A New Reversible Data Hiding Method Using a Proportional Relation between Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio and Embedding Capacity on Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Embedding Algorithm
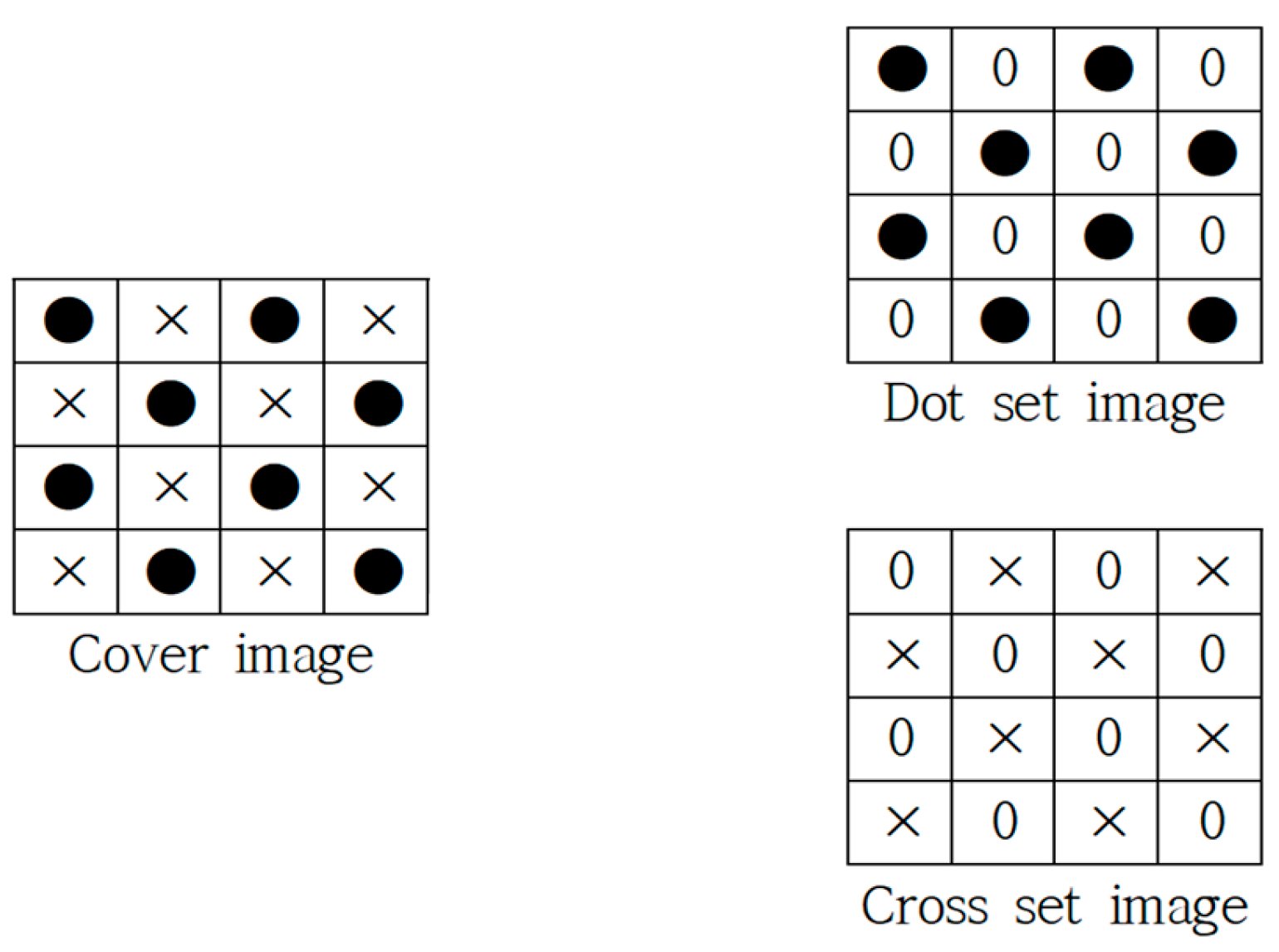
2.1.1. Difference Expansion
2.1.2. Histogram Shifting
2.1.3. Prediction Error Expansion
2.2. CNN-Based Predictor
2.2.1. CNNP
2.2.2. ICNNP
3. The Proposed Method
3.1. CNN Predictor
3.1.1. Preparation for Image Prediction
3.1.2. Network Architecture
3.1.3. Training
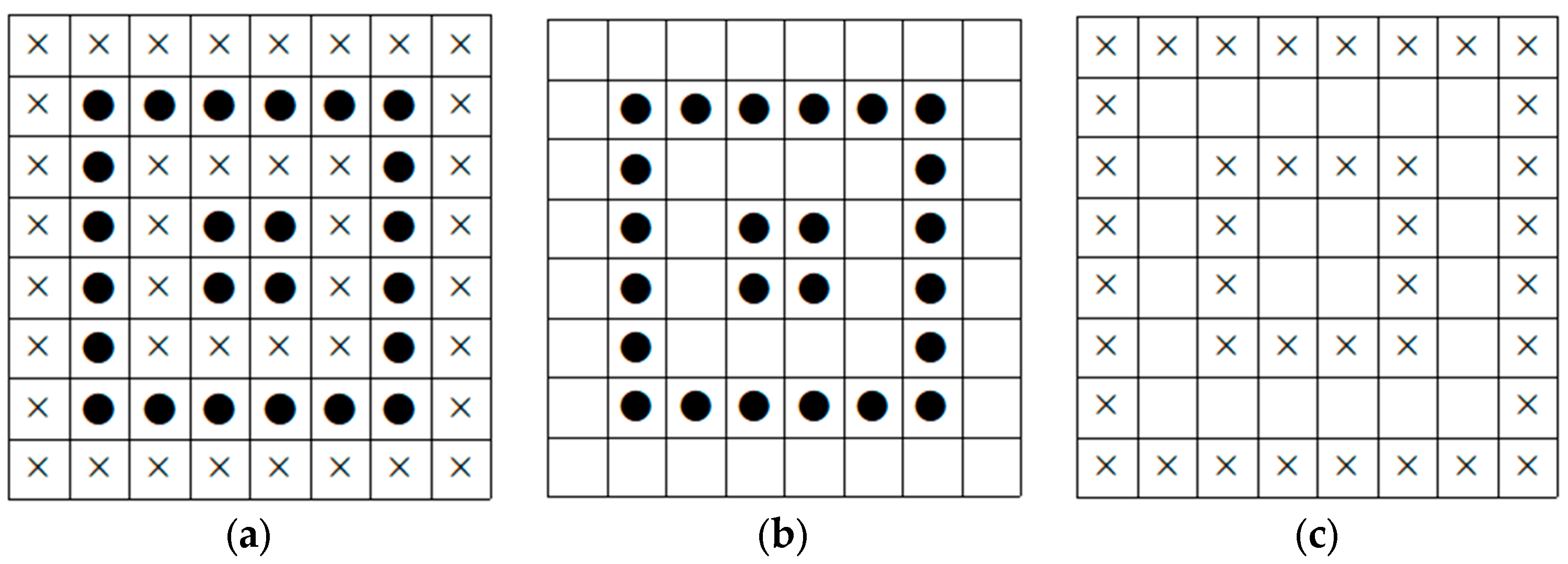
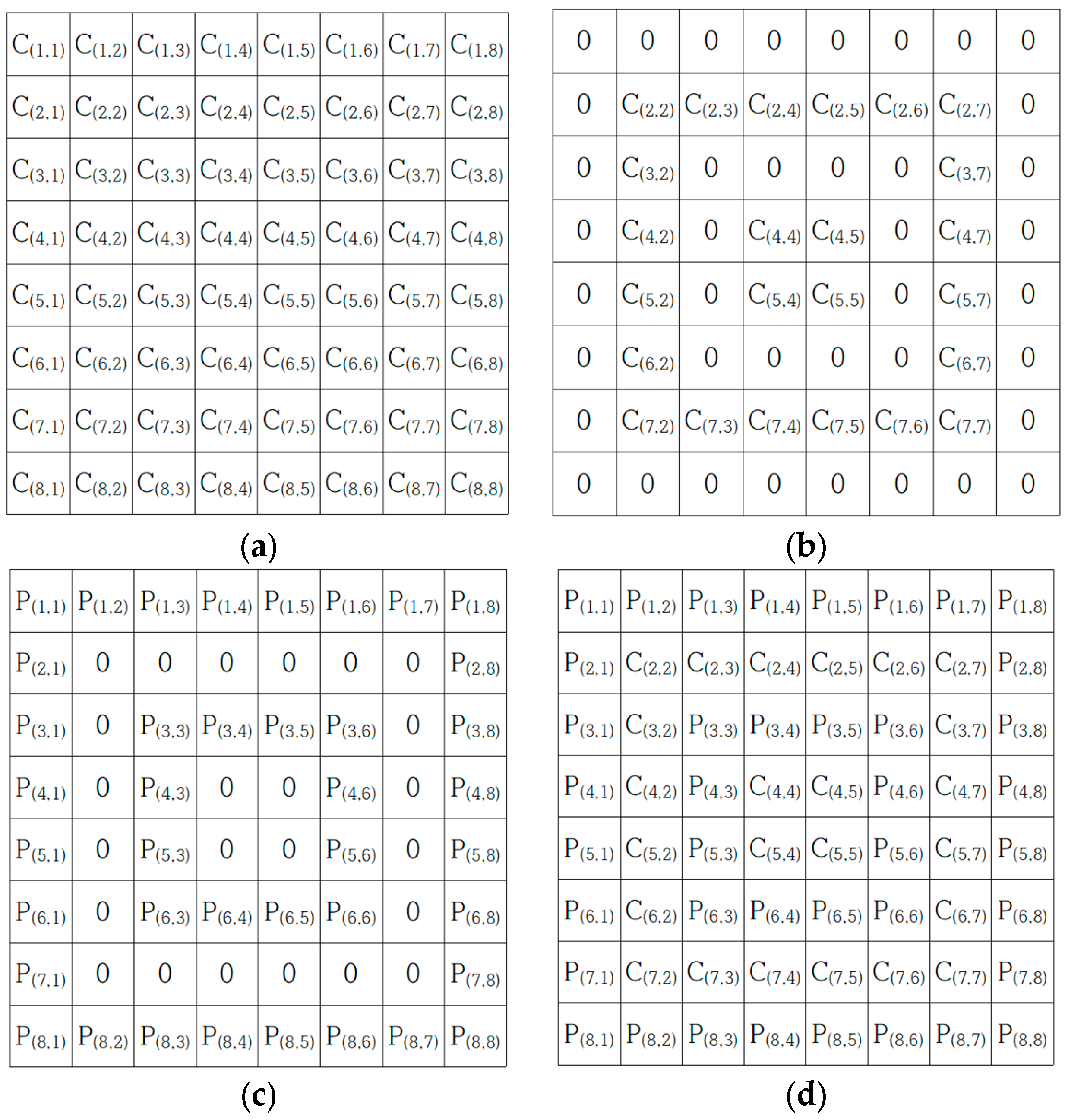
3.2. Pre-Processing
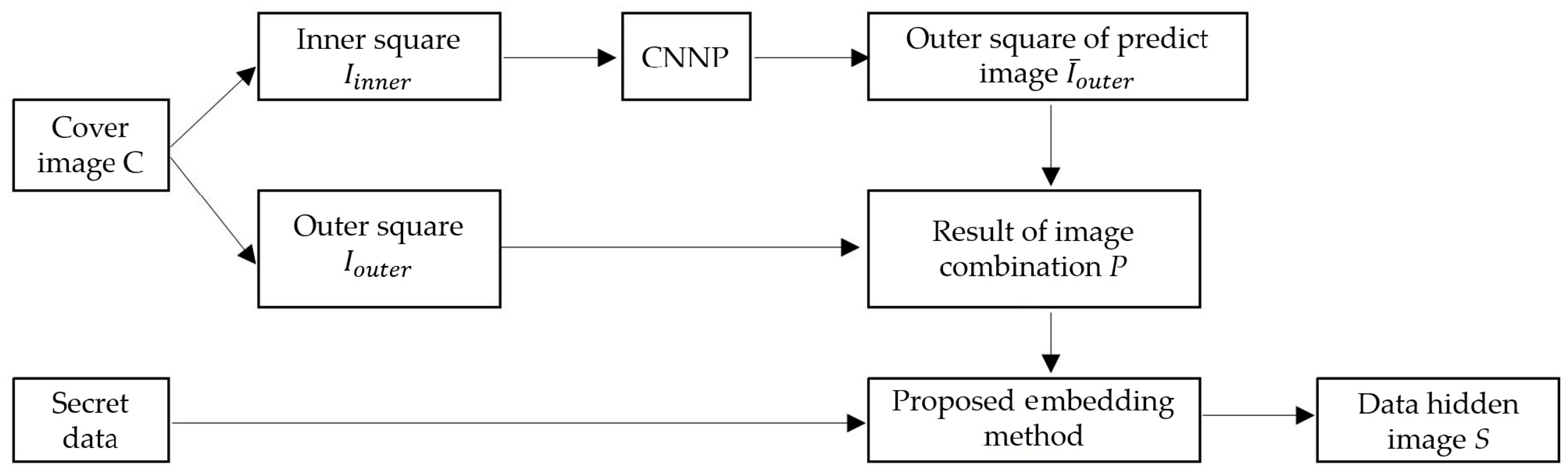
3.3. Embedding
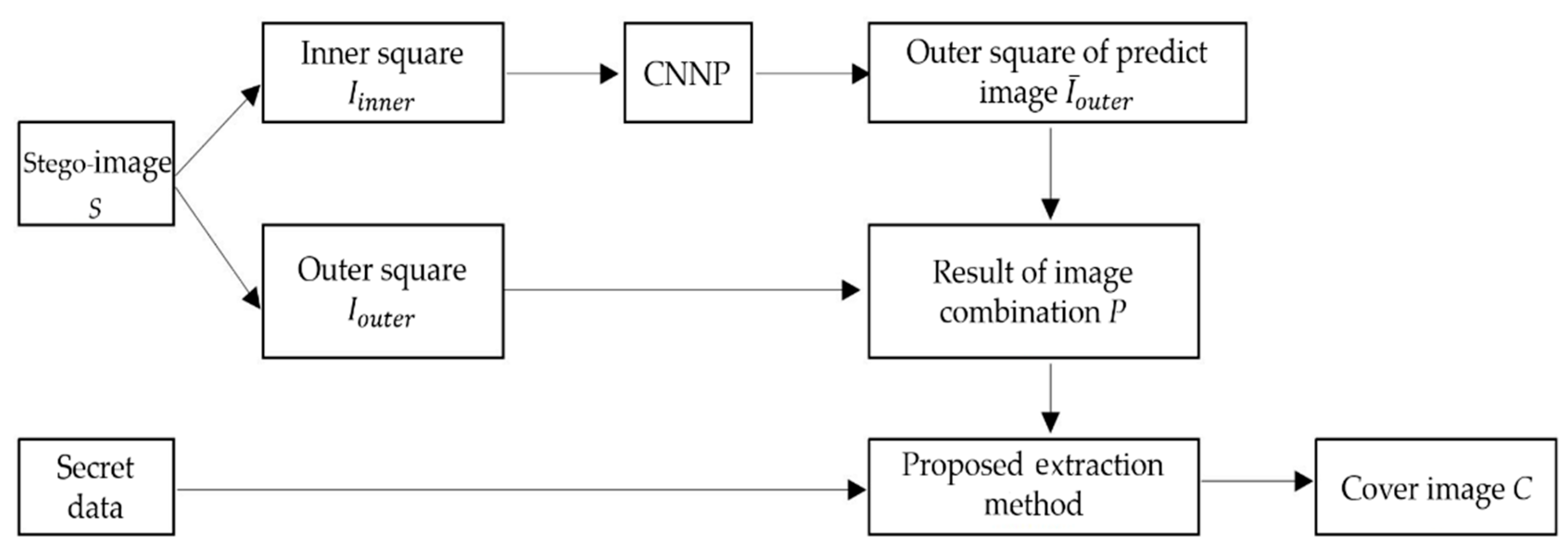
3.4. Extraction and Recovery
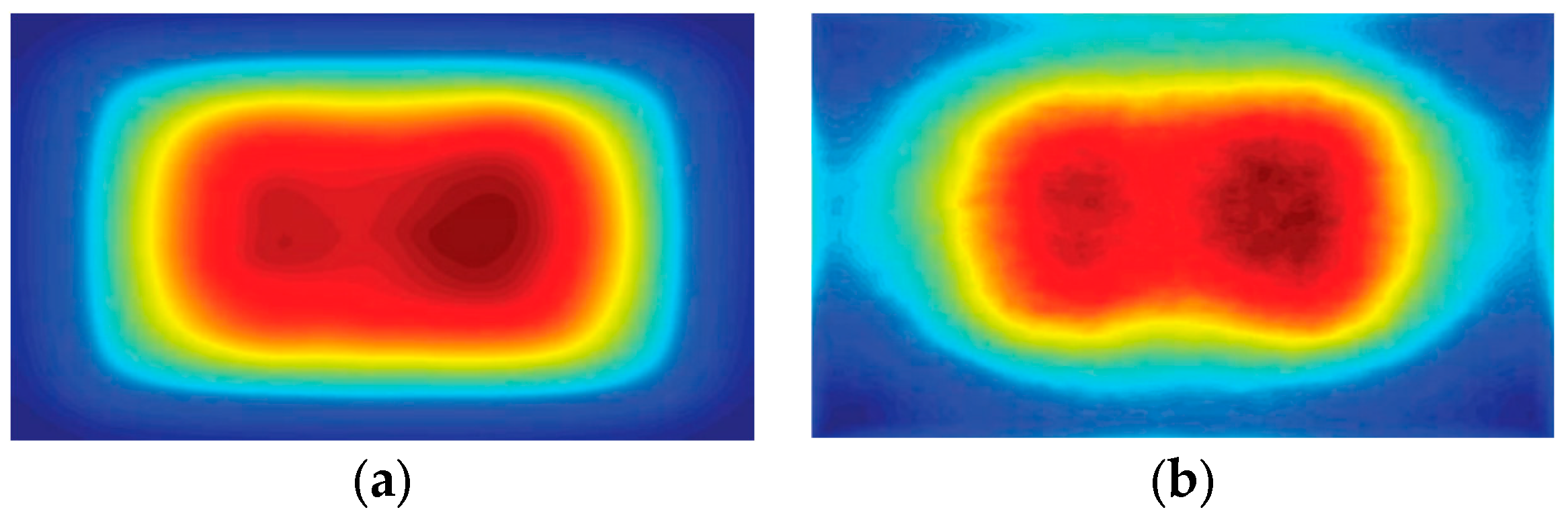
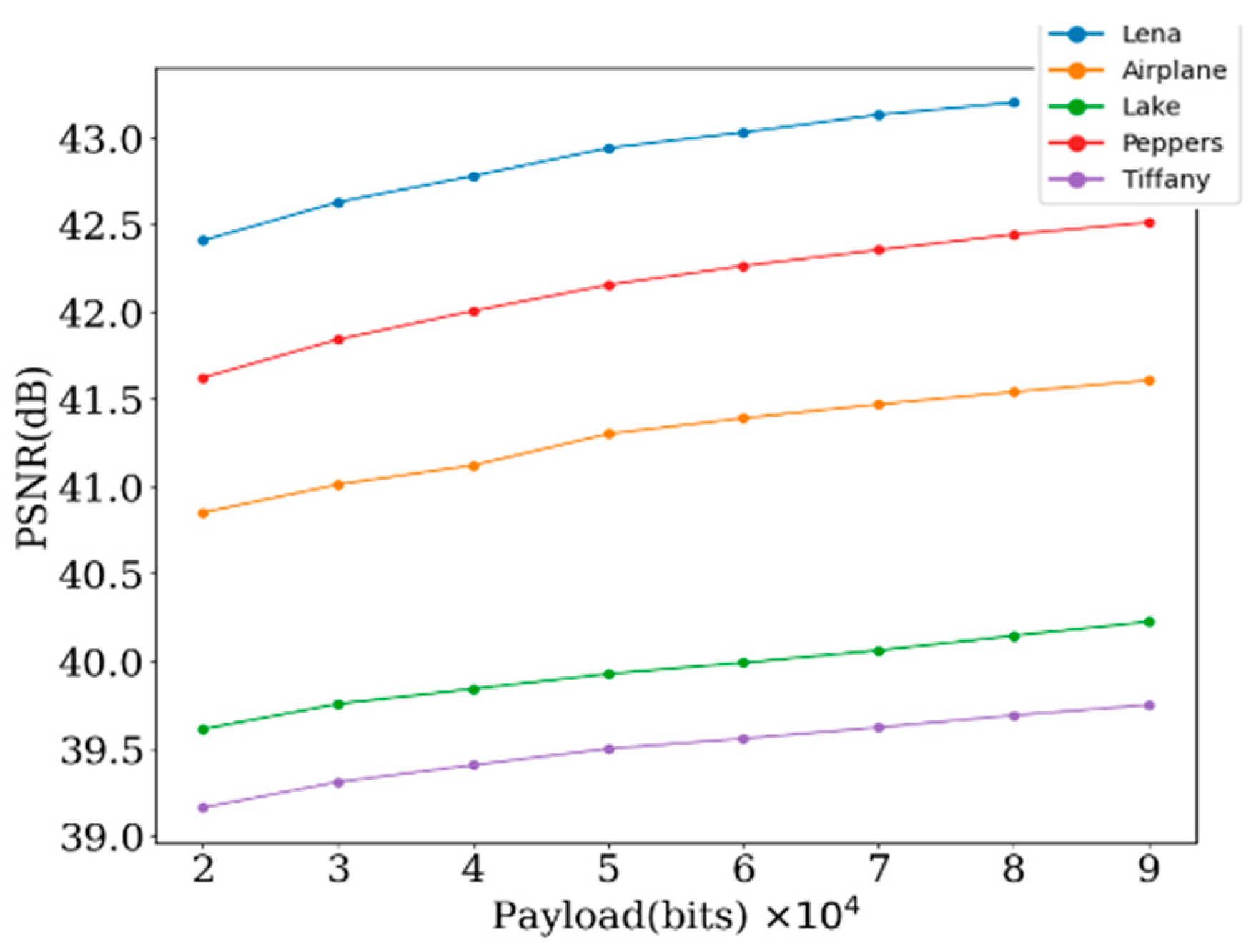
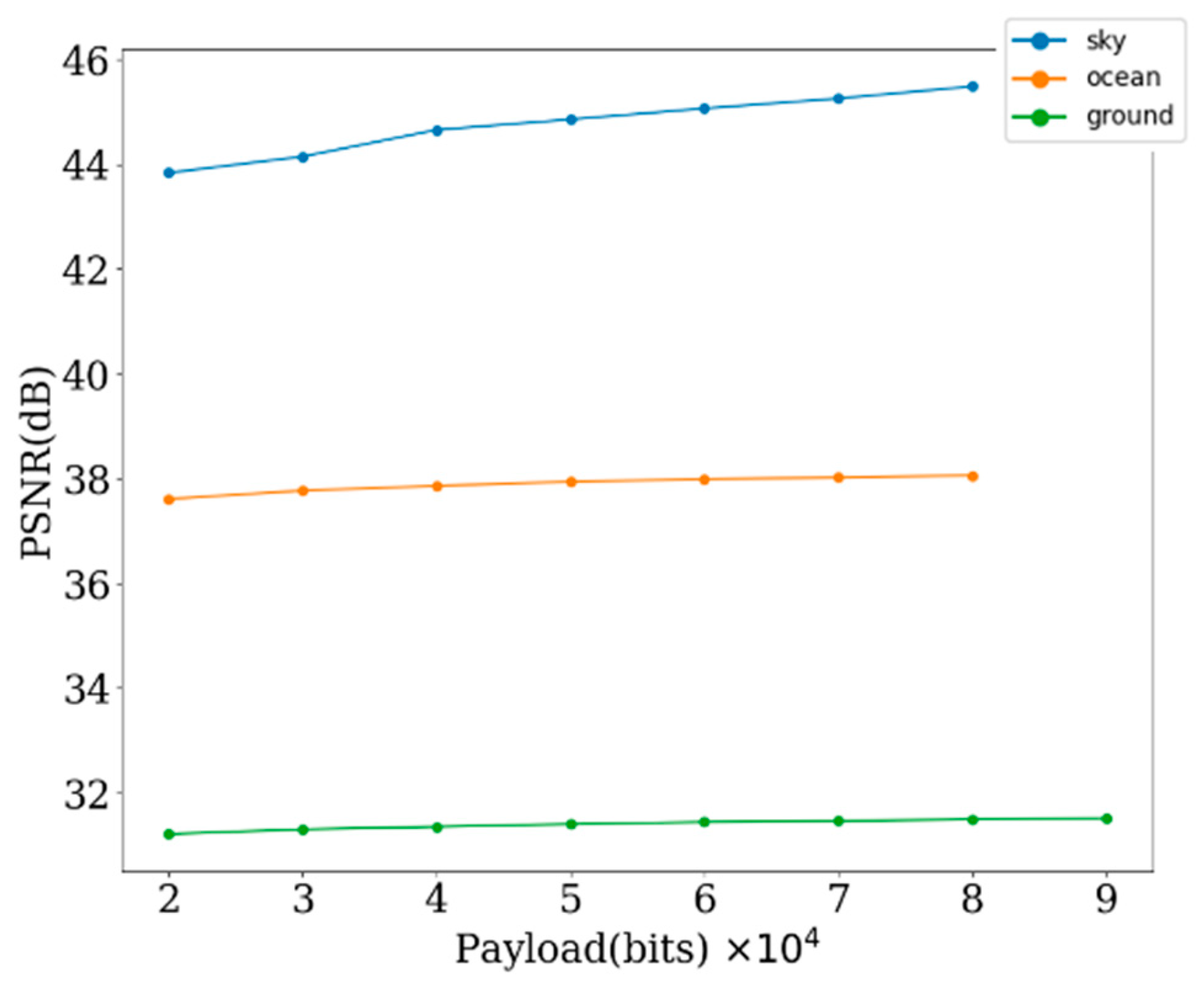
4. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, R.; Xiang, S. CNN Prediction Based Reversible Data Hiding. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2011, 28, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J. Reversible data embedding using a difference expansion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2003, 13, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujjunoori, S.; Oruganti, M. Difference expansion based reversible data embedding and edge detection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 25889–25917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Gui, X.; Yang, B. Efficient Reversible Data Hiding Based on Multiple Histograms Modification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2015, 10, 2016–2027. [Google Scholar]
- Thodi, D.M.; Rodriguez, J.J. Reversible watermarking by prediction-error expansion. In Proceedings of the 6th IEEE Southwest Symposium on Image Analysis and Interpretation, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 28–30 March 2004; pp. 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, H.T.; Ma, B. Reversible data hiding: Advances in the past two decades. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 3210–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Qu, X.; Sachnev, V.; Kim, H.J. Skewed Histogram Shifting for Reversible Data Hiding Using a Pair of Extreme Predictions. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2019, 29, 3236–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Tianxi, C.; Els, G.; Wei, L.J. Model evaluation based on the sampling distribution of estimated absolute prediction error. Biometrika 2007, 94, 297–311. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Li, X.; Yang, B. Efficient reversible image watermarking by using dynamical prediction-error expansion. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Hong Kong, China, 26–29 September 2010; pp. 3673–3676. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Yang, B. High-fidelity reversible data hiding scheme based on pixel-value-ordering and prediction-error expansion. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Cai, Z. An Insight into Pixel Value Ordering Prediction-Based Prediction-Error Expansion. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 15, 3859–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, B.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ni, R. Reversible data hiding using invariant pixel-value-ordering and prediction-error expansion. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2014, 29, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thodi, D.M.; Rodriguez, J.J. Expansion Embedding Techniques for Reversible Watermarking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coltuc, D. Low distortion transform for reversible watermarking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchikkil, S.; Manikandan, V.M.; Zhang, Y.D. A convolutional neural network model based reversible data hiding scheme in encrypted images with block-wise Arnold transform. Optik 2022, 250, 168137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Peng, W.; Lin, X.; Zeng, H.; Qian, Z. Improved CNN Prediction Based Reversible Data Hiding. arXiv 2023, arXiv:abs/2301.01420. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Z.; Shi, Y.Q.; Ansari, N.; Su, W. Reversible data hiding. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2006, 16, 354–362. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Huang, F. New CNN-Based Predictor for Reversible Data Hiding. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 2627–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, L.; Le, H.; Niu, Y.; Liu, F. Rule of Thirds Detection from Photograph. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia, Dana Point, CA, USA, 5–7 December 2011; pp. 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Q.; Li, S.; Lin, Y.; Yu, X. Reversible Data Hiding Using Convolutional Neural Network and Digital Signal Processing Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2022 12th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME), Xiamen, China, 18–20 November 2022; pp. 709–713. [Google Scholar]
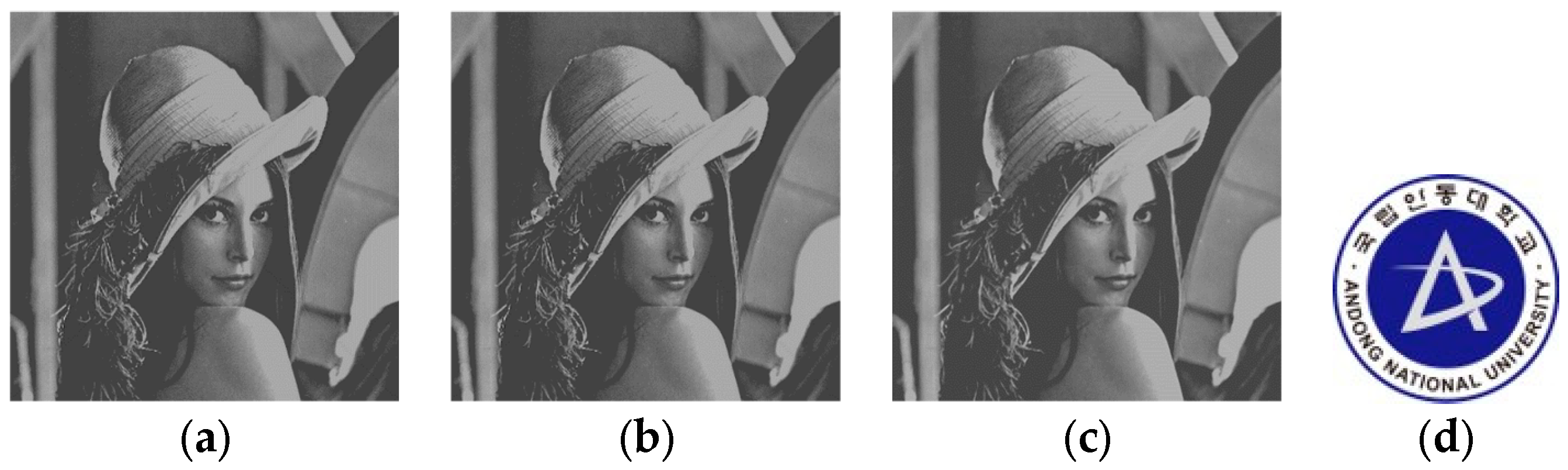

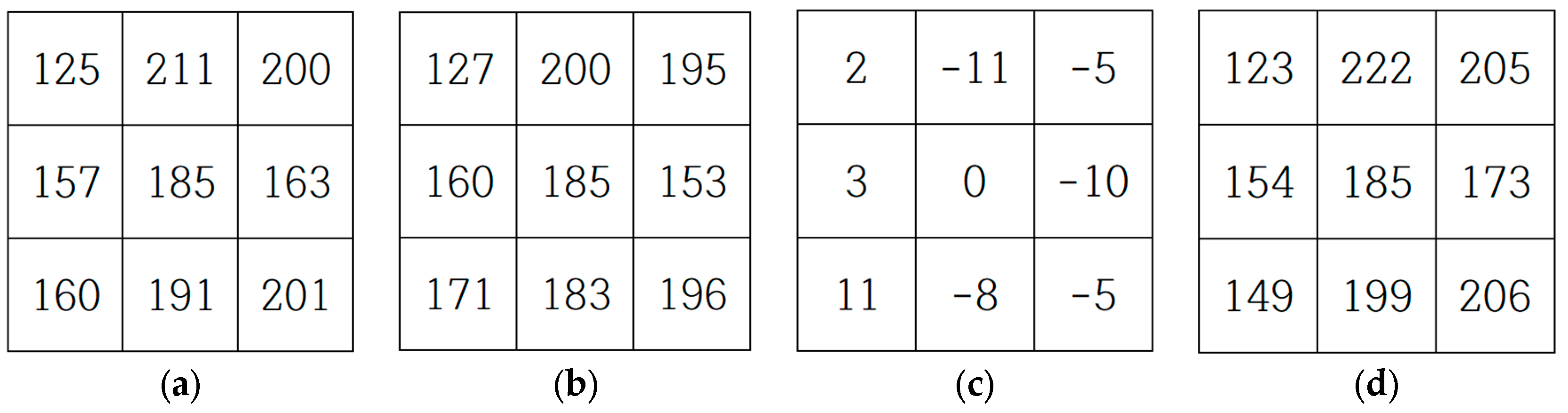


| (a) Lena Image | ||||
| Bits | DE | Skewed HS | PEE | Proposed |
| 20,000~30,000 | −0.19 | −0.19 | −0.02 | 0.02 |
| 30,000~40,000 | −0.13 | −0.13 | −0.12 | 0.02 |
| 40,000~50,000 | −0.09 | −0.09 | −0.08 | 0.02 |
| 50,000~60,000 | −0.07 | −0.07 | −0.06 | 0.01 |
| 60,000~70,000 | −0.06 | −0.06 | −0.05 | 0.01 |
| 70,000~80,000 | −0.06 | −0.06 | −0.05 | 0.01 |
| 80,000~90,000 | −0.06 | −0.06 | −0.05 | 0.01 |
| (b) Airplane Image | ||||
| Bits | DE | Skewed HS | PEE | Proposed |
| 20,000~30,000 | −0.22 | −0.09 | −0.17 | 0.02 |
| 30,000~40,000 | −0.13 | −0.14 | −0.11 | 0.01 |
| 40,000~50,000 | −0.09 | −0.23 | −0.08 | 0.02 |
| 50,000~60,000 | −0.06 | −0.25 | −0.06 | 0.01 |
| 60,000~70,000 | −0.06 | −0.14 | −0.06 | 0.01 |
| 70,000~80,000 | −0.05 | −0.2 | −0.07 | 0.01 |
| 80,000~90,000 | −0.06 | −0.21 | −0.08 | 0.01 |
| (c) Lake Image | ||||
| Bits | DE | Skewed HS | PEE | Proposed |
| 20,000~30,000 | −0.21 | −0.21 | −0.2 | 0.01 |
| 30,000~40,000 | −0.12 | −0.14 | −0.13 | 0.01 |
| 40,000~50,000 | −0.09 | −0.08 | −0.09 | 0.01 |
| 50,000~60,000 | −0.07 | −0.05 | −0.06 | 0.01 |
| 60,000~70,000 | −0.06 | −0.07 | −0.07 | 0.01 |
| 70,000~80,000 | −0.05 | −0.05 | −0.06 | 0.01 |
| 80,000~90,000 | −0.04 | −0.05 | −0.07 | 0.01 |
| 20,000 | 30,000 | 40,000 | 50,000 | 60,000 | 70,000 | 80,000 | 90,000 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | 39.93 | 40.1 | 40.21 | 40.32 | 40.34 | 40.41 | 40.47 | 40.53 | ||||||||
| Rate | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, Y.-Y.; Cho, D.-J.; Jung, K.-H. A New Reversible Data Hiding Method Using a Proportional Relation between Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio and Embedding Capacity on Convolutional Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6370. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146370
Bae Y-Y, Cho D-J, Jung K-H. A New Reversible Data Hiding Method Using a Proportional Relation between Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio and Embedding Capacity on Convolutional Neural Network. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(14):6370. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146370
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Yong-Yeol, Dae-Jea Cho, and Ki-Hyun Jung. 2024. "A New Reversible Data Hiding Method Using a Proportional Relation between Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio and Embedding Capacity on Convolutional Neural Network" Applied Sciences 14, no. 14: 6370. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146370
APA StyleBae, Y.-Y., Cho, D.-J., & Jung, K.-H. (2024). A New Reversible Data Hiding Method Using a Proportional Relation between Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio and Embedding Capacity on Convolutional Neural Network. Applied Sciences, 14(14), 6370. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146370







