Enhanced Biomechanical Risk Assessment in Manual Lifting: Comparing Inertial Measurement Units with Optoelectronic Systems for Composite Lifting Index Calculation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
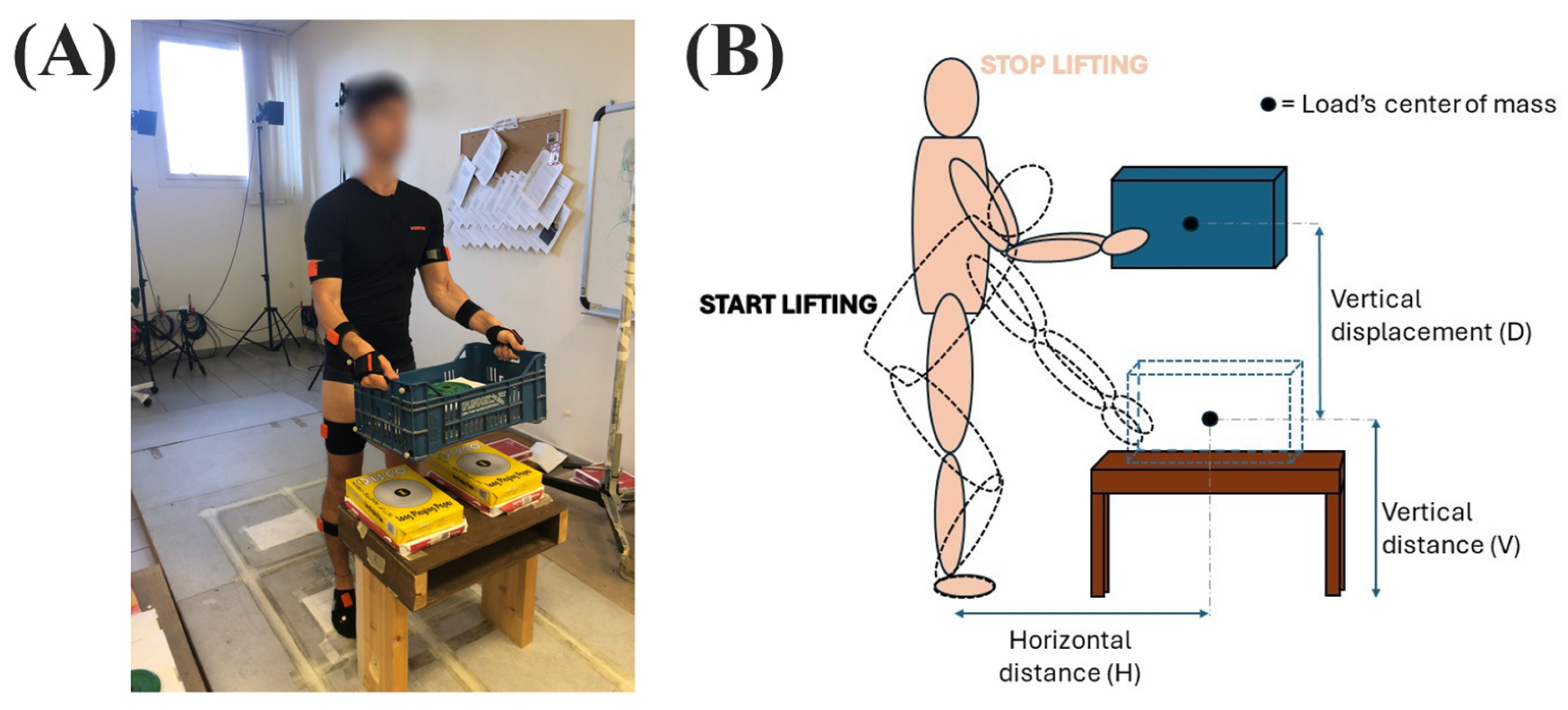
2.1. Data Recordings
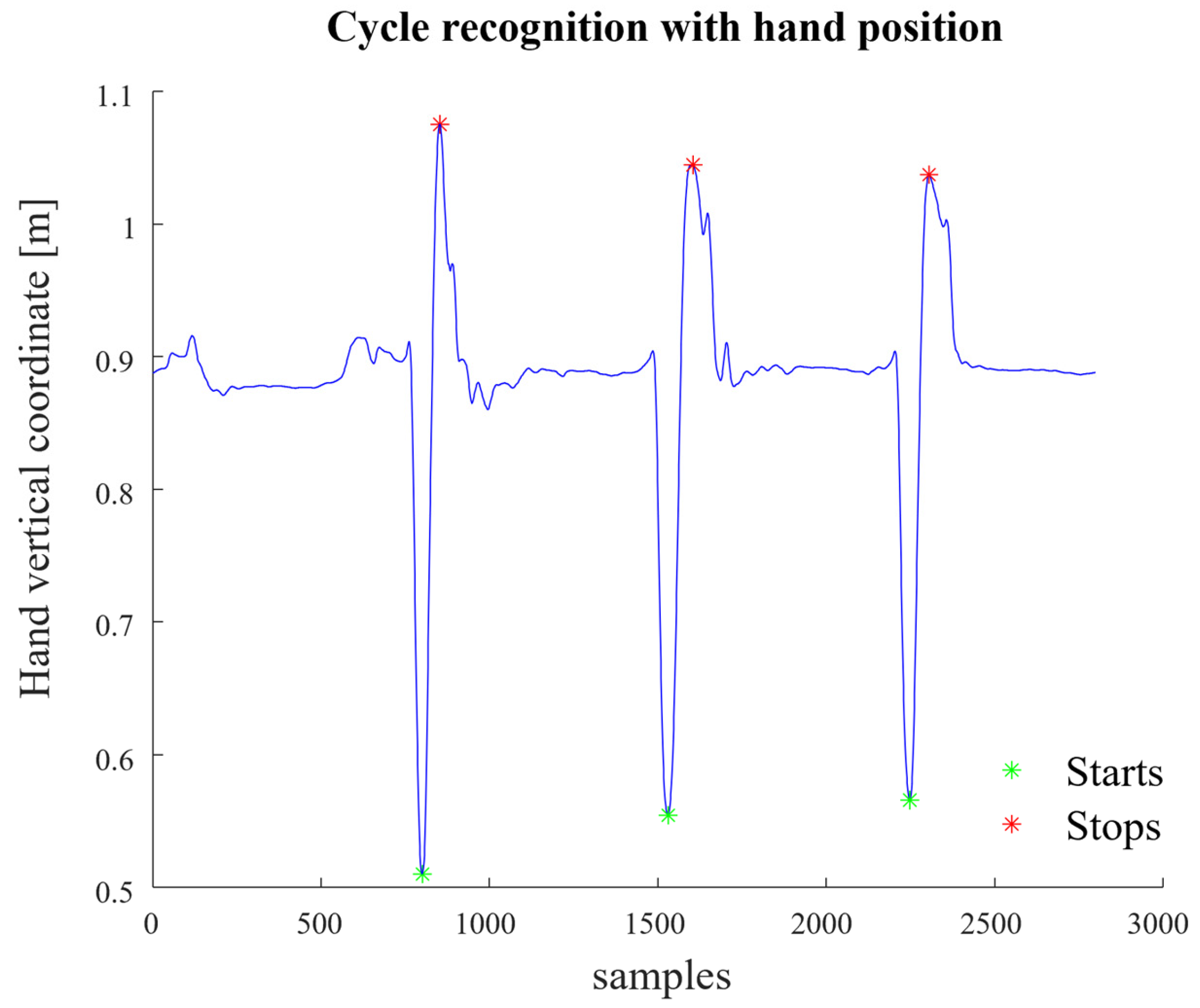
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Composite Lifring Index Algorithm
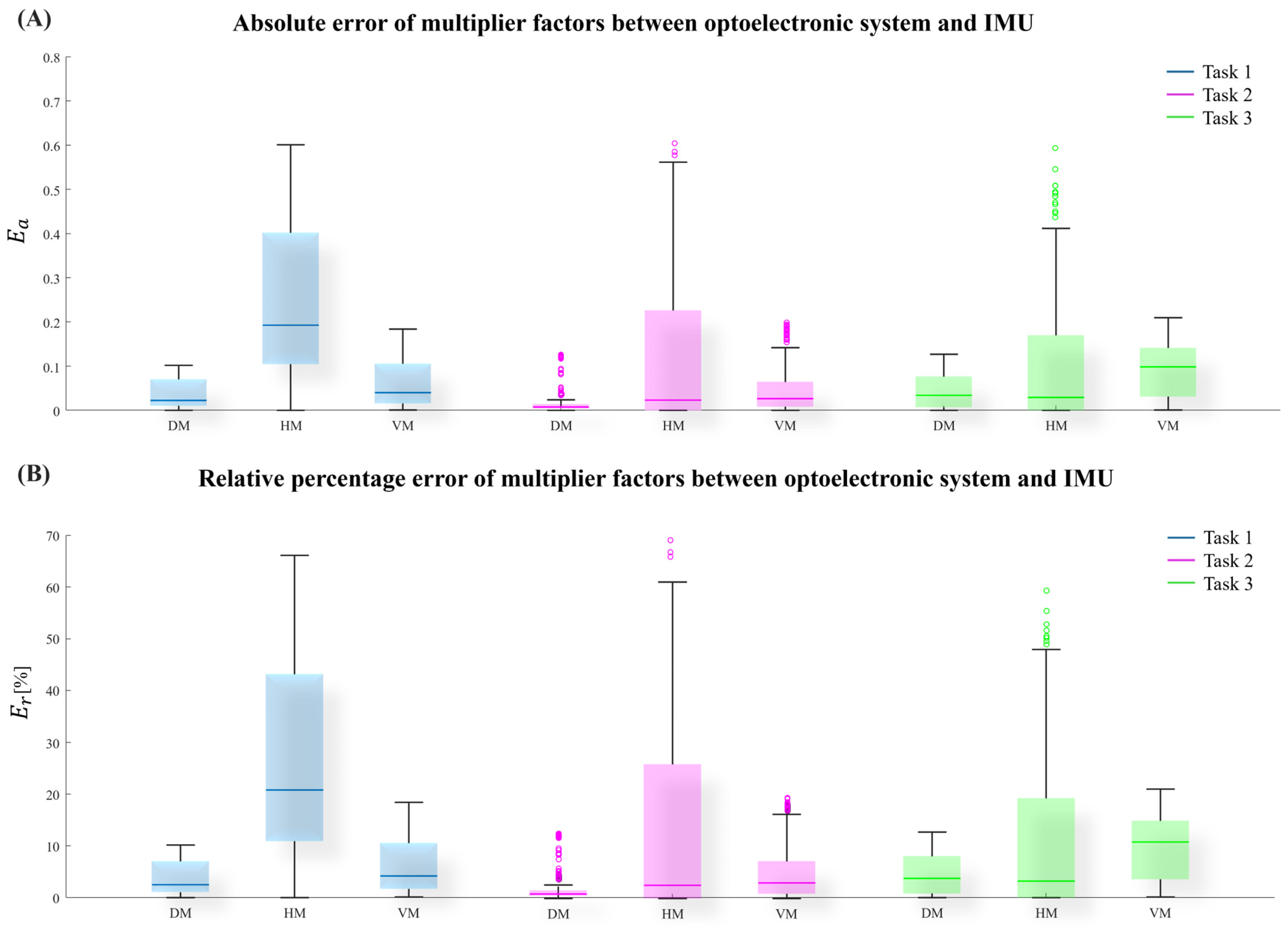
2.4. Errors of Measured Variables
2.5. Statistical Analysis
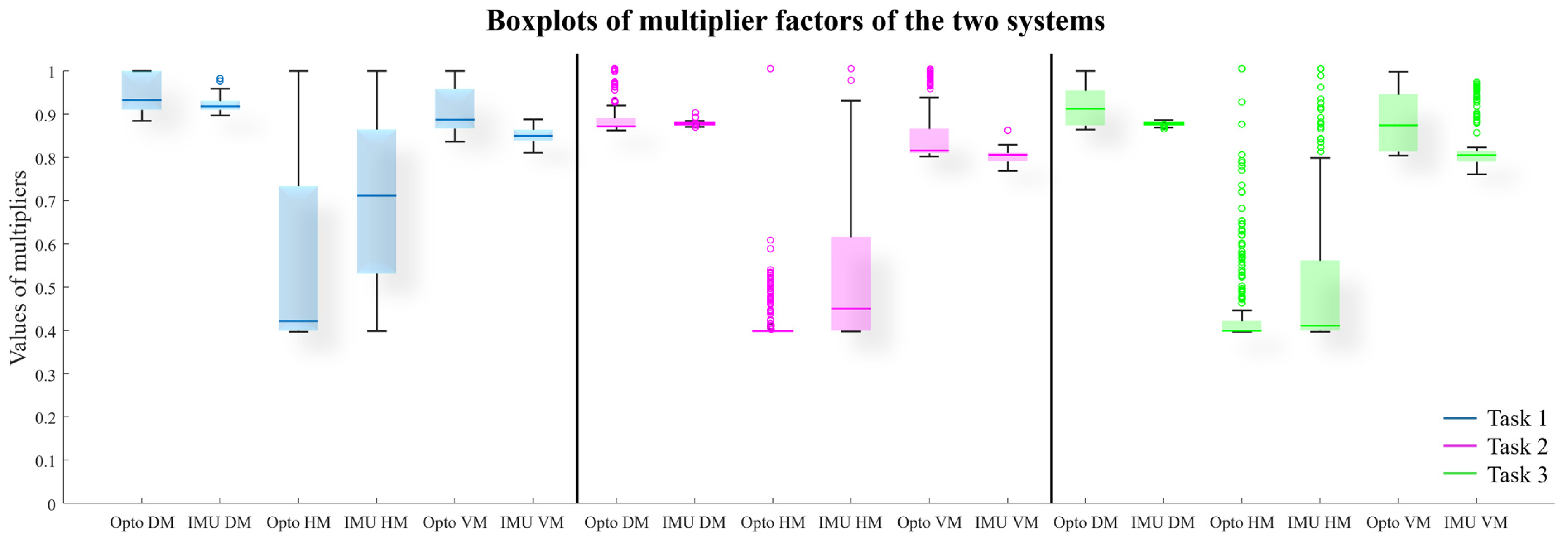
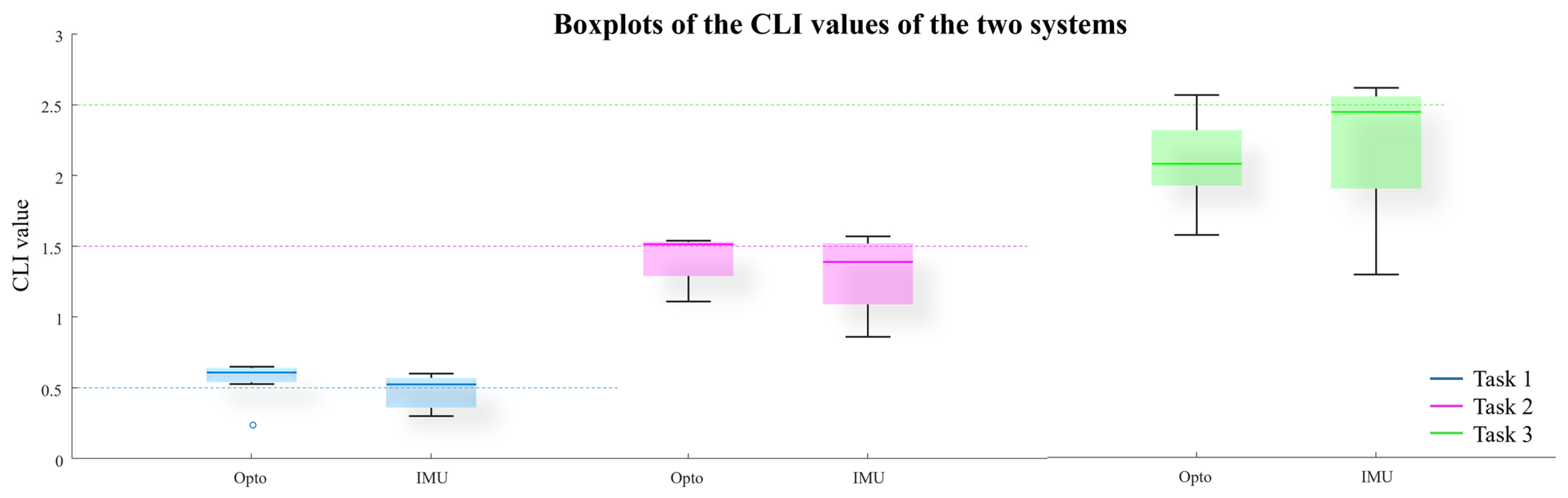
3. Result
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNI-ISO 11228-1:2022; Ergonomics-Manual Handling. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/sist/365f8b92-113b-493f-b06f- (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Waters, T.R.; Putz-Anderson, V.; Garg, A. Application Manual for the Revised NIOSH Lifting Equation. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/ergonomics/about/RNLE.html (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Fox, R.R.; Lu, M.L.; Occhipinti, E.; Jaeger, M. Understanding outcome metrics of the revised NIOSH lifting equation. Appl. Ergon. 2019, 81, 102897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.L.; Putz-Anderson, V.; Garg, A.; Davis, K.G. Evaluation of the Impact of the Revised National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health Lifting Equation. Hum. Factors 2016, 58, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, A.; Boda, S.; Hegmann, K.T.; Moore, J.S.; Kapellusch, J.M.; Bhoyar, P.; Thiese, M.S.; Merryweather, A.; Deckow-Schaefer, G.; Bloswick, D.; et al. The NIOSH lifting equation and low-back pain, part 1: Association with low-back pain in the BackWorks prospective cohort study. Hum. Factors 2014, 56, 6–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesek, R.; Gilkey, D.; Drinkaus, P.; Bloswick, D.S.; Herron, R. Evaluation and quantification of manual materials handling risk factors. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2003, 9, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, P.G.; Burdorf, A.; Fathallah, F.A.; Sorock, G.S.; Hashemi, L. Influence of measurement accuracy on the application of the 1991 NIOSH equation. Appl. Ergon. 2001, 32, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, T.R.; Lu, M.L.; Occhipinti, E. New procedure for assessing sequential manual lifting jobs using the revised NIOSH lifting equation. Ergonomics 2007, 50, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajoudani, A.; Albrecht, P.; Bianchi, M.; Cherubini, A.; Del Ferraro, S.; Fraisse, P.; Fritzsche, L.; Garabini, M.; Ranavolo, A.; Rosen, P.H.; et al. Smart Collaborative Systems for Enabling Flexible and Ergonomic Work Practices [Industry Activities]. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2020, 27, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranavolo, A.; Draicchio, F.; Varrecchia, T.; Silvetti, A.; Iavicoli, S. Wearable monitoring devices for biomechanical risk assessment at work: Current status and future challenges—A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CWA17938; Guideline for Introducing and Implementing Real-Time Instrumental-Based Tools for Biomechanical Risk Assessment. CEN-CENELEC Management Centre: Brussels, Belgium, 2023.
- Chini, G.; Varrecchia, T.; Conforto, S.; De Nunzio, A.M.; Draicchio, F.; Falla, D.; Ranavolo, A. Trunk stability in fatiguing frequency-dependent lifting activities. Gait Posture 2023, 102, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranavolo, A.; Varrecchia, T.; Rinaldi, M.; Silvetti, A.; Serrao, M.; Conforto, S.; Draicchio, F. Mechanical lifting energy consumption in work activities designed by means of the “revised NIOSH lifting equation. Ind. Health 2017, 55, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varrecchia, T.; De Marchis, C.; Draicchio, F.; Schmid, M.; Conforto, S.; Ranavolo, A. Lifting activity assessment using kinematic features and neural networks. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherubini, A.; Navarro, B.; Passama, R.; Tarbouriech, S.; Elprama, S.A.; Jacobs, A.; Niehaus, S.; Wischniewski, S.; Tönis, S.J.; Siahaya, P.L.; et al. Interdisciplinary evaluation of a robot physically collaborating with workers. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0291410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignais, N.; Miezal, M.; Bleser, G.; Mura, K.; Gorecky, D.; Marin, F. Innovative system for real-time ergonomic feedback in industrial manufacturing. Appl. Ergon. 2013, 44, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppeloni, L.; Filippeschi, A.; Ruffaldi, E. Assessment of task ergonomics with an upper limb wearable device. In Proceedings of the Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation, Palermo, Italy, 16–19 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ranavolo, A.; Ajoudani, A.; Chini, G.; Lorenzini, M.; Varrecchia, T. Adaptive Lifting Index (aLI) for Real-Time Instrumental Biomechanical Risk Assessment: Concepts, Mathematics, and First Experimental Results. Sensors 2024, 24, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, T.; Occhipinti, E.; Colombini, D.; Alvarez-Casado, E.; Fox, R. Variable Lifting Index (VLI). Hum. Factors 2016, 58, 695–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, T.; Occhipinti, E.; Columbini, D.; Alvarez, E.; Hernandez, A. The Variable Lifting Index (VLI): A New Method for Evaluating Variable Lifting Tasks Using the Revised NIOSH Lifting Equation. In Proceedings of the 17th Triennial Congress of the International Ergonomics Association, Beijing, China, 9–14 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, M.L.; Waters, T.R.; Krieg, E.; Werren, D. Efficacy of the revised NIOSH lifting equation to predict risk of low-back pain associated with manual lifting: A one-year prospective study. Hum. Factors 2014, 56, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marco, R.; Rossi, S.; Patanè, F. Cappa Technical quality assessment of an optoelectronic system for movement analysis. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2015, 588, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.B. Reflections on Clinical Gait Analysis. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 1997, 7, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rab, G.; Petuskey, K.; Bagley, A. A Method for Determination of Upper Extremity Kinematics. 2002. Available online: https://www.elsevier.com/locate/gaitpost (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Donisi, L.; Cesarelli, G.; Coccia, A.; Panigazzi, M.; Capodaglio, E.M.; D’Addio, G. Work-related risk assessment according to the revised niosh lifting equation: A preliminary study using a wearable inertial sensor and machine learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.L.; Feng, S.; Hughes, G.; Barim, M.S.; Hayden, M.; Werren, D. Development of an algorithm for automatically assessing lifting risk factors using inertial measurement units. In Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society, Seattle, WA, USA, 8 October–1 November 2019; SAGE Publications Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1334–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.; Gomez, B.; Retamal, G.; Peña, G.; Germany, E.; Ortega-Bastidas, P. Aqueveque Comparing Optical and Custom IoT Inertial Motion Capture Systems for Manual Material Handling Risk Assessment Using the NIOSH Lifting Index. Technologies 2024, 12, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, G.; Liu, H. Evaluation of a low-cost MEMS accelerometer for distance measurement. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2001, 30, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandbergen, M.A.; Reenalda, J.; van Middelaar, R.P.; Ferla, R.I.; Buurke, J.H.; Veltink, P.H. Drift-Free 3D Orientation and Displacement Estimation for Quasi-Cyclical Movements Using One Inertial Measurement Unit: Application to Running. Sensors 2022, 22, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittmann, F.; Lambercy, O.; Gassert, R. Magnetometer-Based Drift Correction During Rest in IMU Arm Motion Tracking. Sensors 2019, 19, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzini, M.; Gandarias, J.M.; Fortini, L.; Kim, W.; Ajoudani, A. ErgoTac-Belt: Anticipatory Vibrotactile Feedback to Lead Centre of Pressure during Walking. In Proceedings of the IEEE RAS and EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 21–24 August 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Aggravi, M.; Salvietti, G.; Prattichizzo, D. Haptic wrist guidance using vibrations for Human-Robot teams. In Proceedings of the 25th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), New York, NY, USA, 26–31 August 2016; pp. 113–118. [Google Scholar]
| Task | Subtask | LC [kg] | H [cm] | HM | V [cm] | VM | D [cm] | DM | A [°] | AM | F [Lift/Min] | FM | C | CM | Load [kg] | RWL | FILI | STILI | CLI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | 23 | 44.5 | 0.56 | 20 | 0.84 | 50 | 0.91 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0.88 | Good | 1 | 4 | 8.64 | 0.40 | 0.46 | 0.50 |
| B | 23 | 44.5 | 0.56 | 30 | 0.87 | 40 | 0.93 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0.91 | Good | 1 | 4 | 9.48 | 0.38 | 0.42 | ||
| 2 | C | 23 | 61.5 | 0.41 | 10 | 0.81 | 82 | 0.87 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0.84 | Good | 1 | 7 | 5.53 | 1.06 | 1.27 | 1.50 |
| D | 23 | 56 | 0.45 | 10 | 0.81 | 82 | 0.87 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0.88 | Good | 1 | 7 | 6.36 | 0.96 | 1.10 | ||
| 3 | E | 23 | 61.5 | 0.41 | 10 | 0.81 | 82 | 0.87 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0.84 | Good | 1 | 10 | 5.53 | 1.51 | 1.81 | 2.50 |
| F | 23 | 58.5 | 0.43 | 10 | 0.81 | 82 | 0.87 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0.84 | Good | 1 | 10 | 5.81 | 1.44 | 1.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varrecchia, T.; Motta, F.; Chini, G.; Galli, M.; Ranavolo, A. Enhanced Biomechanical Risk Assessment in Manual Lifting: Comparing Inertial Measurement Units with Optoelectronic Systems for Composite Lifting Index Calculation. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11292. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311292
Varrecchia T, Motta F, Chini G, Galli M, Ranavolo A. Enhanced Biomechanical Risk Assessment in Manual Lifting: Comparing Inertial Measurement Units with Optoelectronic Systems for Composite Lifting Index Calculation. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(23):11292. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311292
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarrecchia, Tiwana, Filippo Motta, Giorgia Chini, Manuela Galli, and Alberto Ranavolo. 2024. "Enhanced Biomechanical Risk Assessment in Manual Lifting: Comparing Inertial Measurement Units with Optoelectronic Systems for Composite Lifting Index Calculation" Applied Sciences 14, no. 23: 11292. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311292
APA StyleVarrecchia, T., Motta, F., Chini, G., Galli, M., & Ranavolo, A. (2024). Enhanced Biomechanical Risk Assessment in Manual Lifting: Comparing Inertial Measurement Units with Optoelectronic Systems for Composite Lifting Index Calculation. Applied Sciences, 14(23), 11292. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311292






