Large Language Models for Intelligent Transportation: A Review of the State of the Art and Challenges
Abstract
1. Introduction
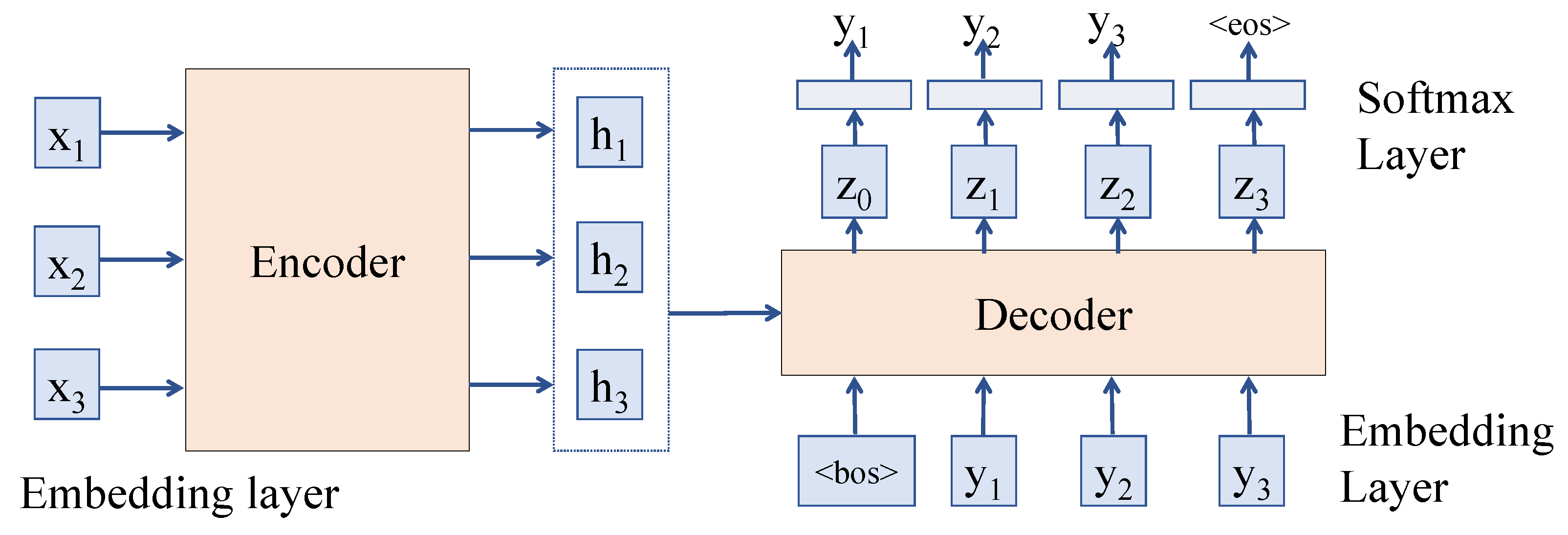
2. Preliminaries on Large Language Models
3. Literature Review
3.1. Autonomous Driving
3.2. Safety
3.3. Tourism
3.4. Traffic
3.5. Other
4. Challenges
4.1. Open-Source Models and Reproducibility
4.2. Human–Machine Interaction
4.3. Real-Time Capabilities of LLMs
4.4. Multi-Modal Integration
4.5. Verification and Validation Efforts
4.6. Ethical Considerations
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, F.; Yao, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, R.; Qiu, Z. SPSRec: An Efficient Signal Phase Recommendation for Signalized Intersections With GAN and Decision-Tree Model. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 15601–15612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Qian, J.; Xin, Y.; Liu, B.; Dong, Y. Distracted Driver Detection Based on a CNN With Decreasing Filter Size. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 6922–6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Yu, F.R.; Liu, P.X.; He, Y. A Hybrid Driving Decision-Making System Integrating Markov Logic Networks and Connectionist AI. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 3514–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogyrbayeva, A.; Meraliyev, M.; Mustakhov, T.; Dauletbayev, B. Machine Learning to Solve Vehicle Routing Problems: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 4754–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y. Decoding Urban Mobility: Application of Natural Language Processing and Machine Learning to Activity Pattern Recognition, Prediction, and Temporal Transferability Examination. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 7151–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cheng, Y. Travel Mode Choice Prediction Using Imbalanced Machine Learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 3795–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, J.; Rawal, A.; Rawat, D.B.; Sadler, B.M. Ensemble Deep Learning for Sustainable Multimodal UAV Classification. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 15425–15434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geske, A.M.; Herold, D.M.; Kummer, S. Integrating AI support into a framework for collaborative decision-making (CDM) for airline disruption management. J. Air Transp. Res. Soc. 2024, 3, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geske, A.M.; Herold, D.M.; Kummer, S. Artificial Intelligence as a driver of efficiency in air passenger transport: A systematic literature review and future research avenues. J. Air Transp. Res. Soc. 2024, 3, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Tay, Y.; Bommasani, R.; Raffel, C.; Zoph, B.; Borgeaud, S.; Yogatama, D.; Bosma, M.; Zhou, D.; Metzler, D.; et al. Emergent abilities of Large Language Models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.07682. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, N.; Lu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Yang, G.; Huo, Y.; Wen, J.; Lu, H.; Song, R.; Gao, X.; Xiang, T.; et al. Towards artificial general intelligence via a multimodal foundation model. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubeck, S.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Eldan, R.; Gehrke, J.; Horvitz, E.; Kamar, E.; Lee, P.; Lee, Y.T.; Li, Y.; Lundberg, S.; et al. Sparks of artificial general intelligence: Early experiments with gpt-4. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.12712. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, D.M.; Bommarito, M.J.; Gao, S.; Arredondo, P. Gpt-4 passes the bar exam. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2023, 382, 20230254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Du, Z.; Ding, M.; Qian, Y.; Yang, Z.; Tang, J. GPT understands, too. AI Open 2023. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Large language models for air transportation: A critical review. J. Air Transp. Res. Soc. 2024, 2, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI Blog 2019, 1, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Min, B.; Ross, H.; Sulem, E.; Veyseh, A.P.B.; Nguyen, T.H.; Sainz, O.; Agirre, E.; Heintz, I.; Roth, D. Recent advances in natural language processing via large pre-trained language models: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 56, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Yuan, K.; Huang, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Feedback is all you need: From ChatGPT to autonomous driving. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2023, 66, 166201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhong, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Khajepour, A. DriveLLM: Charting the Path toward Full Autonomous Driving with Large Language Models. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 9, 1450–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Ma, Y.; Cao, X.; Ye, W.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, K.; Chen, J.; Lu, J.; Yang, Z.; Liao, K.D.; et al. A Survey on Multimodal Large Language Models for Autonomous Driving. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.12320. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Yao, J.; Tu, Z.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, T. TARGET: Traffic Rule-based Test Generation for Autonomous Driving Systems. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.06018. [Google Scholar]
- Dewangan, V.; Choudhary, T.; Chandhok, S.; Priyadarshan, S.; Jain, A.; Singh, A.K.; Srivastava, S.; Jatavallabhula, K.M.; Krishna, K.M. Talk2BEV: Language-enhanced Bird’s-eye View Maps for Autonomous Driving. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.02251. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.; Teng, S.; Chen, H.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Gou, C.; Li, B.; Ma, S.; Miao, Q.; Na, X.; et al. Chat with chatgpt on intelligent vehicles: An IEEE tiv perspective. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 8, 2020–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Li, X.; Wen, L.; Dou, M.; Cai, P.; Shi, B.; Qiao, Y. Drive like a human: Rethinking autonomous driving with large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.07162. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S.X. ChatGPT in connected and autonomous vehicles: Benefits and challenges. Intell. Robot. 2023, 3, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, H.; Mu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, L.; Xu, C.; Luo, P.; Li, S.E.; Tomizuka, M.; Zhan, W.; Ding, M. Languagempc: Large language models as decision makers for autonomous driving. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.03026. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, G. Leveraging ChatGPT for Real-Time Decision-Making in Autonomous Systems. Eduzone Int. Peer Rev./Ref. Multidiscip. J. 2023, 12, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, C.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.Y. VistaGPT: Generative Parallel Transformers for Vehicles With Intelligent Systems for Transport Automation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 8, 4198–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiao, R.; Lang, C.; Zhan, S.S.; Huang, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, Q. Empowering Autonomous Driving with Large Language Models: A Safety Perspective. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.00812. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, L.; Fu, D.; Li, X.; Cai, X.; Ma, T.; Cai, P.; Dou, M.; Shi, B.; He, L.; Qiao, Y. Dilu: A knowledge-driven approach to autonomous driving with large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.16292. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, E.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wong, K.K.; Li, Z.; Zhao, H. Drivegpt4: Interpretable end-to-end autonomous driving via large language model. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.01412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Jia, X.; Li, H.; Yan, J. A Survey of Large Language Models for Autonomous Driving. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.01043. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, H.; Dou, C.; Tao, Z.; Xu, X.; Liu, D. Enhancing the Spatial Awareness Capability of Multi-Modal Large Language Model. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.20357. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, M.; Zagar, B.L.; Yurtsever, E.; Knoll, A.C. Vision language models in autonomous driving and intelligent transportation systems. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.14414. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, S.R.; Walsh, H.S. SafeAeroBERT: Towards a Safety-Informed Aerospace-Specific Language Model. In Proceedings of the AIAA AVIATION 2023 Forum, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–16 June 2023; p. 3437. [Google Scholar]
- Arteaga, C.; Park, J.W. A Large Language Model Framework to Uncover Underreporting in Traffic Crashes. 2023. SSRN 4613378. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4613378 (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Chandra, C.; Jing, X.; Bendarkar, M.V.; Sawant, K.; Elias, L.; Kirby, M.; Mavris, D.N. Aviation-BERT: A Preliminary Aviation-Specific Natural Language Model. In Proceedings of the AIAA AVIATION 2023 Forum, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–16 June 2023; p. 3436. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Duan, Z.; Bu, N.; Liu, Y.; Cao, J.; Gao, Z.; Zuo, P. ERNIE-based Named Entity Recognition Method for Traffic Accident Cases. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Computer and Electrical Engineering (ICCEE 2023), Xian, China, 23–25 June 2023; IOP Publishing: Beijing, China, 2023; Volume 2589, p. 012020. [Google Scholar]
- de Zarzà, I.; de Curtò, J.; Roig, G.; Calafate, C.T. LLM multimodal traffic accident forecasting. Sensors 2023, 23, 9225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Yang, Q.; Ebadi, N.; Luo, X.R.; Rad, P. Identifying incident causal factors to improve aviation transportation safety: Proposing a deep learning approach. J. Adv. Transp. 2021, 2021, 5540046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Chennakesavan, A.; Chandra, C.; Bendarkar, M.V.; Kirby, M.; Mavris, D.N. BERT for Aviation Text Classification. In Proceedings of the AIAA AVIATION 2023 Forum, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–16 June 2023; p. 3438. [Google Scholar]
- Kierszbaum, S.; Klein, T.; Lapasset, L. ASRS-CMFS vs. RoBERTa: Comparing Two Pre-Trained Language Models to Predict Anomalies in Aviation Occurrence Reports with a Low Volume of In-Domain Data Available. Aerospace 2022, 9, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtarin, M.; Chowdhury, M.S.; Wood, J. Large Language Models in Analyzing Crash Narratives—A Comparative Study of ChatGPT, BARD and GPT-4. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.13563. [Google Scholar]
- Raja, K.V.; Siddharth, R.; Yuvaraj, S.; Kumar, K.R. An Artificial Intelligence based automated case-based reasoning (CBR) system for severity investigation and root-cause analysis of road accidents–Comparative analysis with the predictions of ChatGPT. J. Eng. Res. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Tikayat Ray, A.; Bhat, A.P.; White, R.T.; Nguyen, V.M.; Pinon Fischer, O.J.; Mavris, D.N. Examining the Potential of Generative Language Models for Aviation Safety Analysis: Case Study and Insights Using the Aviation Safety Reporting System (ASRS). Aerospace 2023, 10, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Huang, C. Natural Language Processing (NLP) in Aviation Safety: Systematic Review of Research and Outlook into the Future. Aerospace 2023, 10, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, O.; Abdel-Aty, M.; Wang, D.; Wang, C.; Ding, S. TrafficSafetyGPT: Tuning a Pre-trained Large Language Model to a Domain-Specific Expert in Transportation Safety. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.15311. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, O.; Abdel-Aty, M.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Ding, S. ChatGPT is on the horizon: Could a Large Language Model be all we need for Intelligent Transportation? arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.05382. [Google Scholar]
- Ziakkas, D.; Pechlivanis, K. Artificial Intelligence applications in aviation accident classification: A preliminary exploratory study. Decis. Anal. J. 2023, 9, 100358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Yasar, B.; Ali, L.; Dogan, S. Antecedents and consequences of travelers’ trust towards personalized travel recommendations offered by ChatGPT. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2023, 114, 103588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, I.; Ivanov, S. ChatGPT for tourism: Applications, benefits and risks. Tour. Rev. 2023, 79, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, M.; Demir, Ş.Ş. Is ChatGPT the right technology for service individualization and value co-creation? evidence from the travel industry. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2023, 40, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, Ş.Ş.; Demir, M. Professionals’ perspectives on ChatGPT in the tourism industry: Does it inspire awe or concern? J. Tour. Theory Res. 2023, 9, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Pandey, N.; Currie, W.; Micu, A. Leveraging ChatGPT and other generative Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based applications in the hospitality and tourism industry: Practices, challenges and research agenda. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2023, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emrullah, E. Importance of ChatGPT in Tourism. J. Tour. Gastron. Stud. 2023, 11, 780–793. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Cruz, G.; Hinkle, S.D.; Roque, N.A.; Mouloua, M. ChatGPT as the Ultimate Travel Buddy or Research Assistant: A Study on Perceived Attitudes and Usability. In Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 23–27 October 2023; SAGE Publications Sage CA: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2023; pp. 459–464. [Google Scholar]
- Goktas, P.; Dirsehan, T. Optimizing Customer Experience in Hospitality and Tourism with ChatGPT Plugins: A Strategic Guide. 2023. SSRN 4602852. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4602852 (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Gursoy, D.; Li, Y.; Song, H. ChatGPT and the hospitality and tourism industry: An overview of current trends and future research directions. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2023, 32, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harahap, M.A.K.; Ausat, A.M.A.; Rachman, A.; Riady, Y.; Azzaakiyyah, H.K. Overview of ChatGPT Technology and its Potential in Improving Tourism Information Services. J. Minfo Polgan 2023, 12, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskender, A. Holy or unholy? Interview with open AI’s ChatGPT. Eur. J. Tour. Res. 2023, 34, 3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, S.; Soliman, M. Game of algorithms: ChatGPT implications for the future of tourism education and research. J. Tour. Futur. 2023, 9, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; Kim, C.; Jhang, J.; King, B. When ChatGPT Gives Incorrect Answers: The Impact of Inaccurate Information by Generative AI on Tourism Decision-Making. J. Travel Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Hailu, T.B. Effects of AI ChatGPT on travelers’ travel decision-making. Tour. Rev. 2023, 79, 1038–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mich, L.; Garigliano, R. ChatGPT for e-Tourism: A technological perspective. Inf. Technol. Tour. 2023, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nautiyal, R.; Albrecht, J.N.; Nautiyal, A. ChatGPT and tourism academia. Ann. Tour. Res. 2023, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, E.; Yhee, Y.; Koo, C. ChatGPT for Trip Planning: The Effect of Narrowing Down Options. J. Travel Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudirjo, F.; Diawati, P.; Riady, Y.; Ausat, A.M.A.; Suherlan, S. The Role of ChatGPT in Enhancing the Information Search and Decision-Making Process of Travellers. J. Minfo Polgan 2023, 12, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, I.A.; Lian, Q.L.; Sun, D. Autonomous travel decision-making: An early glimpse into ChatGPT and generative AI. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2023, 56, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, L.; Gao, M.; Mei, H.; Wei, H. LLM powered sim-to-real transfer for traffic signal control. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.14284. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Oliaee, A.H.; Le, M.; Pratt, M.P.; Wu, J. Classifying Pedestrian Maneuver Types Using the Advanced Language Model. Transp. Res. Rec. 2023, 2677, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driessen, T.; Dodou, D.; Bazilinskyy, P.; de Winter, J. Putting ChatGPT Vision (GPT-4V) to the test: Risk perception in traffic images. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2023, 11, 231676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, P.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B. A context-aware language model to improve the speech recognition in air traffic control. Aerospace 2021, 8, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Wi, J.; Lee, E.; Kang, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y. TrafficBERT: Pre-trained model with large-scale data for long-range traffic flow forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 186, 115738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Shen, X.; Peng, H.; Liu, X.; Qin, J.; Li, J.; Xie, J.; Gao, P.; Zhou, G.; Gong, J. Surrealdriver: Designing generative driver agent simulation framework in urban contexts based on Large Language Model. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.13193. [Google Scholar]
- Maynard, P.; Clarke, S.S.; Almache, J.; Kumar, S.; Rajkumar, S.; Kemp, A.; Pai, R. Natural Language Processing (NLP) Techniques for Air Traffic Management Planning. In Proceedings of the AIAA AVIATION 2021 Forum, Virtual, 2–6 August 2021; p. 2322. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, B.; Xu, H.; Zhuang, D.; Ma, R.; Guo, X.; Zhao, J. Large Language Models for Travel Behavior Prediction. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.00819. [Google Scholar]
- Qasemi, E.; Francis, J.M.; Oltramari, A. Traffic-domain video question answering with automatic captioning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.09636. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, G. Enhancing Driving Experience and Safety through ChatGPT in Vehicle Systems. Eduzone Int. Peer Rev. Multidiscip. J. 2023, 12, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, G.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, S.; Ruan, J.; Mao, H.; Zhao, R. Reboost Large Language Model-based Text-to-SQL, Text-to-Python, and Text-to-Function—With Real Applications in Traffic Domain. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.18752. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.; Ivanovic, B.; Weng, X.; Pavone, M.; Kraehenbuehl, P. Language conditioned traffic generation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.07947. [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal, M.; Poudel, B.; Li, W. Can ChatGPT Enable ITS? The Case of Mixed Traffic Control via Reinforcement Learning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.08094. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ding, H.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Z. Information Extraction of Air-Traffic Control Instructions via Pre-trained Models. In Artificial Intelligence in China, Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in China, 2022; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 82–91. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; He, Z. ChatGPT as Your Vehicle Co-Pilot: An Initial Attempt. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 8, 4706–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ilievski, F.; Ma, K.; Kollaa, A.; Francis, J.; Oltramari, A. A Study of Situational Reasoning for Traffic Understanding. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.02520. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Pu, J.; Xue, J.; Yang, M.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.Y. HiVeGPT: Human-machine-augmented intelligent vehicles with generative pre-trained transformer. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 8, 2027–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, B.; Cai, P. TrafficGPT: Viewing, Processing and Interacting with Traffic Foundation Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.06719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhou, F.; Wu, L.; Xie, N.; He, Z. Semantic understanding and prompt engineering for large-scale traffic data imputation. Inf. Fusion 2024, 102, 102038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Gawade, S.; Azad, A.P.; Bhattacharyya, P. KITLM: Domain-Specific Knowledge InTegration into Language Models for Question Answering. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.03638. [Google Scholar]
- Chew, P. Pioneering Tomorrow’s AI System through Aerospace Engineering: An Empirical Study of the Peter Chew Method for Overcoming Error in Chat GPT. 2023. SSRN 4646033. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4646033 (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Kim, J.; Lee, J. How does ChatGPT Introduce Transport Problems and Solutions in North America? Findings 2023. [CrossRef]
- Leong, M.; Abdelhalim, A.; Ha, J.; Patterson, D.; Pincus, G.L.; Harris, A.B.; Eichler, M.; Zhao, J. MetRoBERTa: Leveraging Traditional Customer Relationship Management Data to Develop a Transit-Topic-Aware Language Model. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.05012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.; Sonnenfeld, N.; Finkelstein, L.; Alonso, A.; Gomez, C.; Duruaku, F.; Jentsch, F. Using AI Tools to Develop Training Materials for Aviation: Ethical, Technical, and Practical Concerns. In Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 23–27 October 2023; SAGE Publications Sage CA: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2023; p. 21695067231192904. [Google Scholar]
- Tikayat Ray, A.; Cole, B.F.; Pinon Fischer, O.J.; White, R.T.; Mavris, D.N. aeroBERT-Classifier: Classification of Aerospace Requirements Using BERT. Aerospace 2023, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikayat Ray, A.; Pinon-Fischer, O.J.; Mavris, D.N.; White, R.T.; Cole, B.F. aeroBERT-NER: Named-Entity Recognition for Aerospace Requirements Engineering using BERT. In Proceedings of the AIAA SCITECH 2023 Forum, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–16 June 2023; p. 2583. [Google Scholar]
- Voß, S. Bus Bunching and Bus Bridging: What Can We Learn from Generative AI Tools like ChatGPT? Sustainability 2023, 15, 9625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chou, J.; Rouck, D.; Tien, A.; Baumgartner, D.M. Adapting Sentence Transformers for the Aviation Domain. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.09556. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Chou, J.; Zhou, X.; Tien, A.; Baumgartner, D.M. AviationGPT: A Large Language Model for the Aviation Domain. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.17686. [Google Scholar]
- Yenkikar, A.; Babu, C.N. AirBERT: A fine-tuned language representation model for airlines tweet sentiment analysis. Intell. Decis. Technol. 2023, 17, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Anerdi, G.; Tan, D.S.; Bromuri, S. Language Modeling in Logistics: Customer Calling Prediction. In Proceedings of the European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning, Bruges, Belgium, 4–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, I.; Saenz, M.J. From Natural Language to Simulations: Applying GPT-3 Codex to Automate Simulation Modeling of Logistics Systems. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.12107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, I.; Jesus Saenz, M.; Ivanov, D. From natural language to simulations: Applying AI to automate simulation modelling of logistics systems. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 62, 1434–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kmiecik, M. ChatGPT in third-party logistics-the game-changer or a step into the unknown? J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2023, 9, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voß, S. Successfully Using ChatGPT in Logistics: Are We There Yet? In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Logistics, Berlin, Germany, 6–8 September 2023; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, S. A Review of ChatGPT and its Impact in Different Domains. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2023, 18, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, N.L. Multidisciplinary Collaboration: Key Players in Successful Implementation of ChatGPT and Similar Generative Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing, Finance, Retail, Transportation, and Construction Industry. OSF Preprints 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, S.; Crouse, S.R.; Winter, S.R.; Rice, C. The advantages and limitations of using ChatGPT to enhance technological research. Technol. Soc. 2023, 76, 102426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandelt, S.; Sun, X.; Zhang, A. AI-driven assistants for education and research? A case study on ChatGPT for air transport management. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2023, 113, 102483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jiao, F.; Li, X.; Qin, C.; Ravaut, M.; Zhao, R.; Xiong, C.; Joty, S. ChatGPT’s One-year Anniversary: Are Open-Source Large Language Models Catching up? arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.16989. [Google Scholar]
- Kosch, T.; Feger, S. Risk or Chance? Large Language Models and Reproducibility in Human-Computer Interaction Research. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.15782. [Google Scholar]
- Biderman, S.; Schoelkopf, H.; Sutawika, L.; Gao, L.; Tow, J.; Abbasi, B.; Aji, A.F.; Ammanamanchi, P.S.; Black, S.; Clive, J.; et al. Lessons from the Trenches on Reproducible Evaluation of Language Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14782. [Google Scholar]
- Rau, D.; Kamps, J. Query Generation Using Large Language Models: A Reproducibility Study of Unsupervised Passage Reranking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Retrieval, Glasgow, Scotland, UK, 24–28 March 2024; pp. 226–239. [Google Scholar]
- Laskar, M.T.R.; Alqahtani, S.; Bari, M.S.; Rahman, M.; Khan, M.A.M.; Khan, H.; Jahan, I.; Bhuiyan, A.; Tan, C.W.; Parvez, M.R.; et al. A Systematic Survey and Critical Review on Evaluating Large Language Models: Challenges, Limitations, and Recommendations. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.04069. [Google Scholar]
- Ziems, C.; Held, W.; Shaikh, O.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, D. Can Large Language Models transform computational social science? Comput. Linguist. 2024, 50, 237–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franc, J.M.; Cheng, L.; Hart, A.; Hata, R.; Hertelendy, A. Repeatability, reproducibility, and diagnostic accuracy of a commercial Large Language Model (ChatGPT) to perform emergency department triage using the Canadian triage and acuity scale. Can. J. Emerg. Med. 2024, 26, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qiao, A.; Neiswanger, W.; Wang, H.; Tan, B.; Tao, T.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Pangarkar, O.; et al. LLM360: Towards Fully Transparent Open-Source LLMs. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.06550. [Google Scholar]
- Raffel, C.; Shazeer, N.; Roberts, A.; Lee, K.; Narang, S.; Matena, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, P.J. Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 140:1–140:67. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.; Constant, N.; Roberts, A.; Kale, M.; Al-Rfou, R.; Siddhant, A.; Barua, A.; Raffel, C. mT5: A Massively Multilingual Pre-trained Text-to-Text Transformer. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, NAACL-HLT 2021, Online, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 483–498. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, W.; Ren, X.; Su, T.; Wang, H.; Liao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; et al. PanGu-α: Large-scale Autoregressive Pretrained Chinese Language Models with Auto-parallel Computation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.12369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gu, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, S.; Xiao, C.; Sun, Z.; Yao, Y.; Qi, F.; Guan, J.; Ke, P.; et al. CPM-2: Large-scale Cost-effective Pre-trained Language Models. AI Open 2021, 2, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanh, V.; Webson, A.; Raffel, C.; Bach, S.H.; Sutawika, L.; Alyafeai, Z.; Chaffin, A.; Stiegler, A.; Raja, A.; Dey, M.; et al. Multitask Prompted Training Enables Zero-Shot Task Generalization. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2022), Virtual Event, 25–29 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nijkamp, E.; Pang, B.; Hayashi, H.; Tu, L.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Savarese, S.; Xiong, C. Codegen: An open Large Language Model for code with mtulti-turn program synthesis. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.13474. [Google Scholar]
- Black, S.; Biderman, S.; Hallahan, E.; Anthony, Q.; Gao, L.; Golding, L.; He, H.; Leahy, C.; McDonell, K.; Phang, J.; et al. GPT-NeoX-20B: An Open-Source Autoregressive Language Model. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.06745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mishra, S.; Alipoormolabashi, P.; Kordi, Y.; Mirzaei, A.; Naik, A.; Ashok, A.; Dhanasekaran, A.S.; Arunkumar, A.; Stap, D.; et al. Super-NaturalInstructions: Generalization via Declarative Instructions on 1600+ NLP Tasks. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, EMNLP 2022, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 7–11 December 2022; pp. 5085–5109. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, Y.; Dehghani, M.; Tran, V.Q.; García, X.; Wei, J.; Wang, X.; Chung, H.W.; Bahri, D.; Schuster, T.; Zheng, H.; et al. UL2: Unifying Language Learning Paradigms. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.05131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Roller, S.; Goyal, N.; Artetxe, M.; Chen, M.; Chen, S.; Dewan, C.; Diab, M.T.; Li, X.; Lin, X.V.; et al. OPT: Open Pre-trained Transformer Language Models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.01068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-jussà, M.R.; Cross, J.; Çelebi, O.; Elbayad, M.; Heafield, K.; Heffernan, K.; Kalbassi, E.; Lam, J.; Licht, D.; Maillard, J.; et al. No Language Left Behind: Scaling Human-Centered Machine Translation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.04672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Xia, X.; Zou, X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, S.; Xue, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shen, L.; Wang, A.; Li, Y.; et al. CodeGeeX: A Pre-Trained Model for Code Generation with Multilingual Evaluations on HumanEval-X. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.17568. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, A.; Liu, X.; Du, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lai, H.; Ding, M.; Yang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Xia, X.; et al. GLM-130B: An Open Bilingual Pre-trained Model. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.02414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.W.; Hou, L.; Longpre, S.; Zoph, B.; Tay, Y.; Fedus, W.; Li, E.; Wang, X.; Dehghani, M.; Brahma, S.; et al. Scaling Instruction-Finetuned Language Models. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2022, 25, 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- Scao, T.L.; Fan, A.; Akiki, C.; Pavlick, E.; Ilic, S.; Hesslow, D.; Castagné, R.; Luccioni, A.S.; Yvon, F.; Gallé, M.; et al. BLOOM: A 176B-Parameter Open-Access Multilingual Language Model. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.05100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muennighoff, N.; Wang, T.; Sutawika, L.; Roberts, A.; Biderman, S.; Scao, T.L.; Bari, M.S.; Shen, S.; Yong, Z.X.; Schoelkopf, H.; et al. Crosslingual Generalization through Multitask Finetuning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.01786. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, R.; Kardas, M.; Cucurull, G.; Scialom, T.; Hartshorn, A.; Saravia, E.; Poulton, A.; Kerkez, V.; Stojnic, R. Galactica: A Large Language Model for Science. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.09085. [Google Scholar]
- Iyer, S.; Lin, X.V.; Pasunuru, R.; Mihaylov, T.; Simig, D.; Yu, P.; Shuster, K.; Wang, T.; Liu, Q.; Koura, P.S.; et al. OPT-IML: Scaling Language Model Instruction Meta Learning through the Lens of Generalization. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.12017. [Google Scholar]
- Touvron, H.; Lavril, T.; Izacard, G.; Martinet, X.; Lachaux, M.; Lacroix, T.; Rozière, B.; Goyal, N.; Hambro, E.; Azhar, F.; et al. LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.13971. [Google Scholar]
- Biderman, S.; Schoelkopf, H.; Anthony, Q.; Bradley, H.; O’Brien, K.; Hallahan, E.; Khan, M.A.; Purohit, S.; Prashanth, U.S.; Raff, E.; et al. Pythia: A Suite for Analyzing Large Language Models Across Training and Scaling. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.01373. [Google Scholar]
- Nijkamp, E.; Hayashi, H.; Xiong, C.; Savarese, S.; Zhou, Y. CodeGen2: Lessons for Training LLMs on Programming and Natural Languages. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.02309. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Allal, L.B.; Zi, Y.; Muennighoff, N.; Kocetkov, D.; Mou, C.; Marone, M.; Akiki, C.; Li, J.; Chim, J.; et al. StarCoder: May the source be with you! arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.06161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touvron, H.; Martin, L.; Stone, K.; Albert, P.; Almahairi, A.; Babaei, Y.; Bashlykov, N.; Batra, S.; Bhargava, P.; Bhosale, S.; et al. Llama 2: Open foundation and fine-tuned chat models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.09288. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.; Xiao, B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, B.; Yin, C.; Lv, C.; Pan, D.; Wang, D.; Yan, D.; Yang, F.; et al. Baichuan 2: Open large-scale language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.10305. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Bai, S.; Chu, Y.; Cui, Z.; Dang, K.; Deng, X.; Fan, Y.; Ge, W.; Han, Y.; Huang, F.; et al. Qwen technical report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.16609. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Fang, X.; Meng, X.; Fan, S.; Han, P.; Li, J.; Du, L.; Qin, B.; et al. Flm-101b: An open llm and how to train it with $100 k budget. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.03852. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, T.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, B.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Li, B.; Cheng, C.; Lü, W.; Hu, R.; et al. Skywork: A More Open Bilingual Foundation Model. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.19341. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, H.; Shen, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, G.; Bie, Y.; Xu, C. Gpt-4 enhanced multimodal grounding for autonomous driving: Leveraging cross-modal attention with Large Language Models. Commun. Transp. Res. 2024, 4, 100116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.; Oh, S.J.; De Rezende, R.S.; Kalantidis, Y.; Larlus, D. Probabilistic embeddings for cross-modal retrieval. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 8415–8424. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Qian, Y.; Yu, Y.; Qin, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Yao, K.; Han, J.; Liu, J.; Ding, E. Structext: Structured text understanding with multi-modal transformers. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Chengdu, China, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 1912–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Head, C.B.; Jasper, P.; McConnachie, M.; Raftree, L.; Higdon, G. Large language model applications for evaluation: Opportunities and ethical implications. New Dir. Eval. 2023, 2023, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, S.M.; Pan, S.; Erlien, S.M.; Gerdes, J.C. Incorporating Ethical Considerations Into Automated Vehicle Control. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 18, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, P.; Sun, L.; Furey, H.; Jenkins, R.; Phillips, C.R.M.; Powers, T.M.; Ritterson, R.S.; Xie, Y.; Casagrande, R.; Evans, N.G. Modelling Ethical Algorithms in Autonomous Vehicles Using Crash Data. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 7775–7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bešinović, N.; De Donato, L.; Flammini, F.; Goverde, R.M.P.; Lin, Z.; Liu, R.; Marrone, S.; Nardone, R.; Tang, T.; Vittorini, V. Artificial Intelligence in Railway Transport: Taxonomy, Regulations, and Applications. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 14011–14024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Focus |
|---|---|
| Chen et al. [20] | Feedback of ChatGPT and architectural decisions for AD |
| Cui et al. [21] | LLMs’ reasoning abilities for high-level decision-making in the context of AD |
| Cui et al. [22] | Applications and challenges of multi-modal LLMs for AD |
| Deng et al. [23] | Test generation for AD systems based on traffic rules from LLMs |
| Dewangan et al. [24] | Integrating large vision–language models and bird’s-eye view maps for AD |
| Du et al. [25] | Possible applications, challenges and opportunities of ChatGPT in intelligent vehicles |
| Fu et al. [26] | The potential of LLMs for key abilities necessary for AD |
| Lei et al. [27] | Benefits and challenges of ChatGPT for connected and autonomous vehicles |
| Sha et al. [28] | Combining LLMs and model predictive control for high-level decision-making of AD |
| Singh [29] | Elevating real-time decision-making capabilities with ChatGPT in autonomous systems |
| Tian et al. [30] | The automatic composing platform with LLMs for end-to-end driving systems |
| Wang et al. [31] | LLMs for AD, incorporating safety verifiers for contextual safety learning |
| Wen et al. [32] | LLMs-based AD with experiences from real-world datasets and generalization ability |
| Xu et al. [33] | LLMs to improve the interpretability of end-to-end AD |
| Yang et al. [34] | Overview on state of technological advancements concerning LLMs for AD |
| Zhao et al. [35] | Multi-Modal MLL to improve spatial awareness capabilities in industries |
| Zhou et al. [36] | Applications and future trends of vision–language models in AD and ITS |
| Reference | Focus |
|---|---|
| Andrade and Walsh [37] | Document classification based on the text in aviation safety reports |
| Arteaga and Park [38] | Analyzing underreported crash factors based on traffic crash narratives |
| Chandra et al. [39] | Extracting safety concepts by aviation text-data mining |
| Cheng et al. [40] | Mining the key information from traffic accident texts |
| de Zarzà et al. [41] | Forecasting traffic accidents with the context of autonomous driving |
| Dong et al. [42] | Identifying incident causal factors to improve aviation safety |
| Jing et al. [43] | Applying multi-label classification on aviation safety reports |
| Kierszbaum et al. [44] | Predicting anomalies based on the Aviation Safety Reporting System (ASRS) |
| Mumtarin et al. [45] | Comparing the performance of ChatGPT, BARD and GPT-4 in traffic crashes |
| Raja et al. [46] | Analyzing ChatGPT in severity investigation of road crashes |
| Tikayat Ray et al. [47] | Investigating the potential of ChatGPT in aviation safety analysis |
| Yang and Huang [48] | A systematic review of natural language processing (NLP) in aviation safety |
| Zheng et al. [49] | Tuning a pre-trained LLM of the open-source LLaMA in transportation safety |
| Zheng et al. [50] | Smarter traffic safety decision-making with LLMs |
| Ziakkas and Pechlivanis [51] | A comparative analysis of ChatGPT in aviation accident classification |
| Reference | Focus |
|---|---|
| Ali et al. [52] | Impacts of ChatGPT’s personalized travel recommendation on travelers |
| Carvalho and Ivanov [53] | Applications, benefits and risks of ChatGPT in tourism |
| Demir and Demir [54] | Impacts of ChatGPT on service individualization and value co-creation |
| Demir and Demir [55] | Interviewing professionals in tourism industry about ChatGPT |
| Dwivedi et al. [56] | Impacts of generative AI on the tourism industry |
| Emrullah [57] | Possible contributions of ChatGPT to the tourism sector |
| Flores-Cruz et al. [58] | Perceived attitudes and usability with ChatGPT on research and travel |
| Goktas and Dirsehan [59] | ChatGPT to optimize customer experience in tourism |
| Gursoy et al. [60] | Benefits and potential challenges of ChatGPT in tourism and hospitality |
| Harahap et al. [61] | ChatGPT to improve information services in the tourism industry |
| Iskender [62] | ChatGPT as an interviewee for the tourism industry and education |
| Ivanov and Soliman [63] | Implications of ChatGPT for tourism education and research |
| Kim et al. [64] | Impacts of inaccurate information on travelers’ acceptance of suggestions |
| Kim et al. [65] | Travelers’ intentions to use ChatGPT and drivers of decision-making |
| Mich and Garigliano [66] | ChatGPT’s adoption guidelines and issues in e-tourism |
| Nautiyal et al. [67] | Usage of ChatGPT in tourism and interdisciplinary contexts |
| Shin et al. [68] | Travelers’ perceptions of ChatGPT when reducing multiple travel options |
| Sudirjo et al. [69] | Impacts of ChatGPT on tourists’ information search and decision making |
| Wong et al. [70] | ChatGPT’s ability to enhance the tourist decision-making process |
| Reference | Focus |
|---|---|
| Da et al. [71] | Pre-trained LLMs for traffic signal control by learning a more realistic policy |
| Das et al. [72] | Classifying pedestrian maneuver types from unstructured textual content |
| Driessen et al. [73] | Applying GPT-4V for risk perception in forward-facing traffic images |
| Guo et al. [74] | Improving the automatic speech recognition in air traffic control |
| Jin et al. [75] | Long-range traffic flow forecasting with a pre-trained model |
| Jin et al. [76] | Developing human-like driving styles with a ‘coach agent’ module based on LLMs |
| Maynard et al. [77] | Analyzing air traffic management documents for optimizing operations |
| Mo et al. [78] | Travel behavior prediction without data-based parameter learning |
| Qasemi et al. [79] | Video Question Answering (VidQA) in intelligent traffic monitoring |
| Singh [80] | Personalized driver assistance in electric vehicles (EVs) |
| Sui et al. [81] | Reboost LLM-based Text-to-SQL for identifying traffic flow patterns |
| Tan et al. [82] | LLMs with a transformer-based decoder for dynamic traffic scene generation |
| Villarreal et al. [83] | Developing ChatGPT to solve complex mixed traffic control problems |
| Wang et al. [84] | Analyzing the information extraction performance of LLMs in air-traffic control |
| Wang et al. [85] | Serving as co-pilots for path tracking control and trajectory planning |
| Zhang et al. [86] | Performing situational decision-making for traffic monitoring |
| Zhang et al. [87] | Different applications of ChatGPT in the domain of intelligent vehicles |
| Zhang et al. [88] | Aiding human decision-making in traffic control |
| Zhang et al. [89] | Analyzing the spatio-temporal dynamics of traffic across road networks |
| Reference | Focus |
|---|---|
| Agarwal et al. [90] | A knowledge base integration method for question-answering in the aviation domain |
| Chew [91] | Enhancing the ability of ChatGPT in aerospace engineering |
| Kim and Lee [92] | Analyzing ChatGPT’s answers for transport issues and solutions |
| Leong et al. [93] | Developing a transit-topic-related LLM to classify open-ended text |
| Nguyen et al. [94] | Providing challenges of AI-based applications in aviation |
| Tikayat Ray et al. [95] | Classifying the design, functional, and performance requirements in aviation |
| Tikayat Ray et al. [96] | Developing an annotated aerospace corpus and fine-tuned BERT language model |
| Voß [97] | Exploring the use of ChatGPT in public transportation |
| Wang et al. [98] | A two-stage adapting sentence transformer-based model in the aviation domain |
| Wang et al. [99] | Achieving the versatility to tackle NLP problems in the aviation domain |
| Yenkikar and Babu [100] | A fine-tuned LLM to polarize customer sentiments automatically |
| Chen et al. [101] | Language model to predict customer calling of logistics |
| Jackson and Saenz [102] | GPT-3 Codex to develop simulation models for logistics |
| Jackson et al. [103] | Human-AI collaboration to model logistics systems |
| Kmiecik [104] | Impacts of ChatGPT on third-party logistics operators |
| Voß [105] | Applications of ChatGPT within the logistics domain |
| Aggarwal [106] | Developments and advancements of ChatGPT in different domains |
| Rane [107] | Cross-functional teams with ChatGPT in different industries |
| Rice et al. [108] | Capabilities, weaknesses and implications of ChatGPT in technological research |
| Wandelt et al. [109] | ChatGPT as an assistant in education and research |
| Model | Release Time | Size (B) | Base Model | IT | RLHF | Pre-Train Data Scale | Latest Data Timestamp | Hardware (GPUs / TPUs) | Training Time | ICL | CoT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T5 [118] | Oct-2019 | 11 | - | - | - | 1T tokens | Apr-2019 | 1024 TPU v3 | - | ✓ | - |
| mT5 [119] | Oct-2020 | 13 | - | - | - | 1T tokens | - | - | - | ✓ | - |
| PanGu- [120] | Apr-2021 | 13 | - | - | - | 1.1TB | - | 2048 Ascend 910 | - | ✓ | - |
| CPM-2 [121] | Jun-2021 | 198 | - | - | - | 2.6TB | - | - | - | - | - |
| T0 [122] | Oct-2021 | 11 | T5 | ✓ | - | - | - | 512 TPU v3 | 27 h | ✓ | - |
| CodeGen [123] | Mar-2022 | 16 | - | - | - | 577B tokens | - | - | - | ✓ | - |
| GPT-NeoX-20B [124] | Apr-2022 | 20 | - | - | - | 825GB | - | 96 40G A100 | - | ✓ | - |
| Tk-Instruct [125] | Apr-2022 | 11 | T5 | ✓ | - | - | - | 256 TPU v3 | 4 h | ✓ | - |
| UL2 [126] | May-2022 | 20 | - | - | - | 1T tokens | Apr-2019 | 512 TPU v4 | - | ✓ | ✓ |
| OPT [127] | May-2022 | 175 | - | - | - | 180B tokens | - | 992 80G A100 | - | ✓ | - |
| NLLB [128] | Jul-2022 | 54.5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - |
| CodeGeeX [129] | Sep-2022 | 13 | - | - | - | 850B tokens | - | 1536 Ascend 910 | 60 d | ✓ | - |
| GLM [130] | Oct-2022 | 130 | - | - | - | 400B tokens | - | 768 40G A100 | 60 d | ✓ | - |
| Flan-T5 [131] | Oct-2022 | 11 | T5 | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | ✓ |
| BLOOM [132] | Nov-2022 | 176 | - | - | - | 366B tokens | - | 384 80G A100 | 105 d | ✓ | - |
| mT0 [133] | Nov-2022 | 13 | mT5 | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - |
| Galactica [134] | Nov-2022 | 120 | - | - | - | 106B tokens | - | - | - | ✓ | ✓ |
| BLOOMZ [133] | Nov-2022 | 176 | BLOOM | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - |
| OPT-IML [135] | Dec-2022 | 175 | OPT | ✓ | - | - | - | 128 40G A100 | - | ✓ | ✓ |
| LLaMA [136] | Feb-2023 | 65 | - | - | - | 1.4T tokens | - | 2048 80G A100 | 21 d | ✓ | - |
| Pythia [137] | Apr-2023 | 12 | - | - | - | 300B tokens | - | 256 40G A100 | - | ✓ | - |
| CodeGen2 [138] | May-2023 | 16 | - | - | - | 400B tokens | - | - | - | ✓ | - |
| StarCoder [139] | May-2023 | 15.5 | - | - | - | 1T tokens | - | 512 40G A100 | - | ✓ | ✓ |
| LLaMA2 [140] | Jul-2023 | 70 | - | ✓ | ✓ | 2T tokens | - | 2000 80G A100 | - | ✓ | - |
| Baichuan2 [141] | Sep-2023 | 13 | - | ✓ | ✓ | 2.6T tokens | - | 1024 A800 | - | ✓ | - |
| QWEN [142] | Sep-2023 | 14 | - | ✓ | ✓ | 3T tokens | - | - | - | ✓ | - |
| FLM [143] | Sep-2023 | 101 | - | ✓ | - | 311B tokens | - | 192 A800 | 22 d | ✓ | - |
| Skywork [144] | Oct-2023 | 13 | - | - | - | 3.2T tokens | - | 512 80G A800 | - | ✓ | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wandelt, S.; Zheng, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X. Large Language Models for Intelligent Transportation: A Review of the State of the Art and Challenges. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7455. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177455
Wandelt S, Zheng C, Wang S, Liu Y, Sun X. Large Language Models for Intelligent Transportation: A Review of the State of the Art and Challenges. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(17):7455. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177455
Chicago/Turabian StyleWandelt, Sebastian, Changhong Zheng, Shuang Wang, Yucheng Liu, and Xiaoqian Sun. 2024. "Large Language Models for Intelligent Transportation: A Review of the State of the Art and Challenges" Applied Sciences 14, no. 17: 7455. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177455
APA StyleWandelt, S., Zheng, C., Wang, S., Liu, Y., & Sun, X. (2024). Large Language Models for Intelligent Transportation: A Review of the State of the Art and Challenges. Applied Sciences, 14(17), 7455. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177455









