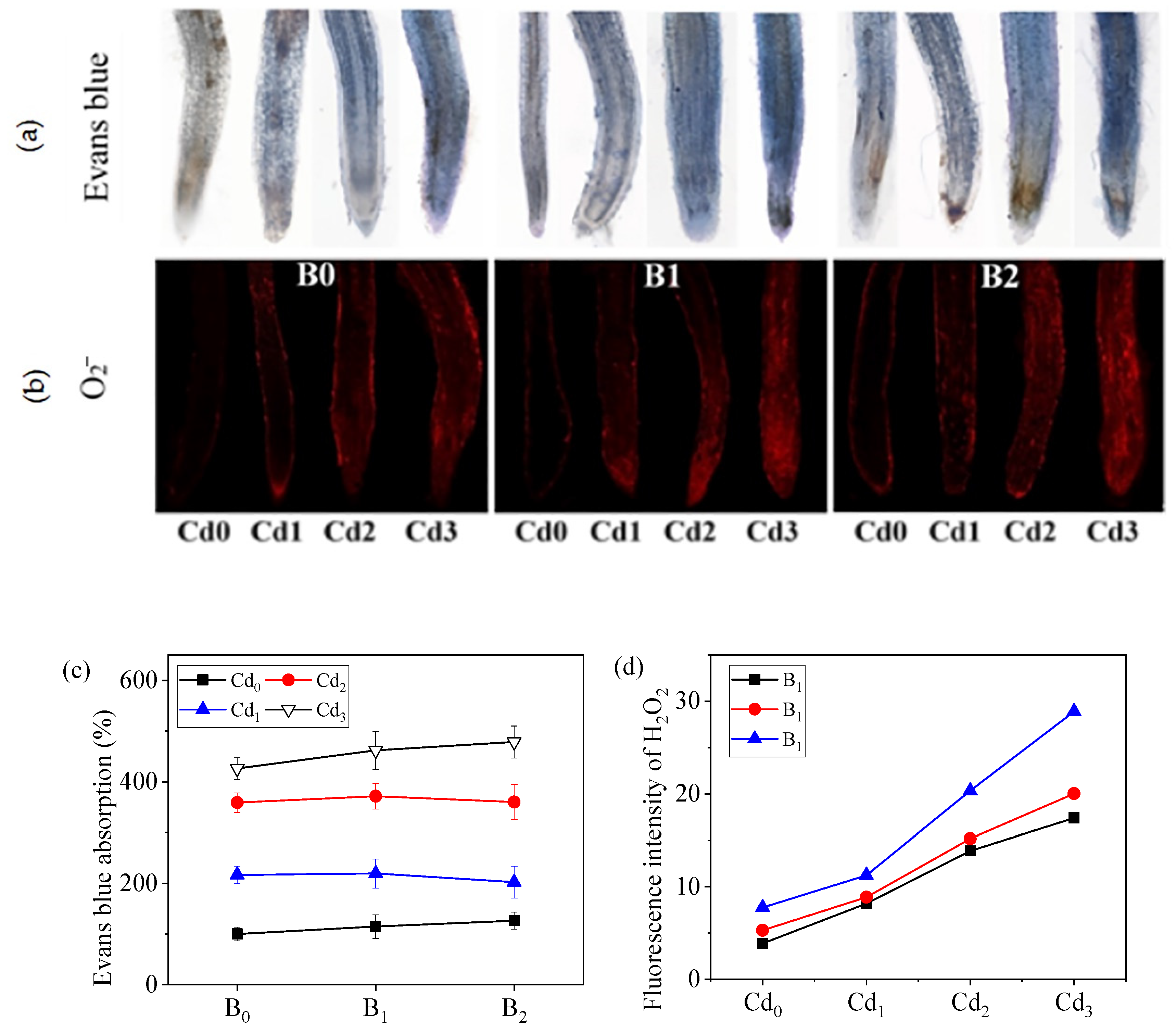
3.5. Apical Plasma Membrane Integrity and Apical ·O2− Fluorescence Intensity
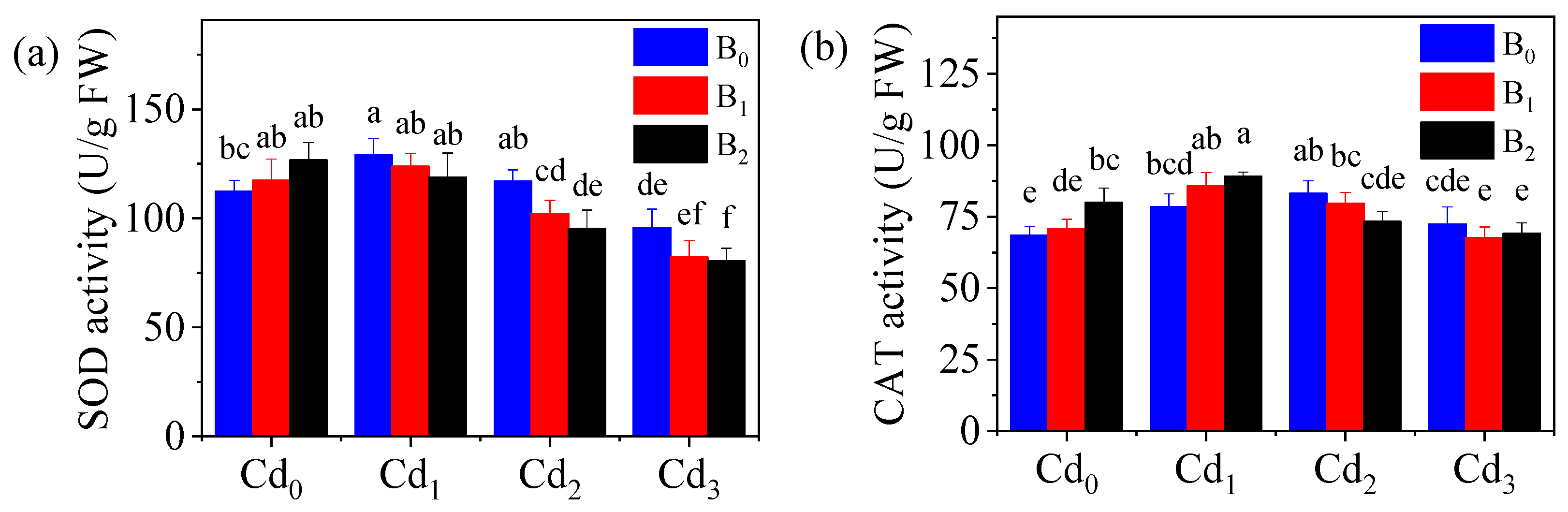
3.6. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity Affected by the Combined Pollutants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clemens, S.; Aarts, M.; Thomine, S.; Verbruggen, N. Plant science: The key to preventing slow cadmium poisoning. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.X.; Wang, N.; Zhang, H.L.; Yang, X.Y. Heavy metal contamination and risk assessment of human exposure near an e-waste processing site. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B—Soil Plant Sci. 2017, 67, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.P.; Ma, C.X.; Jia, W.L.; Wang, D.; Sun, H.W.; Xing, B.S. Combined effects of dissolved humic acids and tourmaline on the accumulation of 2, 2′, 4, 4′, 5, 5′-hexabrominated diphenyl ether (BDE-153) in Lactuca sativa. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.H.; Huang, H.L.; Wen, B.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.Z. Phytotoxicity of brominated diphenyl ether-47 (BDE-47) and its hydroxylated and methoxylated analogues (6-OH-BDE-47 and 6-MeO-BDE-47) to maize (Zea mays L.). Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, D.M.; Zhong, T.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Cheng, M.; Li, X.H. Assessment of cadmium (Cd) concentration in arable soil in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4932–4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mapanda, F.; Mangwayana, E.N.; Nyamangara, J.; Giller, K.E. The effect of long-term irrigation using wastewater on heavy metal contents of soils under vegetables in Harare, Zimbabwe. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 107, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M.; Song, Q.J.; Tang, Y.; Li, W.L.; Xu, J.M.; Wu, J.J.; Wang, F.; Brookes, P.C. Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil-vegetable system: A multi-medium analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveena, S.M.; Omar, N.A. Heavy metal exposure from cooked rice grain ingestion and its potential health risks to humans from total and bioavailable forms analysis. Food Chem. 2017, 235, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.Z.; Xiao, W.D.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhao, S.P.; Wang, G.J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in vegetables and relationships with soil heavy metal distribution in Zhejiang province, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Yang, L.S.; Li, Y.H.; Li, H.R.; Wang, W.Y.; Ye, B.X. Impacts of lead/zinc mining and smelting on the environment and human health in China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 2261–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Y.; Yu, M.; Luo, X.J.; Chen, S.J.; Mai, B.X. The factors controlling the partitioning of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated biphenyls in the water-column of the Pearl River Estuary in South China. Mar. Pollut. Bulletin. 2011, 62, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.F.; Wang, X.T.; Zhu, K.; Wu, M.H.; Sheng, G.Y.; Fu, J.M. Occurrence, compositional profiles and possible sources of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in urban soils of Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.W.; Zhu, S.Z.; Chen, P.; Zhu, L.Y. Bioaccumulation and bioavailability of polybrominated diphynel ethers (PBDEs) in soil. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2387–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usenko, C.Y.; Robinson, E.M.; Usenko, S.; Brooks, B.W.; Bruce, E.D. PBDE developmental effects on embryonic zebrafish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, G.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Choi, Y.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.; Moon, H.B.; et al. Occurrences of major polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in maternal and fetal cord blood sera in Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 491, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Lin, K.F.; Deng, J.J.; Fu, X.X.; Xu, Z.M. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in indoor air during waste TV recycling process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 238, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.C.; Yu, S.Y.; Wu, D.; Huang, J.X.; Liu, T.; Xiao, J.P.; Huang, W.X.; Gao, Y.H.; Li, X.; Zeng, W.L.; et al. Disruption of thyroid hormone regulated proteins and gene expression by polychlorinated biphenyls, polybrominated diphenyl ethers and new flame retardants in residents of an e-waste region. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.Y.; Zhao, Y.X.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Qin, Z.F.; Ruan, X.L.; Zhang, Y.C.; Chen, B.J.; Li, Y.; Yan, S.S.; Qin, X.F.; et al. Determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in human semen. Environ. Int. 2012, 42, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moukas, A.I.; Maragou, N.C.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Calokerinos, A.C. Determination of pybrominated dphenyl eher fame rtardants in srface wter by lquid cromatography-amospheric pessure potoionization tndem mss sectrometry. Anal. Lett. 2018, 51, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.D.; Zhao, X.Z.; Wang, Y.F.; Shi, Z.X. Tetrabromobisphenol A, hexabromocyclododecane isomers and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in foodstuffs from Beijing, China: Contamination levels, dietary exposure and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cang, L.; Zhou, D.M.; Wang, Q.Y.; Wu, D.Y. Effects of electrokinetic treatment of a heavy metal contaminated soil on soil enzyme activities. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1602–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.R.; Wang, Y.; Luo, C.L.; Jiang, L.F.; Song, M.K.; Zhang, D.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, G. Could uptake and acropetal translocation of PBDEs by corn be enhanced following Cu exposure? Evidence from a root damage experiment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Su, X.L.; Xu, Y.X.; Wu, X.J.; Zhang, M. Effect of copper on in vivo fate of BDE-209 in pumpkin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.; An, S.; Xiong, B.; Li, H.; Cui, C.Z.; Lin, K.F. Ecotoxicological effects of decabromodiphenyl ether and cadmium contamination on soil microbes and enzymes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 82, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.Z.; Liu, M.; Tian, S.Y.; Zhu, L.Y. Bioaccumulation and single and joint toxicities of penta-BDE and cadmium to earthworms (Eisenia fetida) exposed to spiked soils. Sci. China Chem. 2010, 53, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.L.; Ma, C.X.; White, J.C.; Yin, M.F.; Cao, H.M.; Wang, J.C.; Wang, C.P.; Sun, H.W.; Xing, B.S. Effects of biochar on 2, 2′, 4, 4′, 5, 5′-hexabrominated diphenyl ether (BDE-153) fate in Amaranthus mangostanus L.: Accumulation, metabolite formation, and physiological response. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1154–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnon, D.I. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1949, 24, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Matsumoto, H. Lipid peroxidation is an early symptom triggered by aluminum, but not the primary cause of elongation inhibition in pea roots. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.; Fryer, M.; Grosso, A. Plant uptake of non-ionic organic chemicals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Xia, B.; Zhu, L.; Chen, B.J.; Sun, X.M.; Zhao, X.G.; Tang, X.X.; Qu, K.M. Acute toxicity of four polybrominated diphenyl ether congeners to marine organisms: Chlorella pyrenoidosa, daphnia magna, and scophthalmus maximus. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2019, 40, 88–97. [Google Scholar]
- Bizkarguenaga, E.; Iparraguirre, A.; Oliva, E.; Quintana, J.B.; Rodil, R.; Fernandez, L.A.; Zuloaga, O.; Prieto, A. Uptake of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by carrot and lettuce crops grown in compost-amended soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 3847–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biteau, B.; Hochmuth, C.E.; Jasper, H. Activity in somatic stem cells causes loss of tissue homeostasis in the aging drosophila gut. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 3, 442–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchon, N.; Broderick, N.A.; Chakrabarti, S.; Lemaitre, B. Invasive and indigenous microbiota impact intestinal stem cell activity through multiple pathways in Drosophila. Genes 2009, 23, 2333–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amcheslavsky, A.; Jiang, J.; Ip, Y.T. Tissue Damage-induced intestinal stem cell division in drosophila. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 4, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.L.; Zhang, S.Z.; Christie, P.; Wang, S.; Xie, M. Behavior of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) in the soil-plant system: Uptake, translocation, and metabolism in plants and dissipation in soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Rengel, Z.; Meney, K.; Pantelic, L.; Tomanovic, R. Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) mediate cadmium toxicity to an emergent wetland species. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, A.; Alexander, T.; Brandt, S.; Haas, R.; Werner, D. Reduction by fluoranthene of copper and lead accumulation in Triticum aestivum L. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1994, 53, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutzendubel, A.; Schwanz, P.; Teichmann, T.; Gross, K.; Langenfeld-Heyser, R.; Godbold, D.L.; Polle, A. Cadmium-induced changes in antioxidative systems, hydrogen peroxide content, and differentiation in scots pine roots. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; He, W.; Wang, A.; Xia, T.; Xu, B.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X. PBDE-47-induced oxidative stress, DNA damage and apoptosis in primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Neurotoxicology 2008, 29, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Puertas, M.C.; Rodriguez-Serrano, M.; Corpas, F.J.; Gomez, M.; Del Rio, L.A.; Sandalio, L.M. Cadmium-induced subcellular accumulation of O2.- and H2O2 in pea leaves. Plant Cell Environ. 2004, 27, 1122–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, K.; Cuypers, A.; Lambrechts, A.; Semane, B.; Hoet, P.; Van Laere, A.; Vangronsveld, J. Induction of oxidative stress and antioxidative mechanisms in phaseolus vulgaris after Cd application. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2005, 43, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; White, J.C.; Dhankher, O.P.; Xing, B. Metal-based nanotoxicity and detoxification pathways in higher plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7109–7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Devi, S.R.; Rikiishi, S.; Matsumoto, H. Aluminum toxicity is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction and the production of reactive oxygen species in plant cells. Plant Physiol. 2002, 128, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, W.; Wang, J.; Cui, S.; Wu, S.; Wang, C. Migration Behaviour of the Combined Pollutants of Cadmium and 2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-Hexabrominated Diphenyl Ether (BDE-153) in Amaranthus mangostanus L. and Their Toxicity to A. mangostanus. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14062631
Pan W, Wang J, Cui S, Wu S, Wang C. Migration Behaviour of the Combined Pollutants of Cadmium and 2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-Hexabrominated Diphenyl Ether (BDE-153) in Amaranthus mangostanus L. and Their Toxicity to A. mangostanus. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(6):2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14062631
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Weijie, Jicheng Wang, Shengyan Cui, Sai Wu, and Cuiping Wang. 2024. "Migration Behaviour of the Combined Pollutants of Cadmium and 2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-Hexabrominated Diphenyl Ether (BDE-153) in Amaranthus mangostanus L. and Their Toxicity to A. mangostanus" Applied Sciences 14, no. 6: 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14062631
APA StylePan, W., Wang, J., Cui, S., Wu, S., & Wang, C. (2024). Migration Behaviour of the Combined Pollutants of Cadmium and 2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-Hexabrominated Diphenyl Ether (BDE-153) in Amaranthus mangostanus L. and Their Toxicity to A. mangostanus. Applied Sciences, 14(6), 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14062631




