Collaborative Encoding Method for Scene Text Recognition in Low Linguistic Resources: The Uyghur Language Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We created a real-world Uyghur text recognition dataset comprising 7267 training images and 1815 test images. Additionally, we employed data augmentation techniques to generate two enhanced datasets, Aug1 and Aug2, containing 254,345 and 3,052,140 scene images, respectively.
- (2)
- In the context of the low-resource Uyghur language, we propose a Collaborative Encoding Method (CEM) for scene text recognition. The encoding consists of three key modules: a Filter module, a Dual-Branch Feature Extraction (DBFE) module, and a Dynamic Fusion (DF) module. The Filter module aims to obtain multi-level low-level features, emphasizing textual information in the images and reducing irrelevant background noise. The DBFE module enables the model to effectively capture global and local details, thereby improving its ability to discern intricate features. The DF module provides the flexibility to choose the most suitable Transformer and CNN encoding weights, allowing optimal performance.
- (3)
- Our method achieves state-of-the-art results in Uyghur scene text recognition.
- (4)
- This article provides reference examples for other low-resource languages lacking real-world scene text recognition data, such as Mongolian, Kazakh, and Kyrgyz.
2. Related Work
3. Methodology
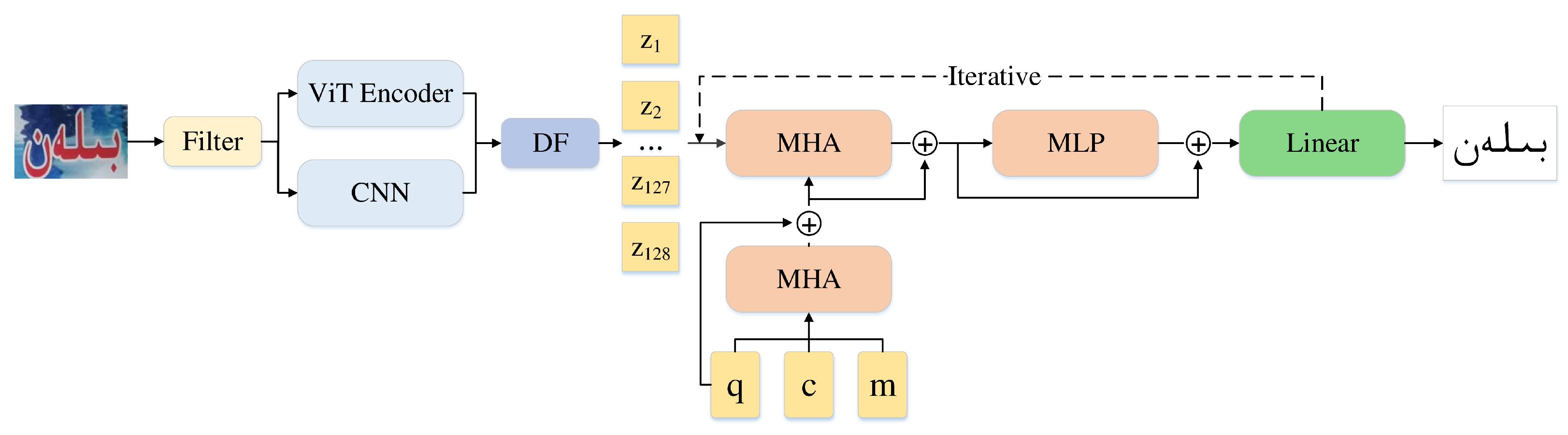
3.1. Encoder
3.1.1. Filter Module
3.1.2. Dual-Branch Feature Extraction Module
3.1.3. DF Module
3.2. Decoder
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Data Augmentation
4.3. Experimental Setup
4.4. Comparative Analysis with Existing Methods
4.5. Ablation Experiments
- (1)
- Using the filter module before the dual-branch feature extraction module and not using the filter module.
- (2)
- Utilizing three consecutive convolutional layers, ResNet17, and ResNet33 for the CNN branch.
- (3)
- Applying the CBAM module and not applying the CBAM module in the CNN branch.
- (4)
- Employing the dynamic fusion module and not employing the dynamic fusion module.
- (5)
- Investigating the impact of different encoding layers in the Transformer branch on model performance.
4.6. Failure Cases
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baek, J.; Kim, G.; Lee, J.; Park, S.; Han, D.; Yun, S.; Oh, S.J.; Lee, H. What is wrong with scene text recognition model comparisons? dataset and model analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 4715–4723. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Meng, G.; Pan, C. Scene text detection and recognition with advances in deep learning: A survey. Int. J. Doc. Anal. Recognit. 2019, 22, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; He, X.; Yao, C. Scene text detection and recognition: The deep learning era. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 161–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Doermann, D. Text detection and recognition in imagery: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 37, 1480–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yao, C.; Bai, X. Scene text detection and recognition: Recent advances and future trends. Front. Comput. Sci. 2016, 10, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tao, Y.; Du, K.; Ding, W.; Wang, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, W. Character-level street view text spotting based on deep multisegmentation network for smarter autonomous driving. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2021, 3, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.S.; Chen, H.; Chen, D.; Schroth, G.; Grzeszczuk, R.; Girod, B. Mobile visual search on printed documents using text and low bit-rate features. In Proceedings of the 2011 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 11–14 September 2011; pp. 2601–2604. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, N.; Islam, Z.; Noor, N. A survey on optical character recognition system. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.05703. [Google Scholar]
- Sabu, A.M.; Das, A.S. A survey on various optical character recognition techniques. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Emerging Devices and Smart Systems (ICEDSS), Namakkal, India, 2–3 March 2018; pp. 152–155. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, G. Twenty years of document image analysis in PAMI. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 38–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, A.; Mandaviya, K.; Badelia, P.; Ghosh, S.K. Optical Character Recognition Systems for Different Languages with Soft Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Somerville, P.J. Method and Apparatus for Barcode Recognition in a Digital Image. U.S. Patent 4,992,650, 12 February 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Babenko, B.; Belongie, S. End-to-end scene text recognition. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 1457–1464. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Belongie, S. Word spotting in the wild. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2010: 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; Proceedings, Part I 11. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 591–604. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, C.; Bai, X.; Shi, B.; Liu, W. Strokelets: A learned multi-scale representation for scene text recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 4042–4049. [Google Scholar]
- Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O.; Le, Q.V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.3215. [Google Scholar]
- Rang, M.; Bi, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Han, K. Large OCR Model: An Empirical Study of Scaling Law for OCR. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2401.00028. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Fujitake, M. Dtrocr: Decoder-only transformer for optical character recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 4–8 January 2024; pp. 8025–8035. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jia, C.; Yin, X.; Li, C.; Du, Y.; Jiang, Y.G. Context Perception Parallel Decoder for Scene Text Recognition. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.12270. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Da, C.; Yao, C. Multi-granularity prediction for scene text recognition. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 339–355. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Zhu, J.; Peng, L.; Guo, Y. RNN based Uyghur text line recognition and its training strategy. In Proceedings of the 2016 12th IAPR Workshop on Document Analysis Systems (DAS), Santorini, Greece, 11–14 April 2016; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrayim, M.; Simayi, W.; Hamdulla, A. Unconstrained online handwritten Uyghur word recognition based on recurrent neural networks and connectionist temporal classification. Int. J. Biom. 2021, 13, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Mahpirat; Kang, W.; Aysa, A.; Ubul, K. Multi-lingual Hybrid Handwritten Signature Recognition Based on Deep Residual Attention Network. In Proceedings of the Biometric Recognition: 15th Chinese Conference, CCBR 2021, Shanghai, China, 10–12 September 2021; Proceedings 15. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 148–156. [Google Scholar]
- Xamxidin, N.; Mahpirat; Yao, Z.; Aysa, A.; Ubul, K. Multilingual Offline Signature Verification Based on Improved Inverse Discriminator Network. Information 2022, 13, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Dong, L.; Zhang, W.N.; Liu, T.; Wei, F. Clip models are few-shot learners: Empirical studies on vqa and visual entailment. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.07190. [Google Scholar]
- Patashnik, O.; Wu, Z.; Shechtman, E.; Cohen-Or, D.; Lischinski, D. Styleclip: Text-driven manipulation of stylegan imagery. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 2085–2094. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.; Kwon, T.; Ye, J.C. Diffusionclip: Text-guided diffusion models for robust image manipulation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2426–2435. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Ji, L.; Zhong, M.; Chen, Y.; Lei, W.; Duan, N.; Li, T. Clip4clip: An empirical study of clip for end to end video clip retrieval and captioning. Neurocomputing 2022, 508, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.; Merrill, W.; Darrell, T.; Gardner, M.; Singh, S.; Rohrbach, A. Reclip: A strong zero-shot baseline for referring expression comprehension. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.05991. [Google Scholar]
- Hessel, J.; Holtzman, A.; Forbes, M.; Bras, R.L.; Choi, Y. Clipscore: A reference-free evaluation metric for image captioning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.08718. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y. Symmetrical Linguistic Feature Distillation with CLIP for Scene Text Recognition. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 509–518. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Xue, X. Chinese Text Recognition with A Pre-Trained CLIP-Like Model through Image-IDS Aligning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 11943–11952. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Yang, Y. CLIP4STR: A Simple Baseline for Scene Text Recognition with Pre-trained Vision-Language Model. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.14014. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, A.; Fernández, S.; Gomez, F.; Schmidhuber, J. Connectionist temporal classification: Labelling unsegmented sequence data with recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 25–29 June 2006; pp. 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Borisyuk, F.; Gordo, A.; Sivakumar, V. Rosetta: Large scale system for text detection and recognition in images. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018; pp. 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, B.; Bai, X.; Yao, C. An end-to-end trainable neural network for image-based sequence recognition and its application to scene text recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 2298–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Huang, W.; Qiao, Y.; Loy, C.; Tang, X. Reading scene text in deep convolutional sequences. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 12–17 February 2016; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Atienza, R. Vision transformer for fast and efficient scene text recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Lausanne, Switzerland, 5–10 September 2021; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 319–334. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jia, C.; Yin, X.; Zheng, T.; Li, C.; Du, Y.; Jiang, Y.G. Svtr: Scene text recognition with a single visual model. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.00159. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, S.; Xie, H.; Wang, Y.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, Y. Read like humans: Autonomous, bidirectional and iterative language modeling for scene text recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 7098–7107. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Lv, T.; Chen, J.; Cui, L.; Lu, Y.; Florencio, D.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Wei, F. Trocr: Transformer-based optical character recognition with pre-trained models. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 13094–13102. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, C.; Yang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Parekh, Z.; Pham, H.; Le, Q.; Sung, Y.H.; Li, Z.; Duerig, T. Scaling up visual and vision-language representation learning with noisy text supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 4904–4916. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Chen, D.; Chen, Y.L.; Codella, N.; Dai, X.; Gao, J.; Hu, H.; Huang, X.; Li, B.; Li, C.; et al. Florence: A new foundation model for computer vision. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.11432. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Z. A Three-Stage Uyghur Recognition Model Combining the Attention Mechanism and Different Convolutional Recurrent Networks. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrayim, M.; Mattohti, A.; Hamdulla, A. An effective method for detection and recognition of uyghur texts in images with backgrounds. Information 2022, 13, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ao, N.; Guo, R.; Mamat, H.; Ubul, K. Scene Uyghur Recognition with Embedded Coordinate Attention. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning (PRML), Chengdu, China, 22–24 July 2022; pp. 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Kong, F.; Xu, M.; Silamu, W.; Li, Y. Scene Uyghur Recognition Based on Visual Prediction Enhancement. Sensors 2023, 23, 8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Osindero, S. Recursive recurrent nets with attention modeling for ocr in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2231–2239. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, T.; Han, J.; Liu, J.; Ding, E. Towards accurate scene text recognition with semantic reasoning networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 12113–12122. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T.; Chen, Z.; Fang, S.; Xie, H.; Jiang, Y.G. Cdistnet: Perceiving multi-domain character distance for robust text recognition. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2111.11011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, D.; Atienza, R. Scene text recognition with permuted autoregressive sequence models. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 178–196. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, M.; Silamu, W.; Li, Y. A data augmentation strategy for scene text recognition. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Control, Electronics and Computer Technology (ICCECT), Jilin, China, 28–30 April 2023; pp. 968–973. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]





| Models | Optimizer | lr | Image_Size | Patch_Size | En_Layer | De_Layer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRNN | Adam | [32, 128] | − | − | − | |
| TRBA | Adam | [32, 128] | − | − | − | |
| ViTSTR | Adam | [224, 224] | [16, 16] | 12 | − | |
| PARSeq | Adam | [32, 128] | [4, 8] | 12 | 1 | |
| CDistNet | Adam | [32, 128] | − | 3 | 3 | |
| MGP-tiny-char | Adadelta | 1 | [32, 128] | [4, 4] | 12 | − |
| CEM(ours) | Adam | [32, 128] | [4, 8] | 6 | 1 |
| Models | Test Accuracy (%)/Train Dataset | Params (M) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw + A1 | Raw + A1 + A2 | ||
| CRNN | 78.7 | 80.2 | 8.3 |
| TRBA | 87.2 | 90.3 | 49.8 |
| ViTSTR | - | 73.1 | 21.7 |
| PARSeq | 45.7 | 80.0 | 23.8 |
| CDistNet | 64.7 | 82.5 | 65.5 |
| MGP-tiny-char | 27.2 | 33.6 | 5.4 |
| CEM-tiny(ours) | 91.7 | 90.4 | 24.1 |
| CEM-base(ours) | 94.1 | 91.7 | 26.2 |
| Filter | CNN | CBAM | DF | Test Accuracy (%)/Train Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw + A1 | ||||
| ✓ | 3-Con | ✓ | ✓ | 91.7 |
| ✗ | 3-Con | ✓ | ✓ | 83.5 |
| ✓ | 3-Con | ✗ | ✓ | 91.5 |
| ✓ | 3-Con | ✓ | ✗ | 91.6 |
| ✓ | ResNet17 | ✓ | ✓ | 94.1 |
| ✗ | ResNet17 | ✓ | ✓ | 93.5 |
| ✓ | ResNet17 | ✗ | ✓ | 93.2 |
| ✓ | ResNet17 | ✓ | ✗ | 92.3 |
| ✓ | ResNet33 | ✓ | ✓ | 93.4 |
| ✗ | ResNet33 | ✓ | ✓ | 92.6 |
| ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | 79.2 |
| Transformer Encoder Layers | Test Accuracy (%)/Train Dataset | Params (M) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw + A1 | Raw + A1 + A2 | ||
| 6 | 91.7 | 90.4 | 24.1 M |
| 8 | 91.7 | 90.2 | 27.7 M |
| 12 | 91.1 | 90.4 | 34.8 M |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, M.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Silamu, W.; Li, Y. Collaborative Encoding Method for Scene Text Recognition in Low Linguistic Resources: The Uyghur Language Case Study. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14051707
Xu M, Zhang J, Xu L, Silamu W, Li Y. Collaborative Encoding Method for Scene Text Recognition in Low Linguistic Resources: The Uyghur Language Case Study. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(5):1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14051707
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Miaomiao, Jiang Zhang, Lianghui Xu, Wushour Silamu, and Yanbing Li. 2024. "Collaborative Encoding Method for Scene Text Recognition in Low Linguistic Resources: The Uyghur Language Case Study" Applied Sciences 14, no. 5: 1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14051707
APA StyleXu, M., Zhang, J., Xu, L., Silamu, W., & Li, Y. (2024). Collaborative Encoding Method for Scene Text Recognition in Low Linguistic Resources: The Uyghur Language Case Study. Applied Sciences, 14(5), 1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14051707






