Automated Deep Learning Model for Sperm Head Segmentation, Pose Correction, and Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
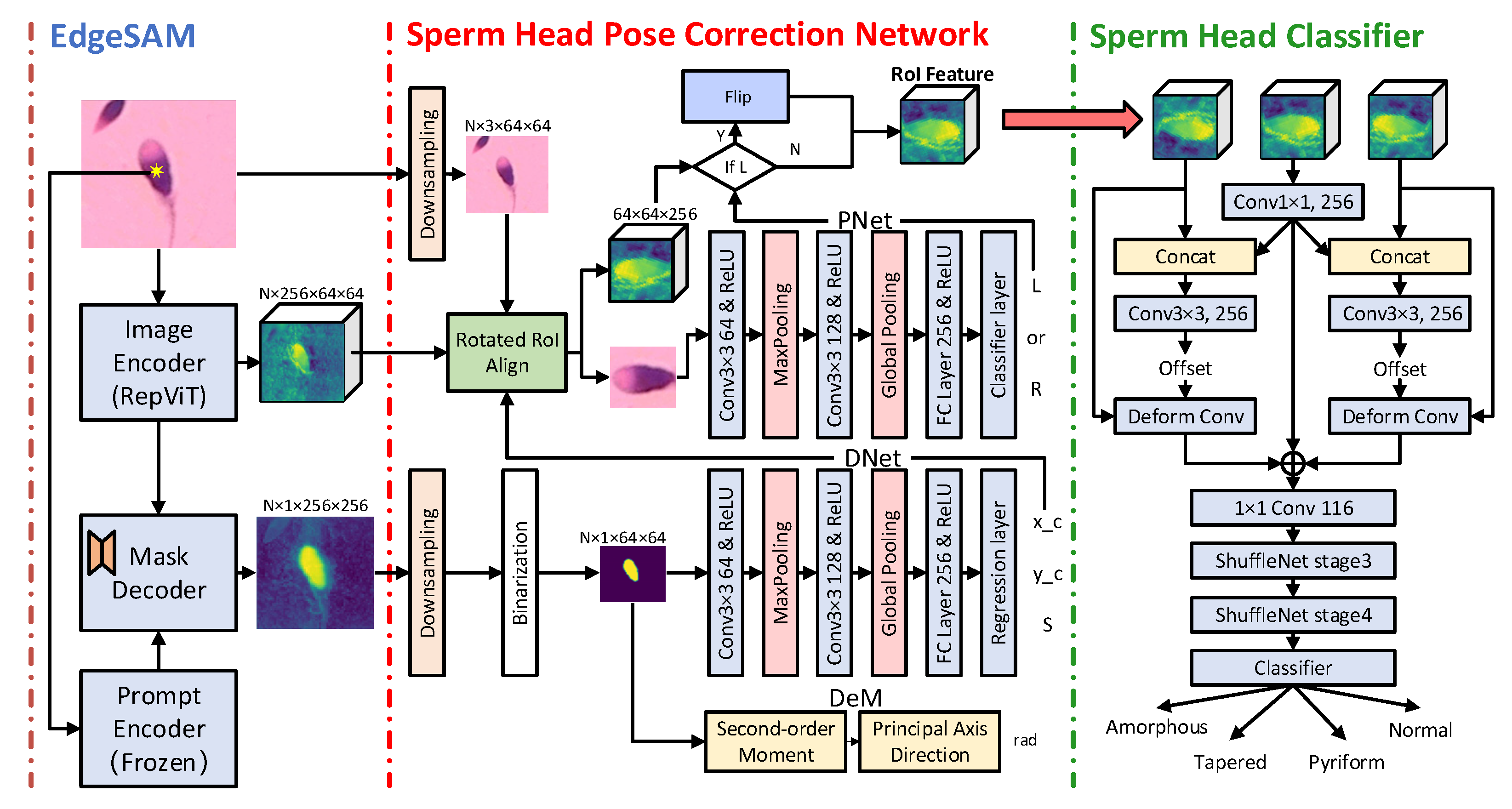
- We introduce EdgeSAM into the sperm head segmentation task, using a single coordinate point as a prompt to indicate the rough location of the sperm head, enabling accurate feature extraction and segmentation for the specific sperm.
- We propose a sperm head pose correction network that can accurately predict the position, angle, and orientation of the sperm head, achieving standardization with a low computational cost. This significantly improves the accuracy and efficiency of sperm head morphology classification.
- We propose a flip feature fusion module that leverages the symmetry of pyriform and amorphous sperm heads by processing flipped feature maps to enhance the accuracy of sperm head morphology classification.
2. Materials and Methods
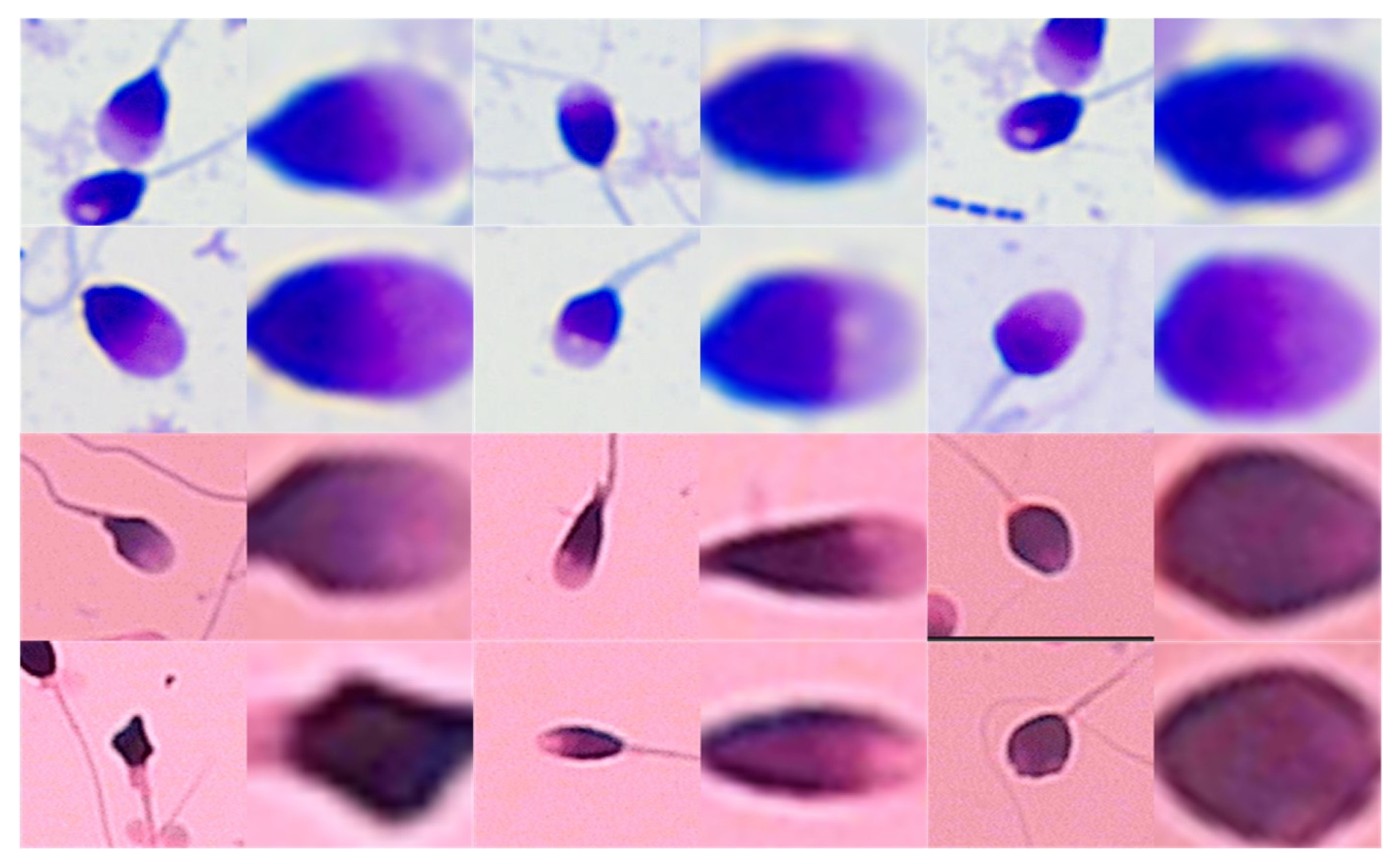
2.1. Dataset Collection and Preprocessing
2.2. Model Construction
2.2.1. Sperm Feature Extraction and Segmentation
2.2.2. Sperm Head Pose Correction Network
2.2.3. Sperm Head Classification Network
2.2.4. Three-Phase Training Strategy
3. Implementation Detail
4. Evaluation Metric
5. Results
6. Discussion
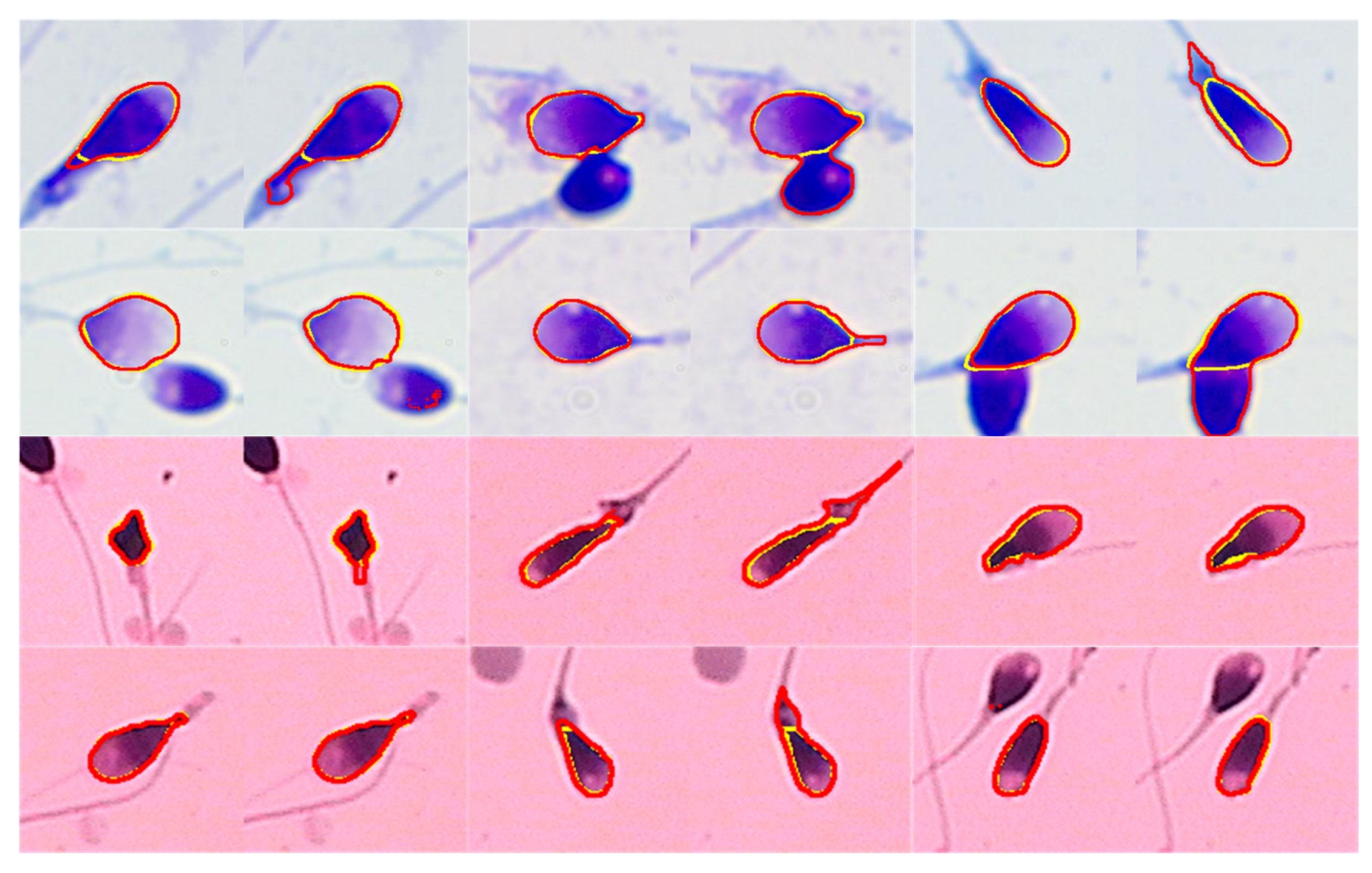
6.1. Segmentation Result
6.2. Pose Correction Result
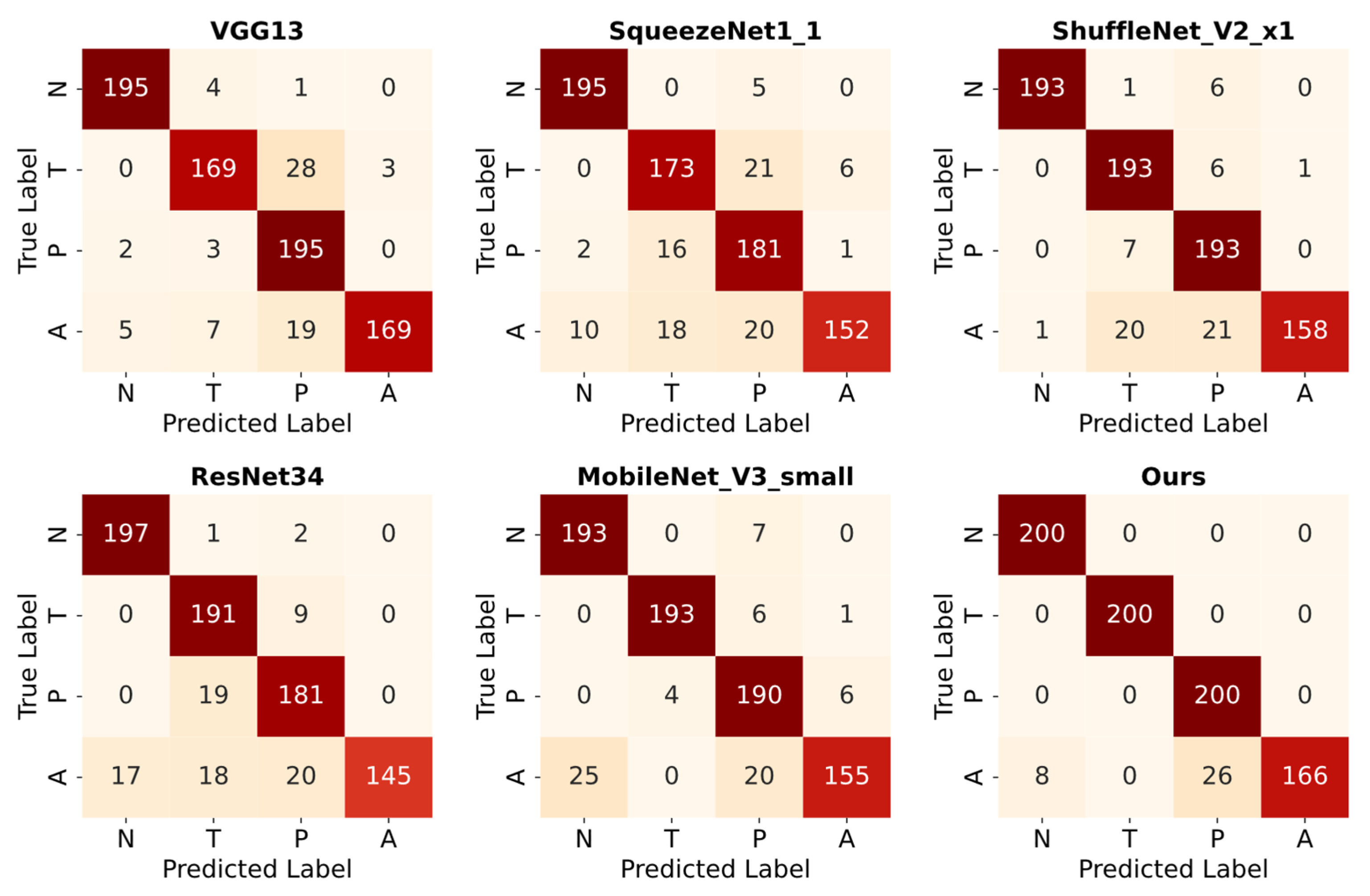
6.3. Classification Results on Augmented Test Data
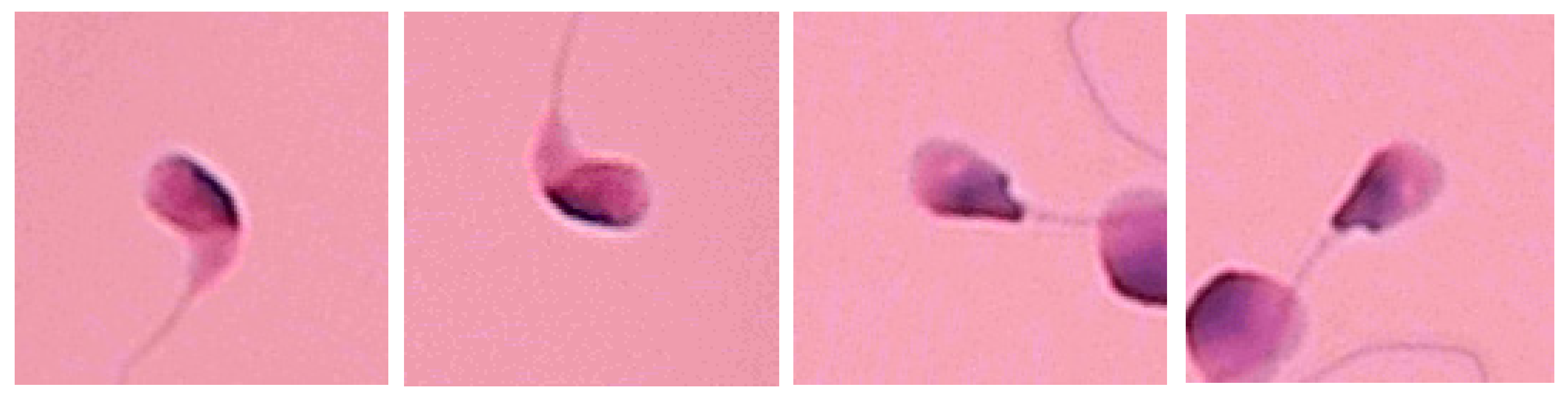
7. Limitations and Future Work
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agarwal, A.; Mulgund, A.; Hamada, A.; Chyatte, M.R. A Unique View on Male Infertility around the Globe. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2015, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, M.Z.; Saadeldin, I.M. Physiology of the Reproductive System. In Recent Advances in Biotechnology; Saadeldin, I.M., Ed.; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2022; Volume 5, pp. 1–59. ISBN 978-981-5051-66-7. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Laboratory Manual for the Examination and Processing of Human Semen, 6th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Chang, V.; Heutte, L.; Petitjean, C.; Härtel, S.; Hitschfeld, N. Automatic Classification of Human Sperm Head Morphology. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 84, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, F.; Monadjemi, S.A.; Alirezaie, J.; Naghsh-Nilchi, A.R. A Dictionary Learning Approach for Human Sperm Heads Classification. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 91, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, T.F.; Menkveld, R.; Stander, F.S.H.; Lombard, C.J.; Van Der Merwe, J.P.; Van Zyl, J.A.; Smith, K. Sperm Morphologic Features as a Prognostic Factor in in Vitro Fertilization. Fertil. Steril. 1986, 46, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, T.P.; Kohn, J.R.; Ramasamy, R. Effect of Sperm Morphology on Pregnancy Success via Intrauterine Insemination: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Urol. 2018, 199, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Jia, Y.; Xiong, C.; Meng, T.; Guan, H.; Xia, W.; Ding, M.; Yuchi, M. Variability in the Morphologic Assessment of Human Sperm: Use of the Strict Criteria Recommended by the World Health Organization in 2010. Fertil. Steril. 2014, 101, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beletti, M.E.; Costa, L.D.F.; Viana, M.P. A Comparison of Morphometric Characteristics of Sperm from Fertile Bos Taurus and Bos Indicus Bulls in Brazil. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2005, 85, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, V.; Garcia, A.; Hitschfeld, N.; Härtel, S. Gold-Standard for Computer-Assisted Morphological Sperm Analysis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 83, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Riordon, J.; McCallum, C.; Sinton, D. Deep Learning for the Classification of Human Sperm. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 111, 103342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.00567. [Google Scholar]
- Ilhan, H.O.; Sigirci, I.O.; Serbes, G.; Aydin, N. A Fully Automated Hybrid Human Sperm Detection and Classification System Based on Mobile-Net and the Performance Comparison with Conventional Methods. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2020, 58, 1047–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yüzkat, M.; Ilhan, H.O.; Aydin, N. Multi-Model CNN Fusion for Sperm Morphology Analysis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 137, 104790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabour, S.; Frosst, N.; Hinton, G.E. Dynamic Routing Between Capsules. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Guyon, I., Luxburg, U.V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Jabbari, H.; Bigdeli, N. New Conditional Generative Adversarial Capsule Network for Imbalanced Classification of Human Sperm Head Images. Neural. Comput. Applic. 2023, 35, 19919–19934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Liang, P.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zha, X.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, Y.; Chen, D.Z. Shmc-Net: A Mask-Guided Feature Fusion Network for Sperm Head Morphology Classification. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Athens, Greece, 27–30 May 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, L.; Fernando, J.; Akbaridoust, F.; Ackermann, K.; Nosrati, R. Ensembled Deep Learning for the Classification of Human Sperm Head Morphology. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2022, 4, 2200111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahali, M.I.; Leu, J.-S.; Darmawan, J.T.; Avian, C.; Bachroin, N.; Prakosa, S.W.; Faisal, M.; Putro, N.A.S. A Dual Architecture Fusion and AutoEncoder for Automatic Morphological Classification of Human Sperm. Sensors 2023, 23, 6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azulay, A.; Weiss, Y. Why Do Deep Convolutional Networks Generalize so Poorly to Small Image Transformations? arXiv 2019, arXiv:1805.12177. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R. Making Convolutional Networks Shift-Invariant Again. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; Chaudhuri, K., Salakhutdinov, R., Eds.; PMLR: Birmingham, UK, 2019; Volume 97, pp. 7324–7334. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Wang, M.; Wang, M.; Yin, J.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, J. Automatic Microscopy Analysis with Transfer Learning for Classification of Human Sperm. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Li, X.; Loy, C.C.; Dai, B. EdgeSAM: Prompt-In-the-Loop Distillation for On-Device Deployment of SAM. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2312.06660. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Sivakumar, V.; Mnatsakanyan, M.; Pang, G. Improving Rotated Text Detection with Rotation Region Proposal Networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.07031. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Song, H.; Dai, C.; Jiang, A.; Shan, G.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Abdalla, K.; Dhanani, S.N.; Fatemeh Moosavi, K.; et al. Automated Sperm Morphology Analysis Based on Instance-Aware Part Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 13–17 May 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 17743–17749. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, E.J.; Shen, Y.; Wallis, P.; Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.09685. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Guo, S.; Tan, X.; Xu, K.; Wang, M.; Ma, L. Rethinking Efficient Lane Detection via Curve Modeling. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.02431. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, I.; Mustafa, G.; Ma, J. Deep Learning-Based Morphological Classification of Human Sperm Heads. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
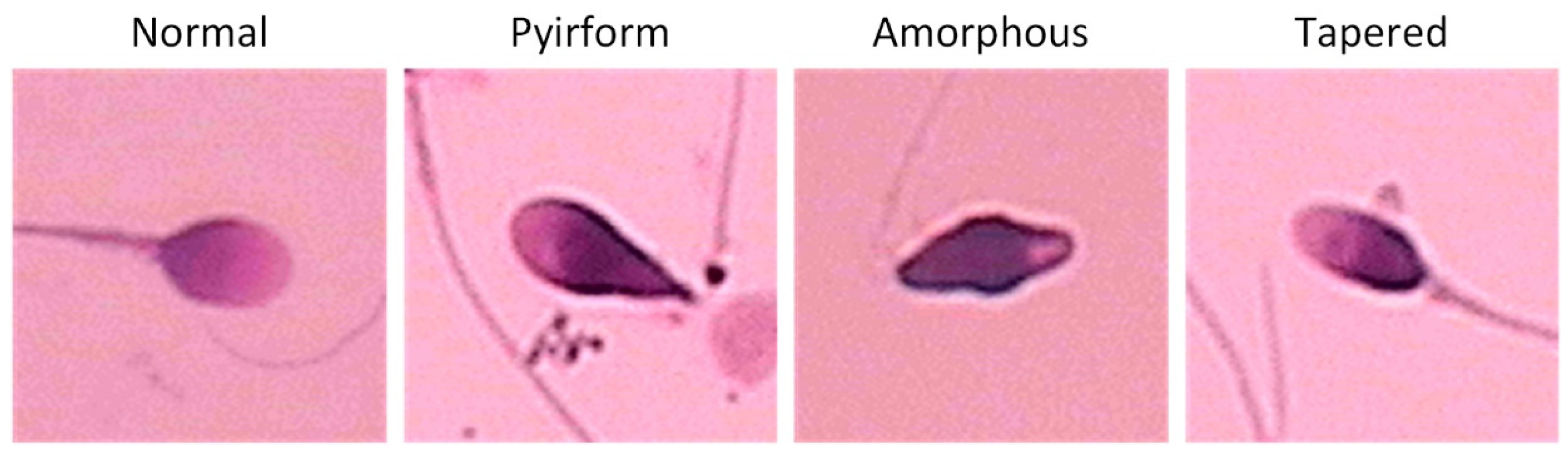
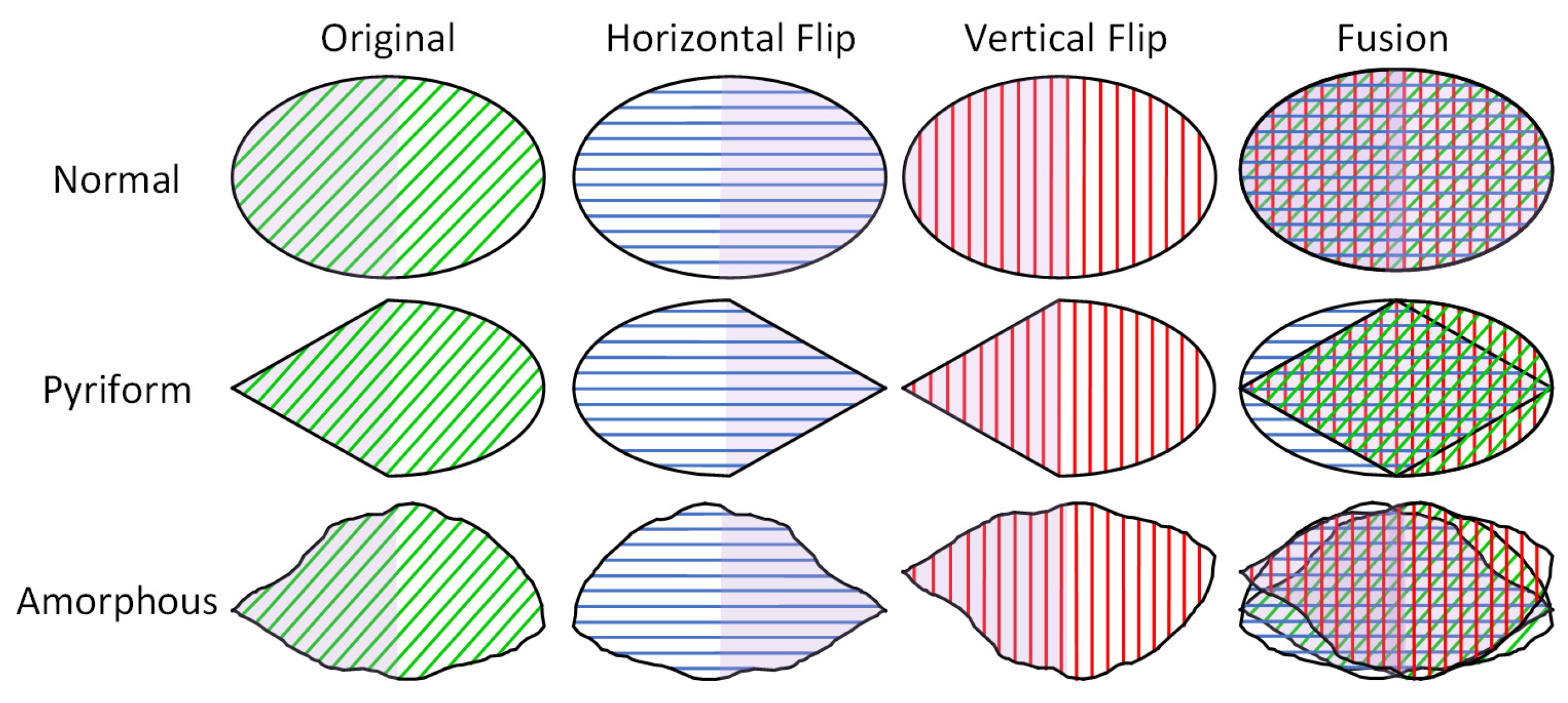
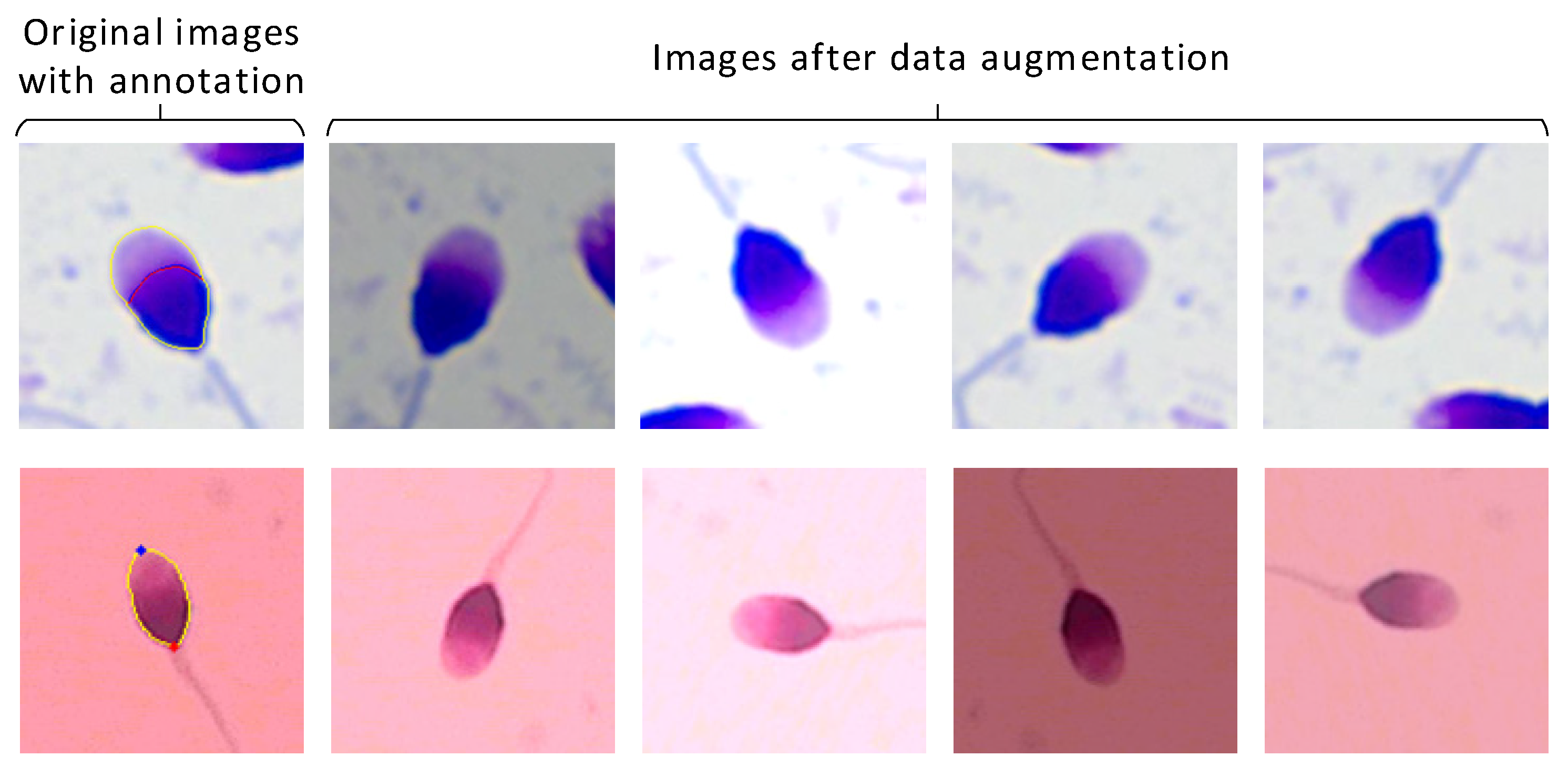
| Amorphous | 1 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 11 | 15 | 18 | 24 | 35 | 42 |
| Normal | 5 | 8 | 11 | 15 | 26 | 28 | 37 | 39 | 48 | 50 |
| Pyriform | 5 | 15 | 21 | 24 | 25 | 35 | 39 | 46 | 48 | 57 |
| Tapered | 6 | 14 | 23 | 27 | 32 | 37 | 41 | 48 | 50 | 52 |
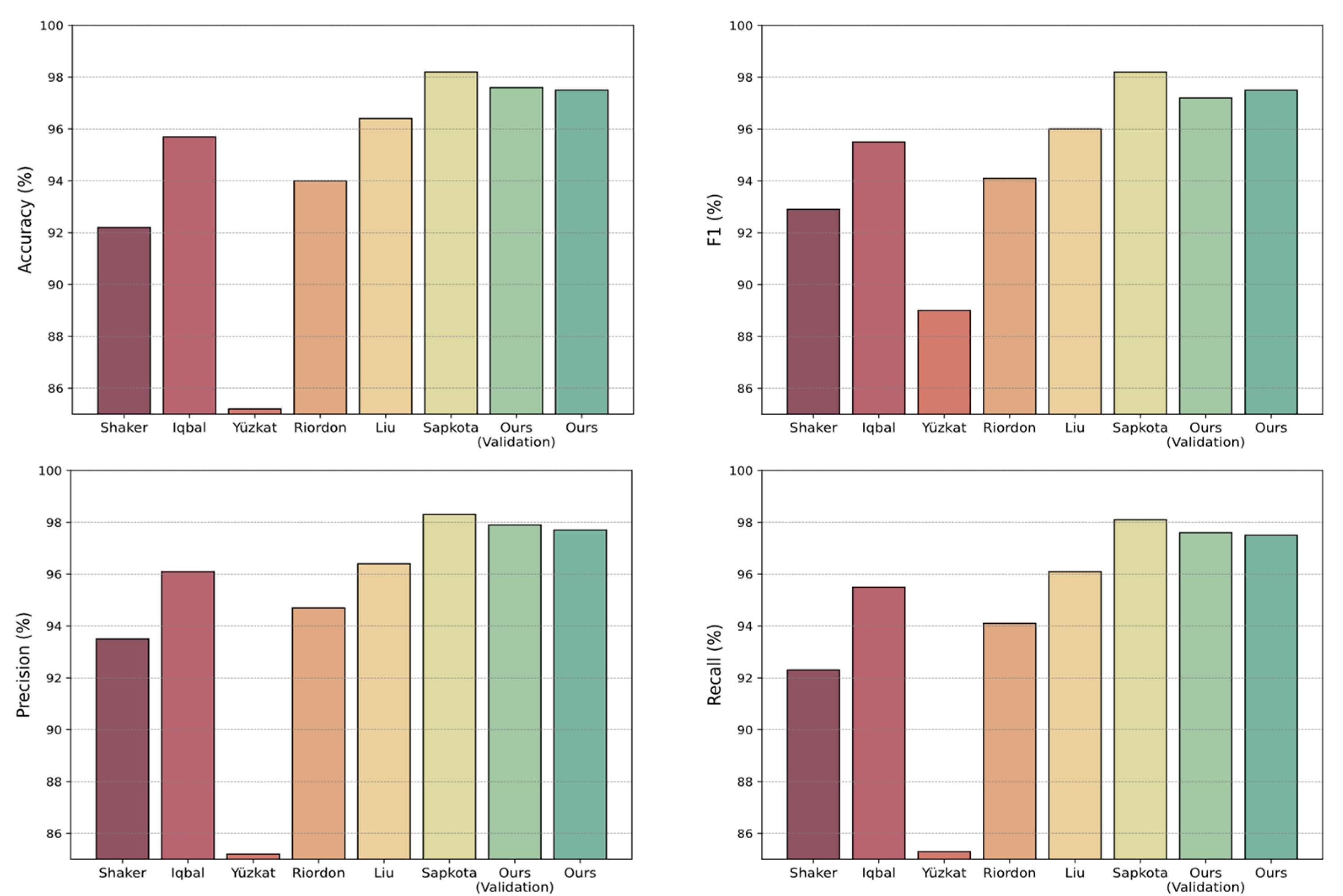
| Method | PC | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shaker et al., 2017 [5] | M | 92.2 | 93.5 | 92.3 | 92.9 |
| Iqbal et al., 2020 [29] | M | 95.7 | 96.1 | 95.5 | 95.5 |
| Yüzkat et al., 2021 [15] | - | 85.2 | 85.2 | 85.3 | 89 |
| Riordon et al., 2019 [12] | M | 94.0 | 94.7 | 94.1 | 94.1 |
| Liu et al., 2021 [23] | A | 96.4 | 96.4 | 96.1 | 96.0 |
| Sapkota et al., 2024 [18] | A | 98.2 ± 0.3 | 98.3 ± 0.3 | 98.1 ± 0.3 | 98.2 ± 0.3 |
| Ours (validation) | A | 97.6 ± 0.01 | 97.9 ± 0.01 | 97.6 ± 0.01 | 97.2 ± 0.01 |
| Ours | A | 97.5 | 97.7 | 97.5 | 97.5 |
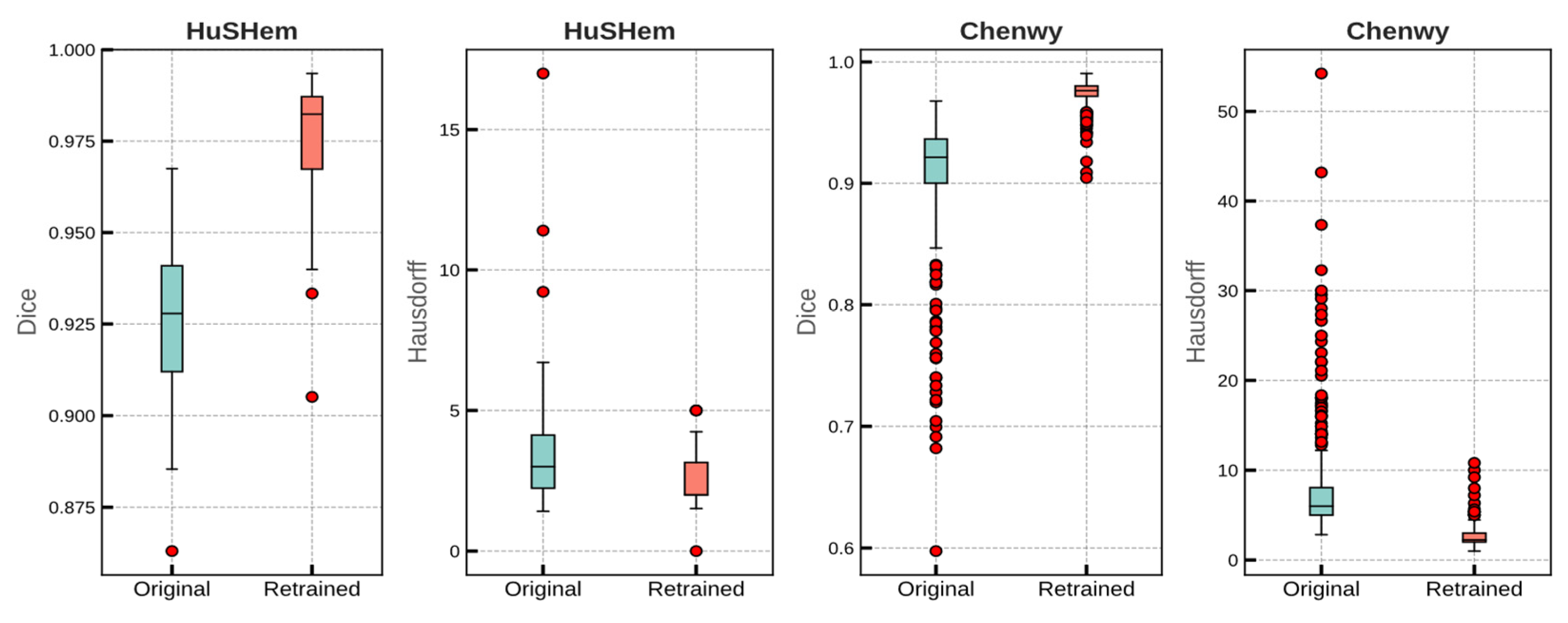
| Task | Dataset | Module | Dice Coefficient | Hausdorff Distance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std | Mean | Std | |||
| Validation (5 fold) | Chenwy | Original | 0.905 | 0.005 | 8.19 | 0.424 |
| Retrained | 0.975 | 0.002 | 2.785 | 0.086 | ||
| HuSHem | Original | 0.924 | 0.003 | 3.615 | 0.335 | |
| Retrained | 0.975 | 0.002 | 3.145 | 0.332 | ||
| Test | Chenwy | Original | 0.906 | 0.054 | 7.962 | 6.208 |
| Retrained | 0.974 | 0.011 | 2.011 | 1.594 | ||
| HuSHem | Original | 0.925 | 0.023 | 3.867 | 2.832 | |
| Retrained | 0.973 | 0.021 | 2.615 | 1.096 | ||
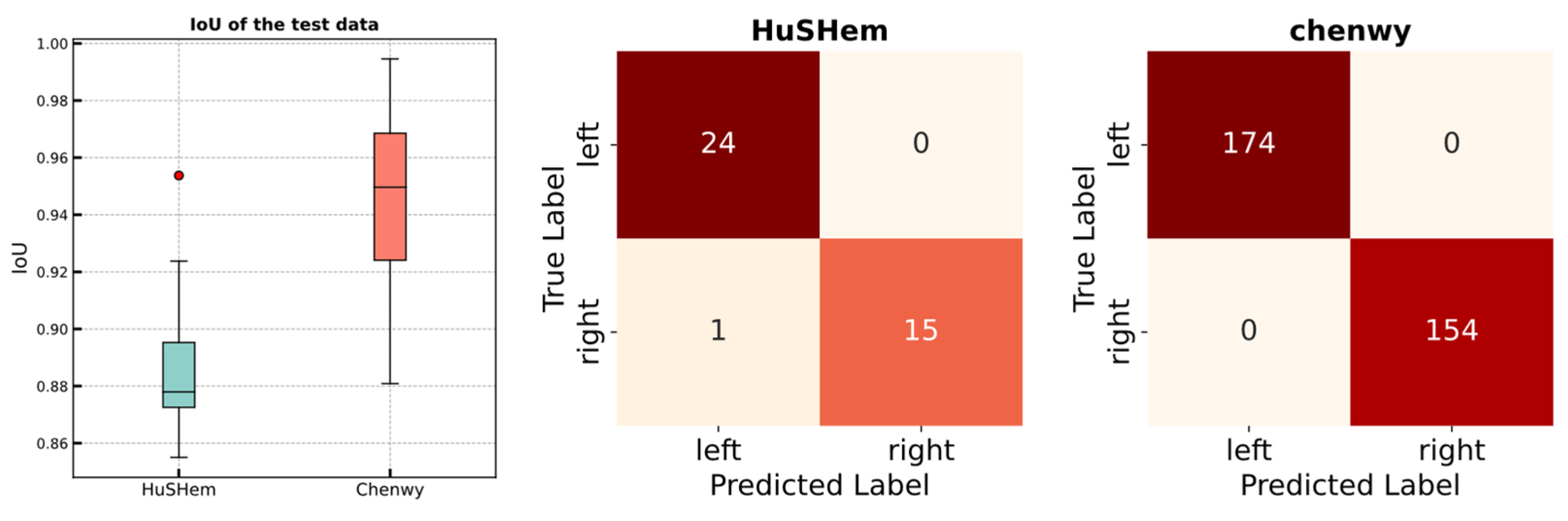
| Task | Dataset | IoU | Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std | Mean | Std | ||
| Validation (5 fold) | Chenwy | 0.950 | 0.001 | 100 | 0 |
| HuSHem | 0.916 | 0.009 | 100 | 0 | |
| Test | Chenwy | 0.946 | - | 100 | - |
| HuSHem | 0.887 | - | 97.5 | - | |
| Method | Cross Validation | Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (%) | Macro—F1 (%) | Accuracy (%) | Macro—F1 (%) | |||
| Mean | Std | Mean | Std | |||
| VGG11 | 91.7 | 0.029 | 91.4 | 0.03 | 80.0 | 79.7 |
| VGG13 | 91.1 | 0.043 | 91.1 | 0.041 | 92.5 | 92.6 |
| VGG16 | 92.3 | 0.064 | 92.1 | 0.066 | 82.5 | 81.8 |
| VGG19 | 88.8 | 0.034 | 88.4 | 0.036 | 80.0 | 79.7 |
| ResNet18 | 92.3 | 0.024 | 92.4 | 0.024 | 85.0 | 84.8 |
| ResNet34 | 90.6 | 0.015 | 90.5 | 0.015 | 90.0 | 89.6 |
| ResNet50 | 89.3 | 0.042 | 89.4 | 0.041 | 82.5 | 81.9 |
| ResNet101 | 92.9 | 0.031 | 93.1 | 0.03 | 87.5 | 87.4 |
| ResNet152 | 91.7 | 0.034 | 92.0 | 0.034 | 82.5 | 82.3 |
| SqueezeNet1_0 | 94.7 | 0.035 | 94.5 | 0.037 | 87.5 | 87.2 |
| SqueezeNet1_1 | 90.9 | 0.023 | 90.3 | 0.023 | 90.0 | 90.1 |
| DenseNet121 | 92.9 | 0.023 | 92.8 | 0.024 | 82.5 | 82.6 |
| DenseNet161 | 91.7 | 0.012 | 91.6 | 0.012 | 85.0 | 84.3 |
| DenseNet169 | 91.7 | 0.054 | 91.6 | 0.054 | 85.0 | 85.1 |
| DenseNet201 | 92.9 | 0.015 | 92.9 | 0.014 | 87.5 | 87.5 |
| ShuffleNet_v2_x0_5 | 86.4 | 0.035 | 86.4 | 0.033 | 85.0 | 84.8 |
| ShuffleNet_v2_x1_0 | 91.7 | 0.047 | 91.6 | 0.047 | 90.0 | 90.0 |
| MobileNet_v2 | 90.6 | 0.06 | 90.5 | 0.061 | 87.5 | 87.6 |
| MobileNet_v3_small | 88.2 | 0.041 | 88.3 | 0.04 | 90.0 | 90.0 |
| MobileNet_v3_large | 88.8 | 0.039 | 88.6 | 0.04 | 80.0 | 79.6 |
| ResNeXt50_32x4d | 94.1 | 0.026 | 94.1 | 0.026 | 80.0 | 79.5 |
| ResNeXt101_32x8d | 91.1 | 0.033 | 91.1 | 0.034 | 82.5 | 82.6 |
| WideResNet50_2 | 92.9 | 0.015 | 92.9 | 0.014 | 87.5 | 87.2 |
| WideResNet101_2 | 89.3 | 0.025 | 89.3 | 0.025 | 82.5 | 82.3 |
| Ours | 97.6 | 0.012 | 97.2 | 0.011 | 97.5 | 97.5 |
| Method | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGG13 | 91.0 | 91.8 | 91.0 | 91.0 |
| SqueezeNet1_1 | 87.6 | 88.3 | 87.6 | 87.6 |
| ResNet34 | 89.3 | 90.2 | 89.3 | 89.0 |
| ShuffleNet_V2_x1_0 | 92.1 | 92.9 | 92.1 | 92.1 |
| MobileNet_V3_small | 91.4 | 91.9 | 91.4 | 91.3 |
| Ours | 95.8 | 96.2 | 95.8 | 95.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Hong, K.; Wang, B.; Zhu, W.; Li, Y.; Lv, T.; Wang, L. Automated Deep Learning Model for Sperm Head Segmentation, Pose Correction, and Classification. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11303. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311303
Guo Y, Li J, Hong K, Wang B, Zhu W, Li Y, Lv T, Wang L. Automated Deep Learning Model for Sperm Head Segmentation, Pose Correction, and Classification. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(23):11303. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311303
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yunbo, Junbo Li, Kaicheng Hong, Bilin Wang, Wenliang Zhu, Yuefeng Li, Tiantian Lv, and Lirong Wang. 2024. "Automated Deep Learning Model for Sperm Head Segmentation, Pose Correction, and Classification" Applied Sciences 14, no. 23: 11303. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311303
APA StyleGuo, Y., Li, J., Hong, K., Wang, B., Zhu, W., Li, Y., Lv, T., & Wang, L. (2024). Automated Deep Learning Model for Sperm Head Segmentation, Pose Correction, and Classification. Applied Sciences, 14(23), 11303. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311303






