A Low-Complexity Start–Stop True Random Number Generator for FPGAs
Abstract
1. Introduction
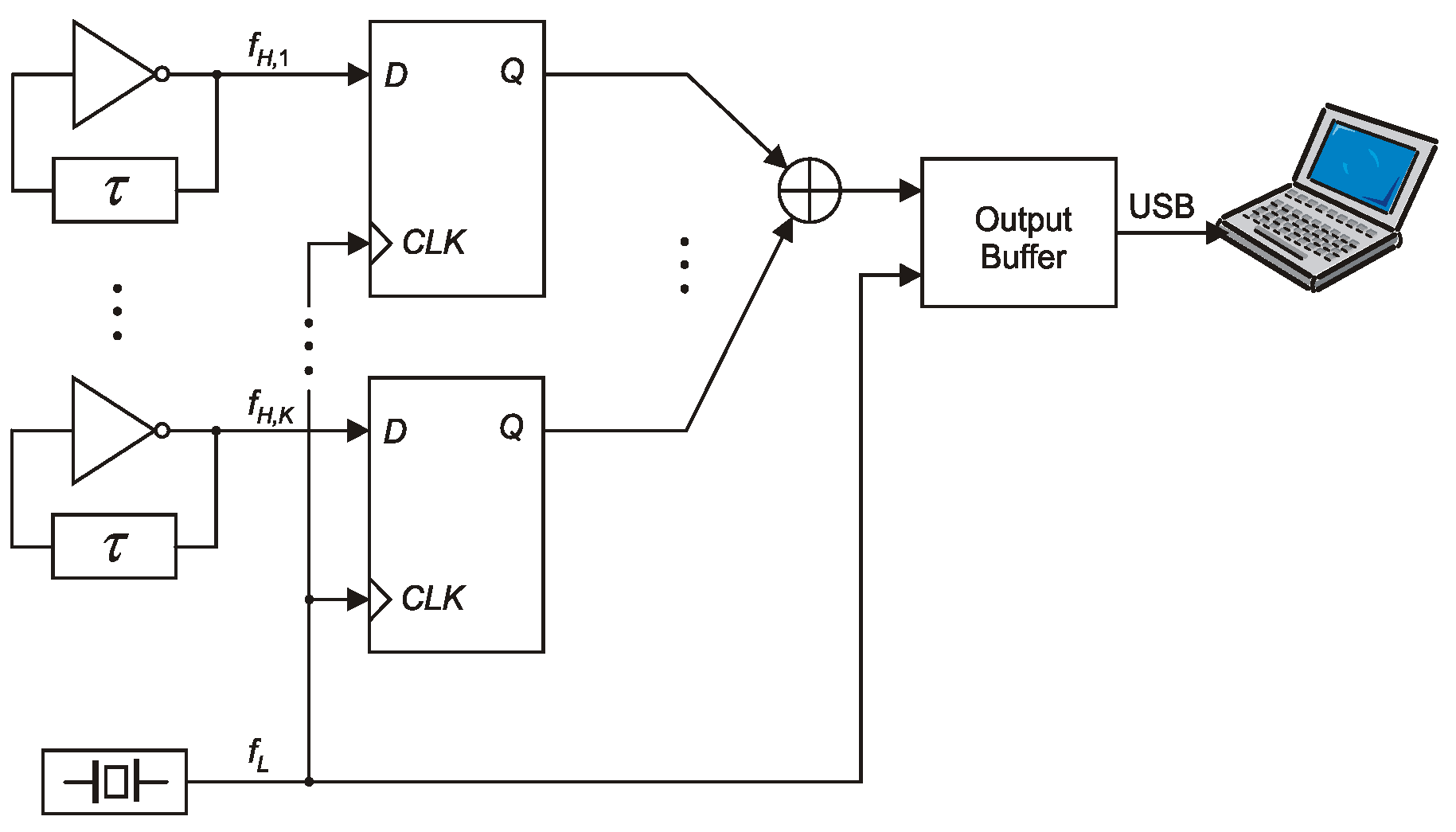
2. A Start–Stop TRNG with Two ROs and a Phase Detector
3. The Quality of Bit Streams Produced by the Proposed Generator
- The generator can be integrated into the same FPGA alongside a digital system that employs random sequences.
- The authors declare that the generator produces IID sequences and that the restart tests described in the SP800-90B are performed.
- The authors declare that the generator produces sequences that pass the randomness tests described in NIST 800-22, so that the proportion of Rβ of strings that pass the test is within the limits set by NIST for all tests and subtests, and so that the distribution of p-values is uniform.
- The authors have specified the FPGA resources for the proposed TRNG.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Menezes, A.J.; van Oorschot, P.C.; Vanstone, S.C. Handbook of Applied Cryptography; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Petrie, C.S.; Connelly, J.A. Modelling and simulation of oscillator-based random number generators. In Proceedings of the the 47th International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, ISCAS’1996, Atlanta, GA, USA, 12 May 1996; Volume 4, pp. 324–327. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, V.; Drutarovski, M. True random number generator embedded in reconfigurable hardware. In Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems CHES; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 415–430. [Google Scholar]
- Kohlbrenner, P.; Gaj, K. An embedded true random number generator for FPGAs. In Proceedings of the the 2004 ACM/SIGDA 12th International Symposium on Field Programmable Gate Arrays, ACM, Monterey CA, USA, 22–24 February 2004; pp. 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Golić, J.D. New methods for digital generation and postprocessing of random data. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2006, 55, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dichtl, M.; Golić, J.D. High speed true random number generation with logic gates only. In Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop, Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems–CHES, Vienna, Austria, 10–13 September 2007; pp. 45–62. [Google Scholar]
- Sunar, B.; Martin, W.J.; Stinson, D.R. A provably secure true random number generator with built-in tolerance to active attacks. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2006, 56, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, K.; Tan, C.H. Analysis and enhancement of random number generator in FPGA based on oscillator rings. Int. J. Reconfigurable Comput. 2009, 2009, 501672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochard, N.; Bernard, F.; Fischer, V. Observing the randomness in RO-based TRNG. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Reconfigurable Computing and FPGAs, Cancun, Mexico, 9–11 December 2009; pp. 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Wold, K.; Petrović, S. Optimizing speed of a true random number generator in FPGA by spectral analysis. In Proceedings of the 2009 Fourth International Conference on Computer Sciences and Convergence Information Technology, ICCIT’09, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 24–26 November 2009; pp. 1105–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Valtchanov, B.; Aubert, A.; Bernard, F.; Fischer, V. Modeling and observing the jitter in ring oscillators implemented in FPGAs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Design and Diagnostics of Electronic Circuits and Systems, DDECS’08, Bratislava, Slovakia, 16–18 April 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Valtchanov, B.; Fischer, V.; Aubert, A.; Bernard, F. Characterization of randomness sources in ring oscillator-based true random number generators in FPGAs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Design and Diagnostics of Electronic Circuits and Systems, DDECS’10, Vienna, Austria, 14–16 April 2010; pp. 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Jessa, M.; Jaworski, M. Randomness of a combined RBG based on the ring oscillator sampling method. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Signals and Electronic Systems, ICSES’10, Gliwice, Poland, 7–10 September 2010; pp. 323–326. [Google Scholar]
- Jessa, M.; Matuszewski, L. Enhancing the Randomness of a Combined True Random Number Generator Based on the Ring Oscillator Sampling Method. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Reconfigurable Computing and FPGAs, Cancun, Mexico, 30 November–2 December 2011; pp. 274–279. [Google Scholar]
- Baudet, M.; Lubicz, D.; Micolod, J.; Tassiaux, A. On the security of oscillator-based random number generators. J. Cryptol. J. Cryptol. 2011, 24, 398–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, K.; Petrović, S. Security properties of oscillator rings in true random number generators. In Proceedings of the 15th Inter-national Symposium on Components, Circuits, Devices and Systems, Tallinn, Estonia, 18–20 April 2012; pp. 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Jessa, M.; Matuszewski, L. Producing random bits with delay-line-based ring oscillators. Int. J. Electron. Telecommun. 2013, 59, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lubicz, D.; Bochard, N. Towards an Oscillator Based TRNG with a Certified Entropy Rate. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2015, 64, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Micco, L.; Larrondo, H.A. Measuring the jitter of ring oscillators by means of information theory quantifiers. In Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 43, pp. 139–150. ISSN 1007-5704. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Chang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, X. An energy-efficient true random number generator based on current starved ring oscillators. In Proceedings of the 2017 Asian Hardware Oriented Security and Trust Symposium (AsianHOST), Beijing, China, 19–20 October 2017; pp. 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkaoui, A.; Fischer, V.; Aubert, A.; Fesquet, L. Comparison of self-timed ring and inverter ring oscillators as entropy sources for FPGAs. In Proceedings of the 2012 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Dresden, Germany, 12–16 March 2012; pp. 1325–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Cherkaoui, A.; Fischer, V.; Aubert, A.; Fesquet, L. A self-timed ring based true random number generator. In Proceedings of the IEEE 19th International Symposium on Asynchronous Circuits and Systems (ASYNC), Santa Monica, CA, USA, 19–22 May 2013; pp. 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Gimenez, G.; Cherkaoui, A.; Frisch, R.; Fesquet, L. Self-timed Ring based True Random Number Generator: Threat model and countermeasures. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2nd International Verification and Security Workshop (IVSW), Thessaloniki, Greece, 3–5 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.; Yu, Y.; Dubrova, E. FPGA Based True Random Number Generators Using Non-Linear Feedback Ring Oscillators. In Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International New Circuits and Systems Conference (NEWCAS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 24–27 June 2018; pp. 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şarkışla, M.A.; Ergün, S. Ring Oscillator Based Random Number Generator Using Wake-up and Shut-down Uncertainties. In Proceedings of the 2018 Asian Hardware Oriented Security and Trust Symposium (AsianHOST), Hong Kong, China, 17–18 December 2018; pp. 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandakumar, N.N.; Sanadhya, S.K.; Hashmi, M.S. FPGA-Based True Random Number Generation Using Programmable Delays in Oscillator-Rings. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 67, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Hui, C.; Song, Z. A new method for true random number generation based on Galois Ring Oscillator with event sampling Architechture in FPGA. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 25–28 May 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Guo, Y.; Yi, M.; Huang, Z.; Qi, H.; Lu, Y. High-throughput portable true random number generator based on jitter-latch structure. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2021, 68, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Di Mateo, S.; Baldanzi, L.; Crocetti, L.; Belli, J.; Fanucci, L. True random number generator based on Fibonacci-Galois ring oscillators for FPGA. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasyltsov, I.; Hambardzumyan, E.; Kim, Y.-S.; Karpinskyy, B. Fast digital TRNG based on metastable ring oscillator. In Proceedings of the Workshop Cryptograph. Hardware Embedded Systems (CHES), Washington, DC, USA, 10–13 August 2008; pp. 164–180. [Google Scholar]
- Bucci, M.; Luzzi, R. Fully digital random bit generators for cryptographic applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2008, 4, 861–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majzoobi, M.; Koushanfar, F.; Devades, S. FPGA-based true random number generation using circuit metastability with adaptive feedback control. In Proceedings of the Workshop Cryptograph. Hardware Embedded Systems (CHES), Nara, Japan, 28 September–1 October 2011; pp. 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wieczorek, P.; Golofit, K. Dual-Metastability Time-Competitive True Random Number Generator. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2014, 61, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, P.Z.; Golofit, K. True Random Number Generator Based on Flip-Flop Resolve Time Instability Boosted by Random Chaotic Source. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2018, 61, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaysici, H.İ.; Ergün, S. Random Number Generator Based on Metastabilities of Ring Oscillators and Irregular Sampling. In Proceedings of the 2020 27th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), Glasgow, UK, 23–25 November 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, R.D.; Bellizia, D.; Scontti, G. A novel ultra-compact FPGA-compatible TRNG architecture exploiting latched ring oscillators. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 3, 1672–1676. [Google Scholar]
- Grujcić, M.; Verbauwhede, I. TROT: A three-edge ring oscillator based true random number generator with time-to-digital conversion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2022, 69, 2435–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, R.D.; Bellizia, D.; Scontti, G. High-throughput FPGA-compatible TRNG architecture exploiting multistimuli metastable cells. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2022, 12, 4886–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Yi, M.; Cao, D.; Yao, L.; Wang, X.; Liang, H.; Huang, Z.; Qi, H.; Ni, T. Design of true random number generator based on multi-stage feedback ring oscillator. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 1752–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, T.; Peng, Q.; Bian, J.; Yao, L.; Huang, Z.; Yan, A.; Wang, S.; Wen, X. Design of True random number generator based on multi-ring convergence oscillator using pulse enhanced randomness. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Mahalingam, H.; Rethinam, S.; Janakiraman, S.; Rengarajan, A. Non-identical inverter rings as an entropy source: MIST-90B-verified TRNG architecture on FPGAs for IoT device integrity. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, R.D.; Scontti, G. Exploiting the DD-Cell as an ultra-compact entropy source for an FPGA-based Re-configurable PUF-TRNG architecture. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 86178–86194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukhin, A.; Soto, J.; Nechvatal, J.; Smid, M.; Barker, E.; Leigh, S.; Levenson, M.; Vangel, M.; Banks, D.; Heckert, A.; et al. A Statistical Test Suite for Random and Pseudorandom Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications. NIST Special Publication 800-22. Available online: https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/Legacy/SP/nistspecialpublication800-22r1a.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- L’Ecuyer, P.; Simard, R. TestU01: A Software Library in ANSIC C for Empirical Testing of Random Number Generators. Software User’s Guide. Available online: http://www.iro.umontreal.ca/~lecuyer (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Brown, R.G. DieHarder, A Gnu Public License Random Number Tester. Available online: https://rurban.github.io/dieharder/manual/dieharder.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- McNeill, J.A.; Ricketts, D.S. The Designer’s Guide to Jitter in Ring Oscillators; Springer: San Hose, VA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Turan, M.S.; Barker, E.; Kelsey, J.; McKay, K.; Baish, M.L.; Boyle, M. Recommendation for the Entropy Sources Used in Random Bit Generation. NIST Special Publication 800-90B. Available online: https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/SpecialPublications/NIST.SP.800-90B.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Barker, E.; Kelsey, J.; McKay, K.; Roginsky, A.; Turan, M.S. Recommendation for Random Bit Generators (RBG) Constructions. NIST Special Publication 800-90C. Available online: https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/SpecialPublications/NIST.SP.800-90C.3pd.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Trischitta, P.R.; Varma, E.L. Jitter in Digital Transmission Systems; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Madhu, N. Note on measures for spectral flatness. Electron. Lett. 2009, 45, 1195–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashlib Python Library. Available online: https://docs.python.org/3/library/hashlib.html (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Peng, Q.; Bian, J.; Huang, Z.; Wang, S.; Yan, A. A Compact TRNG Design for FPGA Based on Metastability of RO-Driven Shift Registers. ACM Trans. Des. Autom. Electron. Syst. 2023; in press. Available online: https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/3610295 (accessed on 5 May 2024). [CrossRef]
- Killmann, W.; Schindler, W. A Proposal for Functionality Classes for Random Number Generators; Technical Reference of AIS 20/31; BSI: Bonn, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, M.; Schindler, W. A Proposal for Functionality Classes for Random Number Generators. v.2.35–DRAFT. 2 September 2022. Available online: https://www.bsi.bund.de/SharedDocs/Downloads/EN/BSI/Certification/Interpretations/AIS_31_Functionality_classes_for_random_number_generators_e.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=4 (accessed on 5 May 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions, and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |


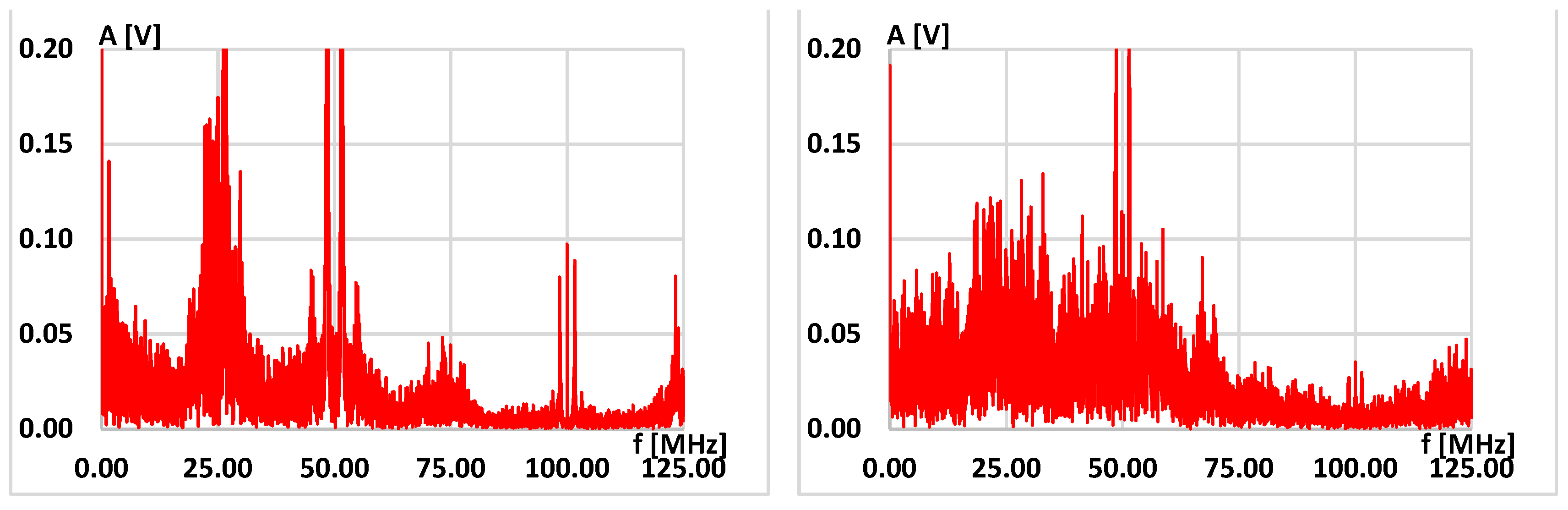
| fL [MHz] | 25 | 15 | 10 | 5 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT2 | 0.228335 | 0.542281 | 0.654215 | 0.784981 | 0.894990 |
| WT3 | 0.893081 | 0.970915 | 0.995306 | 0.995389 | 0.998268 |
| WT4 | 0.994968 | 0.997237 | 0.999889 | 0.999311 | 0.998281 |
| WT2D | 0.999998 | 0.999999 | 0.999999 | 0.999999 | 0.999999 |
| fL [MHz] | 25 | 15 | 10 | 5 | 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tests | IID | RES | IID | RES | IID | RES | IID | RES | IID | RES |
| WT2 | — | — | — | — | — | Y | — | Y | — | Y |
| WT3 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | Y | — | Y |
| WT4 | — | — | — | Y | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| WT2D | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Test | Raw Data | Raw Data + SHA1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT2 | WT3 | WT4 | WT2D | WT2 | WT3 | WT4 | WT2D | |
| 1. Frequency | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 2. Block frequency | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 3. Cumulative sums | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 4. Runs | — | — | — | — | — | — | Y | Y |
| 5. Longest run | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 6. Rank | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 7. DFT | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 8. Nonoverlapping template | — | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y |
| 9. Overlapping template | — | — | — | — | Y | — | — | Y |
| 10. Universal | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 11. Approximate entropy | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 12. Random excursions | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 13. Random excursions variants | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | — | Y |
| 14. Serial | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 15. Linear complexity | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Test | Raw Data | Raw Data + SHA1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT2 | WT3 | WT4 | WT2D | WT2 | WT3 | WT4 | WT2D | |
| 1. Frequency | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 2. Block frequency | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 3. Cumulative sums | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 4. Runs | — | — | — | — | — | — | Y | Y |
| 5. Longest run | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 6. Rank | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 7. DFT | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 8. Nonoverlapping template | — | — | — | — | — | — | Y | Y |
| 9. Overlapping template | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | — | Y |
| 10. Universal | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 11. Approximate entropy | Y | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 12. Random excursions | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 13. Random excursions variants | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | — | Y |
| 14. Serial | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 15. Linear complexity | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Test | Raw Data | Raw Data + SHA1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT2 | WT3 | WT4 | WT2D | WT2 | WT3 | WT4 | WT2D | |
| 1. Frequency | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 2. Block frequency | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 3. Cumulative sums | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 4. Runs | — | — | — | — | — | — | Y | Y |
| 5. Longest run | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 6. Rank | — | Y | Y | Y | — | Y | Y | Y |
| 7. DFT | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 8. Nonoverlapping template | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | Y |
| 9. Overlapping template | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | — | Y |
| 10. Universal | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 11. Approximate entropy | Y | Y | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 12. Random excursions | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 13. Random excursions variants | — | — | — | Y | — | — | — | Y |
| 14. Serial | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 15. Linear complexity | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Test | Raw Data | Raw Data + SHA1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT7 | WT2D | WT7 | WT2D | |||||
| Rβ | PT | Rβ | PT | Rβ | PT | Rβ | PT | |
| 1. Frequency | 0.958 | 0.000 | 0.918 | 0.000 | 0.986 | 0.196 | 0.987 | 0.745 |
| 2. Block frequency | 0.428 | 0.000 | 0.910 | 0.000 | 0.989 | 0.169 | 0.989 | 0.326 |
| 3. Cumulative sums | 0.949 | 0.000 | 0.991 | 0.534 | 0.987 | 0.081 | 0.991 | 0.721 |
| 4. Runs | 0.993 | 0.435 | 0.980 | 0.114 | 0.992 | 0.426 | 0.989 | 0.982 |
| 5. Longest run | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.910 | 0.000 | 0.990 | 0.998 | 0.983 | 0.872 |
| 6. Rank | 0.990 | 0.175 | 0.986 | 0.094 | 0.992 | 0.890 | 0.989 | 0.739 |
| 7. DFT | 0.995 | 0.771 | 0.974 | 0.007 | 0.990 | 0.249 | 0.991 | 0.494 |
| 8. Non overlapping template | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.037 | 0.000 | 0.987 | 0.699 | 0.992 | 0.133 |
| 9. Overlapping template | 0.983 | 0.046 | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.988 | 0.473 | 0.993 | 0.220 |
| 10. Universal | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.808 | 0.000 | 0.991 | 0.152 | 0.991 | 0.173 |
| 11. Approximate entropy | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.991 | 0.004 | 0.989 | 0.684 | 0.991 | 0.957 |
| 12. Random excursions | 0.938 | 0.000 | 0.955 | 0.000 | 0.988 | 0.188 | 0.986 | 0.012 |
| 13. Random excursions variants | 0.961 | 0.000 | 0.998 | 0.012 | 0.993 | 0.000 | 0.996 | 0.077 |
| 14. Serial | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.992 | 0.465 | 0.992 | 0.159 |
| 15. Linear complexity | 0.990 | 0.028 | 0.998 | 0.167 | 0.989 | 0.697 | 0.990 | 0.420 |
| TRNG Design Technique | Number | Throughput [Mbit/s] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LUTs | Flip-Flops | ||
| Self-timed rings [28] | 56 | 19 | 100 |
| Fibonacci-Galois RO [29] | 288 | 190 | 400 |
| Metastability+jitter [36] | 4 | 3 | 0.76 |
| Metastability+jitter [38] | 36 | 0 | 12.50 |
| Multi-stage feedback ring oscillator [39] | 24 | 2 | 290 |
| RO with XOR gates [40] | 13 | 4 | 500 |
| Non-identical ROs [41] | 15 | 13 | 3.50 |
| Delay-Difference-Cell [42] | 256 | 256 | 225 |
| Metastability [52] | 14 | 6 | 25 |
| RO with XOR gates [8] | 23 | 23 | 10 |
| WTD2 (this work) | 11 | 13 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matuszewski, Ł.; Jessa, M. A Low-Complexity Start–Stop True Random Number Generator for FPGAs. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5642. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135642
Matuszewski Ł, Jessa M. A Low-Complexity Start–Stop True Random Number Generator for FPGAs. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(13):5642. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135642
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatuszewski, Łukasz, and Mieczysław Jessa. 2024. "A Low-Complexity Start–Stop True Random Number Generator for FPGAs" Applied Sciences 14, no. 13: 5642. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135642
APA StyleMatuszewski, Ł., & Jessa, M. (2024). A Low-Complexity Start–Stop True Random Number Generator for FPGAs. Applied Sciences, 14(13), 5642. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135642







