Abstract
The paper presents the practical design and implementation of a three-level neutral point clamped (TNPC) six-phase inverter rated at 100 kVA. The study initiates with prior work review, whereby most research work done earlier was mainly simulation-based. Based on the simulation results, this paper focuses on the practical aspects of inverter design, such as the development of a power board on an Insulated Metal Substrate, a gate driver board, an interconnect board, and the main control board. An inverter physical prototype has been built and tested at 500 V and 20 kW of output power. The SiC semiconductor technology is the base of the inverter, which represents the main merit of the work. Finally, high power density, compact design, and high efficiency are shown, which are major contributions of the paper. Tests performed proved that the designed converter was operating reliably and efficiently. While a simple Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation (SPWM) control algorithm has been implemented, the overall performance of the inverter showed great promise for higher-power applications. Compact and high-efficiency TNPC converters are developed for meeting increasing demands of advanced energy, automotive, and industrial applications.
1. Introduction
Multilevel converters have been widely used in many industrial scenarios for medium and high-power applications, such as electric drive, electric traction, and new energy power generation, in recent years due to the rapid growth of power electronics technology [1,2]. The advantage of multilevel inverters over two-level inverters (classical VSI) is characterized by lower dv/dt stress on the switches caused by the staircase output voltage waveform [3] and by the ability to create higher output voltage with a lower total harmonic distortion [4,5,6]. Existing multilevel converters can be categorized into four groups based on the circuit structure: modular multilevel (MMC), cascaded H-bridge (CHB), flying capacitor (FC), and neutral-point clamp converters (NPC) [1,7,8]. However, as the number of levels rises, integrating multilevel converters presents a variety of difficulties. In addition, fault-tolerant modules, circulating current suppression techniques, and capacitor voltage-balancing procedures are the primary considerations when running multilevel converters. Therefore, massive research has been done to solve these issues by upgrading circuit topologies [9,10] and developing control mechanisms to solve these shortcomings [3,5,11,12,13].
Another critical factor for multilevel inverters is the modulation techniques. The well-known modulation techniques are pulse width modulation (PWM), space vector pulse width modulation (SVPWM), sinusoidal pulse width modulation (SPWM), phase shifted carrier PWM (PSC-PWM) and the selective harmonic elimination pulse width modulation technique (SHE—PWM). Many articles for improving modulation strategies have been investigated [1,14,15]. The researchers [16,17] have adopted a SiC technology instead of Si semiconductor switches. This technology contributes to lower switching losses and fast switching speed, improving efficiency and power density [18,19].
Despite the great use of multilevel inverters, these inverters suffer from their shortcomings. As the number of levels in the FC multilevel converter increases, the difficulty of controlling and designing also increases. Therefore, these shortcomings limit their application in this field. Also, in high-voltage and high-power applications, the disadvantage of CHB and MMC is the large number of modules [2,5], large volume, and low efficiency [8,9]. Based on the previous results [20], the TNPC topology was selected based on the simulation results. This topology offers the best results across multiple investigated topologies [21,22]. Investigated topologies were standard six-phase Voltage Source Inverter (VSI), six-phase Neutral Point Clamped (NPC) topology, and six-phase TNPC inverter. The simulation results show that NPC topology has lower losses. On the other hand, the TNPC technology has slightly higher power losses, but from the components point of view, it uses 48 MOSFETs in total. The NPC topology uses 48 MOSFETs, but it contains an additional 24 diodes. All MOSFETs and diodes are doubled due to the power output of the inverter. Based on these simulation results, the TNPC topology was selected for practical verification. Due to its higher complexity, it offers better performance results and better control of the semiconductors. Table 1 shows summary of the different inverter topologies analysis.

Table 1.
Comparison of the topologies based on the publications.
Due to the inverter to be able to deliver required output power, design and simulations in papers calculates with two power components in parallel. Due to this fact, Table 1 shows number of components for this case.
This paper deals with the design and detailed description of the hardware parts of the 6-phase three-level TNPC inverter. Measurements with efficiency evaluation for different voltage levels and modulation indexes are presented at the end of the paper. The paper addresses a novel design of the TNPC inverter for six phase loads utilizing SiC semiconductor technology. Target of the design is maximizing power density.
2. Materials and Methods
As mentioned before, according to the previous publication and comparison of the inverter topologies, the TNPC topology was selected for the practical verification based on lower power losses, superior THD and lower component count compared to the NPC. Despite its higher complexity, the advantages of this topology exceed the disadvantages. Table 2 shows the required specifications and targets set for the six-phase inverter design.

Table 2.
Required inverter specifications.
2.1. Hardware Design Procedure
The development stage was divided into multiple individual groups which followed each other:
- Power module design stage:
In this stage, the power module of the TNPC inverter was designed and developed. The main target was good heat dissipation, a small form factor, and placing all heat-generating semiconductors in one place to maximize heat transfer. The proposed design has all one-phase semiconductors located in one Printed Circuit Board (PCB). This includes top and bottom 1200 V SiC MOSFETs and midpoint 650 V MOSFETs from OnSEMI (Phoenix, AZ, USA). Figure 1 shows diagram of the power transistors configuration with their respective labelling.
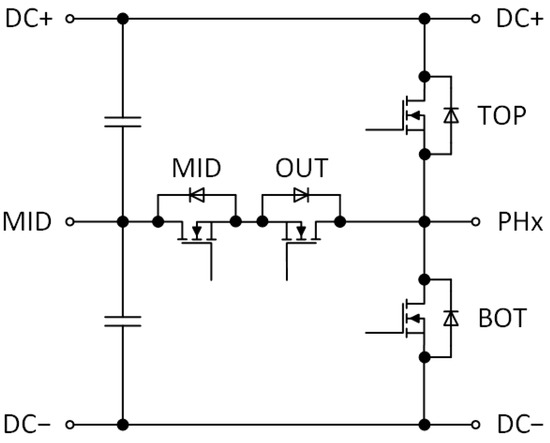
Figure 1.
Power transistors configuration on the IMS board.
Due to the power output of the converter, all MOSFETs must be doubled to ensure current handling capability. In total, 8 MOSFETs must be placed on this PCB. Additionally, gate connectors with protections are located on this board. For heat monitoring, the NTC thermistor is located near the power semiconductors to measure module temperature and implement overtemperature protection. Power connections are made using Würth Elektronik (Waldenburg, Germany) stand-off with M4 internal thread. There are four terminals for DC+, DC−, MID potential, and OUTPUT. Six power PCBs are required to construct a 6-phase TNPC inverter. The 3D model of the PCB is shown in the Figure 2:
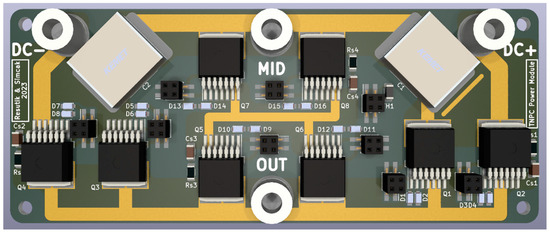
Figure 2.
Power IMS board with semiconductors.
Due to the high-power dissipation from the power MOSFETs, the PCB must transfer this heat to the heatsink. At the power output of 100 kW, the expected power dissipation of one module is around 144 W. This heat must be transferred from the semiconductors to the heatsink. Despite this, the Insulated Metal Substrate (IMS) based PCB was selected. This type of board has a copper or aluminum core, which quickly transfers heat through the PCB. In this application, the aluminum core PCB was selected due to the lower price and sufficient thermal conduction. This IMS comes with a SiO2 insulation layer and 4 oz copper weight to handle the high output currents of the module. Manufactured PCB can be seen in Figure 3:
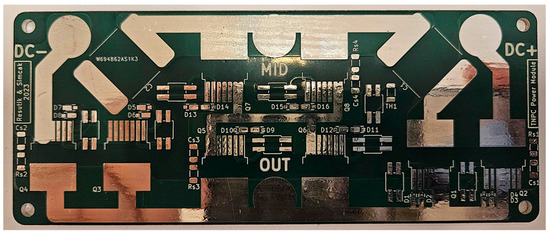
Figure 3.
Manufactured unpopulated power board.
Designed board provides superior thermal cooling of the transistors. Additionally, symmetrical design provides equal current paths which improves EMC performance of the power part of the inverter. The main advantage of the module is that it contains all switches for one phase in one compact PCB.
- Driver design stage:
The second design stage was the insulated driver design to properly drive all transistors in the TNPC configuration. Because the drivers must be insulated, three isolated power supplies are required for this design—one for the bottom transistors, one for the top transistor, and one for the middle transistors. The used power supplies are RS3K from RECOM (Gmunden, Austria), with an output voltage of 20 V and an output power of 3 W. With the help of additional circuits, this voltage is further separated to the +16 V and −4 V to close SiC MOSFETs properly. These voltages are fed to the isolated driver from Texas Instruments UCC21755 (Dallas, TX, USA). This driver is designed for SiC MOSFET driving and has multiple built-in protection circuits, such as desaturation protection or miller clamp. All these circuits, power supplies, and auxiliary components are designed on a 4-layer PCB with dimensions of 123 × 49 mm. The designed PCB can be seen in Figure 4.
Figure 4.
Single phase driver board.
The long pin headers connect the transistors’ gate to the driver’s output. Since the bus-bar PCB is between the driver and the power PCB, the pin headers must be higher.
- Driver interconnection PCB design stage:
Due to the high component count on the driver PCB, it is impossible to populate the connector to the control board right on the driver PCB. Another PCB must be designed to distribute power rails and driving signals to the right places on the driver PCB. This board is created on a 4-layer PCB with the exact dimensions as the driver board, thus 123 × 49 mm. It mainly consists of a 26-pin Insulation Displacement Connector (IDC). The Ready and Fault indication LED was also populated to indicate different driver stages. This PCB is located above the driver PCB. The finalized PCB model can be seen in Figure 5.
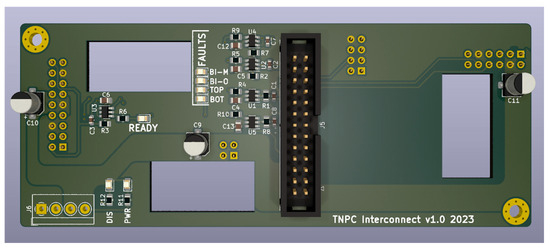
Figure 5.
Interconnect PCB connecting driver and control board.
- Distribution BUS-BAR PCB:
A distribution board must be designed to connect all power modules to the input power supply properly. The PCB is designed as a 4-layer PCB with 6 oz copper layers to handle the converter power output. It connects the input power supply, smoothing DC-BUS capacitors and power modules. The final dimensions are 308 × 310 mm. Figure 6 shows the prototype of the board that was manufactured.
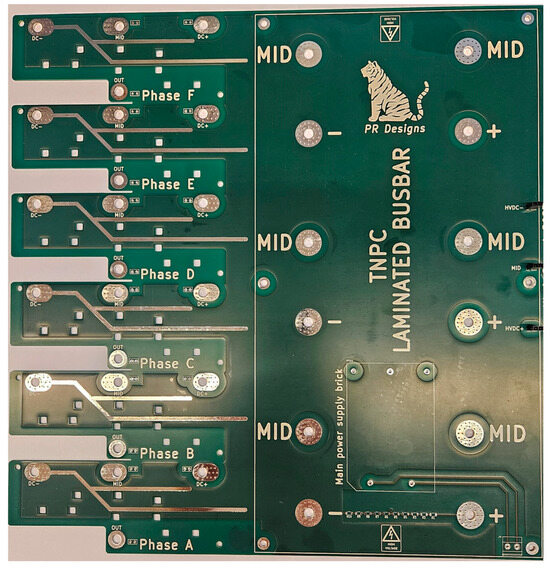
Figure 6.
Power BUS-BAR Laminated PCB.
The novelty of this design of this power distribution PCB enables easy manufacturability of the laminated bus bar, which lower overall cost of the inverter build.
- Control board design stage:
A powerful Digital Signal Processor (DSP) must be selected to control this type of converter properly. In this prototype, the dual-core TMS320F28379D (Dallas, TX, USA) was used. The control board has populated all the necessary circuits for proper inverter operation. In the top right corner, all power supplies are populated. The 12 V power supply powers the board, and on-board power supplies generate the following rails:
- +15 V for resolver driver
- +15 V/−15 V for current sensors
- Isolated 5 V for CAN drivers
- 3.3 V for DSP
- 1.2 V for DSP Core
The board has 6 IDC connectors, distributing all necessary signals to the power module drivers. The board also contains high-voltage measurement of the DC BUS, to monitor voltage properly. Additionally, the resolver and encoder interfaces are populated to monitor the motor position. The designed control board can be seen in Figure 7. The Phase A -F markings show positions of the connectors for the driver board.
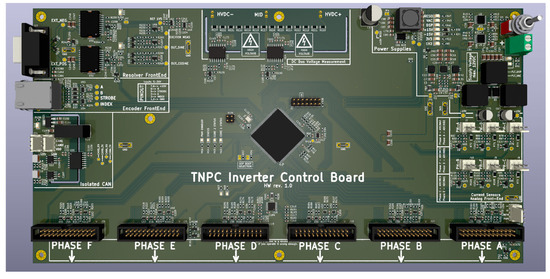
Figure 7.
Control PCB of the 6-phase TNPC.
The final block diagram in Figure 8 shows the composition and construction of the prototype of the TNPC inverter.
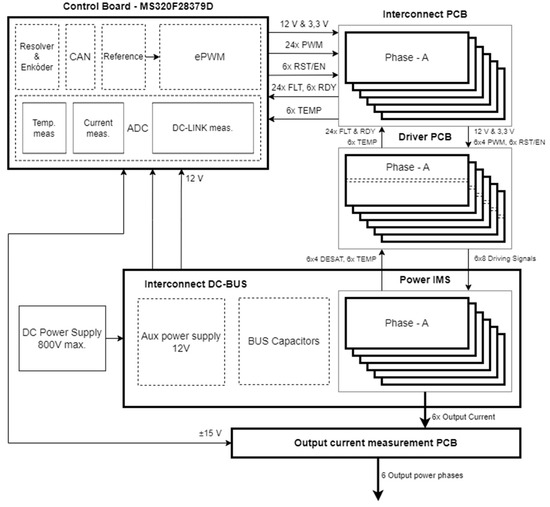
Figure 8.
Block diagram of designed inverter prototype.
The designed boards are assembled to create a 6-phase TNPC inverter with a rated power output of 100 kW. The power modules will be mounted on a liquid-cooled plate. The modules comprise a driver board and an interconnection board, interconnected by a BUS PCB transferring the power. A control board at the top monitors system parameters and manages the power modules. Six HALL current sensors monitor the output current, whose reading goes back to the analog section for feedback and regulation to the control board. The 3D model of the final prototype is shown in Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11.
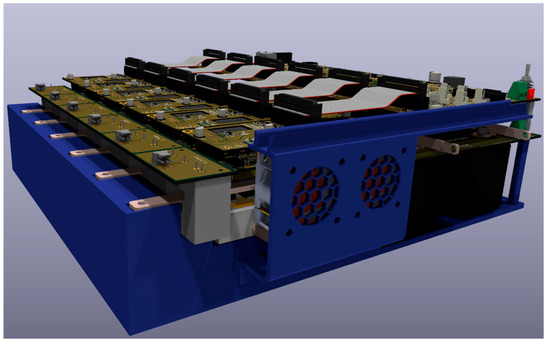
Figure 9.
3D model of the prototype left side view.
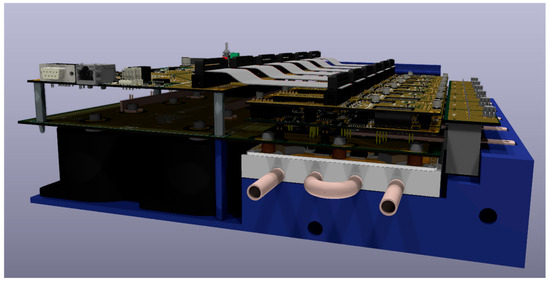
Figure 10.
3D model of the prototype right side view.
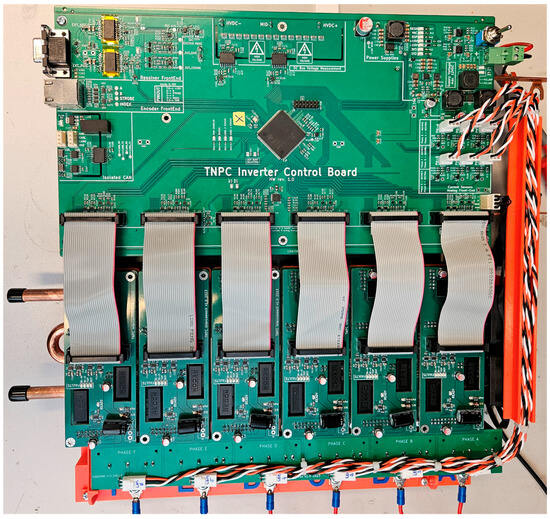
Figure 11.
A practical sample of the TNPC inverter prototype is in the top view.
The design is targeted to the laboratory environment and testing and is not greatly optimized for operation in vehicle. The reliability of inverters in traction applications is greatly influenced by the vibration and fluctuating temperatures of an environmental source. Vibration causes mechanical stress that can result in solder joint fatigue, degraded insulation, and weakened connections between power modules. Temperature fluctuations induce thermal cycling, further accelerating component aging, which degrades the lifetime of the power electronics. Inverter designs, therefore, must consider these stresses carefully with a view to long-term reliability through robust mechanical and thermal management strategies. Design is focusing on the relatively easy access to test points for during inverter operation.
The presented sample was designed to have high power density. This design brings some interesting challenges and trade-offs. Higher power density often leads to decreasing efficiency of the converter due to the smaller components and more heat generation. Additionally, this brings some other challenges in the cooling design. Higher power density can be reached by higher switching frequency, but this increases switching losses and puts extra stress on the components and cooling system. Achieving the right balance between efficiency, power density and components sizing required careful material selections and advanced mechanical and cooling design.
2.2. Control Algorithm
For the prototype evaluation and testing, the well-known control algorithm was implemented. The inverter is controlled by the sinusoidal modulation technique SPWM. For the control, all 24 PWMs of the DSP are utilized. The sinusoidal reference is generated in the control DSP, which is then compared to the sawtooth waveform generated by the ePWM modulator of the DSP. The output is then fed to the dead band module which generates a dead time and provides an inside DSP signals interlock. Additionally, the drivers have another layer of hardware interlock to ensure that the shoot-through condition never occurs. This simple well-known algorithm was used due to its simplicity and rapid deployment to the DSP. For the initial testing, this type of control algorithm is sufficient. A more complex algorithm for inverter control will be developed in future work to further improve the performance of the inverter.
3. Verification of the TNPC Converter
The parameters of the designed prototype of the TNPC inverter are depicted in Table 3.

Table 3.
Designed prototype specifications.
The designed inverter was verified and tested in laboratory conditions. The devices used for the inverter testing are summarized in Table 4.

Table 4.
Devices used for TNPC testing.
Figure 12 shows the test setup used in the TNPC inverter verification:
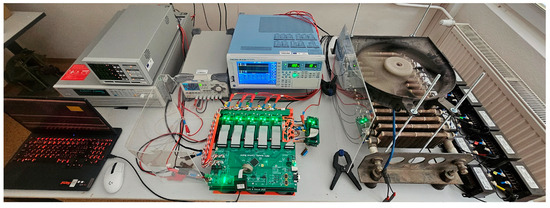
Figure 12.
Test set-up with RL load.
3.1. Test Plan
For inverter initial testing, the following test plan was created for successive testing of individual parts of the converter.
- PWM signals verification without power modules connected using Logic analyzer
- Verification of the soft start
- Output waveform measurement at reduced input voltage
- Verification of current and voltage sensors and their calibration
- Initial temperature verification (components overheating)
- Prototype verification with gradual increasing of input voltage and modulation index
- Measurement of voltages, currents and temperatures at critical components
3.2. Test Procedure
First, the inverter’s switching pattern (Figure 13) was verified using a 16-channel logic analyzer from Saleae (San Francisco, CA, USA). The measured signals shows PWMs to the transistors according to the SPWM modulation. The signals labelling corresponds to the MOSFETs configuration shown in Figure 1. When reference sine wave is in positive half, the TOP and OUT MOSFETs are switching in complementary, MID is turned on and BOT is turned off. Consequently, when reference is in negative half, the BOT and MID are switching in complementary, OUT is turned on and TOP is turned off.
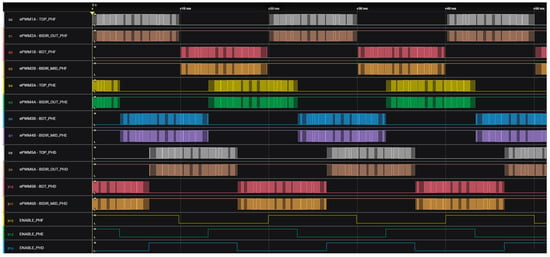
Figure 13.
Switching signals of the power transistors.
The TNPC inverter was verified at different switching frequencies to properly measure the prototype power losses and efficiency. The selected switching frequencies were 10 kHz, 20 kHz, and 30 kHz. The output frequency was chosen to be 50 Hz and was constant during all the measurements. The converter input voltage and modulation index were changed during the measurements to measure different voltages and output power levels. The output power versus modulation index at different input voltages can be seen in Figure 14.
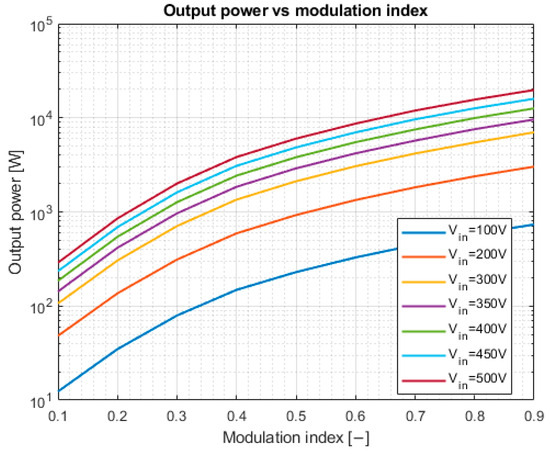
Figure 14.
Output power dependency on the modulation index at fsw = 20 kHz.
The maximum output power is 19,739 W. The available load limits this output power because it cannot dissipate more power. Figure 15 shows the dependency of the efficiency on the output power of the inverter:
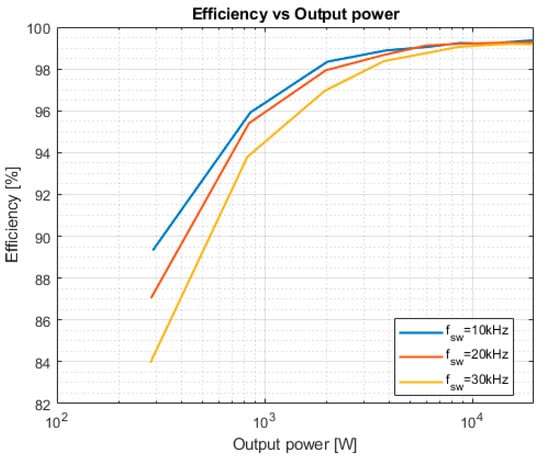
Figure 15.
Efficiency of the prototype at different switching frequencies.
As can be seen, initial efficiency is slightly higher at the switching frequency of 10 kHz. This is caused by the lower losses in the drivers and driving circuits at low output powers. At the output power of 20 kW, the efficiency values at all switching frequencies are nearly the same. This indicates that the converter peak efficiency has not yet been reached. At measured output power, the switching frequency does not significantly affect system efficiency as shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Measured efficiency at different switching frequencies.
At the switching frequency of 10 kHz, the inverter was generating audible noise, primarily from power semiconductors and passive components. For future testing, the switching frequency of 20 kHz will be selected due to the suppression of audible noise and slightly more efficient than 30 kHz. The graphs from Figure 16, Figure 17 and Figure 18 show efficiency maps of the converter:
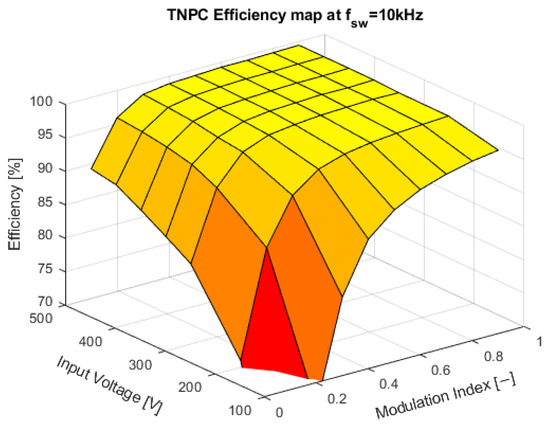
Figure 16.
Efficiency map at a switching frequency of 10 kHz.
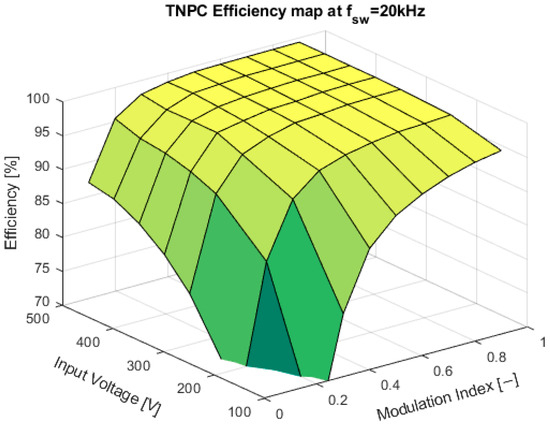
Figure 17.
Efficiency map at a switching frequency of 20 kHz.
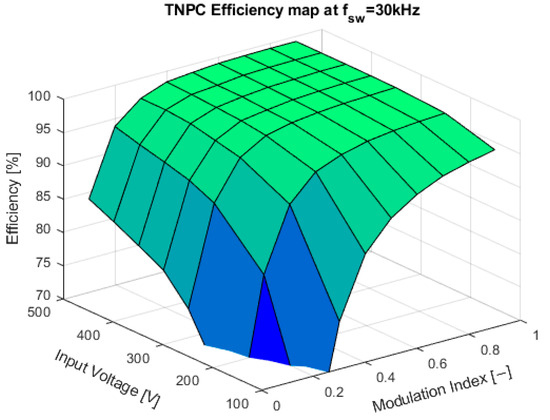
Figure 18.
Efficiency map at a switching frequency of 30 kHz.
Due to the high efficiency of the converter prototype, the water cooling was not connected to the water system. Cooling during this test was only passive with modules connected to the water block. Temperatures at the modules are given in Table 6.

Table 6.
Measured temperature of modules at the different switching frequencies.
From the data above, the modules can only be passively cooled to an average output power of approximately 30 kW. Then, water cooling must be connected to cool the semiconductors properly. Figure 19 shows the output voltages and currents of the TNPC inverter at a switching frequency of 20 kHz and output power of 20 kW.
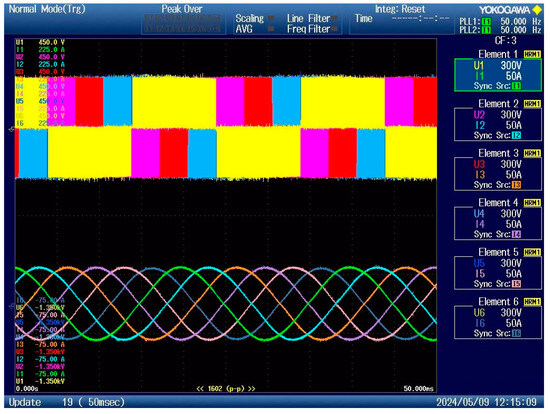
Figure 19.
Output waveforms at 20 kW.
The RMS phase current value measured by the YOKOGAWA (Tokyo, Japan) was 21.68 A and by the on-board current sensor 21.51 A. According to the YOKOGAWA, this measurement proves to be accurate for the onboard measurement. The DSP calculates the value of moving RMS online for all six phases. Figure 20 shows a summary of the measured voltages and currents. The output RMS voltage at phase was only 188 V due to the low value of the DC−BUS. If the DC−BUS voltage is 565 V and the modulation index is set to 1, the phase voltage reaches 230 V RMS.
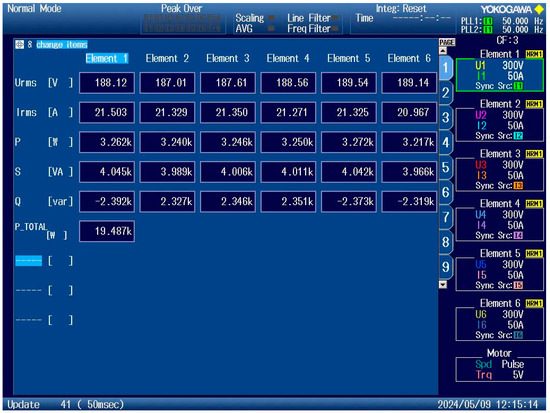
Figure 20.
Output variables at 20 kW.
As seen in Figure 19, the apparent output power of the converter was 24.06 kVA. The active power was 19.48 kW. The output power factor during this test was 0.813.
The thermal image of the converter when delivering 20 kW at the output is shown in Figure 21.
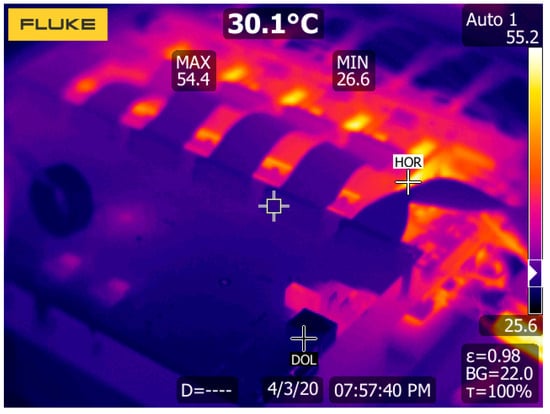

Figure 21.
TNPC inverter temperature at 20 kW.
Due to the power limit of the power resistor at the testing load, the maximum output power that could be safely reached was 20 kW. Figure 22 shows the temperature of the actively cooled power resistors.
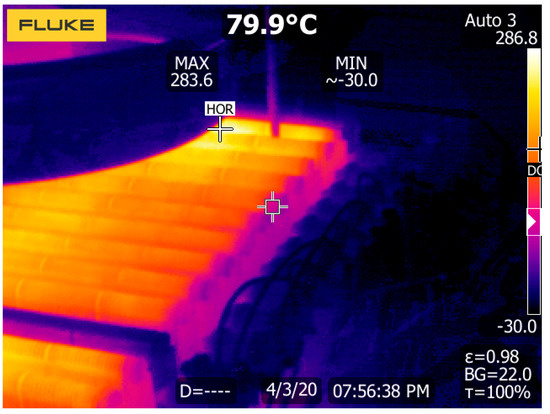
Figure 22.
Load temperatures at 20 kW.
The maximum temperature is around 283 °C. This temperature is reached at the end of the load, where airflow from the cooling fan is limited.
4. Conclusions
This paper presents the design process of a 6-phase TNPC multilevel inverter. The topology was selected based on the simulation results of the other papers and the research. Then, the design process is described in detail, describing the design of the power IMS board with all power semiconductors. The IMS board was selected due to its low thermal resistance and excellent heat transfer from the semiconductor to the heatsink. The measurement also proved this because the inverter was only passively cooled at the output power of 25 kVA. Other presented boards are driving and interconnection, which are driving the power MOSFETs based on the signals from the control board. The control board is designed as a 4-layer PCB consisting of all auxiliary power supplies and control DSP with signal conditioning. Additionally, the communication and resolver interfaces are present on this board. The BUS-BAR board was designed with thick copper layers to ensure low resistance and copper trace capacity to deliver the required power to the individual modules connected to the power supply. Other boards are current measurement and auxiliary boards.
The measurement was done in the laboratory conditions with the passive R-L load simulating drive, with the cos φ set to 0.82. The load was capable of dissipating 20 kW. The inverter was tested at seven input voltages ranging from 100 V to 500 V. The higher input voltage was impossible due to the absence of a high-voltage input power supply. As shown in Figure 13, the efficiency at the output power of 20 kW was from 99.18% to 99.37%, depending on the switching frequency. The final switching frequency for this prototype was selected to be 20 kHz because it offers good efficiency, and the inverter does not produce an audible noise during the operation. The efficiency maps shown in Figure 14 through Figure 16 show flat efficiency at high output power, indicating a perfect power module design. Additionally, the inverter was only passively cooled, and at maximum power output of 20 kW, the temperature of the module was around 53.5 °C.
The following work will focus on additional testing. A more powerful load must be provided to fully test the converter-rated power output. Especially at this power output level, the load should actively recuperate power from the grid. Additionally, a power supply with higher output voltage and power must also be provided for further testing. Implementation of the Field Oriented Control (FOC) is planned to this inverter, due to the advantages it offers compared to the SPWM. FOC offers decoupled control of torque and flux, which results in more accurate and dynamic response in motor control applications. Additionally, the FOC has reduced harmonic distortion compared to the SPWM method. For this control the on-board resolver/encoder interfaces will be used.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.R. and S.K.; methodology, P.R. and M.P.; software, P.R.; validation, S.K. and P.R.; formal analysis, S.K.; investigation, P.R.; resources, P.R.; data curation, P.R. and S.K.; writing—original draft preparation, P.R. and S.K.; writing—review and editing, P.R., S.K. and M.P.; visualization, P.R.; supervision, M.P.; project administration, P.R. and S.K.; funding acquisition, M.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by projects APVV-22-0330, Research of a system for active and optimal management of electrical energy using battery storage system, and VEGA 1/0314/24, Research of a system for active management of electrical energy using the battery storage system. This research was also supported by the University of Žilina, UNIZA Grant Project: “Research of methods for investigation of operating and fault conditions of drives with multiphase asynchronous motor”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hasan, N.S.; Rosmin, N.; Osman, D.A.A.; Jamal, A.H.M. Reviews on multilevel converter and modulation techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 163–174, ISSN 1364-0321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, B.; Zhao, J.; Deng, Y.; He, X.; Xu, Z. Development of a compact 750KVA three-phase NPC three-level universal inverter module with specifically designed busbar. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Palm Springs, CA, USA, 21–25 February 2010; pp. 1266–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Lai, J.S.; Peng, F.Z. Multilevel inverters: A survey of topologies, controls, and applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2002, 49, 724–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.K.; Jain, S. A Novel Multilevel Inverter Based on Switched DC Sources. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 3269–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, L. Hybrid ANPC Grid-Tied Inverter Design with Passivity-Based Sliding Mode Control Strategy. Energies 2024, 17, 3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeh, C.I.; Lewicki, A.; Morawiec, M.; Jąderko, A. Enhanced Four-Level Active Nested Neutral Point-Clamped Inverter. Energies 2024, 17, 3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Xie, Q.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, Z. Simple Voltage Balancing Control of Four-Level Inverter. Electronics 2024, 13, 3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkili, S.; Krishna, R.V.; Bonthagorla, P.K.; Senjyu, T. Performance Analysis of Modular Multilevel Converter with NPC Sub-Modules in Photovoltaic Grid-Integration. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latran, M.B.; Teke, A. Investigation of multilevel multifunctional grid connected inverter topologies and control strategies used in photovoltaic systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 361–376, ISSN 1364-0321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, A.J.; Mahar, M.A.; Larik, A.S.; Shaikh, M.M. A Comprehensive Review of Reduced Device Count Multilevel Inverters for PV Systems. Energies 2023, 16, 5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annoukoubi, M.; Essadki, A.; Akarne, Y. Model predictive control of multilevel inverter used in a wind energy conversion system application. e-Prime—Adv. Electr. Eng. Electron. Energy 2024, 9, 100717, ISSN 2772-6711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadigh, A.K.; Masoud, B.S. Topologies and Control Strategies of Multilevel Converters. In Modeling and Control of Sustainable Power Systems. Green Energy and Technology; Wang, L., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takacs, K.; Frivaldsky, M. Hardware in the loop modeling of T-type voltage source inverter for vehicle to grid applications. Transp. Res. Procedia 2023, 74, 825–830, ISSN 2352-1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Yu, P. Overview of Multilevel Inverter Topologies and Modulation Methods. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Information Technologies for Rail Transportation (EITRT), Qingdao, China, 22–24 October 2021; Springer: Singapore; Volume 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandwani, H.B.; Matnani, M.K. A review of modulation techniques for hybrid multilevel inverter. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Emerging Technology Trends in Electronics, Communication & Networking, Surat, India, 19–21 December 2012; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Aksoz, A.; Geury, T.; Ozturk, S.B.; Kivanc, O.C.; Hegazy, O. A Review of Modular Multilevel Converters for Stationary Applications. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellazzi, A.; Gurpinar, E.; Wang, Z.; Suliman Hussein, A.; Garcia Fernandez, P. Impact of Wide-Bandgap Technology on Renewable Energy and Smart-Grid Power Conversion Applications Including Storage. Energies 2019, 12, 4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svarna, V.; Frivaldsky, M. Silicon Carbide Technology: State-of-the-Art; ELEKTRO (ELEKTRO): Zakopane, Poland, 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biel, Z.; Pcola, M.; Ondrejicka, J.; Franko, M.; Frivaldsky, M. Efficiency Comparison of Si Igbt and Sic Mosfet Based Three-Phase Inverters. Commun.—Sci. Lett. Univ. Zilina 2023, 25, C56–C61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simcak, J.; Frivaldsky, M.; Resutik, P. Performance evaluation of multilevel multiphase inverters by piece-wised linearized simulation models. Automatika 2024, 65, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simcak, J.; Frivaldsky, M.; Resutik, P.; Kindl, V.; Skala, B.; Zavrel, M. Evaluation of the Efficiency Performance of 3-Phase and 6-Phase Voltage Source Inverter; ELEKTRO (ELEKTRO): Zakopane, Poland, 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simcak, J.; Frivaldsky, M.; Resutik, P. The Power Analysis of Semiconductor Devices in Multi-Phase Traction Inverter Topologies Applicable in the Automotive Industry. Commun.—Sci. Lett. Univ. Zilina 2024, 26, C21–C38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).