Characteristics of Removal of Lead, Cadmium and Chromium from Soil Using Biosorbent and Biochar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Biomass Pyrolysis
2.3. Preparation of Model Soil
2.4. Removal of Heavy Metals from the Soil
2.5. Determination of Heavy Metals
2.6. Physicochemical Characteristics
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Result and Discussion
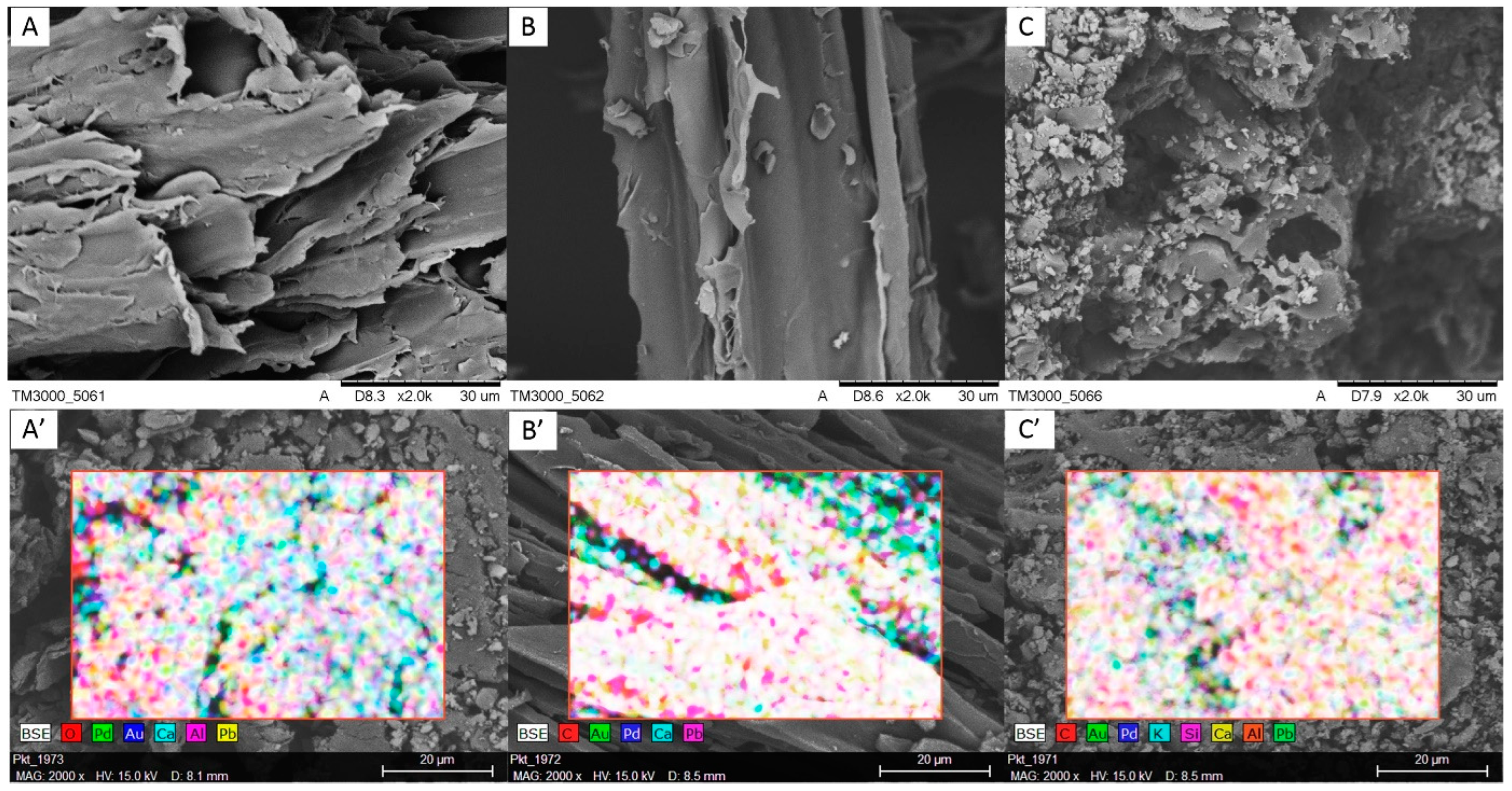
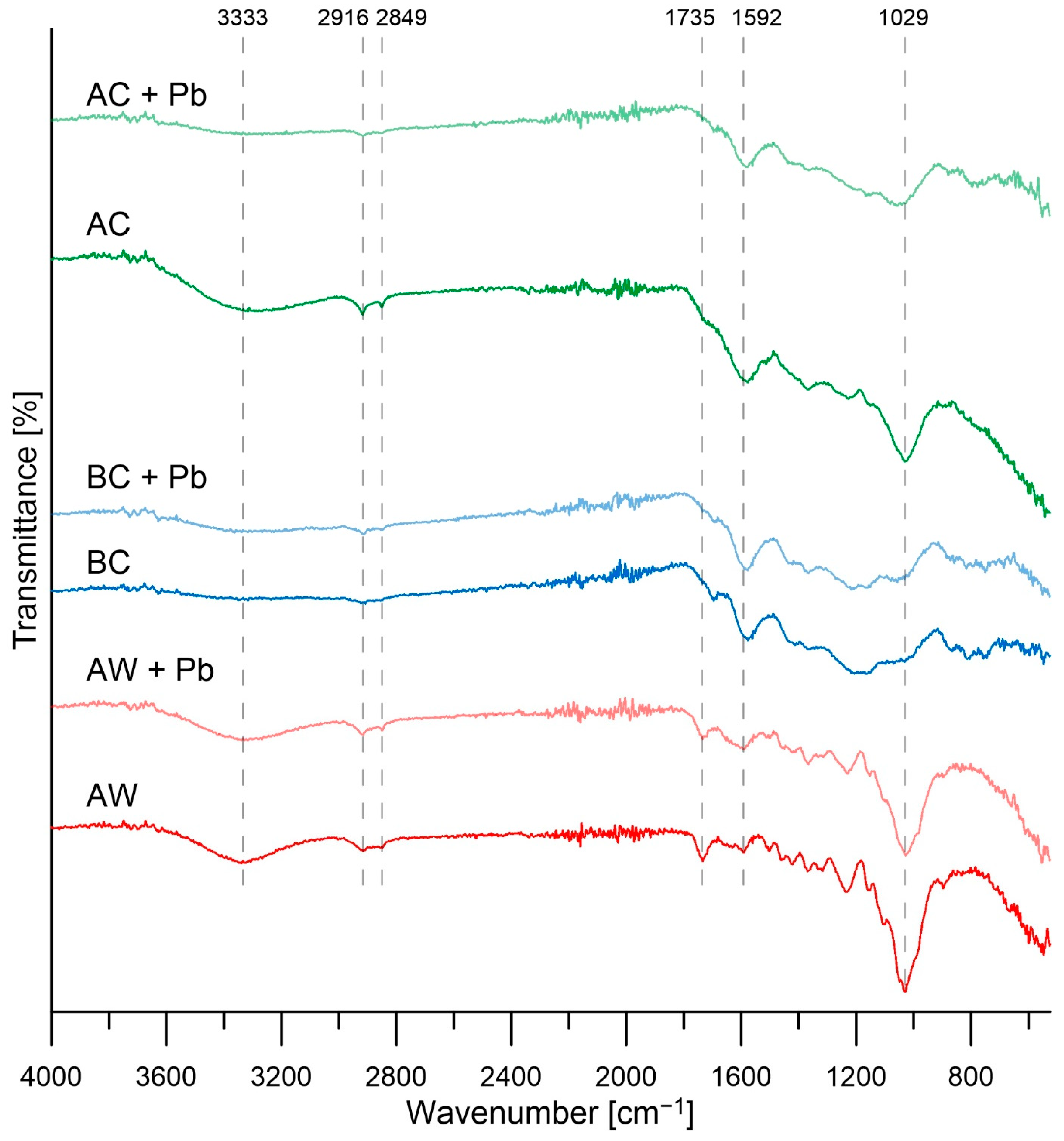
3.1. Characterizations of Materials
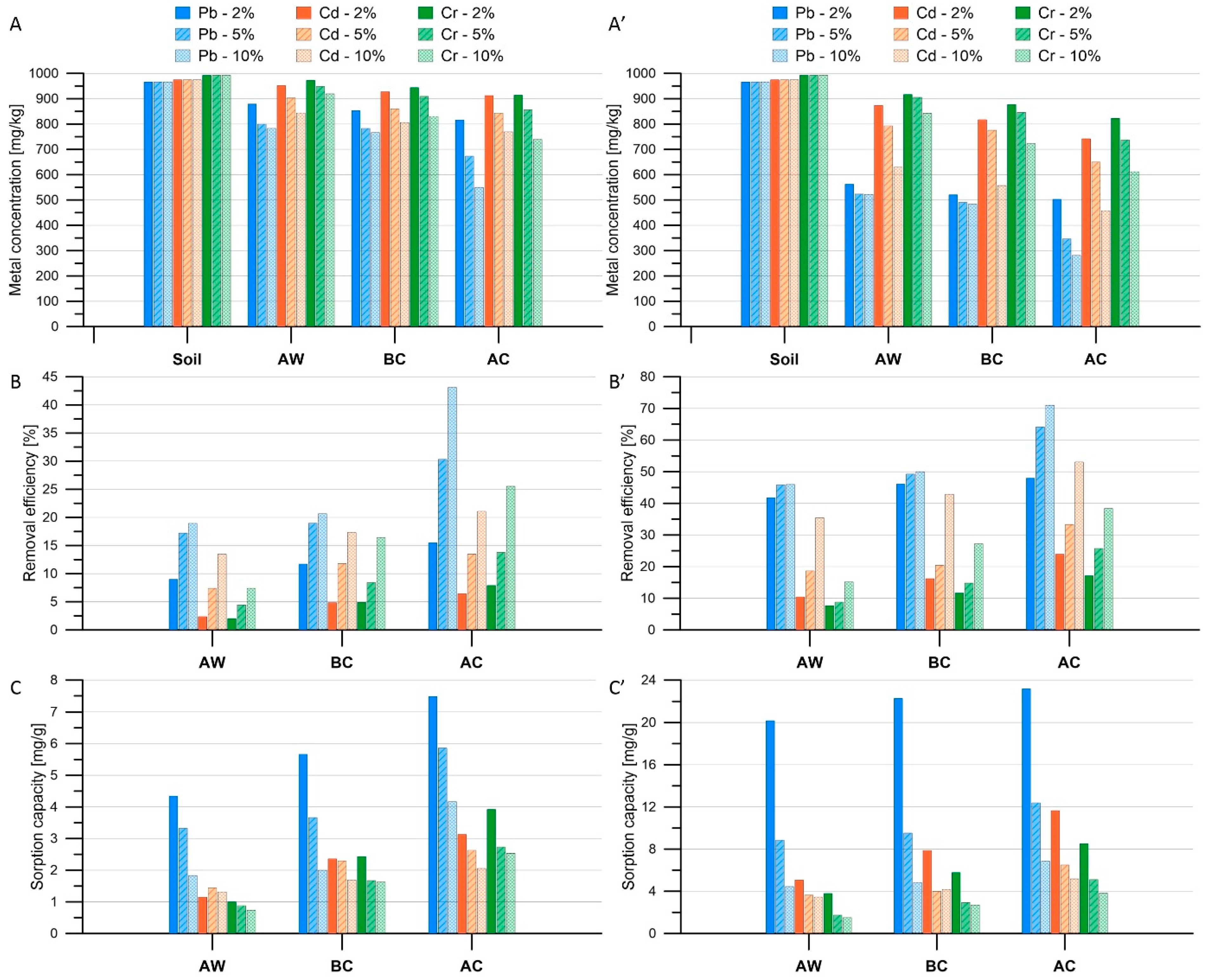
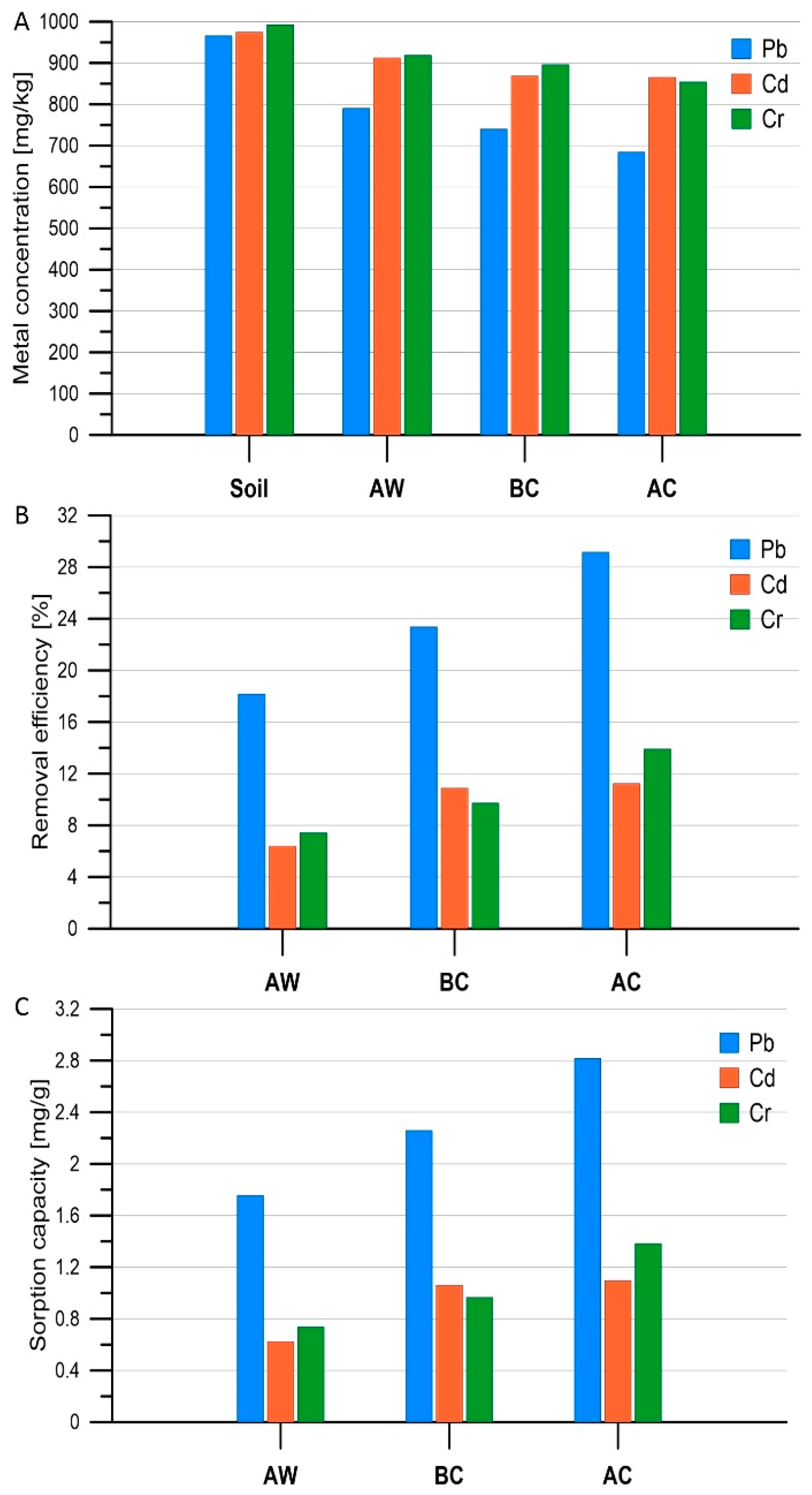
3.2. Removal of Heavy Metals from the Soil
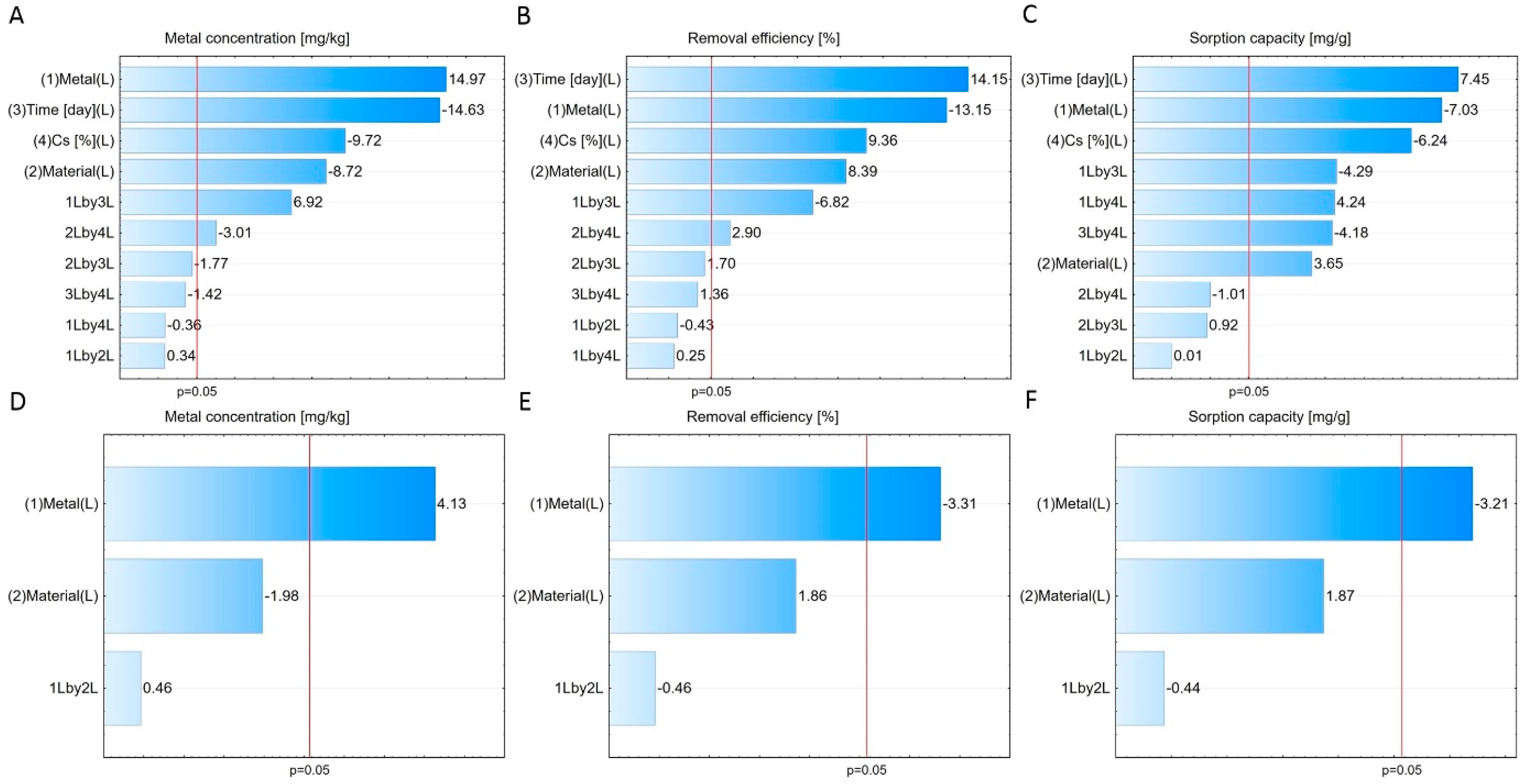
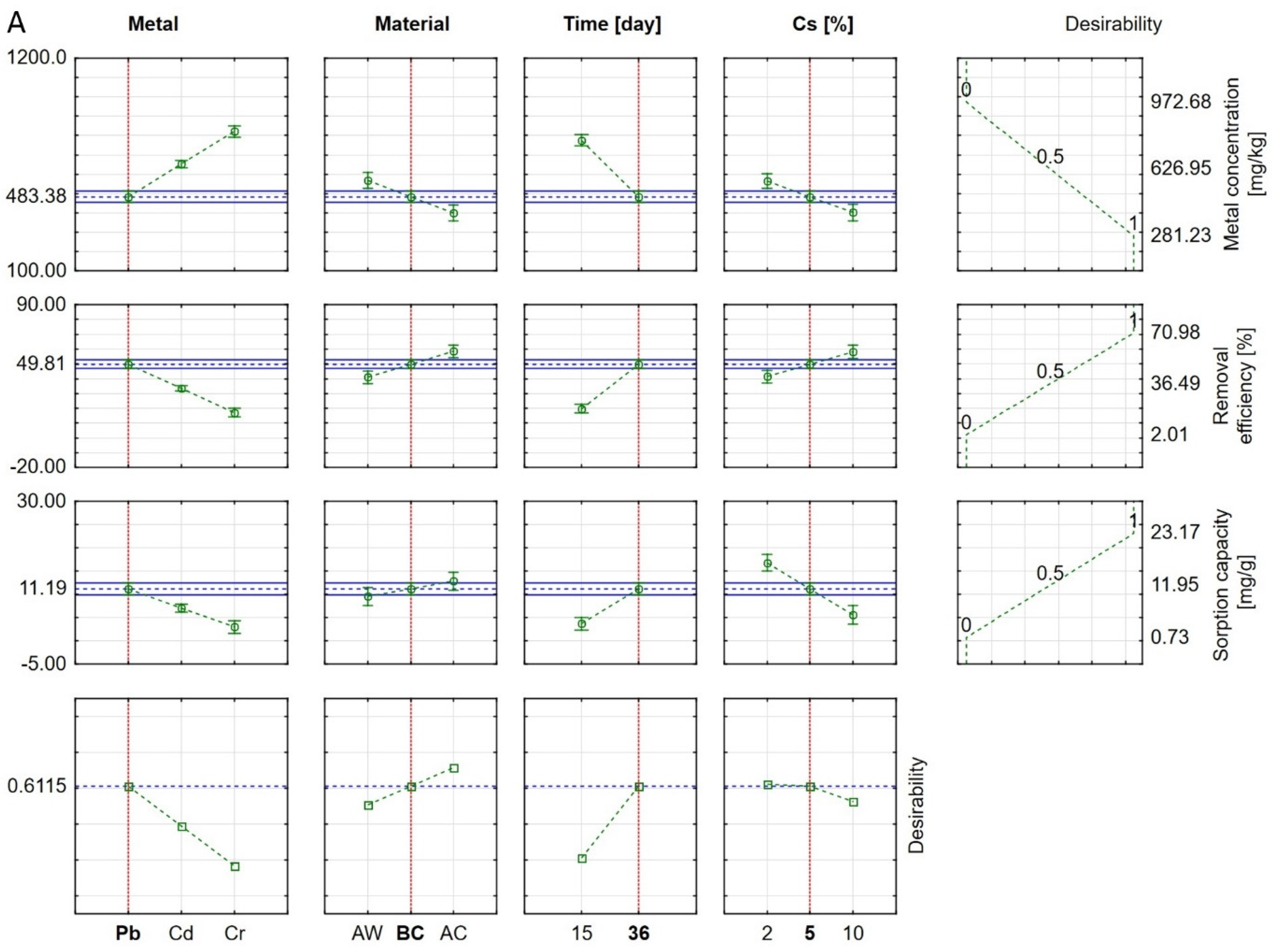
3.3. Statistical Analysis of Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahman, Z.; Singh, V.P. The Relative Impact of Toxic Heavy Metals (THMs) (Arsenic (As), Cadmium (Cd), Chromium (Cr)(VI), Mercury (Hg), and Lead (Pb)) on the Total Environment: An Overview. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali-Mood, M.; Naseri, K.; Tahergorabi, Z.; Khazdair, M.R.; Sadeghi, M. Toxic Mechanisms of Five Heavy Metals: Mercury, Lead, Chromium, Cadmium, and Arsenic. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 643972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakumar, M.; Surendran, U.; Raja, P.; Kumar, A.; Senapathi, V. A Review of Heavy Metals Accumulation Pathways, Sources and Management in Soils. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.; Fatima, F.; Waheed, I.; Akash, M.S.H. Prevalence of Exposure of Heavy Metals and Their Impact on Health Consequences. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 157–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, A.; Agarwal, T. Potential of Biochar for the Remediation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soil. In Biochar Applications in Agriculture and Environment Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjaiah, M.; Datta, S.C.; Ahammed Shabeer, T.P.; Sarkar, B. Chitosan-g-Poly(Acrylic Acid)-Bentonite Composite: A Potential Immobilizing Agent of Heavy Metals in Soil. Cellulose 2018, 25, 3985–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Rinklebe, J.; Tack, F.M.G.; Hou, D. A Review of Green Remediation Strategies for Heavy Metal Contaminated Soil. Soil Use Manag. 2021, 37, 936–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saletnik, B.; Zagula, G.; Bajcar, M.; Tarapatskyy, M.; Bobula, G.; Puchalski, C. Biochar as a Multifunctional Component of the Environment—A Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, N.L.; Pawar, A.; Salvi, B.L. Comprehensive Review on Production and Utilization of Biochar. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatav, H.S.; Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.; Singh, S.K.; Chejara, S.; Gorovtsov, A.; Barakhov, A.; Bauer, T.; Sushkova, S.; Mandzieva, S.; et al. Sustainable Approach and Safe Use of Biochar and Its Possible Consequences. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.X.; Liu, H.T.; Zhang, J. The Role of Biochar in Organic Waste Composting and Soil Improvement: A Review. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 884–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayyat, A.; Javed, M.; Rasheed, I.; Ali, S.; Shahid, M.J.; Rizwan, M.; Javed, M.T.; Ali, Q. Role of Biochar in Remediating Heavy Metals in Soil. Phytoremediation Manag. Environ. Contam. 2016, 3, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, W.A.W.A.K.; Mohd, A.; da Silva, G.; Bachmann, R.T.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Rashid, U.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H. Biochar Production from Waste Rubber-Wood-Sawdust and Its Potential Use in C Sequestration: Chemical and Physical Characterization. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 44, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Xu, L.; Buyong, F.; Chay, T.C.; Li, Z.; Cai, Y.; Hu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X. Modified Biochar: Synthesis and Mechanism for Removal of Environmental Heavy Metals. Carbon Res. 2022, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, F.; Islam, K.; Cakiroglu, C.; Shahriar, A. Effectiveness of Wood Waste Sawdust to Produce Medium- to Low-Strength Concrete Materials. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 103237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.F.; Islam, M.K.; Islam, M.A. Effect of Chemical Treatment on the Mechanical and Physical Properties of Wood Saw Dust Particles Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites. Procedia Eng. 2014, 90, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.A.; Abdellatif, F.H.H.; Hasanin, M.S.; Abdellatif, M.M. Fabrication, Characterization, and Potential Application of Modified Sawdust Sorbents for Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ions and Anionic Dye from Aqueous Solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 332, 130021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, R.A.; Lima, E.C.; Benetti, A.D.; Thue, P.S.; Cunha, M.R.; Cimirro, N.F.G.M.; Sher, F.; Dehghani, M.H.; dos Reis, G.S.; Dotto, G.L. Preparation of Hybrids of Wood Sawdust with 3-Aminopropyl-Triethoxysilane. Application as an Adsorbent to Remove Reactive Blue 4 Dye from Wastewater Effluents. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 125, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, M.; Ahmad, T. A Review on Utilization of Wood Biomass as a Sustainable Precursor for Activated Carbon Production and Application. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 87, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Maniar, A.; Suganya, O.M. Strength Development in Concrete with Wood Ash Blended Cement and Use of Soft Computing Models to Predict Strength Parameters. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Song, W.; Tian, J. Biochar-Facilitated Soil Remediation: Mechanisms and Efficacy Variations. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 521512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Li, X.; Duan, W.; Xie, M.; Dong, X.; Cui, W.; Li, X.; Duan, W.; Xie, M.; Dong, X. Heavy Metal Stabilization Remediation in Polluted Soils with Stabilizing Materials: A Review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 4127–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuana, R.A.; Okieimen, F.E.; Montuelle, B.; Steinman, A.D. Heavy Metals in Contaminated Soils: A Review of Sources, Chemistry, Risks and Best Available Strategies for Remediation. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2011, 2011, 402647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovkova, V.S.; Malyar, Y.N.; Sudakova, I.G.; Chudina, A.I.; Zimonin, D.V.; Skripnikov, A.M.; Miroshnikova, A.V.; Ionin, V.A.; Kazachenko, A.S.; Sychev, V.V.; et al. Composition and Structure of Aspen (Pópulus trémula) Hemicelluloses Obtained by Oxidative Delignification. Polymers 2022, 14, 4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Sole, R.; Fogel, A.A.; Somin, V.A.; Vasapollo, G.; Mergola, L. Evaluation of Effective Composite Biosorbents Based on Wood Sawdust and Natural Clay for Heavy Metals Removal from Water. Materials 2023, 16, 5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanisz, A. Przystępny Kurs Statystyki z Zastosowaniem Statistica PL Tom 2: Modele Liniowe i Nieliniowe; StatSoft: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2007; p. 868. [Google Scholar]
- TIBCO Statistica, version 13; TIBCO Statistica Inc.: Tulsa, OK, USA.
- Yang, H.; Yan, R.; Chen, H.; Lee, D.H.; Zheng, C. Characteristics of Hemicellulose, Cellulose and Lignin Pyrolysis. Fuel 2007, 86, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonasson, S.; Bünder, A.; Niittylä, T.; Oksman, K. Isolation and Characterization of Cellulose Nanofibers from Aspen Wood Using Derivatizing and Non-Derivatizing Pretreatments. Cellulose 2020, 27, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brebu, M.; Vasile, C. Thermal Degradation of Lignin—A Review. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2010, 44, 353–363. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Korpinen, R.; Möttönen, V.; Verkasalo, E. Suberin Fatty Acid Hydrolysates from Outer Birch Bark for Hydrophobic Coating on Aspen Wood Surface. Polymers 2022, 14, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, M.; Liao, Y.; Xu, J.; Wu, S.; Liao, W.; Zhao, X. Removal of Anthracene from Vehicle-Wash Wastewater through Adsorption Using Eucalyptus Wood Waste-Derived Biochar. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 317, 100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evora, M.C.; Gonçalez, O.L.; Dutra, R.C.L.; Diniz, M.F.; Wiebeck, H.; Andrade e Silva, L.G. de Comparação de Técnicas FTIR de Transmissão, Reflexão e Fotoacústica Na Análise de Poliamida-6, Reciclada e Irradiada. Polímeros 2002, 12, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavagna, M.; Dell’Anna, R.; Monti, F.; Rossi, F.; Torriani, S. Use of ATR-FTIR Microspectroscopy to Monitor Autolysis of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Cells in a Base Wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 58, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaduri, D.; Saha, A.; Desai, D.; Meena, H.N. Restoration of Carbon and Microbial Activity in Salt-Induced Soil by Application of Peanut Shell Biochar during Short-Term Incubation Study. Chemosphere 2016, 148, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitter, E.K.; Corso, C.R. FT-IR Analysis of Acid Black Dye Biodegradation Using Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Immobilized with Treated Sugarcane Bagasse. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kabbany, F.; Taha, S.; B1, H.; Hafez, M. Infrared Spectroscopic Anaylsis of Polymorphism in Diphenyl Carbazide. Sci. Pap. Univ. Pardubic. 2011, 78, 981–988. [Google Scholar]
- Wahab, M.A.; Boubakri, H.; Jellali, S.; Jedidi, N. Characterization of Ammonium Retention Processes onto Cactus Leaves Fibers Using FTIR, EDX and SEM Analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 241–242, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, O.; Rebufa, C.; Dupuy, N.; Kister, J. FTIR—Multivariate Curve Resolution Monitoring of Photo-Fenton Degradation of Phenolic Aqueous Solutions: Comparison with HPLC as a Reference Method. Talanta 2008, 77, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherdoud-Chihani, A.; Mouzali, M.; Abadie, M.J.M. Study of Crosslinking Acid Copolymer/DGEBA Systems by FTIR. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 2033–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhre, N.A.; Ibrahim, B.M. The Use of New Chemically Modified Cellulose for Heavy Metal Ion Adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 343, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Tong, S.; Ge, M.; Wu, L.; Zuo, J.; Cao, C.; Song, W. Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution by Carboxylated Cellulose Nanocrystals. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šćiban, M.; Radetić, B.; Kevrešan, Ž.; Klašnja, M. Adsorption of Heavy Metals from Electroplating Wastewater by Wood Sawdust. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Islam, M.R. Effects of PH on Isotherms Modeling for Cu(II) Ions Adsorption Using Maple Wood Sawdust. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 149, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of Copper (II), Chromium (III), Nickel (II) and Lead (II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Meranti Sawdust. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocreto, J.; Go, C.I.; Chua, J.C.; Apacible, C.J.; Vilando, A. Competitive Effects for the Adsorption of Copper, Cadmium and Lead Ions Using Modified Activated Carbon from Bambo. MATEC Web Conf. 2019, 268, 06021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, A.K.; Mishra, G.K.; Rai, P.K.; Rajagopal, C.; Nagar, P.N. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Carbon Aerogel as an Adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 122, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Wang, F.; Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Wu, A.; Zhang, Y. Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewater and Fixation of Heavy Metals in Soil by Manganese Dioxide Nanosorbents with Tailored Hollow Mesoporous Structure. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 459, 141583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvinowanda, C.M.; Okonkwo, J.O.; Shabalala, P.N.; Agyei, N.M. A Novel Adsorbent for Heavy Metal Remediation in Aqueous Environments. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 6, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Pan, J.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, R.; Xu, X. Study the Adsorption of Phenol from Aqueous Solution on Hydroxyapatite Nanopowders. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, R.R.; Lalhmunsiama; Kim, M.; Kim, J.G.; Hong, S.M.; Sawant, S.Y.; Lee, S.M. Efficient Removal of Hazardous Lead, Cadmium, and Arsenic from Aqueous Environment by Iron Oxide Modified Clay-Activated Carbon Composite Beads. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 162, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.J.; Shen, X.J.; Domene, X.; Alcañiz, J.M.; Liao, X.; Palet, C. Comparison of Biochars Derived from Different Types of Feedstock and Their Potential for Heavy Metal Removal in Multiple-Metal Solutions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Li, L.; Li, G.; Xu, G. Feasibility of Sludge-Based Biochar for Soil Remediation: Characteristics and Safety Performance of Heavy Metals Influenced by Pyrolysis Temperatures. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Yang, Z.; Tang, L.; Zeng, G.; Yu, M.; Li, X.; Wu, H.; Qian, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, Y. Changes in Heavy Metal Mobility and Availability from Contaminated Wetland Soil Remediated with Combined Biochar-Compost. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Ren, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Luo, L.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, A. Physicochemical Features, Metal Availability and Enzyme Activity in Heavy Metal-Polluted Soil Remediated by Biochar and Compost. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, T.; Chen, W.; Hu, H.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, G. A Magnetic Macro-Porous Biochar Sphere as Vehicle for the Activation and Removal of Heavy Metals from Contaminated Agricultural Soil. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y. Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solution by Synthetic Allophane Suspension: Isotherm, Kinetics, and Mechanisms. Toxics 2022, 10, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.L.; Qiu, W.; Wang, P.P.; Liu, Y.L.; Zou, J.; Wang, L.; Ma, J. Mechanism Study about the Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) with Iron-Trimesic Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesavento, M.; Profumo, A.; Alberti, G.; Conti, F. Adsorption of Lead(II) and Copper(II) on Activated Carbon by Complexation with Surface Functional Groups. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 480, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, A.; Viraraghavan, T. Oil Removal from Water by Fungal Biomass: A Factorial Design Analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalafyan, A.A.; Temerdashev, Z.A.; Yakuba, Y.F.; Guguchkina, T.I. Computer Analysis of the Sensory Qualities of Red Wines as a Method to Optimize Their Blend Formulation. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumwesigye, S.K.; Montañez, J.C.; Oliveira, J.C.; Sousa-Gallagher, M.J. Novel Intact Bitter Cassava: Sustainable Development and Desirability Optimisation of Packaging Films. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2016, 9, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Staroń, P.; Zawadzka, A.; Radomski, P.; Chwastowski, J. Characteristics of Removal of Lead, Cadmium and Chromium from Soil Using Biosorbent and Biochar. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7241. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14167241
Staroń P, Zawadzka A, Radomski P, Chwastowski J. Characteristics of Removal of Lead, Cadmium and Chromium from Soil Using Biosorbent and Biochar. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(16):7241. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14167241
Chicago/Turabian StyleStaroń, Paweł, Anita Zawadzka, Piotr Radomski, and Jarosław Chwastowski. 2024. "Characteristics of Removal of Lead, Cadmium and Chromium from Soil Using Biosorbent and Biochar" Applied Sciences 14, no. 16: 7241. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14167241
APA StyleStaroń, P., Zawadzka, A., Radomski, P., & Chwastowski, J. (2024). Characteristics of Removal of Lead, Cadmium and Chromium from Soil Using Biosorbent and Biochar. Applied Sciences, 14(16), 7241. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14167241






.png)

