Accelerated Co-Composting of Textile Waste Using the New Strains and Microbial Consortium: Evaluation of Maturity, Stability and Microbial Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of Raw Materials
2.2. Bacterial Strain Isolation
2.3. Bioaugmentation Culture Conditions
2.4. Analysis Methods
2.5. Identification of Micro-Organisms
2.6. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
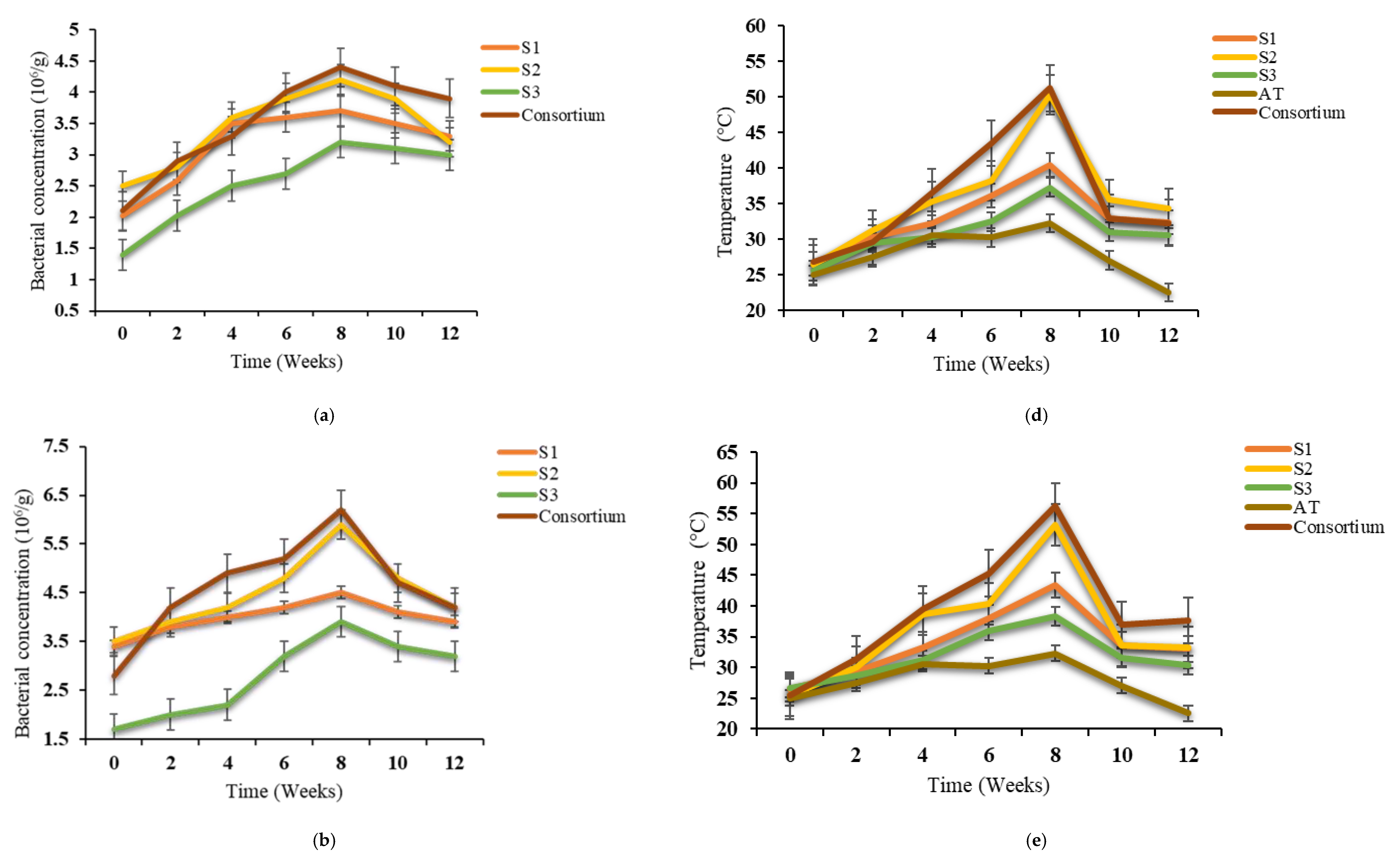
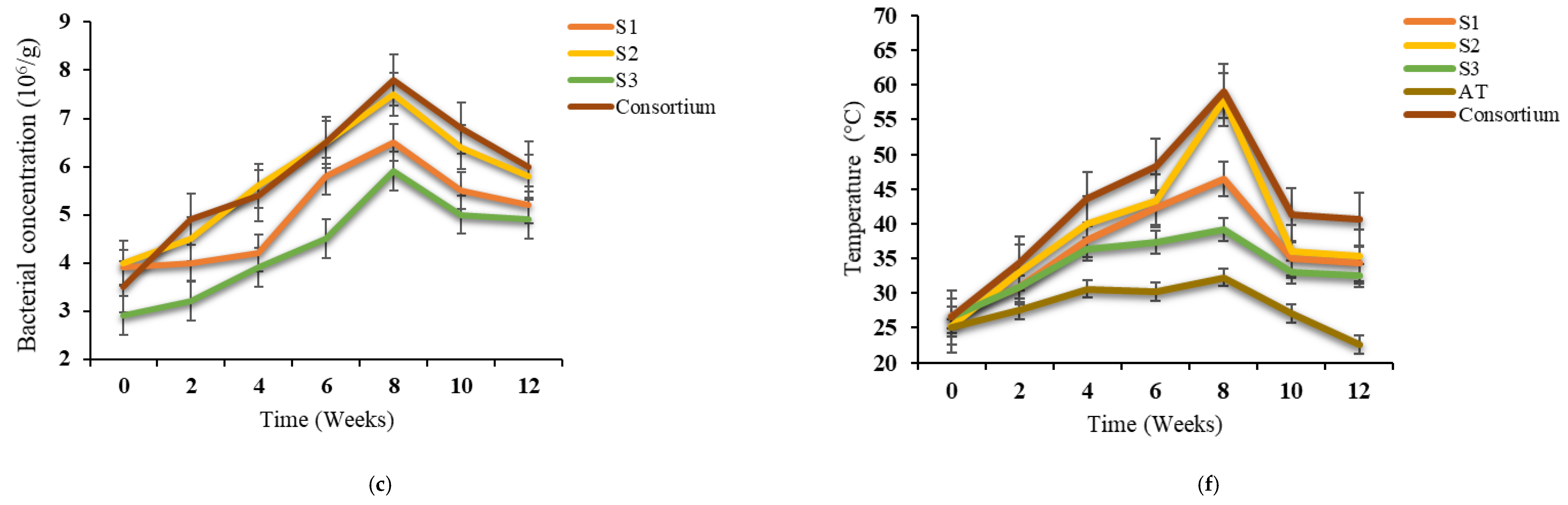
3.1. Changes in Temperature and Bacterial Growth
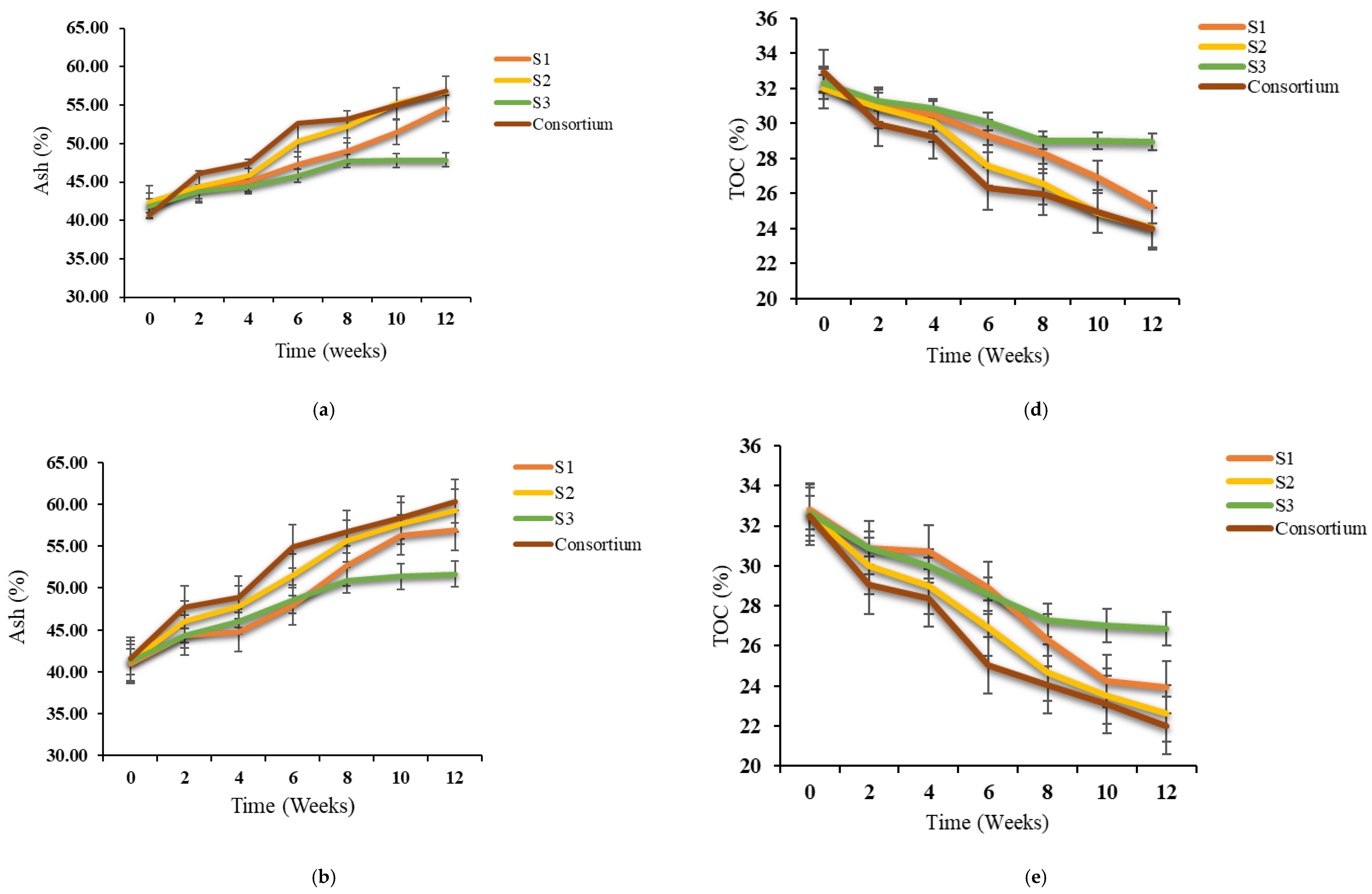
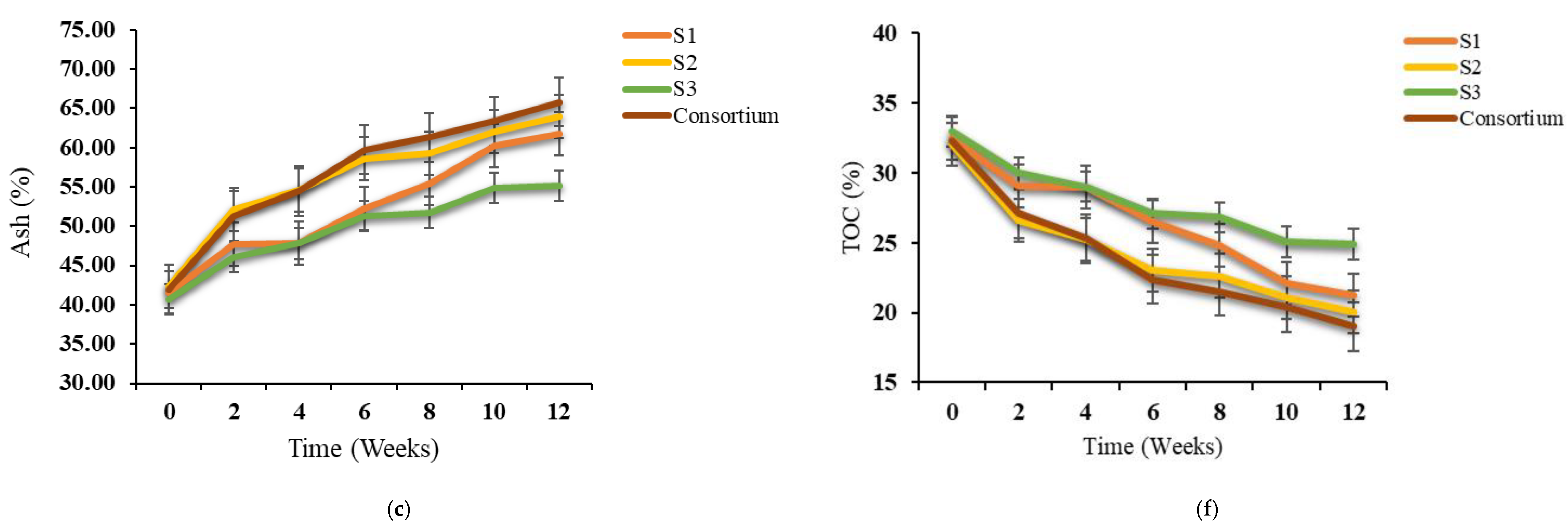
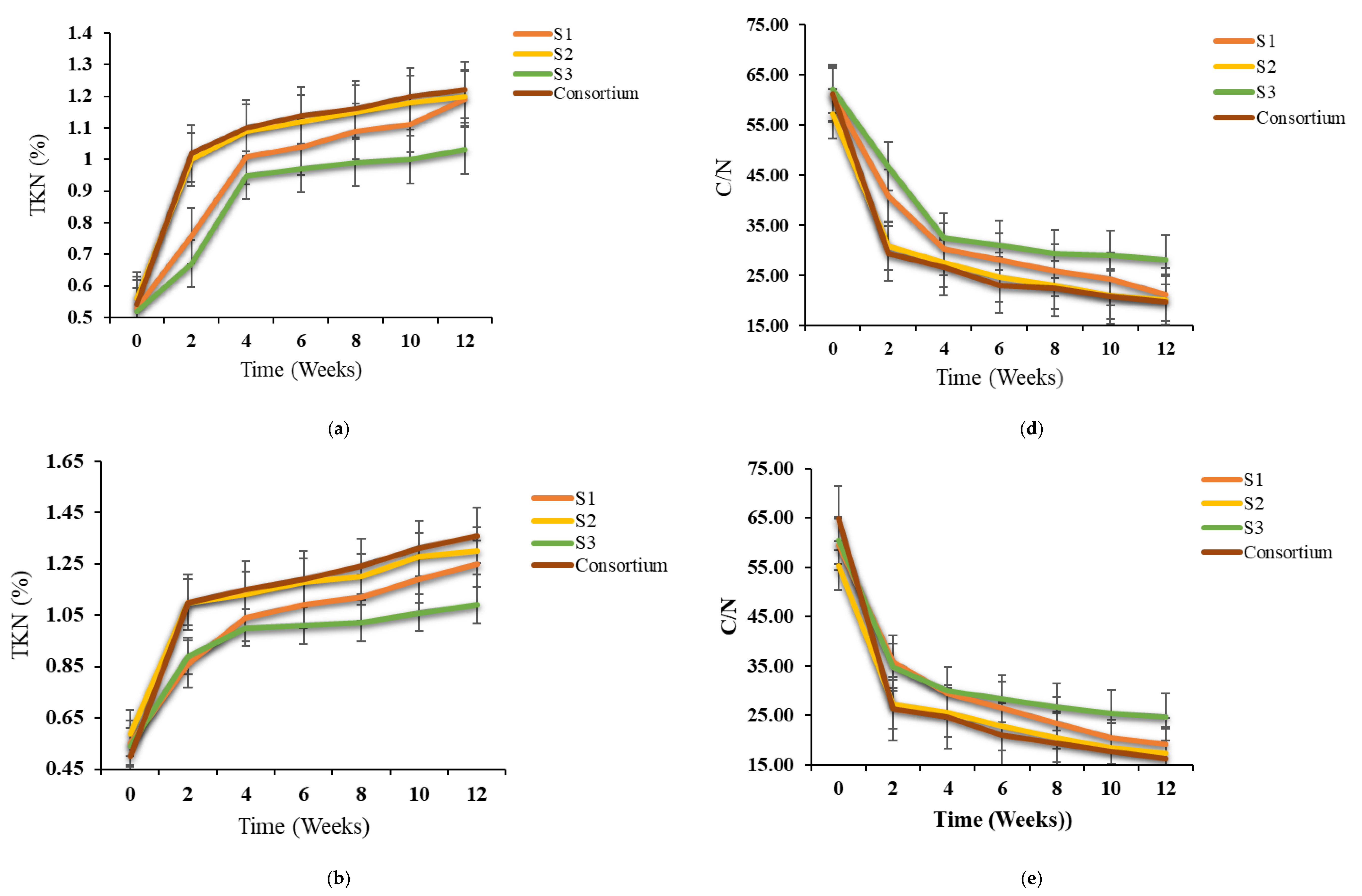
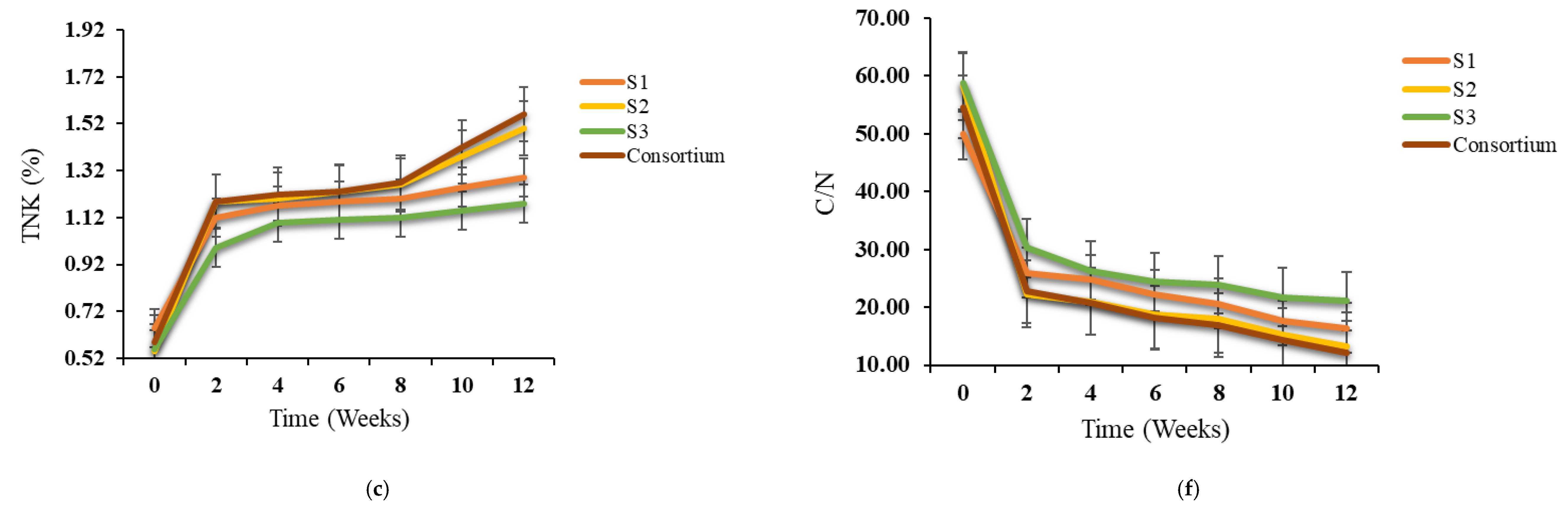
3.2. Variations in TOC, Ash, TKN and C/N Ratio During Bioaugmentation
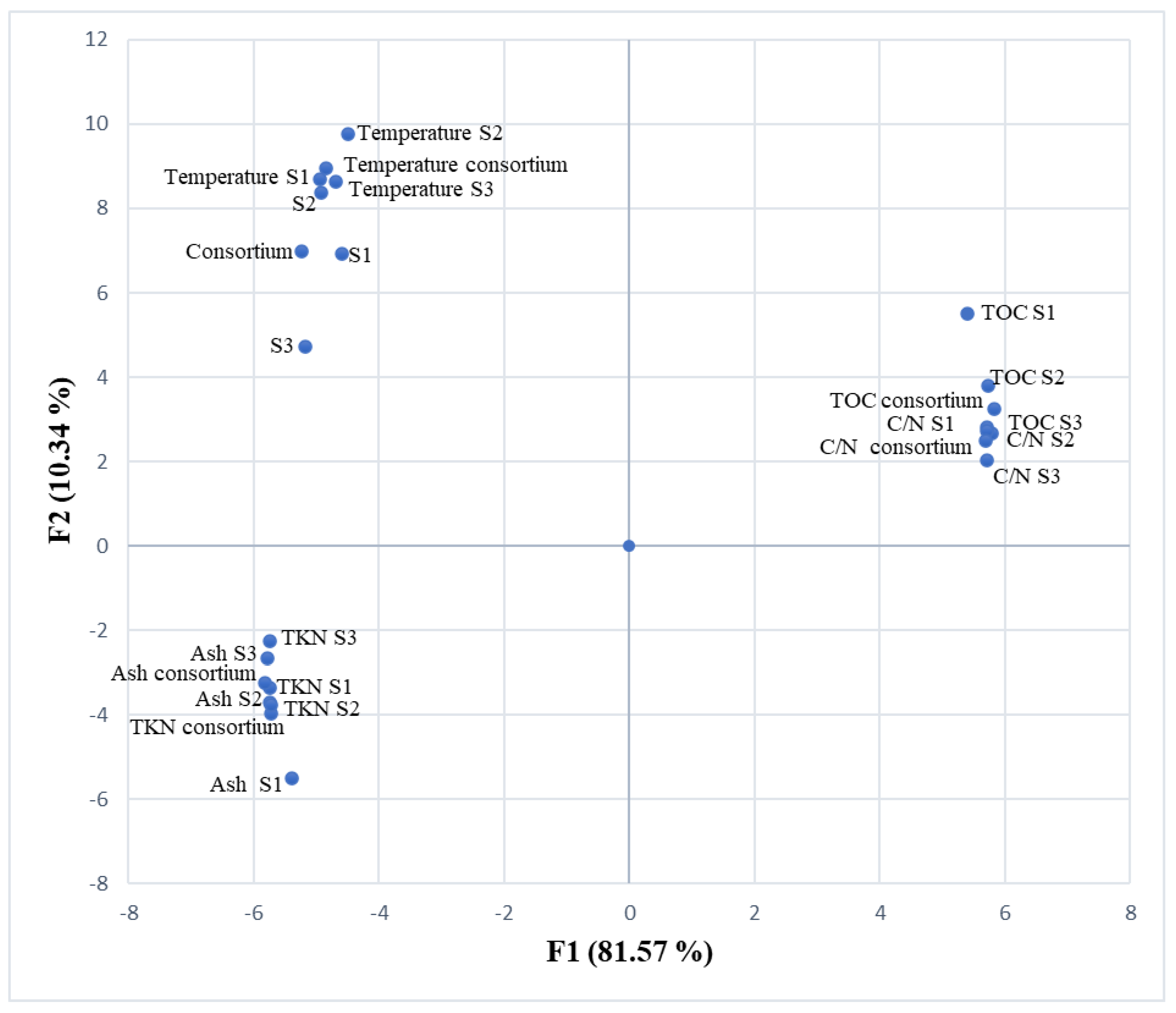
3.3. Correlation Between Bacteria, Consortium and Physical-Chemical Parameters
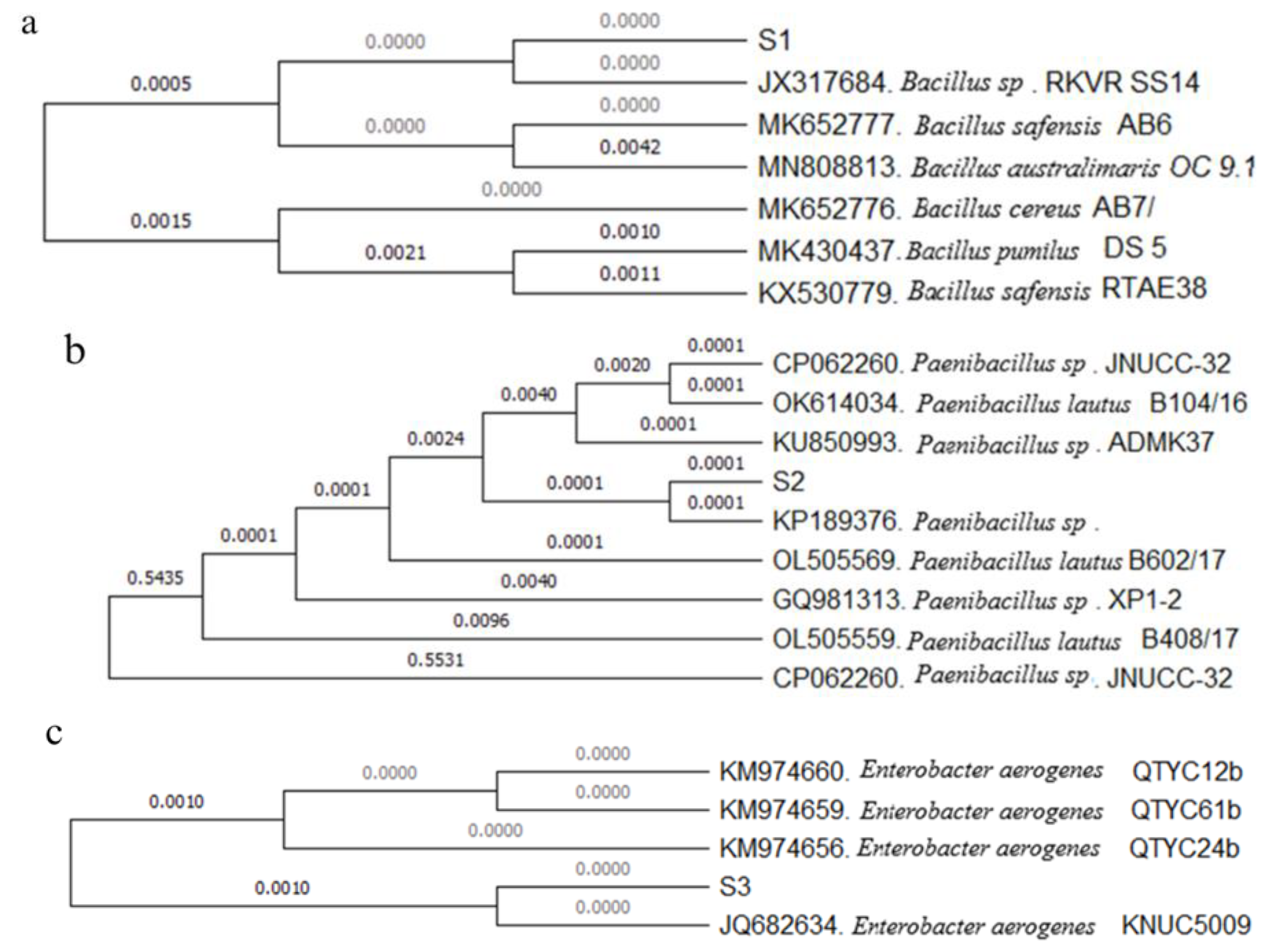
3.4. Identification of Bacteria
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, X.; Zhou, M.; Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Hu, B. Inoculation Enhances Directional Humification by Increasing Microbial Interaction Intensity in Food Waste Composting. Chemosphere 2023, 322, 138191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, F.; Zhou, J.; Yuan, Q.; Hu, N. Fallen Leaves Are Superior to Tree Pruning as Bulking Agents in Aerobic Composting Disposing Kitchen Waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Yang, M.; Sun, H.; Gao, M.; Wang, Q.; Wu, C. Bioconversion of Biowaste into Renewable Energy and Resources: A Sustainable Strategy. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, N.; Jiang, S.; Li, G.; Yuan, J.; Li, Y.; Chang, R.; Gong, X. Composting of Post-Consumption Food Waste Enhanced by Bioaugmentation with Microbial Consortium. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 168107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Qi, C.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Li, G.; Nghiem, L.D.; Luo, W. Regulating Bacterial Dynamics by Lime Addition to Enhance Kitchen Waste Composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graça, J.; Murphy, B.; Pentlavalli, P.; Allen, C.C.R.; Bird, E.; Gaffney, M.; Duggan, T.; Kelleher, B. Bacterium Consortium Drives Compost Stability and Degradation of Organic Contaminants in In-Vessel Composting Process of the Mechanically Separated Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste (MS-OFMSW). Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 13, 100621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Deng, F.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Li, D. Bioaugmentation on Humification during Co-Composting of Corn Straw and Biogas Slurry. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 374, 128756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Gunri, S.K.; Kundu, C.K.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K. Rapid Composting of Groundnut Residues through Novel Microbial Consortium: Evaluating Maturity, Stability and Microbial Activity. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2024, 7, 100277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mendonça Costa, L.A.; de Mendonça Costa, M.S.S.; Damaceno, F.M.; Chiarelotto, M.; Bofinger, J.; Gazzola, W. Bioaugmentation as a Strategy to Improve the Compost Quality in the Composting Process of Agro-Industrial Wastes. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijerathna, P.A.K.C.; Udayagee, K.P.P.; Idroos, F.S.; Manage, P.M. Formulation of Novel Microbial Consortia for Rapid Composting of Biodegradable Municipal Solid Waste: An Approach in the Circular Economy. Environ. Nat. Resour. J. 2024, 22, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Long, H.; Hu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Zheng, X.; Ye, Y.; Shao, R.; Yang, Q. The Co-Inoculation of Trichoderma Viridis and Bacillus Subtilis Improved the Aerobic Composting Efficiency and Degradation of Lignocellulose. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 394, 130285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, S.; Meng, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Ding, F.; Shi, L. Feedstock Optimization with Rice Husk Chicken Manure and Mature Compost during Chicken Manure Composting: Quality and Gaseous Emissions. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 387, 129694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Hao, Y.; Lin, B.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, K.; Li, J. The Bioaugmentation Effect of Microbial Inoculants on Humic Acid Formation during Co-Composting of Bagasse and Cow Manure. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Gao, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pan, J.; Tang, K.H.D.; Scriber, K.E.; Amoah, I.D.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Enhancing Nitrogen Conversion and Microbial Dynamics in Swine Manure Composting Process through Inoculation with a Microbial Consortium. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 423, 138819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biyada, S.; Merzouki, M.; Elkarrach, K.; Benlemlih, M. Spectroscopic Characterization of Organic Matter Transformation during Composting of Textile Solid Waste Using UV–Visible Spectroscopy, Infrared Spectroscopy and X-Ray Diffraction (XRD). Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biyada, S.; Imtara, H.; Elkarrach, K.; Laidi, O.; Saleh, A.; Al Kamaly, O.; Merzouki, M. Bio-Augmentation as an Emerging Strategy to Improve the Textile Compost Quality Using Identified Autochthonous Strains. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fels, L.; El Ouaqoudi, F.-Z.; Barje, F.; Hafidi, M.; Ouhdouch, Y. Two Culture Approaches Used to Determine the Co-Composting Stages by Assess of the Total Microflora Changes during Sewage Sludge and Date Palm Waste Co-Composting. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biyada, S.; Merzouki, M.; Demčenko, T.; Vasiliauskiene, D.; Urbonavičius, J.; Marčiulaitiene, E.; Vasarevičius, S.; Benlemlih, M. Evolution of Microbial Composition and Enzymatic Activities during the Composting of Textile Waste. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association Française de Normal (AFNOR). Amendements Organiques—Dénominations, Spécifications et Marquage; Association Française de Normal (AFNOR): Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Barje, F.; El Fels, L.; El Hajjouji, H.; Winterton, P.; Hafidi, M. Biodegradation of Organic Compounds during Co-Composting of Olive Oil Mill Waste and Municipal Solid Waste with Added Rock Phosphate. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 2965–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemati, A.; Aliasgharzad, N.; Khakvar, R.; Delangiz, N.; Asgari Lajayer, B.; van Hullebusch, E.D. Bioaugmentation of Thermophilic Lignocellulose Degrading Bacteria Accelerate the Composting Process of Lignocellulosic Materials. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 15887–15901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biyada, S.; Merzouki, M.; Dėmčėnko, T.; Vasiliauskienė, D.; Marčiulaitienė, E.; Vasarevičius, S.; Urbonavičius, J. The Effect of Feedstock Concentration on the Microbial Community Dynamics During Textile Waste Composting. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 813488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, T.; Neubauer, P.; Junne, S. Effect of Bioaugmentation with Paenibacillus spp. and Thin Slurry Recirculation on Microbial Hydrolysis of Maize Silage and Bedding Straw in a Plug-Flow Reactor. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 19139–19154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.S.; Pragati; He, W.; Li, C.; Mishra, J.; Feng, Y. Efficient Degradation of Untreated Complex Cellulosic Substrates by Newly Isolated Aerobic Paenibacillus Species. Water 2024, 16, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhan, K.; Patra, R.K.; Sethi, D.; Panda, N.; Sahoo, S.K.; Pattanayak, S.K.; Senapati, A.K. Isolation, Characterization and Identification of Cellulose-Degrading Bacteria for Composting of Agro-Wastes. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Feng, L.; Wang, Z.; Dai, J.; Zhang, H.; Xie, Y. Effects of Bacterial Inoculation on Lignocellulose Degradation and Microbial Properties during Cow Dung Composting. Bioengineered 2023, 14, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhao, M.; Gao, W.; Xie, L.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Song, C.; Wei, Z. Different Bacillus Sp. Play Different Roles on Humic Acid during Lignocellulosic Biomass Composting. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 139901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Han, Z.; Chu, X.; Ge, X.; Lu, F.; Liu, Y. High-Level Production of Xylose from Agricultural Wastes Using GH11 Endo-Xylanase and GH43 β-Xylosidase from Bacillus sp. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 45, 1705–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mironov, V.V.; Shchelushkina, A.A.; Ostrikova, V.V.; Klyukina, A.A.; Vanteeva, A.V.; Moldon, I.A.; Zhukov, V.G.; Kotova, I.B.; Nikolaev, Y.A. Influence of Bioaugmentation of Bacillus subtilis, B. amyloliquefaciens, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa on the Efficiency of Food Waste Composting. Microbiology 2024, 93, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, T.; Xing, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, X.; Yu, Y.; Teng, Z.; Chen, J. Enhanced Lignocellulose Degradation and Composts Fertility of Cattle Manure and Wheat Straw Composting by Bacillus Inoculation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, C.T.; Tran, T.N.; Pham, T.P.; Tran, T.T.T.; Truong, B.P.; Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, T.M.; Bui, T.Q.H.; Nguyen, A.D.; Wang, S.L. Production, Purification, and Characterization of a Cellulase from Paenibacillus elgii. Polymers 2024, 16, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Ju, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, L.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, L. Balancing the Pretreatment Effect of Deep Eutectic Solvents on Biomass and the Activity of β-Glucosidase Originating from Paenibacillus sp. LLZ1. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 400, 12464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, K.Y.; Woo, H.M.; Lee, S.M.; Um, Y. Aerobic and Anaerobic Cellulose Utilization by Paenibacillus sp. CAA11 and Enhancement of Its Cellulolytic Ability by Expressing a Heterologous Endoglucanase. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 268, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews, S.L.; Grunden, A.M.; Pawlak, J. Degradation of Lignocellulose and Lignin by Paenibacillus glucanolyticus. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 110, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, E.N.; MacDonald, J.; Liu, L.; Richman, A.; Yuan, Z.C. Current Knowledge and Perspectives of Paenibacillus: A Review. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plakys, G.; Gasparavičiūtė, R.; Vaitekūnas, J.; Rutkienė, R.; Meškys, R. Characterization of Paenibacillus sp. GKG Endo-β-1, 3-Glucanase, a Member of Family 81 Glycoside Hydrolases. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, F.A.; Yakasai, H.M.; Jagaba, A.H.; Usman, S.; Umar, H.A.; Shukor, M.Y. Bioremediation Potential of Bacillus sp. and Paenebacillus sp. Novel Lead-Resistant Isolates: Identification, Characterization, and Optimization Studies. Microbe 2024, 3, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Melkania, U. Biochar-Enhanced Hydrogen Production from Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste Using Co-Culture of Enterobacter aerogenes and E. coli. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 18865–18874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.; Desai, R.; Yadav, V.K.; Choudhary, N.; Ansari, M.J.; Alharbi, S.A.; Patel, R.; Thakkar, A.; Patel, A. Efficient Degradation of Methyl Red Dye from the Aqueous Solution by Individual Bacterial and Their Consortium in a Sugarcane Bagasse Waste-Based Media. Environ. Res. Commun. 2024, 6, 065010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Physical–Chemical Parameters | Textile Waste | Green Waste | Paper and Cardboard Waste | Norm NF U44-051/A2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture, % | 51.28 ± 1.03 | 61.49 ± 1.41 | 11.28 ± 1.07 | 40–60 |
| pH | 7.4 ± 0.15 | 6.6 ± 0.53 | 7.2 ± 0.35 | 6.5–8.5 |
| Total organic carbon (TOC), % | 31.63 ± 1.48 | 45.67 ± 1.37 | 59.35 ± 0.90 | >20 |
| Total Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN), % | 0.57 ± 0.04 | 1.23 ± 0.04 | 1.05 ± 0.05 | - |
| C/N ratio | 55.1 | 37.2 | 56.7 | 20–40 |
| Strains Used | TOC, % | TKN, % | C/N | Temperature, °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Streptomyces cellulosae | Final values | 24.60 | 1.23 | 20.00 | 33.26 |
| Achromobacter xylosoxidans | Final values | 23.45 | 1.18 | 19.87 | 40.23 |
| Serratia liquefaciens | Final values | 22.20 | 1.15 | 19.30 | 42.56 |
| Consortium | Final values | 20.30 | 1.52 | 13.36 | 54.17 |
| TOC | TKN | C/N | Temperature | Bacillus sp. | Paenibacillus sp. | Enterobacter aerogenes | Consortium | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOC | 1 | |||||||
| TKN | −0.913 | 1 | ||||||
| C/N | 0.888 | −0.989 | 1 | |||||
| Temperature | −0.554 | 0.607 | −0.667 | 1 | ||||
| Bacillus sp. | −0.606 | 0.606 | −0.616 | 0.726 | 1 | |||
| Paenibacillus sp. | −0.660 | 0.596 | −0.585 | 0.755 | 0.949 | 1 | ||
| Enterobacter aerogenes | −0.799 | 0.719 | −0.691 | 0.764 | 0.922 | 0.925 | 1 | |
| Consortium | −0.779 | 0.717 | −0.727 | 0.862 | 0.932 | 0.964 | 0.920 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biyada, S.; Tauraitė, D.; Urbonavičius, J.; Merzouki, M. Accelerated Co-Composting of Textile Waste Using the New Strains and Microbial Consortium: Evaluation of Maturity, Stability and Microbial Activity. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11976. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411976
Biyada S, Tauraitė D, Urbonavičius J, Merzouki M. Accelerated Co-Composting of Textile Waste Using the New Strains and Microbial Consortium: Evaluation of Maturity, Stability and Microbial Activity. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(24):11976. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411976
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiyada, Saloua, Daiva Tauraitė, Jaunius Urbonavičius, and Mohammed Merzouki. 2024. "Accelerated Co-Composting of Textile Waste Using the New Strains and Microbial Consortium: Evaluation of Maturity, Stability and Microbial Activity" Applied Sciences 14, no. 24: 11976. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411976
APA StyleBiyada, S., Tauraitė, D., Urbonavičius, J., & Merzouki, M. (2024). Accelerated Co-Composting of Textile Waste Using the New Strains and Microbial Consortium: Evaluation of Maturity, Stability and Microbial Activity. Applied Sciences, 14(24), 11976. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411976







