Numerical Simulation and Process Parameter Optimization of Warm Forging Near-Net Forming for Spiral Bevel Gear
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Establishment of Finite Element Model and Formulation of Process Plan for Warm Forging–Finishing of Spiral Bevel Gear
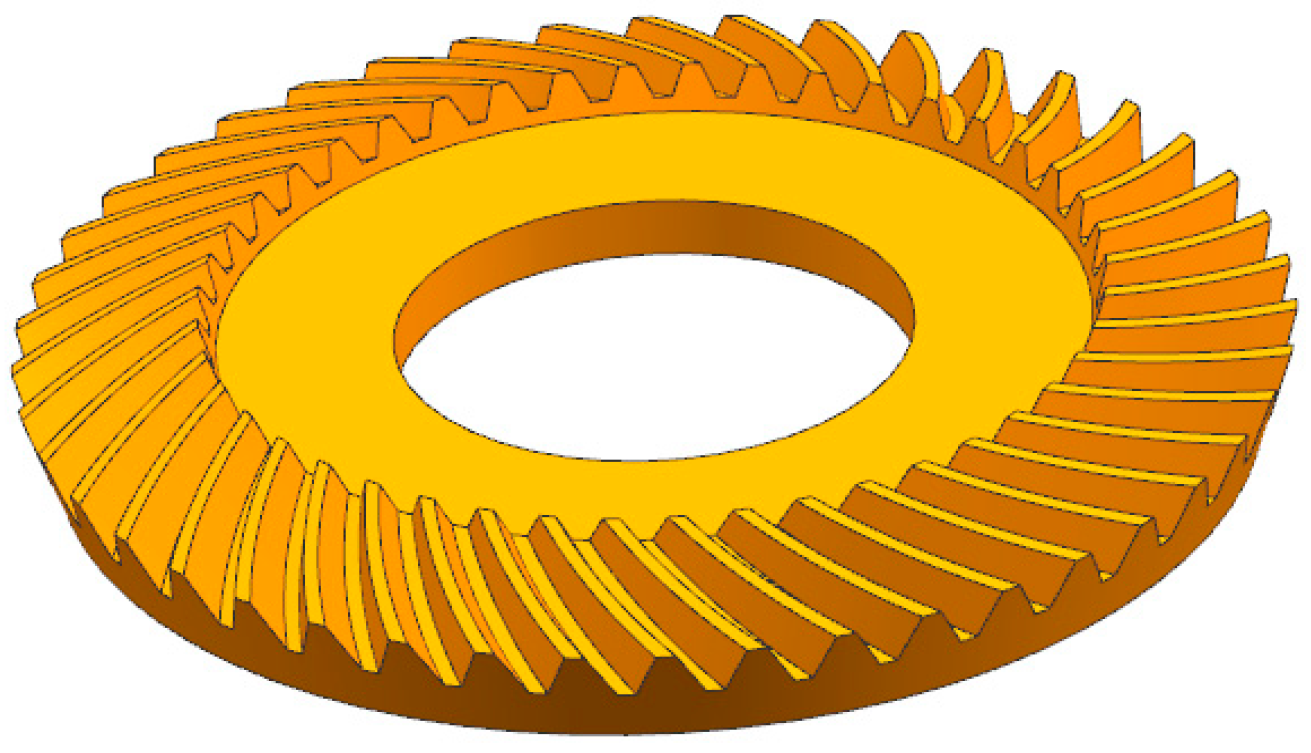
2.1. Three-Dimensional Modeling of Spiral Bevel Gear
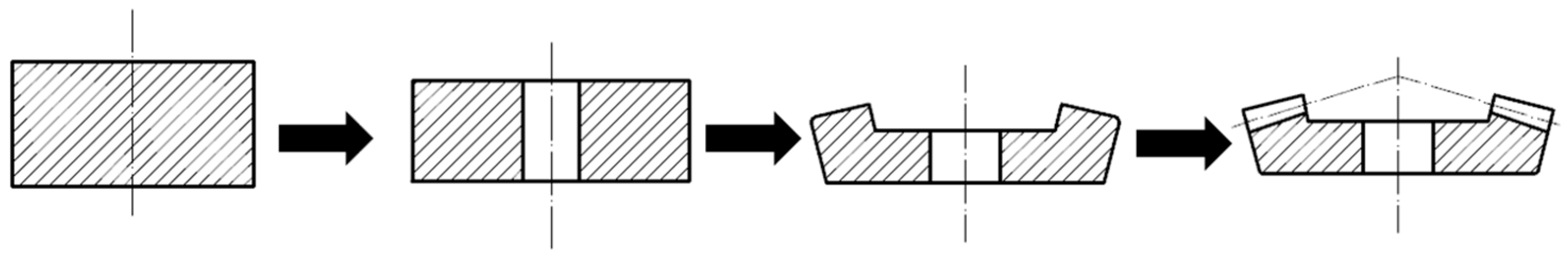
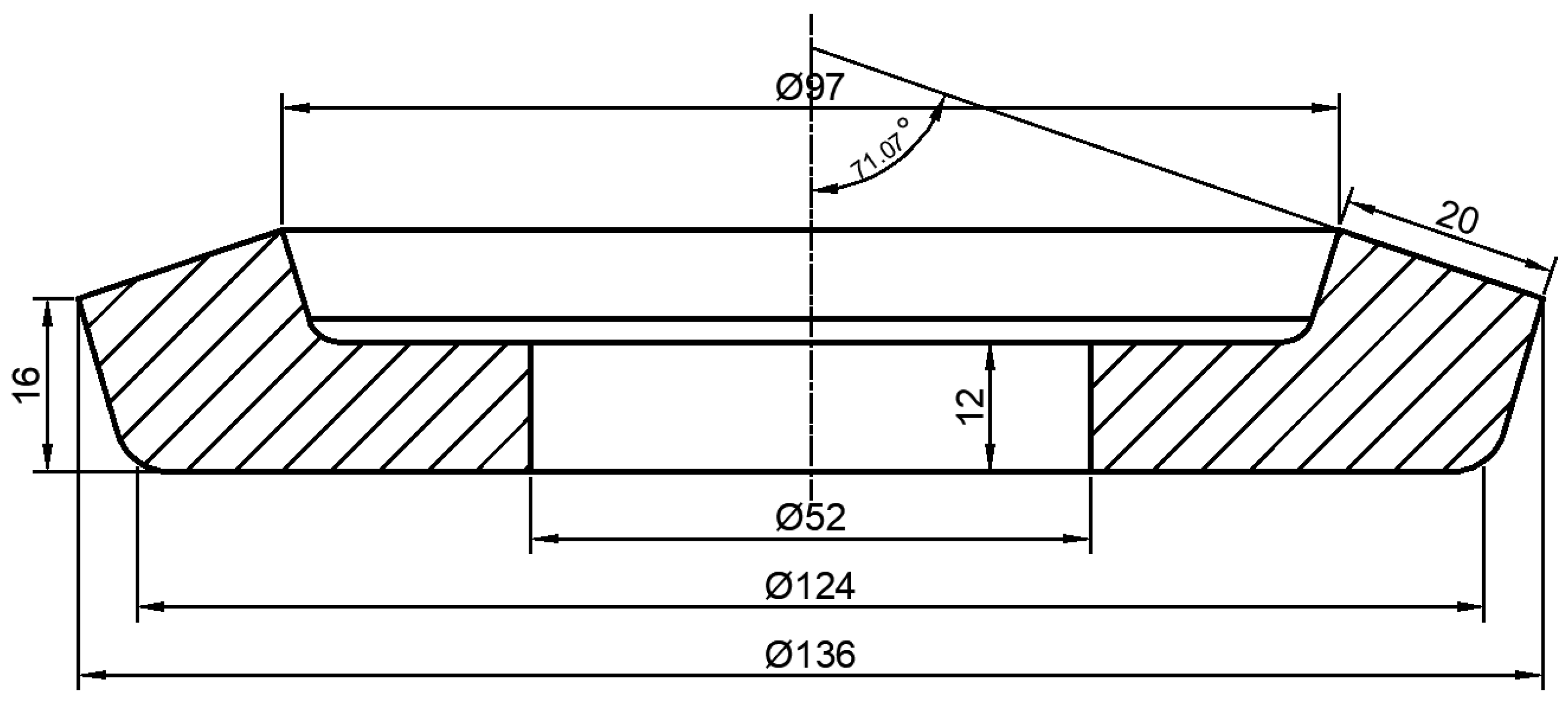
2.2. Design of Forging Gear Blank for Spiral Bevel Gear
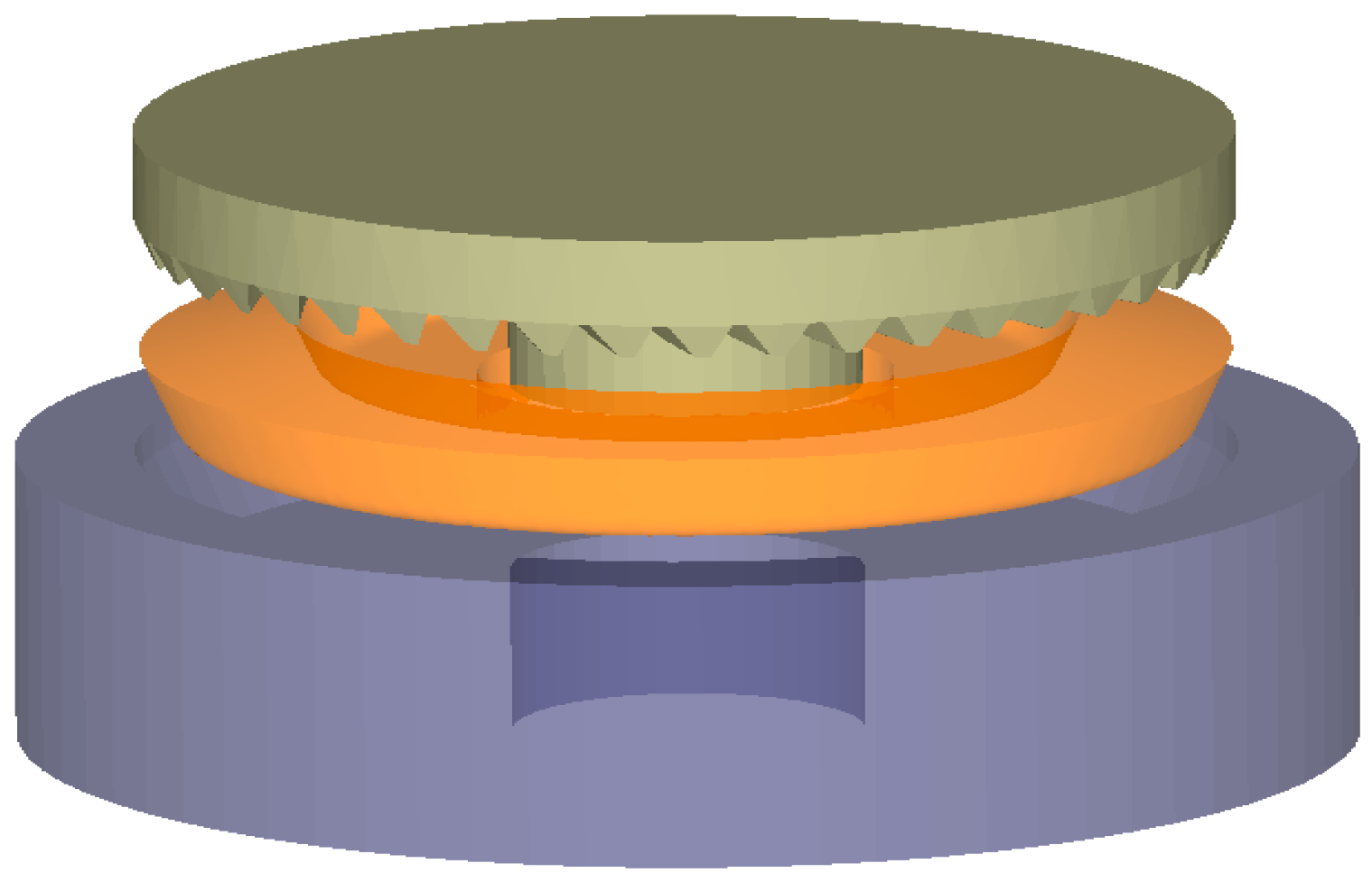
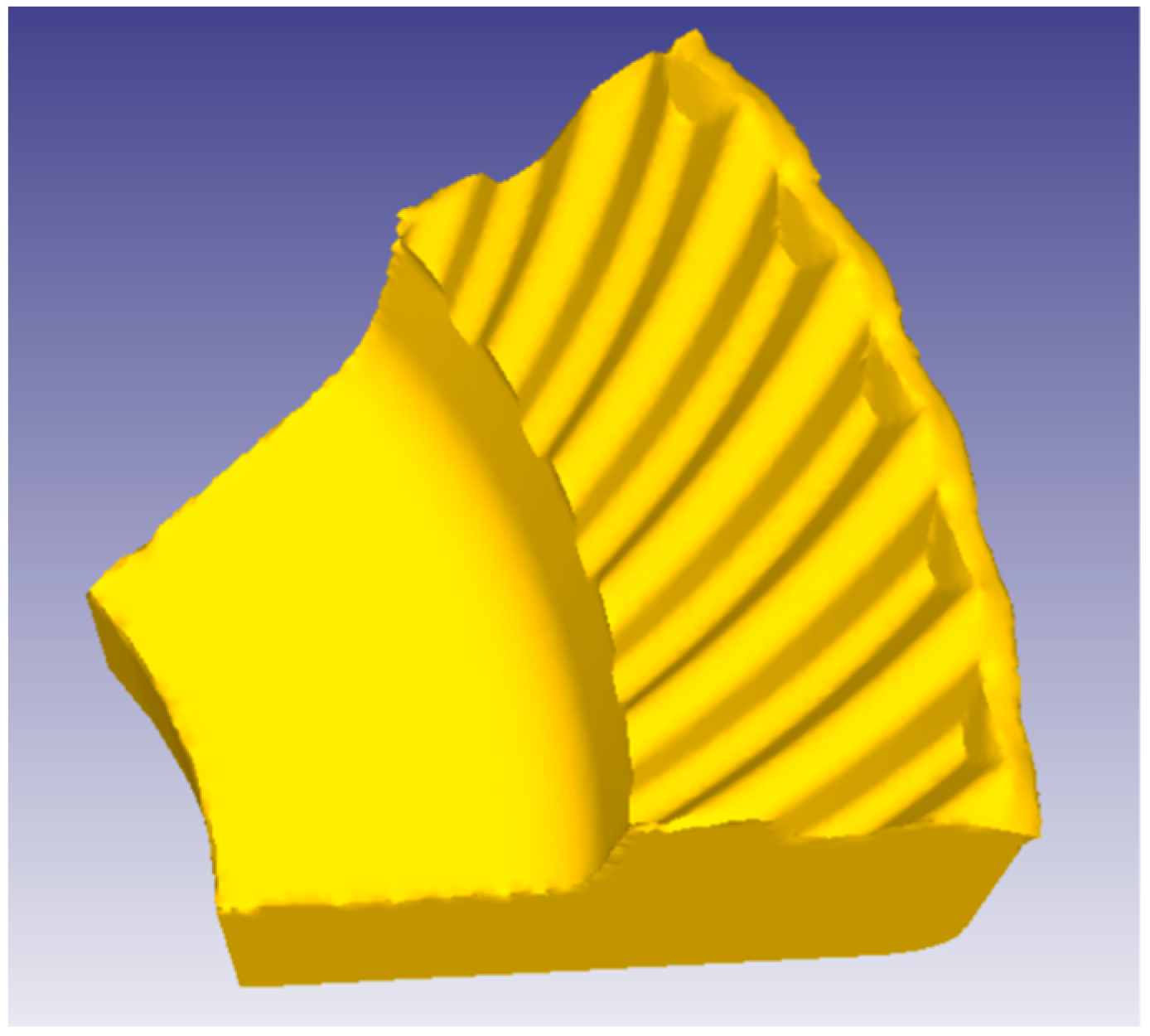
2.3. Establishment of Geometric Model for Numerical Simulation
2.4. Numerical Simulation Process Analysis and Scheme Formulation of Warm Forging–Finishing
3. Numerical Simulation of Warm Forging–Finishing of Spiral Bevel Gear
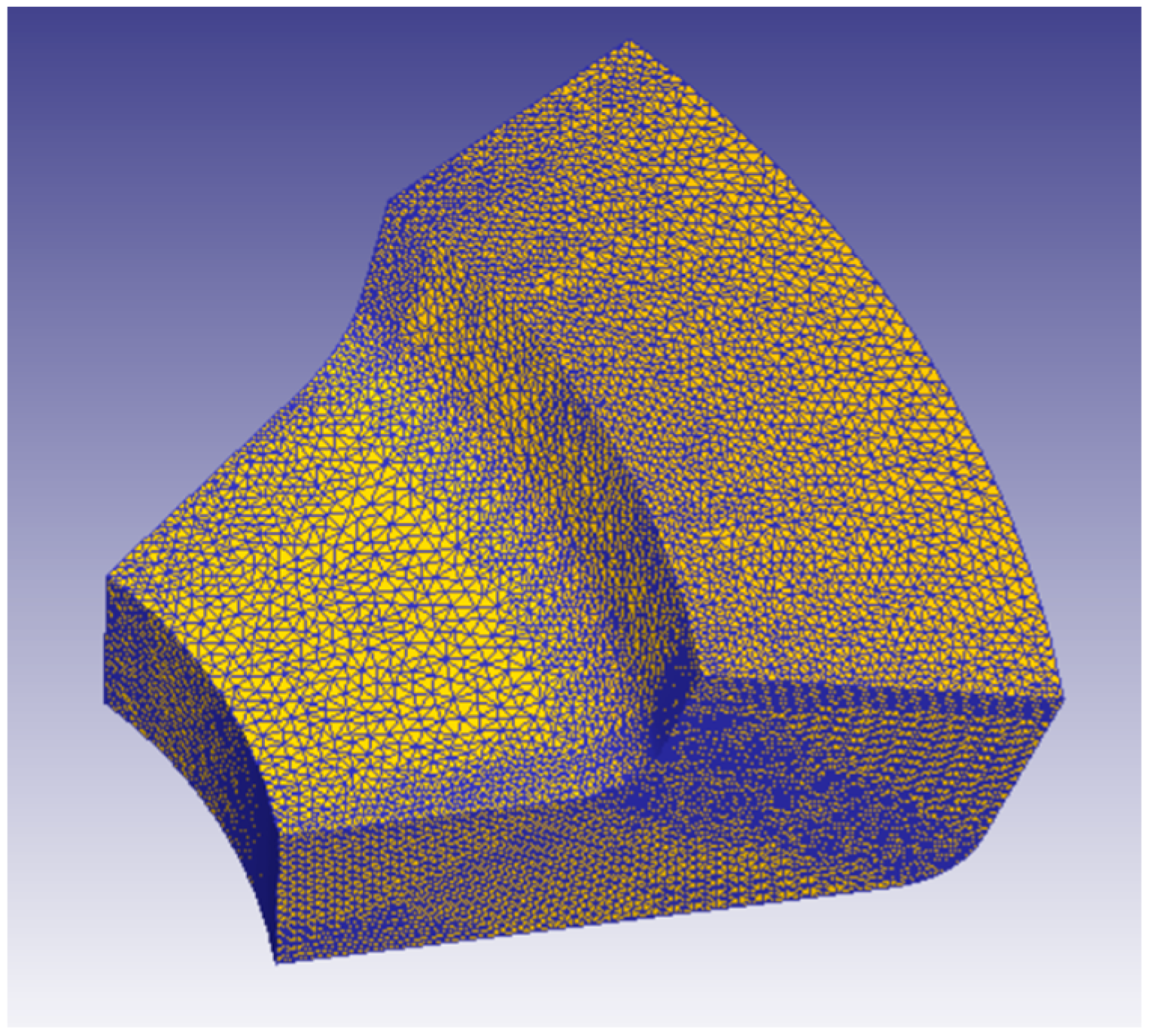
3.1. Numerical Simulation Parameter Settings
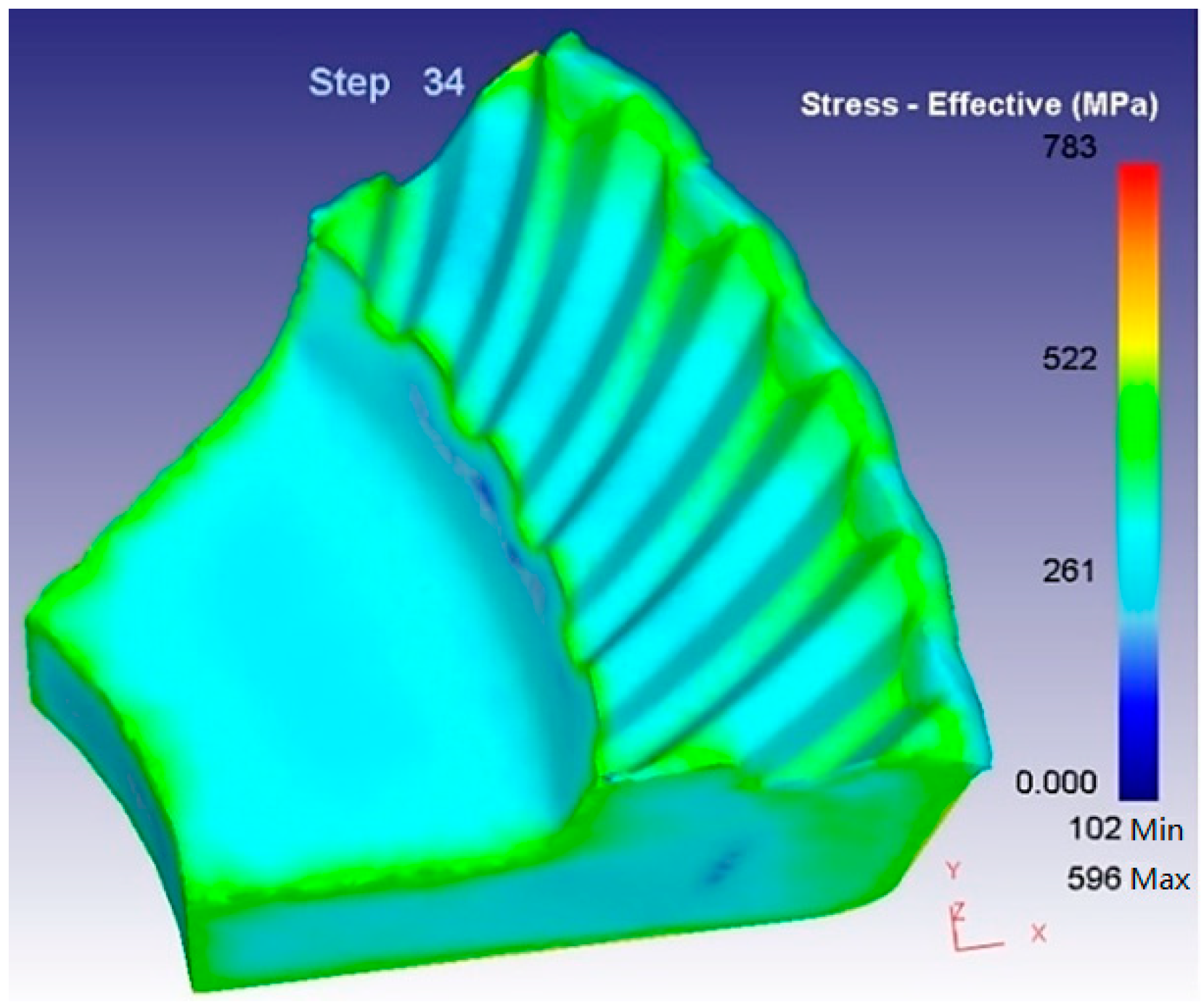
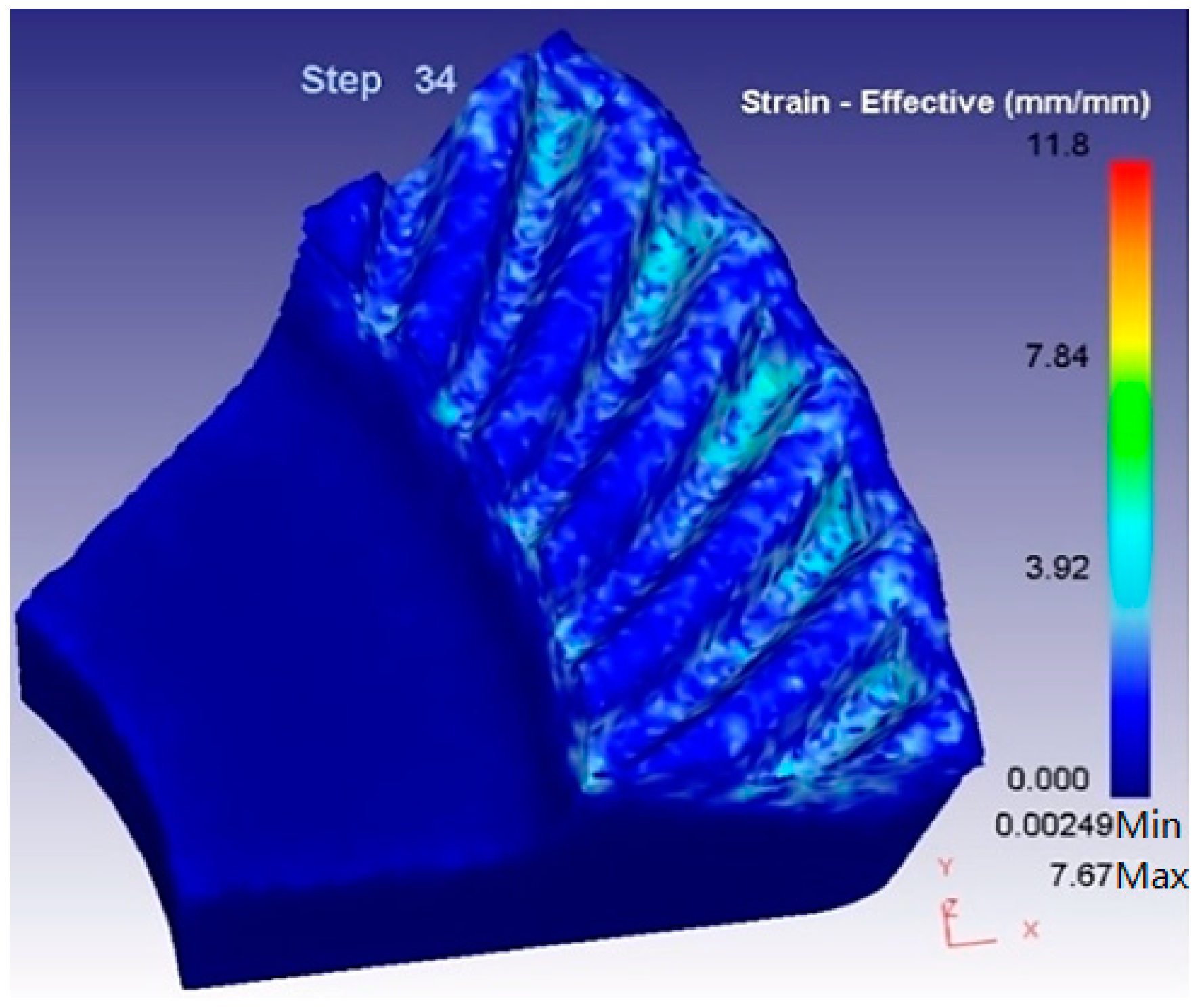
3.2. Brief Analysis on the Forging Process of Spiral Bevel Gear
3.3. Simulation and Result Analysis of Warm-Forging–Finishing of Spiral Bevel
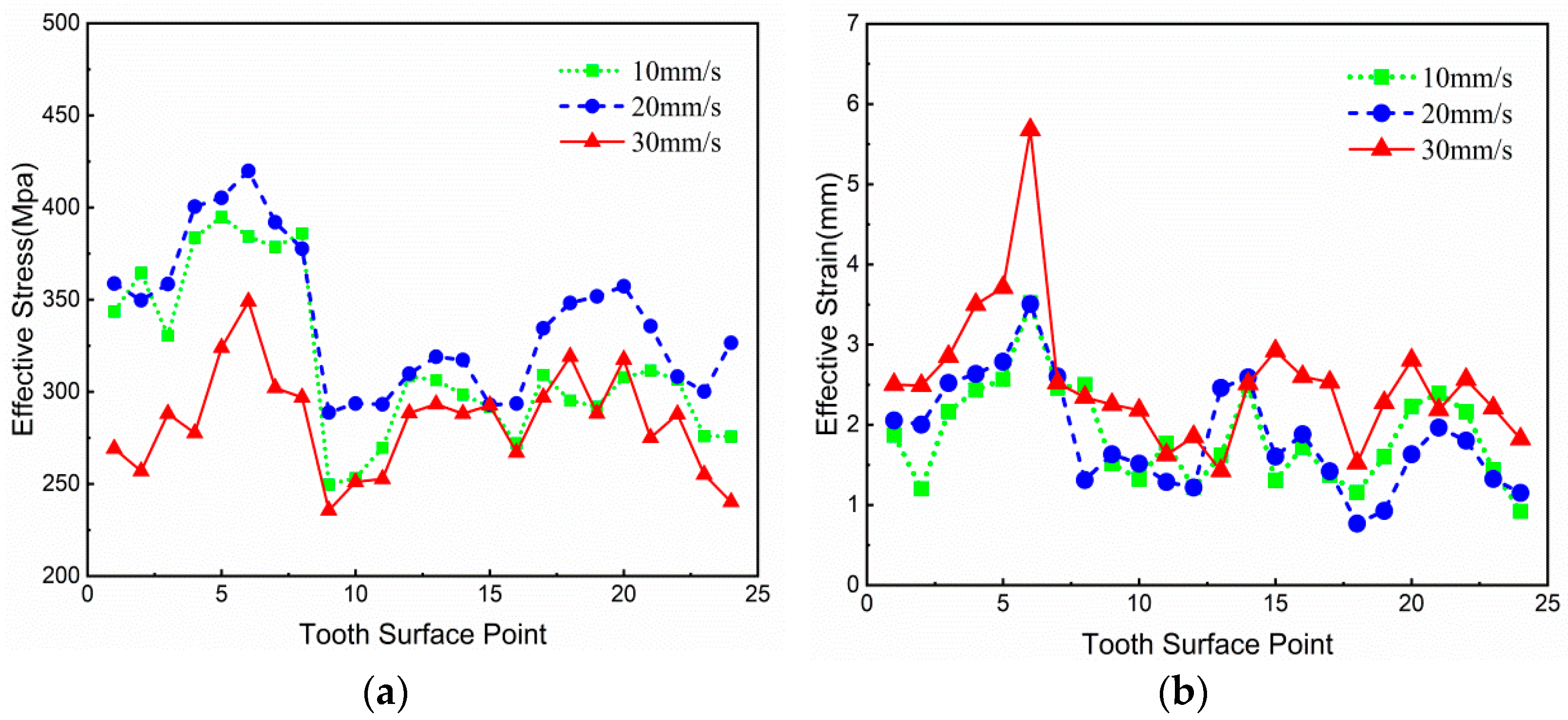
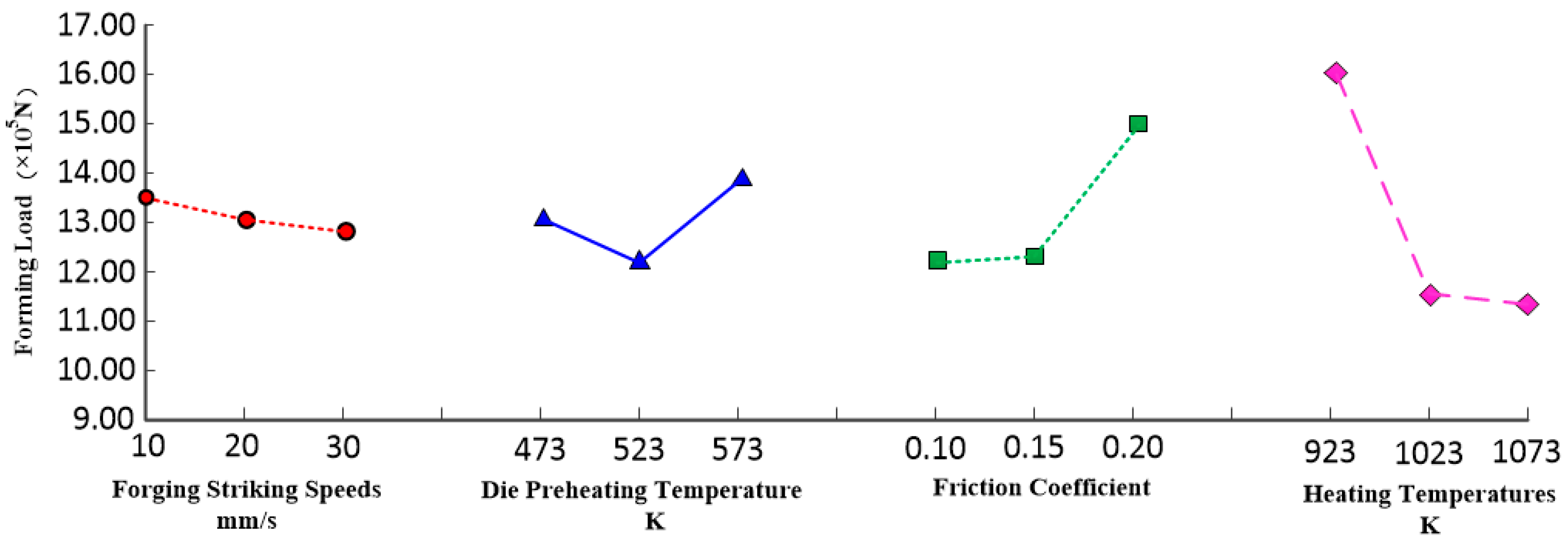
3.3.1. Influence of Forging Striking Speed on Forging Formation
3.3.2. Influence of Die Preheating Temperature on Forging–Forming
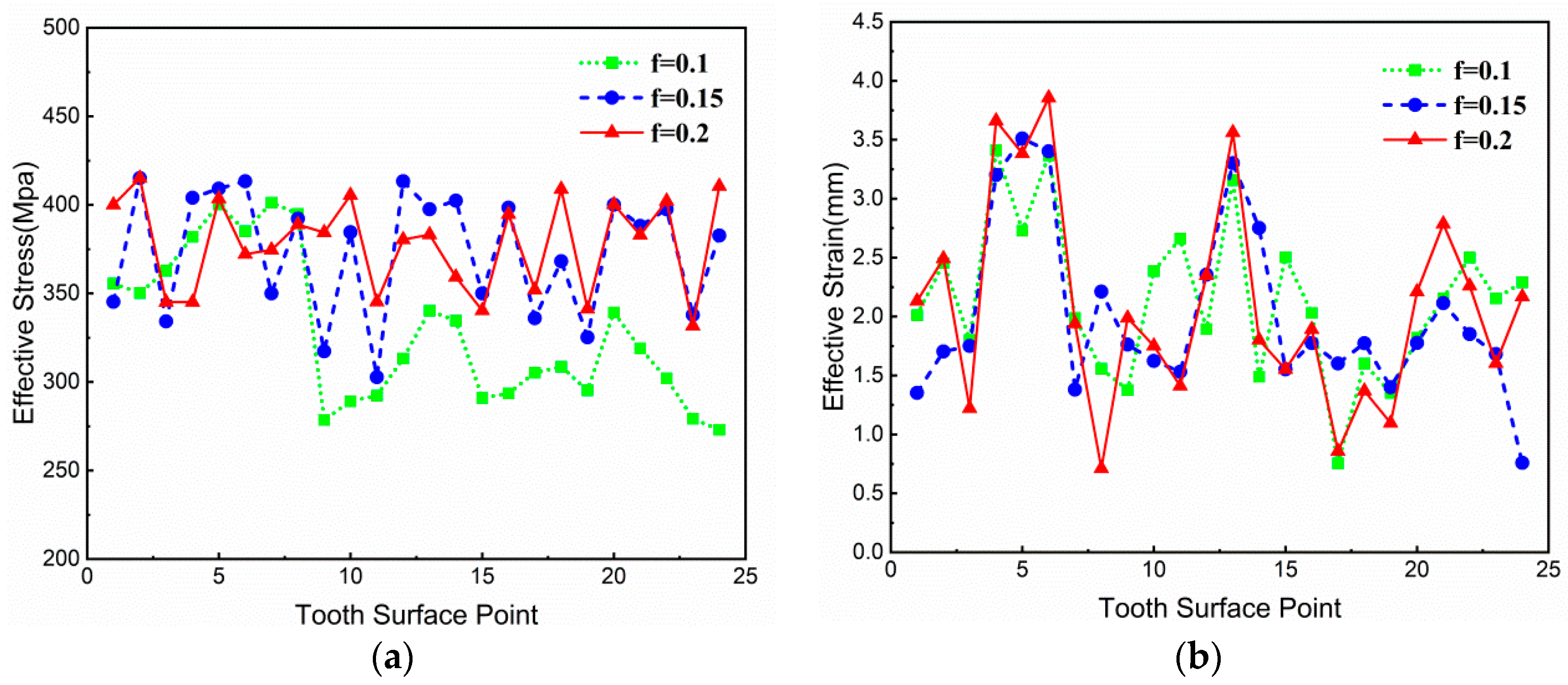
3.3.3. Influence of Friction Factor on Forging–Forming
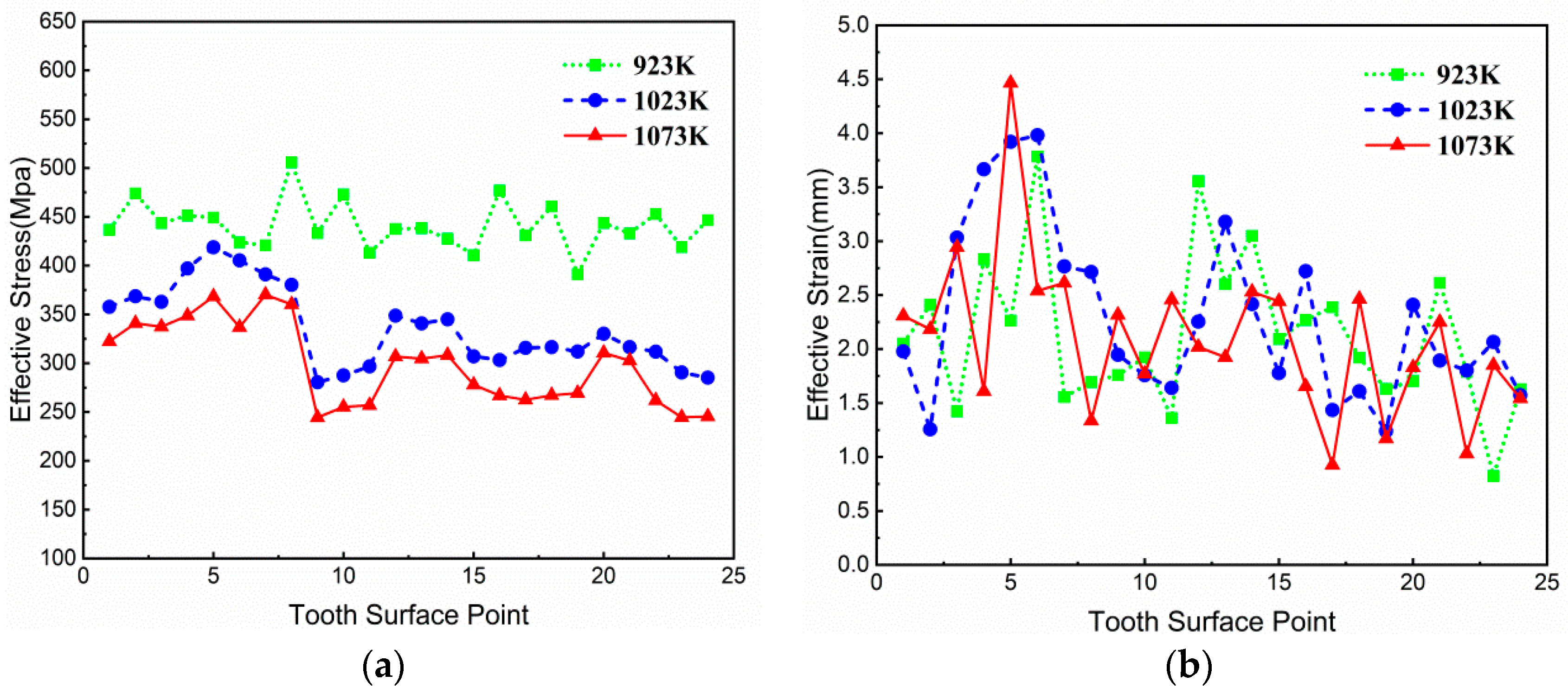
3.3.4. Influence of Workpiece Heating Temperature on Forging–Forming
4. Optimization of Warm-Forging–Finishing Process Parameters of Spiral Bevel Gear
4.1. Identification of Evaluation Indicators
- (1)
- The geometric accuracy of the finished gear will be affected. If the forming force is too large, the metal blank will produce unnecessary elastic deformation; and if the deformation is too large, it will result in a large tooth profile error, tooth alignment error and so on, which will reduce the geometric accuracy of the finished forging.
- (2)
- The service life of the tooth mold will be reduced. Higher forming forces acting on the die during the forging process may cause premature fatigue damage to the surface of the die, thus affecting its service life.
- (3)
- The surface quality of the finished gear can also be affected. Because the forming force is too large, it may cause cracks in the gear, especially in the stress concentration areas, such as the root and top of the gear teeth, thus affecting its surface quality.
4.2. Orthogonal Experimental Design
4.3. Data Analysis and Results of Orthogonal Experiment
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- In the warm-forging process of spiral bevel gear, the maximum deforming force is at the dedendum of the gear big end, and the deforming force increases with the increase in the friction factor in the forging process and decreases with the increase in the forging speed and workpiece heating temperature.
- (2)
- Based on the orthogonal experiment method, the combination of four process parameters was designed, and the combination of process parameters with the minimum warm-forging force of spiral bevel gear was obtained as follows: a forging speed of 30 mm/s, a die preheating temperature of 523 K, the friction factor of 0.1, and a workpiece heating temperature of 1073 K.
- (3)
- The combination of a numerical simulation and orthogonal test can help to work out the warm-forging process scheme of spiral bevel gear quickly, accurately and reasonably.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, J.S.; Li, J.H. Near-net-shape forming technology and manufacturing process of precision die forging for spiral bevel gears. J. Mech. Transm. 2009, 33, 111–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Luo, S.M.; Li, F.Q. Study on precision forming and lift-out process of small cone angle spiral bevel gear by finite element analysis. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 92, 2559–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, S.Y.; Zhao, Y.M.; Wang, H.J.; Zhang, S.H. Deformation characteristics of bevel pinion of automotive output shaft by no-flash die forging. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 1999, 3, 567–572. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, R.; Kuhlmann, D. Guidelines for precision hot forging with applications. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2000, 98, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.H.; Duan, H.J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Zhang, W.Q. Research on precision forming process parameters of spiral bevel gear based on numerical simulation. Forg. Stamp. Technol. 2014, 39, 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.M.; Fang, Y. Numerical simulation of precision forging process of spiral bevel gears. China Mech. Eng. 2009, 20, 485–487. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, J.F.; Yang, J.J.; Li, T.X. Analysis of precision forging process of spiral bevel gears. Mach. Tools Hydraul. 2018, 46, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.S.; Li, J.B.; Deng, X.Z.; Yang, J.J.; Chen, F.X.; Xu, A.J.; Li, L. Research on gear tooth forming control in the closed die hot forging of spiral bevel gear. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 94, 2993–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knust, J.; Stonis, M.; Behrens, B.-A. Preform optimization for hot forging processes using an adaptive amount of flash based on the cross section shape complexity. Prod. Eng. 2016, 10, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.X.; Huang, T.; Guo, J.Q.; Yan, X.J. The study of physical simulation and numerical simulation for precision forming of spiral bevel driven gear. Manuf. Technol. Mach. Tool 2010, 5, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.Y.; Zhou, Z.X.; Wang, W. Influence of process parameters on precision forging process of spiral bevel gear. Equip. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 8, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Wan, Y.; Sha, X.M. Influence of mold loading mode on closed forging process for transmission spiral bevel gear. Forg. Stamp. Technol. 2022, 47, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.B.; Zhang, R.H.; Yu, H.; Yi, X.; OuYang, J.Z.; Cao, C.L. Experimental research on precision forming of driven spiral bevel gear preformed by enlarging die corner. J. Plast. Eng. 2021, 28, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.X.; Zhang, X.L.; Fu, J.Z.; Gao, Z.S.; Wu, S.B.; Yang, C. Influence of the technological parameter and die structure on metal flow line for precision forging car gear blank. J. Mech. Transm. 2015, 39, 154–157. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Bai, X.J.; Hu, C.L. Status and development trend of precision forging technology. Forg. Stamp. Technol. 2018, 43, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Yin, X.Y. Application of precision warm forging technology in auto parts. Die Mould. Technol. 2018, 4, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Raghu, K.; Balachandran, G.; Ravichandar, D. Microstructure and mechanical properties in warm forged 27MnSiVS6 micro-alloyed steel. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2019, 72, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skubisz, P.; Lisiecki, Ł. Warm-Forging Characteristics and Microstructural Response of Medium-Carbon High-Strength Steels for High-Duty Components. Key Eng. Mater. 2014, 611, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.Y.; Xie, J.S.; Chen, W.L.; Liu, D.; Tang, T.; Wang, S.Y. Process parameters optimization for spur gear warm forging. J. Netshape Form. Eng. 2012, 4, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.S.; Deng, J.Y.; Chang, J. Study on intnal helical gear worm forging by finite element analysis. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 465, 1361–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.P. Optimum design of warm forging process and die for shaft gear based on ANSYS. Hot Work. Technol. 2018, 47, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Huang, S.T.; Wu, H.; Dai, X.D.; Cao, J.G. Research on warm forging process and defect control for combined gear based on numerical simulation. Die Mould. Ind. 2021, 47, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.L.; Li, Z.H.; You, S.; Sheng, N.; Zhang, M. Optimization analysis of numerical simulation of warm closed forging die structure for cylindrical gears. Hot Work. Technol. 2016, 45, 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.L.; Tian, Y.J.; Fan, H.W.; Wang, M.Y. Three dimensional modeling technology for spiral bevel gear based on Matlab and UG. Heavy Mach. 2011, 2, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Lin, L.; Luo, Y. The multi-objective optimization design of a new closed extrusion forging technology for a steering knuckle with long rod and fork. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 72, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Gear |
|---|---|
| Tooth number | 44 |
| Module (mm) | 3 |
| Average pressure angle (°) | 20° |
| Midpoint helix angle (°) | 35° |
| Hand of helix | LH |
| Diameter of indexing circle (mm) | 132 |
| Tooth top height (mm) | 1.516 |
| Tooth root height (mm) | 4.148 |
| Matching gear teeth number | 15 |
| Top cone angle (°) | 73°39′3″ |
| Partial cone angle (°) | 71°10′31″ |
| Root cone angle (°) | 67°0′14″ |
| External taper distance (mm) | 69.73 |
| Mounting distance (mm) | 27 ± 0.1 |
| Experimental Scheme | Process Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forging Striking Speeds (mm/s) | Die Preheating Temperature (K) | Friction Factor | Workpiece Heating Temperature (K) | |
| Scheme I | 20 | 523 | 0.15 | 923 |
| 1023 | ||||
| 1073 | ||||
| Scheme II | 10 | 523 | 0.15 | 1023 |
| 20 | ||||
| 30 | ||||
| Scheme III | 20 | 473 | 0.15 | 1023 |
| 523 | ||||
| 573 | ||||
| Scheme IV | 20 | 523 | 0.1 | 1023 |
| 0.15 | ||||
| 0.2 | ||||
| Factor Level | Factors | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (mm/s) | B (K) | C | D (K) | |
| 1 | 10 | 473 | 0.10 | 923 |
| 2 | 20 | 523 | 0.15 | 1023 |
| 3 | 30 | 573 | 0.20 | 1073 |
| Experiment No. | A (mm/s) | B (K) | C | D (K) | Experimental Scheme |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 473 | 0.1 | 923 | A1B1C1D1 |
| 2 | 10 | 523 | 0.15 | 1023 | A1B2C2D2 |
| 3 | 10 | 573 | 0.2 | 1073 | A1B3C3D3 |
| 4 | 20 | 473 | 0.15 | 1073 | A2B1C2D3 |
| 5 | 20 | 523 | 0.2 | 923 | A2B2C3D1 |
| 6 | 20 | 573 | 0.1 | 1023 | A2B3C1D2 |
| 7 | 30 | 473 | 0.2 | 1023 | A3B1C3D2 |
| 8 | 30 | 523 | 0.1 | 1073 | A3B2C1D3 |
| 9 | 30 | 573 | 0.15 | 923 | A3B3C2D1 |
| Experiment No. | A | B | C | D | Forming Load (×105 N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 15.80 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 9.94 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 14.80 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 10.30 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 17.40 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 11.50 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 13.20 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 9.27 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 16.40 |
| K1 | 40.54 | 39.30 | 36.57 | 49.60 | |
| K2 | 39.20 | 36.61 | 36.64 | 34.64 | |
| K3 | 38.47 | 42.30 | 45.40 | 34.37 | |
| k1 | 13.51 | 13.10 | 12.19 | 16.53 | |
| k2 | 13.07 | 12.20 | 12.21 | 11.55 | |
| k3 | 12.82 | 14.10 | 15.13 | 11.46 | |
| R | 2.07 | 5.69 | 8.83 | 15.23 | |
| Primary → Secondary | D → C → B → A | ||||
| A (mm/s) | B (K) | C | D (K) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 523 | 0.1 | 1073 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Wei, B.; Wang, Y. Numerical Simulation and Process Parameter Optimization of Warm Forging Near-Net Forming for Spiral Bevel Gear. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031147
Wang Z, Jiang C, Wei B, Wang Y. Numerical Simulation and Process Parameter Optimization of Warm Forging Near-Net Forming for Spiral Bevel Gear. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(3):1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031147
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhen, Chuang Jiang, Bingyang Wei, and Yongqiang Wang. 2024. "Numerical Simulation and Process Parameter Optimization of Warm Forging Near-Net Forming for Spiral Bevel Gear" Applied Sciences 14, no. 3: 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031147
APA StyleWang, Z., Jiang, C., Wei, B., & Wang, Y. (2024). Numerical Simulation and Process Parameter Optimization of Warm Forging Near-Net Forming for Spiral Bevel Gear. Applied Sciences, 14(3), 1147. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031147





