A Multi-Organ Segmentation Network Based on Densely Connected RL-Unet
Abstract
1. Introduction
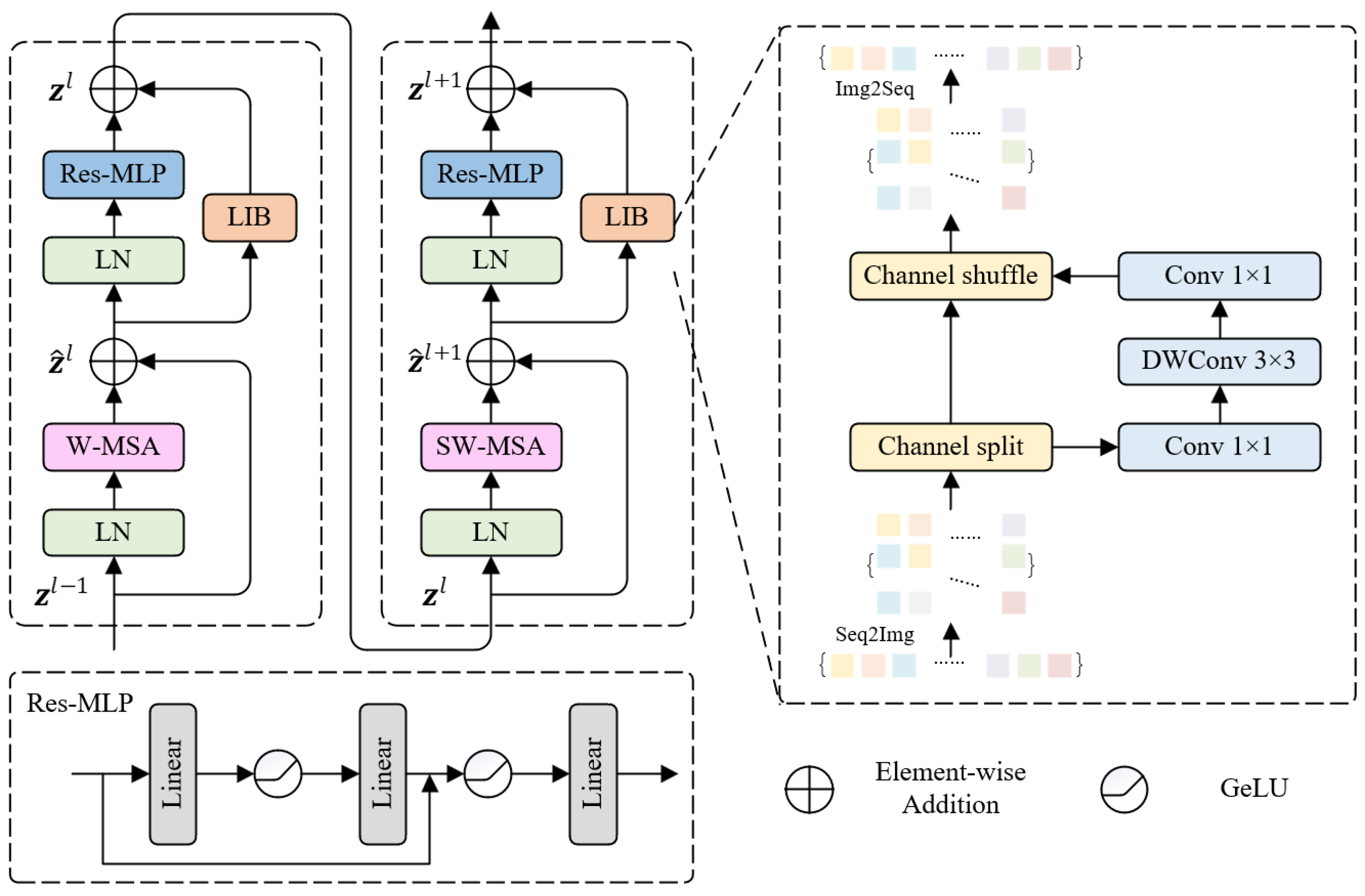
- We add a local induction bias module to the Swin-Transformer block to assist the RLSwin-Transformer module learn local features and remote dependencies, and replace the MLP module with the Res-MLP module to prevent feature loss during transmission, thus increasing segmentation accuracy.
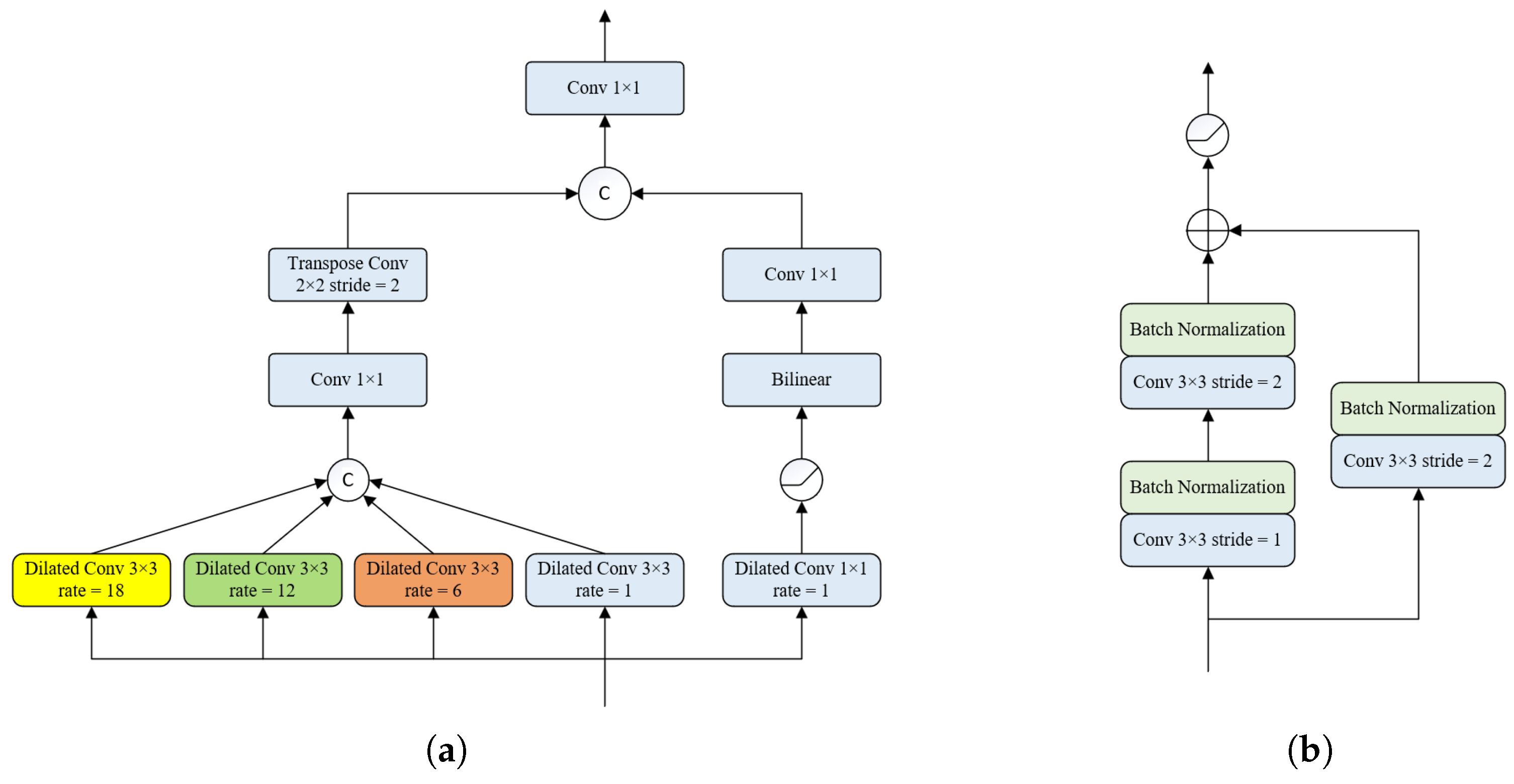
- We design a new double up-sampling module, which includes bilinear up-sampling and expansion convolution with different expansion rates for feature extraction and image restoration.
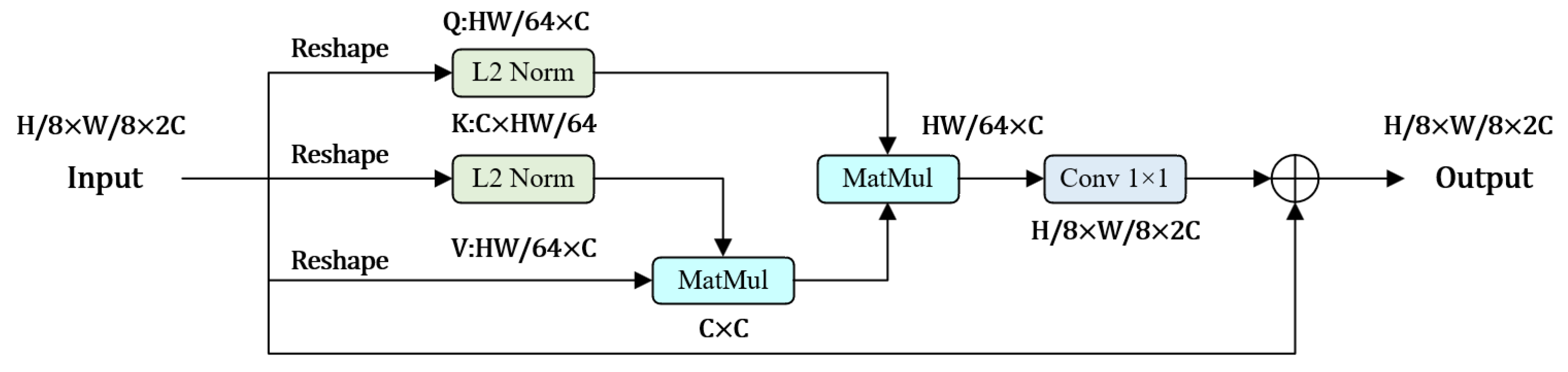
- A dense connection structure is designed at the decoding end, and an attention mechanism is introduced to restore resolution and generate segmentation map.
- To significantly increase the segmentation accuracy of small targets, a novel loss function is proposed.
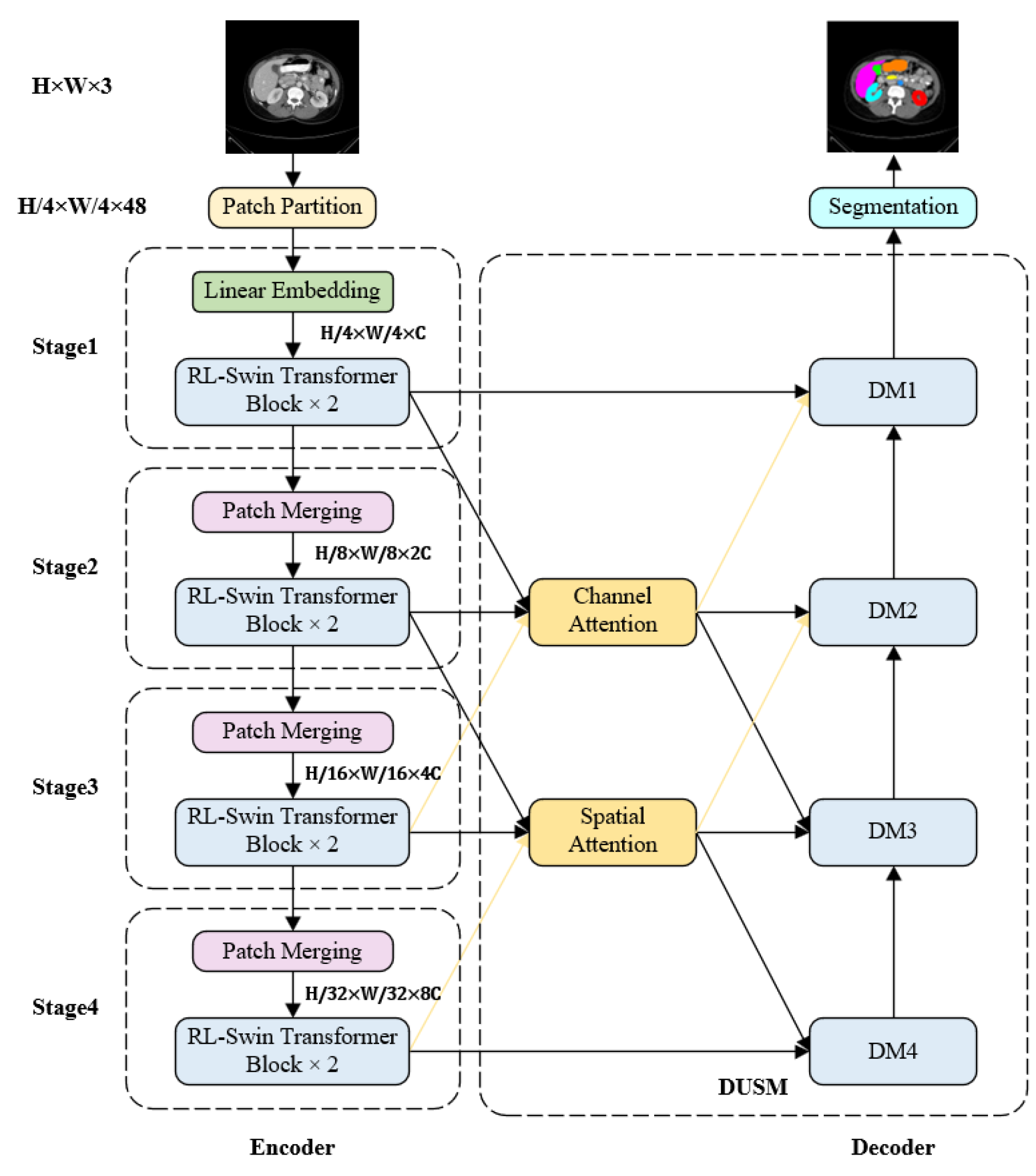
2. Method
2.1. Integral Structure
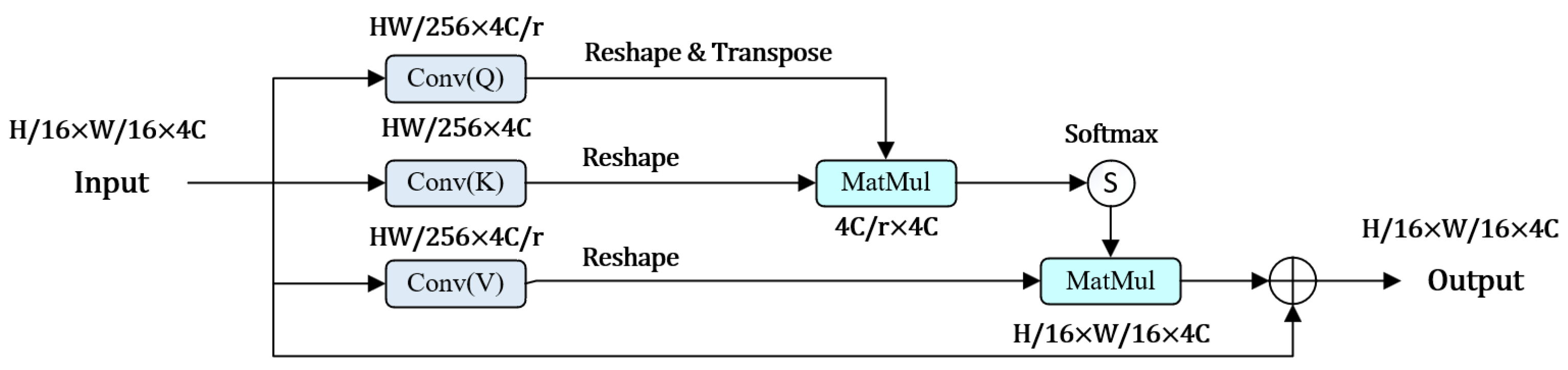
2.2. RLSwin-Transformer Module
2.3. Densely Connected Double Up-Sampling Modules (DUSM)
2.4. New Loss Function
- Focal Loss (FL): Increasing the weight of difficult-to-classify samples in the loss function is the same as using the FL [39] loss function. As a result, the loss of the comparatively simple to anticipate sample is reduced while the loss of the comparatively hard to guess sample is bigger. Consequently, the emphasis is put more on challenging-to-classify samples.
- Dice Loss (DL): A metric function called Dice Loss [40] is used to assess how comparable two samples are. The value is between 0 and 1, and the higher it is, the more related the two are.
- Cross Entropy Loss (CE): CE [41] expresses the distribution relationship between the predicted value and the true value, and the smaller the cross entropy, the more similar the probability distribution between the two.
3. Experiments
3.1. Evaluation Metrics and Datasets
3.2. Experiment Settings
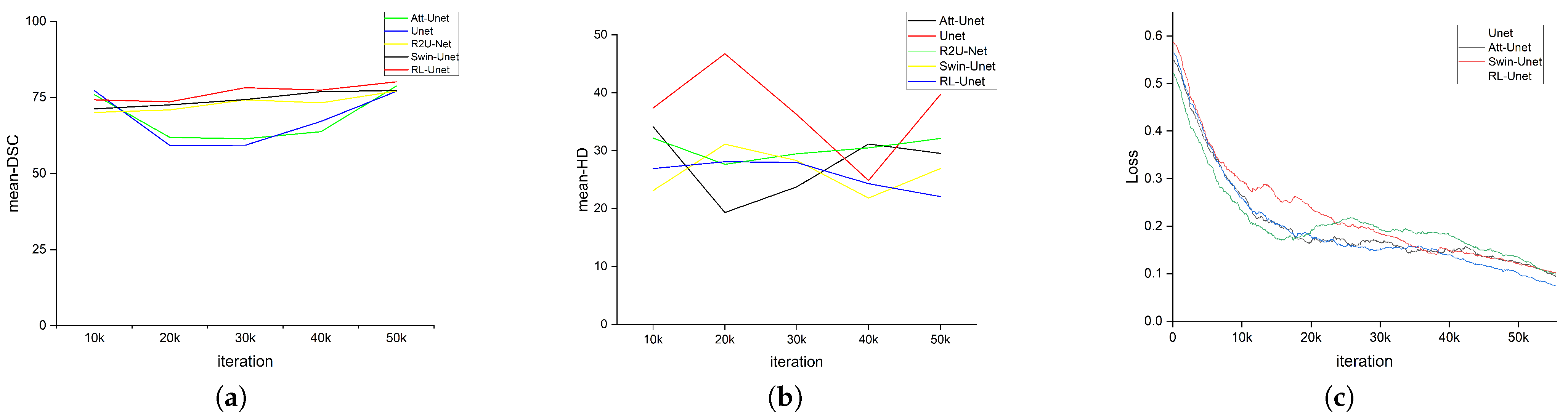
3.3. Experiment Results
| Methods | Aorta | Gallbladder | Kidney (L) | Kidney (R) | Liver | Pancreas | Spleen | Stomach | DSC | HD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ViT [18] | 44.38 | 39.59 | 67.46 | 62.94 | 89.21 | 43.14 | 75.45 | 69.87 | 61.50 | 39.61 |
| U-Net [7] | 89.18 | 65.42 | 76.86 | 70.64 | 93.35 | 55.37 | 89.80 | 76.01 | 77.03 | 39.70 |
| Swin-Unet [20] | 86.34 | 63.45 | 81.13 | 75.69 | 93.63 | 56.83 | 87.94 | 73.22 | 77.28 | 26.93 |
| AttU-Net [10] | 88.59 | 64.42 | 81.73 | 76.77 | 93.99 | 63.68 | 89.56 | 71.18 | 78.74 | 29.54 |
| R2U-Net [42] | 88.26 | 68.97 | 76.94 | 71.36 | 91.86 | 57.36 | 87.36 | 74.88 | 77.12 | 32.12 |
| GCASCADE [28] | 81.55 | 79.75 | 83.06 | 64.46 | 62.89 | 64.43 | 82.87 | 89.39 | 76.05 | 12.34 |
| nnFormer [29] | 92.04 | 70.17 | 86.57 | 86.25 | 96.84 | 83.35 | 90.51 | 86.83 | 86.57 | 10.63 |
| MISSFormer [30] | 86.99 | 68.65 | 85.21 | 82.00 | 94.41 | 65.67 | 91.92 | 80.81 | 81.96 | 18.20 |
| RL-Unet (ours) | 86.95 | 67.48 | 82.68 | 79.47 | 93.84 | 55.97 | 90.21 | 77.41 | 80.13 | 22.07 |
3.4. Ablation Experiment
3.5. Hyperparametric Learning Rate
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azad, R.; Aghdam, E.K.; Rauland, A.; Jia, Y.; Avval, A.H.; Bozorgpour, A.; Karimijafarbigloo, S.; Cohen, J.P.; Adeli, E.; Merhof, D. Medical image segmentation review: The success of u-net. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Li, W.; Zuluaga, M.A.; Pratt, R.; Patel, P.A.; Aertsen, M.; Doel, T.; David, A.L.; Deprest, J.; Ourselin, S.; et al. Interactive medical image segmentation using deep learning with image-specific fine tuning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1562–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, Z. An effective cnn and transformer complementary network for medical image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 136, 109228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Li, L.; Bredell, G.; Li, J.; Unkelbach, J.; Konukoglu, E. Volumetric memory network for interactive medical image segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 83, 102599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—Proceedings of the MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, N.; Paheding, S.; Elkin, C.P.; Devabhaktuni, V. U-net and its variants for medical image segmentation: A review of theory and applications. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 82031–82057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Lin, L.; Tong, R.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Iwamoto, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J. Unet 3+: A full-scale connected unet for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Virtual Conference, 4–8 May 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1055–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S. V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Hua, Q.; Li, X.; Wen, Z.; Yang, M. Biomedical sensor image segmentation algorithm based on improved fully convolutional network. Measurement 2022, 197, 111307. [Google Scholar]
- Bose, S.; Chowdhury, R.S.; Das, R.; Maulik, U. Dense dilated deep multiscale supervised u-network for biomedical image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 143, 105274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlemper, J.; Oktay, O.; Schaap, M.; Heinrich, M.; Kainz, B.; Glocker, B.; Rueckert, D. Attention gated networks: Learning to leverage salient regions in medical images. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 53, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oza, P.; Sharma, P.; Patel, S.; Kumar, P. Deep convolutional neural networks for computer-aided breast cancer diagnostic: A survey. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 1815–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, D. Cswin-pnet: A cnn-swin transformer combined pyramid network for breast lesion segmentation in ultrasound images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 119024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorgpour, A.; Azad, R.; Showkatian, E.; Sulaiman, A. Multi-scale regional attention deeplab3+: Multiple myeloma plasma cells segmentation in microscopic images. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.06238. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. Transunet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q.; Wang, M. Swin-unet: Unet-like pure transformer for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 205–218. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Liu, S.; Wu, F.; Li, G.; Zhong, M.; Guan, X. Rt-unet: An advanced network based on residual network and transformer for medical image segmentation. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2022, 37, 8565–8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y. nnformer: Interleaved transformer for volumetric segmentation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2109.03201. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Deng, Z.; Li, D.; Yuan, X.; Fu, Y. Missformer: An effective transformer for 2d medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 42, 1484–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, R.; Heidari, M.; Shariatnia, M.; Aghdam, E.K.; Karimijafarbigloo, S.; Adeli, E.; Merhof, D. Transdeeplab: Convolution-free transformer-based deeplab v3+ for medical image segmentation. In International Workshop on PRedictive Intelligence In MEdicine; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, R.; Arimond, R.; Aghdam, E.K.; Kazerouni, A.; Merhof, D. Dae-former: Dual attention-guided efficient transformer for medical image segmentation. In International Workshop on PRedictive Intelligence in MEdicine; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Hua, Z. Mpsht: Multiple progressive sampling hybrid model multi-organ segmentation. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2022, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Marculescu, R. G-cascade: Efficient cascaded graph convolutional decoding for 2d medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 1–6 January 2024; pp. 7728–7737. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.-Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y. nnformer: Volumetric medical image segmentation via a 3d transformer. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 4036–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Deng, Z.; Li, D.; Yuan, X. Missformer: An effective medical image segmentation transformer. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.07162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, D.; Xu, C.; Wang, W.; Hong, Q.; Li, Q.; Tian, J. Tfcns: A cnn-transformer hybrid network for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Bristol, UK, 6–9 September 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 781–792. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Fang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, H.; Gao, Z.; Li, Y.; Ser, J.D.; Xia, J.; Yang, G. Swin transformer for fast mri. Neurocomputing 2022, 493, 281–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Chen, B.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, G.; Zhang, D. Ds-transunet: Dual swin transformer u-net for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Fan, F.; Huang, J.; Mei, X.; Ma, Y. Swinfusion: Cross-domain long-range learning for general image fusion via swin transformer. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2022, 9, 1200–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekri-Ershad, S.; Alsaffar, M.F. Developing a tuned three-layer perceptron fed with trained deep convolutional neural networks for cervical cancer diagnosis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, N.; Han, J.; Ding, G.; Sun, J. Repvgg: Making vgg-style convnets great again. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual Conference, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 13733–13742. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.H.; Liu, Z.N.; Mu, T.J.; Hu, S.M. Beyond self-attention: External attention using two linear layers for visual tasks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 5436–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, G.S.; Nghiem, T.P.; Nguyen, V.T.; Luong, C.M.; Burie, J. Improving accuracy of lung nodule classification using deep learning with focal loss. J. Healthc. Eng. 2019, 2019, 156416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Sun, J.; Ding, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, G. Robust liver vessel extraction using 3D u-net with variant dice loss function. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 101, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Niu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, C.; Xiao, F.; Gao, X. Retinal vessel segmentation of color fundus images using multiscale convolutional neural network with an improved cross-entropy loss function. Neurocomputing 2018, 309, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alom, M.Z.; Hasan, M.; Yakopcic, C.; Taha, T.M.; Asari, V.K. Recurrent residual convolutional neural network based on u-net (r2u-net) for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.06955. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Xie, S.; Lin, L.; Iwamoto, Y.; Han, X.-H.; Chen, Y.-W.; Tong, R. Mixed transformer u-net for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 2390–2394. [Google Scholar]

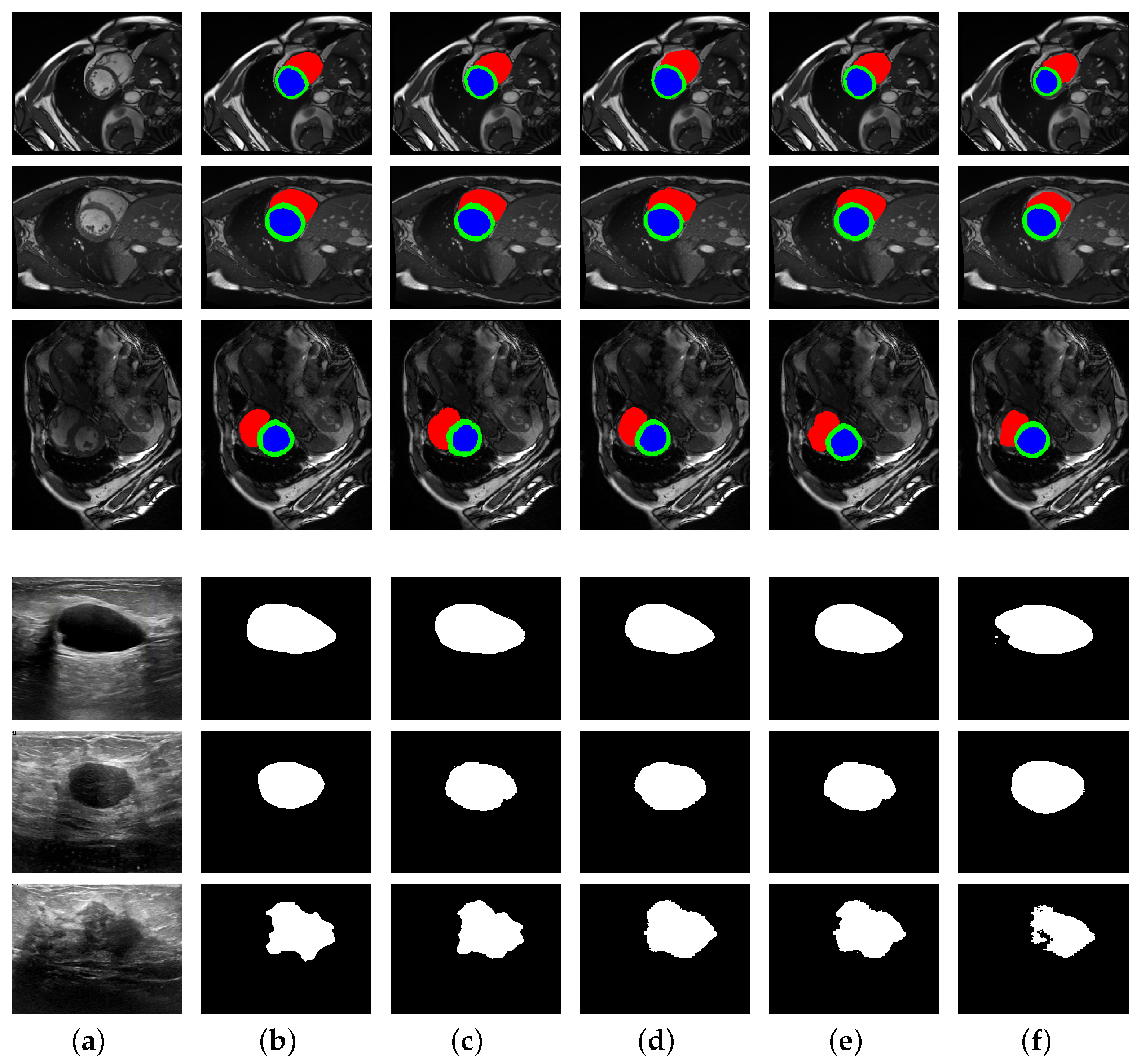
| Methods | ET | TC | WT | DSC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net [7] | 83.92 | 87.71 | 90.70 | 87.44 |
| U-Net++ [24] | 84.21 | 87.76 | 91.30 | 87.76 |
| U-Net3+ [9] | 82.21 | 86.52 | 91.17 | 86.63 |
| nnFormer [29] | 83.93 | 87.82 | 91.52 | 87.74 |
| AttU-Net [10] | 85.08 | 87.76 | 91.53 | 88.12 |
| Swin-Unet [20] | 84.16 | 86.77 | 91.01 | 87.31 |
| RL-Unet (ours) | 85.27 | 88.12 | 91.52 | 88.36 |
| Methods | RV | Myo | LV | DSC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R50+AttnUnet [19] | 87.58 | 79.20 | 93.47 | 86.75 |
| R50+Unet [19] | 87.10 | 80.63 | 94.92 | 87.55 |
| Trans-Unet [19] | 86.67 | 87.27 | 95.18 | 89.71 |
| Swin-Unet [20] | 85.77 | 84.42 | 94.03 | 88.07 |
| MT-Unet [43] | 86.64 | 89.04 | 95.62 | 90.43 |
| PVTCASCADE [28] | 89.97 | 88.90 | 95.50 | 91.46 |
| RL-Unet (ours) | 88.54 | 87.65 | 95.46 | 91.18 |
| Methods | Benign | Malignant | DSC |
|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net [7] | 70.49 | 63.47 | 66.98 |
| AttU-Net [10] | 73.30 | 62.95 | 68.13 |
| Swin-Unet [20] | 73.31 | 62.13 | 67.72 |
| U-Net++ [24] | 75.56 | 65.52 | 70.54 |
| U-Net3+ [9] | 75.07 | 66.19 | 70.67 |
| RL-Unet (ours) | 74.92 | 66.09 | 70.51 |
| Methods | DSC | HD |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 77.28 | 26.93 |
| Baseline+ResMLP | 78.36 | 28.12 |
| Baseline+ResMLP+DUSM | 78.59 | 26.45 |
| Baseline+ResMLP+DUSM+Attention | 79.69 | 26.78 |
| Baseline+ResMLP+DUSM+Attention+L2 | 80.13 | 22.07 |
| Baseline+ResMLP+DUSM+Attention+L1 | 79.95 | 24.21 |
| DSC | HD | |
|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 78.51 | 28.67 |
| 0.05 | 80.13 | 22.07 |
| 0.1 | 78.87 | 27.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Xu, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z. A Multi-Organ Segmentation Network Based on Densely Connected RL-Unet. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7953. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177953
Zhang Q, Xu B, Liu H, Zhang Y, Yu Z. A Multi-Organ Segmentation Network Based on Densely Connected RL-Unet. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(17):7953. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177953
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qirui, Bing Xu, Hu Liu, Yu Zhang, and Zhiqiang Yu. 2024. "A Multi-Organ Segmentation Network Based on Densely Connected RL-Unet" Applied Sciences 14, no. 17: 7953. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177953
APA StyleZhang, Q., Xu, B., Liu, H., Zhang, Y., & Yu, Z. (2024). A Multi-Organ Segmentation Network Based on Densely Connected RL-Unet. Applied Sciences, 14(17), 7953. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177953






