Towards a Timepix3 Radiation Monitor for the Accelerator Mixed Radiation Field: Characterisation with Protons and Alphas from 0.6 MeV to 5.6 MeV
Abstract
1. Introduction
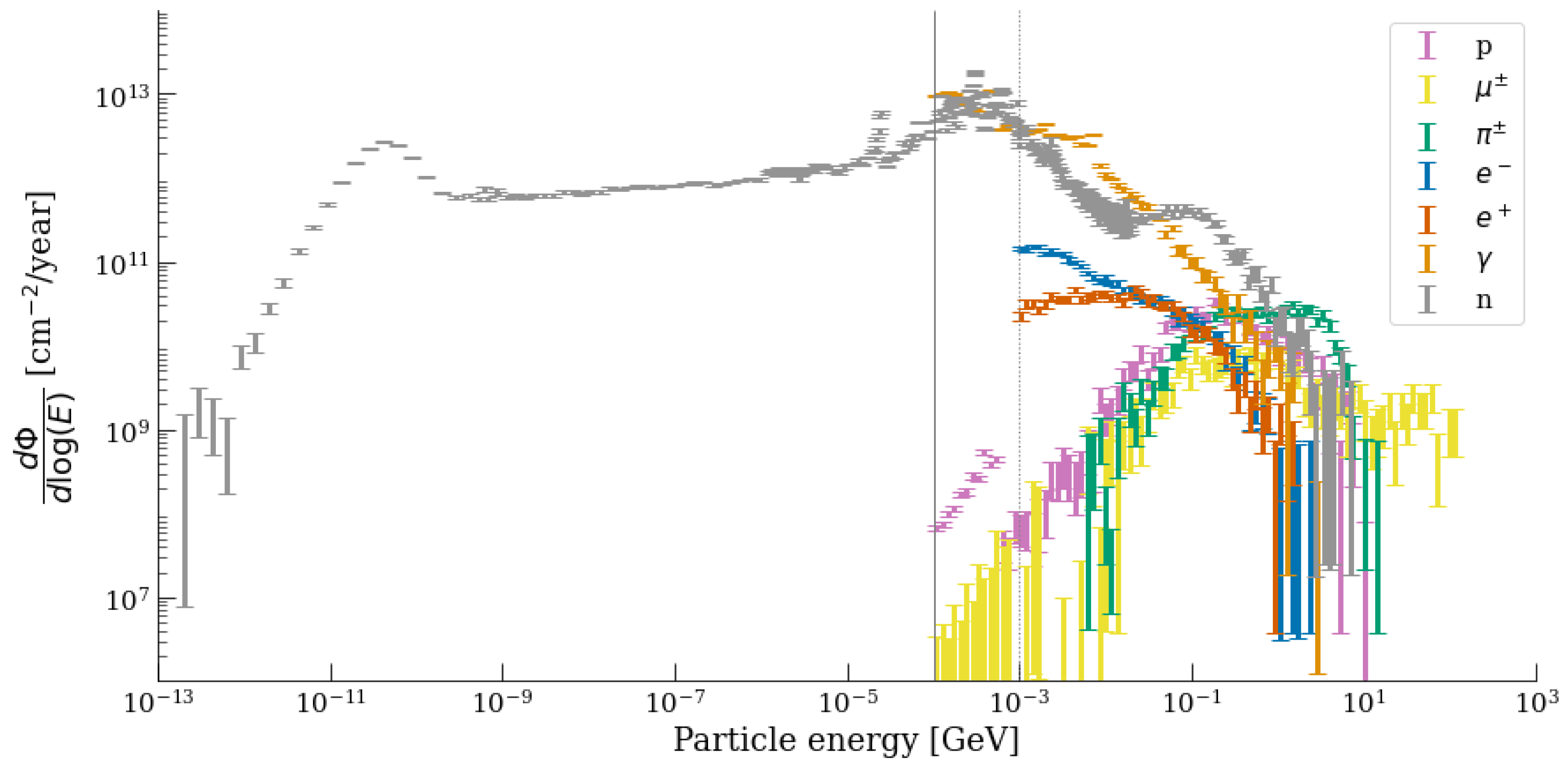
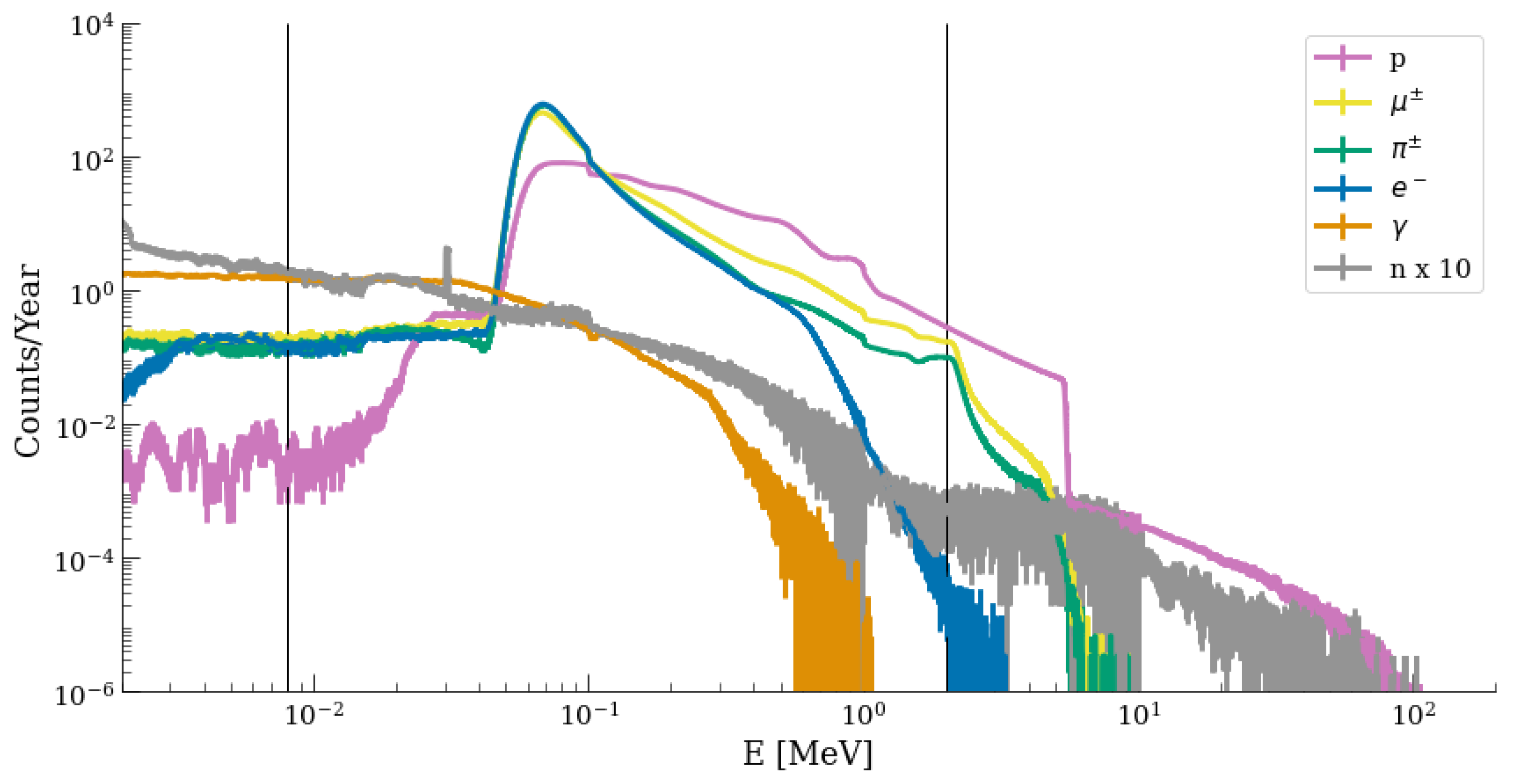
2. The LHC Mixed Radiation Field
3. The Timepix3 Radiation Monitor
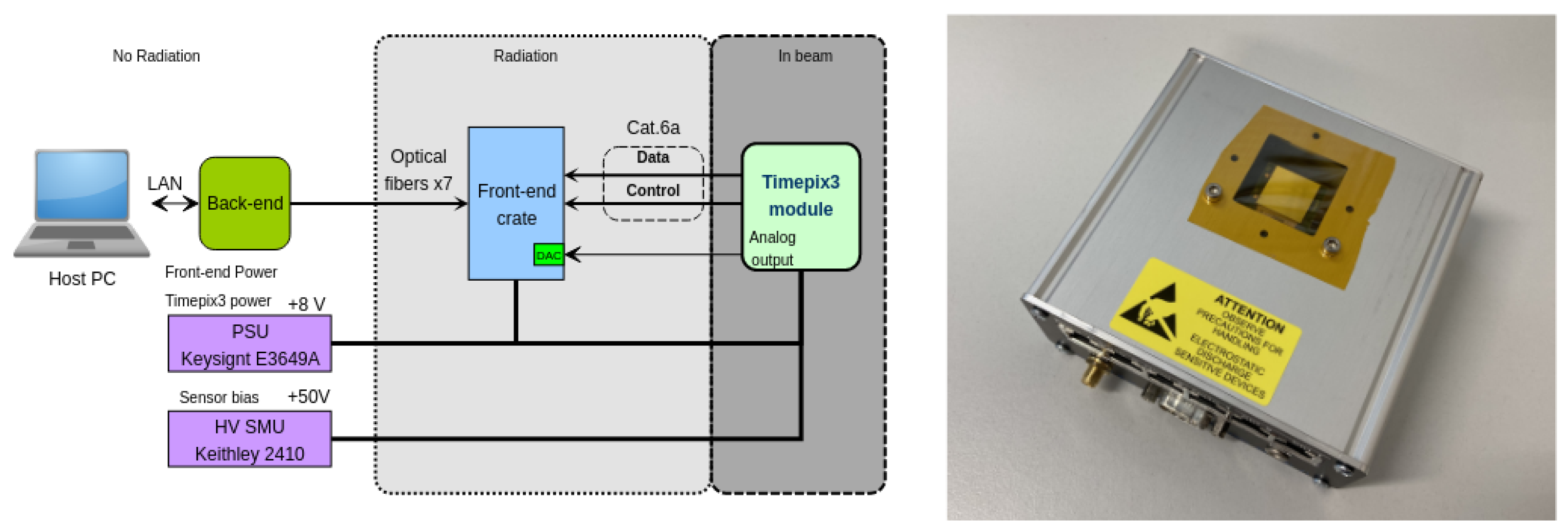
3.1. Setup Description
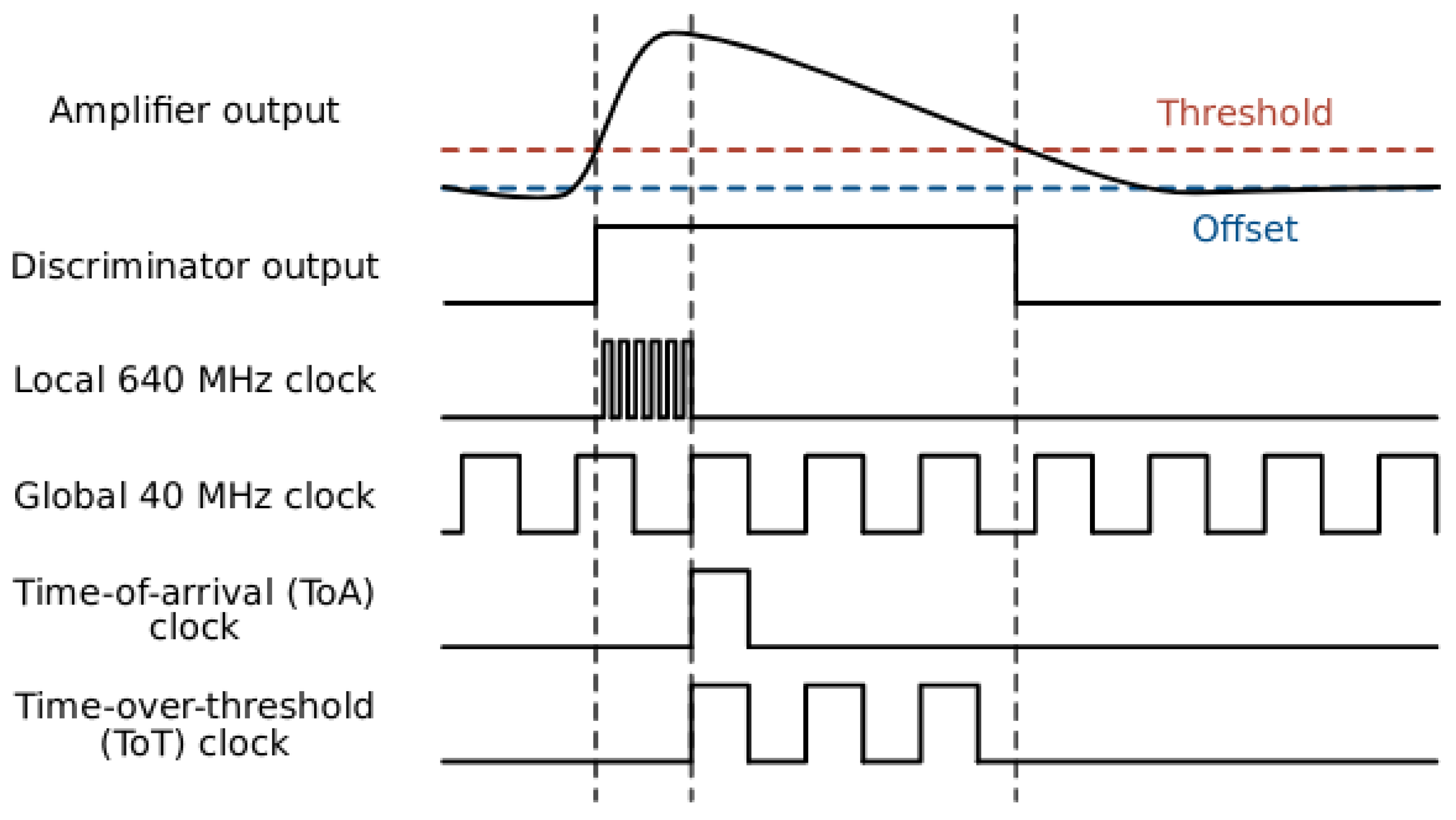
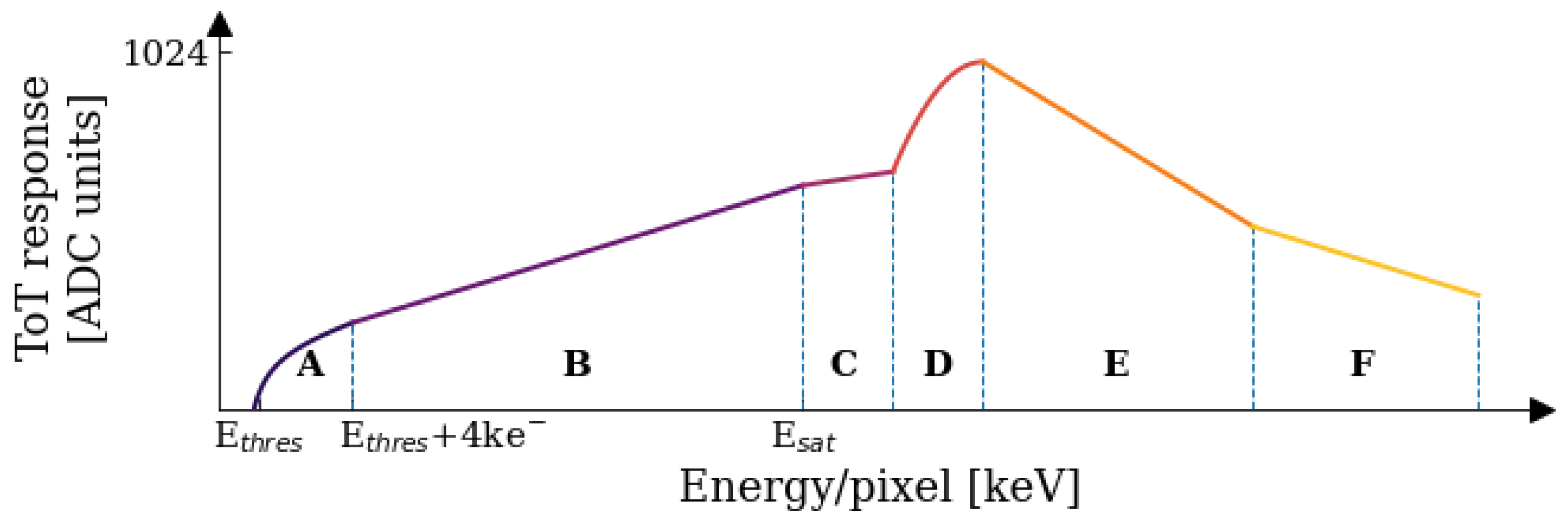
3.2. Operational Principle: Signal Formation
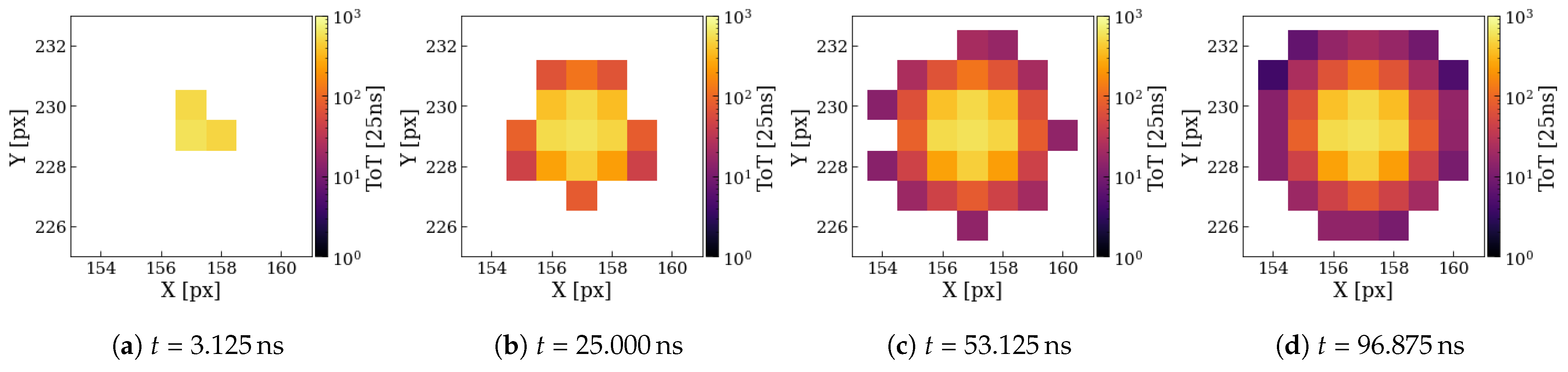
3.3. Clustering
3.4. Pixel Level Energy Calibration Principles
3.5. Cluster-Level Calibration
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Setup at CNA
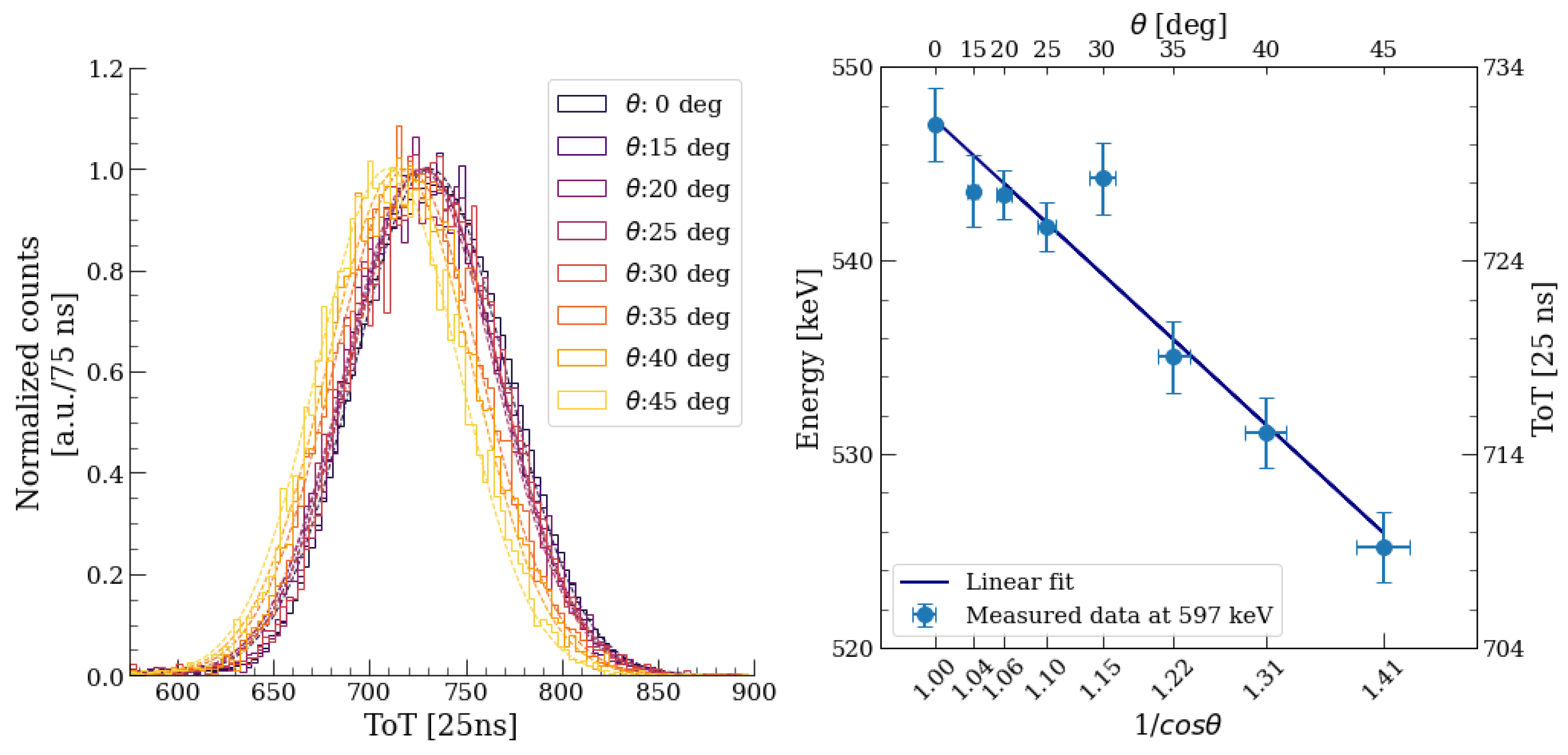
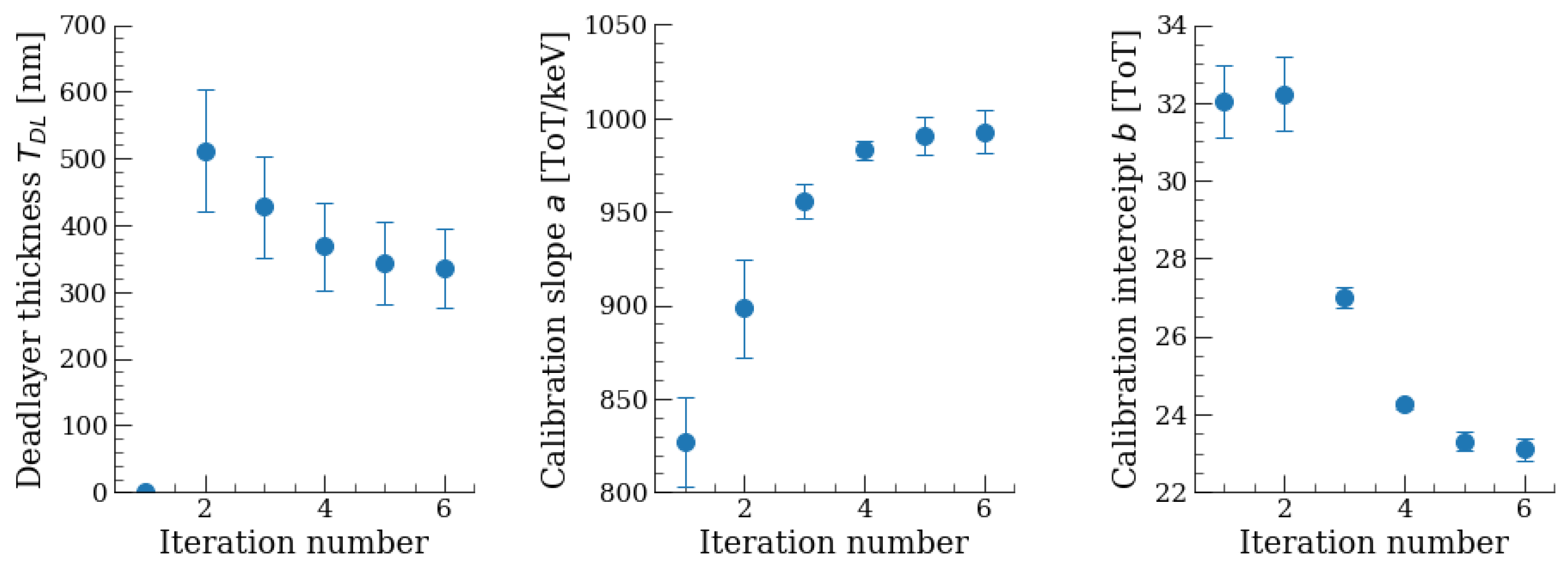
4.2. Energy Calibration and Dead Layer Estimation Strategy
5. Results
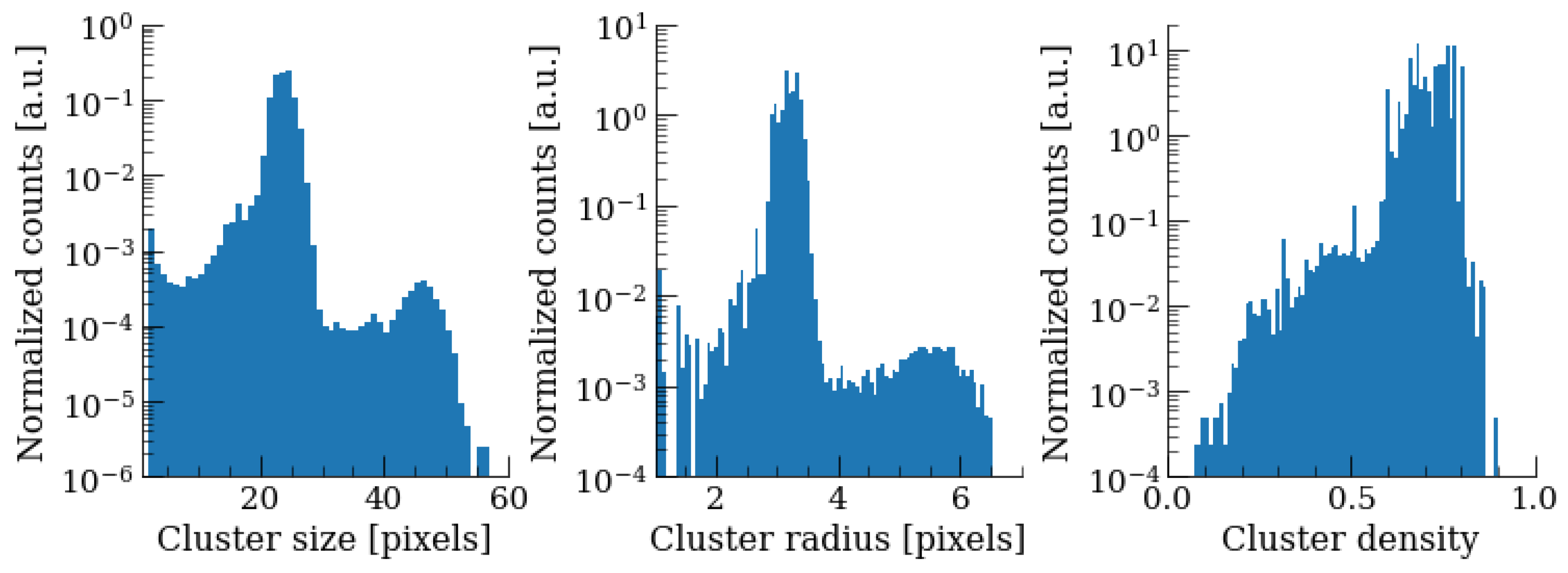
5.1. Event Selection and Cluster Parameters
- Cluster size/area A: The number of pixels within the cluster;
- Cluster centre of geometry : The centre of the cluster, computed as the average point amongst the rows and columns, divided by the cluster area. (Additionally, one could compute the centre of gravity by weighing each pixel by its ToT);
- Cluster radius R: The maximum distance between each pixel and the cluster centre of geometry;
- Cluster density : Defined as the cluster area divided by the area of a circle (); therefore, circular clusters will have a density close to unity.
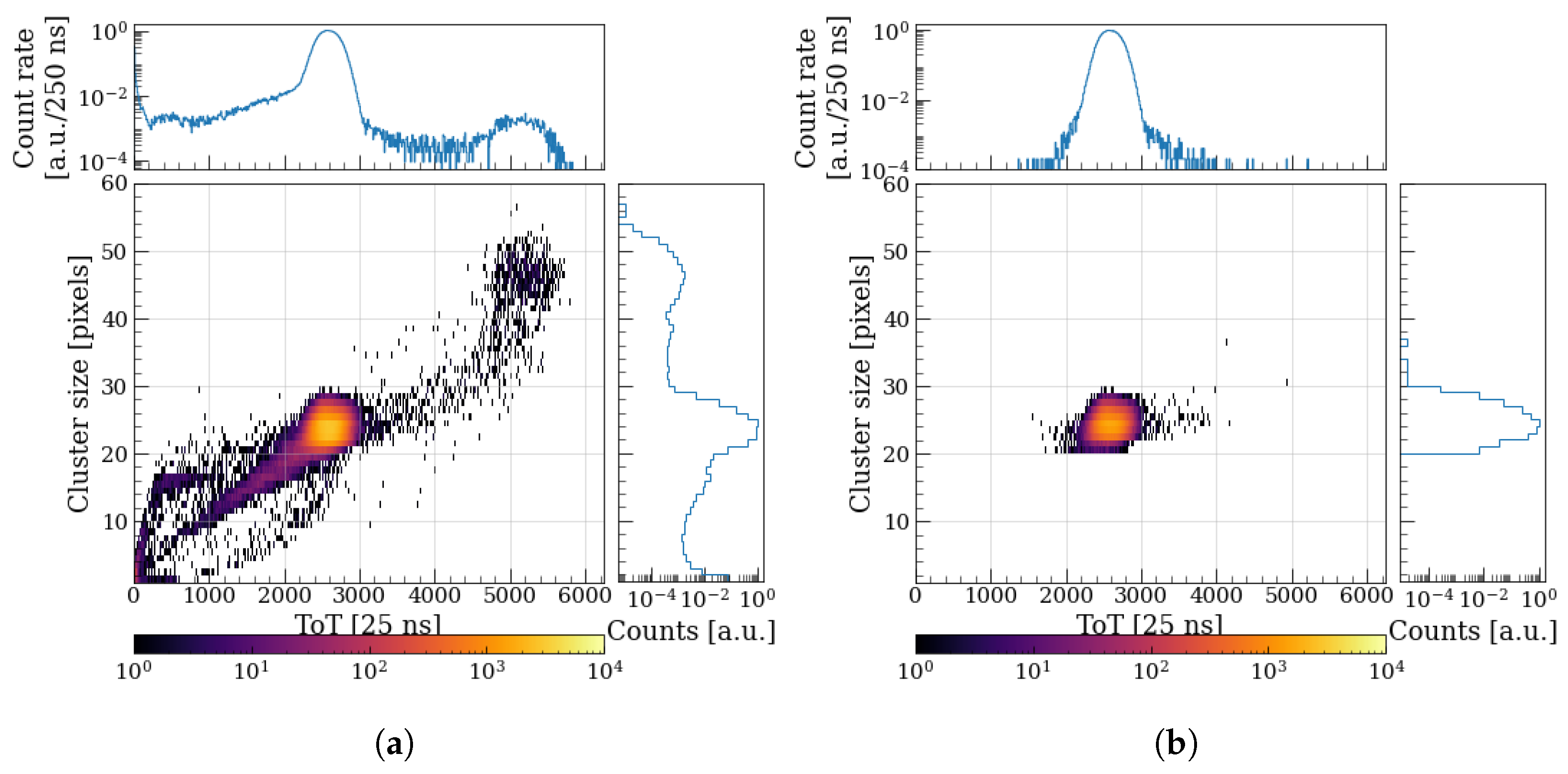
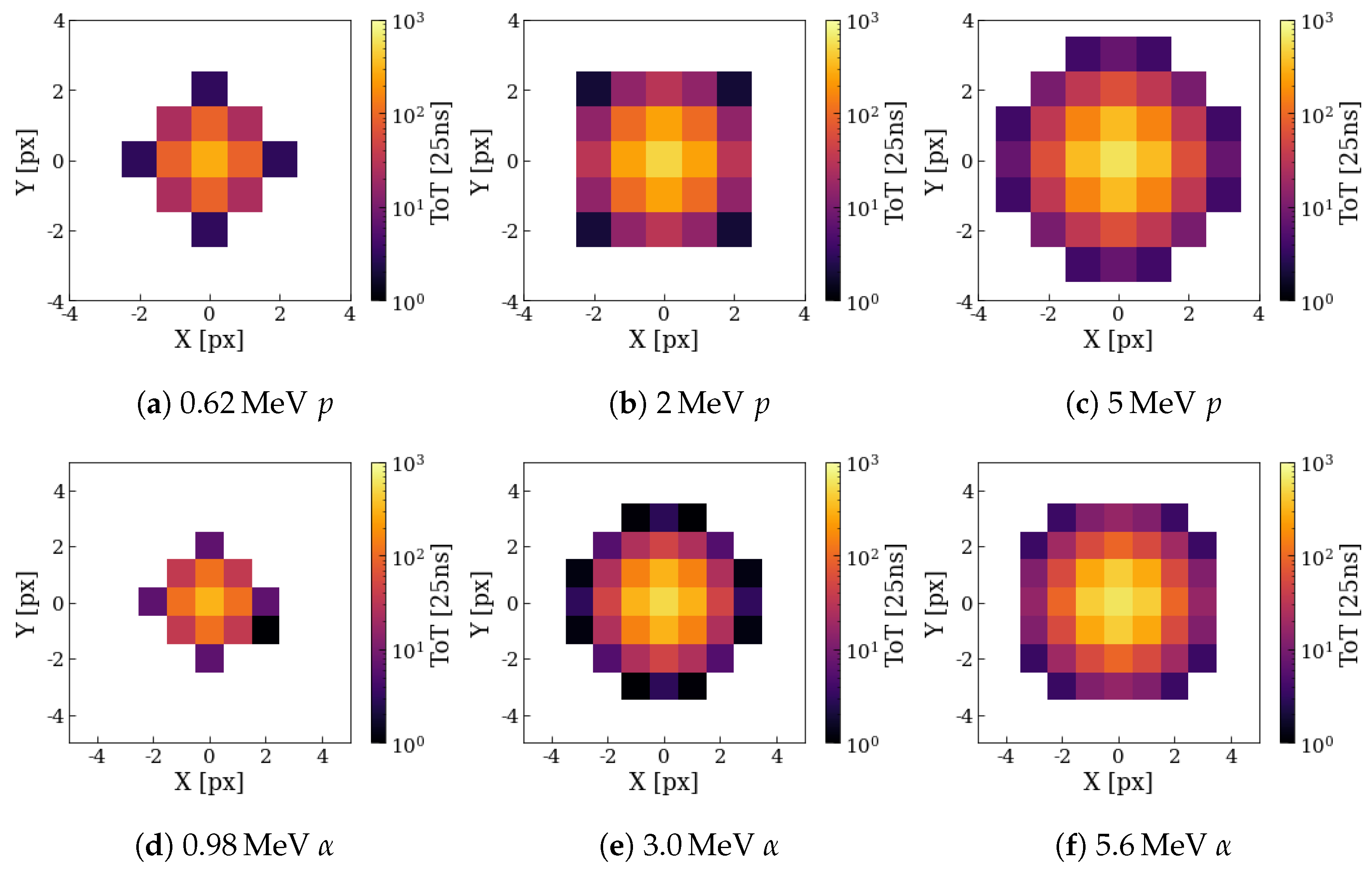
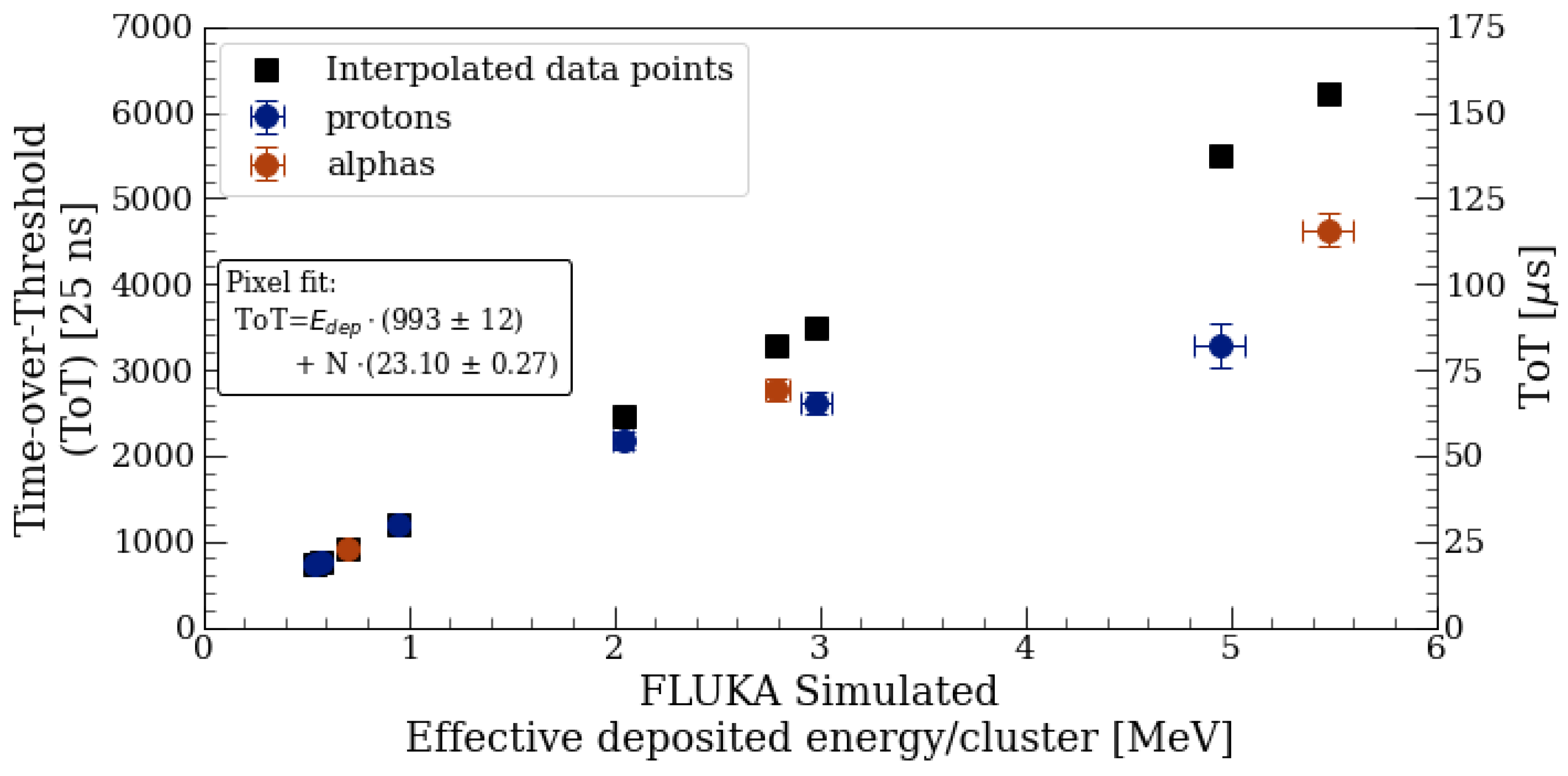
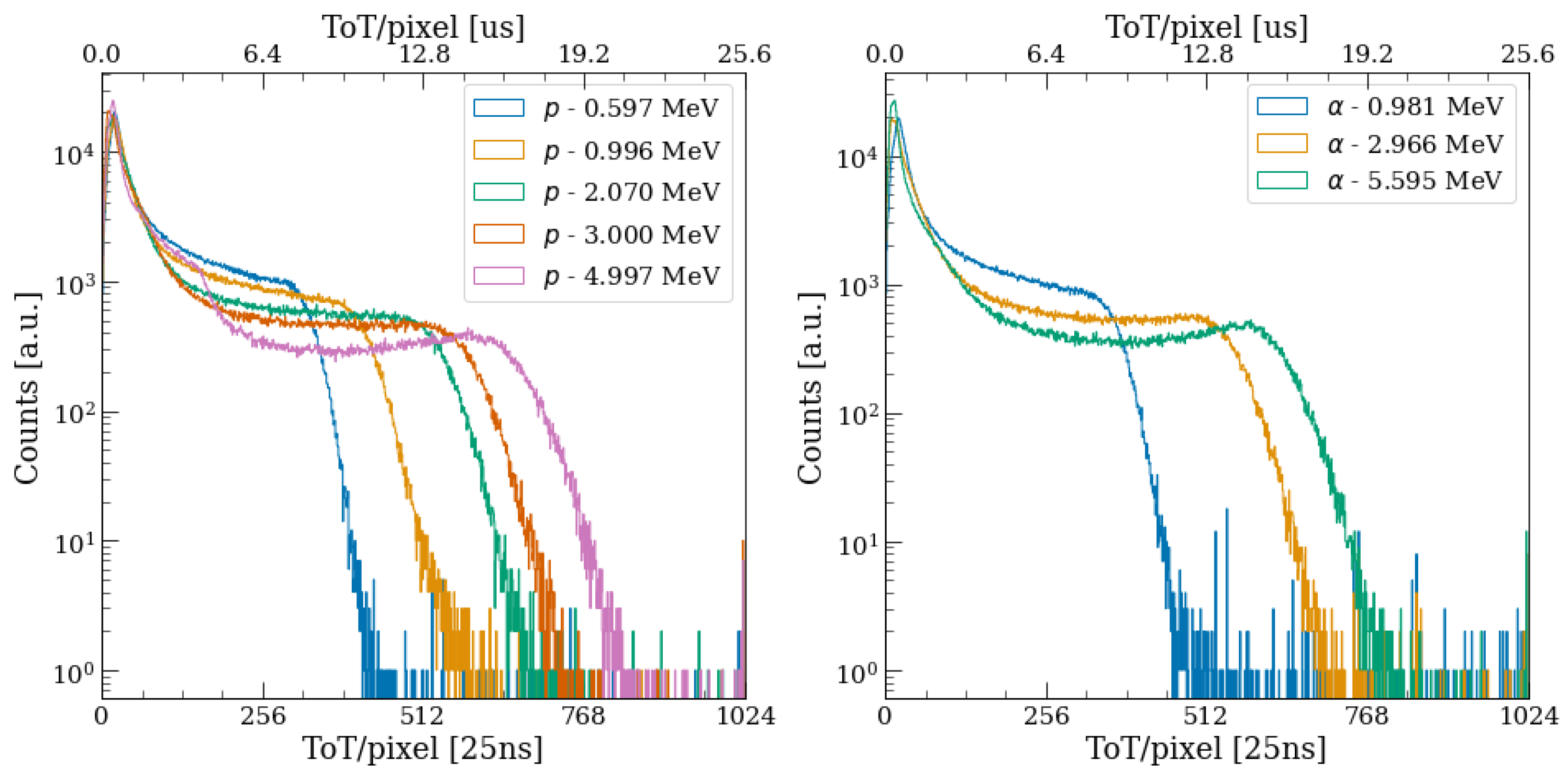
5.2. Proton and Alpha Cluster Measurements
5.3. Energy Calibration and Dead Layer Estimation
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADC | Analogue-to-Digital Converter |
| ASIC | Application-specific integrated circuit |
| BLM | Beam Loss Monitor |
| CERN | European Organization of Nuclear Research |
| CNA | Centro Nacional de Acceleradores |
| DOFRS | Distributed Optical Fibre System |
| FPGA | Field Programmable Gate Array |
| fToA | fast Time-of-Arrival |
| LET | Linear Energy Transfer |
| LHC | Large Hadron Collider |
| LVDS | Low Voltage Differential Signaling |
| MIP | Minimum Ionizing Particle |
| PCB | Printed Circuit Board |
| R2E | Radiation to Electronics |
| SEE | Single Event Effect |
| SFP | Small Form-factor Pluggable |
| ToA | Time-of-Arrival |
| ToT | Time-over-Threshold |
References
- Radiation to Electronics (R2E) at CERN. Available online: https://r2e.web.cern.ch/ (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- García Alía, R.; Brugger, M.; Cerutti, F.; Danzeca, S.; Ferrari, A.; Gilardoni, S.; Kadi, Y.; Kastriotou, M.; Lechner, A.; Martinella, C.; et al. LHC and HL-LHC: Present and future radiation environment in the high-luminosity collision points and RHA implications. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2018, 65, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, E.B.; Dehning, B.; Effinger, E.; Emery, J.; Ferioli, G.; Gonzalez, J.; Gschwendtner, E.; Guaglio, G.; Hodgson, M.; Kramer, D.; et al. Beam loss monitoring system for the LHC. IEEE Nucl. Sci. Symp. 2005, 2, 1052–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiezia, G.; Mekki, J.; Batuca, S.; Brugger, M.; Calviani, M.; Ferrari, A.; Kramer, D.; Losito, R.; Masi, A.; Nyul, A.; et al. The LHC radiation monitoring system—RadMon. Proc. Sci. 2011, 143, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Spiezia, G.; Peronnard, P.; Masi, A.; Brugger, M.; Brucoli, M.; Danzeca, S.; Garcia Alia, R.; Losito, R.; Mekki, J.; Oser, P.; et al. A New RadMon Version for the LHC and its Injection Lines. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2014, 61, 3424–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danzeca, S.; Cass, A.; Masi, A.; Sierra, R.; Zimmaro, A. Wireless IoT in Particle Accelerators: A Proof of Concept with the IoT Radiation Monitor at CERN. JACoW IPAC 2022, 2022, 772–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Francesca, D.; Vecchi, G.L.; Girard, S.; Morana, A.; Reghioua, I.; Alessi, A.; Hoehr, C.; Robin, T.; Kadi, Y.; Brugger, M. Qualification and Calibration of Single-Mode Phosphosilicate Optical Fiber for Dosimetry at CERN. J. Light. Technol. 2019, 37, 4643–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramberger, D.; Aguiar, Y.Q.; Trummer, J.; Vincke, H. Characterization of Radio-Photo-Luminescence (RPL) Dosimeters as Radiation Monitors in the CERN Accelerator Complex. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2022, 69, 1618–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martivsíková, M.; Hartmann, B.; Gwosch, K.C.; Jakubek, C.; Granja, C.; Jakel, O. Study of the capabilities of the Timepix detector for Ion Beam radiotherapy applications. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference Record (NSS/MIC), Anaheim, CA, USA, 27 October–3 November 2012; pp. 4324–4328. [Google Scholar]
- Tremsin, A.; Vallerga, J.; McPhate, J.; Siegmund, O.; Raffanti, R. High Resolution Photon Counting with MCP-Timepix Quad Parallel Readout Operating at >1 KHz Frame Rates. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2013, 60, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffle, N.; Pinsky, L.; Kroupa, M.; Hoang, S.; Idarraga, J.; Amberboy, C.; Rios, R.; Hauss, J.; Keller, J.; Bahadori, A.; et al. Timepix-based radiation environment monitor measurements aboard the International Space Station. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2015, 782, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, A.L. New 3D Colour X-rays Made Possible with CERN Technology. Available online: https://home.cern/news/news/knowledge-sharing/new-3d-colour-x-rays-made-possible-cern-technology (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- Jakubek, J. Imaging Based on Tracking of Individual Particles with the Timepix Pixel Detector. Available online: https://indico.cern.ch/event/48618/contributions/1163509/attachments/958170/1360012/jakubek-psd9-aberystwyth.pdf (accessed on 29 March 2023).
- Bergmann, B.; Billoud, T.; Leroy, C.; Pospisil, S. Characterization of the Radiation Field in the ATLAS Experiment with Timepix Detectors. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2019, 66, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüning, O.S.; Collier, P.; Lebrun, P.; Myers, S.; Ostojic, R.; Poole, J.; Proudlock, P. LHC Design Report, Vol. I: The LHC Main Ring; Collection: CERN Yellow Reports; CERN: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FLUKA Website. Available online: https://fluka.cern (accessed on 30 August 2023).
- Battistoni, G.; Boehlen, T.; Cerutti, F.; Chin, P.W.; Esposito, L.S.; Fassò, A.; Ferrari, A.; Lechner, A.; Empl, A.; Mairani, A.; et al. Overview of the FLUKA code. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2015, 82, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahdida, C.; Bozzato, D.; Calzolari, D.; Cerutti, F.; Charitonidis, N.; Cimmino, A.; Coronetti, A.; D’Alessandro, G.L.; Donadon Servelle, A.; Esposito, L.S.; et al. New Capabilities of the FLUKA Multi-Purpose Code. Front. Phys. 2022, 9, 788253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prelipcean, D. Comparison between Measured Radiation Levels and FLUKA Simulations at CHARM and in the LHC Tunnel of P1-5 within the R2E Project in Run 2. 2021. Available online: https://cds.cern.ch/record/2777059/files/CERN-THESIS-2021-101.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Kroupa, M.; Jakubek, J.; Soukup, P. Optimization of the spectroscopic response of the Timepix detector. J. Instrum. 2012, 7, C02058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turecek, D.; Jakubek, J.; Kroupa, M.; Soukup, P. Energy calibration of pixel detector working in Time-Over-Threshold mode using test pulses. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record, Valencia, Spain, 23–29 October 2011; pp. 1722–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, S.P.; Kroupa, M.; Wheeler, S.; Kodaira, S.; Kitamura, H.; Tlustos, L.; Campbell-Ricketts, T.; Stoffle, N.N.; Semones, E.; Pinsky, L. Very high energy calibration of silicon Timepix detectors. JINST 2018, 13, P11014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroupa, M.; Campbell-Ricketts, T.; Bahadori, A.; Empl, A. Techniques for precise energy calibration of particle pixel detectors. Rev. Sci. Instruments 2017, 88, 033301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, M.; Granja, C.; Kodaira, S.; Ploc, O. High-energy per-pixel calibration of timepix pixel detector with laboratory alpha source. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2022, 1022, 165957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holik, M.; Ahmadov, G.; Broulim, J.; Zich, J.; Berikov, D.; Mora, Y.; Kopatch, Y.; Nuruyev, S.; Abbaszada, N.; Zhumadilov, K. Alpha calibration of the Timepix pixel detector exploiting energy information gained from a common electrode signal. J. Instrum. 2019, 14, C06022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leidner, J.; Murtas, F.; Silari, M. Energy calibration of the GEMPix in the energy range of 6 keV to 2 MeV. J. Instrum. 2021, 16, P10004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubek, J. Precise energy calibration of pixel detector working in time-over-threshold mode. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2011, 633, S262–S266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour Tehrani, N. Test-Beam Measurements and Simulation Studies of Thin Pixel Sensors for the CLIC Vertex Detector. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, M.; Heijne, E.; Holý, T.; Idárraga, J.; Jakůbek, J.; Lebel, C.; Leroy, C.; Llopart, X.; Pospíšil, S.; Tlustos, L.; et al. Study of the charge sharing in a silicon pixel detector by means of α-particles interacting with a Medipix2 device. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2008, 591, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, E.G. Charge diffusion in undepleted regions of silicon particle detectors: Analysis and simulation. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2005, 539, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centro Nacional de Acceleradores. Available online: http://cna.us.es/index.php/en/facilities/tandem-3mv-accelerator/89-lines (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Morilla, Y.; Martín-Holgado, P.; Romero, A.; Labrador, J.; Fernandez, B.; Praena, J.; Lindoso, A.; Garcia-Valderas, M.; Pena-Fernandez, M.; Entrena, L. Progress of CNA to become the Spanish facility for combined irradiation testing in aerospace. In Proceedings of the 2018 18th European Conference on Radiation and Its Effects on Components and Systems (RADECS), Goteborg, Sweden, 16–21 September 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, A.; Auchmann, B.; Baer, T.; Bahamonde Castro, C.; Bruce, R.; Cerutti, F.; Esposito, L.S.; Ferrari, A.; Jowett, J.M.; Mereghetti, A.; et al. Validation of energy deposition simulations for proton and heavy ion losses in the CERN Large Hadron Collider. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 2019, 22, 071003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaboration, A. The ATLAS Experiment at the CERN Large Hadron Collider. J. Instrum. 2008, 3, S08003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, H. Development of a Novel Transverse Beam Profile and Emittance Monitor for the CERN Proton Synchrotron. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Poikela, T.; Plosila, J.; Westerlund, T.; Campbell, M.; Gaspari, M.D.; Llopart, X.; Gromov, V.; Kluit, R.; van Beuzekom, M.; Zappon, F.; et al. Timepix3: A 65K channel hybrid pixel readout chip with simultaneous ToA/ToT and sparse readout. J. Instrum. 2014, 9, C05013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ADVACAM: Timepix3 Licence. Available online: https://medipix.web.cern.ch/news/news/timepix/advacam-timepix3-licence (accessed on 8 January 2024).
- Llopart, X.; Ballabriga, R.; Campbell, M.; Tlustos, L.; Wong, W. Timepix, a 65k programmable pixel readout chip for arrival time, energy and/or photon counting measurements. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2007, 581, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medipix Collaboration. Available online: https://medipix.web.cern.ch/home (accessed on 9 February 2023).
- Shockley, W. Currents to Conductors Induced by a Moving Point Charge. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 9, 635–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramo, S. Currents Induced by Electron Motion. Proc. IRE 1939, 27, 584–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riegler, W. An application of extensions of the Ramo–Shockley theorem to signals in silicon sensors. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2019, 940, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchami, J.; Gutierrez, A.; Houdayer, A.; Jakubek, J.; Lebel, C.; Leroy, C.; Macana, J.; Martin, J.P.; Platkevic, M.; Pospisil, S.; et al. Study of the charge sharing in silicon pixel detector by means of heavy ionizing particles interacting with a Medipix2 device. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2011, 633, S117–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platkevic, M.; Cermak, P.; Jakubek, J.; Pospisil, S.; Stekl, I.; Vykydal, Z.; Zemlicka, J.; Leroy, C.; Allard, P.; Bergeron, G.; et al. Characterization of charge collection in various semiconductor sensors with energetic protons and Timepix device. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record, Valencia, Spain, 23–29 October 2011; pp. 4715–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PSTAR: Stopping Power and Range Tables for Protons. Available online: https://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/Star/Text/PSTAR.html (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- Meduna, L.; Bergmann, B.L.; Burian, P.; Manek, P.; Pospisil, S.; Suk, M. Real-Time Timepix3 Data Clustering, Visualization and Classification with A New Clusterer Framework. Available online: https://indico.cern.ch/event/742793/contributions/3298745/ (accessed on 27 June 2022).
- Wen, J.; Zheng, X.; Gao, H.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, M.; Wu, Y.; Cang, J.; Ma, G.; Zhao, Z. Optimization of Timepix3-based conventional Compton camera using electron track algorithm. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2022, 1021, 165954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek, L.; Granja, C.; Jakubek, J. DPE—Data Processing Engine for Radiation Field Monitoring with Timepix Type Detectors. Available online: https://indico.cern.ch/event/1193219/contributions/5056229/ (accessed on 7 February 2023.).
- Granja, C.; Krist, P.; Chvatil, D.; Solc, J.; Pospisil, S.; Jakubek, J.; Opalka, L. Energy loss and online directional track visualization of fast electrons with the pixel detector Timepix. Radiat. Meas. 2013, 59, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubek, J.; Cejnarova, A.; Holy, T.; Pospisil, S.; Uher, J.; Vykydal, Z. Pixel detectors for imaging with heavy charged particles. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2008, 591, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, S.; Vilalta, R.; Pinsky, L.; Kroupa, M.; Stoffle, N.; Idarraga, J. Data Analysis of Tracks of Heavy Ion Particles in Timepix Detector. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 523, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell-Ricketts, T.; Kroupa, M.; Pinsky, L. Spectroscopy of high-energy ions with Timepix3. J. Instrum. 2016, 11, P11007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.; Ager, F.; Rank, M.; Madrigal, F.; ontalba salamanca, m.; Respaldiza, M.; Ynsa, M. CNA: The first accelerator-based IBA facility in Spain. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2000, 161–163, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Respaldiza, M.; Ager, F.; Carmona, A.; Ferrer, F.; García-León, M.; García-López, J.; Garcia-Orellana, I.; Gómez-Tubío, B.; Morilla, Y.; Ontalba Salamanca, M.; et al. Accelerator-based research activities at “Centro Nacional de Aceleradores”, Seville (Spain). Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2008, 266, 2105–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granja, C.; Jakubek, J.; Polansky, S.; Zach, V.; Krist, P.; Chvatil, D.; Stursa, D.; Sommer, M.; Ploc, O.; Kodaira, S.; et al. Resolving power of pixel detector Timepix for wide-range electron, proton and ion detection. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2018, 908, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, J.; Lee, J.; Lynch, W.; Niu, C.; Tsang, M.; Anderson, C.; Barney, J.; Brown, K.; Chajecki, Z.; Chan, K.; et al. On determining dead layer and detector thicknesses for a position-sensitive silicon detector. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2018, 888, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, B.; Smolyanskiy, P.; Burian, P.; Pospisil, S. Experimental study of the adaptive gain feature for improved position-sensitive ion spectroscopy with Timepix2. J. Instrum. 2022, 17, C01025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granja, C.; Uhlar, R.; Chuprakov, I.; Alexa, P.; Sansarbayar, E.; Gledenov, Y.; Poklop, D.; Olsansky, V.; Marek, L.; Vuolo, M.; et al. Detection of fast neutrons with the pixel detector Timepix3. J. Instrum. 2023, 18, P01003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Particle | [MeV] | [keV] | [keV] | [MeV] | E [%] | No. Pixels |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| proton | 0.597 | 32 | 19 | 0.543 | 9.2 | 8.2 |
| 0.623 | 31 | 18 | 0.573 | 6.6 | 8.4 | |
| 0.996 | 23 | 14 | 0.954 | 6.3 | 11.1 | |
| 2.070 | 13 | 8 | 2.047 | 1.0 | 18.2 | |
| 3.000 | 9 | 5 | 2.978 | 0.6 | 21.9 | |
| 4.997 | 6 | 3 | 4.978 | 1.0 | 24.9 | |
| alpha | 0.981 | 169 | 106 | 0.706 | 23.3 | 9.6 |
| 2.966 | 111 | 62 | 2.795 | 10.2 | 22.5 | |
| 5.595 | 71 | 43 | 5.481 | 2.2 | 40.1 |
| Particle | Below Threshold | Linear Regime | Saturation Effects | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Counts [%] | TID [%] | Counts [%] | TID [%] | Counts [%] | TID [%] | |
| Protons | 12 | 1.14 | 97 | 76 | 3 | 24 |
| Muons | 0.7 | 7.51 | 99 | 93 | 0.8 | 7 |
| Pions | 15 | 8.16 | 99 | 95 | 0.3 | 5 |
| Electrons | 12 | 9.73 | 99 | 99 | 1.25 | 2.93 |
| Photons | 22 | 2 | 78 | 98 | 0 | 0 |
| Neutrons | 92 | 1 | 7.4 | 28 | 0.4 | 71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prelipcean, D.; Lerner, G.; Slipukhin, I.; Lucsanyi, D.; Sandberg, H.; Storey, J.; Martin-Holgado, P.; Romero-Maestre, A.; Morilla García, Y.; García Alía, R. Towards a Timepix3 Radiation Monitor for the Accelerator Mixed Radiation Field: Characterisation with Protons and Alphas from 0.6 MeV to 5.6 MeV. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020624
Prelipcean D, Lerner G, Slipukhin I, Lucsanyi D, Sandberg H, Storey J, Martin-Holgado P, Romero-Maestre A, Morilla García Y, García Alía R. Towards a Timepix3 Radiation Monitor for the Accelerator Mixed Radiation Field: Characterisation with Protons and Alphas from 0.6 MeV to 5.6 MeV. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(2):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020624
Chicago/Turabian StylePrelipcean, Daniel, Giuseppe Lerner, Ivan Slipukhin, David Lucsanyi, Hampus Sandberg, James Storey, Pedro Martin-Holgado, Amor Romero-Maestre, Yolanda Morilla García, and Rubén García Alía. 2024. "Towards a Timepix3 Radiation Monitor for the Accelerator Mixed Radiation Field: Characterisation with Protons and Alphas from 0.6 MeV to 5.6 MeV" Applied Sciences 14, no. 2: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020624
APA StylePrelipcean, D., Lerner, G., Slipukhin, I., Lucsanyi, D., Sandberg, H., Storey, J., Martin-Holgado, P., Romero-Maestre, A., Morilla García, Y., & García Alía, R. (2024). Towards a Timepix3 Radiation Monitor for the Accelerator Mixed Radiation Field: Characterisation with Protons and Alphas from 0.6 MeV to 5.6 MeV. Applied Sciences, 14(2), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020624







