eJamar: A Novel Exergame Controller for Upper Limb Motor Rehabilitation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Method
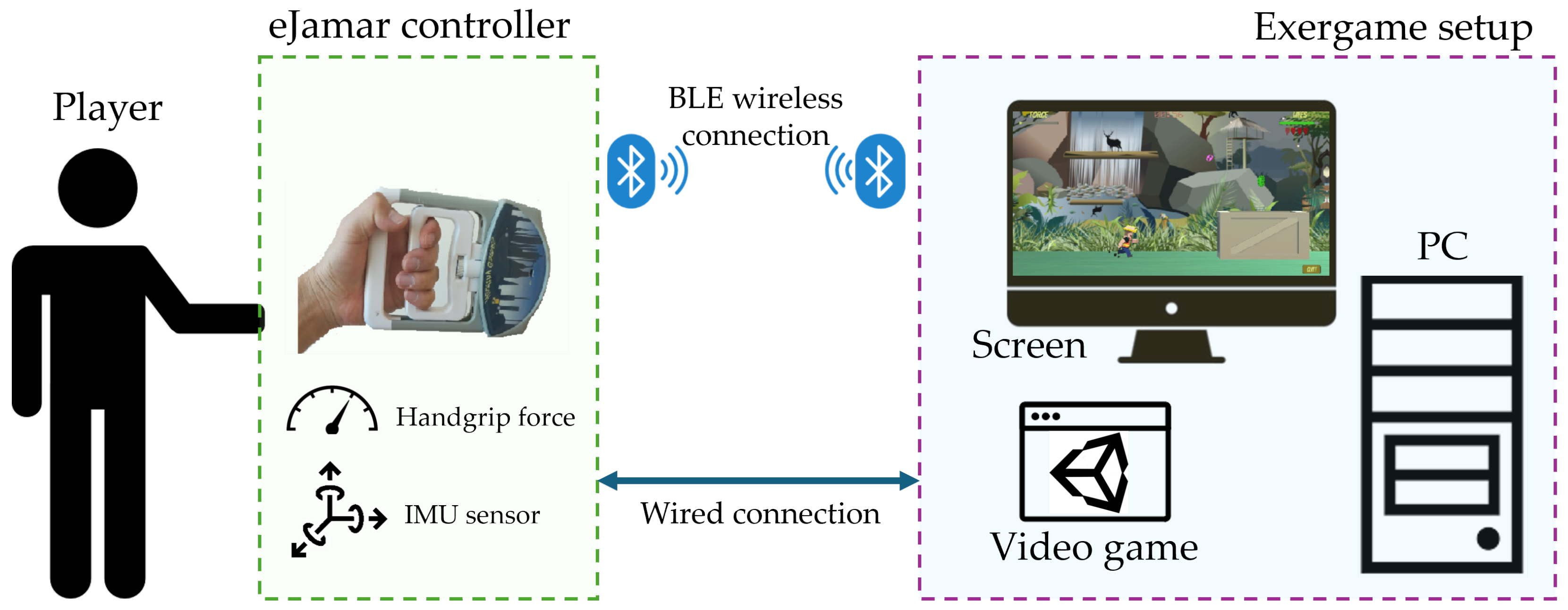
3.1. The eJamar GC
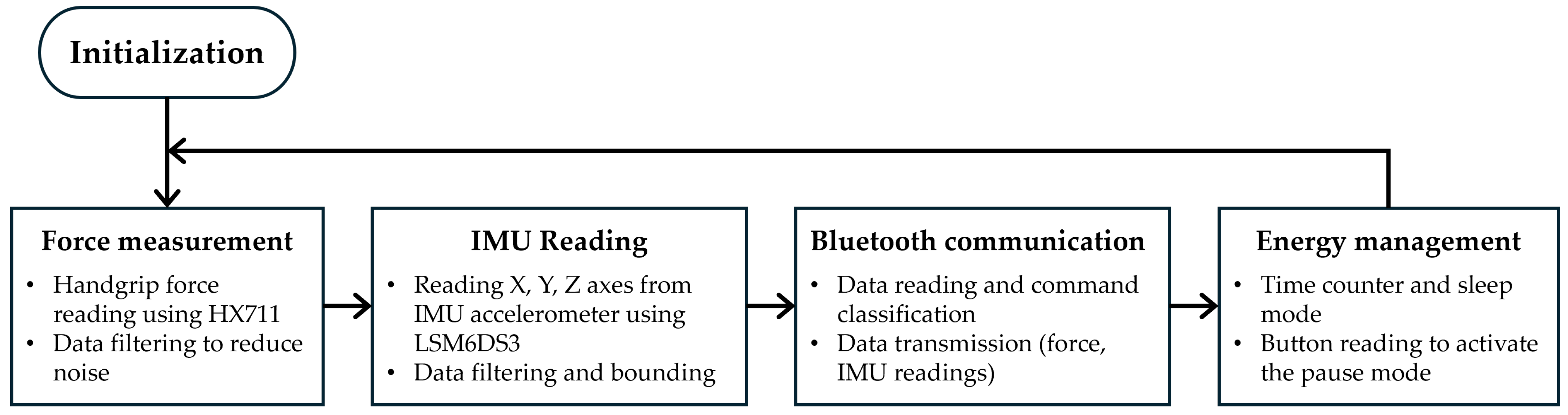
3.1.1. Electronic System
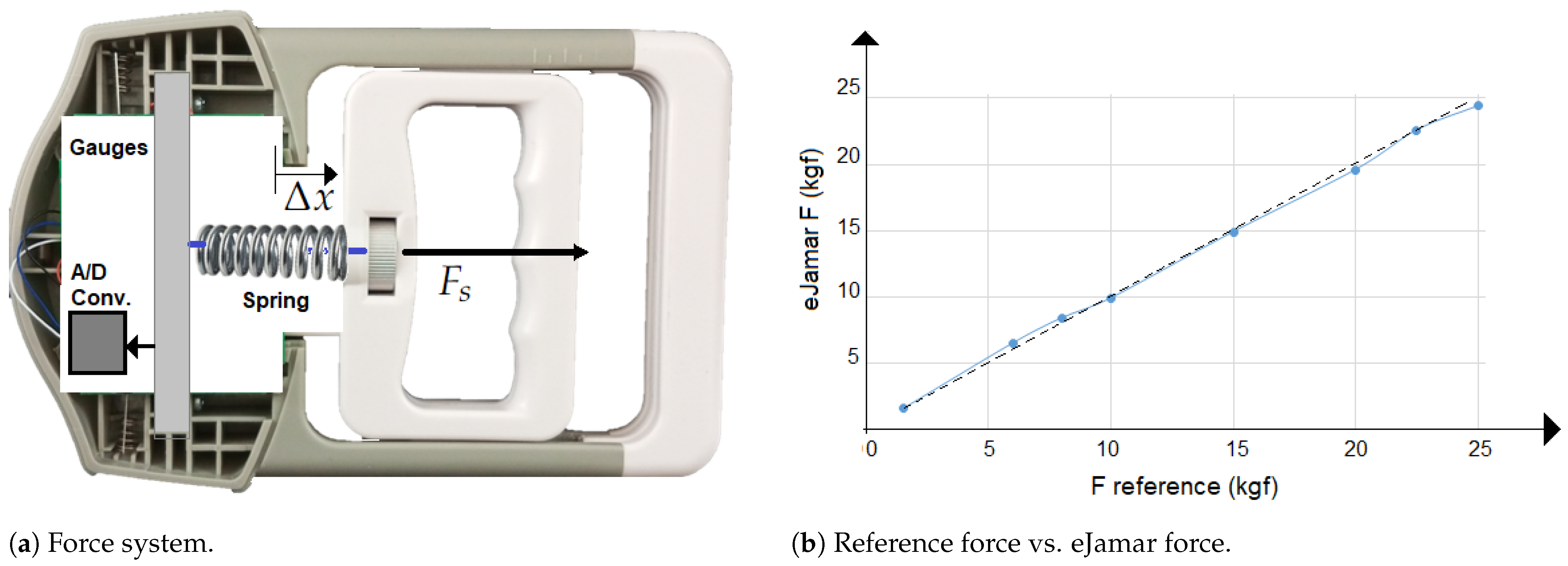
3.1.2. Grasping Force Detection and Calibration
3.2. GC Functioning
3.2.1. Peter Jumper Game
3.2.2. Andromeda Game
3.3. Requirements for Operation
3.3.1. System Requirements
3.3.2. Bluetooth Connection
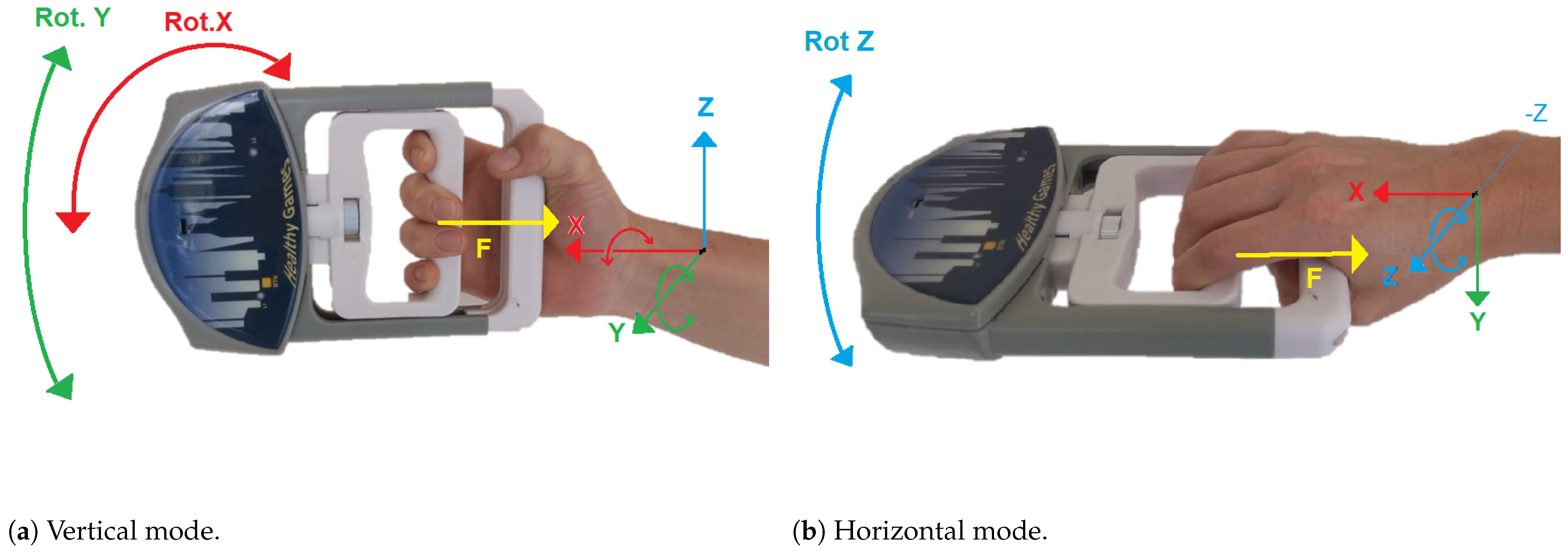
3.3.3. Measurement Ranges
4. Preliminary System Validation
4.1. Experimental Protocol
4.2. USE Questionnaire: Usefulness, Satisfaction, and Ease of Use
5. Discussion
Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADC | Analog-to-digital converter |
| IMU | Inertial measurement unit |
| GC | Game controller |
| ADL | Activities of daily living |
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Brainin, M.; Norrving, B.; Martins, S.; Sacco, R.L.; Hacke, W.; Fisher, M.; Pandian, J.; Lindsay, P. World Stroke Organization (WSO): Global Stroke Fact Sheet 2022. Int. J. Stroke Off. J. Int. Stroke Soc. 2022, 17, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüth, M.; Schmelzer, M.; Burtniak, K.; Kaspar, K. Commercial exergames for rehabilitation of physical health and quality of life: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials with adults in unsupervised home environments. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1155569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Yang, S. Defining exergames & exergaming. Proc. Meaningful Play. 2010, 2010, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Cuesta-Gómez, A.; Martín-Díaz, P.; Sánchez-Herrera Baeza, P.; Martínez-Medina, A.; Ortiz-Comino, C.; Cano-de-la Cuerda, R. Nintendo Switch Joy-Cons’ Infrared Motion Camera Sensor for Training Manual Dexterity in People with Multiple Sclerosis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, N.; Karimi, H.; Ahmad, A.; Gilani, S.A.; Khalid, K.; Aslam, A.S.; Hanif, A. Virtual Reality Training Using Nintendo Wii Games for Patients With Stroke: Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Serious Games 2022, 10, e29830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques-Sule, E.; Arnal-Gómez, A.; Buitrago-Jiménez, G.; Suso-Martí, L.; Cuenca-Martínez, F.; Espí-López, G.V. Effectiveness of Nintendo Wii and Physical Therapy in Functionality, Balance, and Daily Activities in Chronic Stroke Patients. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2021, 22, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, M.; Domingo Soria, B.; Terroso Gil, N. Finding Effective Adjustment Levels for Upper Limb Exergames: Focus Group Study With Children With Physical Disabilities. JMIR Serious Games 2023, 11, e36110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, M.A.; Aboelnour, N.H.; Alsharidah, A.S.; Kamel, F.H. Effect of exercise mode on physical function and quality of life in breast cancer–related lymphedema: A randomized trial. Support. Care Cancer 2022, 30, 2101–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.; Bubyr, L.; Archambault, P.S.; Higgins, J.; Levin, M.F.; Kairy, D. Virtual Reality–Based Rehabilitation as a Feasible and Engaging Tool for the Management of Chronic Poststroke Upper-Extremity Function Recovery: Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Serious Games 2022, 10, e37506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, I.; Cha, B.; Cho, D.; Park, E.; Lee, K.; Kim, M. Safety and Potential Usability of Immersive Virtual Reality for Brain Rehabilitation: A Pilot Study. Games Health J. 2023, 12, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo-Prieto, P.; Cancela-Carral, J.M.; Rodríguez-Fuentes, G. Wearable Immersive Virtual Reality Device for Promoting Physical Activity in Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Sensors 2022, 22, 3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamikokuryo, K.; Haga, T.; Venture, G.; Hernandez, V. Adversarial Autoencoder and Multi-Armed Bandit for Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment in Immersive Virtual Reality for Rehabilitation: Application to Hand Movement. Sensors 2022, 22, 4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Chen, K. Task-Oriented and Imitation-Oriented Movements in Virtual Reality Exercise Performance and Design. Hum. Factors 2023, 65, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heutinck, L.; Jansen, M.; Van Den Elzen, Y.; Van Der Pijl, D.; De Groot, I.J. Virtual Reality Computer Gaming with Dynamic Arm Support in Boys with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2018, 5, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsiana, E.; Ladakis, I.; Fotopoulos, D.; Chytas, A.; Kilintzis, V.; Chouvarda, I. Serious Gaming Technology in Upper Extremity Rehabilitation: Scoping Review. JMIR Serious Games 2020, 8, e19071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.; Lee, H.J.; Chang, W.H.; Ko, S.H.; Shin, Y.I.; Kim, Y.H. A Smart Glove Digital System Promotes Restoration of Upper Limb Motor Function and Enhances Cortical Hemodynamic Changes in Subacute Stroke Patients with Mild to Moderate Weakness: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.S.; An, C.S.; Lim, C.G. Effects of a Rehabilitation Program Using a Wearable Device on the Upper Limb Function, Performance of Activities of Daily Living, and Rehabilitation Participation in Patients with Acute Stroke. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Kafy, E.; Alshehri, M.A.; El-Fiky, A.; Guermazi, M.; Mahmoud, H. The Effect of Robot-Mediated Virtual Reality Gaming on Upper Limb Spasticity Poststroke: A Randomized-Controlled Trial. Games Health J. 2022, 11, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, M.; Held, J.P.O.; Wittmann, F.; Valladares, B.; Lambercy, O.; Sturzenegger, C.; Palla, A.; Lutz, K.; Luft, A.R. Reward During Arm Training Improves Impairment and Activity After Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2022, 36, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdea, G.; Kim, N.; Polistico, K.; Kadaru, A.; Grampurohit, N.; Hundal, J.; Pollack, S. Robotic Table and Serious Games for Integrative Rehabilitation in the Early Poststroke Phase: Two Case Reports. JMIR Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2022, 9, e26990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- House, G.; Burdea, G.; Polistico, K.; Grampurohit, N.; Roll, D.; Damiani, F.; Keeler, S.; Hundal, J. A Rehabilitation First—Tournament Between Teams of Nursing Home Residents with Chronic Stroke. Games Health J. 2016, 5, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilbride, C.; Scott, D.J.M.; Butcher, T.; Norris, M.; Ryan, J.M.; Anokye, N.; Warland, A.; Baker, K.; Athanasiou, D.A.; Singla-Buxarrais, G.; et al. Rehabilitation via HOMe Based gaming exercise for the Upper-limb post Stroke (RHOMBUS): Protocol of an intervention feasibility trial. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e026620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilbride, C.; Warland, A.; Stewart, V.; Aweid, B.; Samiyappan, A.; Ryan, J.; Butcher, T.; Athanasiou, D.A.; Baker, K.; Singla-Buxarrais, G.; et al. Rehabilitation using virtual gaming for Hospital and hOMe-Based training for the Upper limb post Stroke (RHOMBUS II): Protocol of a feasibility randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e058905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahlani, S.S.; Shirvani, H.; Butt, J.; Mirzaee, I.; Esfahlani, K.S. Machine Learning role in clinical decision-making: Neuro-rehabilitation video game. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 201, 117165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, I.A.; Alves, C.M.; Rezende, A.R.; Mendes, L.C.; Paiva, T.S.D.; Cyrino, G.F.; Souza, J.T.D.; Silva, M.A.M.; Souza, L.A.P.S.D.; Naves, E.L.M. Virtual reality and serious game therapy for post-stroke individuals: A preliminary study with humanized rehabilitation approach protocol. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2022, 49, 101681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera-Rubio, Á.; Cuesta-Gómez, A.; Mallo-López, A.; Jardón-Huete, A.; Oña-Simbaña, E.D.; Alguacil-Diego, I.M. Feasibility and efficacy of a virtual reality game-based upper extremity motor function rehabilitation therapy in patients with chronic stroke: A pilot study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotopoulos, D.; Ladakis, I.; Kilintzis, V.; Chytas, A.; Koutsiana, E.; Loizidis, T.; Chouvarda, I. Gamifying rehabilitation: MILORD platform as an upper limb motion rehabilitation service. Front. Comput. Sci. 2022, 4, 932342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oña, E.D.; Garcia-Haro, J.M.; Jardón, A.; Balaguer, C. Robotics in health care: Perspectives of robot-aided interventions in clinical practice for rehabilitation of upper limbs. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdea, G.; Kim, N.; Polistico, K.; Kadaru, A.; Grampurohit, N.; Roll, D.; Damiani, F. Assistive game controller for artificial intelligence-enhanced telerehabilitation post-stroke. Assist. Technol. 2021, 33, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.S.; Chen, J.L.; Hsu, H.C. Novel Upper-Limb Rehabilitation System Based on Attention Technology for Post-Stroke Patients: A Preliminary Study. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 2720–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzo, A.; Jung, J.H.; Arcas-Ruiz-Ruano, J.; Perry, J.C.; Keller, T. ArmAssist: A Telerehabilitation Solution for Upper-Limb Rehabilitation at Home. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2023, 30, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, R.R.; Yong, W.Q.; Bin Heyat, M.B.; Ali, L.; Qiang, S.; Ali, A.; Rauf, H.T.; Wu, Z. Design of a Smart Elbow Brace as a Home-Based Rehabilitation Device. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cela, A.F.; Oña, E.D.; Jardón, A. Serious gaming for upper limbs rehabilitation—Game controllers features: A Scoping Review. Games Health J. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Türkbey, T.; Kutlay, S.; Gök, H. Clinical feasibility of Xbox KinectTM training for stroke rehabilitation: A single-blind randomized controlled pilot study. J. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 49, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fluet, G.G.; Qiu, Q.; Patel, J.; Cronce, A.; Merians, A.S.; Adamovich, S.V. Autonomous Use of the Home Virtual Rehabilitation System: A Feasibility and Pilot Study. Games Health J. 2019, 8, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leon, N.; Bhatt, S.; Al-Jumaily, A. Augmented reality game based multi-usage rehabilitation therapist for stroke patients. Int. J. Smart Sens. Intell. Syst. 2014, 7, 1044–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, A.; Sepulveda-Munoz, D.; Gil-Agudo, A.; de los Reyes Guzman, A. Serious game platform with haptic feedback and EMG monitoring for upper limb rehabilitation and smoothness quantification on spinal cord injury patients. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, M.C.; Elexpuru, J.; Dias, P.; Santos, B.S.; Amorim, P. Immersive virtual reality for upper limb rehabilitation: Comparing hand and controller interaction. Virtual Real. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Hou, Z.G.; Peng, L.; Luo, L.; Wang, W. Robot assisted rehabilitation of the arm after stroke: Prototype design and clinical evaluation. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2017, 60, 073201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Kazuki, N.; Quan, C.; Luo, Z. On robotic rehabilitation of human dual arms’ coordinative function. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2016, 52, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsekleves, E.; Paraskevopoulos, I.T.; Warland, A.; Kilbride, C. Development and preliminary evaluation of a novel low cost VR-based upper limb stroke rehabilitation platform using Wii technology. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2016, 11, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, H.; Kamal, A.; Narayanan, A. A simple upper limb rehabilitation trainer. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2017, 9, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Burdea, G.C.; Grampurohit, N.; Kim, N.; Polistico, K.; Kadaru, A.; Pollack, S.; Oh-Park, M.; Barrett, A.; Kaplan, E.; Masmela, J.; et al. Feasibility of integrative games and novel therapeutic game controller for telerehabilitation of individuals chronic post-stroke living in the community. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2020, 27, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordan, O.; Dincay, D.A.; Yurdakul Toker, C.; Oksuz, E.B.; Semizoglu, S. (Eds.) Game Design Education: Proceedings of PUDCAD 2020; Springer Series in Design and Innovation; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyaman, S.; Alppay, E.C. A Critical Review of Video Game Controller Designs. In Proceedings of the Game + Design Education, online, 24–26 June 2020; Cordan, O., Dincay, D.A., Yurdakul Toker, C., Oksuz, E.B., Semizoglu, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, L.A.; Klassen, T.K.; Janssen, J.; Thetford, C.; Eng, J.J. Delivering Intensive Rehabilitation in Stroke: Factors Influencing Implementation. Phys. Ther. 2018, 98, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elor, A.; Teodorescu, M.; Kurniawan, S. Project Star Catcher: A Novel Immersive Virtual Reality Experience for Upper Limb Rehabilitation. ACM Trans. Access. Comput. 2018, 11, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozevink, S.G.; Van Der Sluis, C.K.; Garzo, A.; Keller, T.; Hijmans, J.M. HoMEcare aRm rehabiLItatioN (MERLIN): Telerehabilitation using an unactuated device based on serious games improves the upper limb function in chronic stroke. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Kelleher, C.L.; Engsberg, J.R. Developing Home-Based Virtual Reality Therapy Interventions. Games Health J. 2013, 2, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.; Alawna, M. Tele-Rehabilitation Strategies for a Patient With Post-stroke Spasticity: A Powerful Tool Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic. Cureus 2021, 13, e19311. [Google Scholar]
- Oña Simbaña, E.D.; Sánchez-Herrera Baeza, P.; Jardón Huete, A.; Balaguer, C. Review of automated systems for upper limbs functional assessment in neurorehabilitation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 32352–32367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-de Pablo, C.; Balasubramanian, S.; Savić, A.; Tomić, T.D.; Konstantinović, L.; Keller, T. Validating ArmAssist Assessment as outcome measure in upper-limb post-stroke telerehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 4623–4626. [Google Scholar]
- Oña, E.D.; Jardón, A.; Cuesta-Gómez, A.; Sánchez-Herrera-Baeza, P.; Cano-de-la Cuerda, R.; Balaguer, C. Validity of a fully-immersive VR-based version of the box and blocks test for upper limb function assessment in Parkinson’s disease. Sensors 2020, 20, 2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

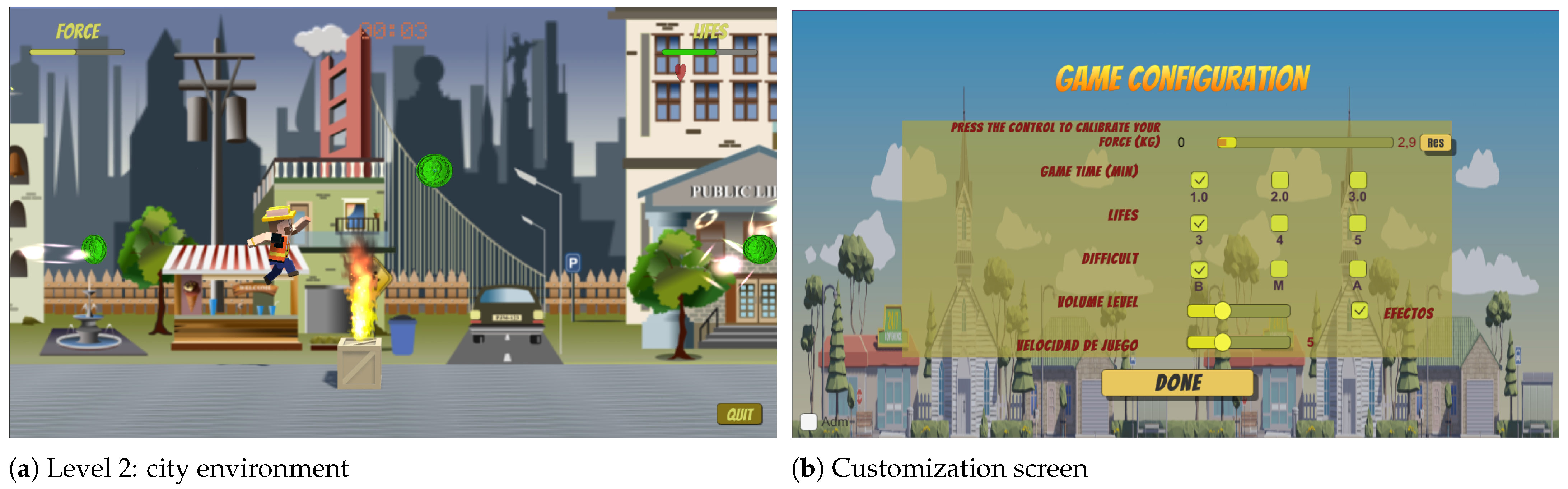
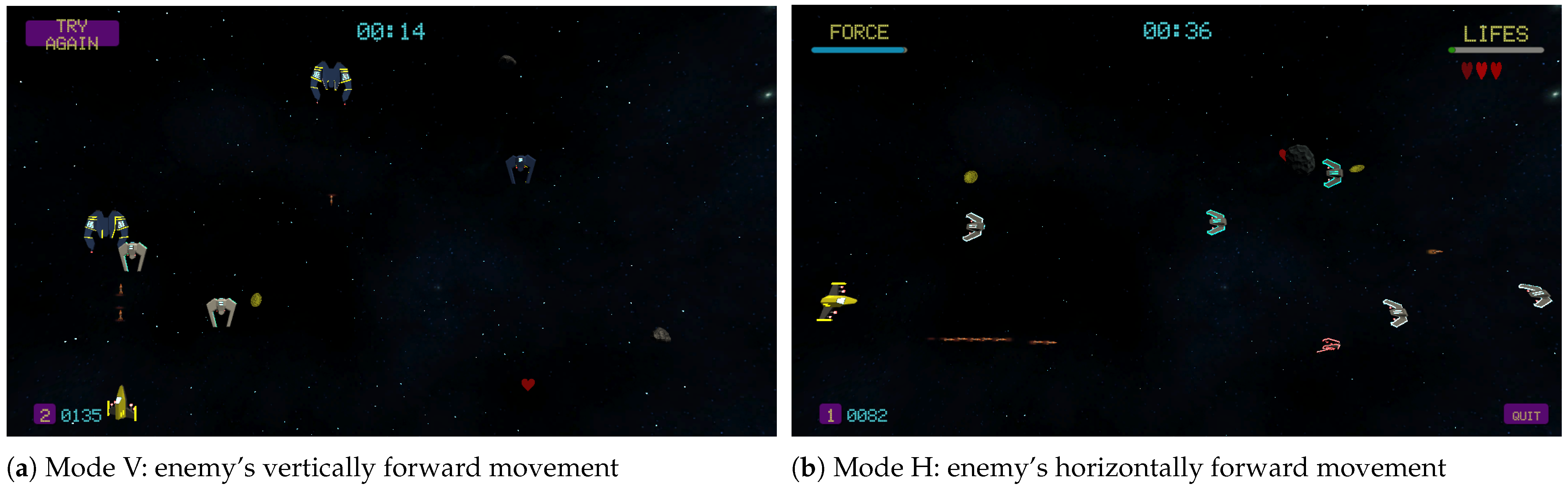
| Level | Name | Details | Incentive | Obstacles | Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rural Fantasy | It is a rural environment with pastel colors. The environment has classic houses and nature. | Coins | Boxes, cylinders, and fences | 10% MAX |
| 2 | Capital City | It is a city with a cold climate with streets, houses, and buildings of the main city. | Coins and hearts | Big boxes, Medium boxes, and fire boxes | 15% MAX |
| 3 | Amazonas | It is the jungle, with mountains, rivers, lakes, flora, and fauna typical of the flora and fauna of the zone | Coins and hearts | Big boxes, Medium boxes, and fire boxes | 20% MAX |
| Mode | Movements | Level | Details | Incentive | Enemies | Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical | Pronation/supination (to move the spaceship laterally) | 1 | The user appears at the bottom of the screen and enemies appear randomly appear at the top of the screen | Coins and projectiles | Little ships and asteroids | 10% MAX |
| 2 | The user appears at the bottom of the screen and enemies appear randomly at the top of the screen | Coins, hearts, and projectiles | Big ships, asteroids, and projectiles | 15% MAX | ||
| Horizontal | Radial and cubital wrist deviations (to move the spaceship vertically) | 1 | The user is on the left side of the screen and enemies appear randomly from the right | Coins and projectiles | Little ships and asteroids | 10% MAX |
| 2 | The user is on the left side of the screen and enemies appear randomly from the right | Coins, hearts, and projectiles | Big ships, asteroids, and projectiles | 15% MAX |
| ID | Age | Gender | Dominant Hand | Years of School | Prior Computer Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 33 | F | Right | 18 | Yes |
| P2 | 36 | F | Left | 18 | Yes |
| P3 | 55 | F | Right | 12 | No |
| P4 | 62 | F | Right | 12 | No |
| P5 | 64 | M | Left | 14 | Yes |
| P6 | 65 | M | Right | 18 | Yes |
| P7 | 68 | F | Right | 12 | No |
| P8 | 71 | M | Right | 14 | Yes |
| ID | Question | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 | P8 | Mean | STD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Playability | |||||||||||
| Q1 | Was the Peter Jumper Game (PJG) friendly? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1.5 | 0.53 |
| Q2 | Was PJG interesting for you? | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0.63 | 1.19 |
| Q3 | Would you use PJG at home? | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1.4 | 0.52 |
| Q4 | Was the graphic design of PJG adequate (player, obstacles, environment, etc.)? friendly? | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1.5 | 0.53 |
| Q5 | Was PJG intuitive and easy to play? | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1.8 | 0.5 |
| Q6 | Have you been able to play PJG without a therapist’s support? | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1.9 | 0.4 |
| Q7 | Was the Andromeda Game (AG) friendly? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1.4 | 0.52 |
| Q8 | Was AG interesting for you? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1.4 | 0.52 |
| Q9 | Would you use AG at home? | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1.6 | 0.52 |
| Q10 | Was the graphic design of AG adequate (spaceship, enemies, environment, etc.)? | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1.4 | 0.74 |
| Q11 | Was AG intuitive and easy to play? | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1.9 | 0.35 |
| Q12 | Have you been able to play AG without a therapist’s support? | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1.8 | 0.46 |
| Usability | |||||||||||
| Q13 | Have you been able to use the Game Controller (GC) easily? | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1.8 | 0.46 |
| Q14 | In general, was it easy to control the game actions with the GC? | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1.8 | 0.46 |
| Q15 | Was the weight of the GC suitable? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | −1 | 2 | 1 | 1.0 | 0.93 |
| Q16 | Were elements of the GC easy to handle? | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1.6 | 0.74 |
| Q17 | Have you felt comfort in your hand when taking the GC? | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1.5 | 0.76 |
| Q18 | There were no disconnection issues during the session (GC and PC) | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1.9 | 0.35 |
| Q19 | Do you find the vibration mode useful? | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1.3 | 0.89 |
| Satisfaction | |||||||||||
| Q20 | Have you been able to perform all the game levels successfully? | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2.0 | 0.0 |
| Q21 | Have the games taken a lot of effort from you? (fatigue) | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.4 | 0.52 |
| Q22 | In general, the difficulty level of the games is adequate. | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1.5 | 0.53 |
| Q23 | Were you able to easily calibrate the rigidity of the device? | −1 | −1 | −1 | 2 | 2 | −1 | 0 | 2 | 0.25 | 1.49 |
| Q24 | If possible, would you like to continue using this system (GC + games)? | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1.6 | 0.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cela, A.F.; Oña, E.D.; Jardón, A. eJamar: A Novel Exergame Controller for Upper Limb Motor Rehabilitation. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11676. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411676
Cela AF, Oña ED, Jardón A. eJamar: A Novel Exergame Controller for Upper Limb Motor Rehabilitation. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(24):11676. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411676
Chicago/Turabian StyleCela, Andrés F., Edwin Daniel Oña, and Alberto Jardón. 2024. "eJamar: A Novel Exergame Controller for Upper Limb Motor Rehabilitation" Applied Sciences 14, no. 24: 11676. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411676
APA StyleCela, A. F., Oña, E. D., & Jardón, A. (2024). eJamar: A Novel Exergame Controller for Upper Limb Motor Rehabilitation. Applied Sciences, 14(24), 11676. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411676








