Stress Evolution and Rock Burst Prevention in Triangle Coal Pillars under the Influence of Penetrating Faults: A Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
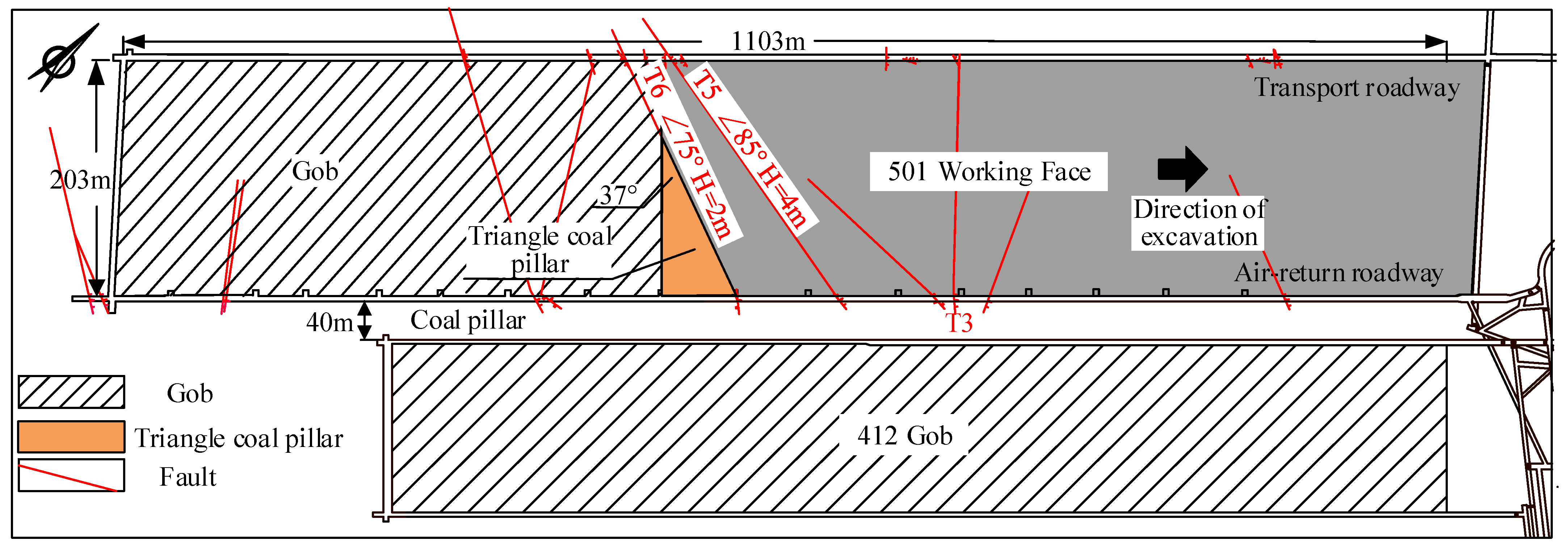
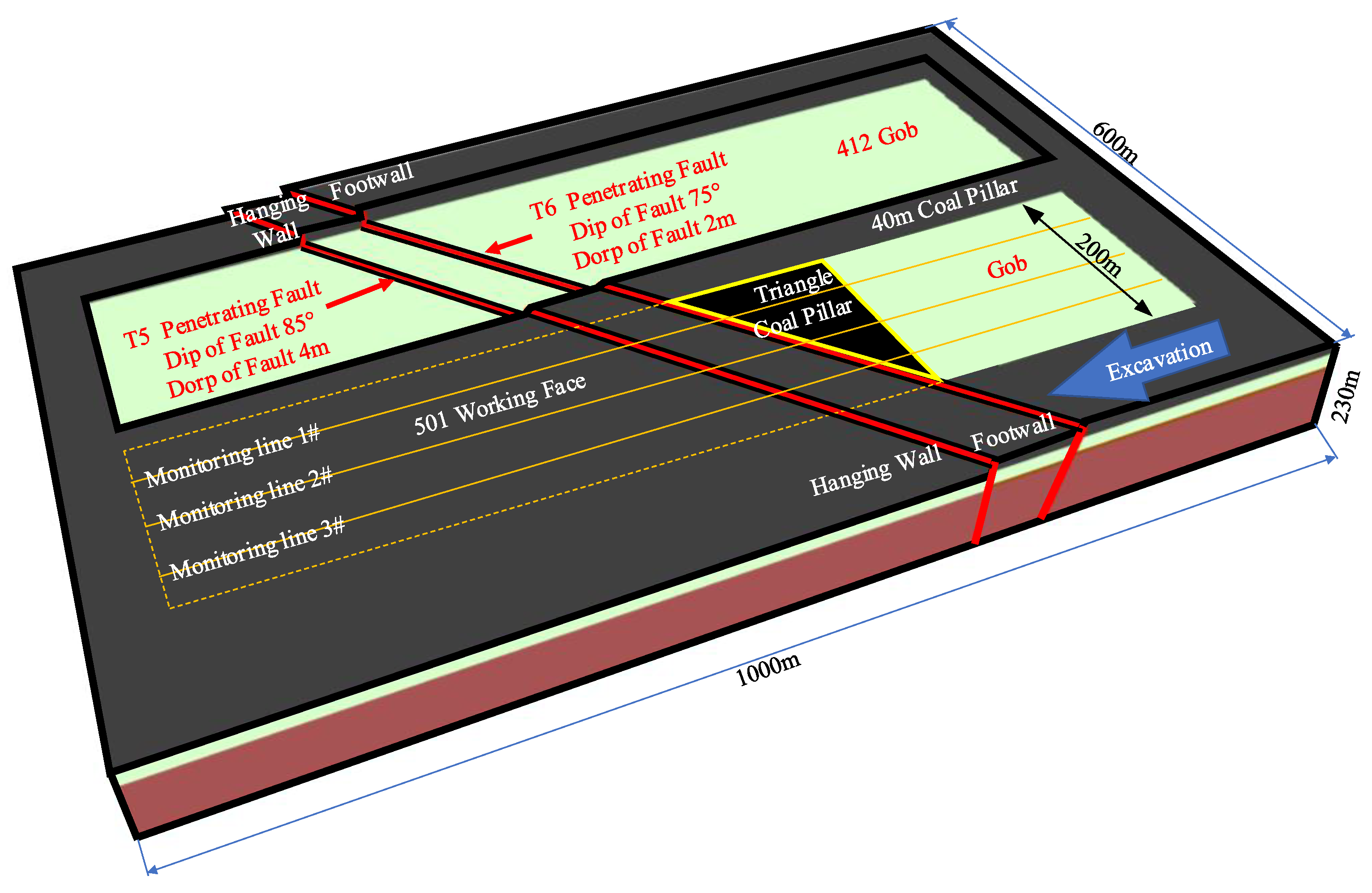
2. Engineering Background
3. Rock Burst Mechanism of Triangle Coal Pillar with Penetrating Fault
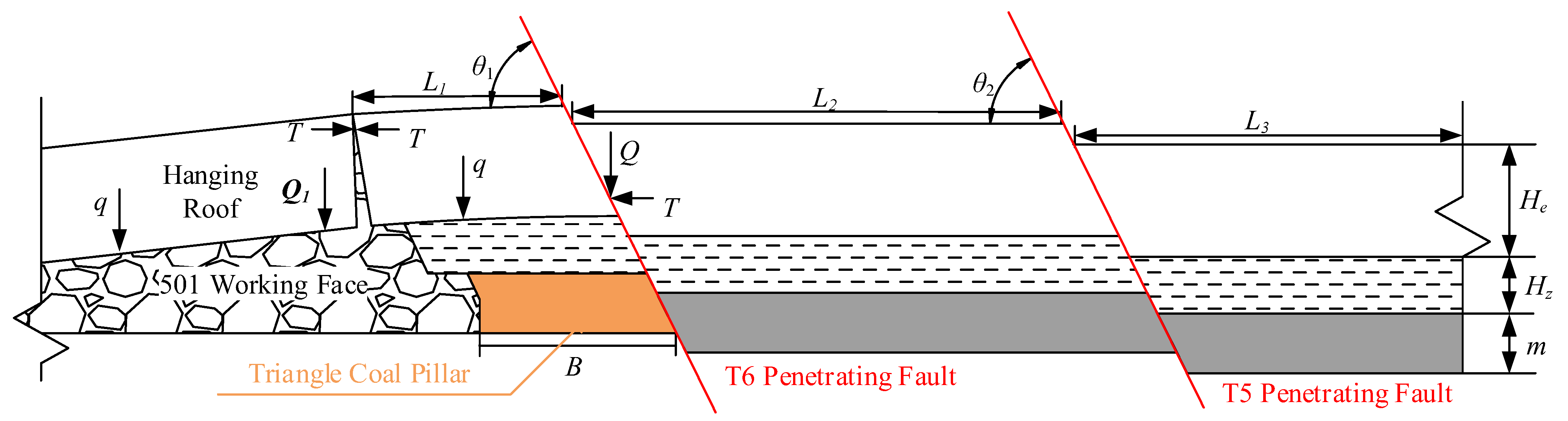
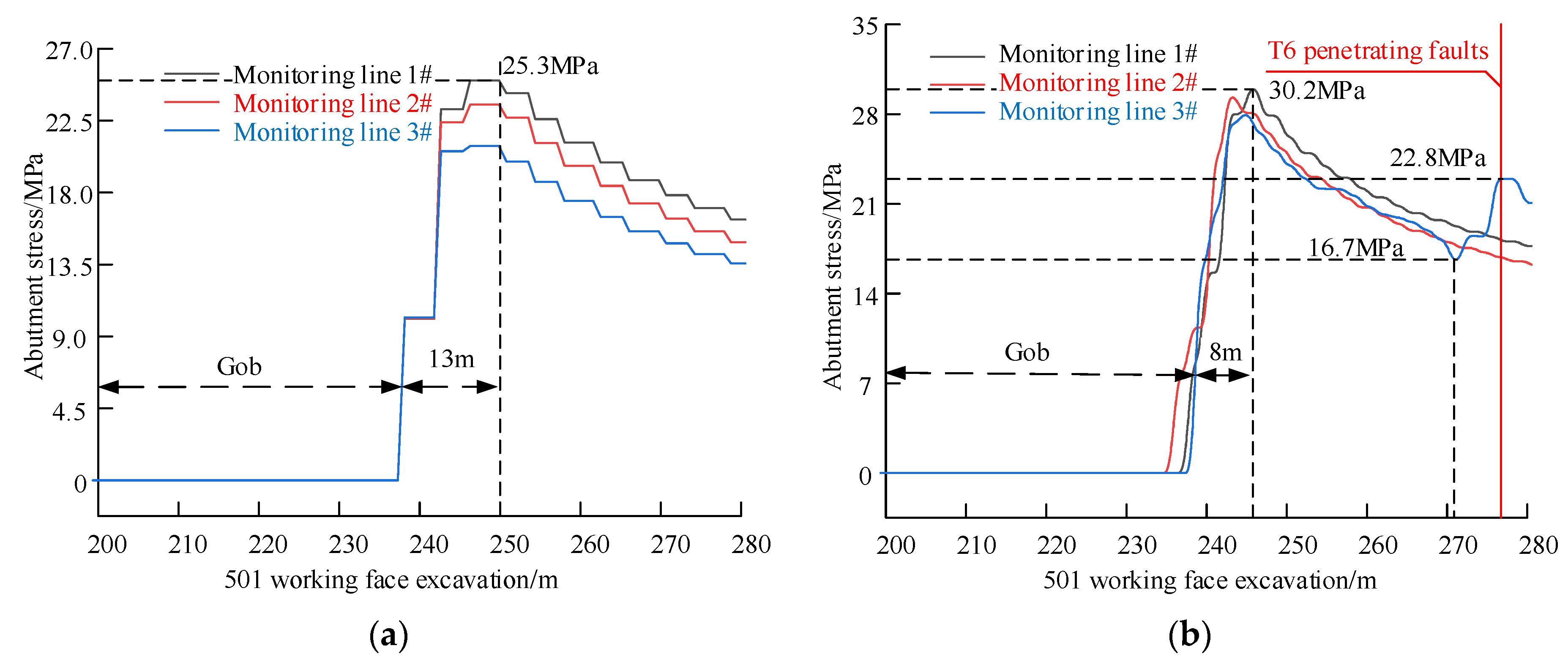
Abutment Stress Characteristics of Triangle Coal Pillar with Penetrating Fault
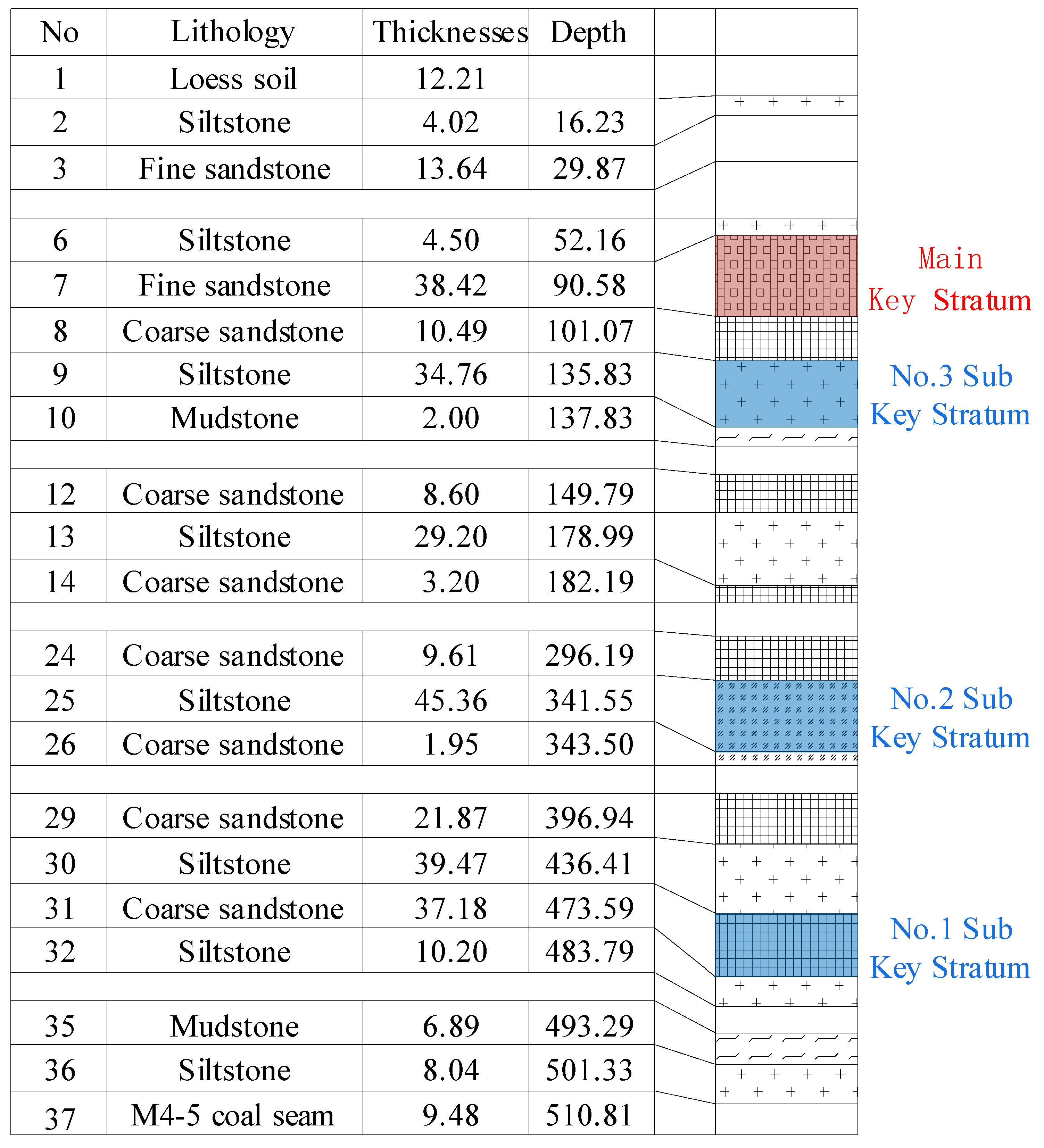
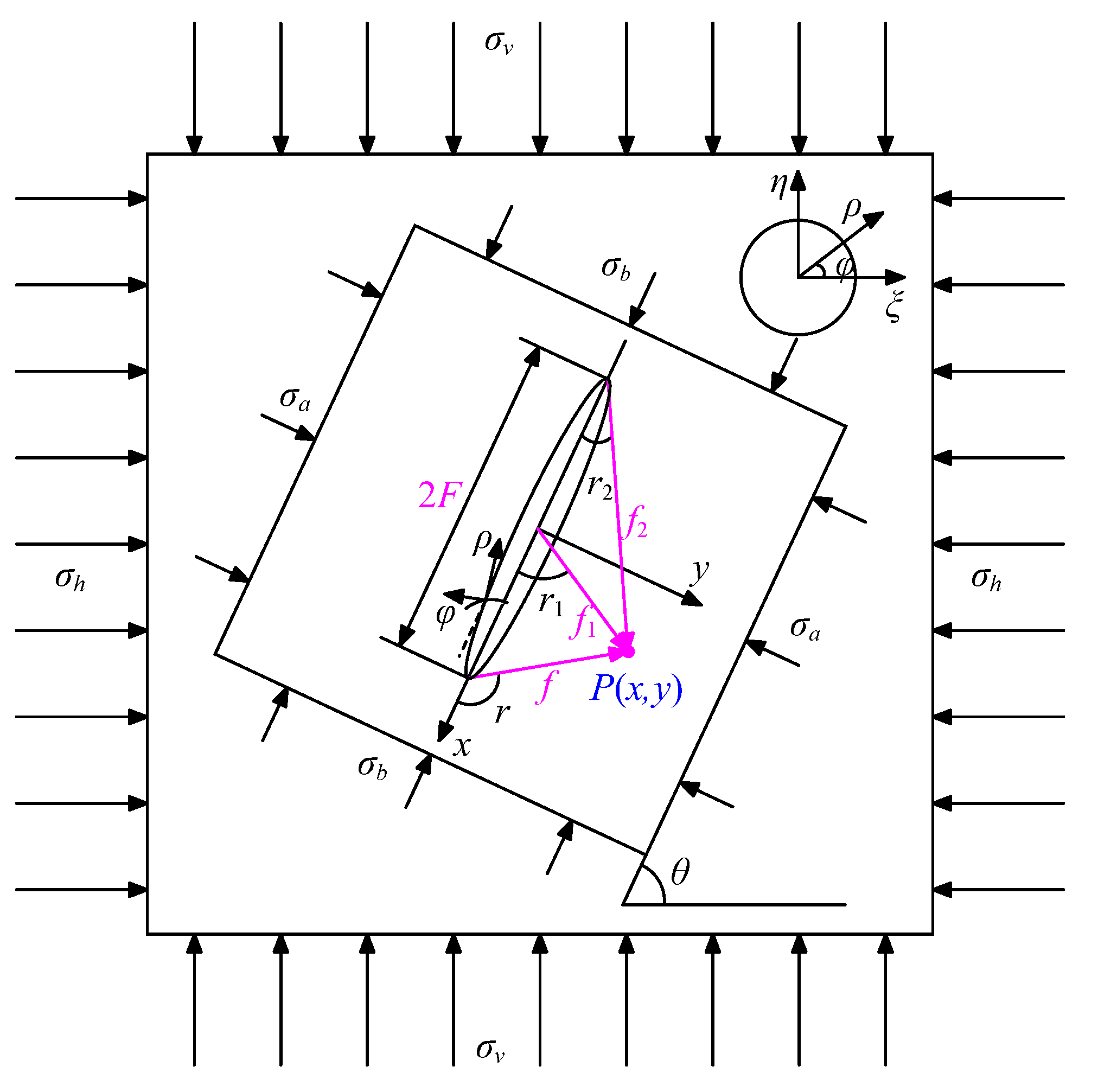
4. Tectonic Stress Characteristics of Triangle Coal Pillar with Penetrating Fault
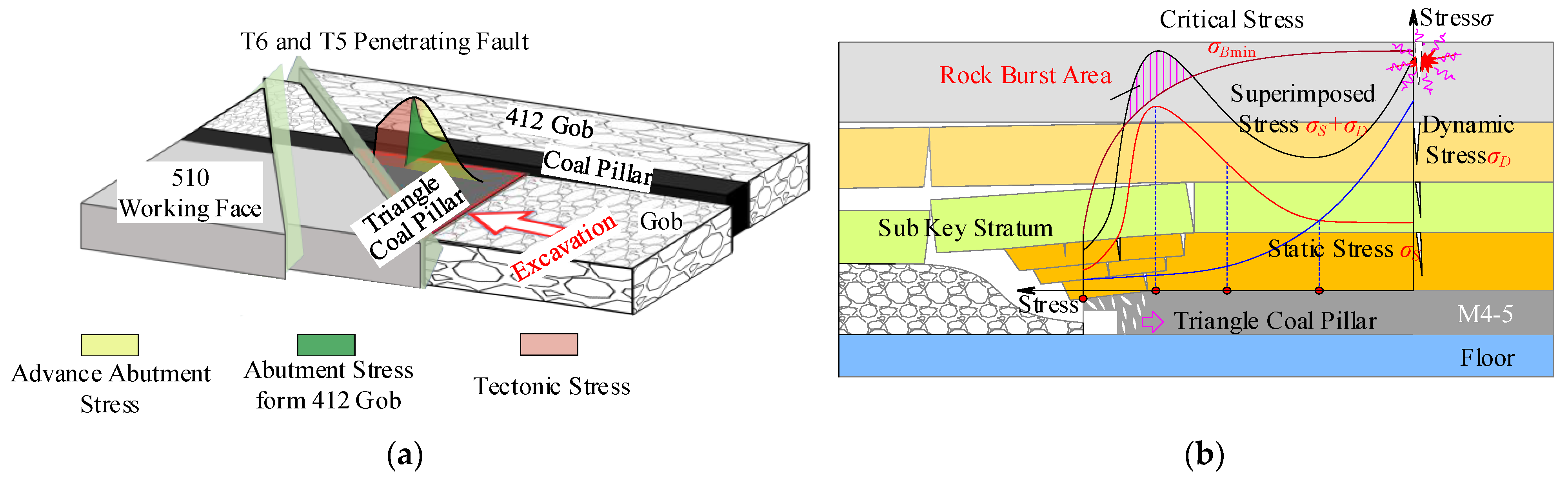
5. Rock Burst Mechanism of Triangle Coal Pillar
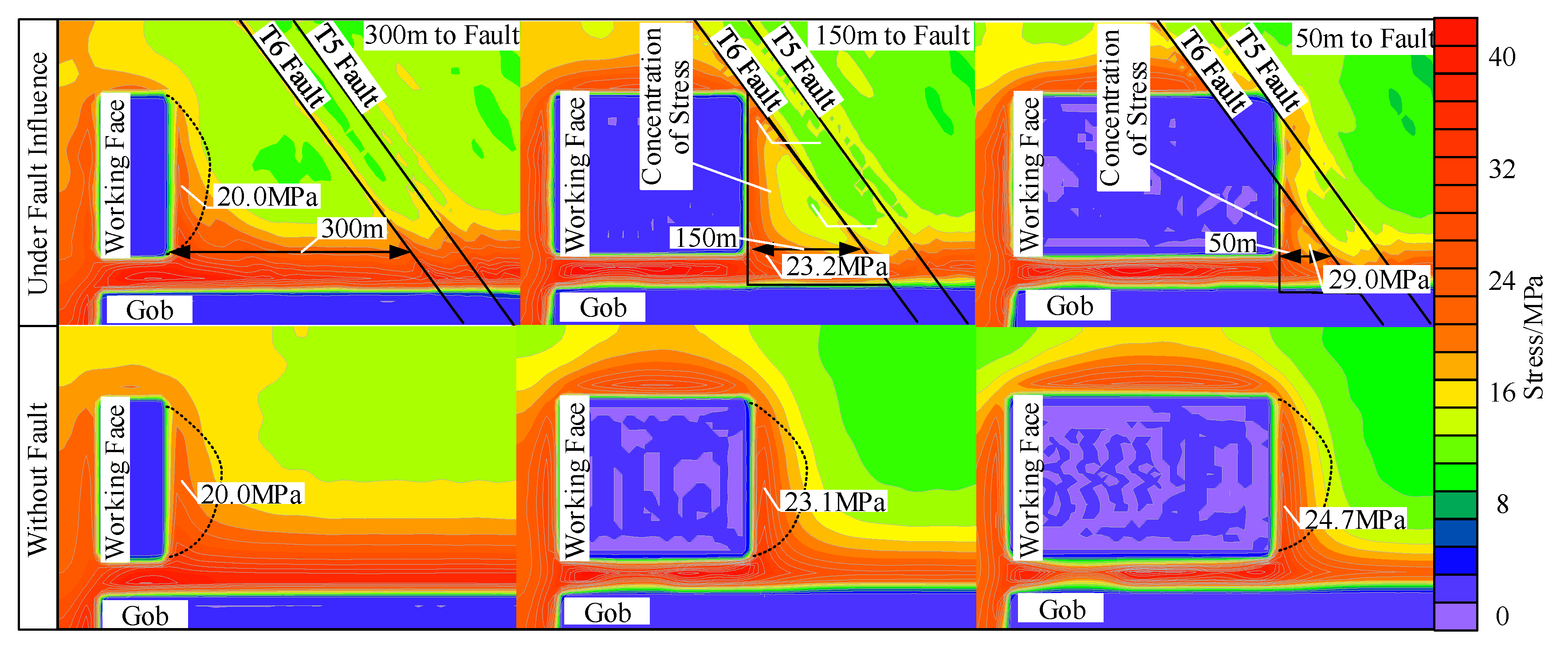
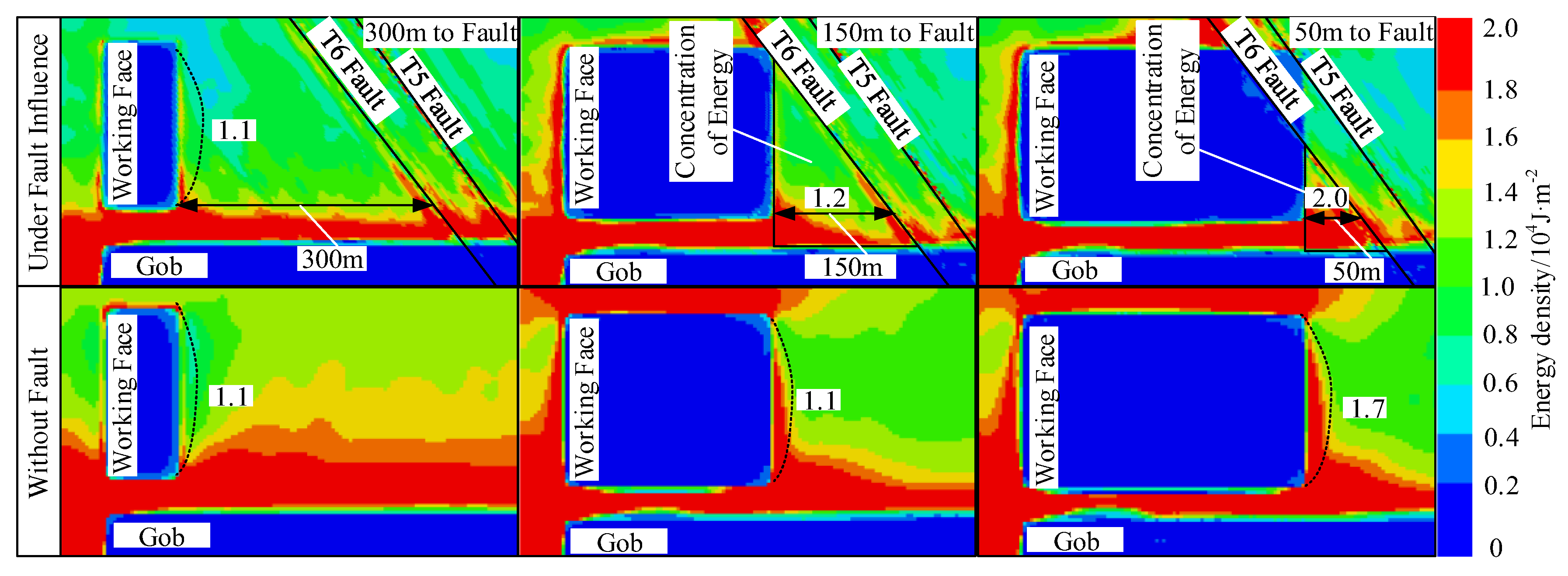
6. Stress and Energy Evolution of Triangular Coal Pillars
Numerical Modelling of Triangular Coal Pillars
7. Stress Evolution of Triangular Coal Pillars
8. Energy Evolution of Triangular Coal Pillars
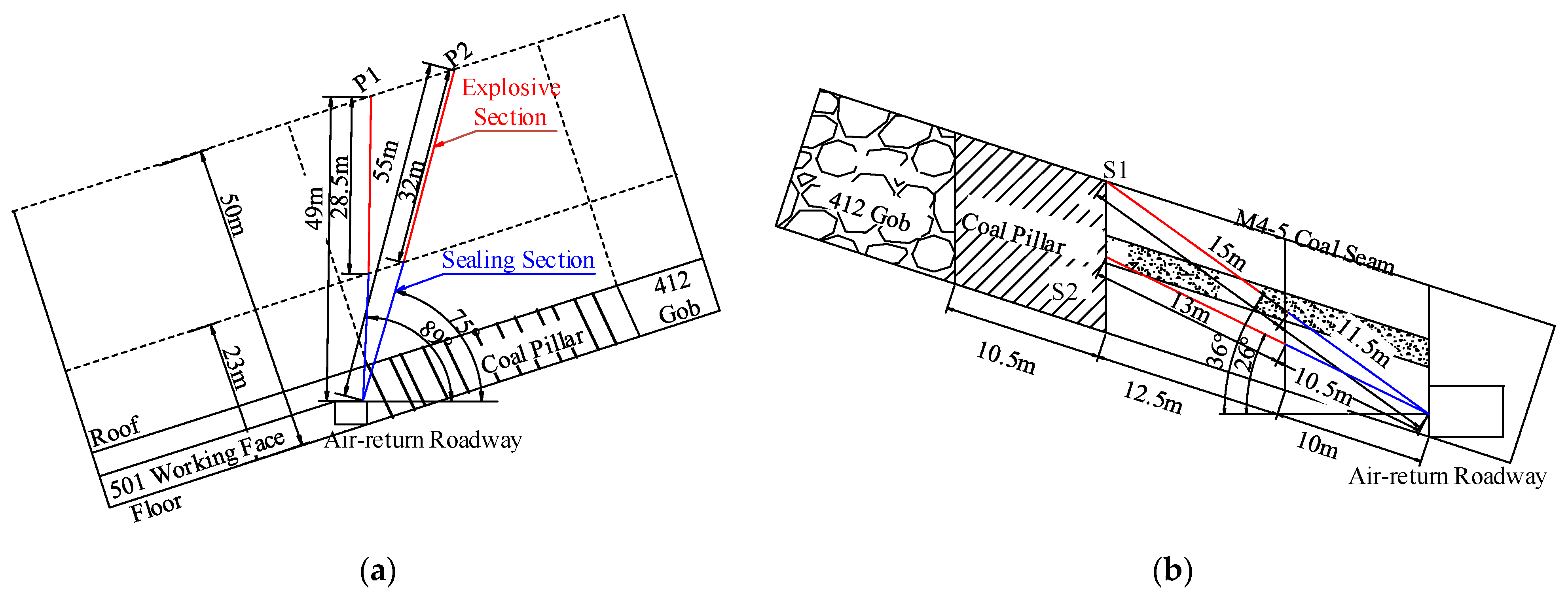
9. Engineering Case
Measures of Stress Relief
10. Effectiveness of Stress Relief Measures
11. Conclusions
- (1)
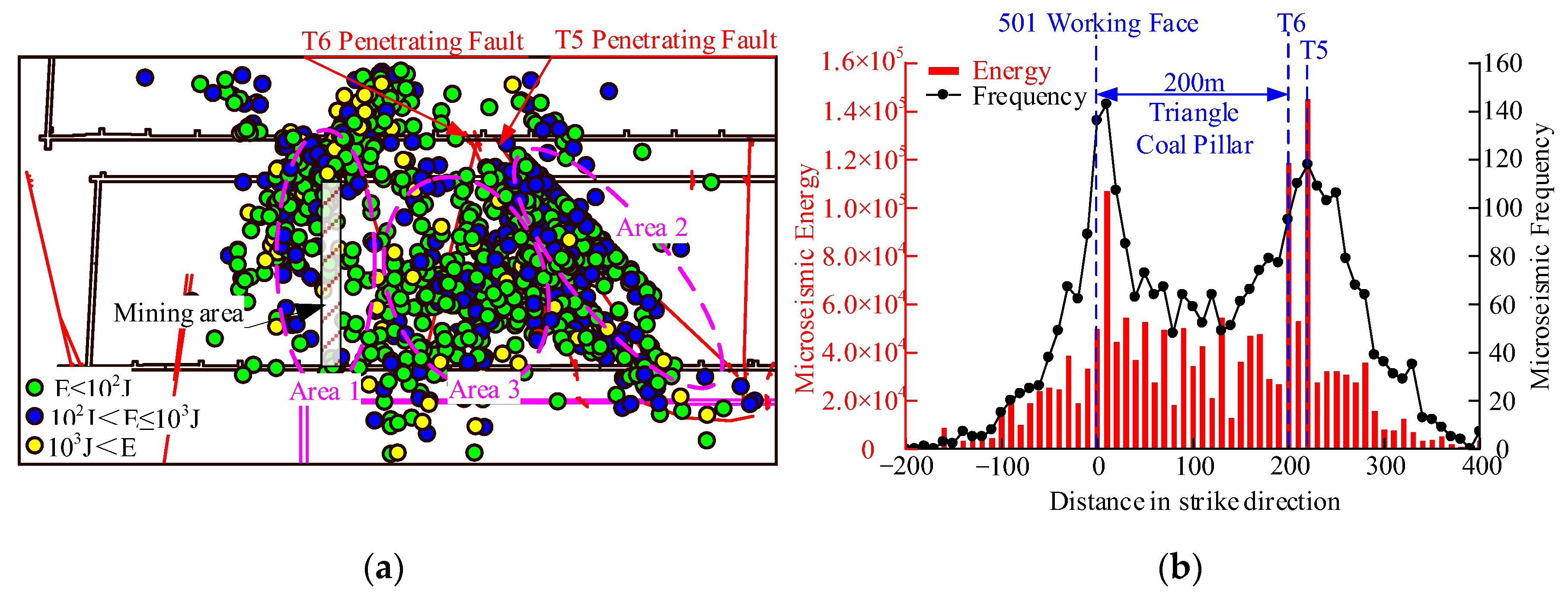
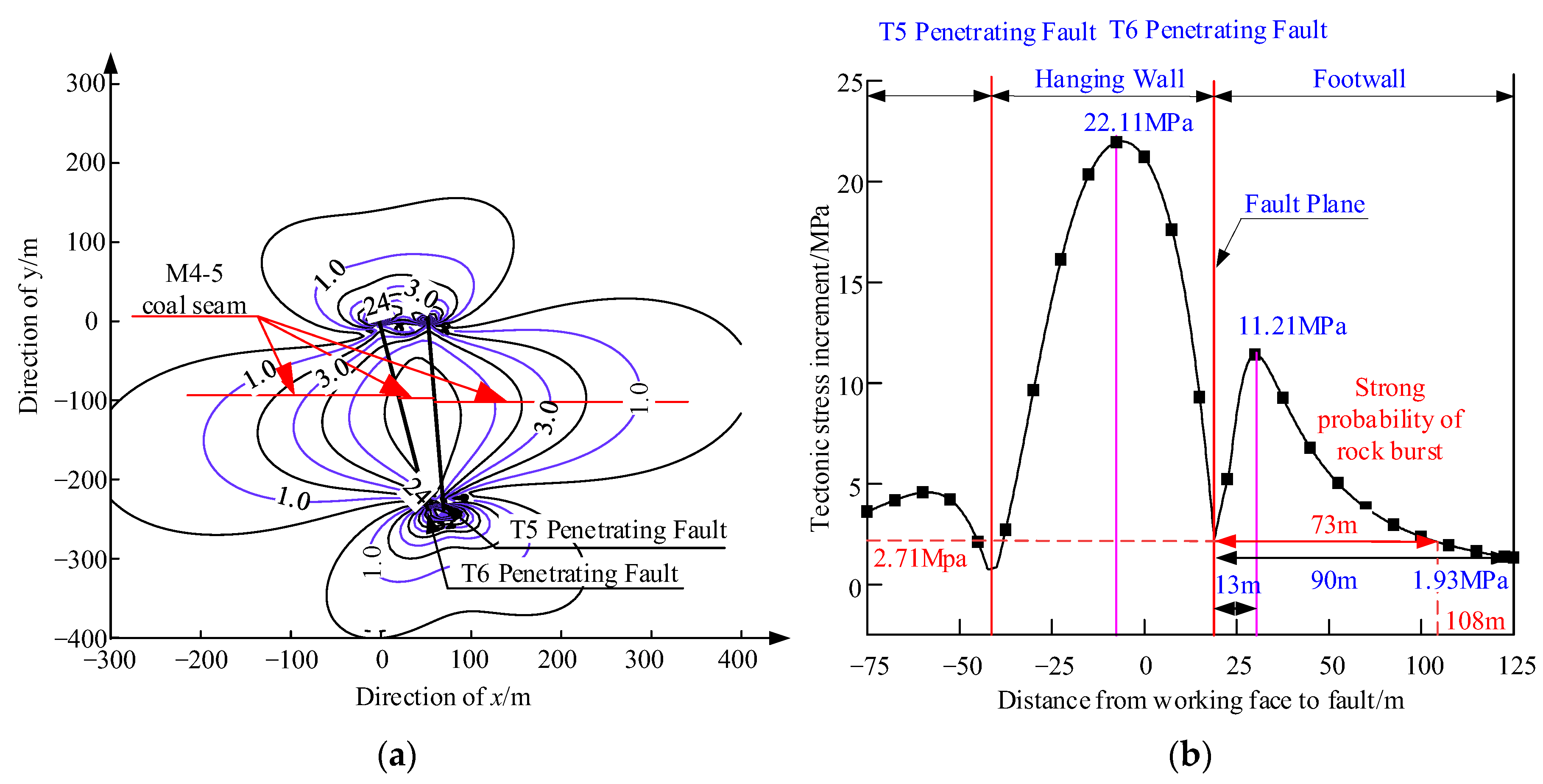
- The superimposed tectonic stress resulting from the T6 and T5 penetrating faults exhibited asymmetric distribution and had an influence range of about 90 m in the triangular coal pillar, reaching peak value of 11.21 MPa at a distance of 13 m from the fault plane.
- (2)
- Affected by the barrier effect of penetrating faults, the abutment stress of the working face was concentrated in the triangular coal pillar, and the magnitude of the abutment stress was positively and negatively correlated with the fault plane barrier effect and the width of the triangular coal pillar, respectively.
- (3)
- The barrier effect of the fault caused the stress and energy in the triangular coal pillar to increase as the width of the triangular coal pillar decreased. When the working face was 150 m away from the fault, energy and stress began to accumulate, and when the working face was 50 m away from the fault, energy and stress approached their peak.
- (4)
- The constructed stress index indicates that triangular coal pillars possess moderate rock burst risks when their widths range from 73 to 200 m, and high rock burst risks when their widths are between 0 and 73 m. The analysis of the energy accumulation pattern within the triangular coal pillar reveals that the range of 50 to 150 m in width represents the most critical zone for implementing stress relief measures. Meanwhile, for the range of 0 to 50 m, specific measures should be undertaken to further enhance the effectiveness of stress relief.
- (5)
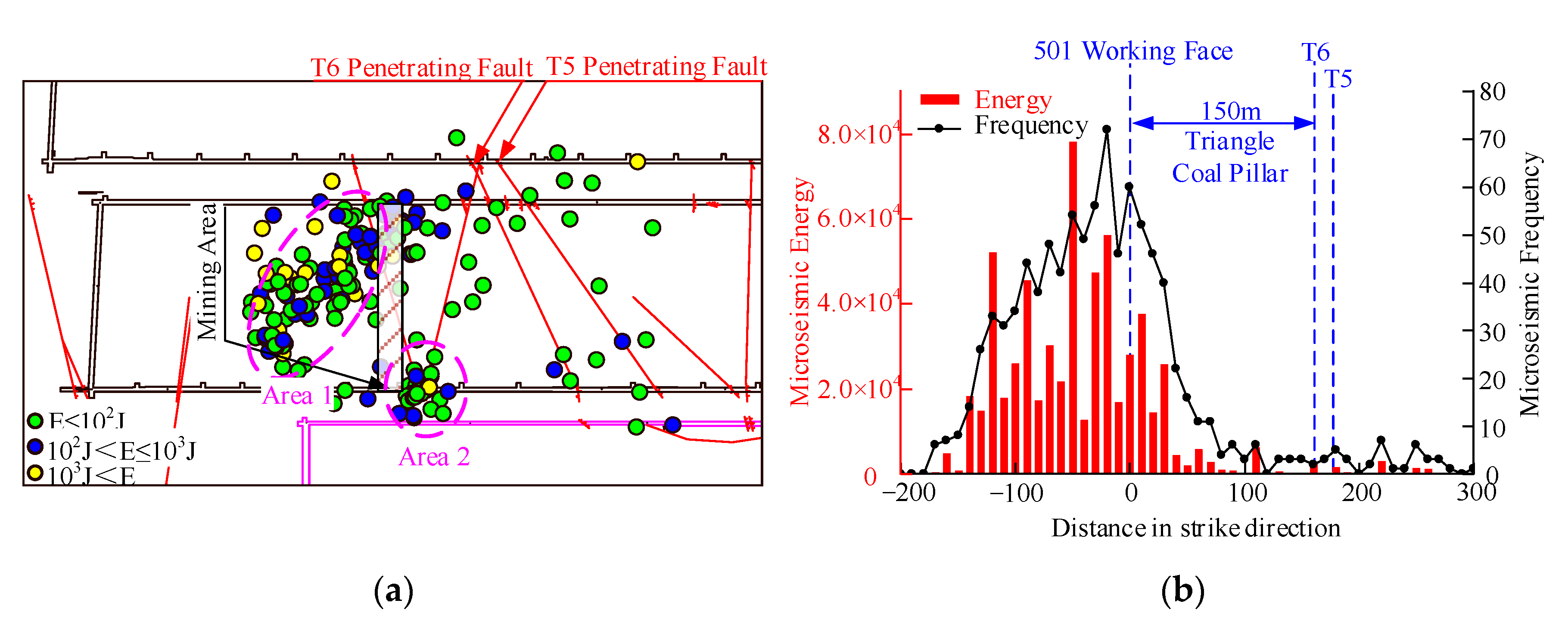
- Roof blasting is employed to reduce abutment stress, and coal seam blasting is employed to reduce tectonic stress. After implementing the stress relief measures, the microseismic activity transformed from fault activation to roof caving, concentrated within range of 150 m behind the working face. The maximum total energy of microseismic was 8.0 × 104 J, a decrease of 70.0%, verifying the effectiveness of the stress relief measures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, H.; Liao, Q.; Li, S.; Xiao, D.; Wang, G.; Guo, R.; Xue, Z.; Li, X. Early Paleozoic tectonic evolution and magmatism in the Eastern Tianshan, NW China: Evidence from geochronology and geochemistry of volcanic rocks. Gondwana Res. 2022, 102, 354–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Ao, S.; Windley, B.F.; Zhang, Z.; Sang, M.; Tan, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, R.; Xiao, W.; Pan, Z. Middle–Late Triassic southward-younging granitoids: Tectonic transition from subduction to collision in the Eastern Tianshan–Beishan Orogen, NW China. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2022, 134, 2206–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Luan, H. Size effect analysis of remaining coal pillar on rock burst caused by fault. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesh, N.; Nima, N.; Zhao, Y.; Teng, T.; Masoudian, M. Prediction of interactive effects of CBM production, faulting stress regime, and fault in coal reservoir: Numerical simulation. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2022, 99, 104419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shen, W.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Q.; Lu, X.; Xue, T. Abutment Pressure Distribution Law and Support Analysis of Super Large Mining Height Face. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2023, 20, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, L.; Li, C.; Gu, S.; Yu, X.; Xu, Z.; Sun, L. Research on dynamic response characteristics of normal fault footwall working face and rock burst prevention technology under the influence of the gob area. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Dou, L.; Li, Z.; He, J.; He, H.; Ding, Y. Mechanical Initiation and Propagation Mechanism of a Thrust Fault: A Case Study of the Yima Section of the Xiashi-Yima Thrust (North Side of the Eastern Qinling Orogen, China). Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2015, 48, 1927–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, F.; Liu, J. Analysis on control action of geologic structure on rock burst and typical cases. J. China Coal Soc. 2012, 37, 263–268. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhu, H.; Xie, F.; Dou, L.; Chen, J. Mechanism of rock burst caused by fracture of key strata during irregular working face mining and its prevention methods. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2019, 29, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Ge, D.; Jiang, F.; Wang, C.; Li, D.; Shang, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z. Rock Burst Mechanism under Coupling Action of Working Face Square and Regional Tectonic Stress. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021, 5538179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, J.; Zheng, P.; Li, W. Strata Behaviors and Rock Burst-Inducing Mechanism under the Coupling Effect of a Hard, Thick Stratum and a Normal Fault. Int. J. Geomech. 2018, 18, 04017135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Dou, L.; Cai, W.; Wang, G.; He, J.; Gong, S.; Ding, Y. Investigation and analysis of the rock burst mechanism induced within fault-pillars. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2014, 70, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Gu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. An effective control method of rock burst induced by shear instability of fault structure under complicated geological conditions. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zou, J.; Wang, J.; Jiao, Y.; Xu, H. Mechanism of coal bump induced by joint slipping under static and dynamic stresses in graben structural area. Acta Geotech. 2024, 19, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Yang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Mao, Z.; Xu, F. A study on microseismic monitoring of rock burst in coal mine. Chin. J. Geophys. Chin. Ed. 2006, 5, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, M.; Wang, T.; Li, K. A Numerical Analysis of Coal Burst Potential after the Release of the Fault-Slip Energy. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2023, 56, 3317–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.; Liu, R.; Xing, L.; Li, Z.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Z. Study on the dynamic response and the hazard of rock burst under the influence of fault slip. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 10, 1034332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, D.; Lin, X. Pre-evaluation of fault stability for underground mining based on geomechanical fault-slip analysis. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2022, 13, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Dou, L.; Liu, Y.; Su, Z.; Li, H.; Kong, Y.; Li, Z. Dynamic Behavior of Fault Slip Induced by Stress Waves. Shock Vib. 2016, 2016, 4386836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Hu, L.; Zhuang, Z. Distinct element modelling of mining-induced instability of a heterogeneous fault. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryer, B.; Giorgetti, C.; Passelegue, F.; Momeni, S.; Lecampion, B.; Violay, M. The Influence of Roughness on Experimental Fault Mechanical Behavior and Associated Microseismicity. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2022, 127, e2022JB025113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Hao, J.; Dai, X.; Kong, L. Response mechanism characteristics of mining-induced fault activation. Coal Geol. Explor. 2024, 52, 12–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shan, R.; Liu, D.; Wang, H.; Tong, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y. Study of the fracture instability and fault slip risk of overlying strata during mining near faults. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2023, 82, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tian, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, R. Investigation on the mutation effect induced by the coupled destabilization of fault and overburden rock strata during coal mining. J. China Coal Soc. 2023, 48, 2961–2975. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Shi, R.; Li, Z.; Feng, F.; Xia, Z.; Li, X. Formation process of thrust faults in coal measures and its influence on mining disaster. J. China Coal Soc. 2023, 48, 2995–3008. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Qiao, W.; He, H.; Lusini, E.; Meng, X. Characteristics of regional geostress field and its impact on rock burst: A case study on the Binchang mining area, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Yang, S.; Du, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. Study on fault-slip process and seismic mechanism under dynamic loading of hard roof fracture disturbance. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 163, 108598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Dou, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, K.; Cao, J.; Kan, J. Mechanism of Coal Burst Triggered by Mining-Induced Fault Slip Under High-Stress Conditions: A Case Study. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 884974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; He, M.; Li, S.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, B.; Xu, S.; Wei, H. Experimental study on the mechanism of pressure releasing control in deep coal mine roadways located in faulted zone. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2022, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.; Wang, C.; Xing, L.; Liang, M.; He, J. Study on the fault slip rule and the rockburst mechanism induced by mining the panel through fault. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2023, 9, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.; Yuan, A.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z. Study on fault slip dynamic response and rock burst potential under the influence of different horizontal stresses. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2022, 13, 1321–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yu, W.; Wu, G.; Li, K.; Liao, Z. Mechanism of Stratum Instability and Dynamic Deformation under Discontinuous Boundary Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Yang, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, C.; Chang, X.; Wu, X. Mechanism and surrounding rock control of gob-side entry formation passing through normal fault: A case study. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, H.; He, C.; Yang, W.; Wu, F.; Nie, J.; Xie, J.; Fu, J.; Xiao, L. Distribution Characteristics of In Situ Stress Field for a Deep-Buried Tunnel in the Fault Area. Int. J. Geomech. 2023, 23, 04023074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, S.; Liang, X.; Dong, Y. Analysis and Prevention of Rock Burst Risk of Working Face under the Influence of Continuous Irregular Triangular Coal Pillar Stress Concentration Area. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 12927–12940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Ma, Y.; Elmo, D.; Ding, S.; Zhu, H.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Chen, W. Parameters and surrounding rock control of gob-side driving under double key stratum after roof cutting. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jiao, J.; Wu, Y.; Song, Y.; Xie, P.; Luo, S. Main factors that control roadway damage when a steeply dipping coal seam crosses a fault. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2024, 15, 2344798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Ma, L.; Zong, D. Creep Damage Evolution Law and Stability Analysis of Remnant Coal Pillars in Longwall Goafs. Int. J. Geomech. 2024, 24, 04024116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, C.; Jiang, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Chen, M.; Cong, Y. Study on damage law and width optimization design of coal pillar with the discrete element method. Geomech. Eng. 2024, 37, 555–563. [Google Scholar]
- Du, F.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Fan, X.; Ren, H.; Cao, Z. Breaking law of overburden rock and key mining technology for narrow coal pillar working face in isolated island. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13045. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Huang, Q.; He, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wei, Y. A study on the mechanism and control technology of strong mine pressure in parallel coal pillar and hard roof mining. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 12, 1407084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancer, J.; Petros, V.; Hudecek, V.; Zapletal, P. Strength and Deformation of Pillars during Mining in the Shaft Pillar. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Fan, G.; Zhang, D.; Guo, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Fan, Z. Study on Characteristics of Front Abutment Pressure and Rational Stop-Mining Coal Pillar Width in Large Height Working Face. Processes 2024, 12, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Simao, F. Multiscale study on coal pillar strength and rational size under variable width working face. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1338642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yao, Z.; Chen, K.; Lu, F.; Han, J.; Wang, L. Experimental study on the influence of width-height ratio on coal pillar type rock burst. J. China Coal Soc. 2024, 49, 1303–1317. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, F.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Wan, X.; Yang, T.; Zhu, C.; Li, J. Research on the mechanism of overall instability type rock burst of fault coal pillars in deep topsoil fully mechanized top coal caving mining area. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2024, 43, 713–727. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, Y.; Liu, P.; Guo, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S. The different effects of polished and post-slip roughnesses on fault stability. Tectonophysics 2024, 877, 230281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhao, X.; Ding, Z.; Hu, Q.; Wang, D.; Cao, Z. Numerical study on the influence of fault orientation on risk level of fault slip burst disasters in coal mines: A quantitative evaluation model. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, C.; Deng, C. Numerical modeling of fault barrier effects on three kinds of stresses: A case of footwall mining on the normal fault. Prog. Geophys. 2020, 35, 1605–1611. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Q. A new method of mining pressure control for roof cutting in advance working face. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 161, 108302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Sui, L.; Hou, T.; Jiang, D. Assessment of pillar stability and its control in a double roadway layout. Energy Sci. Eng. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Xu, R.; Zhao, J. Research on instability of the triangular coal alongside the goaf in a fully mechanized top-coal caving work face. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2011, 40, 678–683. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, N.; Han, C.; Yan, G.; Mu, F.; Zhang, W. Differential roof cutting for roadway support in dual gob-side entry retention on a single working face—Multilevel continuous anchor-grouting control technology: A case study. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 163, 108475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypkowski, K. A new design of support for burst-prone rock mass in underground ore mining. E3S Web Conf. EDP Sci. 2018, 71, 00006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Guo, Z.; He, M.; Chen, F.; Miao, C. Stability control measures for roof cutting and NPR supporting of mining roadways in fault areas of kilometre-deep coal mine. J. Mt. Sci. 2023, 20, 3051–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Wu, J.; Kan, J.; Yang, K.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y. Bolting control of a coal roadway under multi-seam mining—A case study. Arch. Min. Sci. 2024, 69, 303–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Dou, L.; Gong, S.; Li, J.; Ma, Z. Rock burst assessment and prediction by dynamic and static stress analysis based on micro-seismic monitoring. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2017, 93, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhai, M.; Guo, X.; Wen, J.; Liu, X.; Ma, X. Evaluation of rock burst hazard based on the classification of stress and surrounding rock. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2017, 36, 1041–1052. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, F.; Dou, L.; Ju, Y. State of the art review on mechanism and prevention of coal bumps in China. J. China Coal Soc. 2014, 39, 205–213. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Li, W.; Fan, K.; Qiao, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, L. A method for predicting the water-flowing fractured zone height based on an improved key stratum theory. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2023, 33, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, K.; Tu, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Guo, B. Utilization of broken rock in shallow gobs for mitigating mining-induced water inrush disaster risks and environmental damage: Experimental study and permeability model. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Wu, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, F.; Xie, H.; Jiao, Y. Effective evaluation of deep-hole blasting for controlling strong tremors induced by deep coal mining-A case study. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2022, 159, 105211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Elmo, D.; He, M.; Ma, Z.; Gao, C. Ground response mechanism of entries and control methods induced by hard roof in longwall top coal caving panel. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 144, 106940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Xia, B.; Zuo, Y.; Yu, B.; Ou, C. Mechanism and control technology of strong ground pressure behaviour induced by high-position hard roofs in extra-thick coal seam mining. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Shan, C.; Li, Z.; Nan, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Chu, T. Stability control of overburden and coal pillars in the gob-side entry under dynamic pressure. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2023, 170, 105490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hu, H. Study of dynamic mechanical response characteristics of working face passing through reverse fault. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2019, 48, 54–63. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, K.; Li, K. Shale Reservoir Fracture Mechanism Under Impacts of Additional Stress Field and Leak-off. J. Hunan Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2020, 35, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lyu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Mechanism of faults acting on in-situ stress field direction. Oil Gas Geol. 2016, 37, 387–393. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Cao, A.; Hu, Y.; Xue, C.; Liu, Y.; Lv, D. Stress distribution and rockburst characteristics of roadway group under the influence of fault and fold structures: A case study. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2022, 13, 736–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Feng, X.; Xiang, T.; Su, G. Rockburst characteristics and numerical simulation based on a new energy index: A case study of a tunnel at 2500 m depth. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2010, 69, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Lin, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, D.; Xiong, W.; Peng, Y. New method for introducing gradient stress into rock-burst prediction. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2020, 42, 2098–2105. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liang, Z. Mining-Induced Stress and Ground Pressure Behavior Characteristics in Mining a Thick Coal Seam With Hard Roofs. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 843191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; Yu, G. Experimental and Numerical Analysis of Rock Burst Tendency and Crack Development Characteristics of Tianhu Granite. Geofluids 2021, 2021, 6681261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Dou, L.; Mu, Z.; Cao, A.; Gong, S. Numerical simulation study on hard-thick roof inducing rock burst in coal mine. J. Cent. South Univ. 2016, 23, 2314–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmstrom, A. Measurements of and correlations between block size and rock quality designation (RQD). Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2005, 20, 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M. Principles of rock support in burst-prone ground. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2013, 36, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Yan, J.; Li, X.; Luo, S. A peak-strength strain energy storage index for rock burst proneness of rock materials. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2019, 117, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gong, S.; Li, Z.; Dou, L.; Cai, W.; Mao, Y. Evolution of Stress Concentration and Energy Release Before Rock Bursts: Two Case Studies from Xingan Coal mine, Hegang, China. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2016, 49, 3393–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Lithology | Rock | RQD | Rock Mass | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elastic Modulus Er/GPa | Elastic Modulus Em/GPa | Shear Modulus/GPa | ||
| Coarse sandstone | 11.78 | 90 | 12.60 | 22.0 |
| Fine sandstone | 5.28 | 81 | 1.01 | 3.8 |
| Siltstone | 1.20 | 86 | 1.10 | 5.6 |
| Mudstone | 19.64 | 75 | 9.90 | 18.0 |
| M4-5 coal | 11.42 | 65 | 7.68 | 13.2 |
| Lithology | Density/(kg/m3) | Bulk Modulus/GPa | Shear Modulus/GPa | Cohesive Force/MPa | Friction Angle/° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coarse sandstone | 2700 | 30.0 | 22.0 | 130.0 | 38 |
| Mudstone | 2600 | 5.6 | 18.0 | 7.6 | 39 |
| Fine sandstone | 2700 | 19.4 | 3.8 | 12.8 | 35 |
| M4-5 coal | 1400 | 1.5 | 13.2 | 1.1 | 25 |
| Siltstone | 2500 | 13.1 | 5.6 | 3.0 | 33 |
| Fault plane | Cohesion force is 2.0 MPa, friction angle is 30° | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, W.; Ma, X.; Wen, Y.; Cao, X. Stress Evolution and Rock Burst Prevention in Triangle Coal Pillars under the Influence of Penetrating Faults: A Case Study. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8585. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14198585
Guo W, Ma X, Wen Y, Cao X. Stress Evolution and Rock Burst Prevention in Triangle Coal Pillars under the Influence of Penetrating Faults: A Case Study. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(19):8585. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14198585
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Wenhao, Xuezhou Ma, Yingyuan Wen, and Xiaojie Cao. 2024. "Stress Evolution and Rock Burst Prevention in Triangle Coal Pillars under the Influence of Penetrating Faults: A Case Study" Applied Sciences 14, no. 19: 8585. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14198585
APA StyleGuo, W., Ma, X., Wen, Y., & Cao, X. (2024). Stress Evolution and Rock Burst Prevention in Triangle Coal Pillars under the Influence of Penetrating Faults: A Case Study. Applied Sciences, 14(19), 8585. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14198585






