Experimental Study of the Influence of Occupants on Speech Intelligibility in an Automotive Cabin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Measurements
2.2. STI Measurements
2.3. Subjective Experiments
2.3.1. Participants
2.3.2. Stimuli
2.3.3. Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Occupants on RT
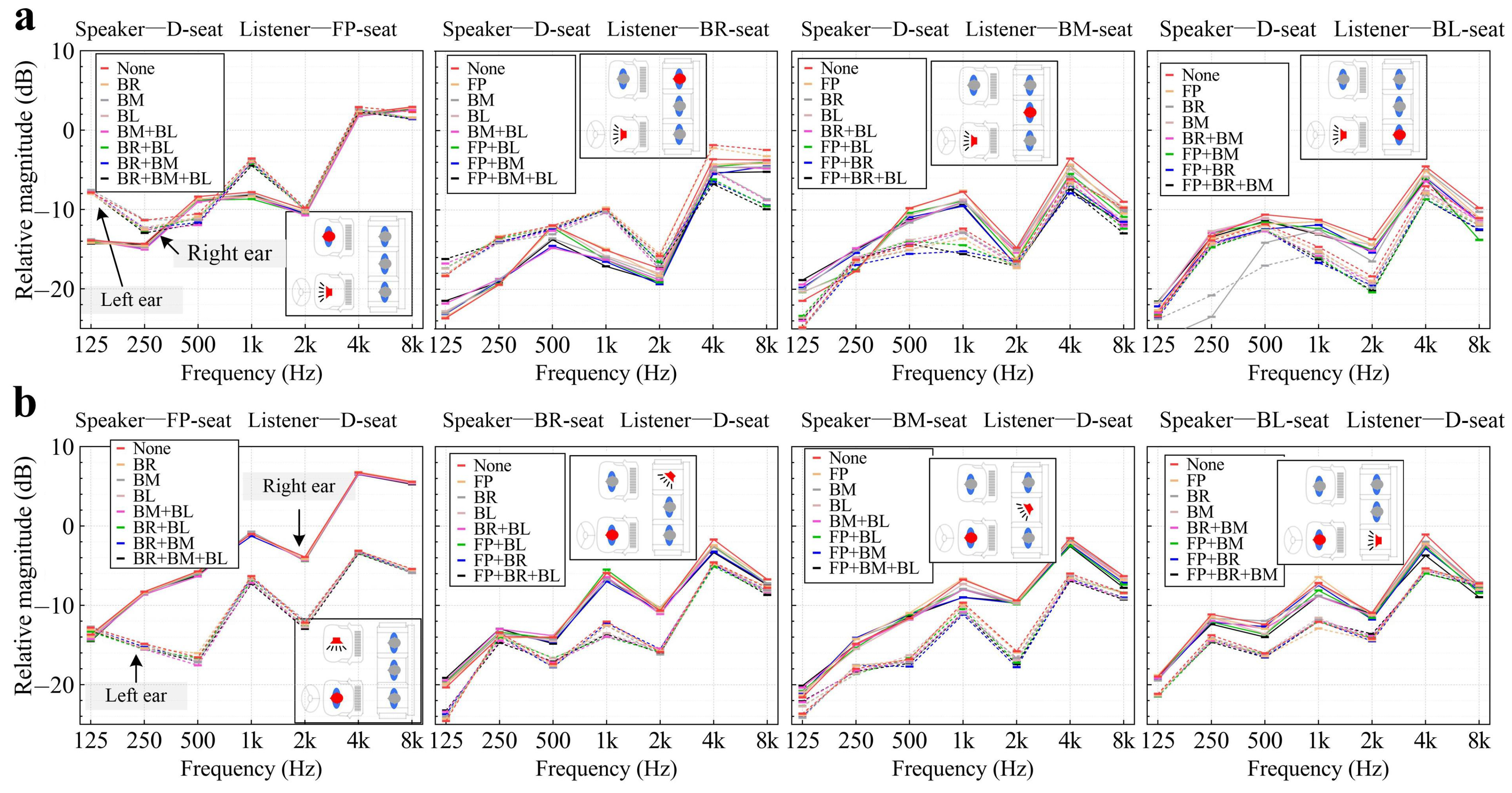
3.2. Effect of the Occupants on Magnitude Spectrum
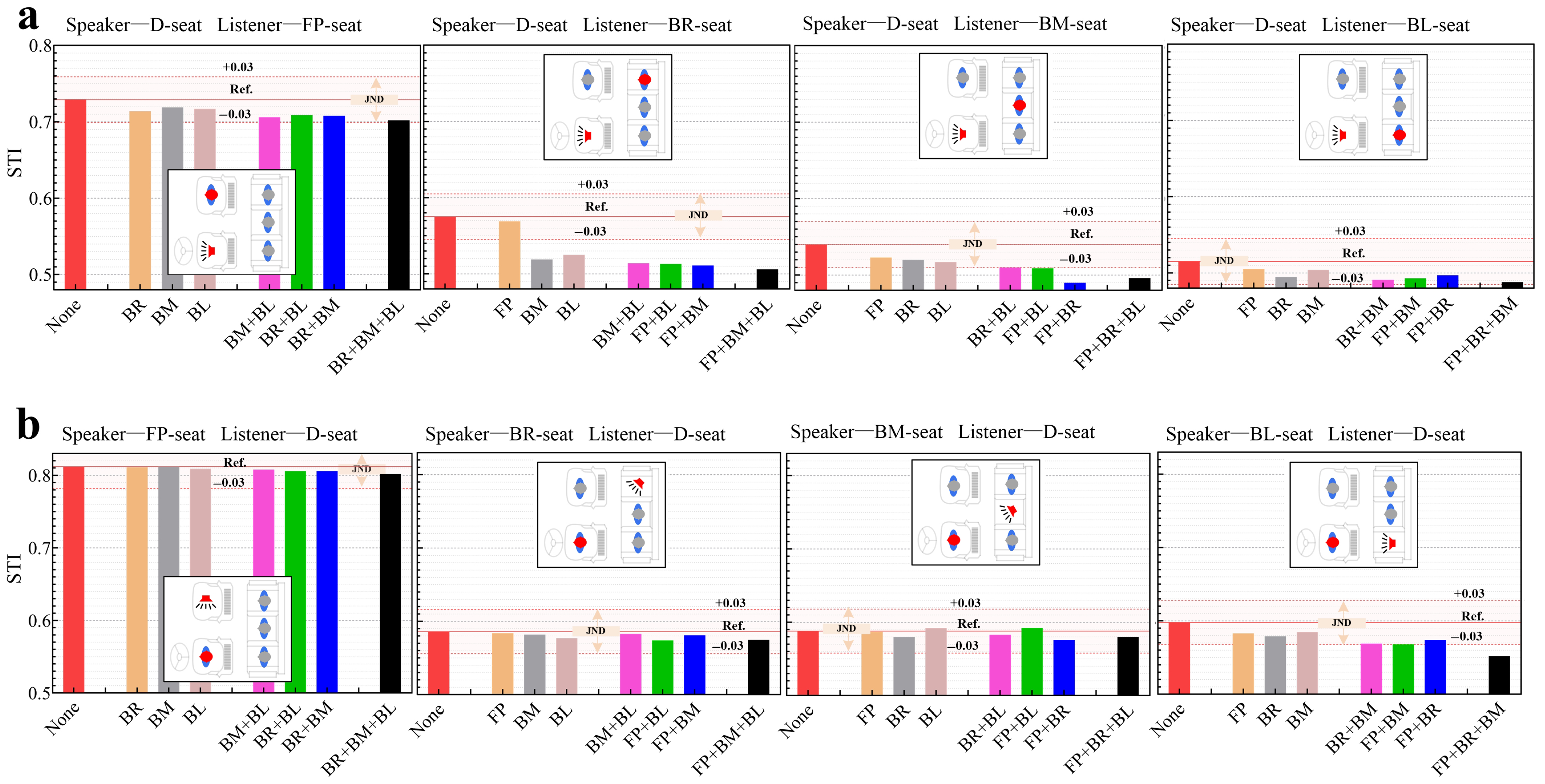
3.3. Effect of the Occupants on STI Results
3.4. Effect of Occupants on Subjective SRT Results
3.5. Implications and Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| STI | Speech Transmission Index |
| SRT | Speech–Reception Threshold |
| JND | Just-Noticeable Difference |
| BRIR | Binaural Room Impulse Response |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| FP-seat | Front Passenger Seat |
| BR-seat | Back-Right Seat |
| BM-seat | Back-Middle Seat |
| BL-seat | Back-Left Seat |
References
- Goujard, B.; Sakout, A.; Valeau, V. Acoustic comfort on board ships: An evaluation based on a questionnaire. Appl. Acoust. 2005, 66, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanka, S.; Fredianelli, L.; Artuso, F.; Fidecaro, F.; Licitra, G. Evaluation of Acoustic Comfort and Sound Energy Transmission in a Yacht. Energies 2023, 16, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borelli, D.; Gaggero, T.; Rizzuto, E.; Schenone, C. Onboard ship noise: Acoustic comfort in cabins. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 177, 107912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizet, E. Speech intelligibility mappings in a car compartment. Int. J. Veh. Des. 1993, 14, 132–144. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.X.; Bei, C.; Sun, H. Relationship between chinese speech intelligibility and speech transmission index in rooms based on auralization. Speech Commun. 2011, 53, 986–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.; Sato, H.; Picard, M. On the importance of early reflections for speech in rooms. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 113, 3233–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granier, E.; Dalenback, B.I.; Svensson, P.; Kleiner, B. Experimental auralization of car audio installations. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1996, 44, 835–849. Available online: http://www.aes.org/e-lib/browse.cfm?elib=7882 (accessed on 1 October 1996).
- Meissner, M. Acoustics of small rectangular rooms: Analytical and numerical determination of reverberation parameters. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 120, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumsey, F. Automotive audio: They know where you sit. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2016, 64, 705–708. Available online: http://www.aes.org/e-lib/browse.cfm?elib=18378 (accessed on 19 September 2016).
- Kleiner, M.; Tichy, J. Acoustics of Small Rooms, 1st ed.; CRC Applied Mathematics Research Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Arweiler, I.; Buchholz, J.M. The influence of spectral characteristics of early reflections on speech intelligibility. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 130, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warzybok, A.; Rennies, J.; Brand, T.; Doclo, S.; Kollmeier, B. Effects of spatial and temporal integration of a single early reflection on speech intelligibility. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbitt, G.L.; Remtema, T.M. Automotive speech intelligibility measurements. Sound Vib. 2017, 51, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, C.; Donoso-Garcia, P.; Medeiros, E. Intelligibility in low-cost automotive audio systems. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2016, 64, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samardzic, N.; Novak, C. In-vehicle speech intelligibility for different driving conditions using the speech transmission index. Noise Control Eng. J. 2011, 59, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samardzic, N.; Novak, C. In-vehicle application of common speech intelligibility metrics. Int. J. Veh. Noise Vib. 2011, 7, 328–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizet, E. The influence of speech importance function upon articulation index computation in cars. Noise Control Eng. J. 1992, 38, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tan, G.; Chen, S.; Jiang, J.; Su, L. Research on speech intelligibility of sound field inside passenger car. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 403, 5214–5219. [Google Scholar]
- Dal-Degan, N.; Prati, C. Acoustic noise analysis and speech enhancement techniques for mobile radio applications. Signal Process. 1988, 15, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qatu, M.; Abdelhamid, M.; Pang, J.; Sheng, G. Overview of automotive noise and vibration. Int. J. Veh. Noise Vib. 2009, 5, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visintainer, A.; VanBuskirk, J. Effects of sound absorption on speech intelligibility in an automotive environment. In Proceedings of the Noise and Vibration Conference, Traverse City, MI, USA, 20 May 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, L.D.; Yu, L.; Zhao, T.; Meng, Q.L.; Yu, G.Z. Speech intelligibility for various head orientations of a listener in an automobile using the speech transmission index. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 149, 2686–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.D.; Yu, G.Z.; Zhou, H.L.; Meng, Q.L. Effect of listener head orientation on speech reception threshold in an automotive environment. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 193, 108782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.D.; Yu, G.Z. Binaural speech transmission index with spatialized virtual speaker in near field: Distance and direction dependence. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 148, EL202–EL207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.D.; Yu, G.Z. Azimuth-dependent model of binaural speech transmission index based on near-field head-related transfer functions. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 195, 10855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.D.; Yu, G.Z. The combined effect of source directivity and binaural listening on near-field binaural speech transmission index evaluation. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 203, 109198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.D.; Yu, G.Z. Effect of speaker orientation on speech intelligibility in an automotive environment. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 205, 109269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilzi, P.; Bozzoli, F.; Farina, A. Influence of artificial mouth’s directivity in determining speech transmission index. In Proceedings of the 119th Audio Engineering Society Convention, New York, NY, USA, 7–10 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.X.; Wang, T.; Wu, S.X. Investigation on the effects of source directivity of chinese speech intelligibility in real and virtual rooms. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.S.; Mo, F.S.; Kang, J. Influence of sound source characteristics in determining objective speech intelligibility metrics. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 89, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wijngaarden, S.J.; Drullman, R. Binaural intelligibility prediction based on the speech transmission index. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 4514–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.D.; Ren, M. The effect of listener head orientation on front-to-rear speech intelligibility in an automotive cabin. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 211, 109517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martellotta, F.; D’alba, M.; Crociata, S.D. Laboratory measurement of sound absorption of occupied pews and standing audiences. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J. Modeling chairs and occupants to closely approximate the sound absorption of occupied full scale theatre chairs. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 75, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J. Effect of occupancy on acoustical conditions in university classrooms. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 114, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J. Effects of the distribution of occupants in partially occupied classrooms. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 140, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martellotta, F.; Crociata, S.D.; D’Alba, M. On site validation of sound absorption measurements of occupied pews. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Bradley, J.S. Evaluation of acoustical conditions for speech communication in working elementary school classrooms. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 2064–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kath, U. The influence of clothes on the sound absorption of single persons. Acta Acust. United Acust. 1966, 17, 234–237. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, J.S. The sound absorption of occupied auditorium seating. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1996, 99, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.S.; Choi, Y.J.; Jeong, D.U. Understanding chair absorption characteristics using the perimeter-to-area method. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Bradley, J.S.; Jeong, D.U. Towards better predictions of theatre chair absorption using the perimeter-to-area method. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 76, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desarnaulds, V.; Carvalho, A.P.; Monay, G. Church acoustics and the influence of occupancy. Build. Acoust. 2002, 9, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, M. Experimental investigation of the acoustical characteristics of university classrooms. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 106, 1810–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.S. Some further investigations of the seat dip effect. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1991, 90, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, M. Rating, ranking, and understanding acoustical quality in university classrooms. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 112, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgson, M.; Nosal, E. Effect of noise and occupancy on optimal reverberation times for speech intelligibility in classrooms. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 111, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Morales, L.; Martellotta, F. A geometrical acoustic simulation of the effect of occupancy and source position in historical churches. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 91, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Bradley, J.S. Effects of varied row spacing and adding cushions, carpet and occupants on pew sound absorption. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 99, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Bradley, J.S.; Jeong, D.U. Experimental investigation of chair type, row spacing, occupants, and carpet on theatre chair absorption. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 137, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speech Intelligibility Measurement Kit. 2022. Available online: https://bedrock-usa.com/speech-intelligibility-measurement-kit/ (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- IEC 60268-16; Sound System Equipment. Part 16: Objective Rating of Speech Intelligibility by Speech Transmission Index. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- GB/T23461-2009; 3D Dimensions of Male Adult Head Forms. Echnical Report. National Standard of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Majdak, P.; Balazs, P.; Labac, B. Multiple exponential sweep method for fast measurement of head related transfer functions. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2007, 55, 632–646. [Google Scholar]
- Houtgast, T.; Steeneken, H.; Plomp, R. Predicting speech intelligibility in rooms from the modulation transfer function.III. general room acoustics. Acta Acust. United Acust. 1980, 46, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, M.R. Modulation transfer functions: Definition and measurement. Acta Acust. United Acust. 1981, 49, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rife, D. Modulation transfer function measurement with maximum length sequences. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1992, 40, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 7347-1987; The Standard Spectrum of Chinese Speech. National Standard of China: Beijing, China, 1987.
- Hu, H.; Xi, X.; Wong, L.L.; Hochmuth, S.; Warzybok, A.; Kollmeier, B. Construction and evaluation of the mandarin chinese matrix (CMNmatrix) sentence test for the assessment of speech recognition in noise. Int. J. Audiol. 2018, 57, 838–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, G.S. The decorrelation of audio signals and its impact on spatial imagery. Comput. Music J. 1995, 19, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.S.; Shi, B.; Xiang, N. Audio signal decorrelation based on reciprocal-maximal length sequence filters and its applications to spatial sound. In Proceedings of the Audio Engineering Society Convention, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, N.; Schroeder, M.R. Reciprocal maximum-length sequence pairs for acoustical dual source measurements. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 113, 2754–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, T.; Kollmeier, B. Efficient adaptive procedures for threshold and concurrent slope estimates for psychophysics and speech intelligibility tests. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 111, 2801–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO3382-1; Acoustics–Measurement of the Reverberation Time–Part 1: Performance Spaces. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Xu, S.H.; Peng, J.X.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, W.Q. The effect of low frequency reverberation on Chinese speech intelligibility in two classrooms. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 182, 108241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.S.; Reich, R.; Norcross, S.G. A just noticeable difference in C50 for speech. Appl. Acoust. 1999, 58, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
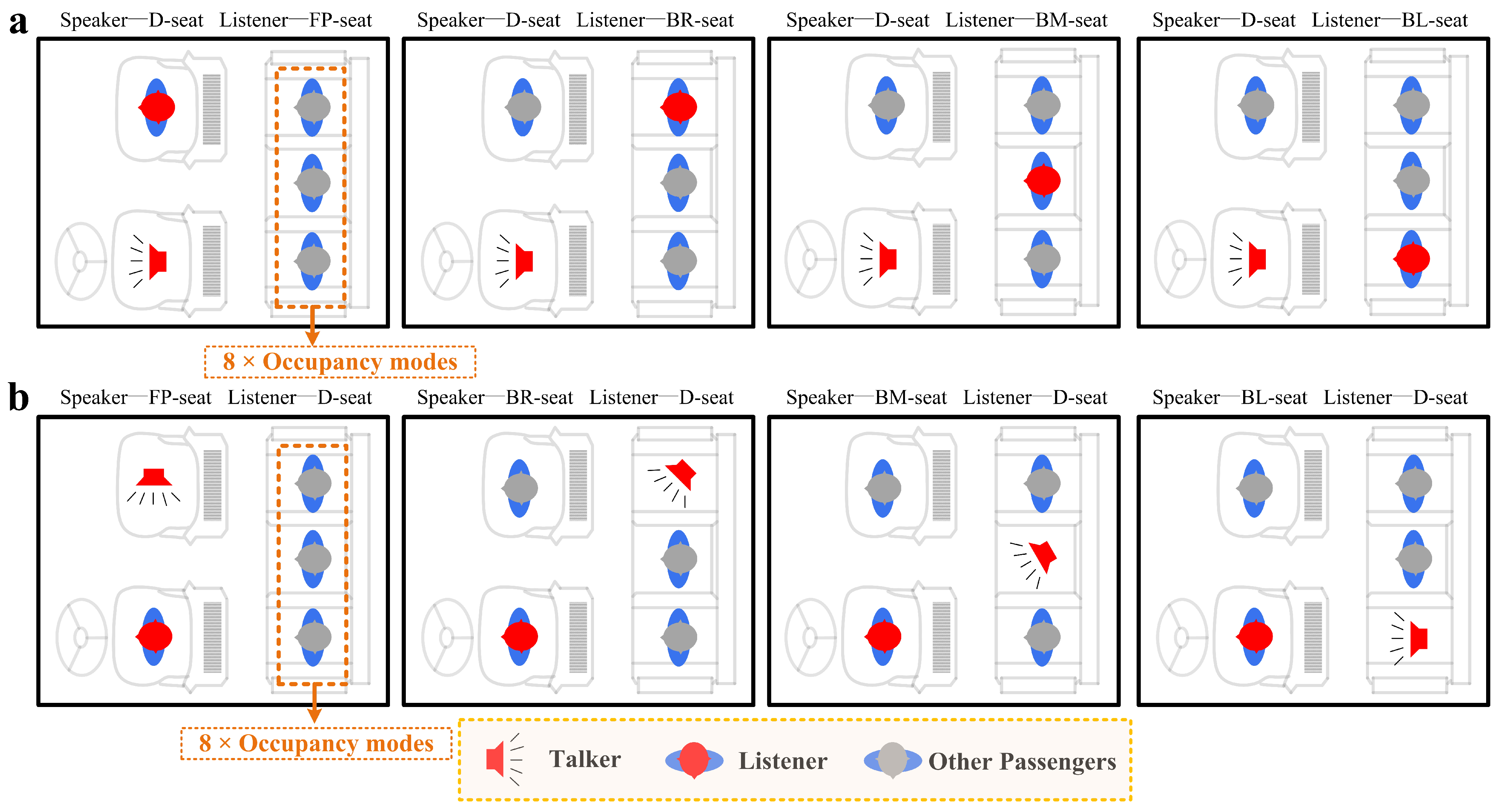


| Group 1 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speaker | Listener | Occupancy Modes | |||||||
| D seat | FP seat | None | BR | BM | BL | BM+BL | BR+BL | BR+BM | BR+BM+BL |
| D seat | BR seat | None | FP | BM | BL | BM+BL | FP+BL | FP+BM | FP+BM+BL |
| D seat | BM seat | None | FP | BR | BL | BR+BL | FP+BL | FP+BM | FP+BM+BL |
| D seat | BL seat | None | FP | BR | BM | BR+BM | FP+BM | FP+BR | FP+BR+BM |
| Group 2 | |||||||||
| Speaker | Listener | Occupancy modes | |||||||
| FP seat | D seat | None | BR | BM | BL | BM+BL | BR+BL | BR+BM | BR+BM+BL |
| BR seat | D seat | None | FP | BM | BL | BM+BL | FP+BL | FP+BM | FP+BM+BL |
| BM seat | D seat | None | FP | BR | BL | BR+BL | FP+BL | FP+BM | FP+BM+BL |
| BL seat | D seat | None | FP | BR | BM | BR+BM | FP+BM | FP+BR | FP+BR+BM |
| Speaker | Listener | Variation Range in Magnitude (dB) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 125 Hz | 250 Hz | 500 Hz | 1 kHz | 2 kHz | 4 kHz | 8 kHz | |||
| D seat | FP seat | Left | 0.49 | 1.68 | 1.41 | 0.90 | 0.54 | 0.60 | 0.91 |
| Right | 0.55 | 0.73 | 0.68 | 0.88 | 0.74 | 0.39 | 0.41 | ||
| BR seat | Left | 2.15 | 0.88 | 1.09 | 0.67 | 1.95 | 4.92 | 7.46 | |
| Right | 2.20 | 0.77 | 2.88 | 2.21 | 2.00 | 1.87 | 1.48 | ||
| BM seat | Left | 1.63 | 0.96 | 1.75 | 3.21 | 0.86 | 2.09 | 3.35 | |
| Right | 2.62 | 2.96 | 1.83 | 1.95 | 2.29 | 3.90 | 2.86 | ||
| BL seat | Left | 1.13 | 6.91 | 5.23 | 2.00 | 2.01 | 1.65 | 1.50 | |
| Right | 4.90 | 10.80 | 3.53 | 1.86 | 2.79 | 1.88 | 4.05 | ||
| FP seat | D seat | Left | 0.64 | 0.73 | 1.53 | 1.00 | 1.08 | 0.40 | 0.49 |
| Right | 0.83 | 0.37 | 0.64 | 0.57 | 0.52 | 0.32 | 0.35 | ||
| BR seat | Left | 2.09 | 1.12 | 1.41 | 1.51 | 2.02 | 0.96 | 0.88 | |
| Right | 1.47 | 1.39 | 0.84 | 2.39 | 0.50 | 1.07 | 1.48 | ||
| BM seat | Left | 1.33 | 1.28 | 1.16 | 1.93 | 0.74 | 0.55 | 1.09 | |
| Right | 1.19 | 1.17 | 1.00 | 1.52 | 0.85 | 1.67 | 0.71 | ||
| BL seat | Left | 0.34 | 0.88 | 0.53 | 1.35 | 0.92 | 0.64 | 0.57 | |
| Right | 0.67 | 1.23 | 2.04 | 2.43 | 0.92 | 2.64 | 1.50 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, L.; Ren, M.; Liao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xiong, W.; Ou, L. Experimental Study of the Influence of Occupants on Speech Intelligibility in an Automotive Cabin. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7942. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177942
Liang L, Ren M, Liao L, Zhao Y, Xiong W, Ou L. Experimental Study of the Influence of Occupants on Speech Intelligibility in an Automotive Cabin. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(17):7942. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177942
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Linda, Miao Ren, Linghui Liao, Ye Zhao, Wei Xiong, and Liuying Ou. 2024. "Experimental Study of the Influence of Occupants on Speech Intelligibility in an Automotive Cabin" Applied Sciences 14, no. 17: 7942. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177942
APA StyleLiang, L., Ren, M., Liao, L., Zhao, Y., Xiong, W., & Ou, L. (2024). Experimental Study of the Influence of Occupants on Speech Intelligibility in an Automotive Cabin. Applied Sciences, 14(17), 7942. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177942






