A Parallel Monte Carlo Algorithm for the Life Cycle Asset Allocation Problem
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Life Cycle Asset Allocation Model
2.1.1. Utility Function Selection
2.1.2. Financial Asset
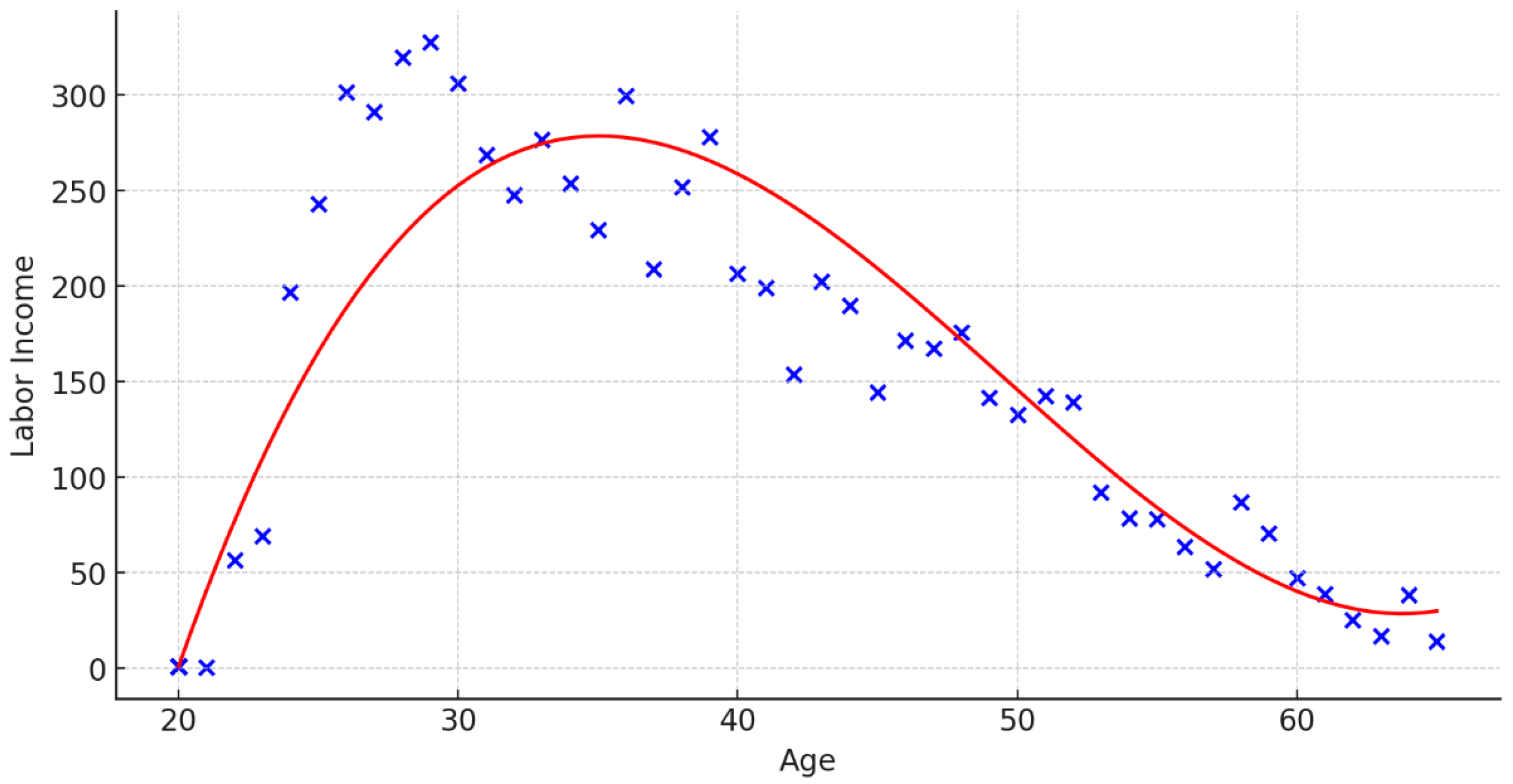
2.1.3. Labor Income Patterns in China: Insights from the China General Social Survey (CGSS)
2.1.4. Optimization Problem
- (1)
- Before maturity of the product:
- (2)
- Obtain the Bellman equation:
2.2. Description of Monte Carlo-Based Algorithm for Solving the Bellman Equation
| Algorithm 1: Monte Carlo Method for Solving the Bellman Equation |
5: For do , while for , for . do 11: end for 15: end for |
3. Results
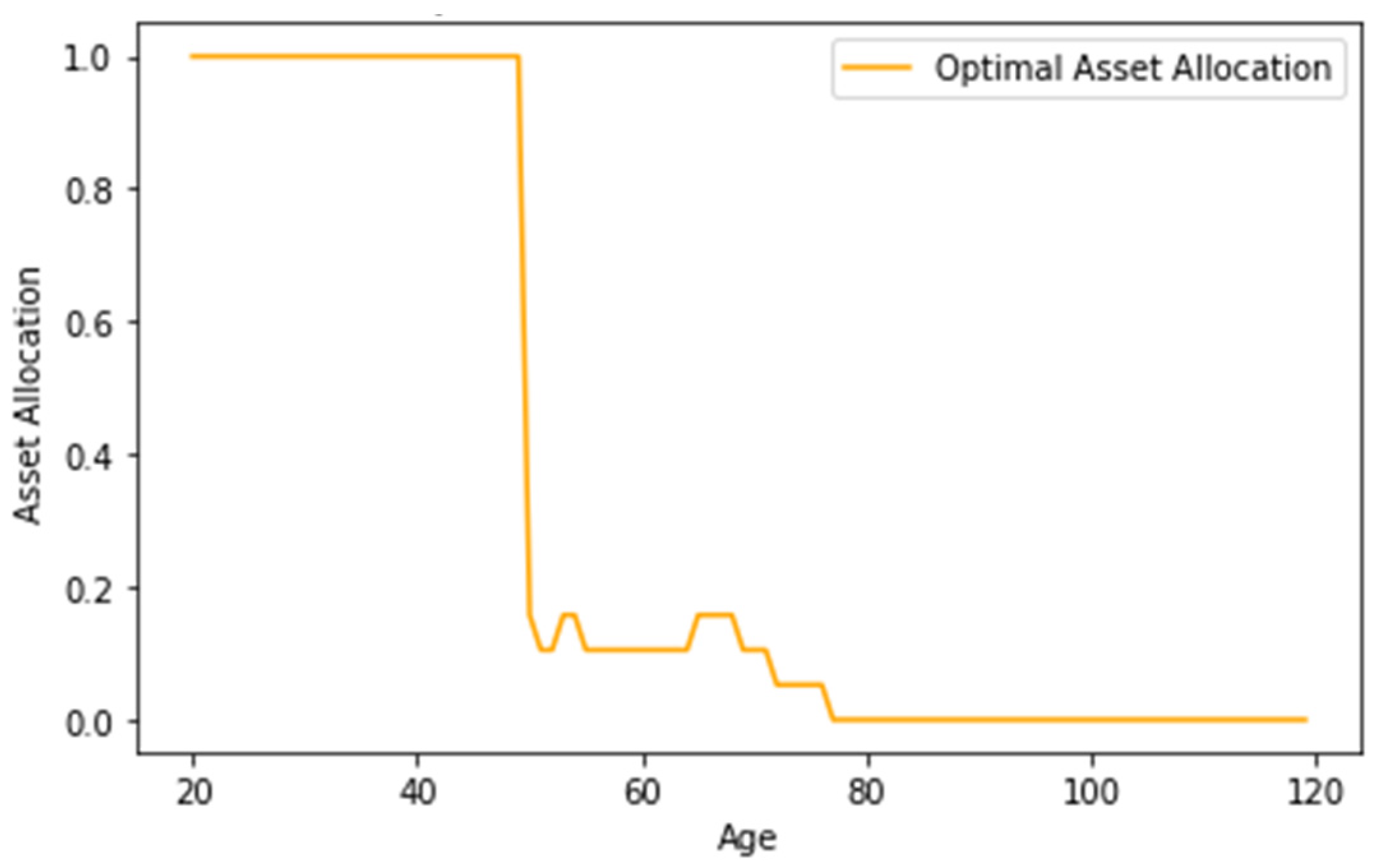
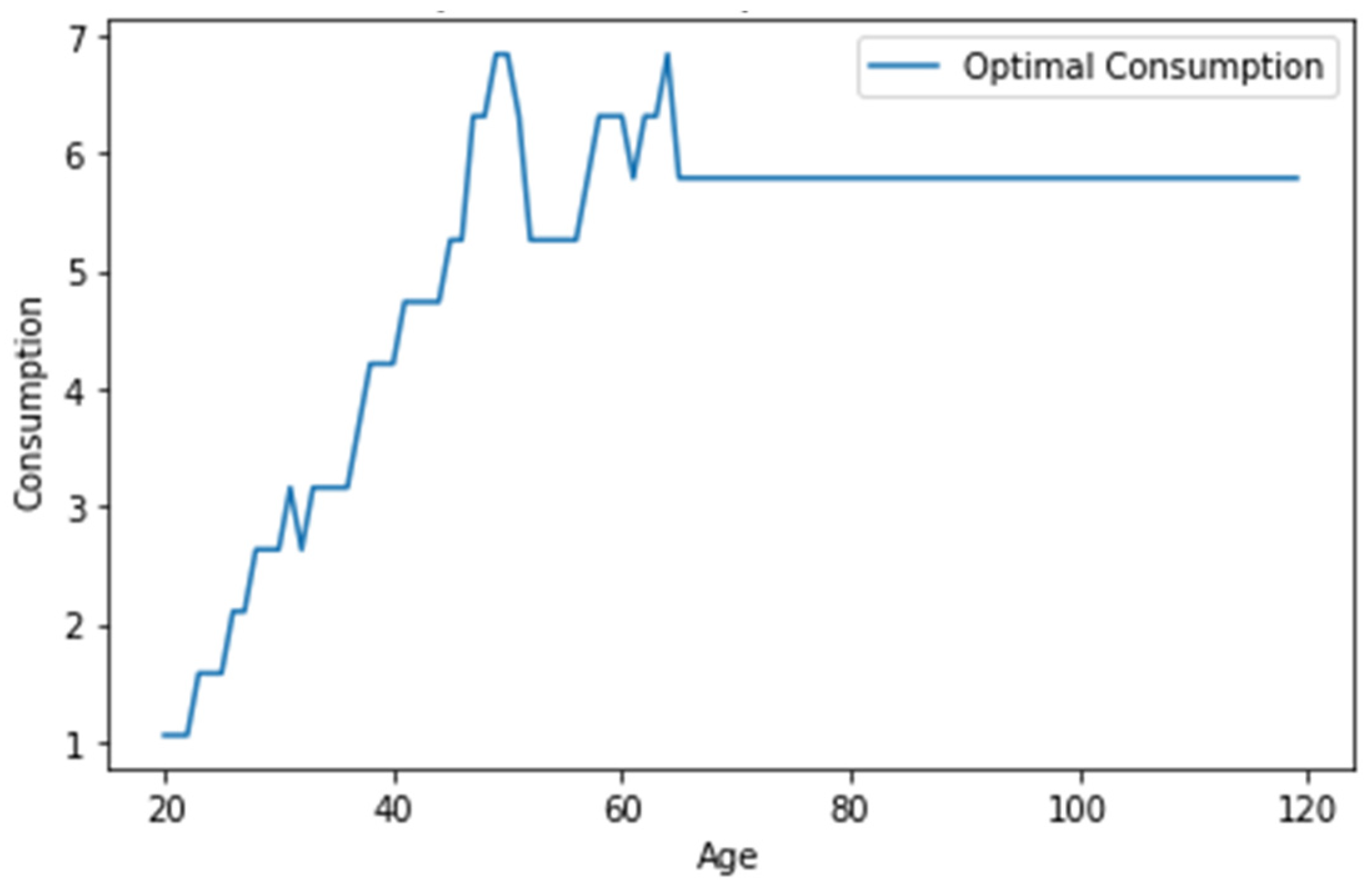
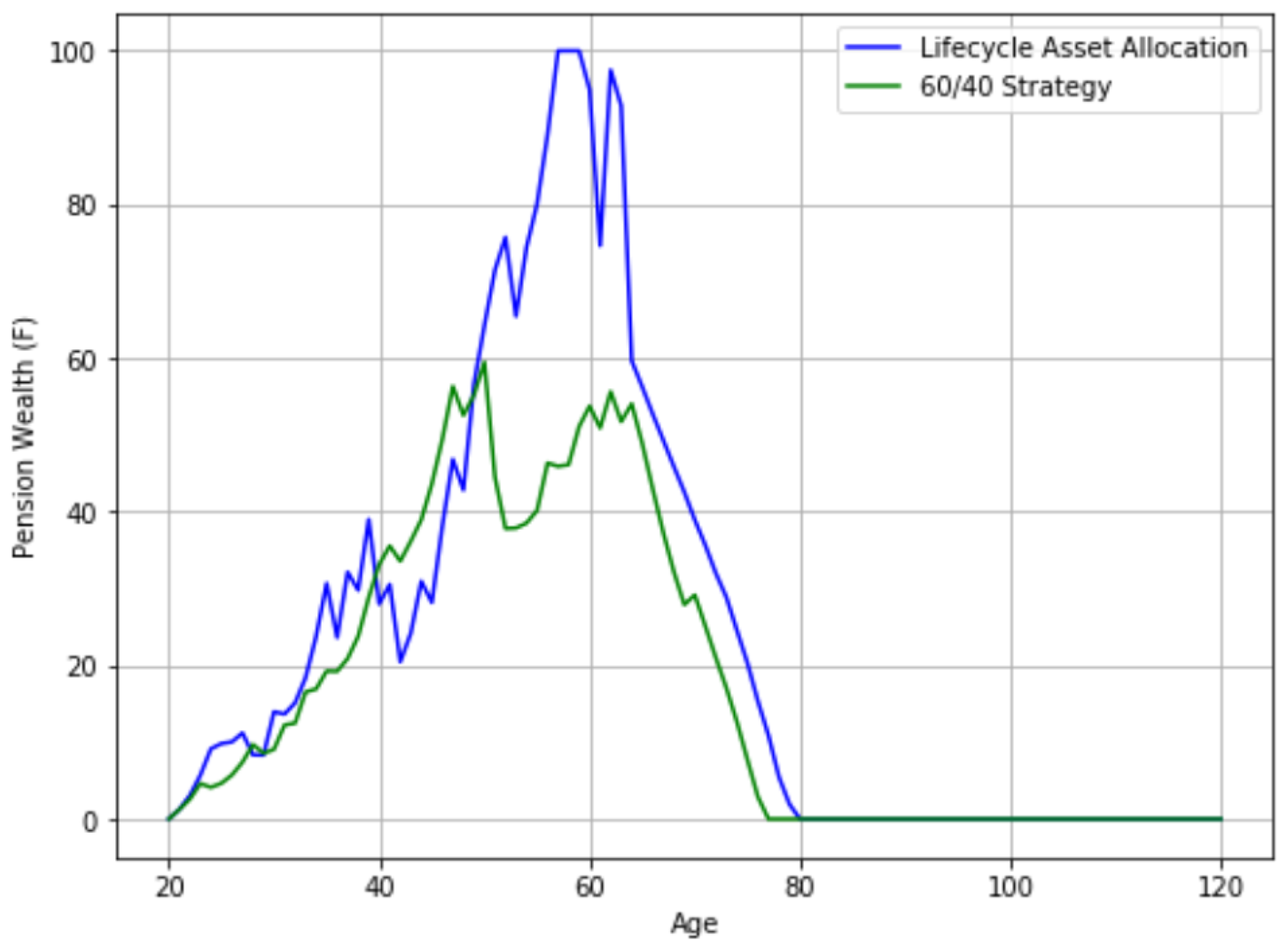
3.1. Glide Path
3.2. Parallel Monte Carlo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, X.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Z. A Survey of Models and Algorithms of Numerical Methods Based on Pension Target Funds. Front. Data Comput. 2023, 5, 85–96. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz, H. Portfolio selection. J. Financ. 1952, 7, 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Modigliani, F. The life cycle hypothesis of saving, the demand for wealth and the supply of capital. Soc. Res. 1966, 33, 160–217. [Google Scholar]
- Merton, R.C. Lifetime portfolio selection under uncertainty: The continuous-time case. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1969, 51, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodie, Z.; Merton, R.C.; Samuelson, W.F. Labor supply flexibility and portfolio choice in a life cycle model. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 1992, 16, 427–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocco, J.F.; Gomes, F.J.; Maenhout, P.J. Consumption and portfolio choice over the life cycle. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2005, 18, 491–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.Y.; Feldstein, M. Risk Aspects of Investment-Based Social Security Reform; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, F.; Michaelides, A. Life-cycle asset allocation: A model with borrowing constraints, uninsurable labor income risk and stock-market participation costs. Uninsurable Labor Income Risk Stock. Mark. Particip. Costs 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.; Michaelides, A. Optimal life-cycle asset allocation: Understanding the empirical evidence. J. Financ. 2005, 60, 869–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, D.; Wright, D.; Zhang, Y. Age-dependent investing: Optimal funding and investment strategies in defined contribution pension plans when members are rational life cycle financial planners. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 2014, 38, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z. Variants of Bellman equation on reinforcement learning problems. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Automation, and High-Performance Computing (AIAHPC 2022), Zhuhai, China, 25–27 February 2022; Volume 12348, pp. 104–111. [Google Scholar]
- Rantzer, A. Explicit solution to Bellman equation for positive systems with linear cost. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 61st Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Cancun, Mexico, 6–9 December 2022; pp. 2678–2683. [Google Scholar]
- Cosso, A.; Gozzi, F.; Kharroubi, I.; Pham, H.; Rosestolato, M. Master Bellman equation in the Wasserstein space: Uniqueness of viscosity solutions. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 2024, 377, 31–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstenberg, J.; Neininger, R.; Spiegel, D. On solutions of the distributional Bellman equation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.00081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeta, Y. A continuous-time utility maximization problem with borrowing constraints in macroeconomic heterogeneous agent models: A case of regular controls under Markov chain uncertainty. Available SSRN 2023, 4510320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z. Exponential Bellman equation and improved regret bounds for risk-sensitive reinforcement learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 20436–20446. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xie, Q. Risk-sensitive reinforcement learning: Near-optimal risk-sample tradeoff in regret. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 22384–22395. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z. Risk-sensitive reinforcement learning with function approximation: A debiasing approach. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Online, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 3198–3207. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, M.; Peet, M.M. A generalization of Bellman’s equation with application to path planning, obstacle avoidance and invariant set estimation. Automatica 2021, 127, 109510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, C.; Jentzen, A.; Kleinberg, K.; Kruse, T. Nonlinear Monte Carlo methods with polynomial runtime for Bellman equations of discrete time high-dimensional stochastic optimal control problems. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.03390. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, C.; Jentzen, A.; Kruse, T. Nonlinear Monte Carlo methods with polynomial runtime for high-dimensional iterated nested expectations. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.13989. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, S.; Cheridito, P.; Jentzen, A.; Welti, T. Solving high-dimensional optimal stopping problems using deep learning. Eur. J. Appl. Math. 2021, 32, 470–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonon, L. Deep neural network expressivity for optimal stopping problems. Financ. Stoch. 2024, 28, 865–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, C.; Mu, C. An overview on algorithms and applications of deep reinforcement learning. Chin. J. Intell. Sci. Technol. 2020, 2, 314–326. [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen, D.; Mogensen, P.K.; Moon, J.M.; Schjerning, B. Solving dynamic discrete choice models using smoothing and sieve methods. J. Econom. 2021, 223, 328–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, D.; Veness, J. Monte-Carlo planning in large POMDPs. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6-9 December 2010; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- Fatica, M.; Phillips, E. Pricing American options with least squares Monte Carlo on GPUs. In Proceedings of the 6th Workshop on High Performance Computational Finance, New York, NY, USA, 18 November 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas-Turki, L.A.; Vialle, S.; Lapeyre, B.; Mercier, P. Pricing derivatives on graphics processing units using Monte Carlo simulation. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2014, 26, 1679–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Zhang, K.; Xie, Q.; Basar, T. Poly-hoot: Monte-carlo planning in continuous space mdps with non-asymptotic analysis. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 4549–4559. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, J.; Lin, M.; Huang, S.; Liu, B.; Makoviichuk, D.; Makoviychuk, V.; Liu, Z.; Song, Y.; Luo, T.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Envpool: A highly parallel reinforcement learning environment execution engine. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 22409–22421. [Google Scholar]
- Cairns, A.J.; Blake, D.; Dowd, K. Stochastic lifestyling: Optimal dynamic asset allocation for defined contribution pension plans. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 2006, 30, 843–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| 0.04 | |
| 0.2 | |
| 5.0 | |
| 0.2 | |
| 0.96 | |
| 20 | |
| 65 | |
| T | 120 |
| 0.99 |
| Server | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Nodes | AMD EPYC 7773X 64-Core Processor |
| Operating | Centos7.6 |
| MPI | hpcx-2.4.1 |
| Network | HDR Infiniband (200 Gb) |
| Thread Number | Computing Time (min) | |
|---|---|---|
| Value Iteration Method | 1 | 41.15 |
| Our Method (Proposed) | 1 | 29.88 |
| 2 | 15.74 | |
| 4 | 8.06 | |
| 8 | 4.17 | |
| 16 | 2.69 | |
| 32 | 1.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Lu, Z. A Parallel Monte Carlo Algorithm for the Life Cycle Asset Allocation Problem. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10372. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210372
Yang X, Li C, Li X, Lu Z. A Parallel Monte Carlo Algorithm for the Life Cycle Asset Allocation Problem. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(22):10372. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210372
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xueying, Chen Li, Xu Li, and Zhonghua Lu. 2024. "A Parallel Monte Carlo Algorithm for the Life Cycle Asset Allocation Problem" Applied Sciences 14, no. 22: 10372. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210372
APA StyleYang, X., Li, C., Li, X., & Lu, Z. (2024). A Parallel Monte Carlo Algorithm for the Life Cycle Asset Allocation Problem. Applied Sciences, 14(22), 10372. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210372






