Exploring Non-Thermal Mechanisms of Biological Reactions to Extremely Low-Frequency Magnetic Field Exposure
Abstract
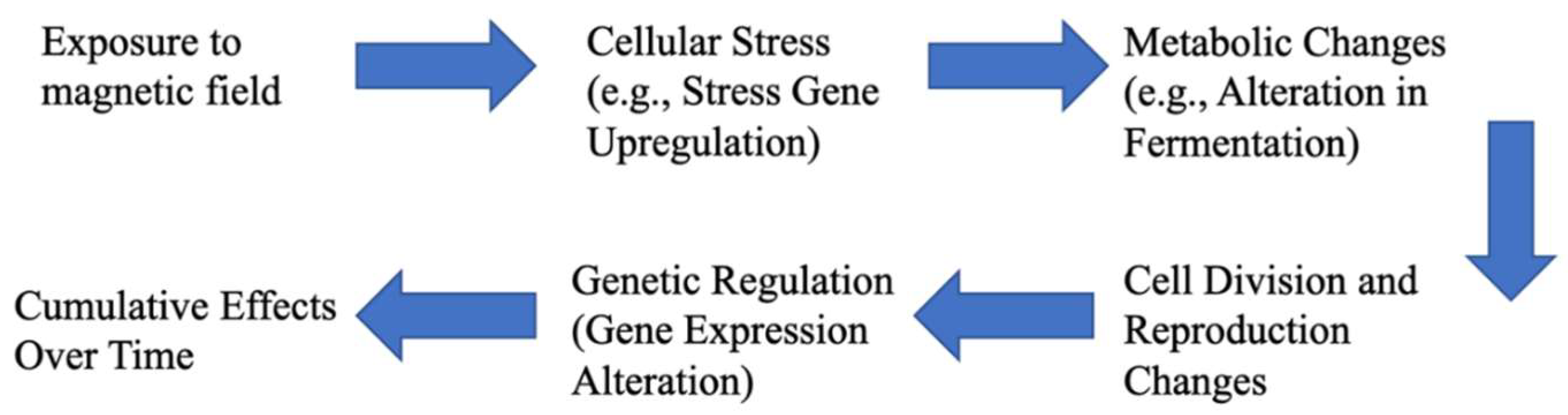
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Configuration for Continuous Exposure
2.2. Exposure Settings with Nonspecific Conditions
2.3. Artificial Settings of IPR Conditions
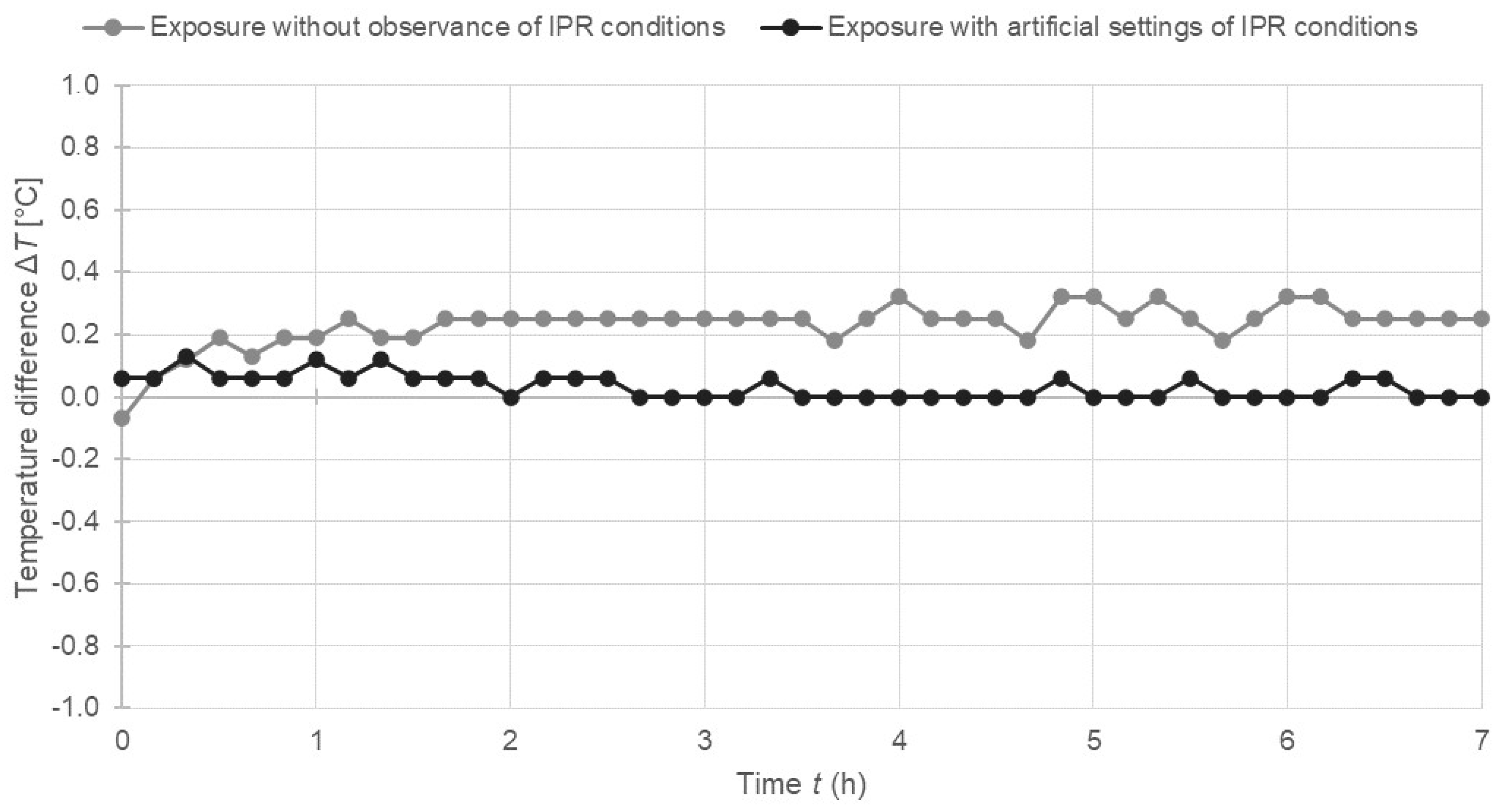
2.4. Temperature Monitoring
2.5. Experimental Protocol
2.6. Statistical Analysis
- without observance of IPR conditions,
- with artificial settings of IPR conditions.
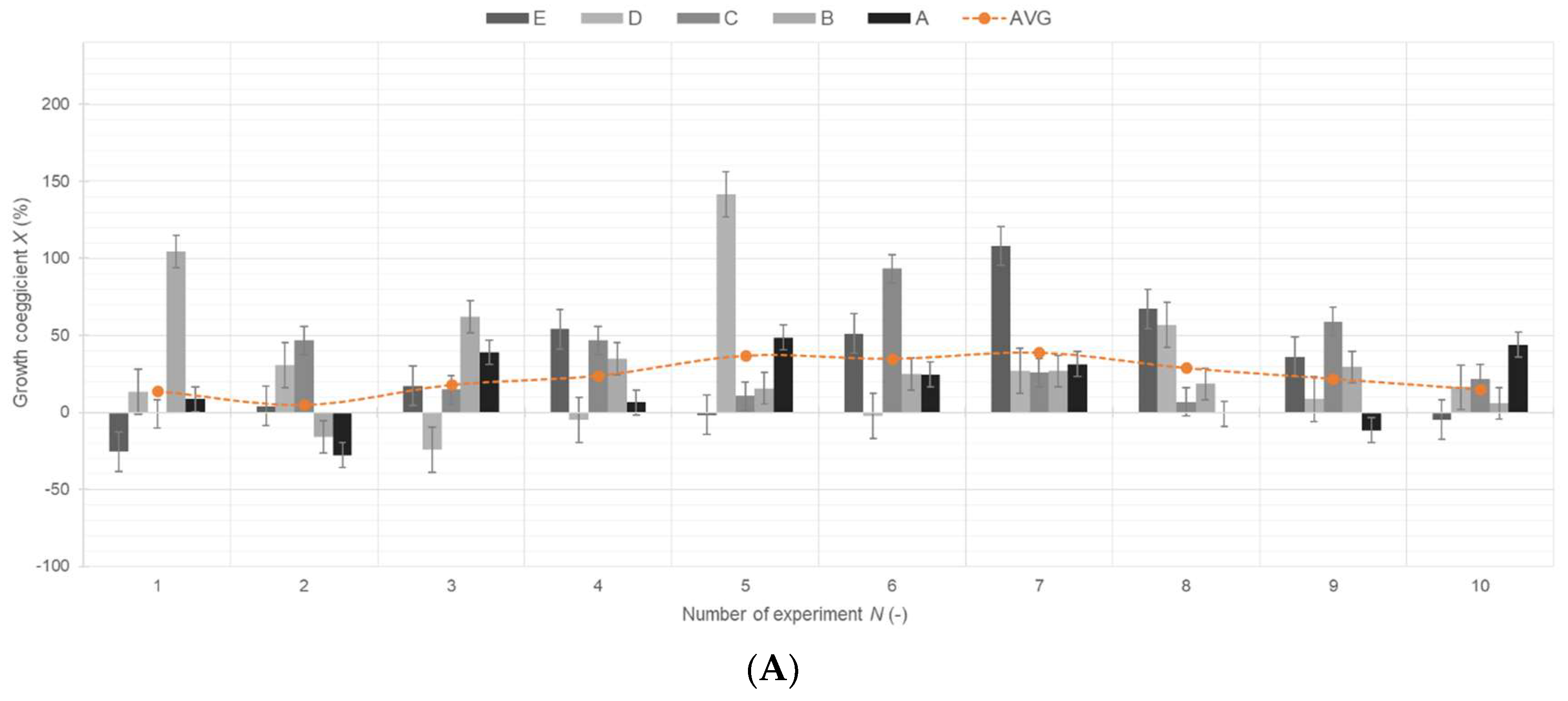
3. Results
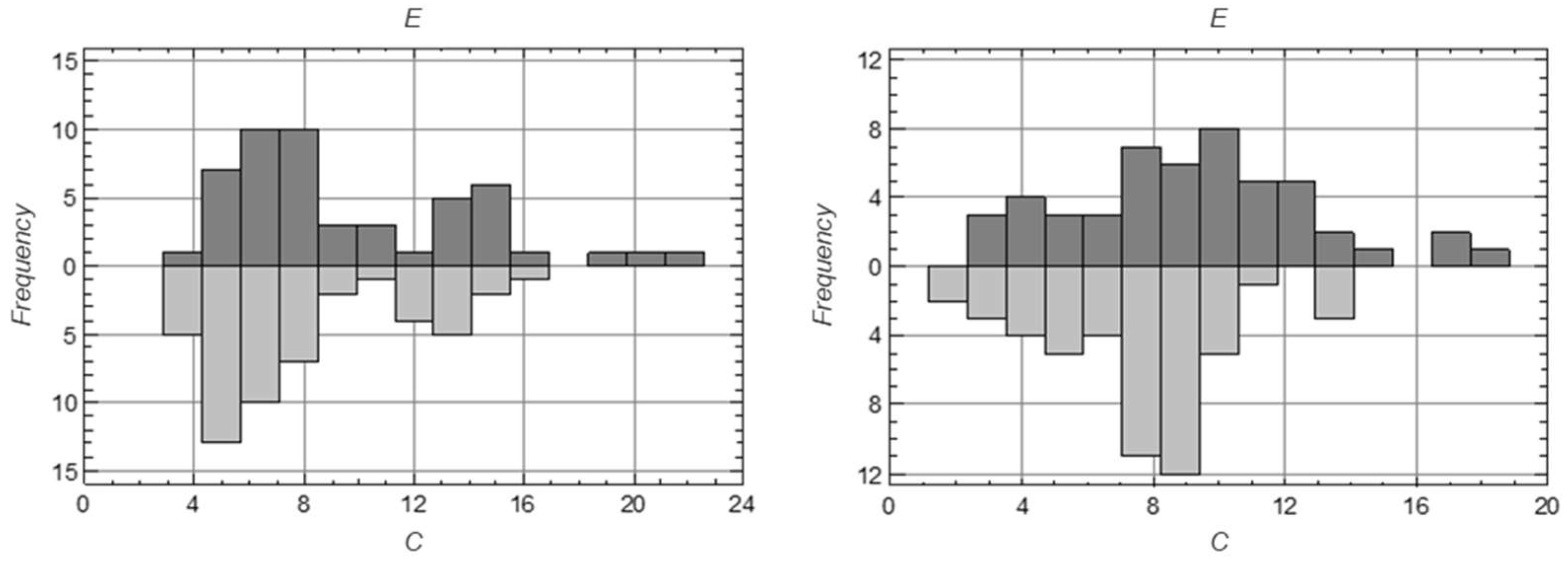
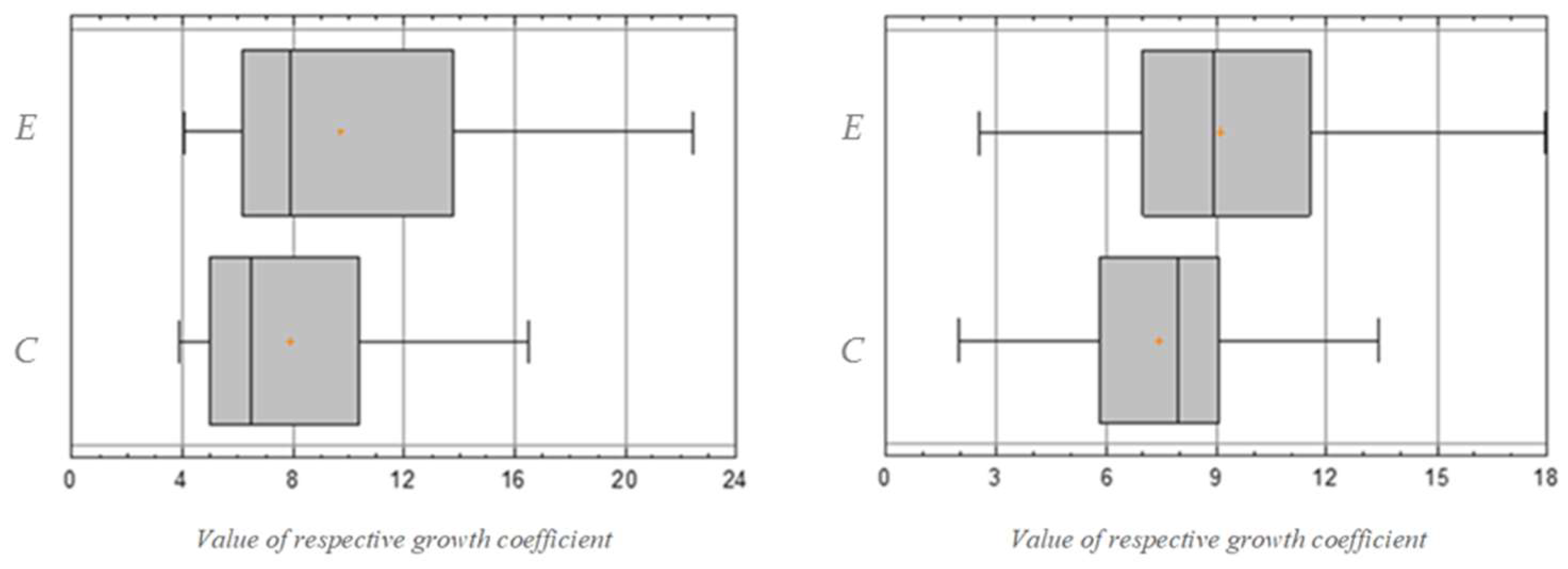
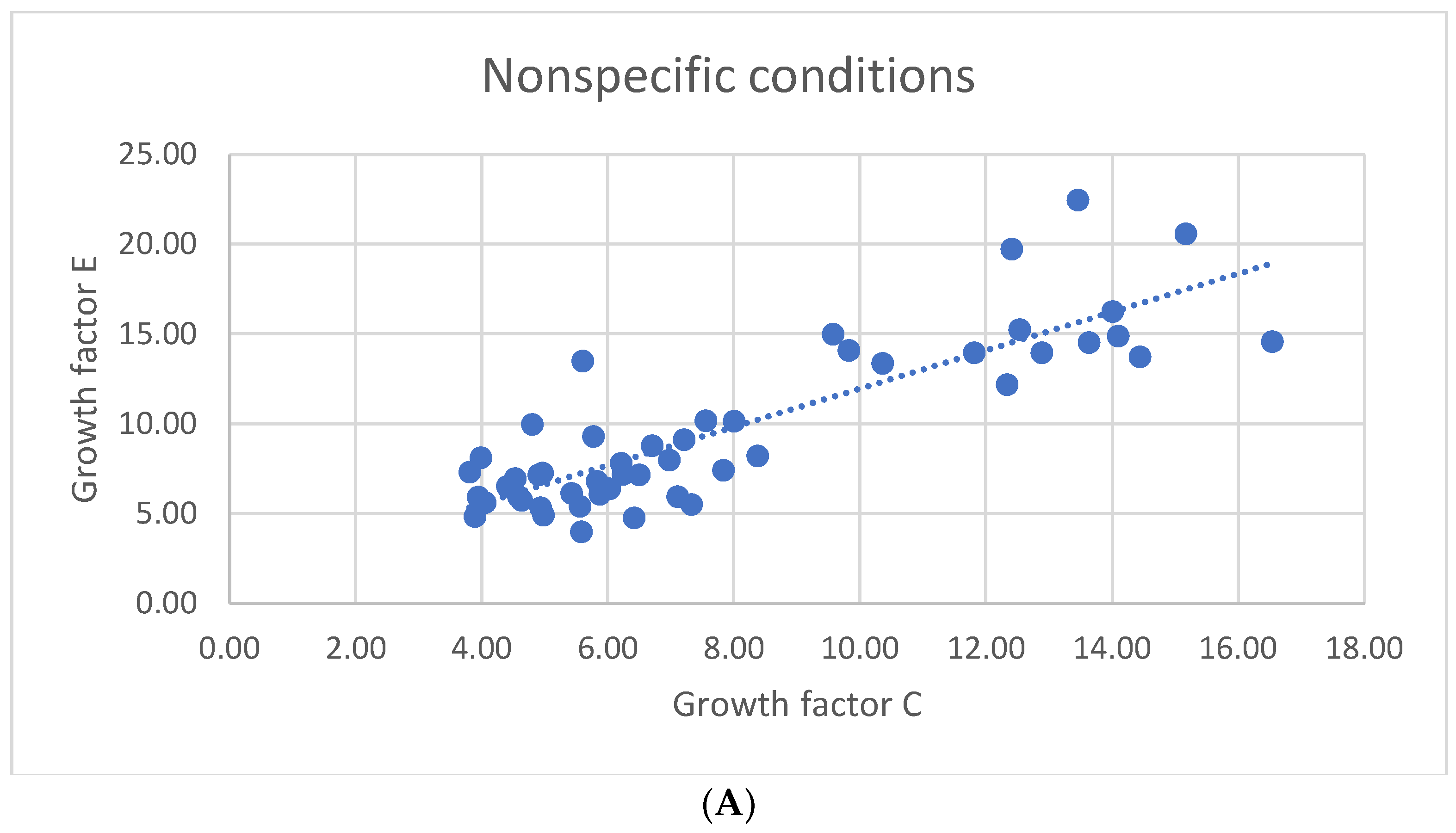
3.1. Results of Statistical Analysis of Experimental Data
Comparison of Means
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hirata, A.; Diao, Y.; Onishi, T.; Sasaki, K.; Ahn, S.; Colombi, D.; De Santis, V.; Laakso, I.; Giaccone, L.; Wout, J.; et al. Assessment of Human Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields: Review and Future Directions. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2021, 63, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohan, M.; Spronglova, M.; Visnovcova, N.; Misek, J.; Spanikova, G.; Jakusova, V.; Jakus, J. Monitoring of data transmission and changes in values of electromagnetic field in living environment. Commun.-Sci. Lett. Univ. Žilina 2020, 22, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kljajic, D.; Djuric, N. Comparative analysis of EMF monitoring campaigns in the campus area of the University of Novi Sad. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 14735–14750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Guidici, P.; Genier, J.C.H.; Martin, S.; Dore, J.F.; Ducimetiere, P.; Evrard, A.S.; Letertre, T.; Ségala, C. Radiofrequency exposure of people living near mobile-phone base stations in France. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandani, R.; Zibaii, M.I. Unveiling the biological effects of radio-frequency and extremely-low frequency electromagnetic fields on the central nervous system performance. BioImpacts BI 2024, 14, 30064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek, A.; Rogalska, J. Extremely low-frequency magnetic field as a stress factor—Really detrimental?—Insight into literature from the last decade. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, K.A. The impact of the low frequency of the electromagnetic field on human. In Cell Biology and Translational Medicine, Volume 7; Stem Cells and Therapy: Emerging Approaches; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedani, B.G.; Goliaei, B.; Shariatpanahi, S.P.; Nezamtaheri, M. An overview of the biological effects of extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields combined with ionizing radiation. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2022, 172, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, G.D.; Khalaf, W.; Hayden, K.E.; Miller, E.J.; Dowray, V.R.; Creekmore, A.L.; Carruthers, C.W., Jr.; Williams, M.W.; Gailey, P.C. Power frequency magnetic field exposure and gap junctional communication in Clone 9 cells. Bioelectrochemistry 2000, 51, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Levitt, B.B. Cellular and molecular effects of non-ionizing electromagnetic fields. Rev. Environ. Health 2024, 39, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Moghaddam, F.G.; Valipour, M. Insights in the biology of extremely low-frequency magnetic fields exposure on human health. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 5621–5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Zhu, H.; Gao, C.; Shi, M.; Yang, D.; Jin, M.; Wang, F.; Sui, X. System-level biological effects of extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields: An in vivo experimental review. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1247021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; World Health Organization; International Agency for Research on Cancer. Non-Ionizing Radiation: Static and Extremely Low-Frequency (ELF) Electric and Magnetic Fields; IARC: Lyon, France, 2002; Volume 80, ISBN 92-832-1280-0. ISSN 1017-1606. [Google Scholar]
- Mild, K.H.; Mattsso, M.O.; Hardell, L.; Bowman, J.D.; Kundi, M. Occupational carcinogens: ELF MFs. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, A726–A727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Miller, A.B.; Morgan, L.L.; Udasin, I.; Davis, D.L. Cancer epidemiology update, following the 2011 IARC evaluation of radiofrequency electromagnetic fields (Monograph 102). Environ. Res. 2018, 167, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieliszek, J.; Wyszkowska, J.; Sobiech, J.; Puta, R. Assessment of the electromagnetic field exposure during the use of portable radios in the context of potential health effects. Energies 2020, 13, 6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Al, M.; Amar, A.S.; Elfergani, I.; Littlehales, R.; Ojaroudi Parchin, N.; Al-Yasir, Y.; See, C.H.; Zhou, D.; Abidin, Z.Z.; Alibakhshikenari, M.; et al. Wireless electromagnetic radiation assessment based on the specific absorption rate (SAR): A review case study. Electronics 2022, 11, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICNIRP. Guidelines for Limiting Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields (100 kHz to 300 GHz). Health Phys. 2020, 118, 483–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wust, P.; Stein, U.; Ghadjar, P. Non-thermal membrane effects of electromagnetic fields and therapeutic applications in oncology. Int. J. Hyperth. 2021, 38, 715–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocklehurst, B.; McLauchlan, K.A. Free radical mechanism for the effects of environmental electromagnetic fields on biological systems. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 1996, 69, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, C.D. Oxidative stress-induced biological damage by low-level EMFs: Mechanism of free radical pair electron spin-polarization and biochemical amplification. In Non-Thermal Effects and Mechanisms of Interaction between Electromagnetic Fields and Living Matter; Ramazzini Institute: Bologna, Italy, 2010; pp. 63–113. ISBN 978-88-6261-166-4. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, F.S.; Greenebaum, B. The effects of weak magnetic fields on radical pairs. Bioelectromagnetics 2015, 36, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.S.; Yoon, Y.; Robotham, J.L.; Anders, M.W.; Sheu, S.S. Calcium, ATP, and ROS: A mitochondrial love-hate triangle. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2004, 287, C817–C833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H. Exposure to static and extremely-low frequency electromagnetic fields and cellular free radicals. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2019, 38, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishabh, R.; Zadeh-Haghighi, H.; Salahub, D.; Simon, C. Radical pairs may explain reactive oxygen species-mediated effects of hypomagnetic field on neurogenesis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1010198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri Hosseinabadi, M.; Khanjani, N.; Norouzi, P.; Mirbadie, S.R.; Fazli, M.; Mirzaii, M. Oxidative stress associated with long term occupational exposure to extremely low frequency electric and magnetic fields. Work 2021, 68, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadeh-Haghighi, H.; Simon, C. Magnetic field effects in biology from the perspective of the radical pair mechanism. J. R. Soc. Interface 2022, 19, 20220325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia, U.; Bergandi, L.; Grisolia, G.; Fino, D.; Mareschi, K.; Marini, E.; Niclot, A.G.; Tirtei, E.; Asaftei, S.D.; Fagioli, F.; et al. The exposure to extremely low frequency electromagnetic-fields inhibits the growth and potentiates the sensitivity to chemotherapy of bidimensional and tridimensional human osteosarcoma models. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 177, 117162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofani, S. Magnetic fields and apoptosis: A possible mechanism. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2022, 41, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lednev, V.V. Possible mechanism for the influence of weak magnetic fields on biological systems. Bioelectromagnetics 1991, 12, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liboff, A.R. Geomagnetic cyclotron resonance in living cells. J. Biol. Phys. 1985, 13, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lednev, V.V. Possible mechanism for the effect of weak magnetic fields on the biological systems: Correction of the basic expression and its consequences. In Electricity and Magnetism in Biology and Medicine; San Francisco Press: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 550–552. [Google Scholar]
- Lednev, V.V. Bioeffects of weak combined, constant and variable magnetic fields. Biophysics 1996, 41, 241–252. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8714474 (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- Lednev, V.V. Biological effects of the extremely weak alternating magnetic fields: The identification of primary targets. Model. Geophys. Process. 2003, 130–136. [Google Scholar]
- Belova, N.A.; Panchelyuga, V.A. Lednev’s model: Theory and experiment. Biophysics 2010, 55, 661–674. Available online: http://link.springer.com/10.1134/S0006350910040263 (accessed on 14 June 2024). [CrossRef]
- Belova, N.A.; Ermakova, O.N.; Ermakov, A.M. The bioeffects of extremely weak alternating magnetic fields. Environmentalist 2007, 27, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belova, N.A.; Ermakov, A.M.; Znobishcheva, A.V.; Srebnitskaya, L.K.; Lednev, V.V. The influence of extremely weak alternating magnetic fields on the regeneration of planarians and the gravitropic response of plants. Biophysics 2010, 55, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halgamuge, M.N.; Perssont, B.R.R.; Salford, L.G.; Mendis, P.; Eber-hardt, J. Comparison Between Two Models for Interactions Between Electric and Magnetic Fields and Proteins in Cell Membranes. Environ. Eng Sci. 2009, 26, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincze, G.; Szasz, A.; Liboff, A.R. New theoretical treatment of ion resonance phenomena. Bioelectromagnetics 2008, 29, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belova, N.A.; Ermakov, A.M.; Lednev, V.V. Effect of weak combined magnetic fields tuned resonance for nuclear spins on the regeneration of planaria. In Proceedings of the Annual Joint Meeting of the Bioelectromagnetics Society and the European BioElectromagnetics Association (BIOEM ’13), Thessaloniki, Greece, 10–14 June 2013; pp. 230–232. [Google Scholar]
- Belova, N.A.; Acosta-Avalos, D. The effect of extremely low frequency alternating magnetic field on the behavior of animals in the presence of the geomagnetic field. J. Biophys. 2015, 2015, 423838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurhan, H.; Bruzon, R.; Kandala, S.; Greenebaum, B.; Barnes, F. Effects induced by a weak static magnetic field of different intensities on HT-1080 fibrosarcoma cells. Bioelectromagnetics 2021, 42, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICNIRP. Gaps in knowledge relevant to the Guidelines for limiting exposure to time-varying electric and magnetic fields (1 Hz–100 kHz). Health Phys. 2020, 118, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judakova, Z.; Radil, R.; Janousek, L.; Pobocikova, I. Sensitivity of Cell Cultures on Time-Varying Low-Frequency Magnetic Field Changes. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng Tai, S.; Daran-Lapujade, P.; Walsh, M.C.; Pronk, J.T.; Daran, J.-M. Acclimation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to Low Temperature: A Chemostat-based Transcriptome Analysis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 5100–5112. Available online: http://www.molbiolcell.org/cgi/doi/10.1091/mbc.E07-02-0131 (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Cheung, T.; Ko, J.; Lee, J.; Manpreet, T. The effect of temperature on the growth rate of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Expedition 2014, 4, 1–10. Available online: https://ojs.library.ubc.ca/index.php/expedition/article/view/186399 (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Salvadó, Z.; Arroyo-López, F.N.; Guillamón, J.M.; Salazar, G.; Querol, A.; Barrio, E. Temperature adaptation markedly determines evolution within the genus Saccharomyces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2292–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajtos, M.; Radil, R.; Stefanakova, M.; Janousek, L.; Skurcak, L. Bioimpact of Hypomagnetic Fields. Lékař A Tech.-Clin. Technol. 2024, 54, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judakova, Z.; Janousek, L.; Radil, R.; Carnecka, L. Low-Frequency Magnetic Field Exposure System for Cells Electromagnetic Biocompatibility Studies. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liboff, A.R. ION cyclotron resonance: Geomagnetic strategy for living systems? Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2019, 38, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adair, R.K. Criticism of Lednev’s mechanism for the influence of weak magnetic fields on biological systems. Bioelectromagnetics 1992, 13, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adair, R.K. A physical analysis of the ion parametric resonance model. Bioelectromagnetics 1998, 19, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engström, S. Dynamic properties of Lednev’s parametric resonance mechanism. Bioelectromagnetics 1996, 17, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radil, R.; Barabas, J.; Janousek, L.; Bereta, M. Frequency Dependent Alterations of S. Cerevisiae Proliferation Due to LF EMF Exposure. Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2020, 18, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabáš, J.; Radil, R.; Malíková, I. Modification of S. cerevisiae Growth Dynamics Using Low Frequency Electromagnetic Fields in the 1–2 kHz Range. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 694713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszkowska, J.; Maliszewska, J.; Gas, P. Metabolic and Developmental Changes in Insects as Stress-Related Response to Electromagnetic Field Exposure. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinistian, L.; Belyaev, I. Toward ELF Magnetic Fields for the Treatment of Cancer. In Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields for Clinical Applications, 1st ed.; Markov, M.S., Ryaby, J.T., Waldorff, E.I., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinistian, L.; Vives, L. Devices, Facilities, and Shielding for Biological Experiments with Static and Extremely Low Frequency Magnetic Fields. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. 2024, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, F.; Kandala, S. Effects of time delays on biological feedback systems and electromagnetic field exposures: Gain and sign changes with time delay. Bioelectromagnetics 2018, 39, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Qin, J.C.; Zhang, Y.G.; Ding, G. Diagnostically analyzing 1 H NMR spectra of sub-types in chaetoglobosins for dereplication. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 1946–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haspel, N.; Moll, M.; Baker, M.L.; Chiu, W.; Kavraki, L.E. Tracing conformational changes in proteins. BMC Struct. Biol. 2010, 10, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichorowski, R.; Kocikowska, O.; Bajtoš, M.; Radil, R.; Janoušek, L.; De Carrillo, D.G.; Student, S. Biological Influence of Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Field Exposition Based on Selected Cell Death Markers. In Proceedings of the 2024 ELEKTRO, Zakopane, Poland, 20–22 May 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
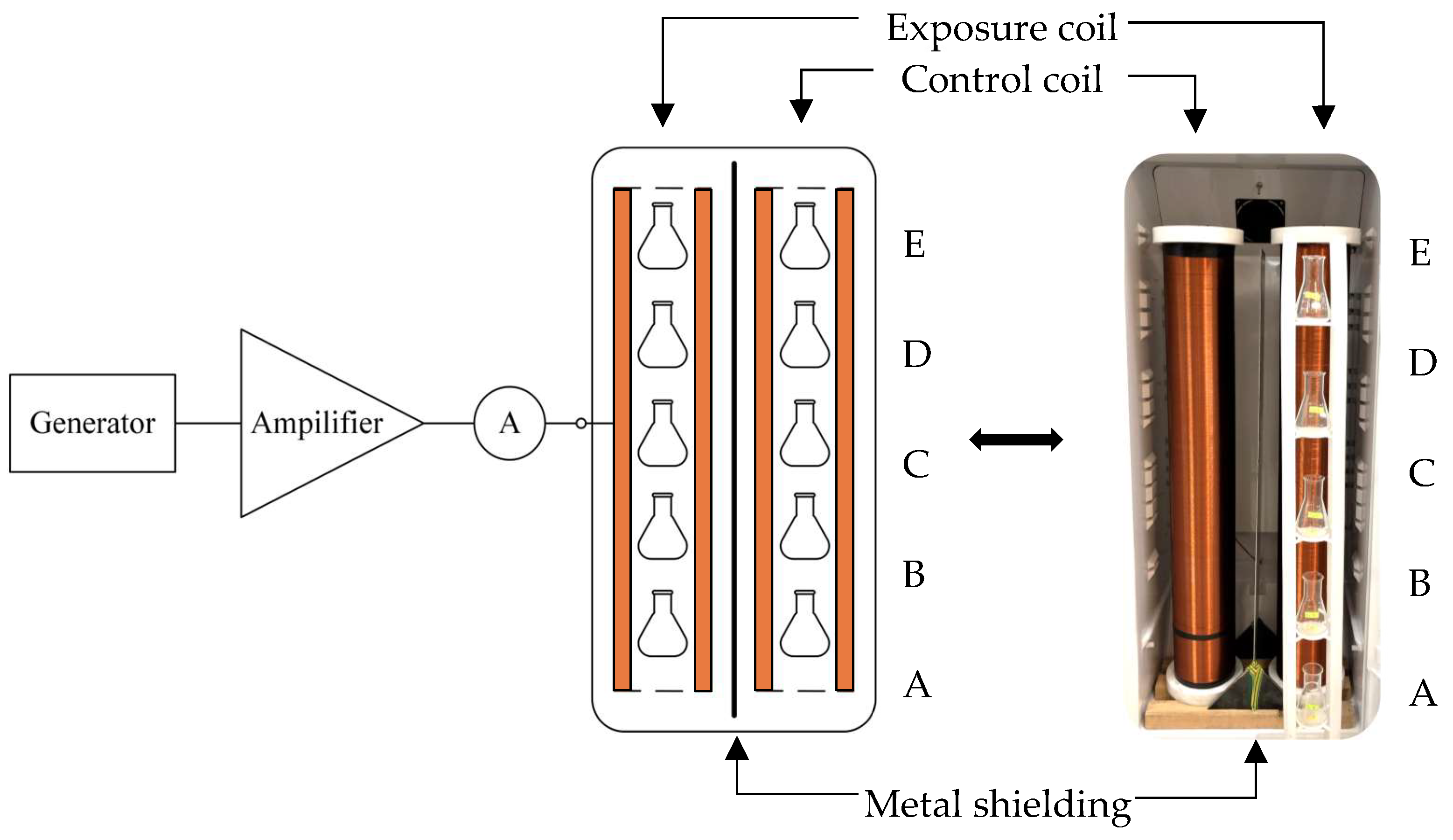



| Induction of DC MF BDC (µT) | Induction of AC MF BAC (µT) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | E | C | E | |
| First experiment (Exposure settings with nonspecific conditions) | 39 | 39 | No AC field | 70.2 (50 Hz) |
| Second experiment (Artificial settings of IPR conditions) | 50.92 | 254.6 | No AC field | 458.28 µT |
| Targeted Ion | Charge to Mass Ratio (C/kg) | Frequency of Time-Varying Magnetic Field (Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium Ca2+ | 29.8862 | |
| Hydronium H+ | 594.1544 | |
| Sodium Na+ | 26.0502 | |
| Potassium K+ | 15.3175 | |
| Chlorine Cl− | 16.8925 | |
| Magnesium Mg2+ | 2 × 3.9698 × 106 | 49.2811 |
| Zinc Zn2+ | 18.3202 | |
| Nitrogen N−5 | 213.7865 | |
| Iron Fe−3 | 32.1724 | |
| Phosphorus P3+ | 38.6707 |
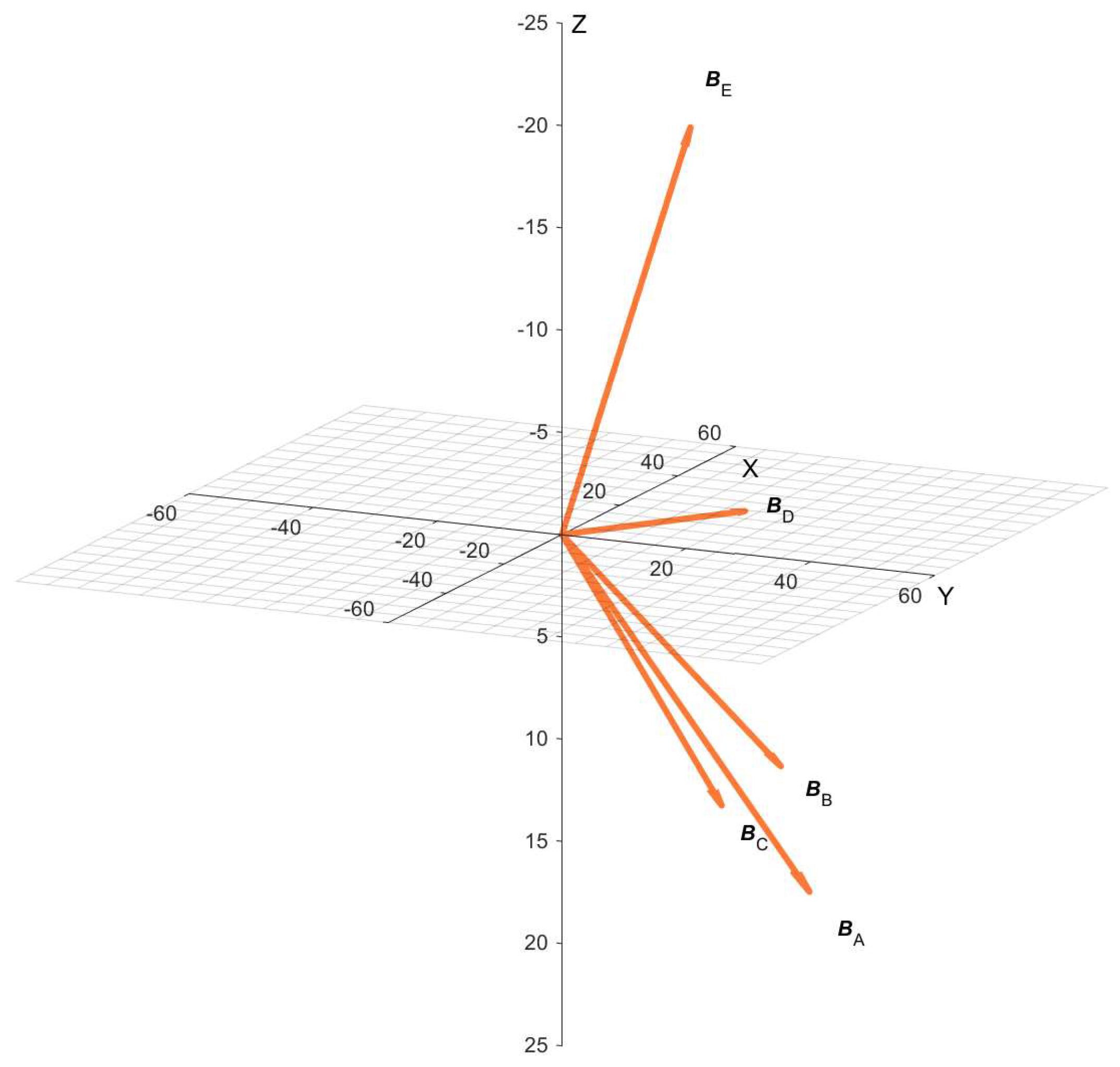
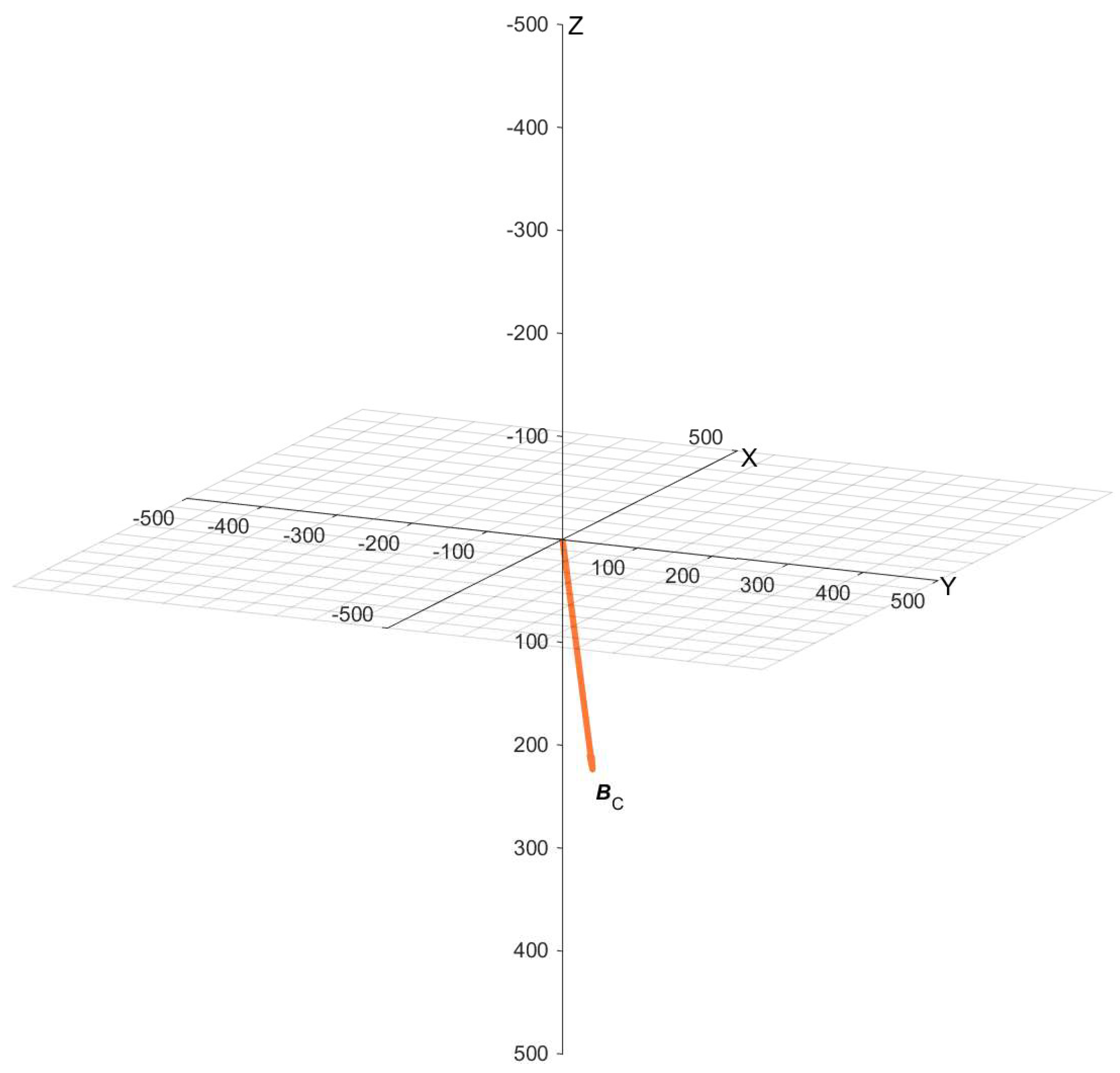
| Position | BX (µT) | BY (µT) | BZ (µT) | BDC (µT) | α (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | 24.1 | 11.8 | −20.8 | 34 | 127.7 |
| D | 45.5 | 11.6 | 1.6 | 47 | 88.1 |
| C | 40.4 | 9.78 | 17.3 | 45 | 67.4 |
| B | 41.4 | 19.9 | 14.9 | 48.3 | 72 |
| A | 50 | 21 | 22.3 | 58.6 | 67.6 |
| Targeted Ion | Charge to Mass Ratio (C/kg) | Frequency of Time-Varying Magnetic Field (Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium Ca2+ | 39.0206 | |
| Hydrogen H+ | 775.7524 | |
| Sodium Na+ | 34.0122 | |
| Potassium K+ | 2.4678 × 106 | 19.999220 |
| Chlorine Cl− | 22.0555 | |
| Magnesium Mg2+ | 64.3434 | |
| Zinc Zn2+ | 23.9197 | |
| Nitrogen N−5 | 279.1284 | |
| Iron Fe−3 | 42.0056 | |
| Phosphorus P3+ | 50.4900 |
| Sample | Count | Average | Standard Deviation | Standard Error | Minimum | Maximum | Effect Size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposure with nonspecific conditions | Cohen’s d | Glass’s delta | ||||||
| 50 | 9.7024 | 4.5384 | 0.6418 | 4.02 | 22.49 | 0.456626 | 0.536129 | |
| 50 | 7.8668 | 3.4238 | 0.4842 | 3.8 | 16.54 | |||
| Exposure with artificial settings of IPR conditions | ||||||||
| 50 | 9.1046 | 3.5815 | 0.5065 | 2.5 | 17.98 | 0.525688 | 0.616607 | |
| 50 | 7.436 | 2.7061 | 0.3827 | 1.96 | 13.41 | |||
| t-Statistic (t Value) | p-Value |
|---|---|
| Exposure with nonspecific conditions | |
| 2.2339 | 0.0278 |
| Exposure with artificial settings of IPR conditions | |
| 2.6285 | 0.0100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radil, R.; Carnecka, L.; Judakova, Z.; Pobocikova, I.; Bajtos, M.; Janousek, L. Exploring Non-Thermal Mechanisms of Biological Reactions to Extremely Low-Frequency Magnetic Field Exposure. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9409. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14209409
Radil R, Carnecka L, Judakova Z, Pobocikova I, Bajtos M, Janousek L. Exploring Non-Thermal Mechanisms of Biological Reactions to Extremely Low-Frequency Magnetic Field Exposure. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(20):9409. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14209409
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadil, Roman, Lucia Carnecka, Zuzana Judakova, Ivana Pobocikova, Marek Bajtos, and Ladislav Janousek. 2024. "Exploring Non-Thermal Mechanisms of Biological Reactions to Extremely Low-Frequency Magnetic Field Exposure" Applied Sciences 14, no. 20: 9409. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14209409
APA StyleRadil, R., Carnecka, L., Judakova, Z., Pobocikova, I., Bajtos, M., & Janousek, L. (2024). Exploring Non-Thermal Mechanisms of Biological Reactions to Extremely Low-Frequency Magnetic Field Exposure. Applied Sciences, 14(20), 9409. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14209409







