Subcrestal versus Bone-Level One-Stage Implants: Early Bone and Soft Tissues Modification: One-Year Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
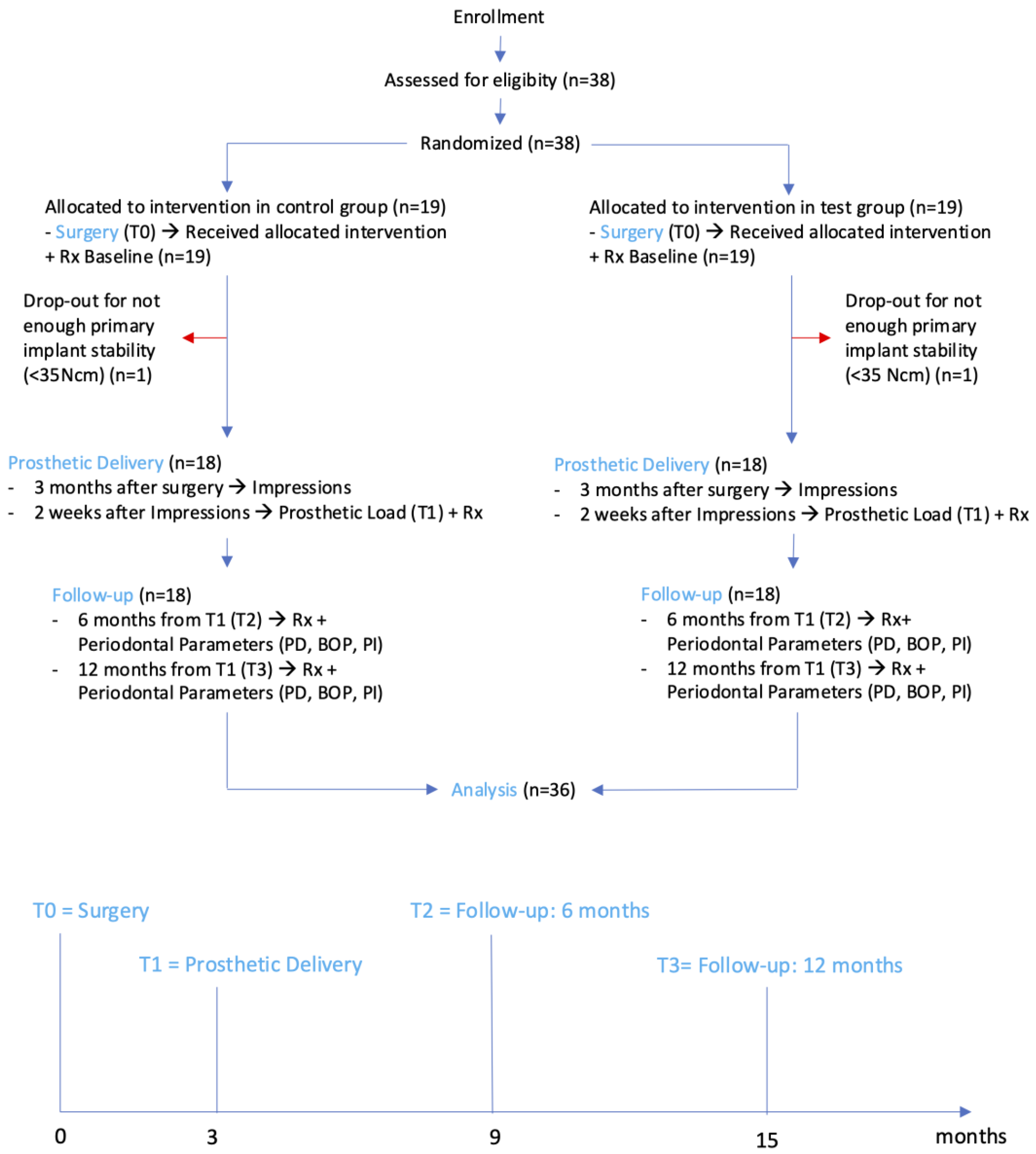
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
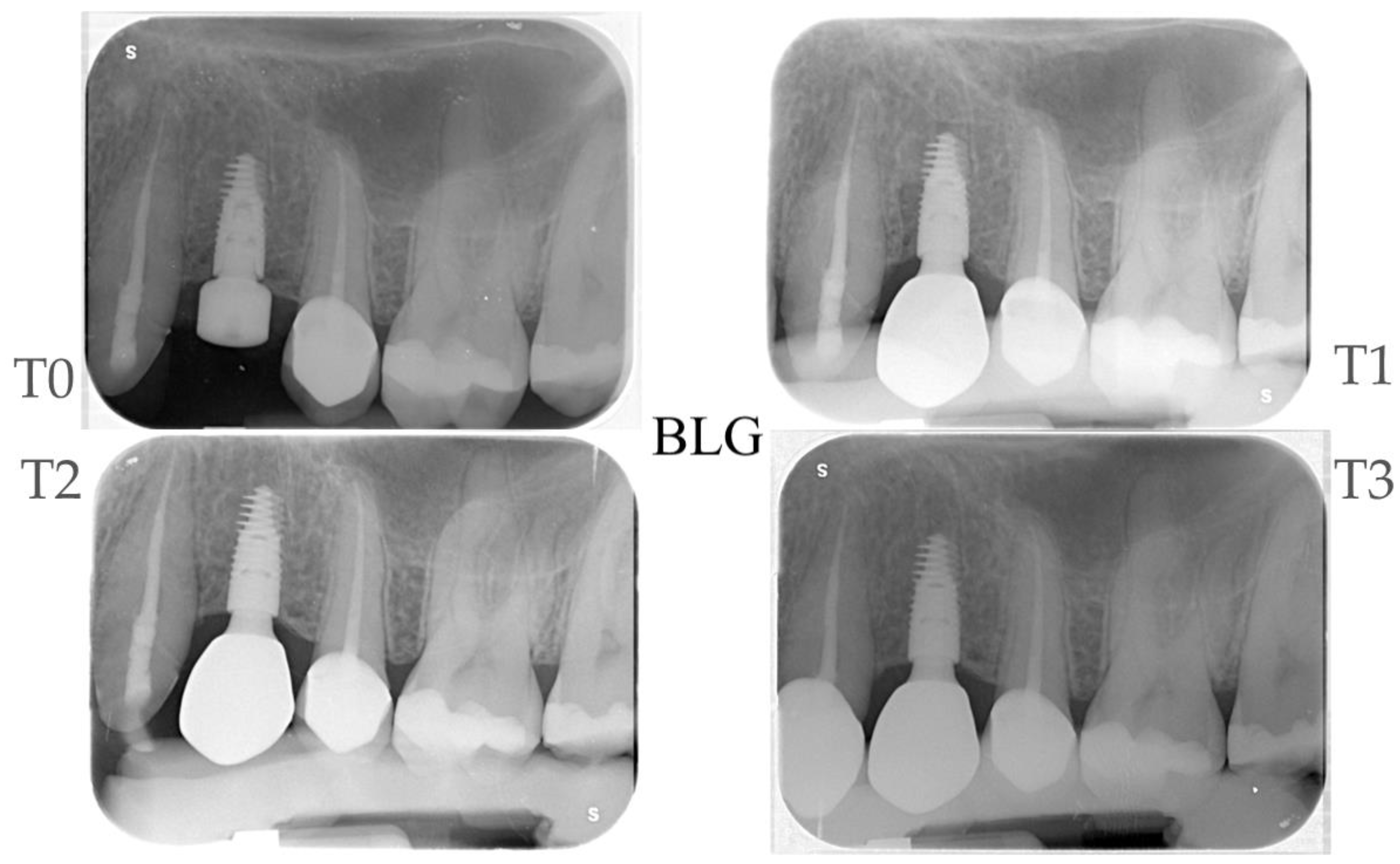
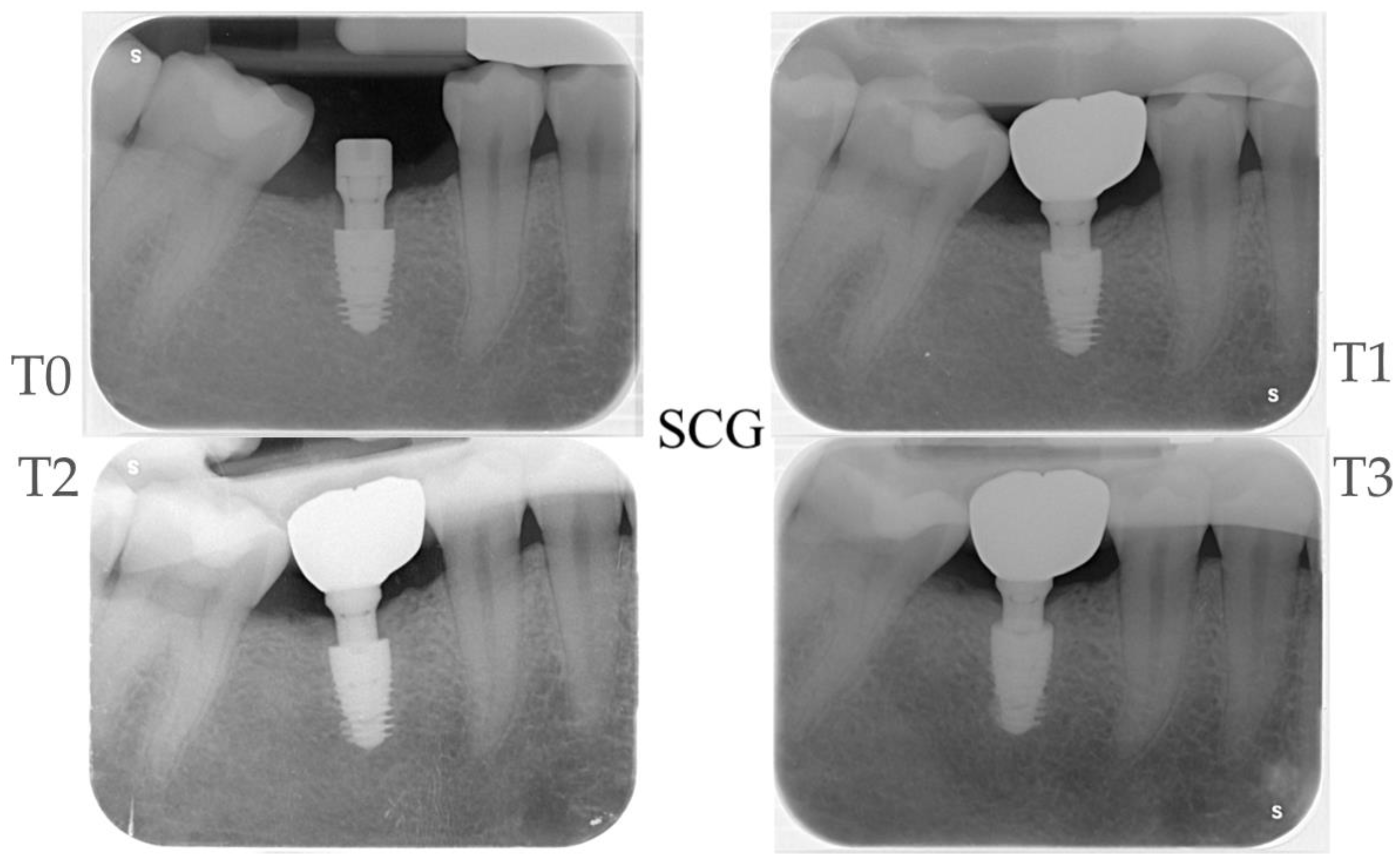
2.2. Surgical Procedures
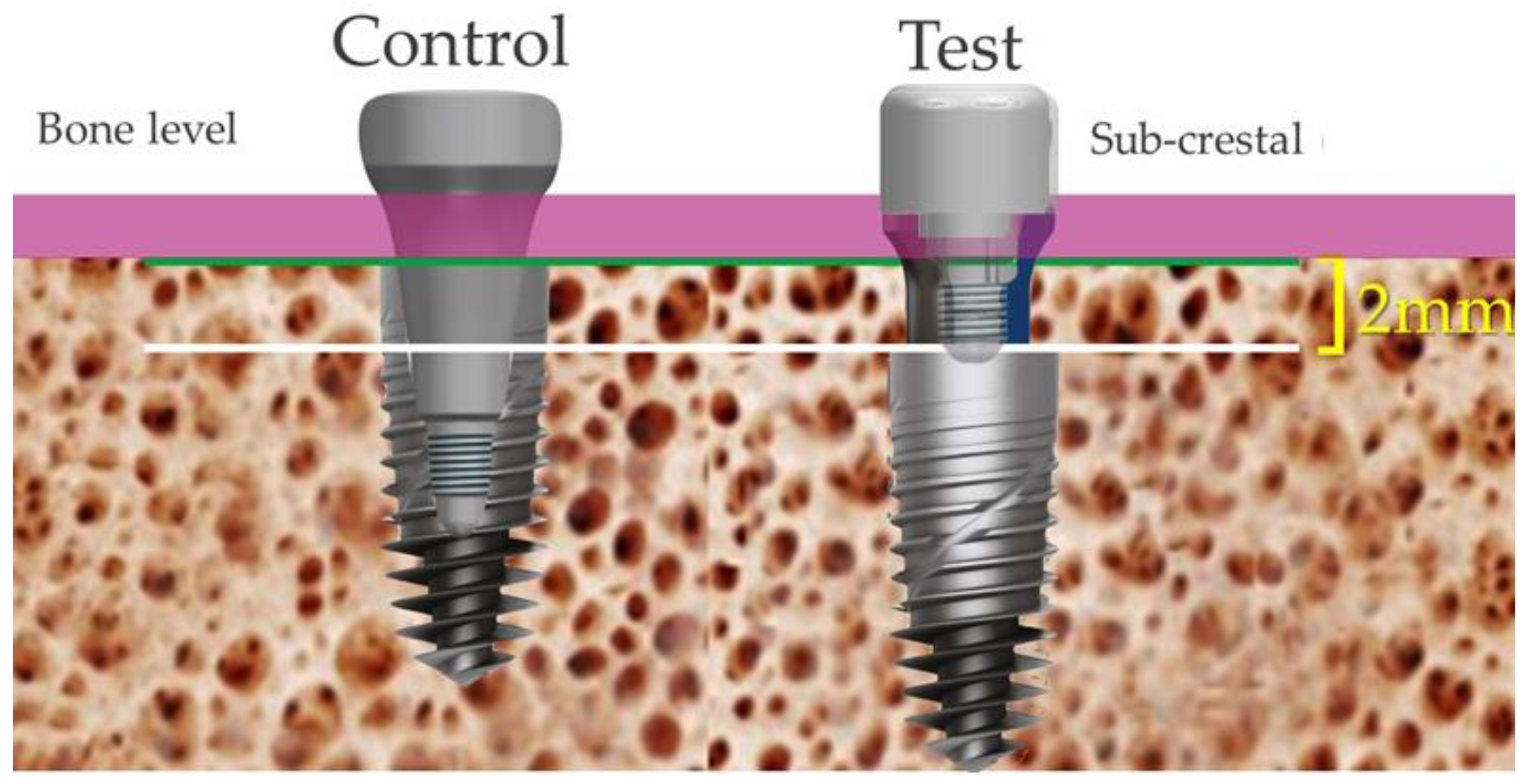
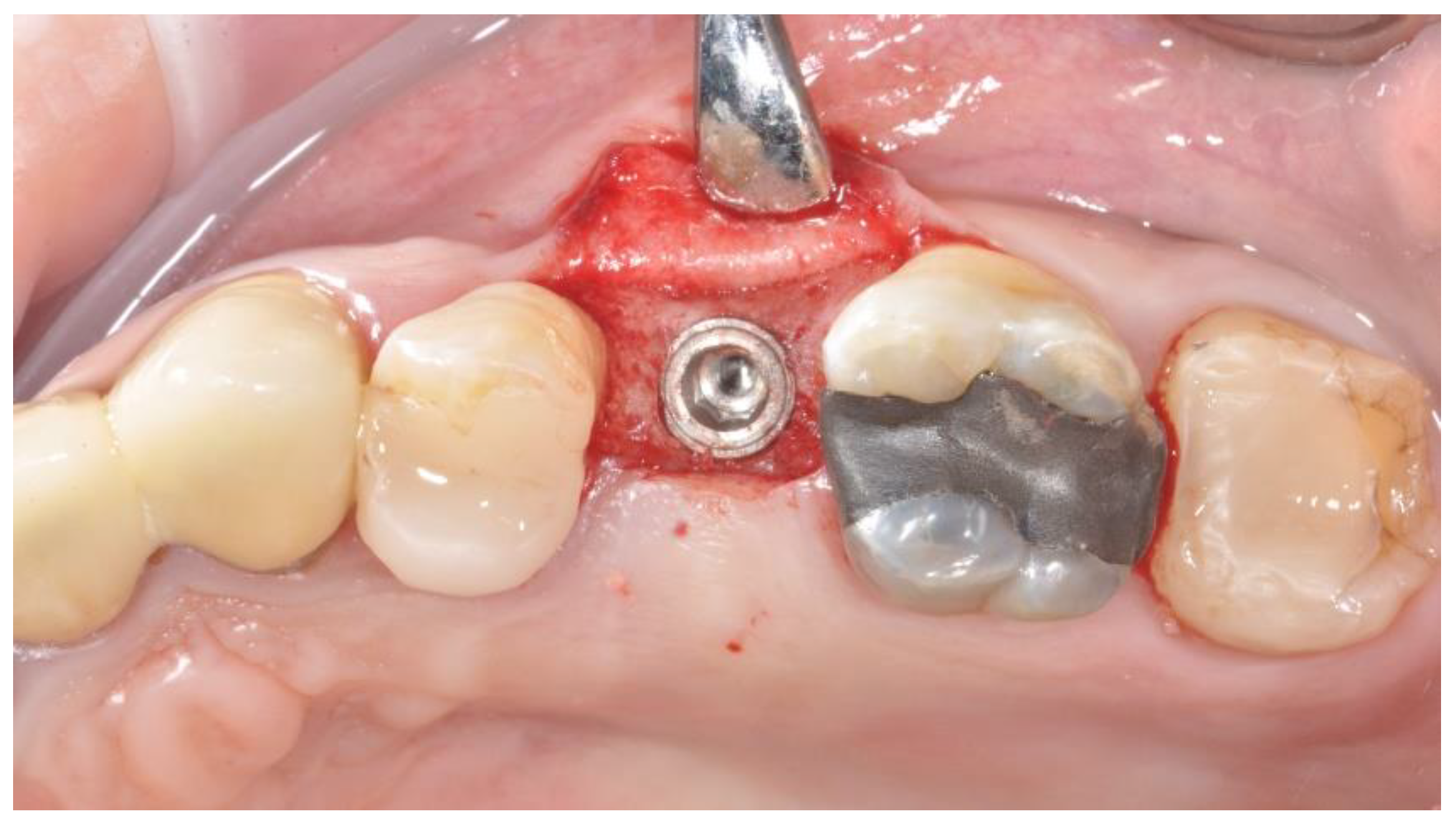
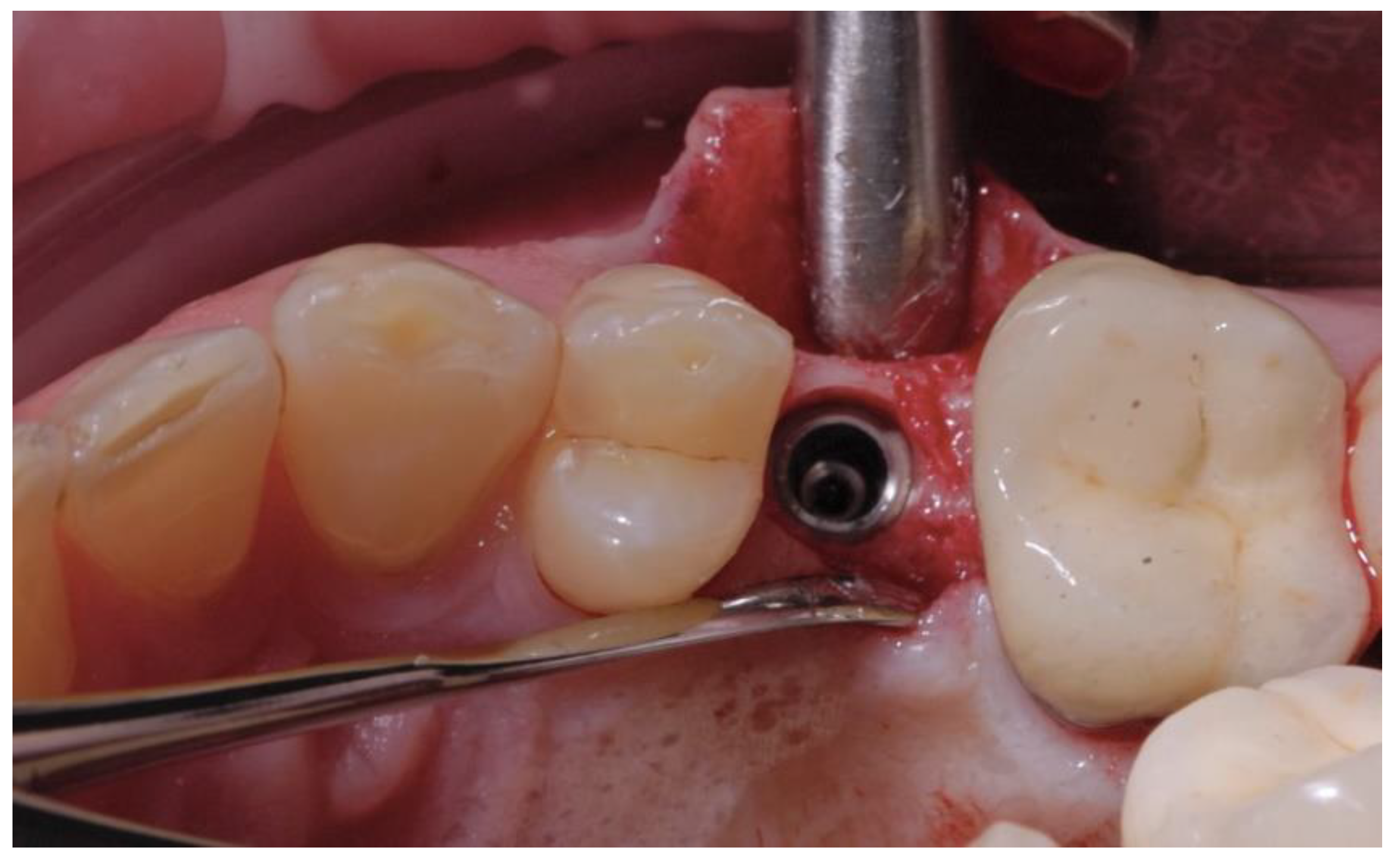
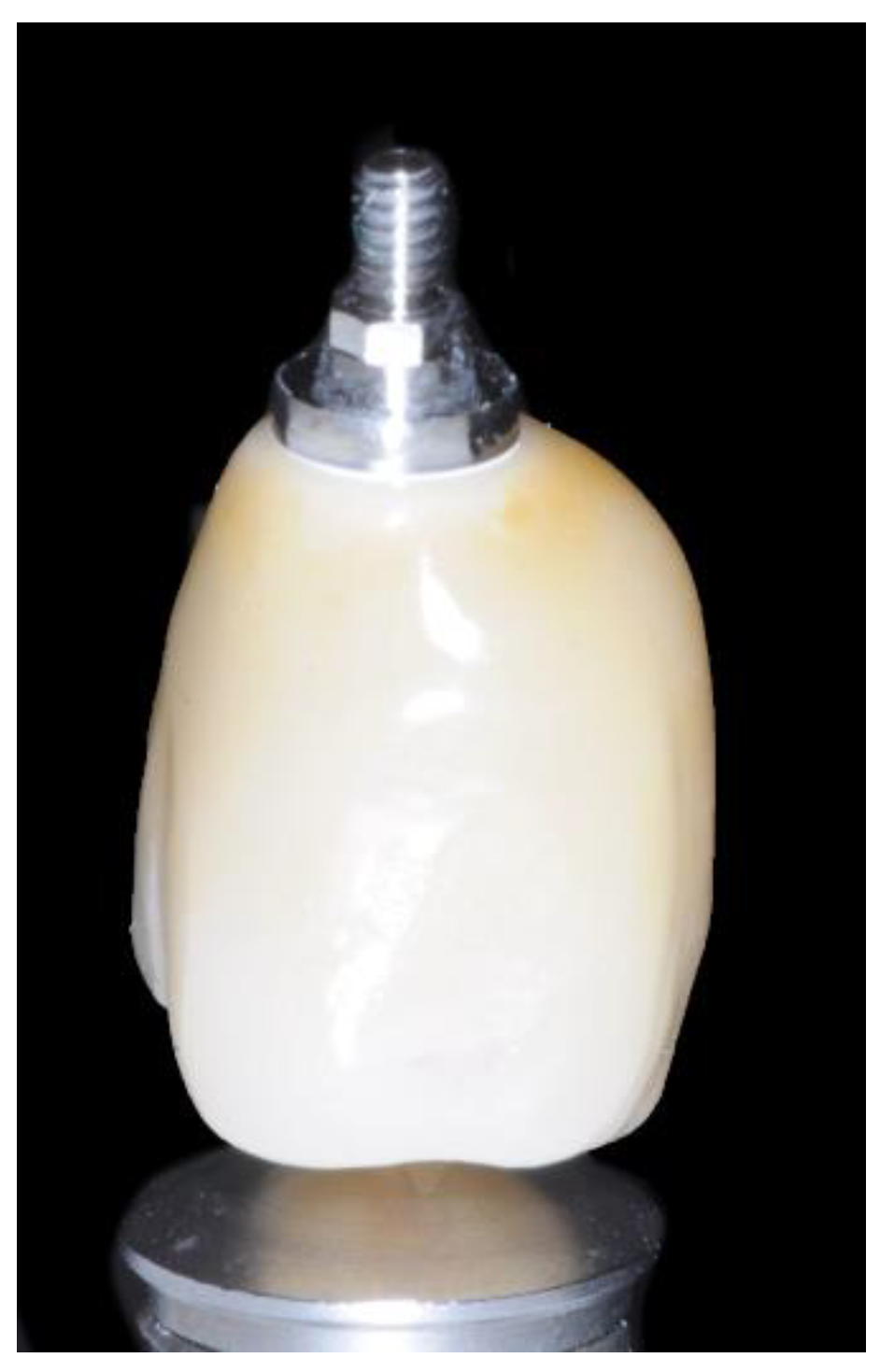
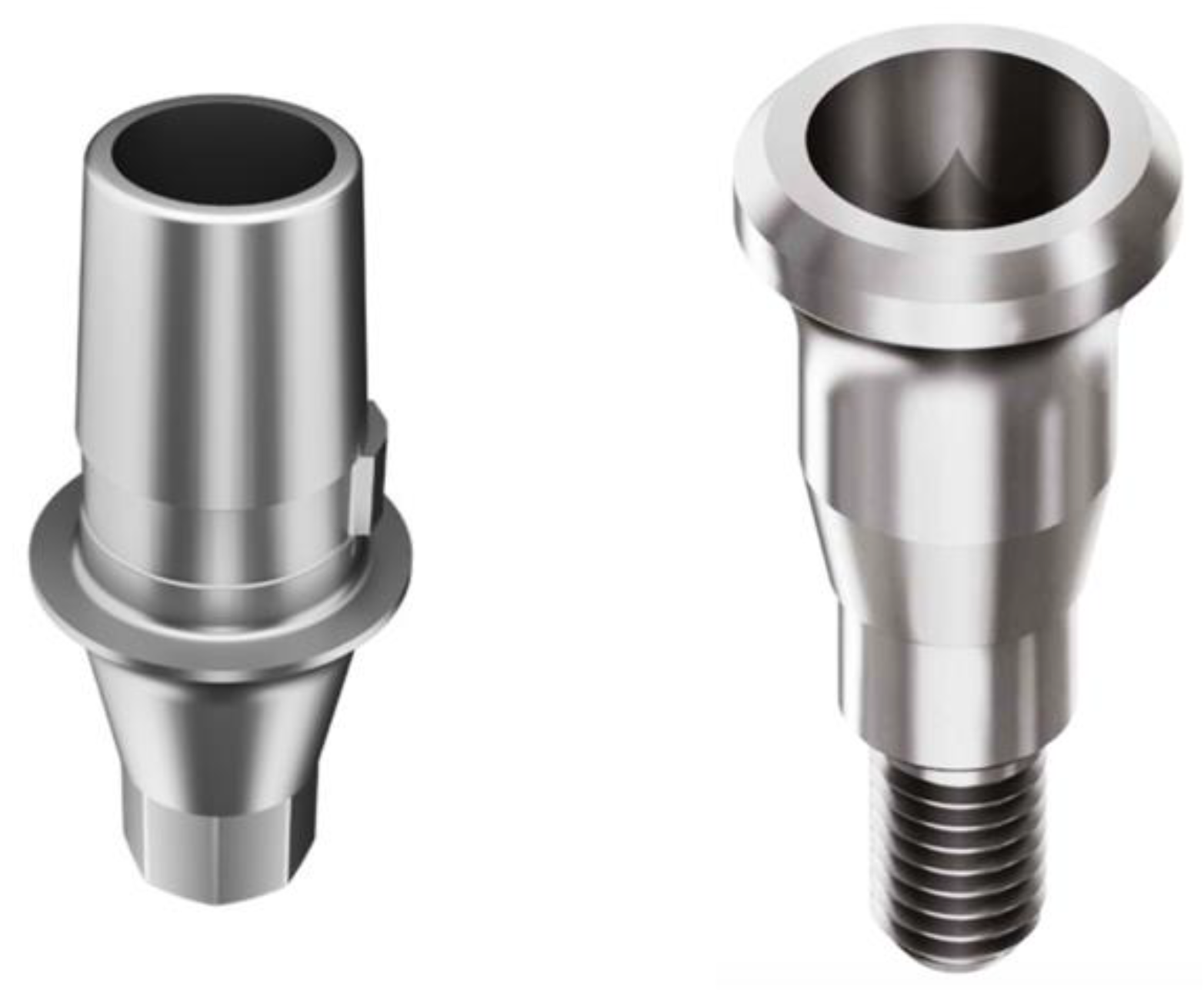
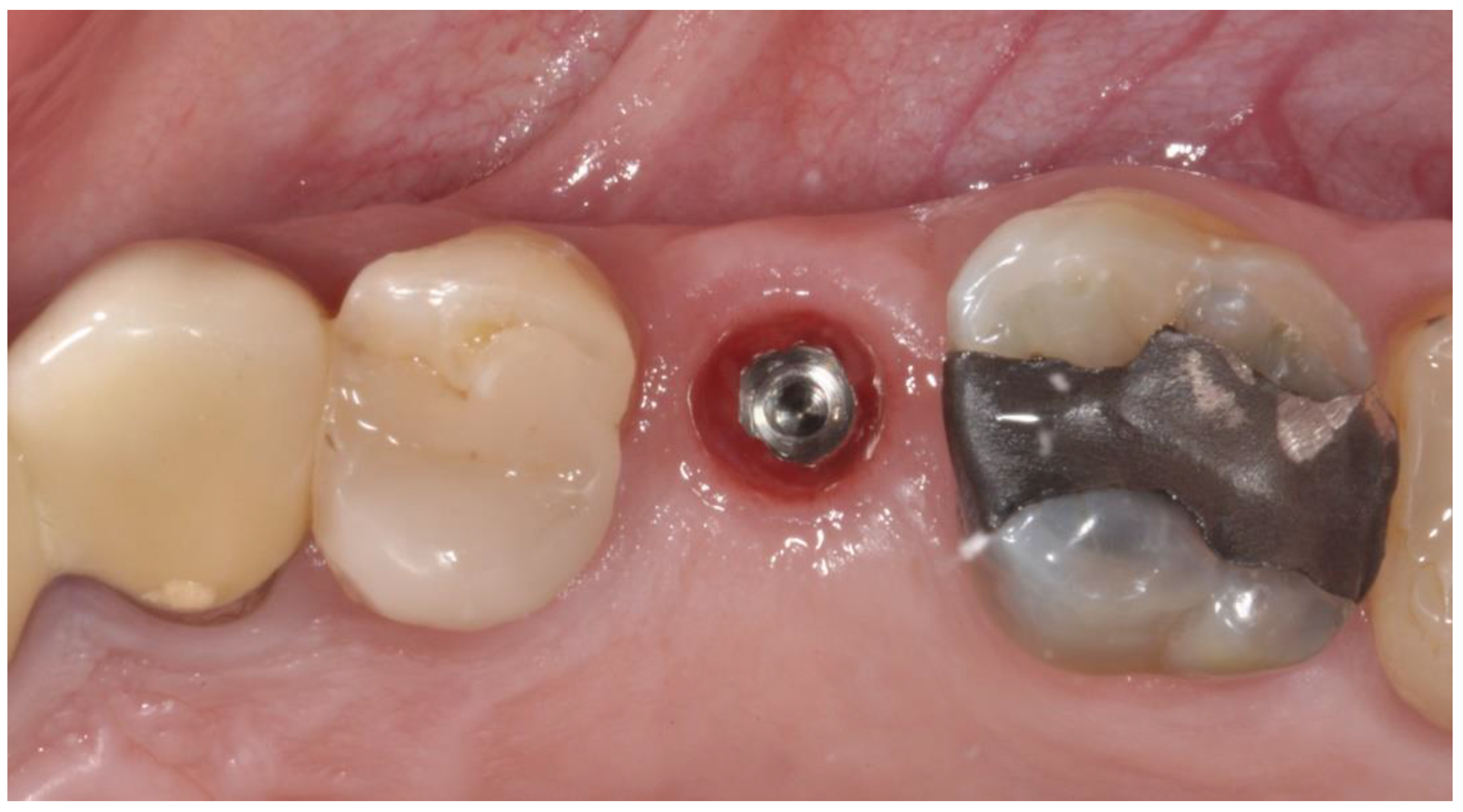
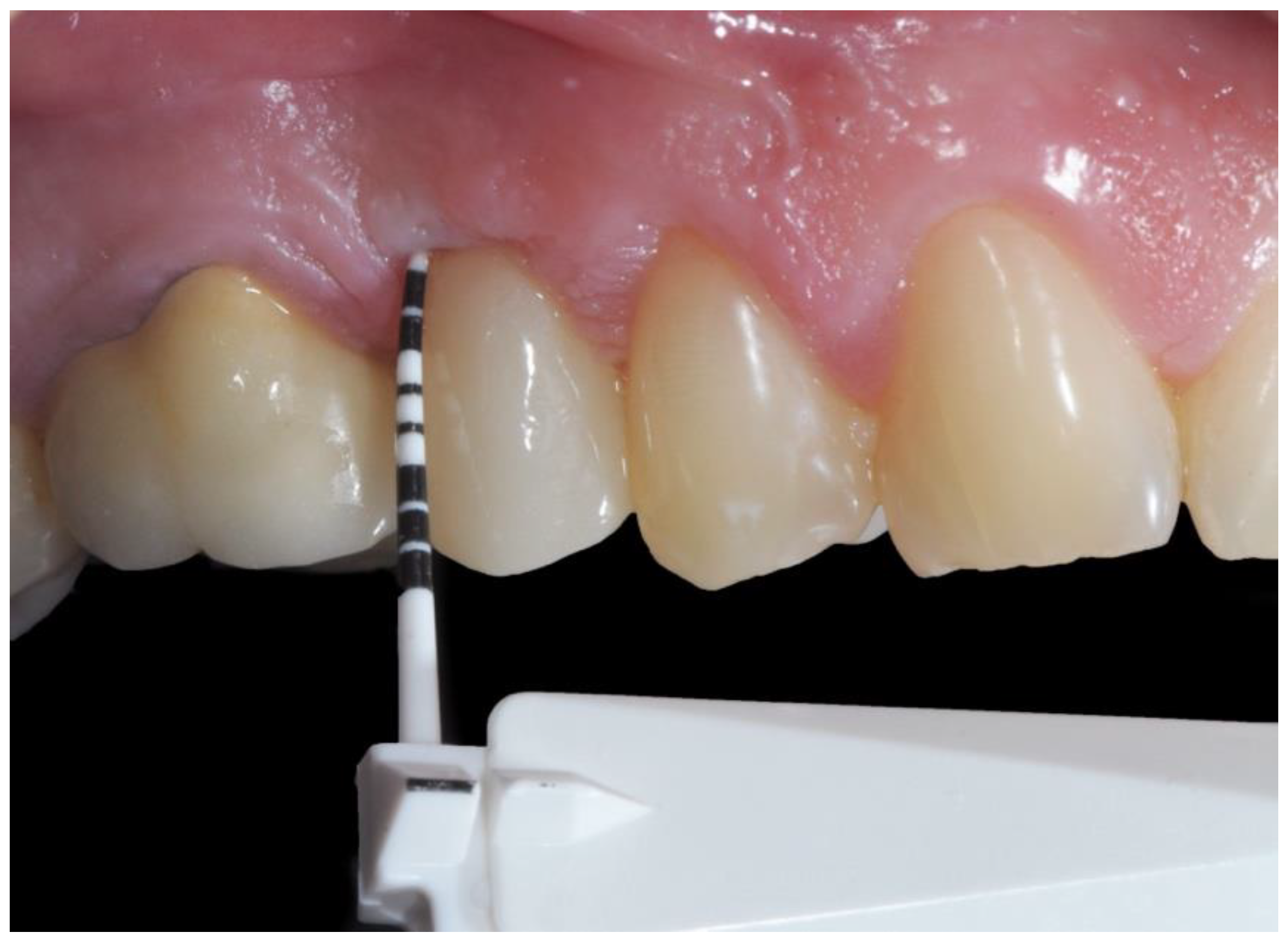
2.3. Prosthetic Protocol
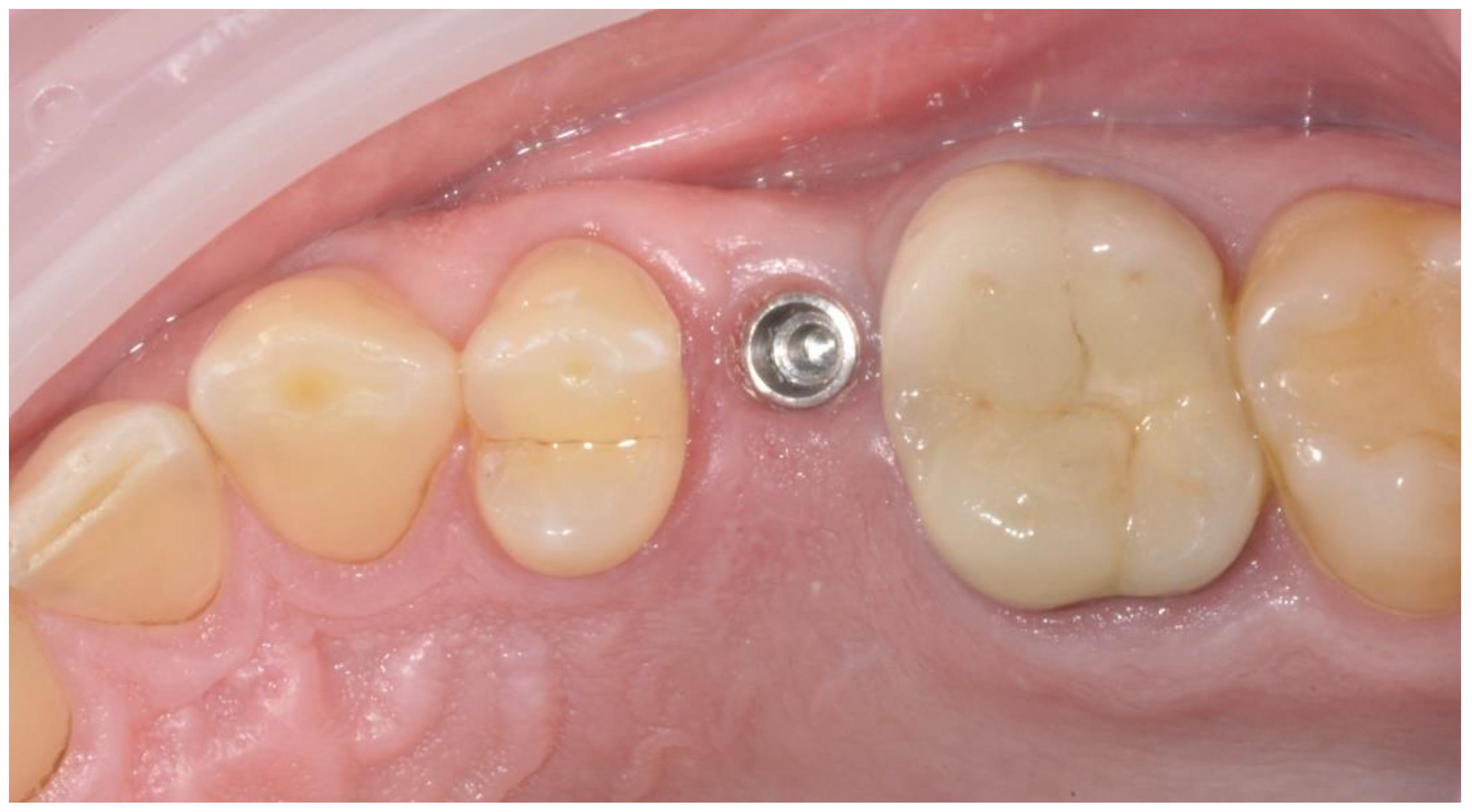
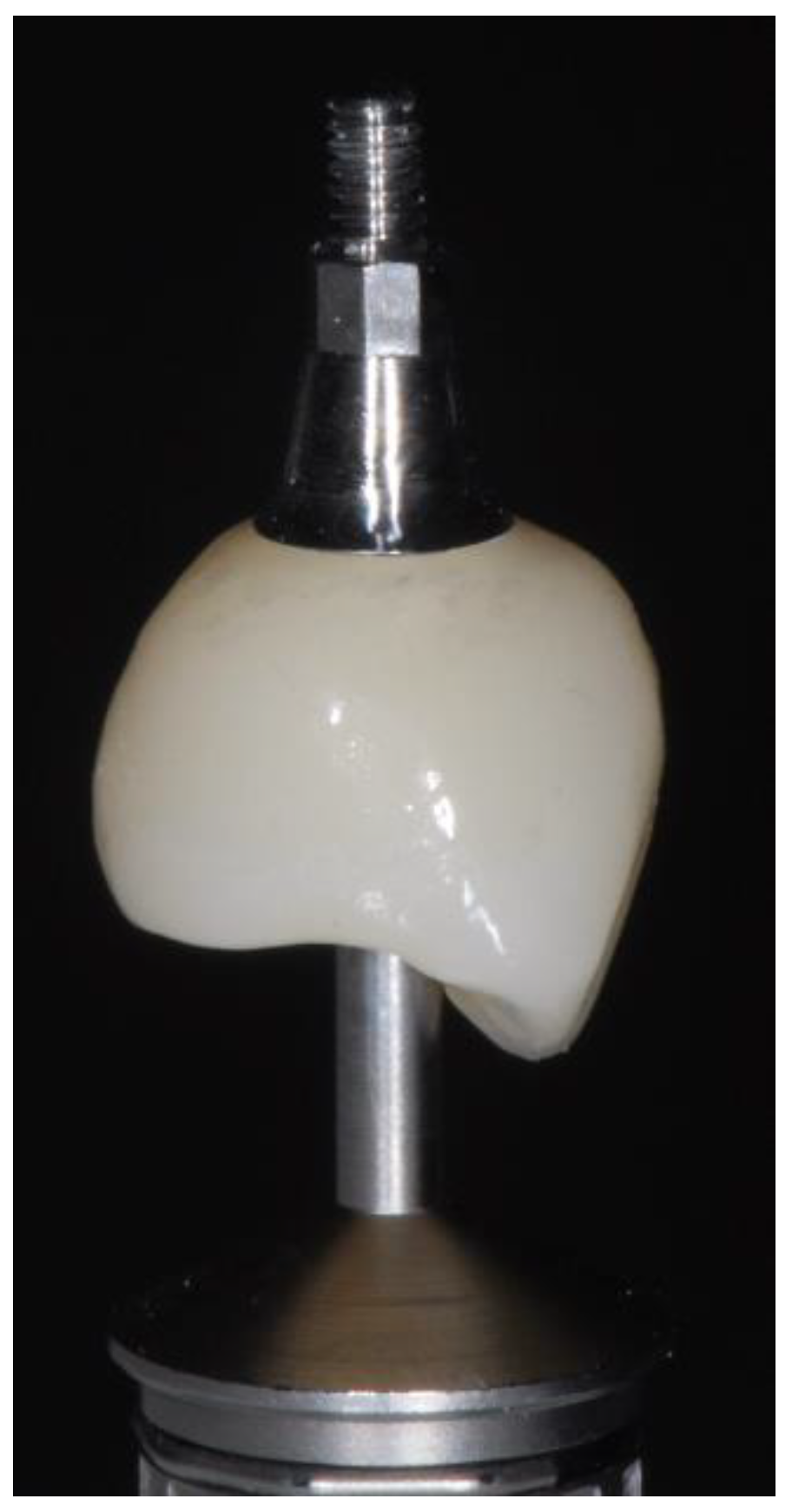


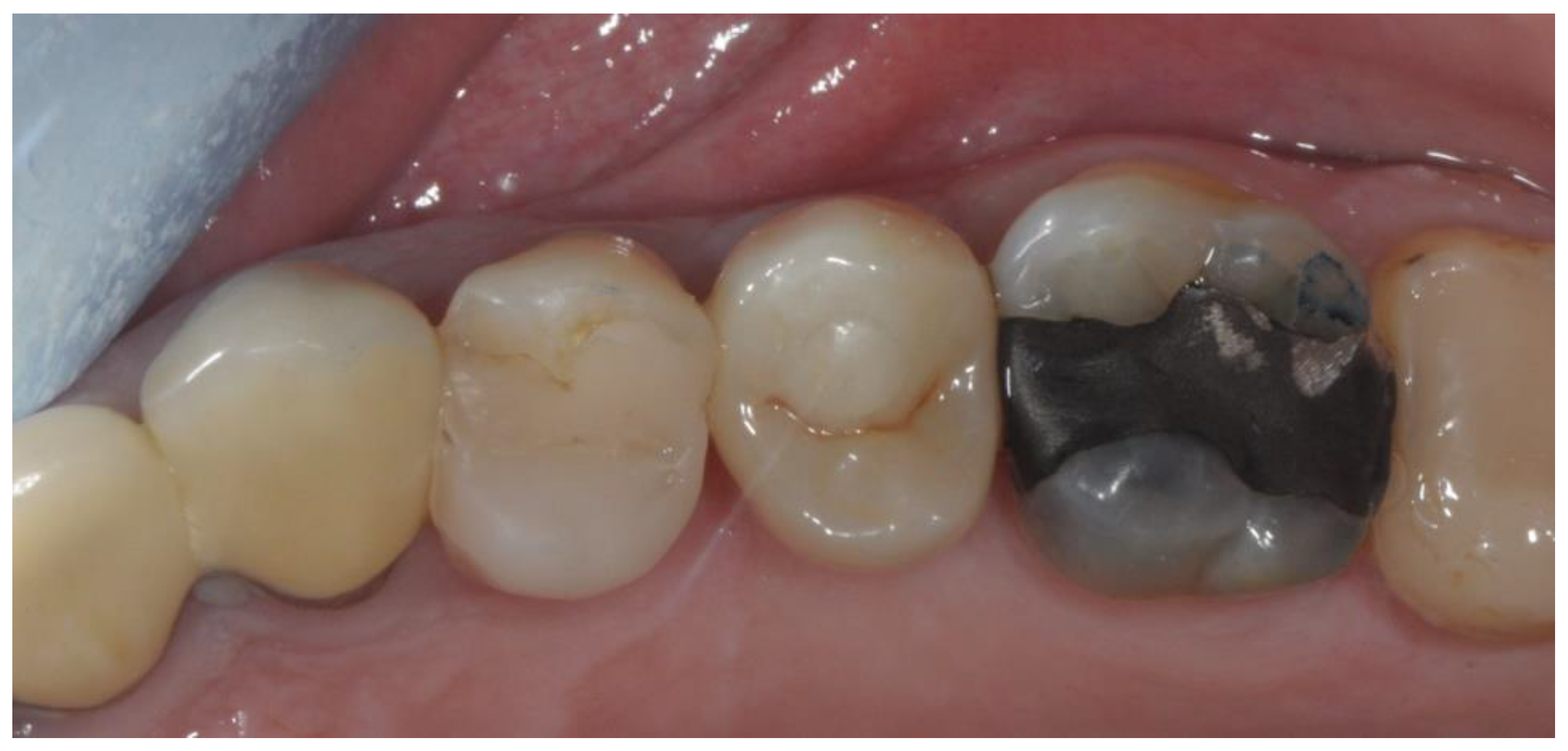
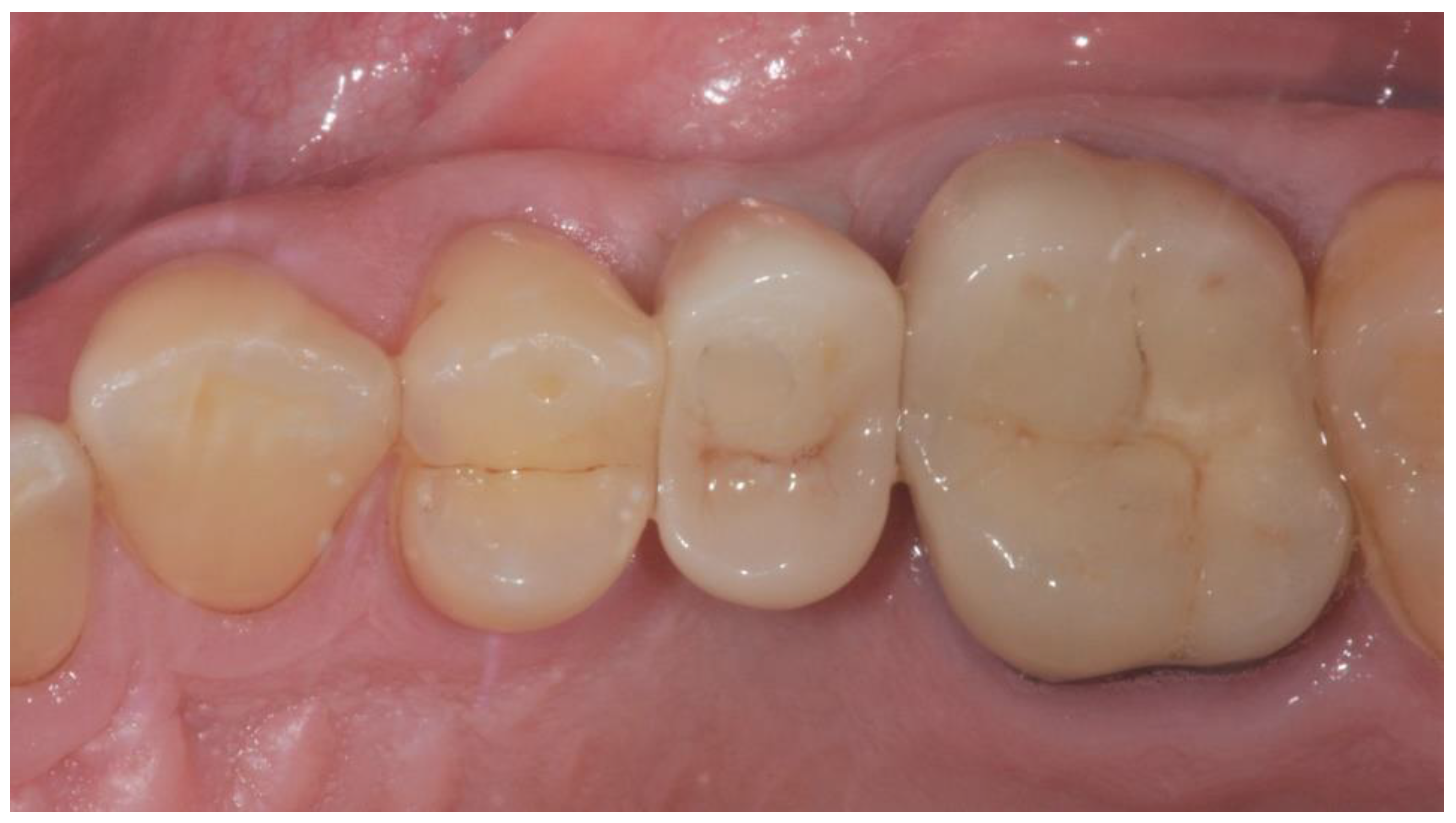
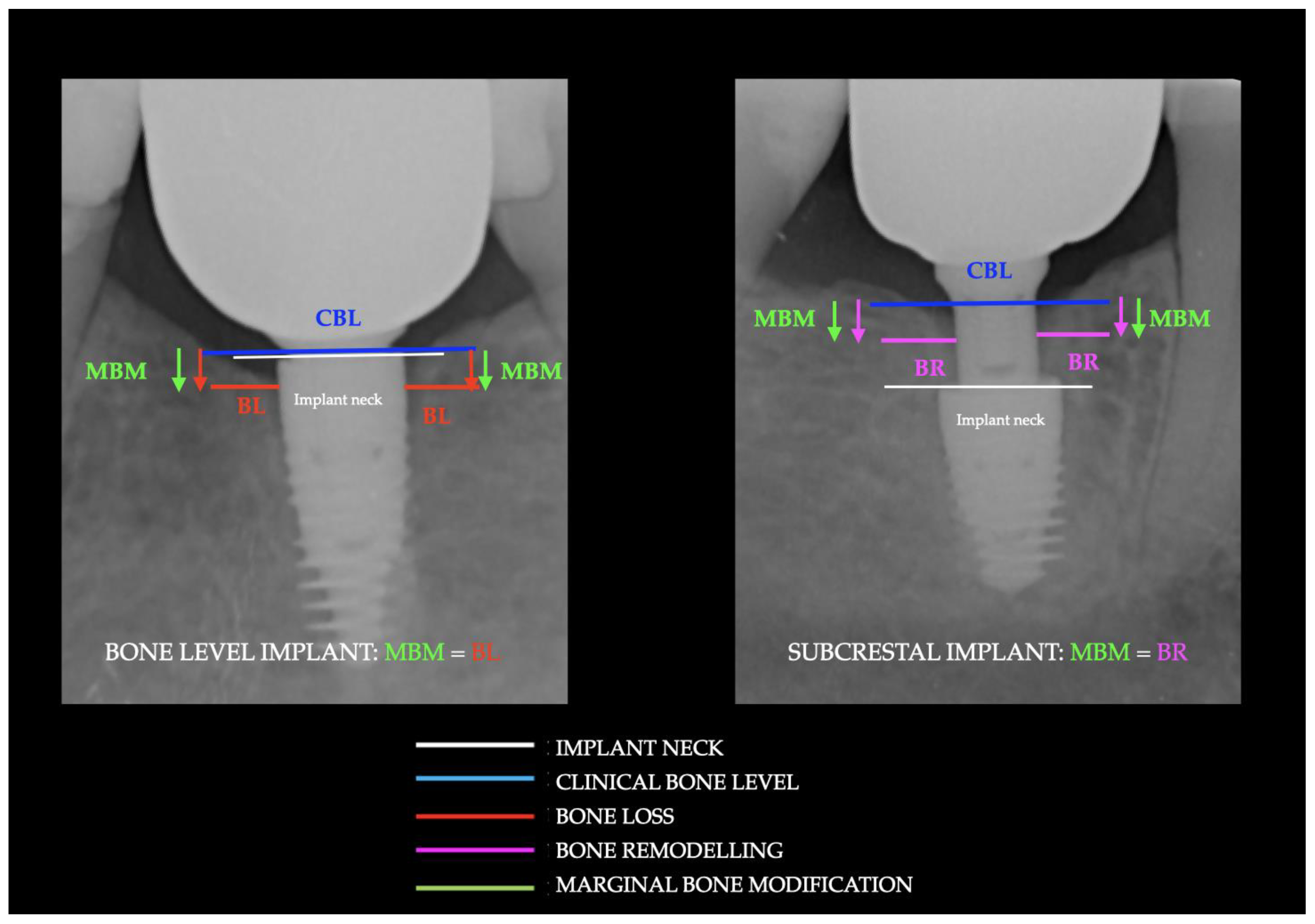
2.4. Radiographic Evaluations
2.5. Clinical Evaluations
2.6. Sample Size and Randomization
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buser, D.; Mericske-Stern, R.; Dula, K.; Lang, N.P. Clinical Experience with One-Stage, Non-Submerged Dental Implants. Adv. Dent. Res. 1999, 13, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios-Garzón, N.; Velasco-Ortega, E.; López-López, J. Bone Loss in Implants Placed at Subcrestal and Crestal Level: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Materials 2019, 12, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; He, L.; Wang, H.C. Clinical and Radiographic Performance of One-Piece and Two-Piece Implant: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2021, 65, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candotto, V.; Gabrione, F.; Oberti, L.; Lento, D.; Severino, M. The Role of Implant-Abutment Connection in preventing Bacterial Leakage: A Review. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2019, 3, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Annibali, S.; Bignozzi, I.; Cristalli, M.P.; Graziani, F.; La Monaca, G.; Polimeni, A. Peri-Implant Marginal Bone Level: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies Comparing Platform Switching versus Conventionally Restored Implants. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2012, 39, 1097–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, D.L.; Mau, L.P.; Higginbottom, F.L.; Wilson, T.G.; Bosshardt, D.D.; Schoolfield, J.; Jones, A.A. Soft and Hard Tissue Histologic Dimensions Around Dental Implants in the Canine Restored with Smaller-Diameter Abutments: A Paradigm Shift in Peri-Implant Biology. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2013, 28, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Windael, S.; Collaert, B.; De Buyser, S.; De Bruyn, H.; Vervaeke, S. Early Peri-Implant Bone Loss as a Predictor for Peri-Implantitis: A 10-Year Prospective Cohort Study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2021, 23, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann, J.S.; Buser, D.; Schenk, R.K.; Cochran, D.L. Crestal Bone Changes Around Titanium Implants. A Histometric Evaluation of Unloaded Non-Submerged and Submerged Implants in the Canine Mandible. J. Periodontol. 2001, 71, 1412–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.; Yoon, J.; Misch, C.E.; Wang, H. The Causes of Early Implant Bone Loss: Myth or Science? J. Periodontol. 2002, 73, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarakis, N.; Bashutski, J.; Wang, H.L.; Oh, T.J. Early Implant Bone Loss: Preventable or Inevitable? Implant. Dent. 2012, 21, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.E.; Zarb, G.A. Criteria for Success of Osseointegrated Endosseous Implants. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1989, 62, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Chrcanovic, B.; Östman, P.O.; Sennerby, L. Initial and Long-Term Crestal Bone Responses to Modern Dental Implants. Periodontology 2000, 73, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vervaeke, S.; Matthys, C.; Nassar, R.; Christiaens, V.; Cosyn, J.; De Bruyn, H. Adapting the Vertical Position of Implants with a Conical Connection in Relation to Soft Tissue Thickness Prevents Early Implant Surface Exposure: A 2-Year Prospective Intra-Subject Comparison. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacchi, C.; Lamazza, L.; Rapani, A.; Troiano, G.; Messina, M.; Antonelli, A.; Giudice, A.; Lombardi, T. Marginal Bone Changes around Platform-Switched Conical Connection Implants Placed 1 or 2 Mm Subcrestally: A Multicenter Crossover Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2023, 25, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinato, S.; Bernardello, F.; Lombardi, T.; Soardi, C.M.; Messina, M.; Zaffe, D.; Stacchi, C. Influence of Apico-Coronal Positioning of Tissue-Level Implants on Marginal Bone Stability during Supracrestal Tissue Height Establishment: A Multi-Center Prospective Study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2022, 24, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vervaeke, S.; Dierens, M.; Besseler, J.; De Bruyn, H. The Influence of Initial Soft Tissue Thickness on Peri-Implant Bone Remodeling. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Amri, M.D. Crestal bone loss around submerged and nonsubmerged dental implants: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanos, G.E.; Aydin, E.; Gaertner, K.; Nentwig, G.H. Long-Term Results after Subcrestal or Crestal Placement of Delayed Loaded Implants. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkevicius, T.; Puisys, A.; Linkevicius, R.; Alkimavicius, J.; Gineviciute, E.; Linkeviciene, L. The Influence of Submerged Healing Abutment or Subcrestal Implant Placement on Soft Tissue Thickness and Crestal Bone Stability. A 2-Year Randomized Cliniokcal Trial. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2020, 22, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Dai, R.; Cao, C.Y.; Fang, H.; Han, M.; Li, Q.L. One-Time versus Repeated Abutment Connection for Platform-Switched Implant: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatėnas, I.; Linkevičius, T. One Abutment One Time vs. Repeatable Abutment Disconnections in Implants, Restored with Cemented/Screw Retained Fi Xed Partial Dentures: Marginal Bone Level Changes. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Stomatologija 2021, 23, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grandi, T.; Guazzi, P.; Samarani, R.; Garuti, G. Immediate Positioning of Definitive Abutments versus Repeated Abutment Replacements in Immediately Loaded Implants: Effects on Bone Healing at the 1-Year Follow-up of a Multicentric Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2012, 5, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ríos-Santos, J.V.; Tello-González, G.; Lázaro-Calvo, P.; Mur, F.J.G.; Ríos-Carrasco, B.; Fernández-Palacín, A.; Herrero-Climent, M. One Abutment One Time: A Multicenter, Prospective, Controlled, Randomized Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcaterra, R.; Di Girolamo, M.; Mirisola, C.; Baggi, L. Effects of Repeated Screw Tightening on Implant Abutment Interfaces in Terms of Bacterial and Yeast Leakage in Vitro: One-Time Abutment Versus the Multiscrewing Technique. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2016, 36, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.; Pelekos, G.; Ho, D.; Cortellini, P.; Tonetti, M.S. The Depth of the Implant Mucosal Tunnel Modifies the Development and Resolution of Experimental Peri-Implant Mucositis: A Case–Control Study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canullo, L.; Penarrocha-Oltra, D.; Soldini, C.; Mazzocco, F.; Penarrocha, M.; Covani, U. Microbiological Assessment of the Implant-Abutment Interface in Different Connections: Cross-Sectional Study after 5 Years of Functional Loading. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.M.; Nogueira-Filho, G.; Tenenbaum, H.C.; Lai, J.Y.; Brito, C.; Döring, H.; Nonhoff, J. Performance of Conical Abutment (Morse Taper) Connection Implants: A Systematic Review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res.-Part A 2014, 102, 552–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetromilla, B.M.; Brondani, L.P.; Pereira-Cenci, T.; Bergoli, C.D. Influence of different implant-abutment connection designs on the mechanical and biological behavior of single-tooth implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 121, 398–403.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, D.; Nagata, M.J.H.; Bosco, A.F.; de Melo, L.G.N. Influence of Micro-gap Location and Configuration on Radiographic Bone Loss Around Submerged Implants: An Experimental Study in Dogs. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2011, 26, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weng, D.; Nagata, M.J.H.; Leite, C.M.; de Melo, L.G.N.; Bosco, A.F. Influence of Microgap Location and Configuration on Radiographic Bone Loss in Nonsubmerged Implants: An Experimental Study in Dogs. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2011, 24, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lazzara, R.J.; Porter, S.S. Platform Switching: A New Concept in Implant for Controlling Postrestorative Crestal Bone. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2006, 26, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, J.S.; Schenk, R.K.; Schoolfield, J.D. Biologic Width around One- and Two-Piece Titanium Implants A Histometric Evaluation of Unloaded Nonsubmerged and Submerged Implants in Tbe. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2001, 12, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailer, I.; Mühlemann, S.; Zwahlen, M.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Schneider, D. Cemented and Screw-Retained Implant Reconstructions: A Systematic Review of the Survival and Complication Rates. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23, 163–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.G., Jr. The Positive Relationship Between Excess Cement and Peri-Implant Disease: A Prospective Clinical Endoscopic Study. J. Periodontol. 2009, 80, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkevicius, T.; Vindasiute, E.; Puisys, A.; Peciuliene, V. The Influence of Margin Location on the Amount of Undetected Cement Excess after Delivery of Cement-Retained Implant Restorations. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitz-Mayfield, L.J.A.; Salvi, G.E.; Botticelli, D.; Mombelli, A.; Faddy, M.; Lang, N.P. Anti-Infective Treatment of Peri-Implant Mucositis: A Randomised Controlled Clinical Trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schätzle, M.; Lang, N.P.; Ånerud, Å.; Boysen, H.; Bürgin, W.; Löe, H. The Influence of Margins of Restorations on the Periodontal Tissues over 26 Years. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2001, 28, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Moreno, P.; León-Cano, A.; Ortega-Oller, I.; Monje, A.; Suárez, F.; O’Valle, F.; Spinato, S.; Catena, A. Prosthetic Abutment Height Is a Key Factor in Peri-Implant Marginal Bone Loss. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 80S–85S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mombelli, A.; Lang, N.P. Clinical Parameters for the Evaluation of Dental Implants. Periodontology 2000, 4, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombelli, L.; Farina, R.; Silva, C.O.; Tatakis, D.N. Plaque-Induced Gingivitis: Case Definition and Diagnostic Considerations. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, S44–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, T.J.; Drake, R.B.; Naylor, J.E. The Plaque Control Record. J. Periodontol. 1972, 43, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolle, C.; Gustin, M.P.; Fau, D.; Exbrayat, P.; Boivin, G.; Grosgogeat, B. Early Periimplant Tissue Healing on 1-Piece Implants with a Concave Transmucosal Design: A Histomorphometric Study in Dogs. Implant Dent. 2015, 24, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasi, C.; Tessarolo, F.; Caola, I.; Wennström, J.; Nollo, G.; Berglundh, T. Morphogenesis of Peri-Implant Mucosa Revisited: An Experimental Study in Humans. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevins, M.; Kim, D.M.; Jun, S.-H.; Guze, K.; Schupbach, P.; Nevins, M.L. Histologic Evidence of a Connective Tissue Attachment to Laser Microgrooved Abutments: A Canine Study. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2012, 30, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkevicius, T.; Puisys, A.; Steigmann, M.; Vindasiute, E.; Linkeviciene, L. Influence of Vertical Soft Tissue Thickness on Crestal Bone Changes Around Implants with Platform Switching: A Comparative Clinical Study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkevicius, T.; Apse, P.; Grybauskas, S.; Puisys, A. Reaction of Crestal Bone around Implants Depending on Mucosal Tissue Thickness. A 1-Year Prospective Clinical Study. Stomatologija 2009, 11, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heitz-Mayfield, L.J.A.; Salvi, G.E. Peri-Implant Mucositis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, S237–S245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitz-Mayfield, L.J.A.; Heitz, F.; Lang, N.P. Implant Disease Risk Assessment IDRA—A Tool for Preventing Peri-Implant Disease. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2020, 31, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutouzis, T.; Gholami, F.; Reynolds, J.; Lundgren, T.; Kotsakis, G. Abutment Disconnection/Reconnection Affects Peri-Implant Marginal Bone Levels: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2017, 32, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, A.; Sanz-Sánchez, I.; Martín, C.; Blanco, J.; Sanz, M. The Effect of One-Time Abutment Placement on Interproximal Bone Levels and Peri-Implant Soft Tissues: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel De Carvalho Barbara, J.; Luz, D.; Vianna, K.; Porto Barboza, E. The Influence of Abutment Disconnections on Peri-Implant Marginal Bone: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Implantol. 2019, 12, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Praça, L.d.F.G.; Teixeira, R.C.; Rego, R.O. Influence of Abutment Disconnection on Peri-Implant Marginal Bone Loss: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2020, 31, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutouzis, T.; Koutouzis, G.; Gadella, H.; Neiva, R. The Effect of Healing Abutment Reconnection and Disconnection on Soft and Hard Peri-Implant Tissues: A Short-Term Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2013, 28, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, R.E.; Zembic, A.; Pjetursson, B.E.; Zwahlen, M.; Thoma, D.S. Systematic review of the survival rate and the incidence of biological, technical, and aesthetic complications of single crowns on implants reported in longitudinal studies with a mean follow-up of 5 years. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23 (Suppl. S6), 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkevicius, T.; Linkevicius, R.; Gineviciute, E.; Alkimavicius, J.; Mazeikiene, A.; Linkeviciene, L. The Influence of New Immediate Tissue Level Abutment on Crestal Bone Stability of Subcrestally Placed Implants: A 1-Year Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2021, 23, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Factor | Effect on Bone Levels | Influence of Soft Tissues Biotype | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subcrestal vs. Bone level implants | Average <1 mm of bone loss for both placements | In the presence of thin, soft tissues, subcrestal placement should be preferred. | Palacios-Garzón et al., 2019 [2] |
| Comparable bone loss: mean mesial (m) bone loss was 1.41 (±1.65 mm) and 1.84 (±1.49 mm) for subcrestal and bone level, respectively, and mean distal (d) bone loss was 1.34 (±1.60 mm) and 1.73 (±1.31 mm). | Romanos et al., 2015 [18] | ||
| Subcrestal implants show better bone levels in case of thin, soft tissues. | Vervaeke et al., 2018 [13] | ||
| Implants placed 1 or 2 mm subcrestally show comparable bone remodeling (0.49 ± 0.32 mm and 0.46 ± 0.35 mm, respectively) | Stacchi et al., 2023 [14] | ||
| Deeper subcrestal placement is advised in thin biotypes, as they exhibit higher mean marginal bone loss. | Spinato et al., 2022 [15] | ||
| Conical vs. flat connection | Less bone loss observed around conical connection implants in both human and animal models | Better soft tissue esthetics with internal hexagon. | Schmitt et al., 2014 [27] Vetromilla et al., 2019 [28] Weng et al., 2011 [29] Weng et al., 2011 [30] |
| Platform switching vs. platform matching | Less marginal bone loss observed for platform-switched implants, especially in case of larger mismatch | Annibali et al., 2012 [5] | |
| One-time abutment (OTA) vs. repeated abutment removal | Implants restored with an OTA show less vertical bone change | Implants restored with an OTA show fewer soft tissues-level changes. | Wang et al., 2017 [20] |
| No difference in peri-implant bone loss observed | Ríos-Santos et al., 2020 [23] |
| Demographic Characteristics | Total N (%) | Control Group BLG N (%) ** | Test Group SCG N (%) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subjects enrolled | 38 (100%) | 19 (50%) | 19 (50%) |
| Drop Out | 2 (5.3%) | 1 (50%) | 1 (50%) |
| Age (mean) | 49.4 (23–72) | 47.3 (23–69) | 51.5 (33–72) |
| Sex | F: 22 (62%) M: 14 (38.9%) | F: 13 (72.2%) M: 5 (27.8%) | F: 9 (50%) M: 9 (50%) |
| Smokers | 6 (16.7%) | 4 (22.2%) | 2 (11.1%) |
| Sites | Total N (%) | Control Group BLG N (%) ** | Test Group SCG N (%) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dental arch | Upper: 12 (33.3%) Lower: 24 (66.7%) | Upper: 7 (38.9%) Lower: 11 (61%) | Upper: 5 (33.3%) Lower: 13 (66.7%) |
| Site | Premolar: 15 (41.7%) Molar: 21 (53.8%) | Premolar: 9 (50%) Molar: 9 (50%) | Premolar: 15 (41.7%) Molar: 21 (53.8%) |
| STH § (mm) | 1: 0 (0%) 2: 12 (33.3%) 3: 21 (58.4%) 4: 3 (8.3%) | 1: 0 (0%) 2: 4 (22.2%) 3: 13 (72.2%) 4: 1 (5.6%)) | 1: 0 (0%) 2: 8 (44.4%) 3: 8 (44.4%) 4: 2 (11.2%) |
| Implant (Diameter × Length) | 3.6 × 9: 23 (63.9%) 4.3 × 7.5: 13 (36.1%) | 3.6 × 9: 15 (83.3%) 4.3 × 7.5: 3 (16.7%) | 3.6 × 9: 8 (44.4%) 4.3 × 7.5: 10 (55.6%) |
| Bone Density (Misch Classification) | D1: 0 (0%) D2: 4 (11%) D3: 25 (69.4%) D4: 7 (19.4%) | D1: 0 (0%) D2: 3 (16.7%) D3: 14 (77.8%) D4: 1 (5.6%) | D1: 0 (0%) D2: 1 (5.6%) D3: 11 (61.1%) D4: 6 (33.3%) |
| Healing Abutment (mm) control group | 3.5: 6 (33.3%) 4.5: 12 (66.7%) | ||
| GFA § (mm) test group | 3.5: 7 (38.9%) 4.5: 9 (50%) 5.5: 2 (11.1%) |
| Time Points | MBM Control Group Δ (CI 95%) ** | p-Value | Bone Loss Control Group Δ (CI 95%) ** | MBM Test Group Δ (CI 95%) * | p-Value | Bone Loss Test Group Δ (CI 95%) ** | MBM Test vs. Control Δ (CI 95%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1–T0 | −0.44 (−0.67; −0.21) | <0.01 | −0.44 (−0.67; −0.21) | −0.65 (−0.89; −0.42) | <0.01 | 0 | −0.21 (−0.54; 0.11) | 0.195 |
| T2–T0 | −0.49 (−0.72; −0.26) | <0.01 | −0.49 (−0.72; −0.26) | −0.72 (−0.95; −0.49) | <0.01 | 0 | −0.23 (−0.55; 0.10) | 0.168 |
| T3–T0 | −0.52 (−0.75; −0.29) | <0.01 | −0.52 (−0.75; −0.29) | −0.60 (−0.83; −0.36) | <0.01 | 0 | −0.07 (−0.40; 0.25) | 0.657 |
| Clinical Parameter | Control Group ** | Test Group * | TEST vs. Control | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 Months | 1 Year | 1 Year vs. 6 Months | 6 Months | 1 Year | 1 Year vs. 6 Months | 6 Months | 1 Year | |
| PPD (mm) (CI 95%) | 3.18 (2.76; 3.60) | 3.04 (2.64; 3.45) | 0.04 (−0.72; 0.45) p = 0.641 | 2.33 (2.03; 2.63) | 2.38 (2.13; 2.62) | 0.04 (−0.35; 0.43) p = 0.834 | −0.85 (−1.36; −0.33) p = 0.001 | −0.67 (−1.14; −0.19) p = 0.006 |
| BOP (%) (CI 95%) | 55.56 (43.90; 70.31) | 43.06 (33.54; 55.27) | 0.78 (0.56; 1.08) [p = 0.134] | 36.11 (24.51; 53.21) | 50.00 (36.40; 68.68) | 1.38 (0.86; 2.23) [p = 0.180] | 0.65 (0.41; 1.02) [p = 0.0627] | 1.16 (0.78; 1.74) [p = 0.4681] |
| PI (%) (CI 95%) | 12.50 (4.90; 31.89) | 19.44 (10.54; 35.86) | 1.56 (0.49; 4.89) [p = 0.44979] | 11.11 (5.03; 24.53) | 33.33 (21.00; 52.91) | 3.00 (1.33; 6.79) [p = 0.00837] | 0.89 (0.26; 3.03) [p = 0.851] | 1.71 (0.80; 3.69) [p = 0.168] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mensi, M.; Scotti, E.; Calza, S.; Salgarello, S.; Sordillo, A.; Zola, M.; Lops, D. Subcrestal versus Bone-Level One-Stage Implants: Early Bone and Soft Tissues Modification: One-Year Randomized Clinical Trial. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8756. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14198756
Mensi M, Scotti E, Calza S, Salgarello S, Sordillo A, Zola M, Lops D. Subcrestal versus Bone-Level One-Stage Implants: Early Bone and Soft Tissues Modification: One-Year Randomized Clinical Trial. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(19):8756. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14198756
Chicago/Turabian StyleMensi, Magda, Eleonora Scotti, Stefano Calza, Stefano Salgarello, Annamaria Sordillo, Matteo Zola, and Diego Lops. 2024. "Subcrestal versus Bone-Level One-Stage Implants: Early Bone and Soft Tissues Modification: One-Year Randomized Clinical Trial" Applied Sciences 14, no. 19: 8756. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14198756
APA StyleMensi, M., Scotti, E., Calza, S., Salgarello, S., Sordillo, A., Zola, M., & Lops, D. (2024). Subcrestal versus Bone-Level One-Stage Implants: Early Bone and Soft Tissues Modification: One-Year Randomized Clinical Trial. Applied Sciences, 14(19), 8756. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14198756











