Exploring the Effectiveness of Evaluation Practices for Computer-Generated Nonverbal Behaviour
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Generating and Evaluating Gesture Behaviour
2.2. Listening Behaviour
2.3. Evaluation Strategies for Generated Human Behaviour
3. Designing a Questionnaire for ECAs
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data and Preprocessing
4.2. Models
4.2.1. StyleGestures
4.2.2. Baseline
4.3. Visualisation
4.4. User Studies
4.4.1. General Set-Up
4.4.2. Study 1: Human-Likeness for Gesticulation
4.4.3. Study 2: Appropriateness for Gesticulation
4.4.4. Study 3: Human-Likeness for Listening
4.4.5. Study 4: Appropriateness for Listening
4.4.6. Studies 5 and 6: Questionnaire
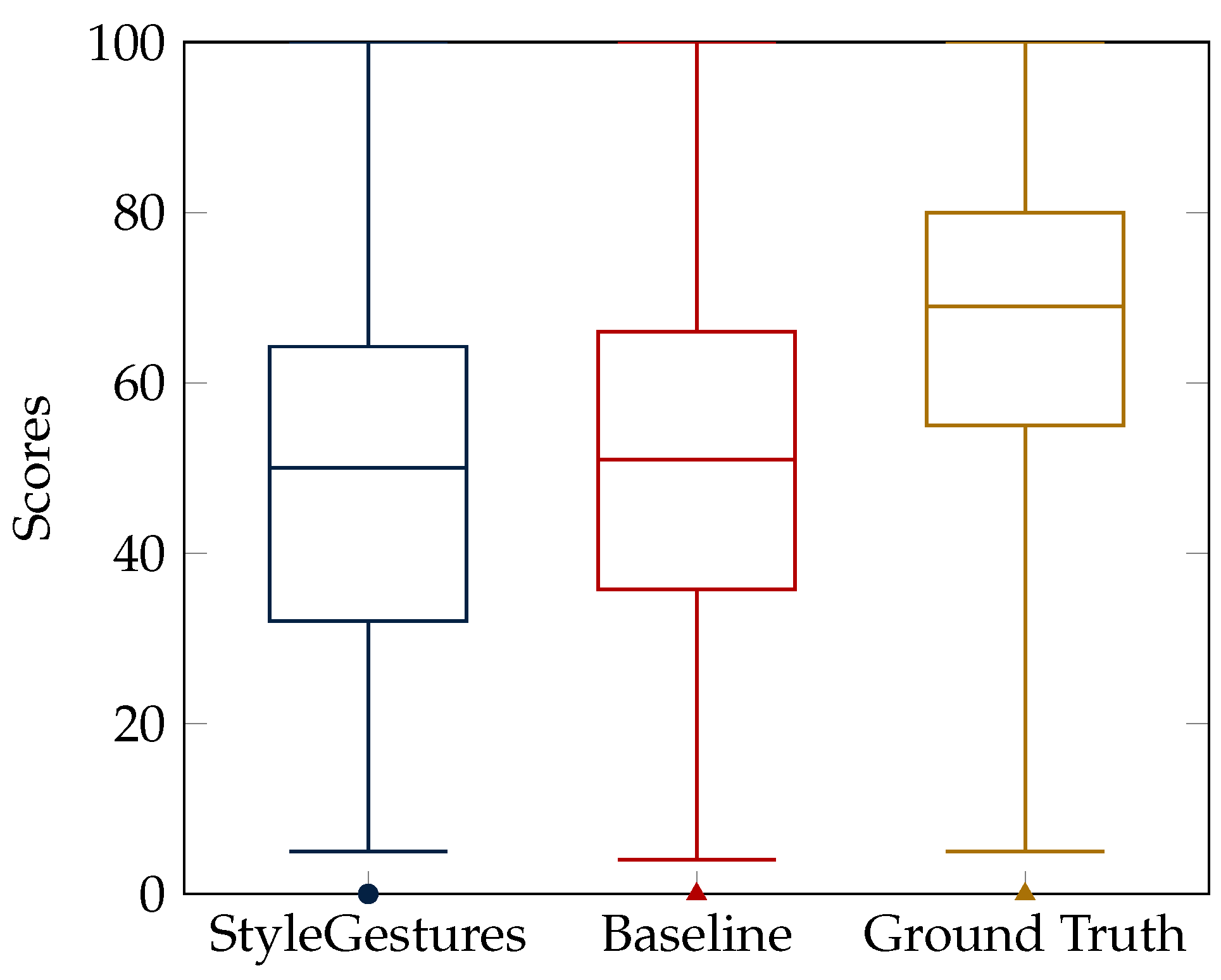
5. Results
5.1. User Studies
5.1.1. Study 1: ‘Human-Likeness for Gesticulation’
5.1.2. Study 2: Appropriateness for Gesticulation
5.1.3. Study 3: ‘Human-Likeness for Listening’
5.1.4. Study 4: Appropriateness for Listening
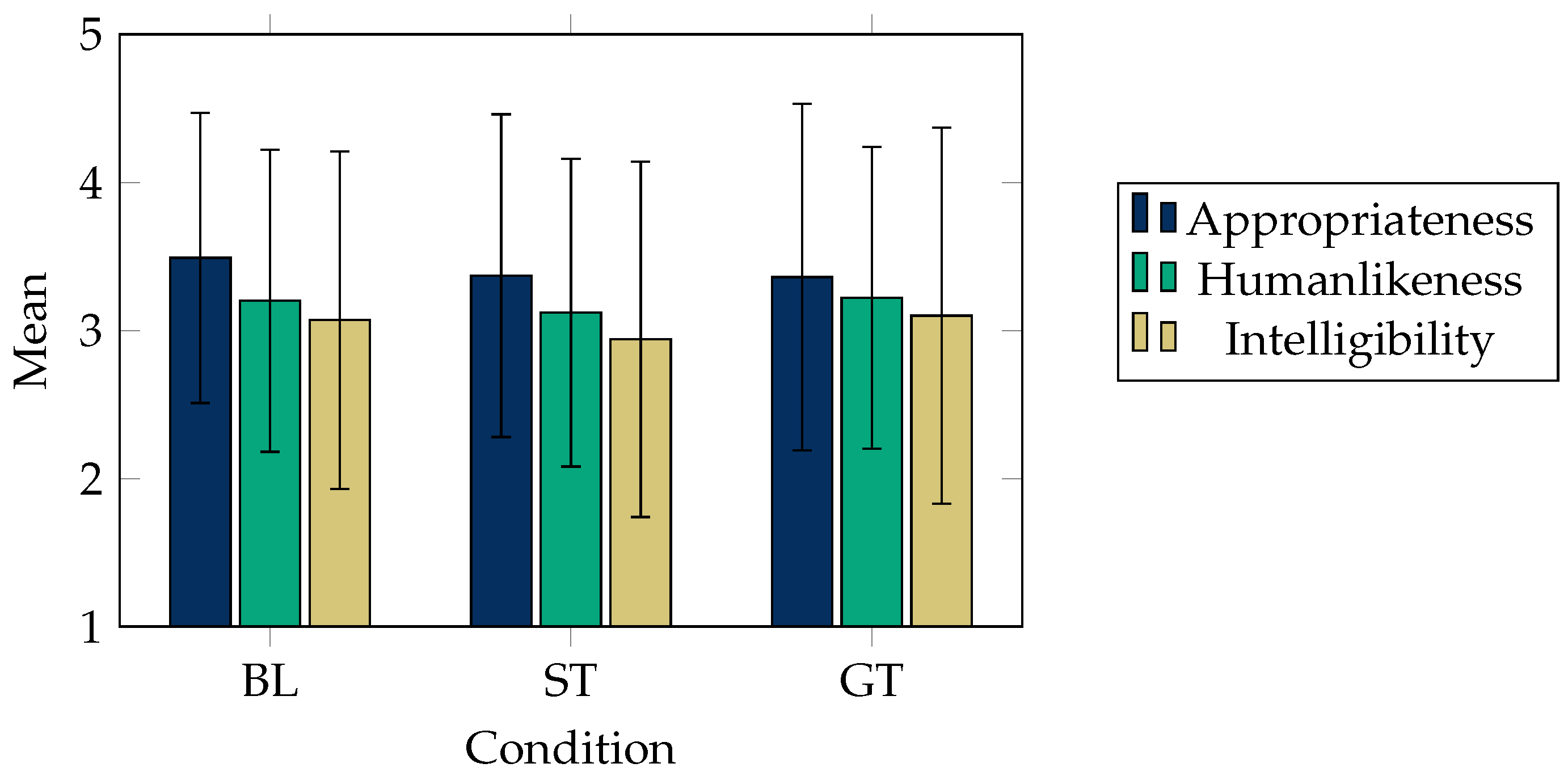
5.1.5. Study 5: Questionnaire for Gesturing
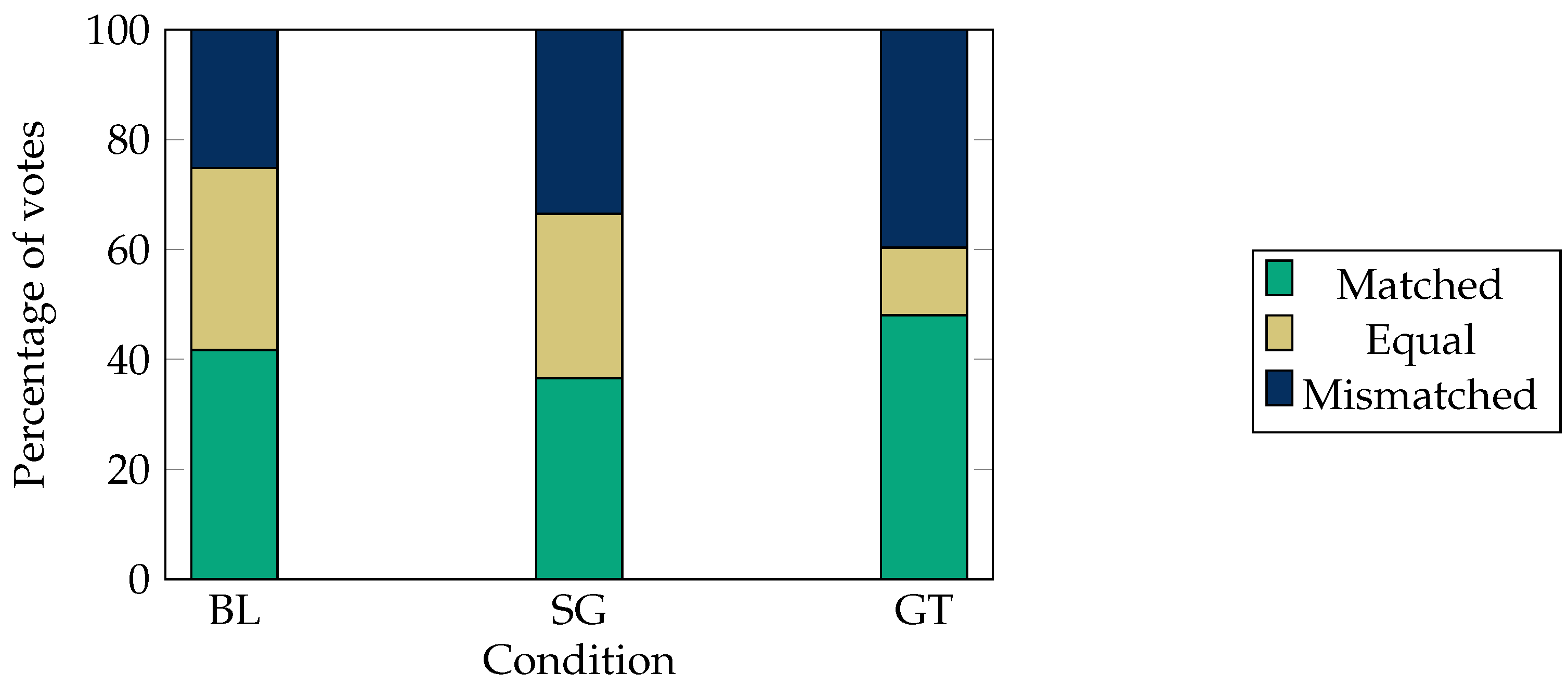
5.1.6. Study 6: Questionnaire for Listening
5.1.7. Completion Times
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolfert, P.; Robinson, N.; Belpaeme, T. A Review of Evaluation Practices of Gesture Generation in Embodied Conversational Agents. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2022, 52, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, M.L.; Hall, J.A.; Horgan, T.G. Nonverbal Communication in Human Interaction; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- McNeill, D. Hand and Mind: What Gestures Reveal about Thought; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1992; Volume 351. [Google Scholar]
- Holler, J.; Kendrick, K.H.; Levinson, S.C. Processing language in face-to-face conversation: Questions with gestures get faster responses. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2018, 25, 1900–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chidambaram, V.; Chiang, Y.H.; Mutlu, B. Designing persuasive robots: How robots might persuade people using vocal and nonverbal cues. In Proceedings of the Seventh Annual ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction, Boston, MA, USA, 5–8 March 2012; pp. 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Ham, J.; Cuijpers, R.H.; Cabibihan, J.J. Combining robotic persuasive strategies: The persuasive power of a storytelling robot that uses gazing and gestures. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2015, 7, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.; Eyssel, F.; Rohlfing, K.; Kopp, S.; Joublin, F. To err is human (-like): Effects of robot gesture on perceived anthropomorphism and likability. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2013, 5, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexanderson, S.; Henter, G.E.; Kucherenko, T.; Beskow, J. Style-Controllable Speech-Driven Gesture Synthesis Using Normalising Flows. In Proceedings of the Computer Graphics Forum; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; Volume 39, pp. 487–496. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja, C.; Lee, D.W.; Morency, L.P. Low-resource adaptation for personalized co-speech gesture generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 20566–20576. [Google Scholar]
- Alexanderson, S.; Nagy, R.; Beskow, J.; Henter, G.E. Listen, Denoise, Action! Audio-Driven Motion Synthesis with Diffusion Models. ACM Trans. Graph. 2023, 42, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, P.; Sagawa, R.; Abe, N.; Venture, G. A Generative Model to Embed Human Expressivity into Robot Motions. Sensors 2024, 24, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.M.; Mutlu, B. Modeling and Evaluating Narrative Gestures for Humanlike Robots. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems; Citeseer: State College, PA, USA, 2013; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, Y.; Wolfert, P.; Kucherenko, T.; Viegas, C.; Nikolov, T.; Tsakov, M.; Henter, G.E. The GENEA Challenge 2022: A large evaluation of data-driven co-speech gesture generation. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Bengaluru, India, 7–11 November 2022; pp. 736–747. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Pereira, A.; Kucherenko, T. Evaluating data-driven co-speech gestures of embodied conversational agents through real-time interaction. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Intelligent Virtual Agents, Faro, Portugal, 6–9 September 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bartneck, C.; Kulić, D.; Croft, E.; Zoghbi, S. Measurement instruments for the anthropomorphism, animacy, likeability, perceived intelligence, and perceived safety of robots. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2009, 1, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfert, P.; Henter, G.E.; Belpaeme, T. “Am I listening?”, Evaluating the Quality of Generated Data-driven Listening Motion. In Proceedings of the Companion Publication of the 25th International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Paris, France, 9–13 October 2023; pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kucherenko, T.; Jonell, P.; Yoon, Y.; Wolfert, P.; Henter, G.E. A large, crowdsourced evaluation of gesture generation systems on common data: The GENEA Challenge 2020. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, College Station, TX, USA, 13–17 April 2021; pp. 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Jonell, P.; Yoon, Y.; Wolfert, P.; Kucherenko, T.; Henter, G.E. HEMVIP: Human Evaluation of Multiple Videos in Parallel. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Montreal, QC, Canada, 18–22 October 2021; pp. 707–711. [Google Scholar]
- Jonell, P.; Kucherenko, T.; Henter, G.E.; Beskow, J. Let’s face it: Probabilistic multi-modal interlocutor-aware generation of facial gestures in dyadic settings. In Proceedings of the 20th ACM International Conference on Intelligent Virtual Agents, Online, 20–22 October 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rebol, M.; Güti, C.; Pietroszek, K. Passing a non-verbal turing test: Evaluating gesture animations generated from speech. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (VR), Lisboa, Portugal, 27 March–1 April 2021; pp. 573–581. [Google Scholar]
- Kucherenko, T.; Nagy, R.; Yoon, Y.; Woo, J.; Nikolov, T.; Tsakov, M.; Henter, G.E. The GENEA Challenge 2023: A large-scale evaluation of gesture generation models in monadic and dyadic settings. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Paris, France, 9–13 October 2023; pp. 792–801. [Google Scholar]
- Kucherenko, T.; Hasegawa, D.; Henter, G.E.; Kaneko, N.; Kjellström, H. Analyzing input and output representations for speech-driven gesture generation. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM International Conference on Intelligent Virtual Agents, Paris, France, 2–5 July 2019; pp. 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, Y.; Ko, W.R.; Jang, M.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, G. Robots learn social skills: End-to-end learning of co-speech gesture generation for humanoid robots. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 4303–4309. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, Y.; Cha, B.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, M.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, G. Speech gesture generation from the trimodal context of text, audio, and speaker identity. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2020, 39, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucherenko, T.; Jonell, P.; Van Waveren, S.; Henter, G.E.; Alexandersson, S.; Leite, I.; Kjellström, H. Gesticulator: A framework for semantically-aware speech-driven gesture generation. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Online, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 242–250. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja, C.; Lee, D.W.; Ishii, R.; Morency, L.P. No gestures left behind: Learning relationships between spoken language and freeform gestures. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2020, Online, 16–20 November 2020; pp. 1884–1895. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja, C.; Ma, S.; Morency, L.P.; Sheikh, Y. To react or not to react: End-to-end visual pose forecasting for personalized avatar during dyadic conversations. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Suzhou, China, 14–18 October 2019; pp. 74–84. [Google Scholar]
- Tuyen, N.T.V.; Celiktutan, O. Agree or Disagree Generating Body Gestures from Affective Contextual Cues during Dyadic Interactions. In Proceedings of the 2022 31st IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Napoli, Italy, 29 August–2 September 2022; pp. 1542–1547. [Google Scholar]
- Ao, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L. GestureDiffuCLIP: Gesture diffusion model with CLIP latents. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.14613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.; Wang, S.; Alexanderson, S.; Beskow, J.; Székely, É.; Henter, G.E. Diff-TTSG: Denoising probabilistic integrated speech and gesture synthesis. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.09417. [Google Scholar]
- Nyatsanga, S.; Kucherenko, T.; Ahuja, C.; Henter, G.E.; Neff, M. A Comprehensive Review of Data-Driven Co-Speech Gesture Generation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.05339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heylen, D.; Bevacqua, E.; Pelachaud, C.; Poggi, I.; Gratch, J.; Schröder, M. Generating listening behaviour. In Emotion-Oriented Systems: The Humaine Handbook; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 321–347. [Google Scholar]
- Buschmeier, H.; Kopp, S. Communicative listener feedback in human-agent interaction: Artificial speakers need to be attentive and adaptive. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 1213–1221. [Google Scholar]
- Maatman, R.; Gratch, J.; Marsella, S. Natural behavior of a listening agent. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Virtual Agents: 5th International Working Conference, IVA 2005, Kos, Greece, 12–14 September 2005; Proceedings 5. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gillies, M.; Pan, X.; Slater, M.; Shawe-Taylor, J. Responsive Listening Behavior. Comput. Animat. Virtual Worlds 2008, 19, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlakar, I.; Kačič, Z.; Rojc, M. Describing and animating complex communicative verbal and nonverbal behavior using Eva-framework. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2014, 28, 470–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppe, R.; Truong, K.P.; Reidsma, D.; Heylen, D. Backchannel strategies for artificial listeners. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Virtual Agents: 10th International Conference, IVA 2010, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 20–22 September 2010; Proceedings 10. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 146–158. [Google Scholar]
- Antonio Gomez Jauregui, D.; Giraud, T.; Isableu, B.; Martin, J.C. Design and evaluation of postural interactions between users and a listening virtual agent during a simulated job interview. Comput. Animat. Virtual Worlds 2021, 32, e2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.; Bartneck, C. Meta analysis of the usage of the godspeed questionnaire series. In Proceedings of the 2015 24th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Kobe, Japan, 31 August–4 September 2015; pp. 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- Fitrianie, S.; Bruijnes, M.; Richards, D.; Abdulrahman, A.; Brinkman, W.P. What are We Measuring Anyway?: -A Literature Survey of Questionnaires Used in Studies Reported in the Intelligent Virtual Agent Conferences. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM International Conference on Intelligent Virtual Agents, Paris, France, 2–5 July 2019; pp. 159–161. [Google Scholar]
- Fitrianie, S.; Bruijnes, M.; Richards, D.; Bönsch, A.; Brinkman, W.P. The 19 unifying questionnaire constructs of artificial social agents: An iva community analysis. In Proceedings of the 20th ACM International Conference on Intelligent Virtual Agents, Online, 20–22 October 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfert, P.; Girard, J.M.; Kucherenko, T.; Belpaeme, T. To rate or not to rate: Investigating evaluation methods for generated co-speech gestures. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Montreal, QC, Canada, 18–22 October 2021; pp. 494–502. [Google Scholar]
- Grassia, F.S. Practical parameterization of rotations using the exponential map. J. Graph. Tools 1998, 3, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papamakarios, G.; Nalisnick, E.; Rezende, D.J.; Mohamed, S.; Lakshminarayanan, B. Normalizing flows for probabilistic modeling and inference. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2021, 22, 2617–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Henter, G.E.; Alexanderson, S.; Beskow, J. Moglow: Probabilistic and controllable motion synthesis using normalising flows. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2020, 39, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.J.; Zhang, S.; Kapadia, M. The IVI Lab entry to the GENEA Challenge 2022–A Tacotron2 based method for co-speech gesture generation with locality-constraint attention mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Bengaluru, India, 7–11 November 2022; pp. 784–789. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Pang, R.; Weiss, R.J.; Schuster, M.; Jaitly, N.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Skerrv-Ryan, R.; et al. Natural tts synthesis by conditioning wavenet on mel spectrogram predictions. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 4779–4783. [Google Scholar]
- Schoeffler, M.; Bartoschek, S.; Stöter, F.R.; Roess, M.; Westphal, S.; Edler, B.; Herre, J. webMUSHRA—A comprehensive framework for web-based listening tests. J. Open Res. Softw. 2018, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrum, M.L.; Johnson, M.; Ghuy, M.; Gombolay, M.C. Four years in review: Statistical practices of likert scales in human-robot interaction studies. In Proceedings of the Companion of the 2020 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction, Cambridge, UK, 23–26 March 2020; pp. 43–52. [Google Scholar]

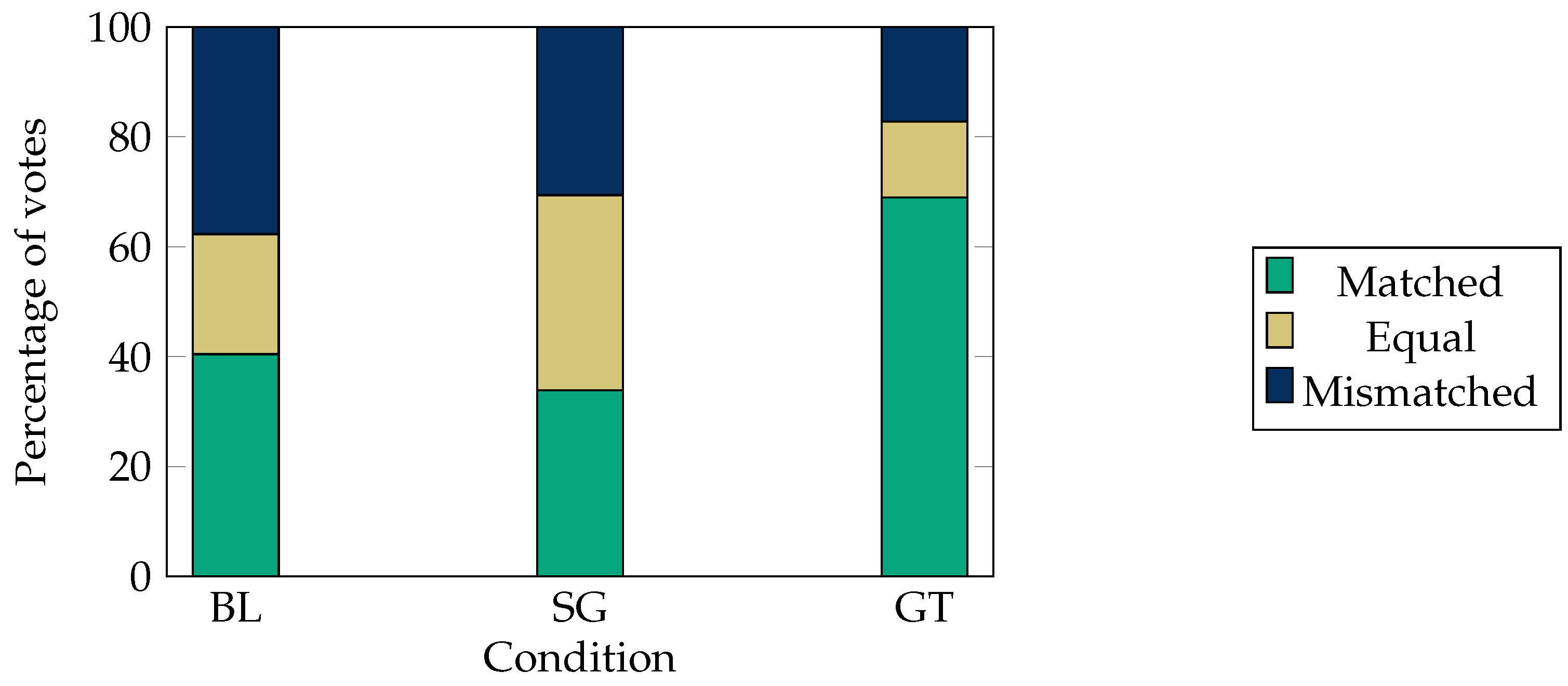

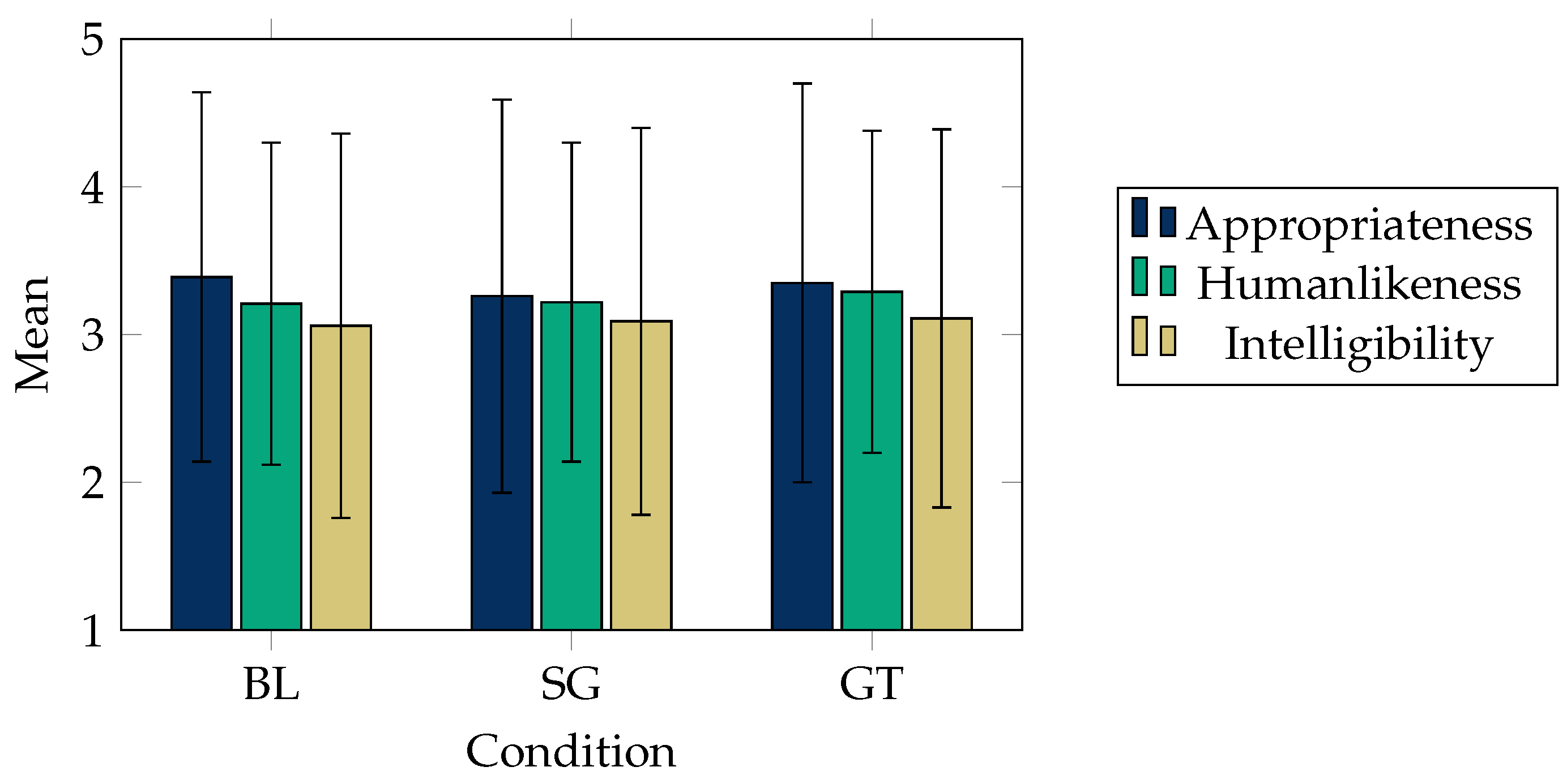
| Study | Study Goal | Question Posed |
|---|---|---|
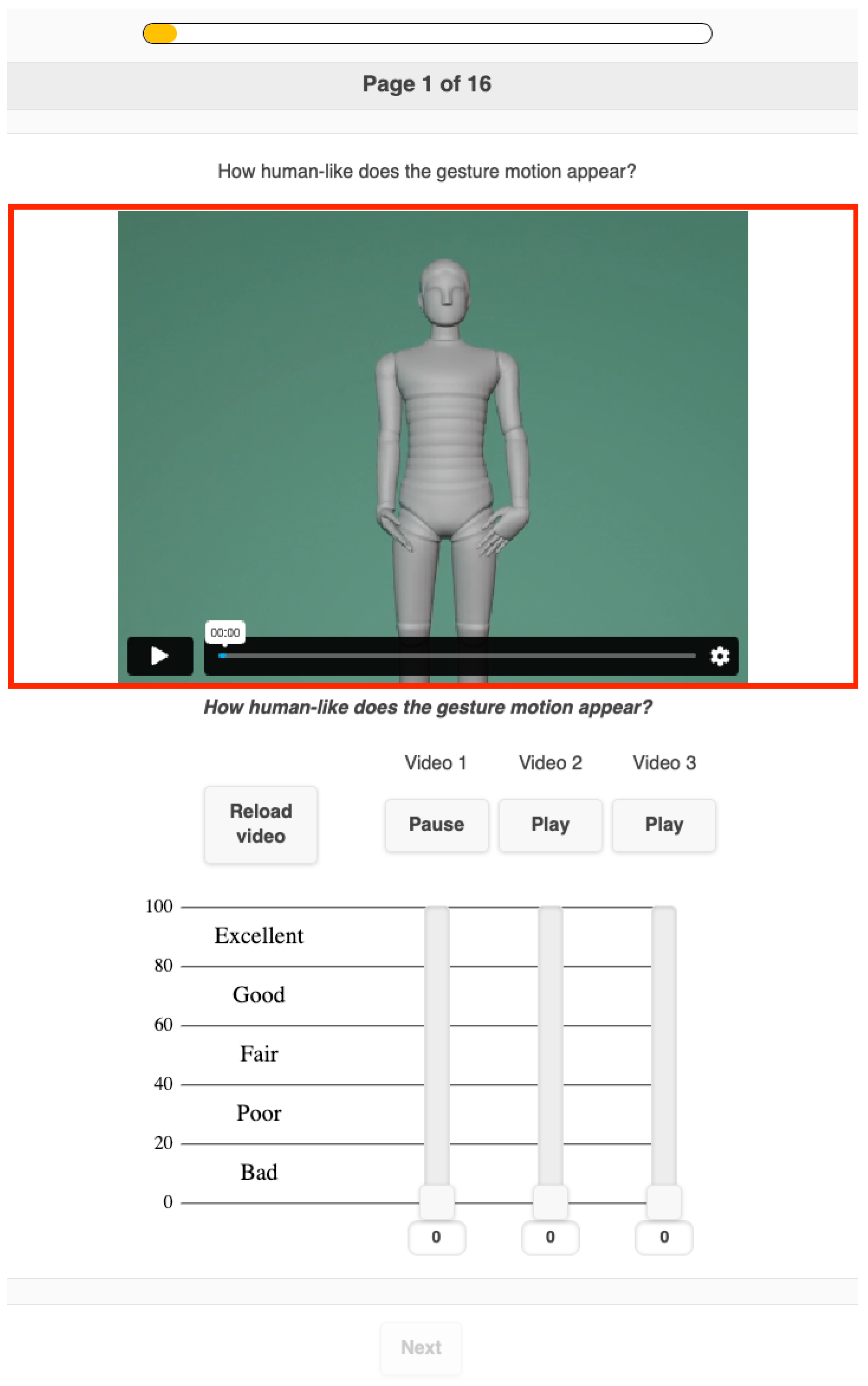
| 1 | Human-likeness of the generated gesture motion | How human-like does the gesture motion appear? |
| 2 | Appropriateness of the generated gesture motion for the conversation | Indicate which character’s motion best matches speech in terms of rhythm, intonation, and meaning. |
| 3 | Human-likeness of the generated listening motion | How human-like does the listening motion appear? |
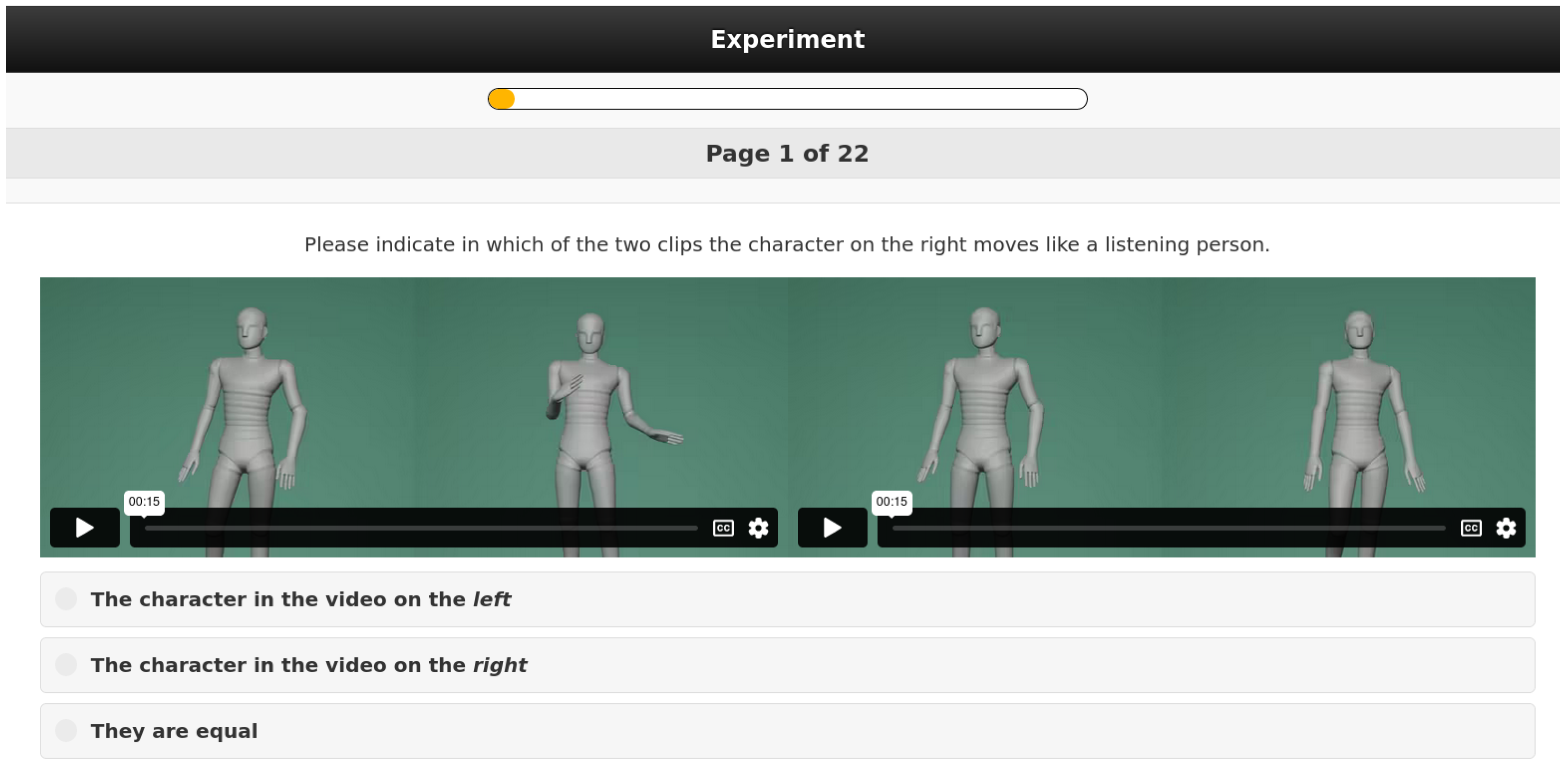
| 4 | Appropriateness of the generated listening motion for the conversation | Indicate which character’s motion shows the most appropriate listening behaviour, considering the speaker’s motion. |
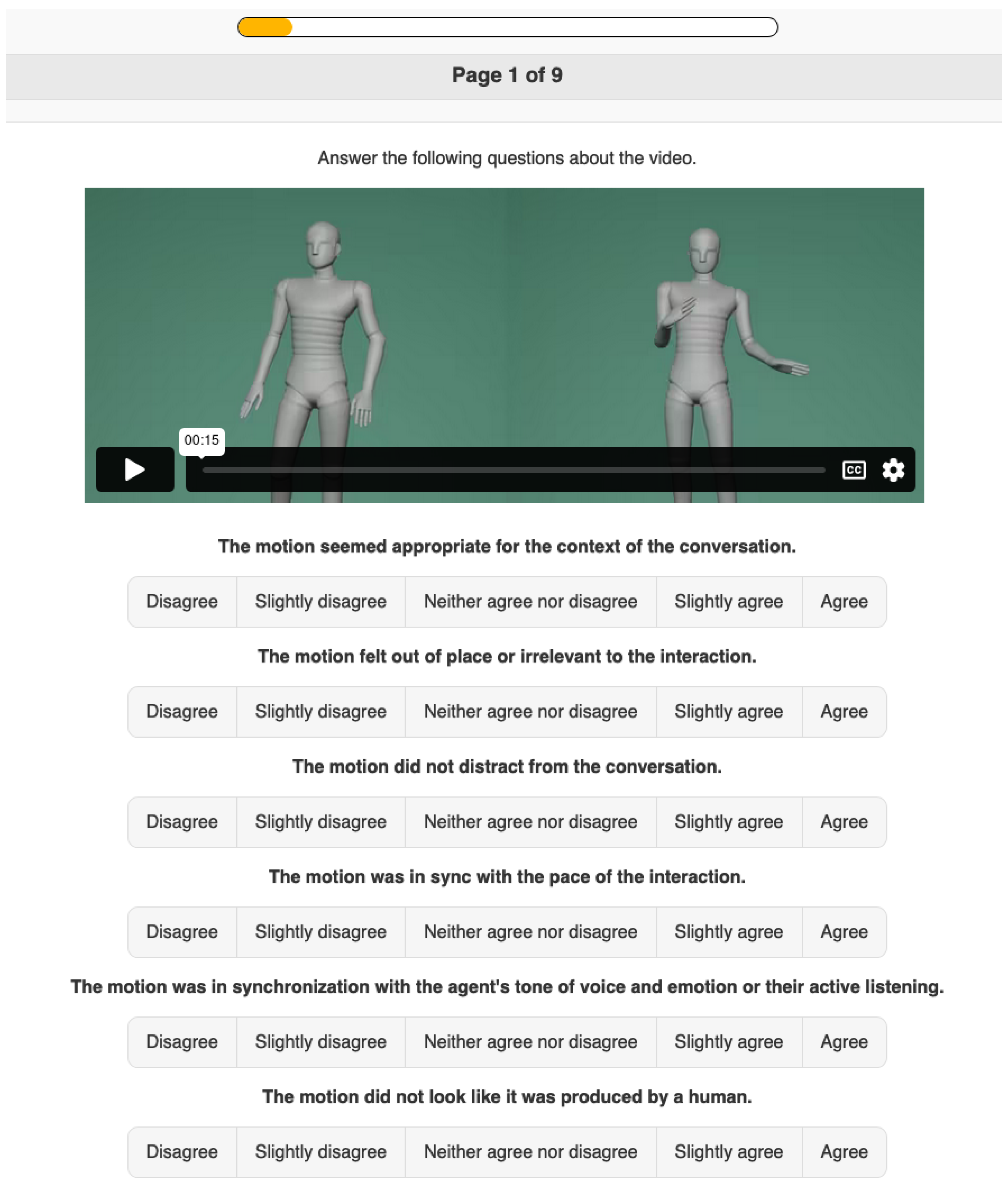
| 5 | Agreement on three constructs for the generated gesture motion: appropriateness, human-likeness, and intelligibility | See Figure 4. |
| 6 | Agreement on three constructs for the generated listening motion: appropriateness, human-likeness, and intelligibility | See Figure 4. |
| Study | N | Mean Age (SD) | Male | Female | Nationality | Education |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 22 | 35.2 (12.4) | 16 | 6 | UK (20), USA (1), IE (1) | P: 0, HS: 0, BS: 12, M: 1, D: 1, O: 8 |
| 2 | 27 | 40 (12.54) | 14 | 13 | UK (21), CA (2), IE (3), AU (1) | P: 0, HS: 0, BS: 14, M: 3, D: 0, O: 10 |
| 3 | 22 | 41.8 (13.94) | 13 | 9 | UK (16), USA (1), IE (2), NZ (2), CAN (1) | P: 0, HS: 0, BS: 10, M: 1, D: 0, O: 8 |
| 4 | 26 | 39 (11.55) | 10 | 16 | UK (15), CA (5), IE (3), AU (3) | P: 0, HS: 0, BS: 9, M: 7, D: 0, O: 10 |
| 5 | 46 | 42 (14.6) | 22 | 24 | UK (40), USA (1), AUS (1), CA (4) | P: 0, HS: 0, BS: 19, M: 7, D: 0, O: 22 |
| 6 | 48 | 37 (13) | 27 | 21 | UK (39), IE (3), CA (3), AU (3) | P: 0, HS: 0, BS: 20, M: 11, D: 0, O: 15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wolfert, P.; Henter, G.E.; Belpaeme, T. Exploring the Effectiveness of Evaluation Practices for Computer-Generated Nonverbal Behaviour. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14041460
Wolfert P, Henter GE, Belpaeme T. Exploring the Effectiveness of Evaluation Practices for Computer-Generated Nonverbal Behaviour. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(4):1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14041460
Chicago/Turabian StyleWolfert, Pieter, Gustav Eje Henter, and Tony Belpaeme. 2024. "Exploring the Effectiveness of Evaluation Practices for Computer-Generated Nonverbal Behaviour" Applied Sciences 14, no. 4: 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14041460
APA StyleWolfert, P., Henter, G. E., & Belpaeme, T. (2024). Exploring the Effectiveness of Evaluation Practices for Computer-Generated Nonverbal Behaviour. Applied Sciences, 14(4), 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14041460






