Novel Drug Combinations in Lung Cancer: New Potential Synergies Between 5-FU and Repurposed Drugs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. In Vitro Drug Treatment
2.4. Cell Viability Assay
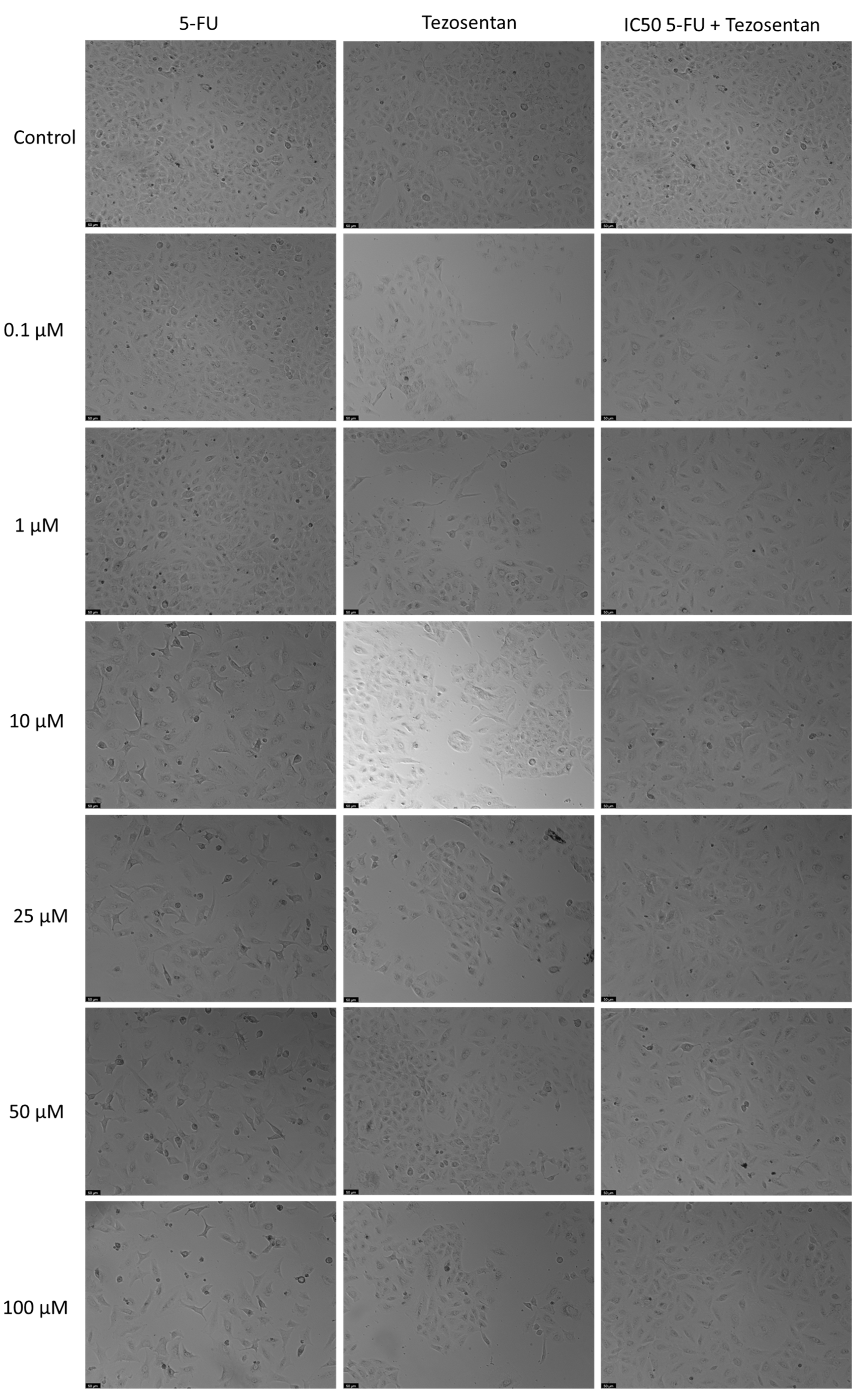
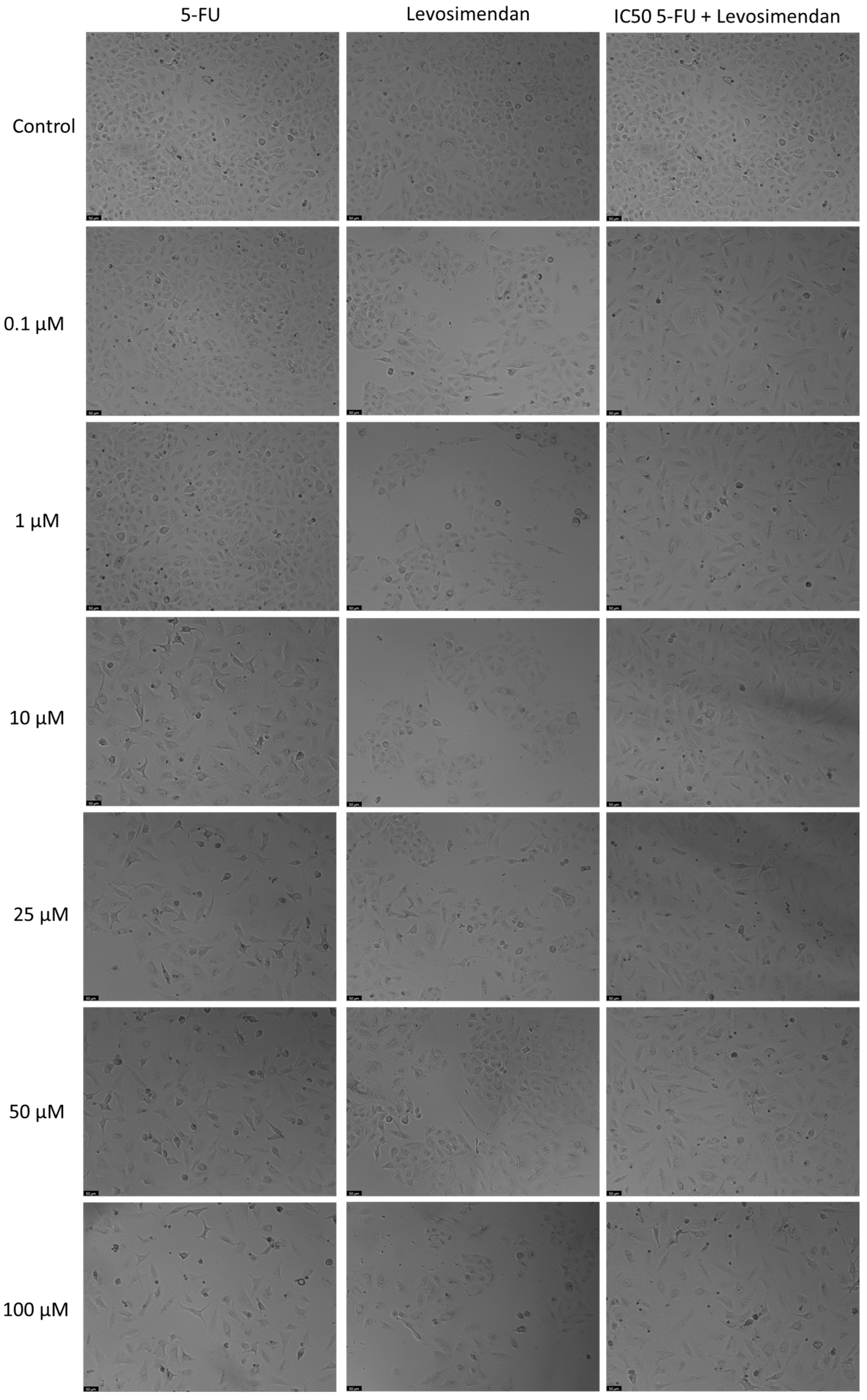
2.5. Microscopic Observation
2.6. Wound Healing Assay
2.7. Clonogenic Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
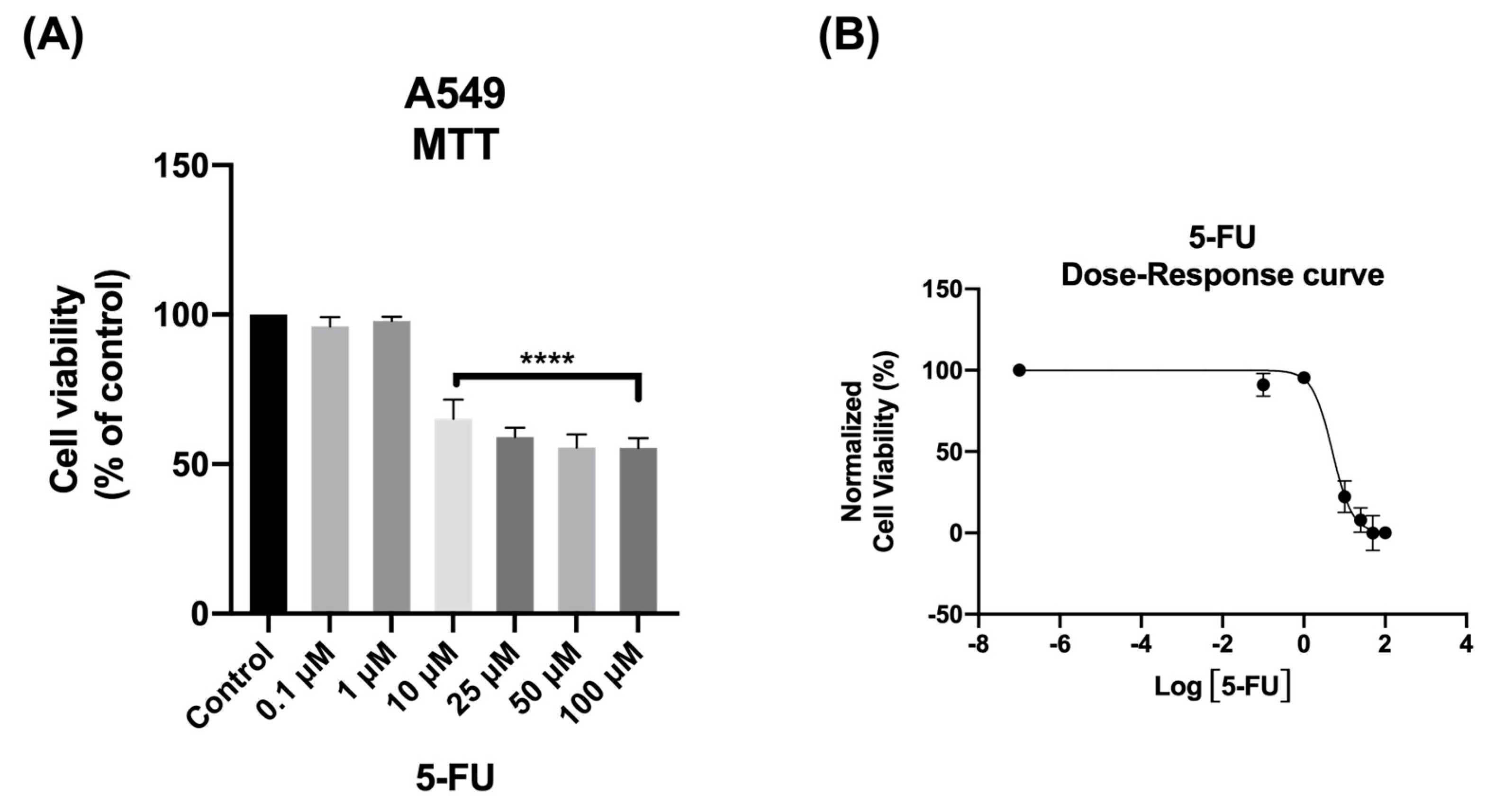
3.1. The Effect of 5-FU as Single Agent on A549 Cellular Viability
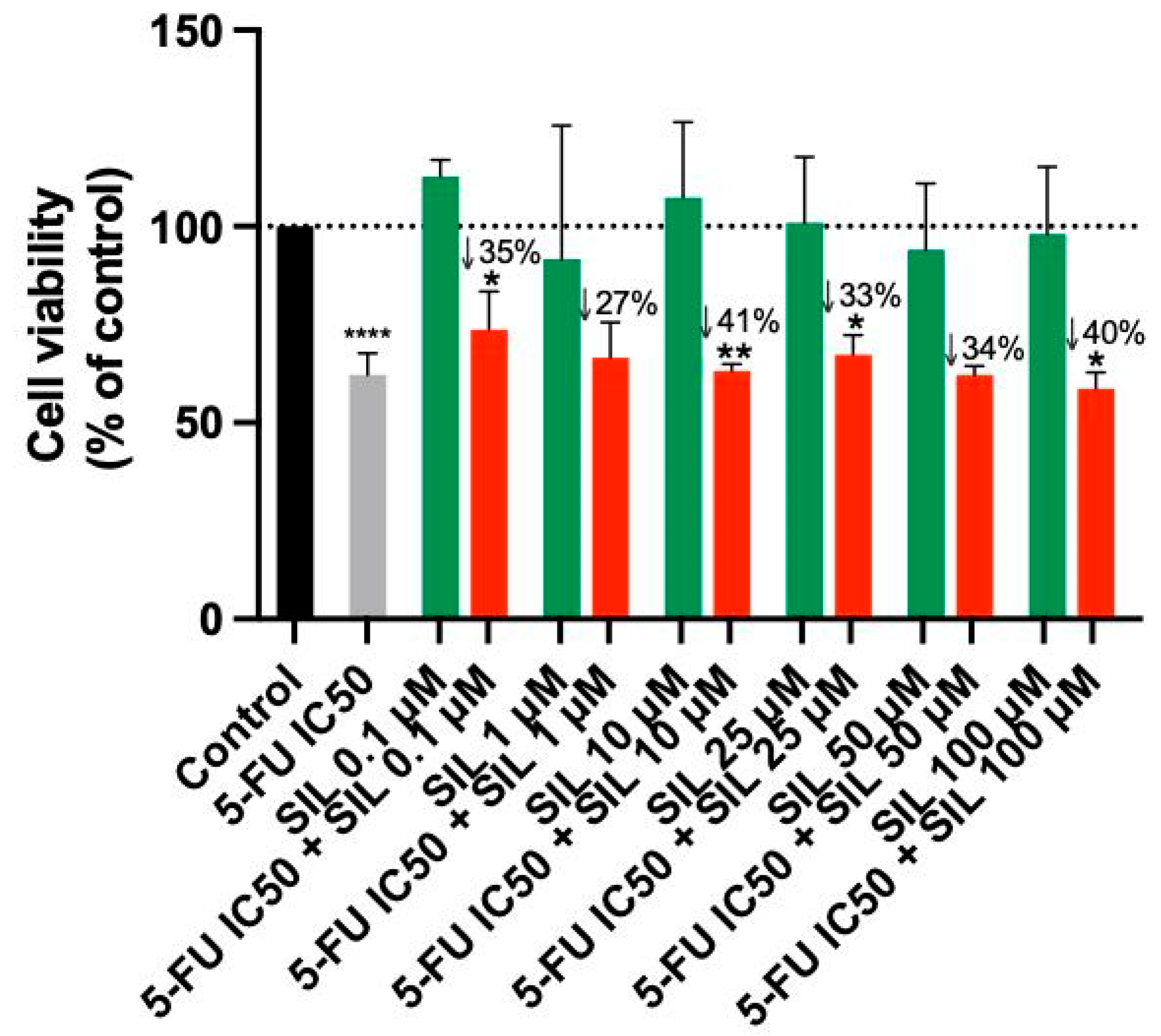
3.2. The Effect of Sildenafil as a Single Agent and in Various Combinations with 5-FU
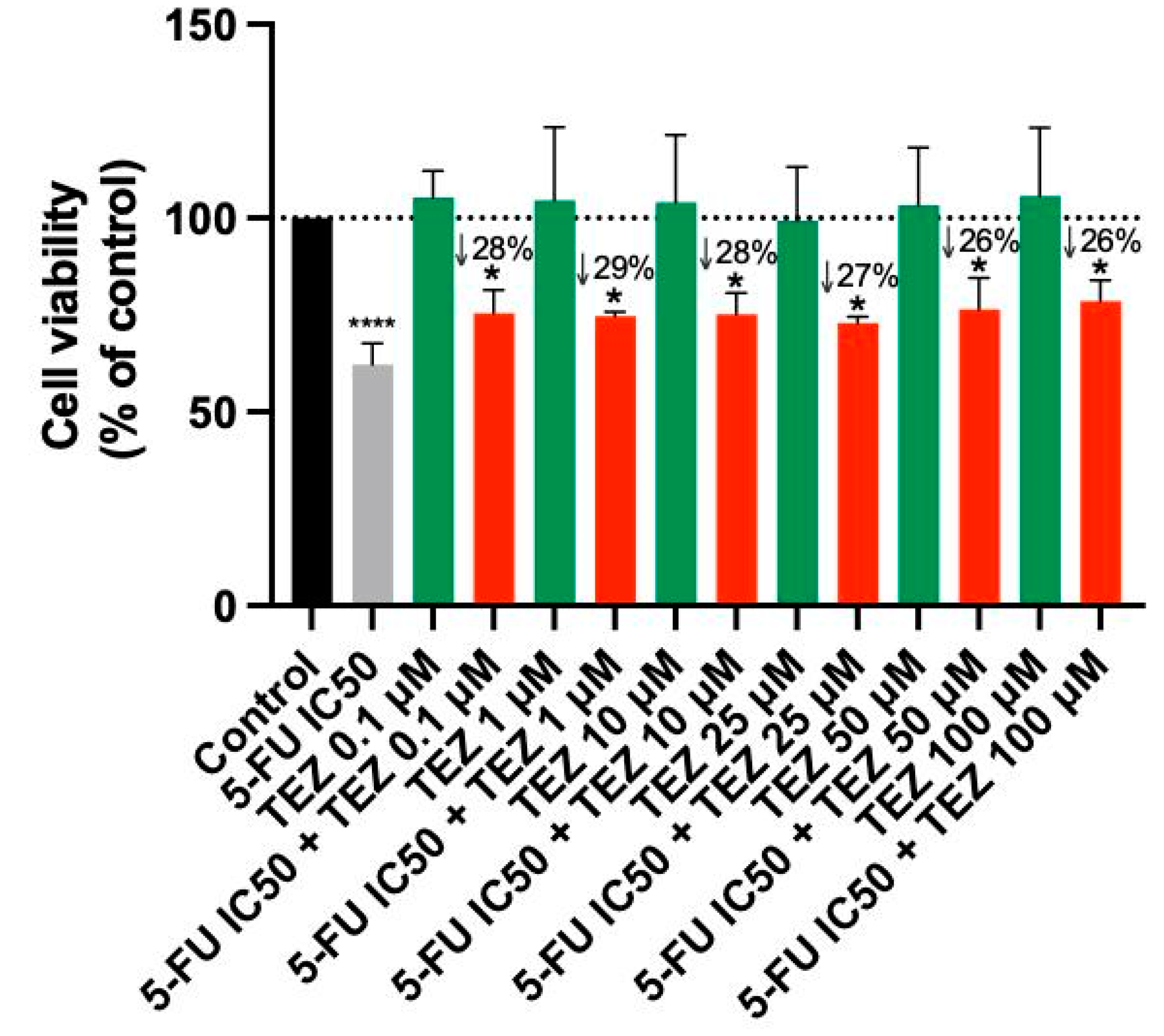
3.3. The Effect of Tezosentan as a Single Agent and in Various Combinations with 5-FU
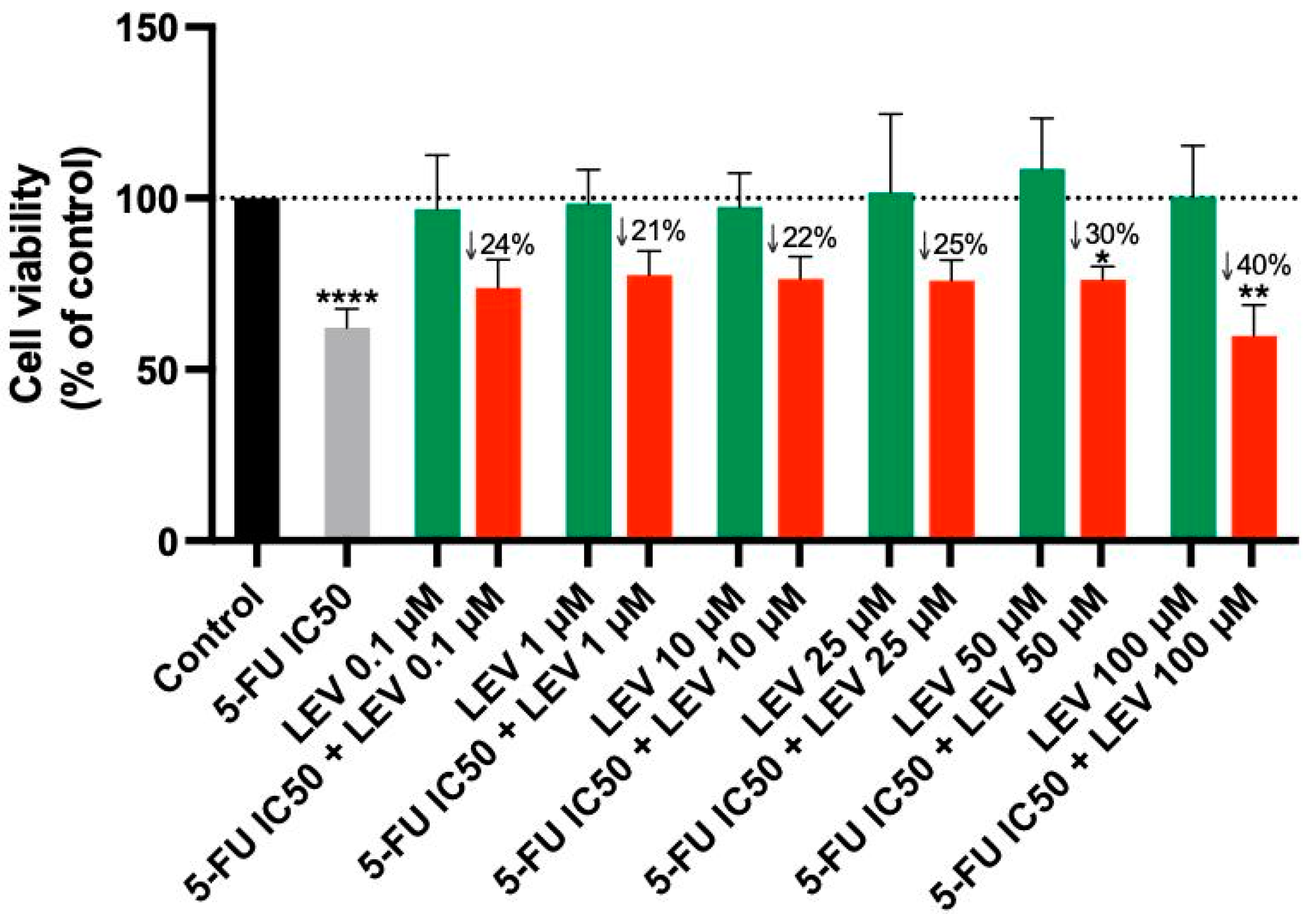
3.4. The Effect of Levosimendan as a Single Agent and in Various Combinations with 5-FU
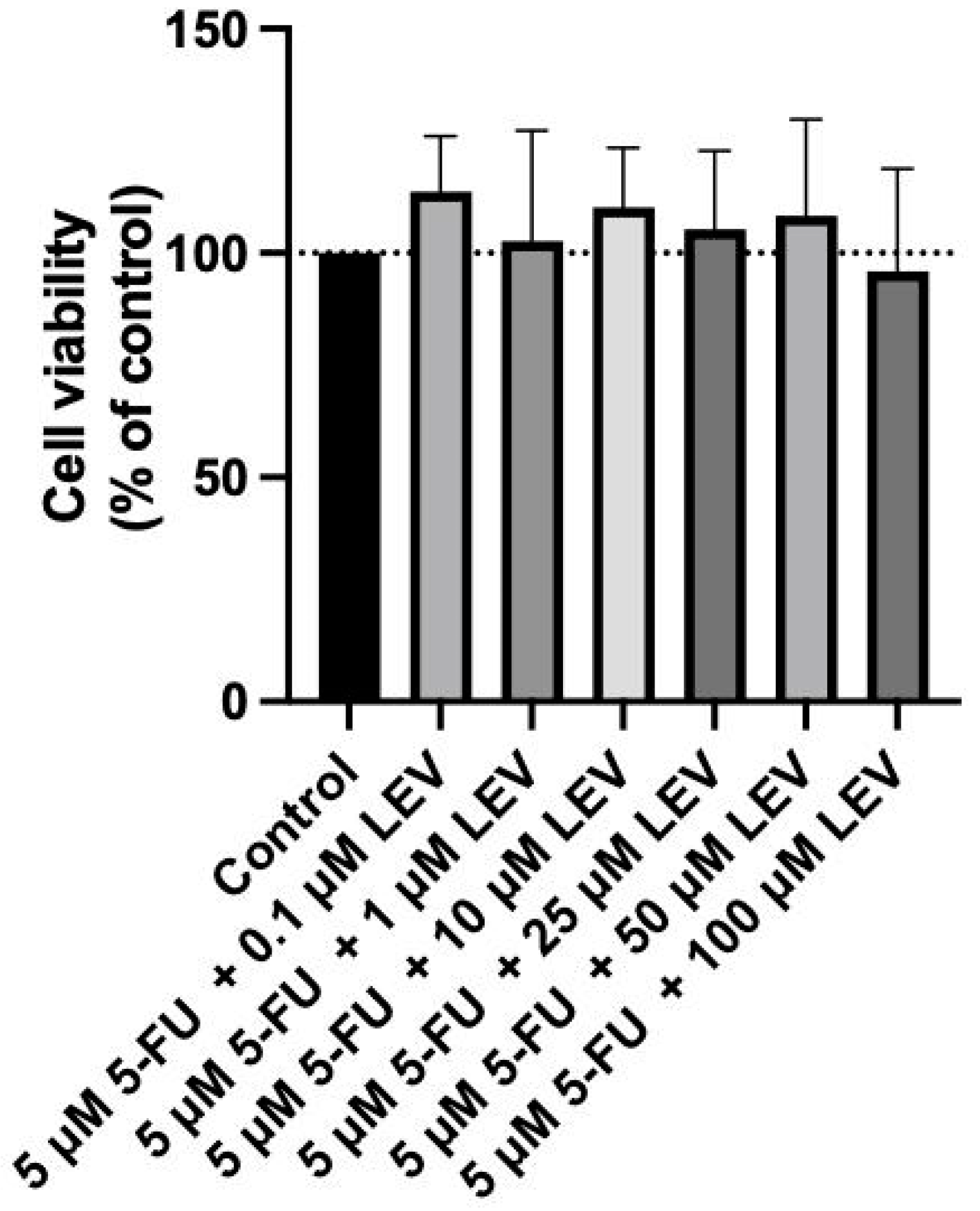
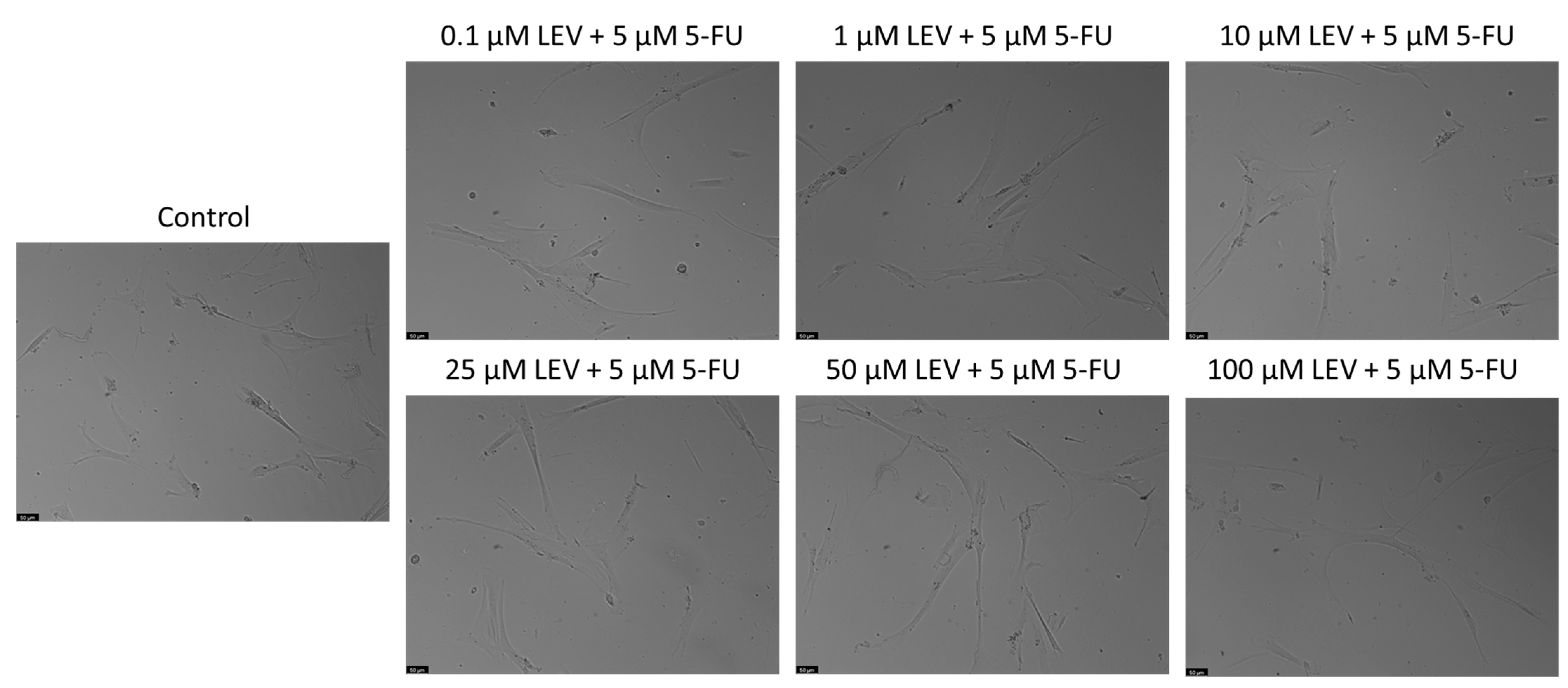
3.5. Safety Assessment of 5-FU and Levosimendan and Their Combination in Non-Cancerous MRC-5 Cells
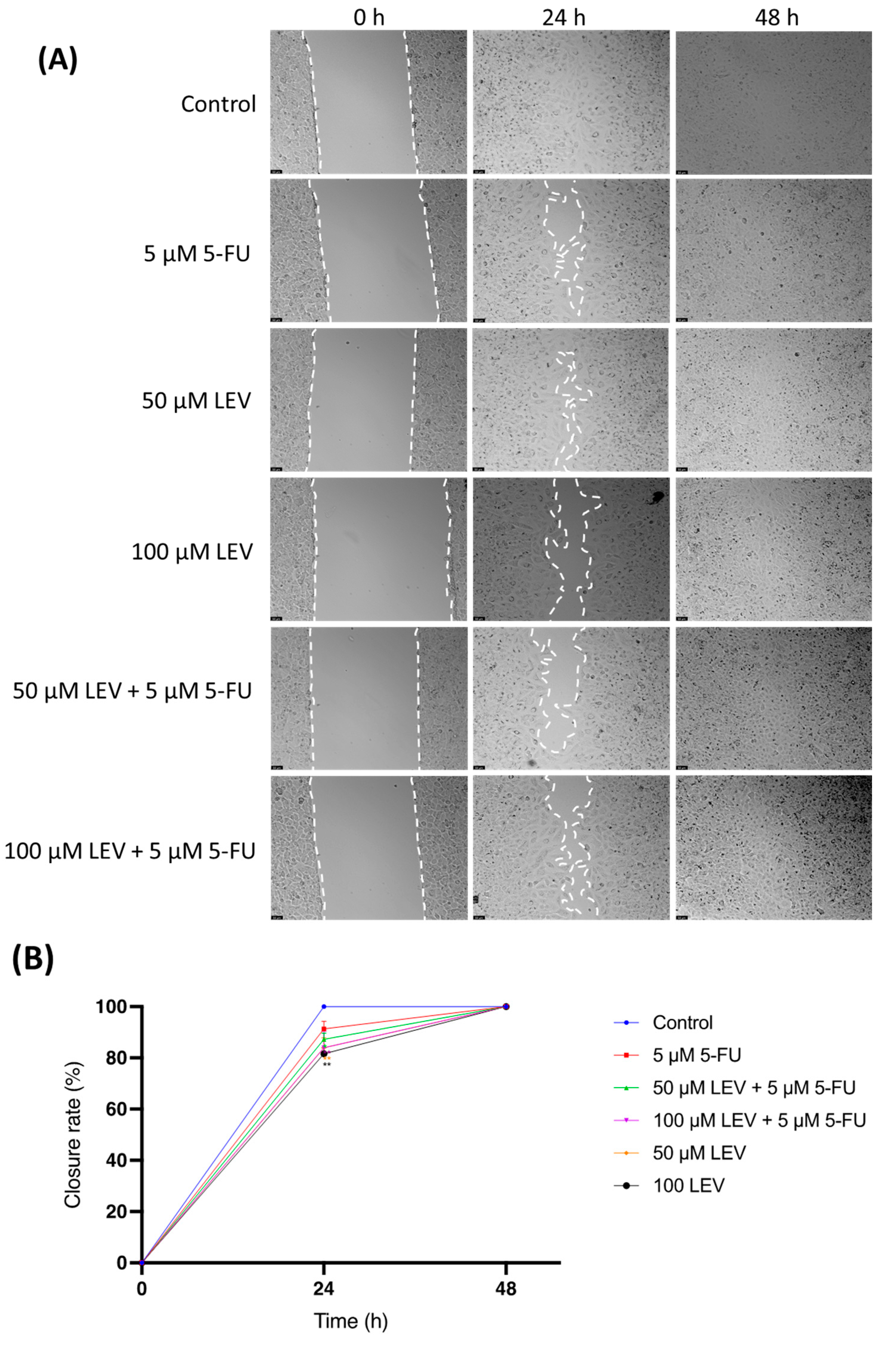
3.6. Transient Inhibition of Lung Cancer Cell Migration by 5-FU and Levosimendan Combination
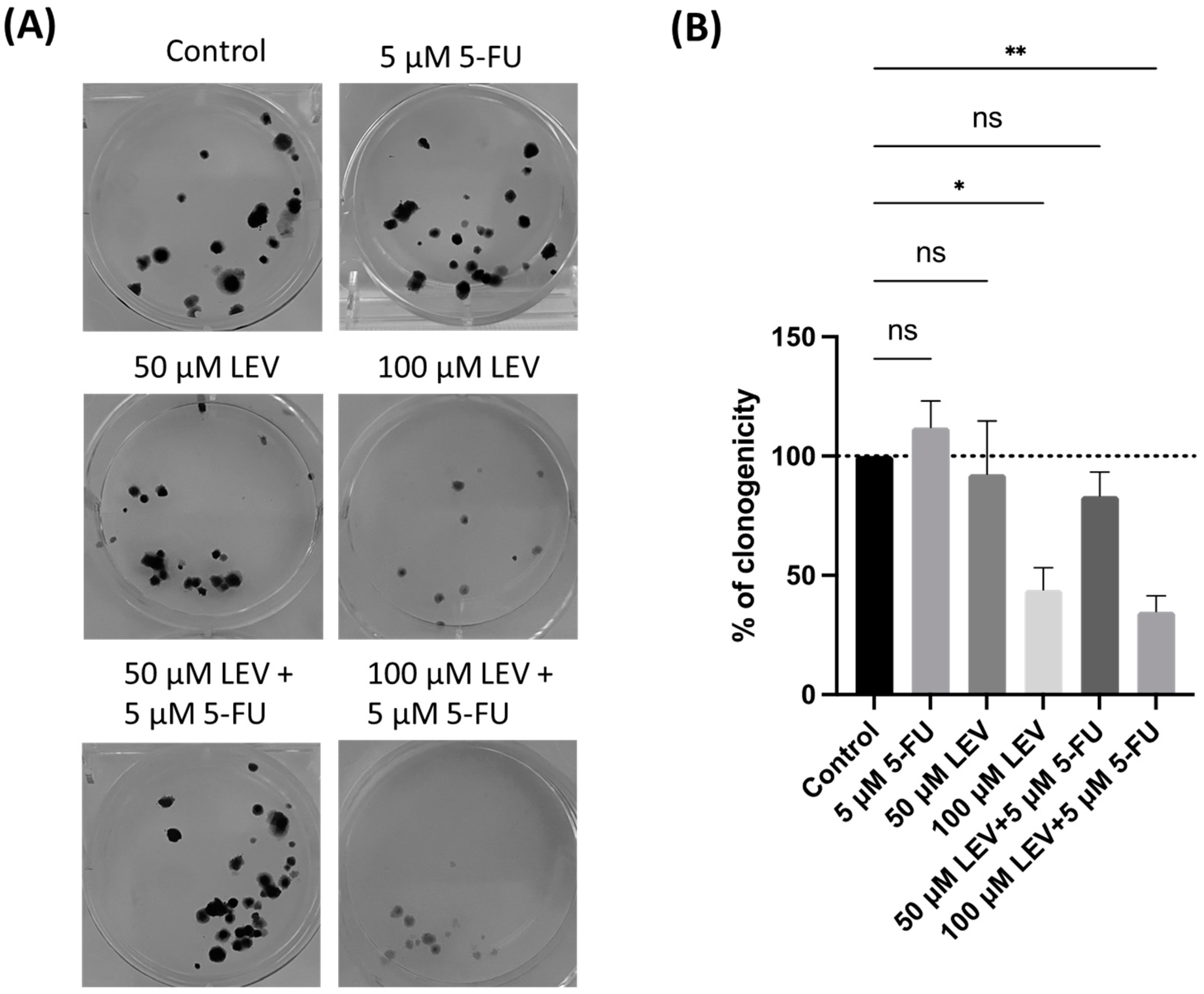
3.7. Levosimendan Enhances the Clonogenic Inhibition of 5-FU in Lung Cancer Cells
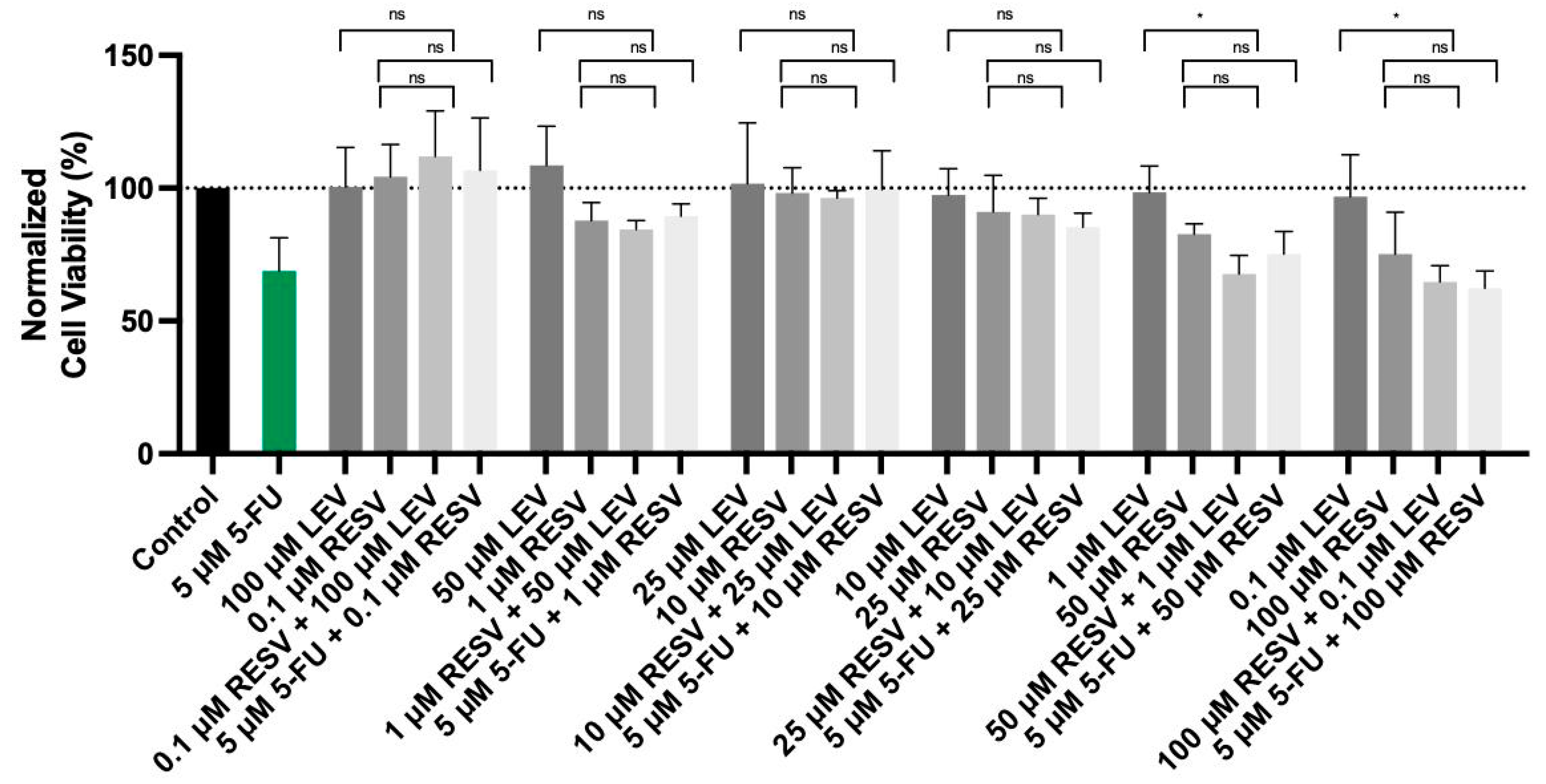
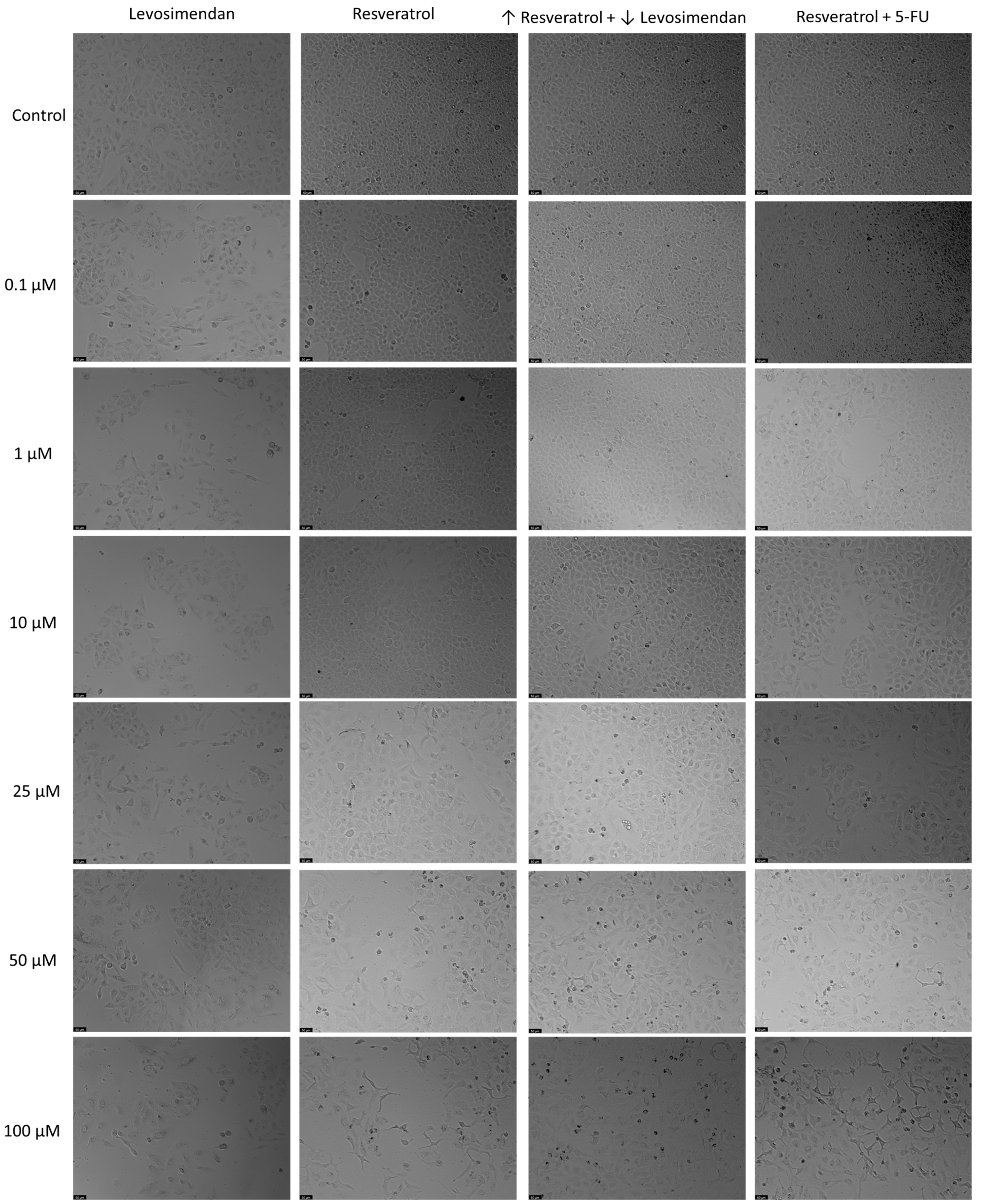
3.8. Impact of Resveratrol on the Cytotoxicity of Levosimendan and 5-FU in Lung Cancer Cells
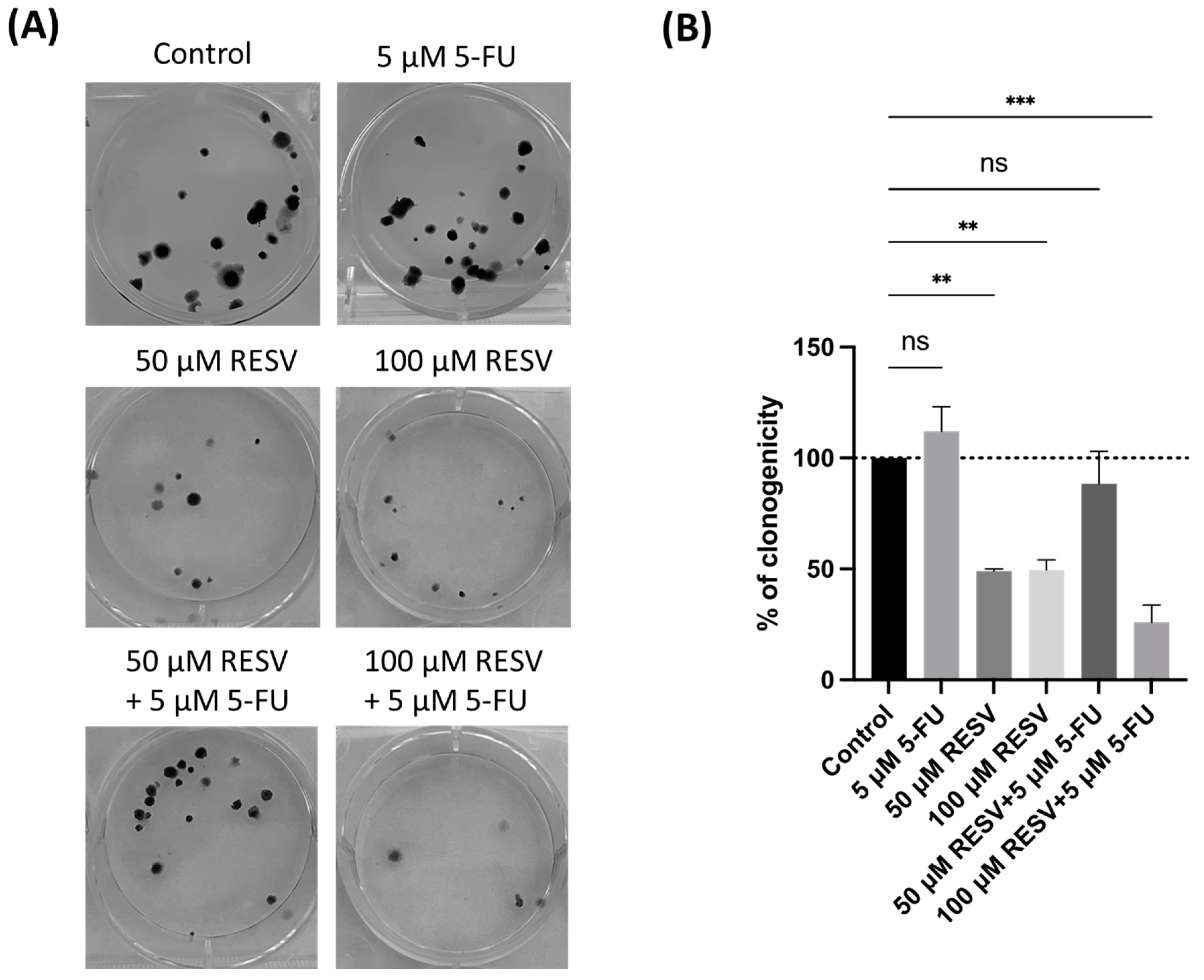
3.9. Synergistic Inhibition of Colony Formation by Resveratrol and 5-FU in A549 Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Obradović, J.; Djordjević, N.; Tošic, N.; Mrdjanović, J.; Stanković, B.; Stanić, J.; Zarić, B.; Perin, B.; Pavlović, S.; Jurišić, V. Frequencies of EGFR single nucleotide polymorphisms in non-small cell lung cancer patients and healthy individuals in the Republic of Serbia: A preliminary study. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 10479–10486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suda, K.; Tomizawa, K.; Mitsudomi, T. Biological and clinical significance of KRAS mutations in lung cancer: An oncogenic driver that contrasts with EGFR mutation. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010, 29, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soh, J.; Toyooka, S.; Matsuo, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Wistuba, I.I.; Lam, S.; Fong, K.M.; Gazdar, A.F.; Miyoshi, S. Ethnicity affects EGFR and KRAS gene alterations of lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 1775–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Shao, Y.; Qin, H.F.; Tai, Y.H.; Gao, H.J. ALK-rearrangement in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbour, K.C.; Riely, G.J. Diagnosis and Treatment of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 31, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendarme, S.; Bylicki, O.; Chouaid, C.; Guisier, F. ROS-1 Fusions in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Evidence to Date. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muminovic, M.; Carracedo Uribe, C.R.; Alvarez-Pinzon, A.; Shan, K.; Raez, L.E. Importance of ROS1 gene fusions in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Drug Resist. 2023, 6, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, C.G.; Andelkovic, V.; Ladwa, R.; Pavlakis, N.; Zhou, C.; Hirsch, F.; Richard, D.; O’Byrne, K. Targeting BRAF mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Guo, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, S.; Li, X. BRAF-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Treatment Status and Future Perspective. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 863043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogi, A.; Kuwano, H. TP53 mutations in nonsmall cell lung cancer. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 583929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, L.G.; Haines, C.; Perkel, R.; Enck, R.E. Lung cancer: Diagnosis and management. Am. Fam. Physician 2007, 75, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dela Cruz, C.S.; Tanoue, L.T.; Matthay, R.A. Lung cancer: Epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin. Chest Med. 2011, 32, 605–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howington, J.A.; Blum, M.G.; Chang, A.C.; Balekian, A.A.; Murthy, S.C. Treatment of stage I and II non-small cell lung cancer: Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2013, 143, e278S–e313S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinod, S.K.; Hau, E. Radiotherapy treatment for lung cancer: Current status and future directions. Respirology 2020, 25 (Suppl. 2), 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasaka, M.; Gadgeel, S.M. Role of chemotherapy and targeted therapy in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2018, 18, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, P.; Singhal, S.; Kulkarni, P.; Horne, D.; Malhotra, J.; Salgia, R.; Singhal, S.S. Advances in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Insights and Future Directions. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Remon, J.; Hellmann, M.D. First-Line Immunotherapy for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lin, X.; Wang, R.; Wang, F.; Xie, S.; Tse, L.A. Hormone therapy and lung cancer mortality in women: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Steroids 2017, 118, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyszczyk, P.; Acevedo, A.; Davidoff, E.J.; Timmins, L.M.; Marrero-Berrios, I.; Patel, M.; White, C.; Lowe, C.; Sherba, J.J.; Hartmanshenn, C.; et al. The growing role of precision and personalized medicine for cancer treatment. Technol. Singap World Sci. 2018, 6, 79–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Abak, A.; Tondro Anamag, F.; Shoorei, H.; Fattahi, F.; Javadinia, S.A.; Basiri, A.; Taheri, M. 5-Fluorouracil: A Narrative Review on the Role of Regulatory Mechanisms in Driving Resistance to This Chemotherapeutic Agent. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 658636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, S.H.; Moon, S.M.; Shin, U.S.; Yang, H.M.; Hwang, D.Y. Effectiveness of Adjuvant Chemotherapy with 5-FU/Leucovorin and Prognosis in Stage II Colon Cancer. J. Korean Soc. Coloproctol. 2011, 27, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magné, N.; François, E.; Broisin, L.; Guardiola, E.; Ramaïoli, A.; Ferrero, J.M.; Namer, M. Palliative 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy for advanced colorectal cancer in the elderly: Results of a 10-year experience. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 25, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethy, C.; Kundu, C.N. 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) resistance and the new strategy to enhance the sensitivity against cancer: Implication of DNA repair inhibition. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azwar, S.; Seow, H.F.; Abdullah, M.; Faisal Jabar, M.; Mohtarrudin, N. Recent Updates on Mechanisms of Resistance to 5-Fluorouracil and Reversal Strategies in Colon Cancer Treatment. Biology 2021, 10, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Goessl, E.; Jin, G.; Collie-Duguid, E.S.; Cassidy, J.; Wang, W.; O’Brien, V. Cell cycle perturbation and acquired 5-fluorouracil chemoresistance. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, M.B.; Lincz, L.F.; Adler, K.; Scorgie, F.E.; Ackland, S.P.; Sakoff, J.A. Predicting 5-fluorouracil toxicity in colorectal cancer patients from peripheral blood cell telomere length: A multivariate analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-W.; Liu, C.-Y.; Lee, H.-C.; Huang, Y.-H.; Li, L.-H.; Chiau, J.-S.C.; Wang, T.-E.; Chu, C.-H.; Shih, S.-C.; Tsai, T.-H. Lactobacillus casei variety rhamnosus probiotic preventively attenuates 5-fluorouracil/oxaliplatin-induced intestinal injury in a syngeneic colorectal cancer model. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, N.; Najam, R.; Qazi, F.; Mateen, A. Gastrointestinal adverse effects in advanced colorectal carcinoma patients treated with different schedules of FOLFOX. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 8089–8093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsusaka, S.; Lenz, H.-J. Pharmacogenomics of fluorouracil-based chemotherapy toxicity. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2015, 11, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sara, J.D.; Kaur, J.; Khodadadi, R.; Rehman, M.; Lobo, R.; Chakrabarti, S.; Herrmann, J.; Lerman, A.; Grothey, A. 5-fluorouracil and cardiotoxicity: A review. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10, 1758835918780140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-J.; Lei, Q.; Zhang, A.-Q.; Zhang, X.-Z. Combinational strategy for high-performance cancer chemotherapy. Biomaterials 2018, 171, 178–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilad, Y.; Gellerman, G.; Lonard, D.M.; O’Malley, B.W. Drug Combination in Cancer Treatment—From Cocktails to Conjugated Combinations. Cancers 2021, 13, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, G.R.; Lehár, J.; Keith, C.T. Multi-target therapeutics: When the whole is greater than the sum of the parts. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallarida, R.J. Quantitative methods for assessing drug synergism. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalofonos, H.P.; Aravantinos, G.; Kosmidis, P.; Papakostas, P.; Economopoulos, T.; Dimopoulos, M.; Skarlos, D.; Bamias, A.; Pectasides, D.; Chalkidou, S.; et al. Irinotecan or oxaliplatin combined with leucovorin and 5-fluorouracil as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer: A multicenter, randomized, phase II study. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutabian, H.; Majdaeen, M.; Ghahramani-Asl, R.; Yadollahi, M.; Gharepapagh, E.; Ataei, G.; Falahatpour, Z.; Bagheri, H.; Farhood, B. A systematic review of the therapeutic effects of resveratrol in combination with 5-fluorouracil during colorectal cancer treatment: With a special focus on the oxidant, apoptotic, and anti-inflammatory activities. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.A.; Lie, J.D. Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) Inhibitors In the Management of Erectile Dysfunction. Pharm. Ther. 2013, 38, 407–419. [Google Scholar]
- Mauro, N.; Cillari, R.; Andrea Utzeri, M.; Costa, S.; Giammona, G.; Nicosia, A.; Cavallaro, G. Controlled delivery of sildenafil by β-Cyclodextrin-decorated sulfur-doped carbon nanodots: A synergistic activation of ROS signaling in tumors overexpressing PDE-5. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 645, 123409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, E.; Vale, N. Repurposing of the Drug Tezosentan for Cancer Therapy. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 5118–5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, E.; Vale, N. Understanding the Clinical Use of Levosimendan and Perspectives on its Future in Oncology. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, E.; Costa, B.; Marques, L.; Vasques-Nóvoa, F.; Vale, N. Enhancing Urological Cancer Treatment: Leveraging Vasodilator Synergistic Potential with 5-FU for Improved Therapeutic Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Enríquez, S.; Pacheco-Velázquez, S.C.; Marín-Hernández, Á.; Gallardo-Pérez, J.C.; Robledo-Cadena, D.X.; Hernández-Reséndiz, I.; García-García, J.D.; Belmont-Díaz, J.; López-Marure, R.; Hernández-Esquivel, L.; et al. Resveratrol inhibits cancer cell proliferation by impairing oxidative phosphorylation and inducing oxidative stress. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 370, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockmueller, A.; Buhrmann, C.; Shayan, P.; Shakibaei, M. Resveratrol induces apoptosis by modulating the reciprocal crosstalk between p53 and Sirt-1 in the CRC tumor microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1225530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, L.; Cui, J.; Huoc, Z.; Xue, J.; Cui, H.; Mao, Q.; Yang, R. Resveratrol inhibits NF-kB signaling through suppression of p65 and IkappaB kinase activities. Pharmazie 2013, 68, 689–694. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Shang, X.; Wu, H.; Gautam, S.C.; Al-Holou, S.; Li, C.; Kuo, J.; Zhang, L.; Chopp, M. Resveratrol downregulates PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in human U251 glioma cells. J. Exp. Ther. Oncol. 2009, 8, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, D.; Guerreiro, I.; Vale, N. Novel Strategies for Cancer Combat: Drug Combination Using Repurposed Drugs Induces Synergistic Growth Inhibition of MCF-7 Breast and HT-29 Colon Cancer Cells. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 4930–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, D.; Vale, N. Combining repurposed drugs to treat colorectal cancer. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, D.; Nunes, M.; Ricardo, S.; Vale, N. Combination of Antimalarial and CNS Drugs with Antineoplastic Agents in MCF-7 Breast and HT-29 Colon Cancer Cells: Biosafety Evaluation and Mechanism of Action. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Yan, M.; Zhang, H. Autophagy inhibition promotes 5-fluorouraci-induced apoptosis by stimulating ROS formation in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Shi, M.; Yu, B.; Cheng, X.; Li, X.; Jia, X. Epigenetic Mechanism of Enrichment of A549 Lung Cancer Stem Cells with 5-Fu. Onco Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 3783–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Li, N.M.; Gao, P.; Yang, S.; Ning, Q.; Huang, W.; Li, Z.P.; Ye, P.J.; Xiang, L.; He, D.X.; et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of macromolecular prodrug GC-FUA based nanoparticle for hepatocellular carcinoma chemotherapy. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, G.R.; Yuen, J.G.; Fesler, A.; Farley, H.; Haley, J.D.; Ju, J. Development of a 5-FU modified miR-129 mimic as a therapeutic for non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2023, 28, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, M.B.; Le, X.; Heymach, J.V. β-Adrenergic Signaling in Lung Cancer: A Potential Role for Beta-Blockers. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020, 15, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xue, M.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, L.; Qian, W.; Duan, W.; Shen, X. Resveratrol inhibits the growth of tumor cells under chronic stress via the ADRB-2-HIF-1α axis. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Feng, W.; Ji, Y.; Jin, L. Resveratrol mediates cell cycle arrest and cell death in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by directly targeting the EGFR signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Hu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression affects proliferation and apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase/microRNA 200a signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 5201–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitelson, M.A.; Arzumanyan, A.; Kulathinal, R.J.; Blain, S.W.; Holcombe, R.F.; Mahajna, J.; Marino, M.; Martinez-Chantar, M.L.; Nawroth, R.; Sanchez-Garcia, I.; et al. Sustained proliferation in cancer: Mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35 (Suppl.), S25–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adan, A.; Kiraz, Y.; Baran, Y. Cell Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assays. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2016, 17, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.C.; Fiscus, R.R. Resveratrol at anti-angiogenesis/anticancer concentrations suppresses protein kinase G signaling and decreases IAPs expression in HUVECs. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Schelz, Z.; Muddather, H.F.; Jaski, F.S.; Bózsity, N.; Zupkó, I. An In Vitro Investigation of the Antiproliferative and Antimetastatic Effects of Levosimendan: Potential Drug Repurposing for Cervical Cancer. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 6566–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Peng, J.; Tang, H.; Wang, S.; Peng, S.; Ye, F.; Wang, J.; Ouyang, K.; Li, J.; et al. Inhibition of NF-κB signaling unveils novel strategies to overcome drug resistance in cancers. Drug Resist. Updates 2024, 73, 101042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Chen, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, C.; Song, Y.; Cao, Z.; Li, W.; Hu, J.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. PI3K/AKT pathway as a key link modulates the multidrug resistance of cancers. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Y.; Tsai, K.W.; Shee, J.J.; Li, Y.Z.; Chen, C.H.; Chuang, J.J.; Liu, Y.W. 4′-Chloro-3,5-dihydroxystilbene, a resveratrol derivative, induces lung cancer cell death. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2010, 31, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, J.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Luo, L.; Peng, Z.; Song, Z.; Zhu, R. Resveratrol induces cell cycle arrest via a p53-independent pathway in A549 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 2459–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Tang, H.; Zeng, X.; Ye, D.; Liu, J. Resveratrol inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion via Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in renal cell carcinoma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 98, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.K.; Chen, Q.; Fu, J.; Shankar, S.; Srivastava, R.K. Resveratrol inhibits growth of orthotopic pancreatic tumors through activation of FOXO transcription factors. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Drug | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|
| 5-FU | 5.03 |
| Sildenafil | 32.59 |
| Tezosentan | >100 |
| Levosimendan | 16.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribeiro, E.; Vale, N. Novel Drug Combinations in Lung Cancer: New Potential Synergies Between 5-FU and Repurposed Drugs. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9658. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219658
Ribeiro E, Vale N. Novel Drug Combinations in Lung Cancer: New Potential Synergies Between 5-FU and Repurposed Drugs. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(21):9658. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219658
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibeiro, Eduarda, and Nuno Vale. 2024. "Novel Drug Combinations in Lung Cancer: New Potential Synergies Between 5-FU and Repurposed Drugs" Applied Sciences 14, no. 21: 9658. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219658
APA StyleRibeiro, E., & Vale, N. (2024). Novel Drug Combinations in Lung Cancer: New Potential Synergies Between 5-FU and Repurposed Drugs. Applied Sciences, 14(21), 9658. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219658







