Study on Steady Flow Force of a Bidirectional Throttling Slide Valve and Its Compensation Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
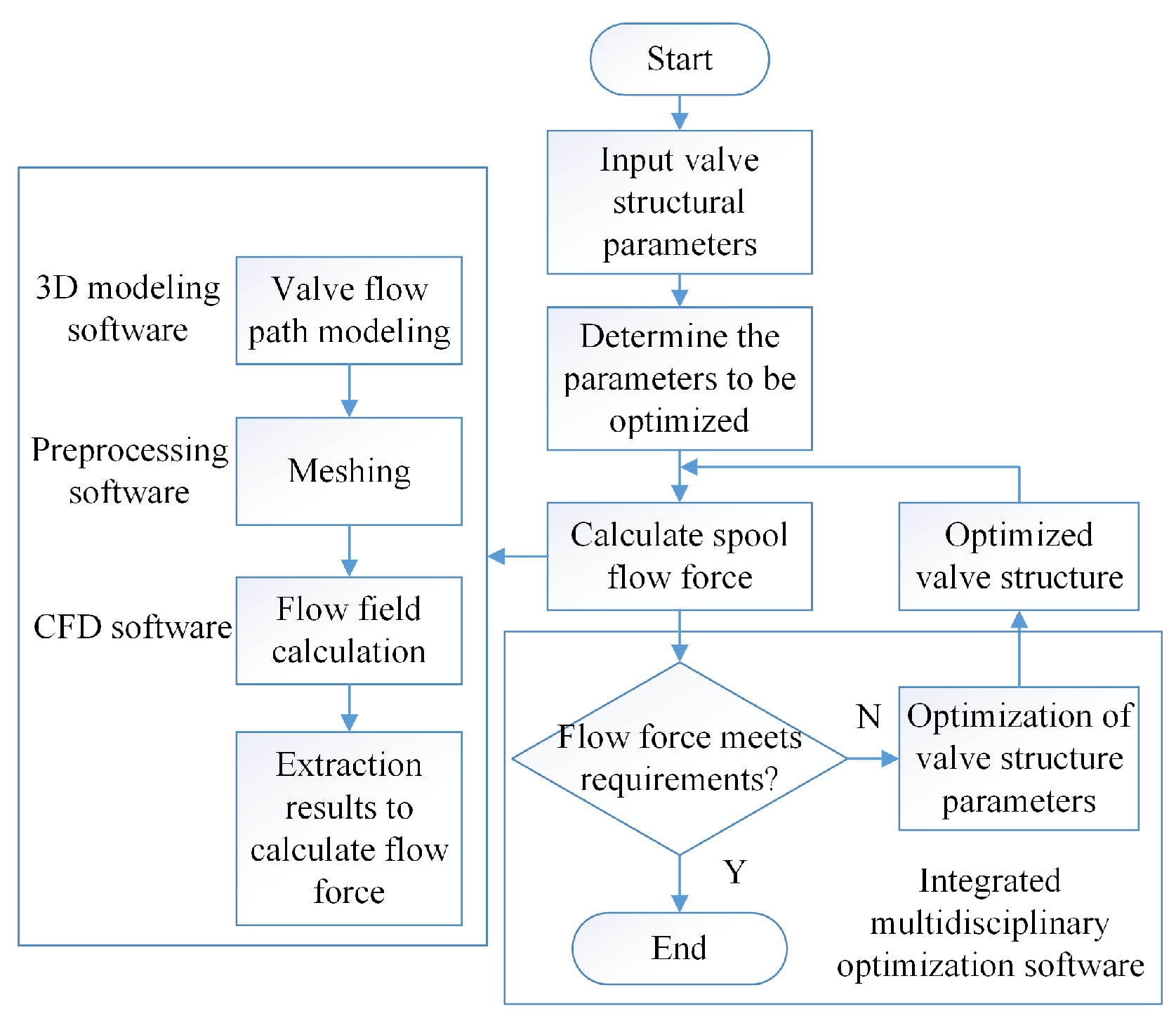
2. Numerical Simulation of Flow Forces in Slide Valves
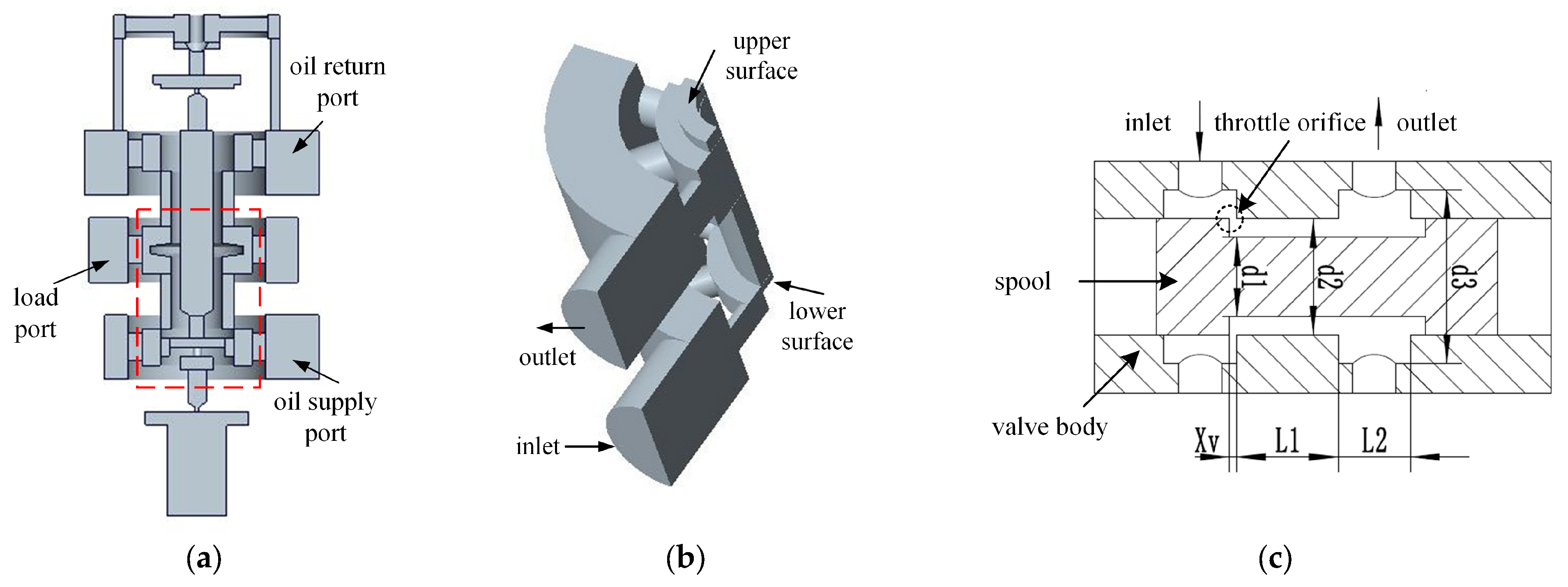
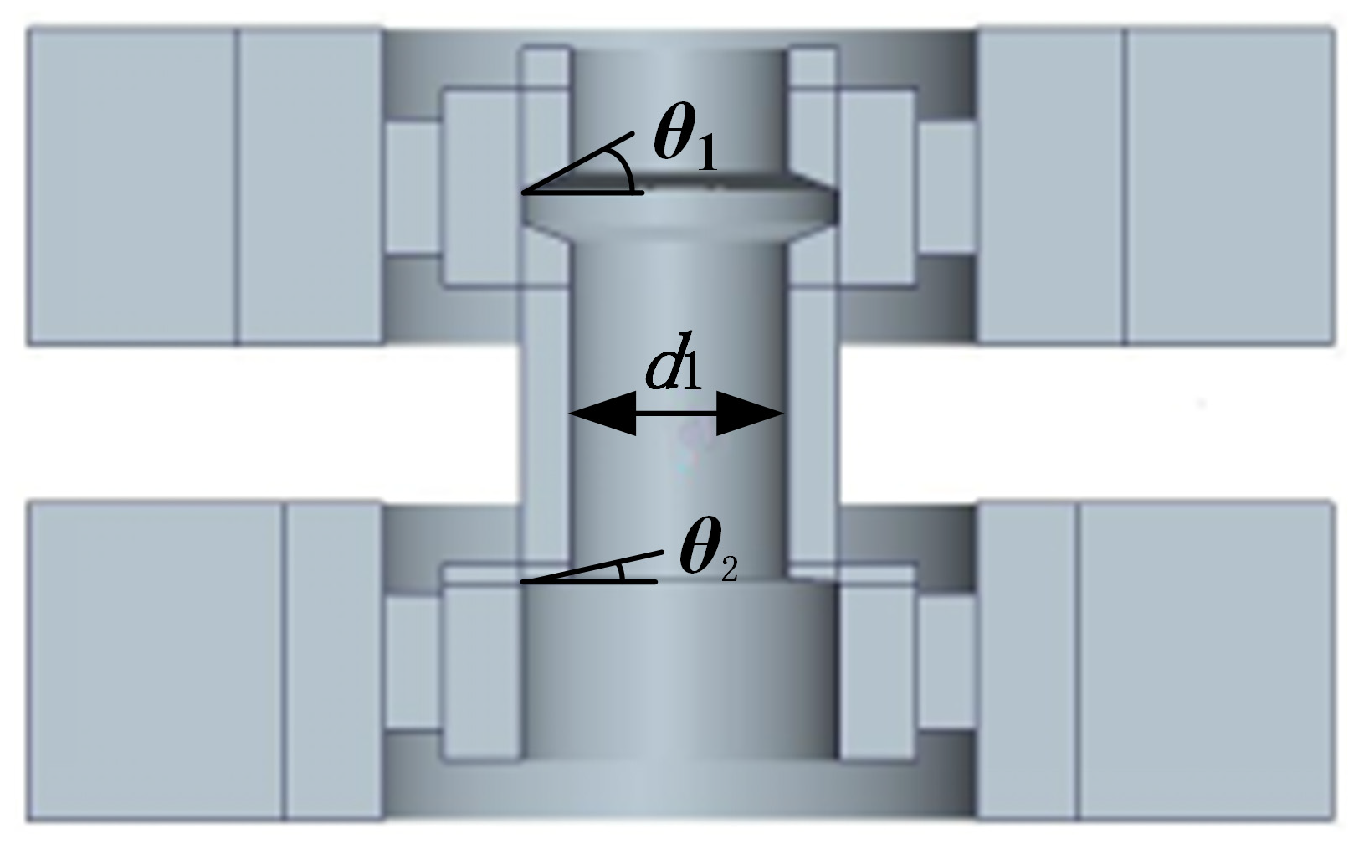
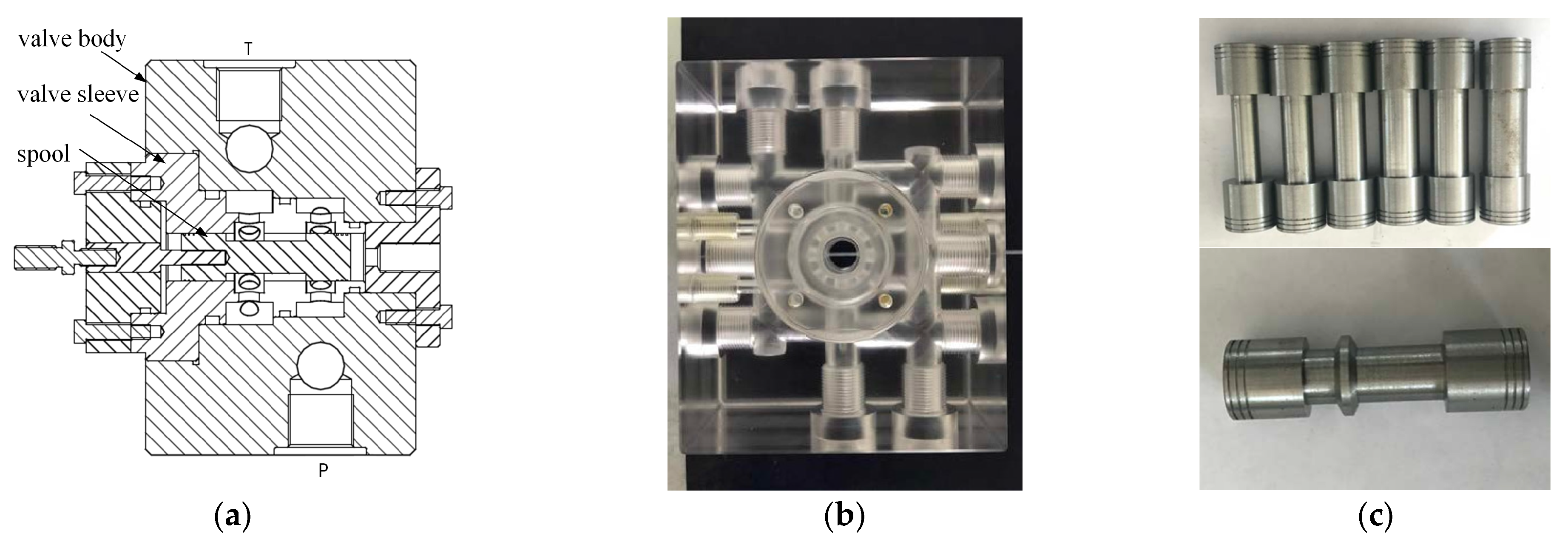
2.1. Slide Valve Structure and Flow Path Modeling
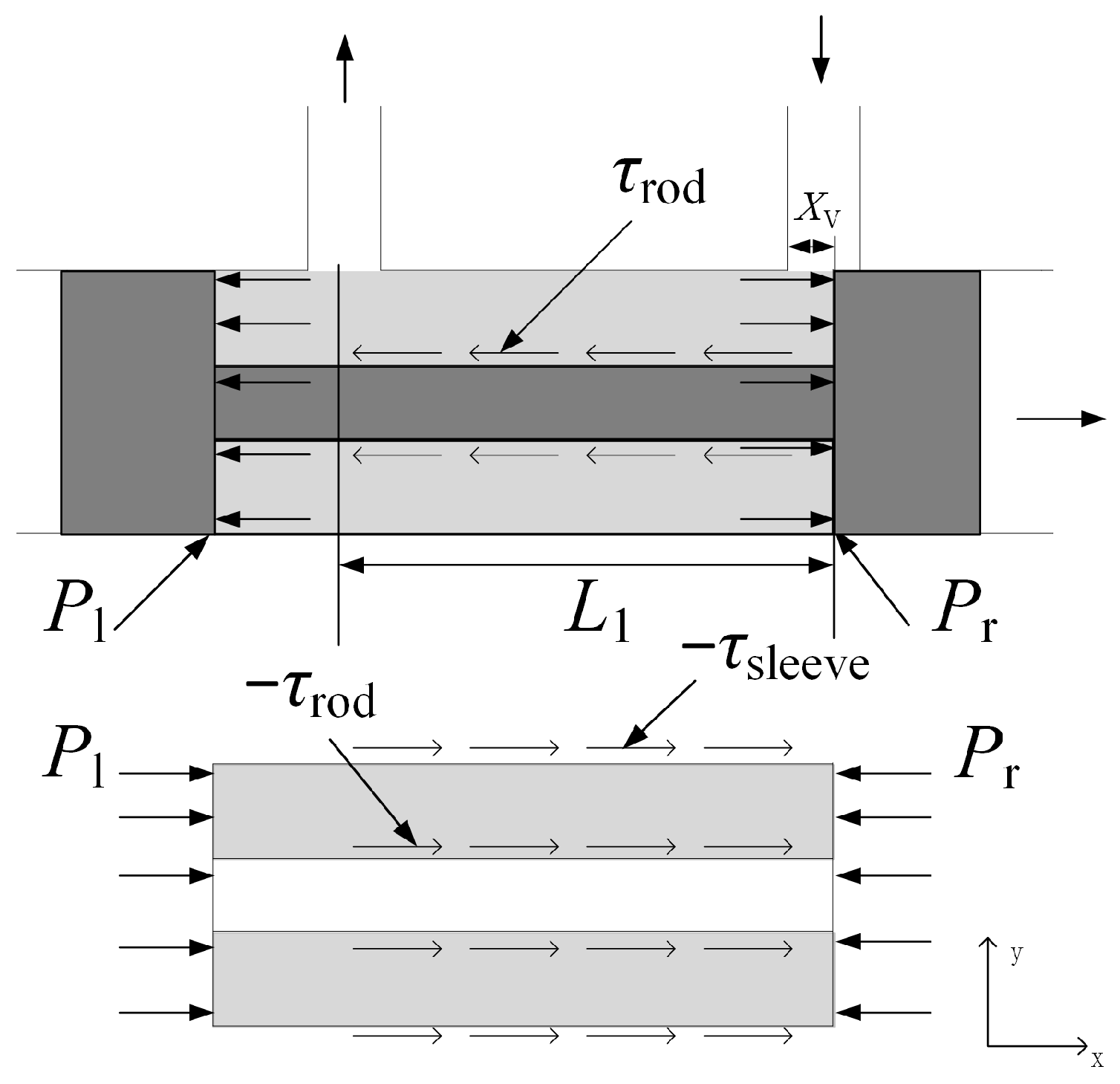
2.2. Calculation of Steady Flow Force
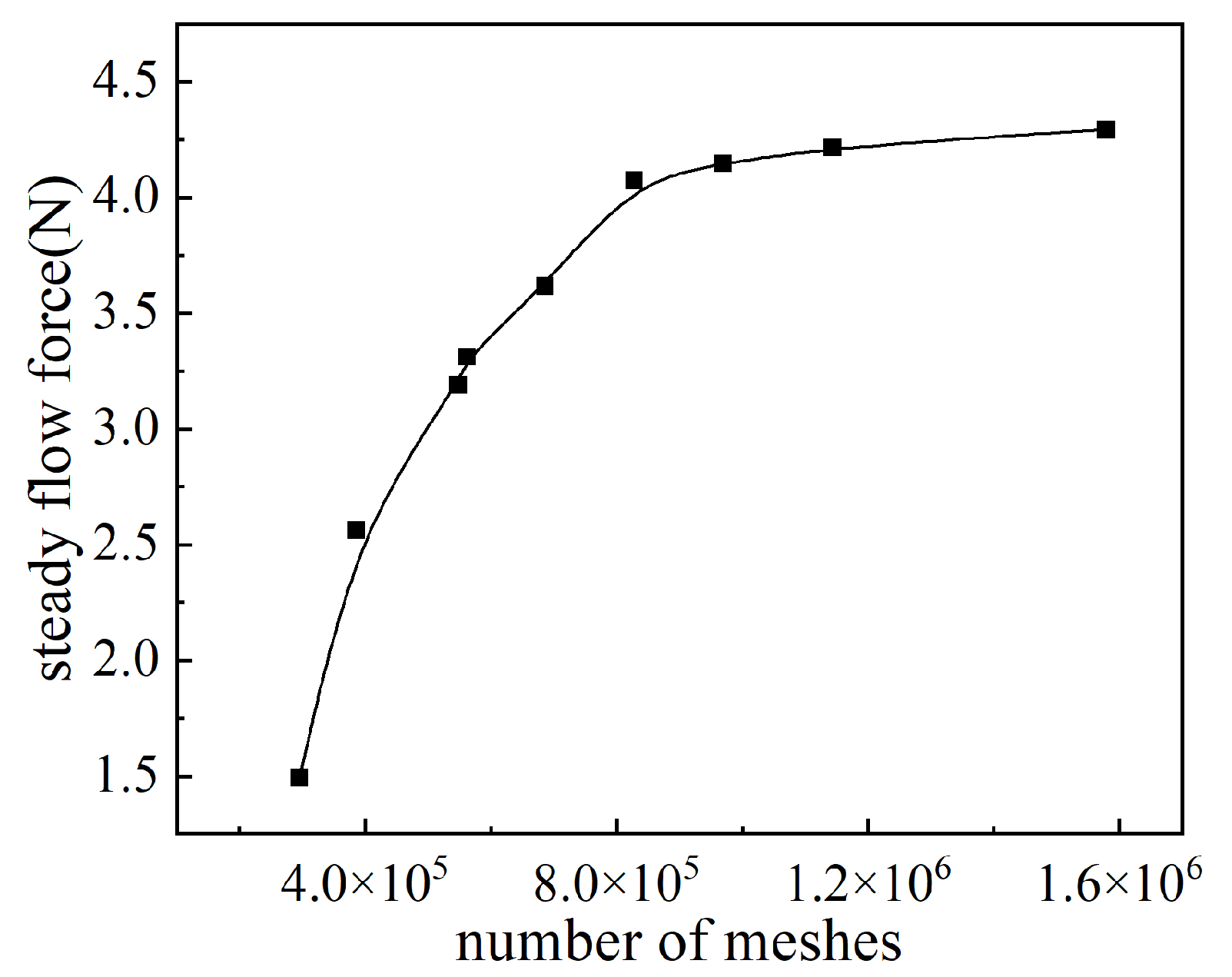
2.3. CFD Simulation of Flow Force
3. Analysis of Flow Force Characteristics of Slide Valves
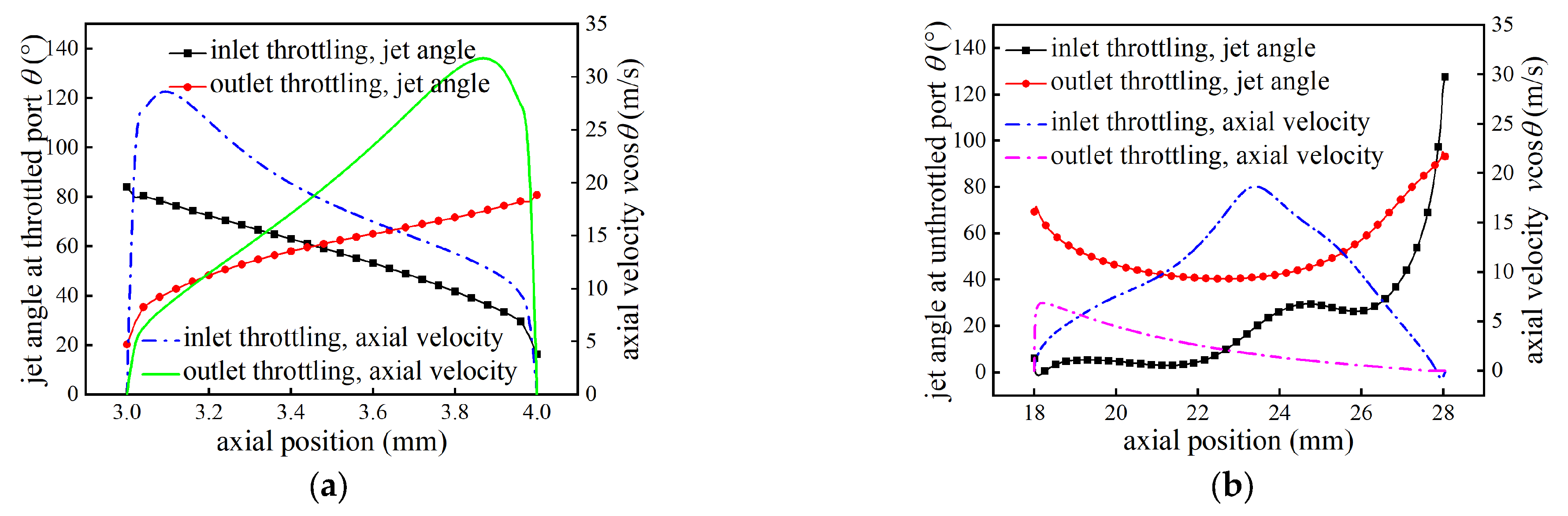
3.1. Flow Force Characteristics of Two Throttling Modes at a Fixed Opening
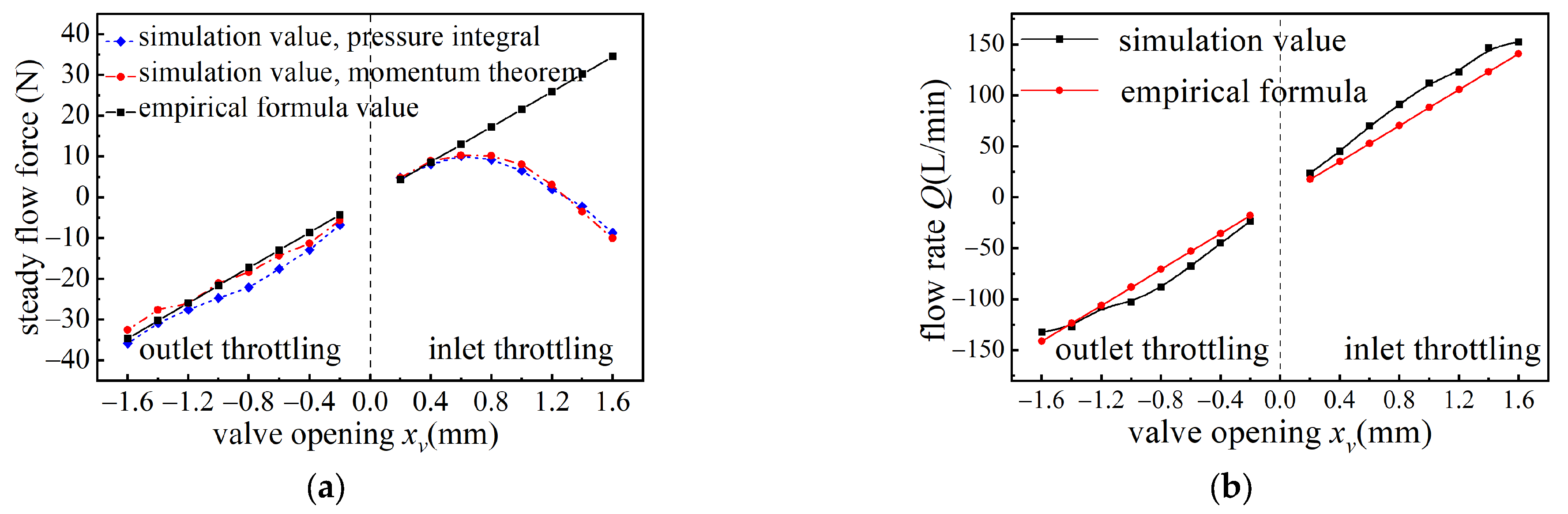
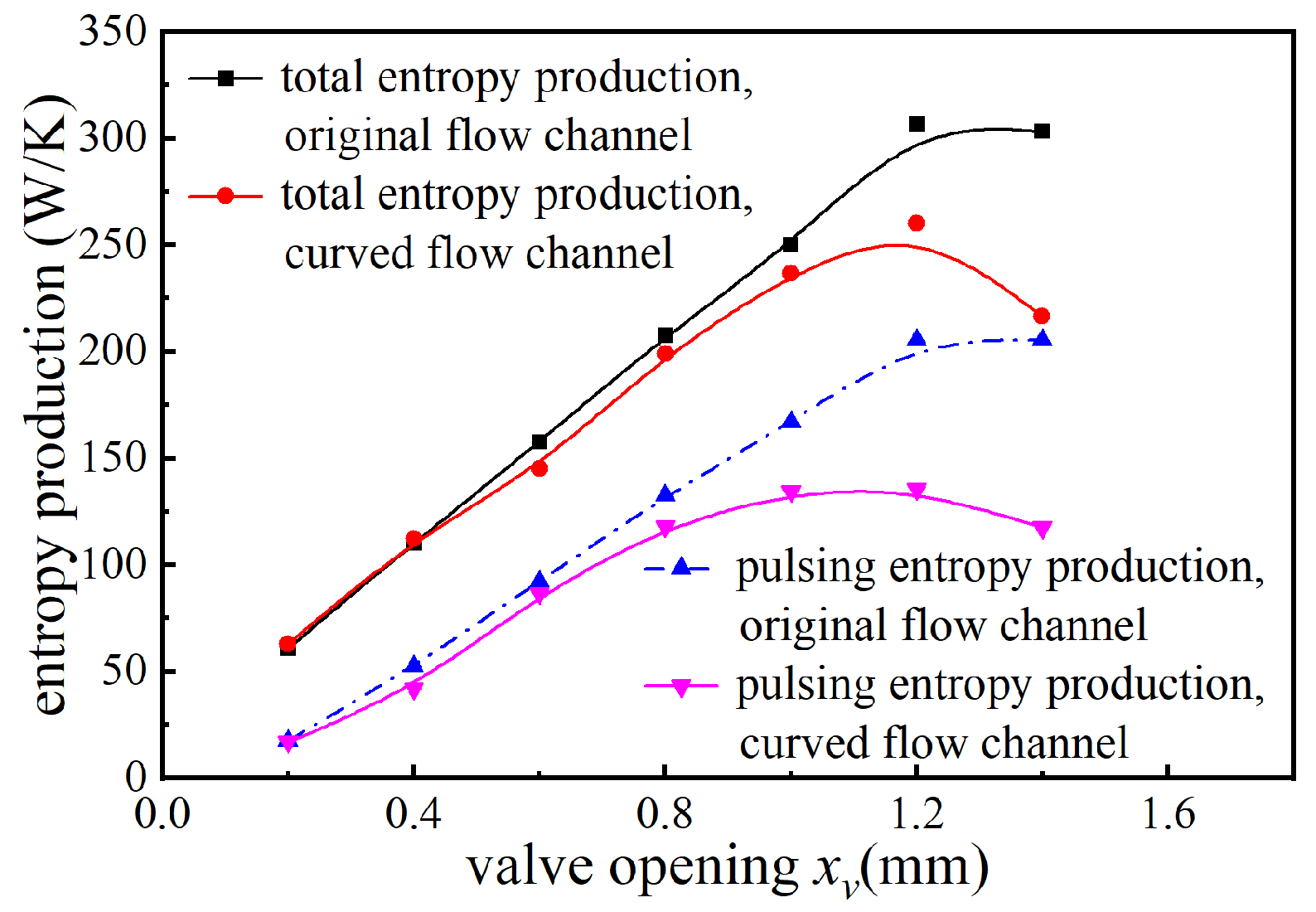
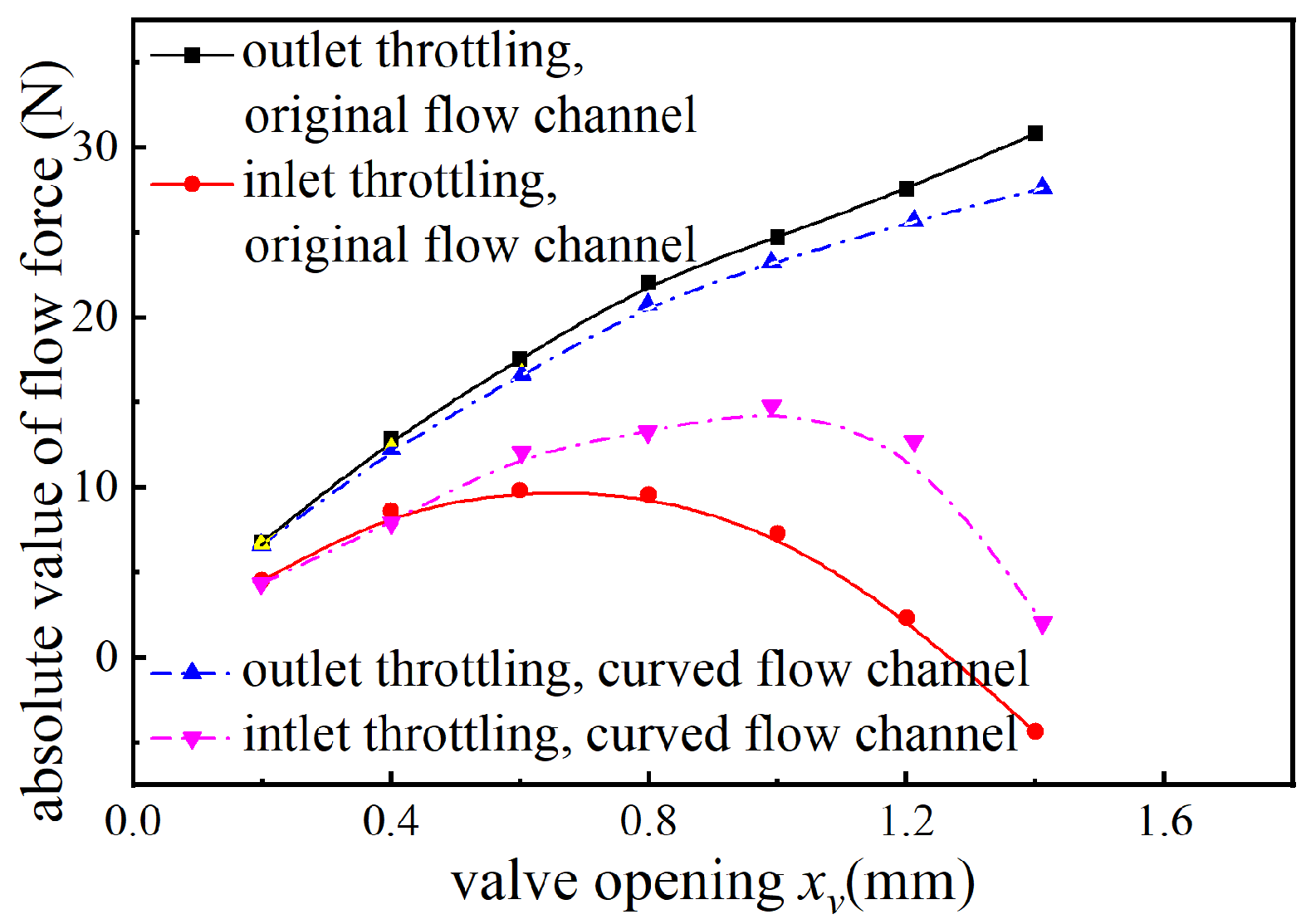
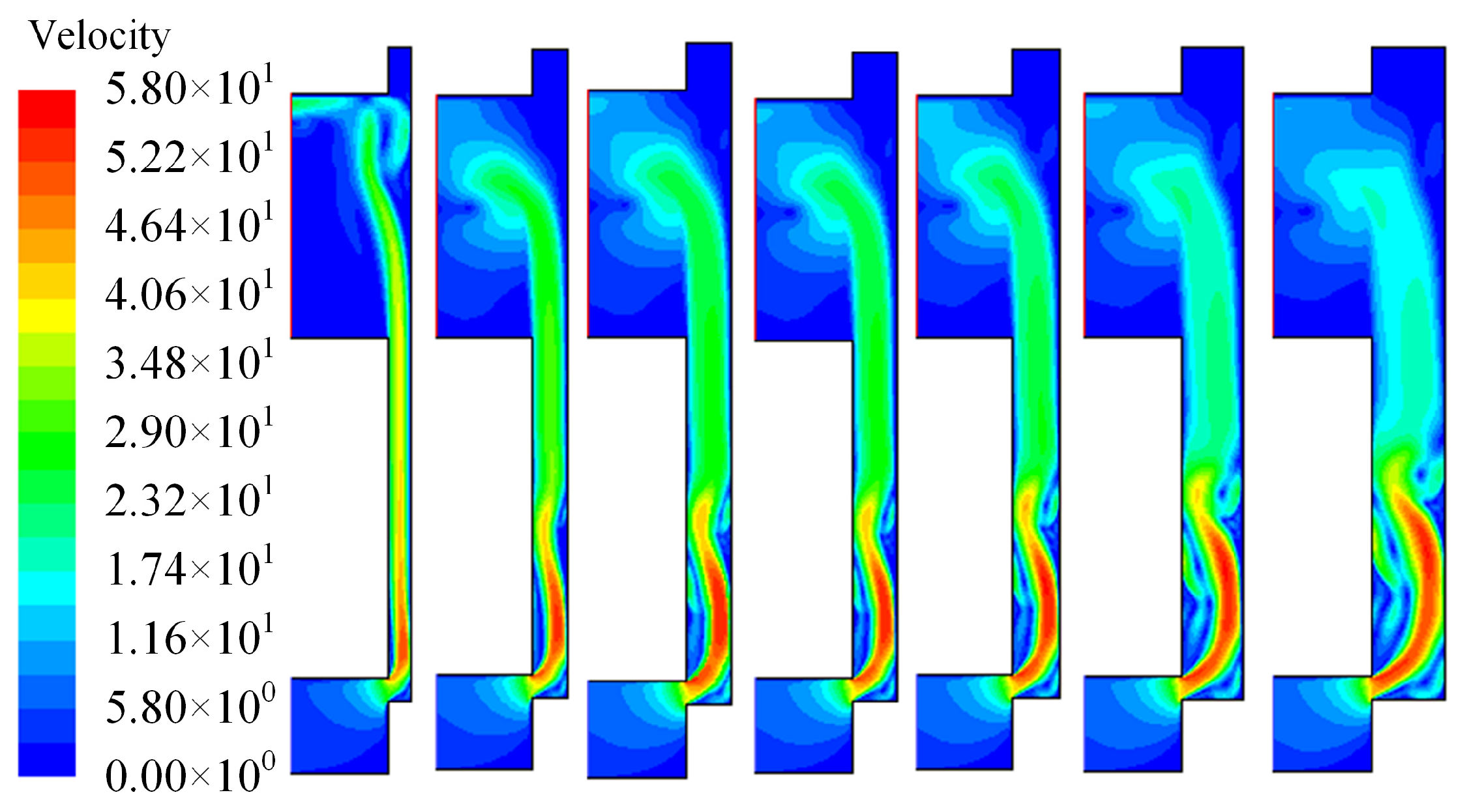
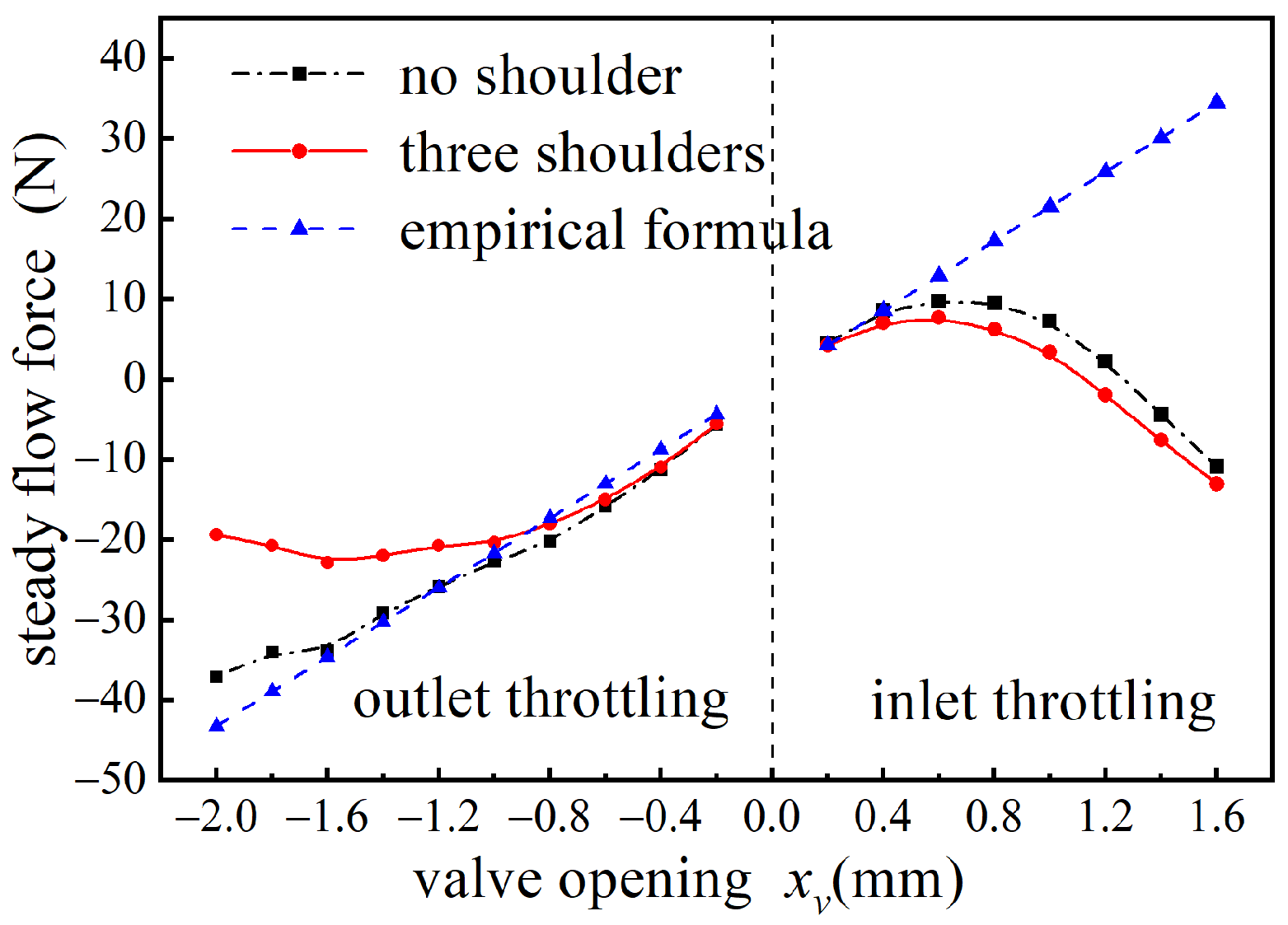
3.2. Flow Force Characteristics of Two Throttling Modes at Variable Openings
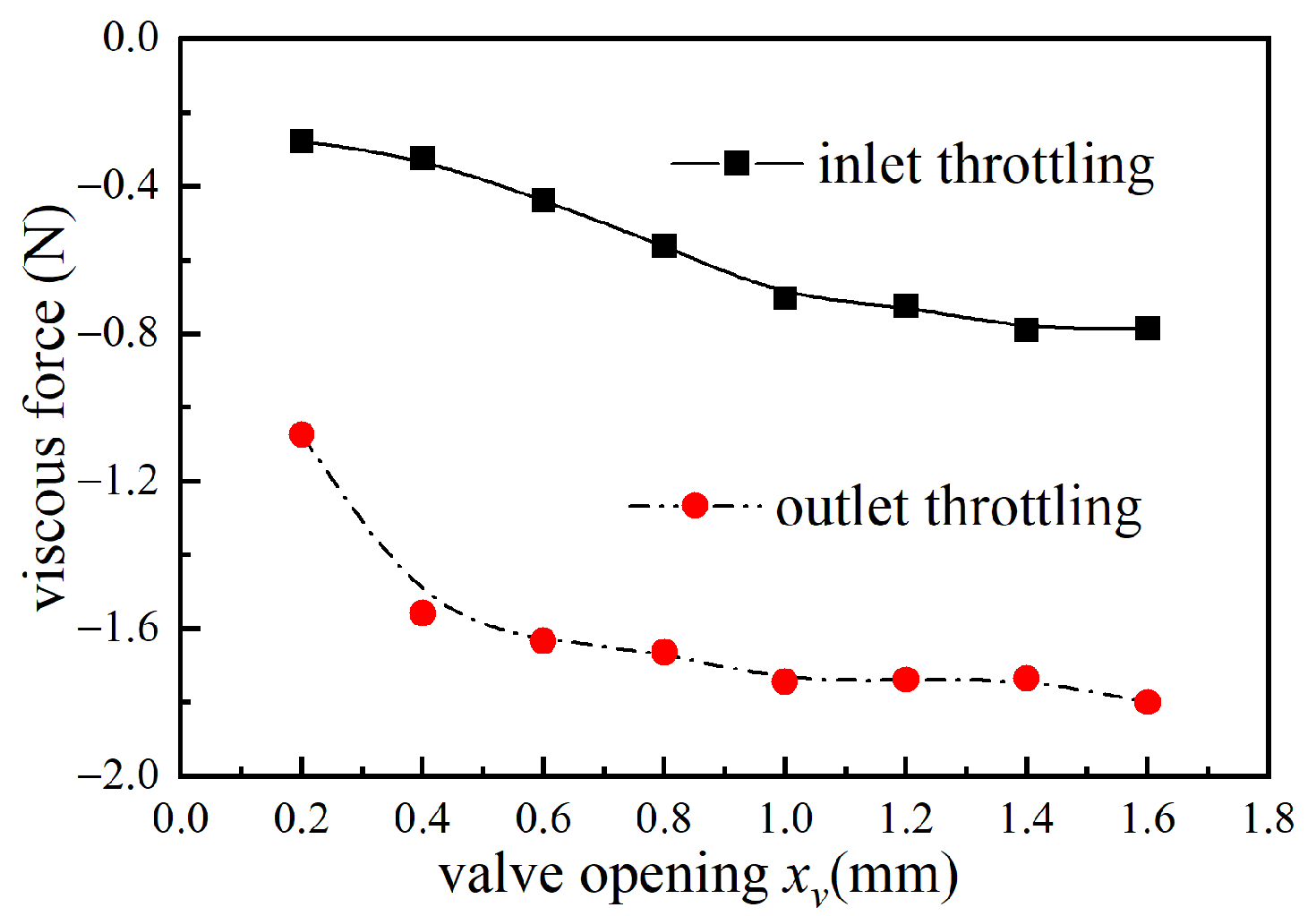
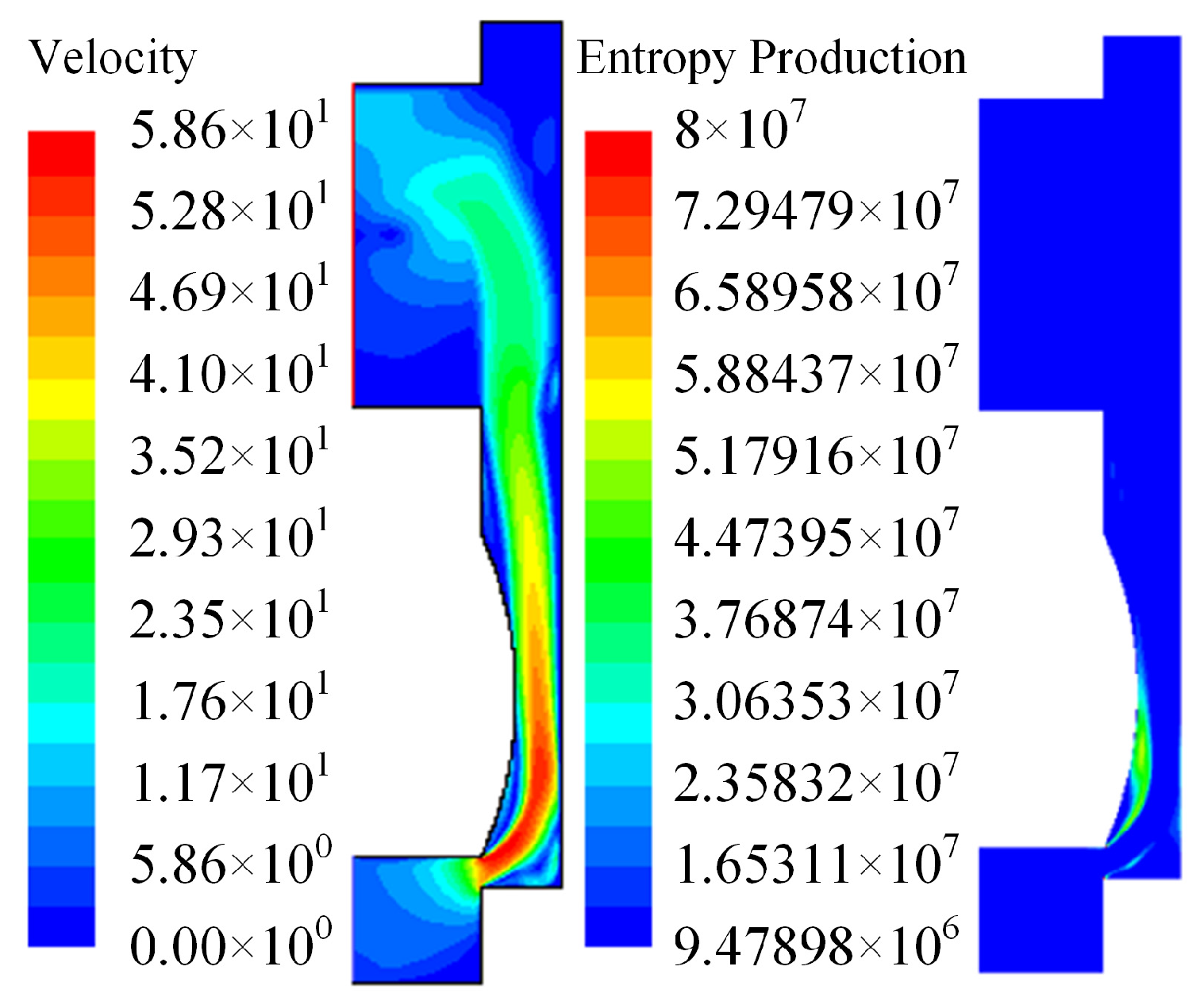
3.3. Effects of Viscous Forces and Vortex Dissipation
4. Steady Flow Force Compensation Optimization
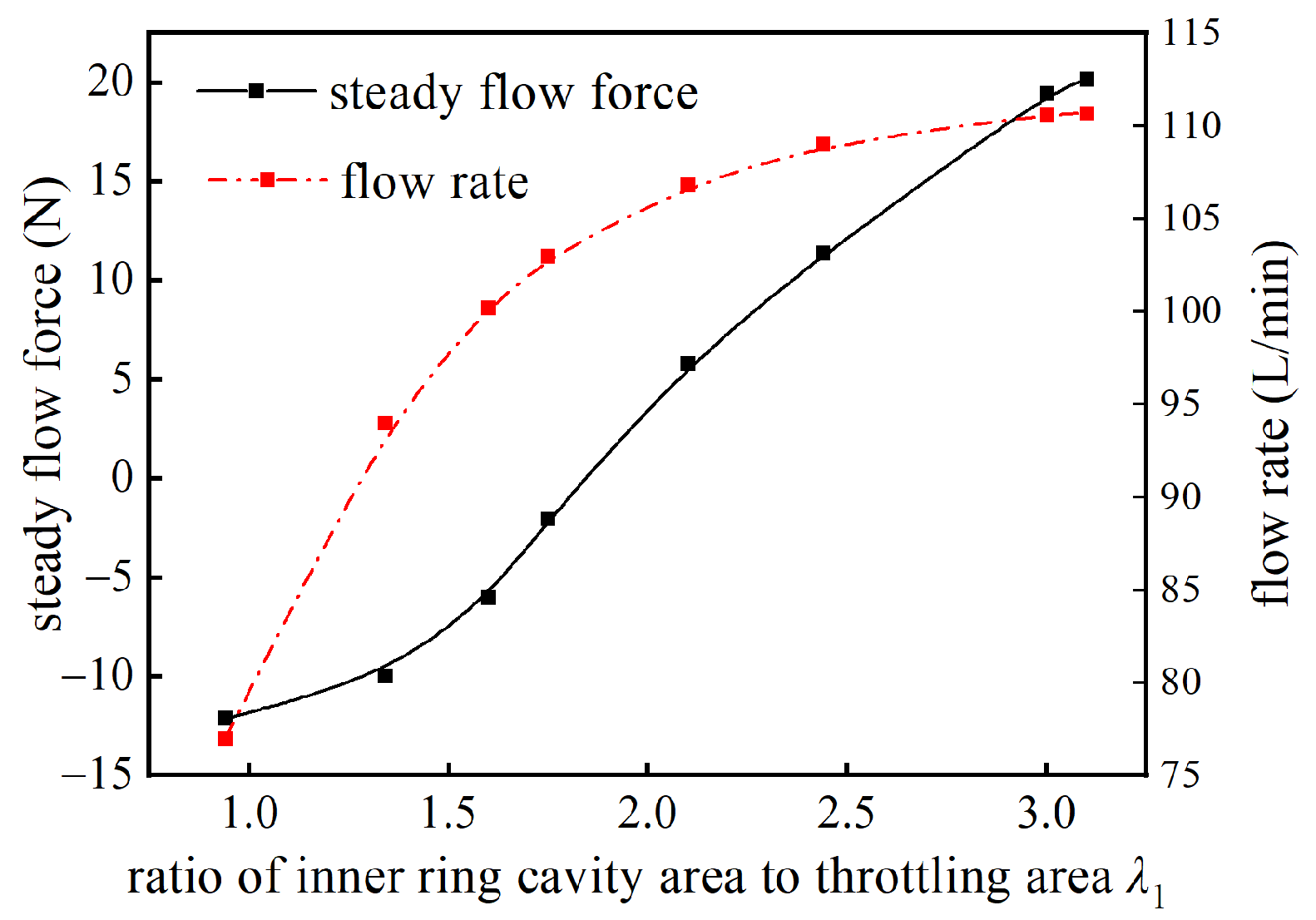
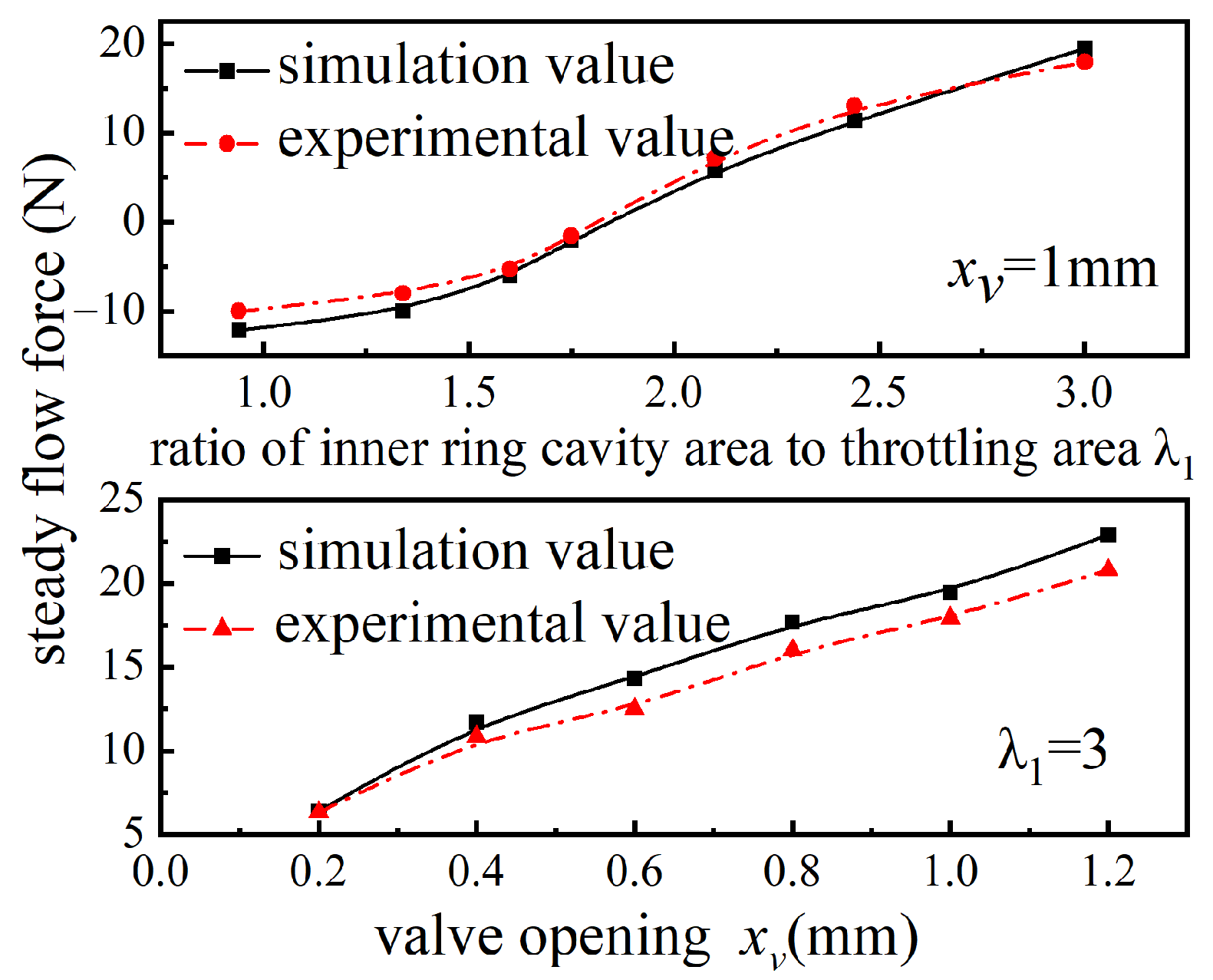
4.1. Influence of Inner Chamber Dimensions on Flow Force Characteristics
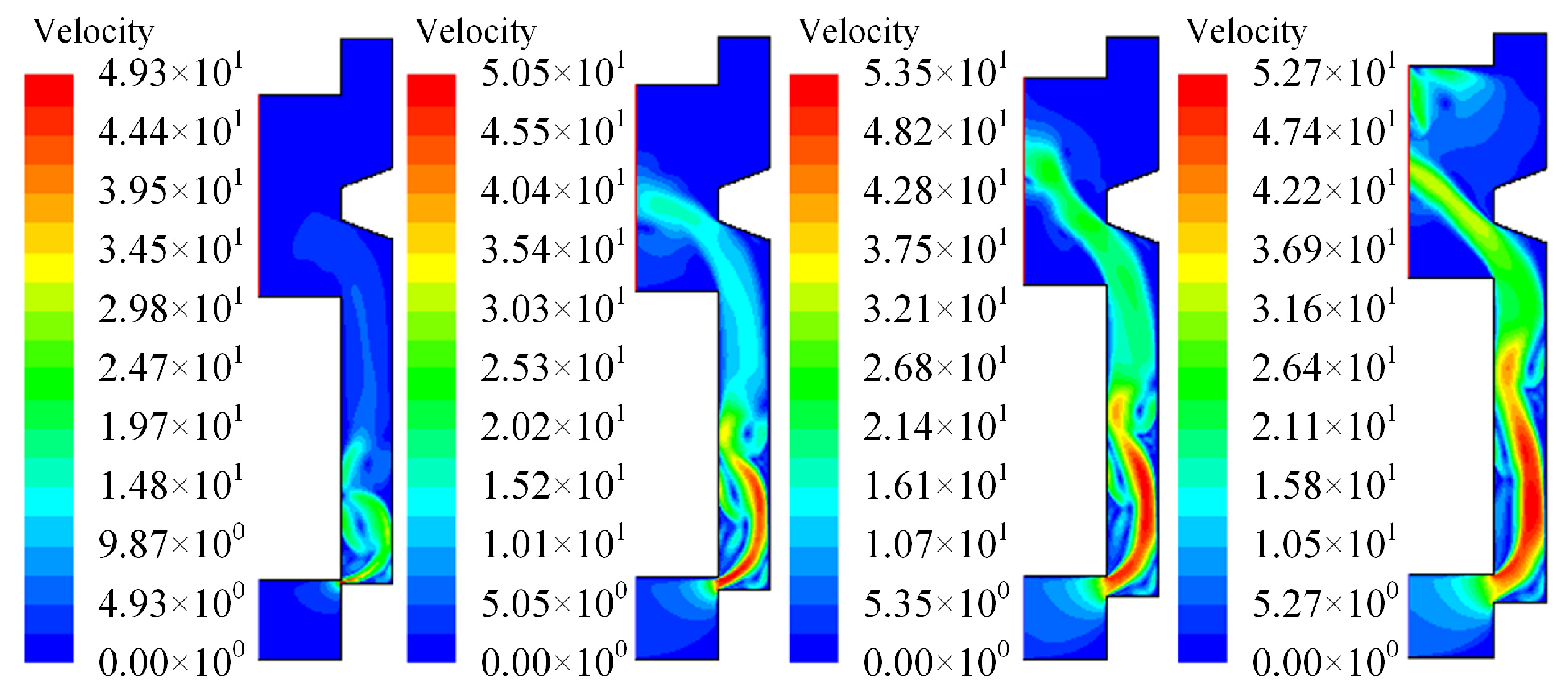
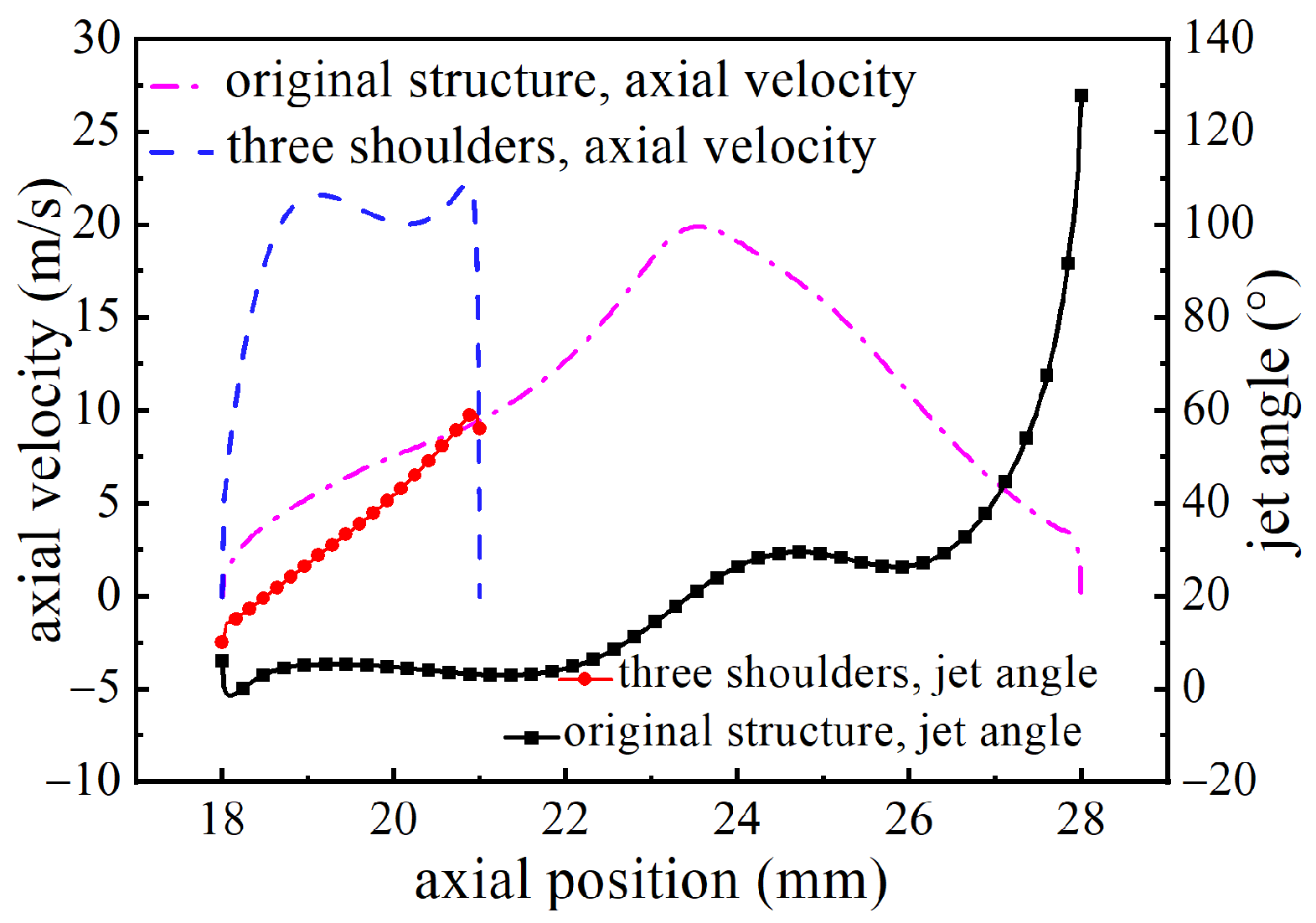
4.2. Flow Field Analysis of Convex Shoulder Compensation Structures
4.3. Optimization of Compensation Structure Parameters
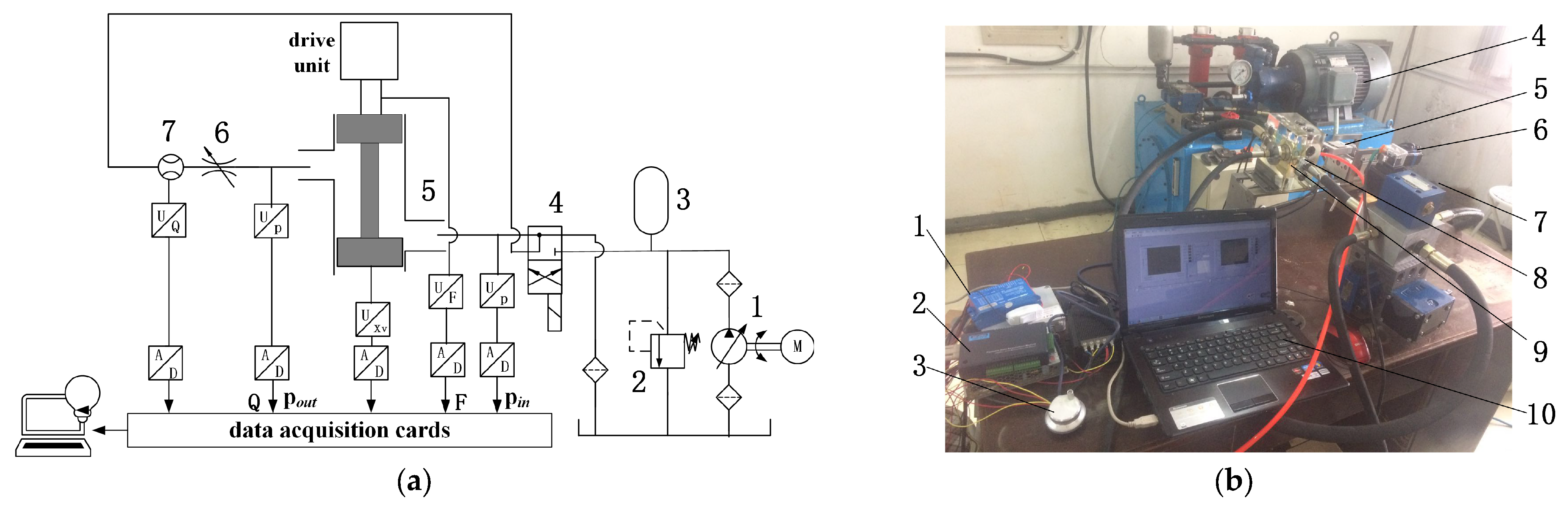
5. Experimental Verification
6. Conclusions
- (1)
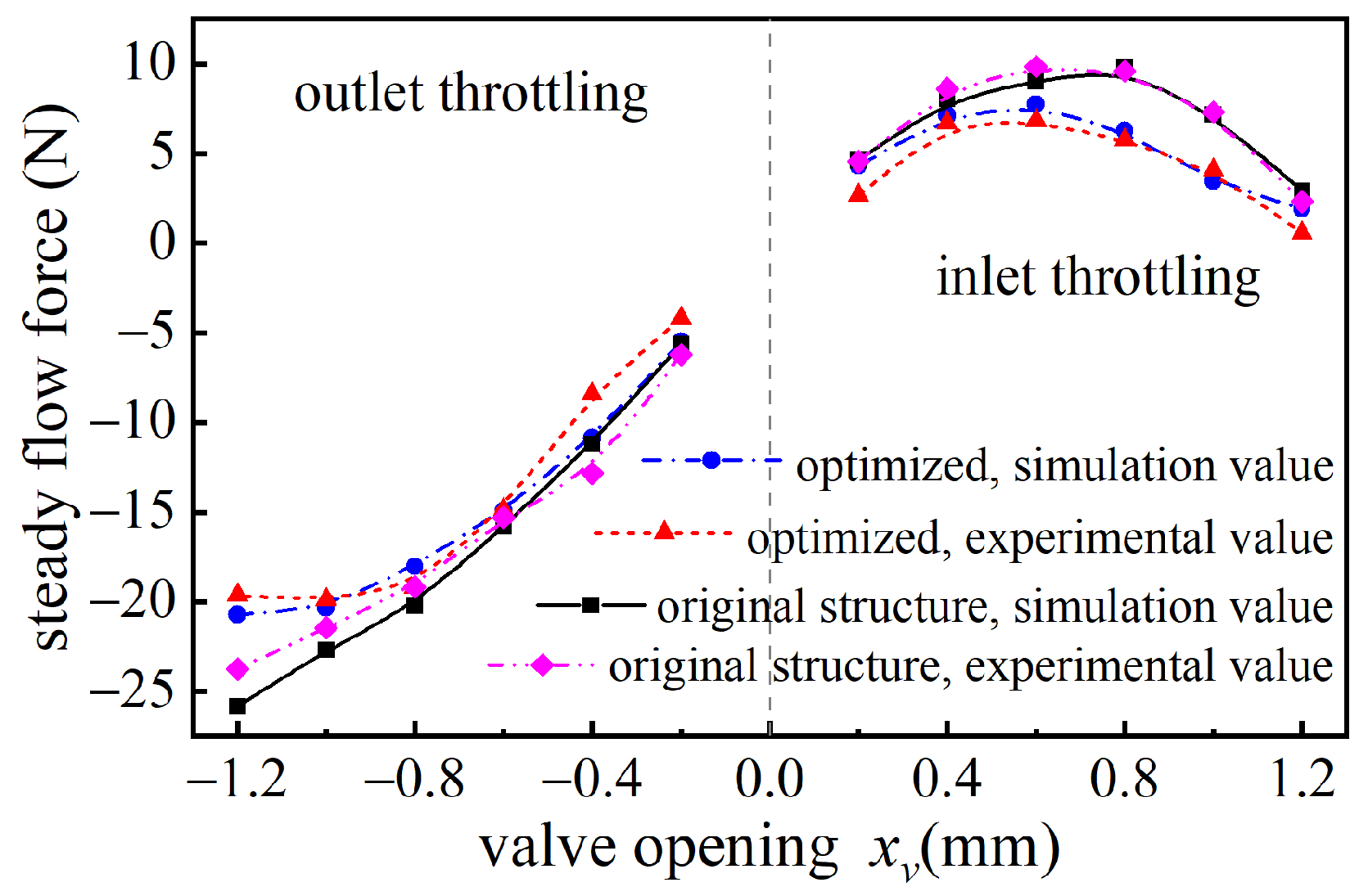
- The primary cause of the asymmetry in steady flow force curves under bidirectional throttling modes is the difference in fluid flow conditions at the non-throttling valve port. For slide valves with large openings in inlet throttling mode, the fluid momentum at the non-throttling valve port significantly influences the steady flow force and can even reverse its direction;
- (2)
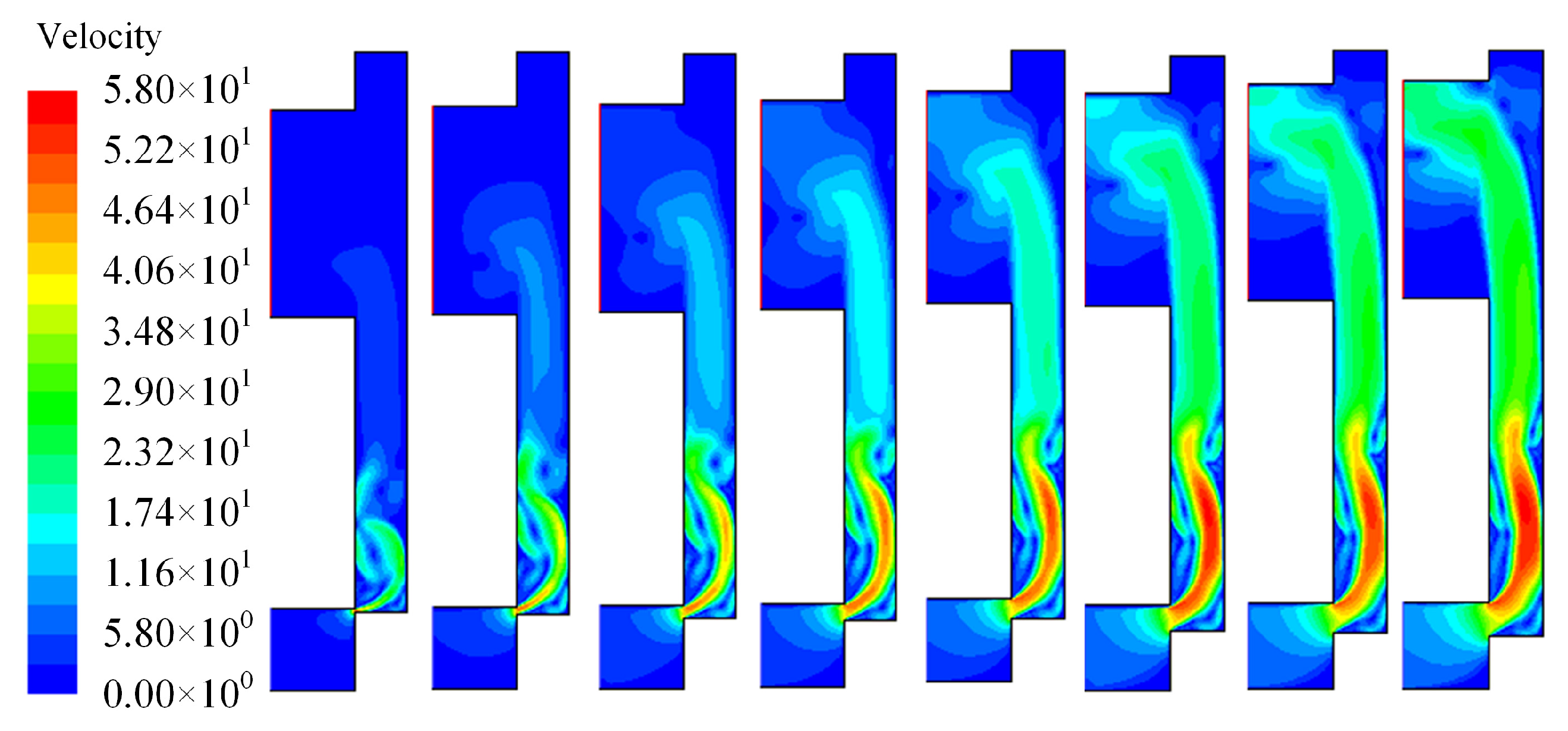
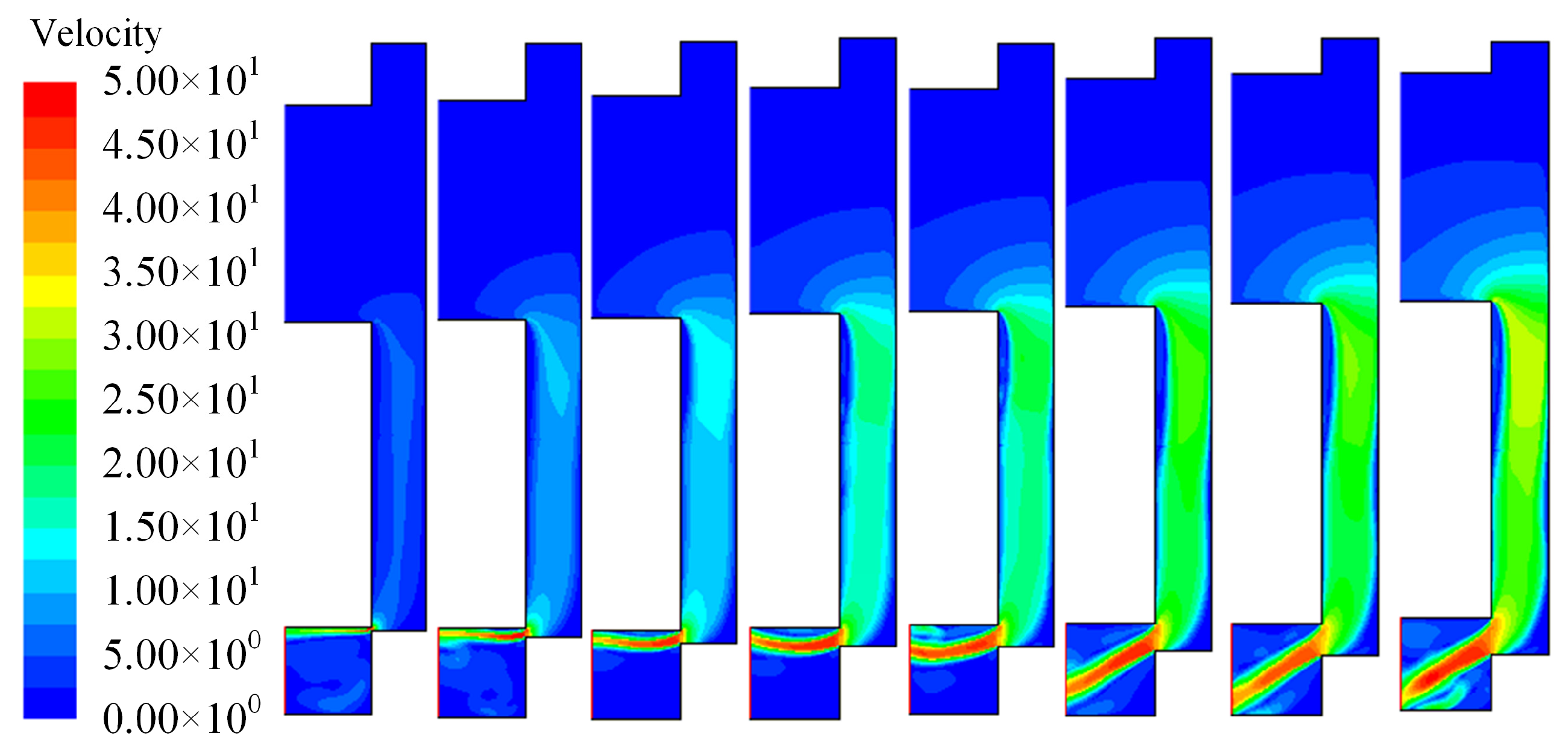
- Vortices caused by turbulent flow are an intrinsic reason for the nonlinearity of flow forces in inlet throttling slide valves. Suppressing vortex formation helps reduce the asymmetry in steady flow forces under bidirectional throttling conditions;
- (3)
- Increasing the fluid momentum at the non-throttling valve port is an effective means to reduce the steady flow force in slide valves. Experimental results show that the proposed compensation structure reduces steady flow forces by 34.45% and 76.47% for the inlet and outlet throttling modes, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tamburrano, P.; Plummer, A.R.; Distaso, E.; Amirante, R. A Review of Direct Drive Proportional Electrohydraulic Spool Valves: Industrial State-of-the-Art and Research Advancements. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2019, 141, 020801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stosiak, M.; Karpenko, M.; Deptuła, A.; Urbanowicz, K.; Skačkauskas, P.; Cieślicki, R.; Deptuła, A.M. Modelling and Experimental Verification of the Interaction in a Hydraulic Directional Control Valve Spool Pair. Appl. Sci. 2022, 13, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Sun, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, P.; Li, D.; Lin, J.; Xia, Y.; Sun, Q. Review of the Research on and Optimization of the Flow Force of Hydraulic Spool Valves. Processes 2023, 11, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herakovič, N. CFD simulation of flow force reduction in hydraulic valves. Teh. Vjesn. 2015, 22, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Li, P.Y. Using steady flow force for unstable valve design: Modeling and experiments. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2005, 127, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manring, N.D.; Zhang, S. Pressure Transient Flow Forces for Hydraulic Spool Valves. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2012, 134, 034501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zong, C.; Liu, F.; Zhang, A.; Xue, T.; Yu, X.; Song, X. Numerical and experimental analysis of fluid force for nuclear valve. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 241, 107939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, J.R.; Miana, M.J.; Núñez, J.L.; Pütz, T. Reduced order model for estimation of fluid flow and flow forces in hydraulic proportional valves. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 1517–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knypiński, Ł.; Kurzawa, M.; Wojciechowski, R.; Gwóźdź, M. Application of the Salp Swarm Algorithm to Optimal Design of Tuned Inductive Choke. Energies 2024, 17, 5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirante, R.; Del Vescovo, G.; Lippolis, A. Evaluation of the flow forces on an open centre directional control valve by means of a computational fluid dynamic analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2006, 47, 1748–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirante, R.; Vescovo, G.D.; Lippolis, A. Flow forces analysis of an open center hydraulic directional control valve sliding spool. Energy Convers. Manag. 2006, 47, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, N.Z.; Yang, Q.; Chen, M.; Li, S. CFD analysis of flow forces and energy loss characteristics in a flapper–nozzle pilot valve with different null clearances. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 83, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Yin, C.-B.; Li, X.-D.; Zhou, W.-J.; Yuan, F.-F. Effects of groove shape of notch on the flow characteristics of spool valve. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 86, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Liu, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhao, X.; Tan, H. A numerical investigation in characteristics of flow force under cavitation state inside the water hydraulic poppet valves. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 111, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simic, M.; Herakovic, N. Reduction of the flow forces in a small hydraulic seat valve as alternative approach to improve the valve characteristics. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 89, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, C.; Jin, B.; Yuan, T. Simulation and experimental research on steady flow force compensation for a servo proportional valve. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2023, 94, 102457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ding, X.; Lin, J.; Chi, F.; Xu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q. Study on the Influence of Triangular Groove Structure on Steady-State Flow Force Compensation Characteristics. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Li, R.; Xu, J.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, J. Study on flow force compensation characteristics and optimization design of jet guiding groove. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2022, 86, 102194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Yuan, W.; Wang, D.; Ji, H.; Chen, S. Design and optimization of hydraulic slide valve spool structure based on steady state flow force. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2024, 96, 102568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Tang, M.; Liu, Y. Research on the dynamic characteristics of water hydraulic servo valves considering the influence of steady flow force. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2021, 80, 101966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Tan, L.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Yang, H. Numerical and experimental investigation on opening direction steady axial flow force compensation of converged flow cartridge proportional valve. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2018, 62, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Xie, H.; Chen, H.; Yang, H. Structure optimization of conical spool and flow force compensation in a diverged flow cartridge proportional valve. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2019, 66, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirante, R.; Moscatelli, P.G.; Catalano, L.A. Evaluation of the flow forces on a direct (single stage) proportional valve by means of a computational fluid dynamic analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 942–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirante, R.; Distaso, E.; Tamburrano, P. Sliding spool design for reducing the actuation forces in direct operated proportional directional valves: Experimental validation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 119, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisowski, E.; Filo, G.; Rajda, J. Analysis of Flow forces in the initial phase of throttle gap opening in a proportional control valve. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2018, 59, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisowski, E.; Czyżycki, W.; Rajda, J. Three dimensional CFD analysis and experimental test of flow force acting on the spool of solenoid operated directional control valve. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 70, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisowski, E.; Filo, G.; Rajda, J. Pressure compensation using flow forces in a multi-section proportional directional control valve. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 103, 1052–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Wang, G.; Lu, Z. Flow field simulation and a flow model of servo-valve spool valve orifice. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 3249–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisowski, E.; Filo, G. Analysis of a proportional control valve flow coefficient with the usage of a CFD method. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2017, 53, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launder, B.; Spalding, D. The numerical computation of turbulent flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1974, 3, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





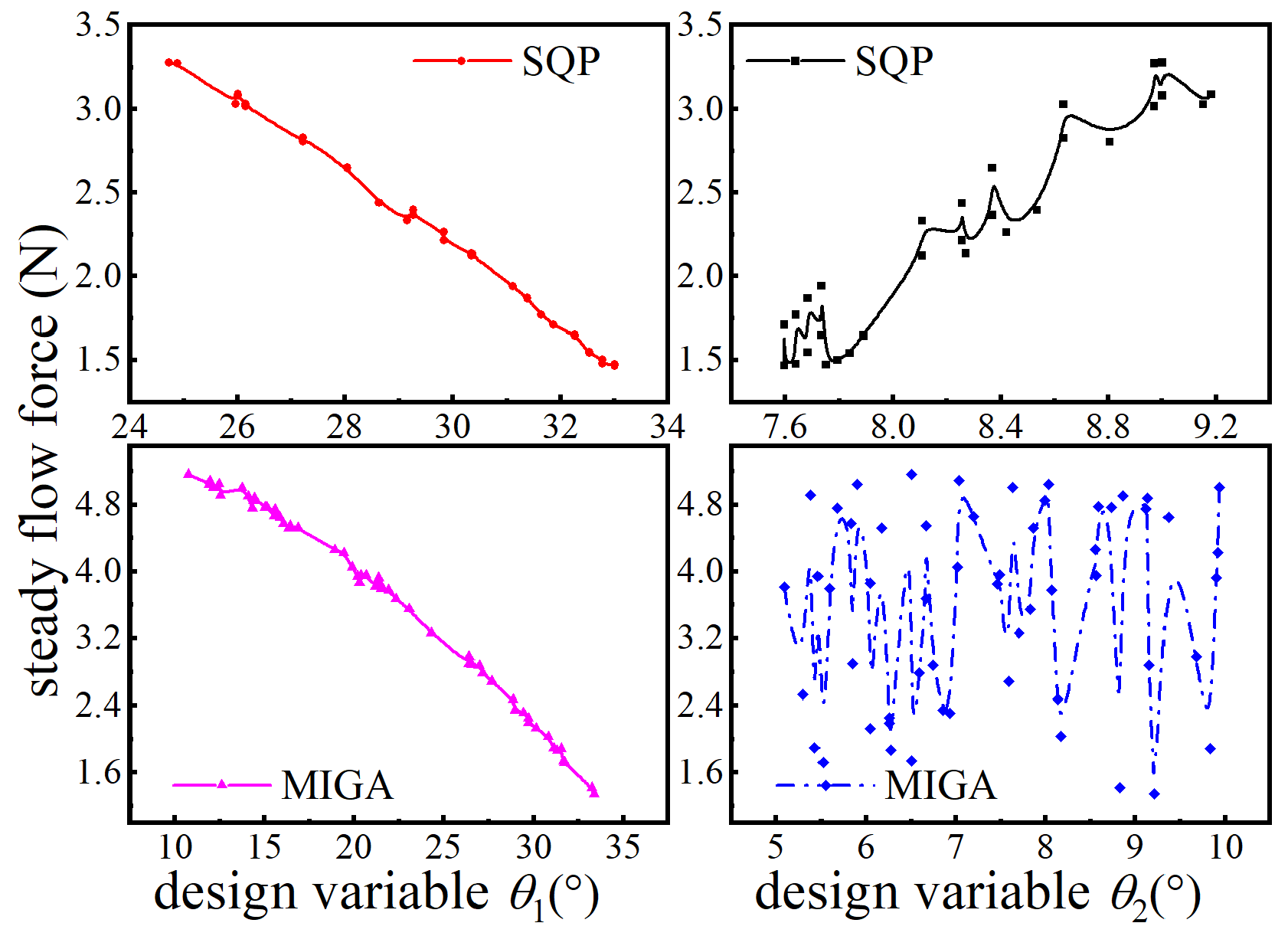
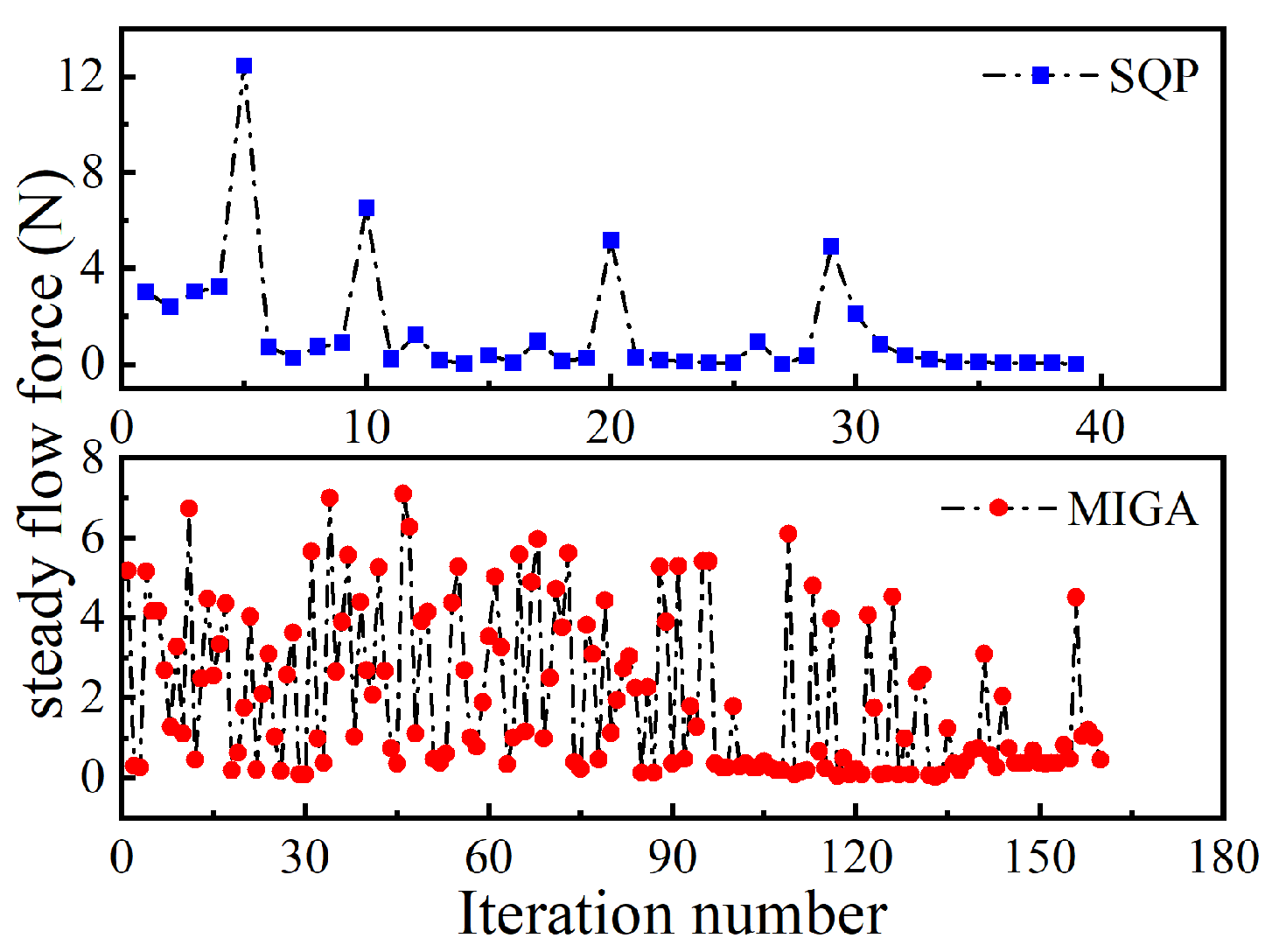
| Optimization Algorithm | θ1/° | θ2/° | Fspool/N |
|---|---|---|---|
| SQP | 7.6 | 33 | 1.46 |
| MIGA | 9.2 | 33.4 | 1.34 |
| Optimization Algorithm | θ1/° | θ2/° | d1/mm | Fspool/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SQP | 9.1 | 26 | 11.8 | 0.12 |
| MIGA | 6.8 | 25.6 | 11.8 | 0.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, Q.; Jia, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, G.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Q. Study on Steady Flow Force of a Bidirectional Throttling Slide Valve and Its Compensation Optimization. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11037. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311037
Mao Q, Jia X, Liu Z, Li G, Cao Y, Yang Q. Study on Steady Flow Force of a Bidirectional Throttling Slide Valve and Its Compensation Optimization. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(23):11037. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311037
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Qi, Xinying Jia, Zhe Liu, Guang Li, Yichi Cao, and Qingjun Yang. 2024. "Study on Steady Flow Force of a Bidirectional Throttling Slide Valve and Its Compensation Optimization" Applied Sciences 14, no. 23: 11037. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311037
APA StyleMao, Q., Jia, X., Liu, Z., Li, G., Cao, Y., & Yang, Q. (2024). Study on Steady Flow Force of a Bidirectional Throttling Slide Valve and Its Compensation Optimization. Applied Sciences, 14(23), 11037. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311037






