Abstract
The use of tuning forks to measure fluid density and viscosity is widely employed in fields such as food, medicine, textiles, automobiles, petrochemicals, and deep drilling. The explicit analytical model based on the Euler–Bernoulli cantilever-beam theory for the relationship between tuning-fork resonance characteristics and the density and viscosity of fluid is only applicable to the situation where the fluid viscous effect is very small. In this paper, the finite element method is used to simulate the influence of large variations in fluid density and viscosity on the resonance characteristic parameters (resonant frequency and quality factor) of the tuning fork. The numerical simulation results are compared with the analytical analysis results and experimental measurement results. Then, the sensitivity of tuning-fork resonance characteristic parameters to fluid density and viscosity is studied. The results show that compared with the analytical results, the numerical simulation results have a higher degree of agreement with the experimental measurement results. The relative difference in resonant frequency is less than 2%, and the relative difference in quality factor is less than 4%. This indicates that the finite element method includes the influence of fluid viscosity on tuning-fork resonance parameters, which is more in line with the actual conditions than the analytical model. Simulating and analyzing the sensitivity of the tuning fork to fluid density and viscosity by the finite element method, it is possible to consider the situation where fluid density and viscosity vary over a large range. Compared with experimental measurements, this method has higher efficiency and can significantly save time and economic costs. This study can overcome the limitation of existing explicit analytical models, which are only applicable when the viscous effects of the fluid are very small. It enables a more accurate simulation of the coupling vibration between tuning forks and fluids, thereby providing theoretical references for further optimizing tuning-fork structural parameters to enhance the accuracy of measuring fluid characteristic parameters.
1. Introduction
The two arms of a tuning fork can be regarded as two symmetrical cantilever beams with one end fixed and the other end free, which can achieve decoupled measurement of fluid density and viscosity. Tuning forks are widely employed in industrial production. For example, tuning forks are used to measure the density and viscosity of wine in real time, thereby achieving quality monitoring of the wine fermentation process [1,2]. Tuning forks are used to measure the density and viscosity of gases, in order to monitor the gas polymerization process in high-temperature and high-pressure containers [3]. The smoke and dust content of engine oil can be monitored by measuring its density and viscosity through tuning forks [4,5]. In the process of oil and gas exploitation [6,7], using a tuning fork to measure the density and viscosity of downhole fluid can identify fluid [8,9], determine fluid composition, and divide the oil–water interface, which is of great significance for optimizing oil and gas reservoir management and intelligent oil-field exploitation [10,11].
In-depth study of the relationship between tuning-fork resonance characteristics and fluid characteristic parameters is helpful in optimizing the design of the tuning fork sensor, thereby enhancing the accuracy of fluid density and viscosity measurements using tuning forks. In 1998, John Elie Sader established an explicit analytical model based on the Euler–Bernoulli cantilever-beam theory, which relates the resonant frequency and quality factor of a cantilever beam vibrating in a fluid to fluid density and viscosity. The model can express the quantitative relationship between the resonant frequency and quality factor of the tuning fork, the size of the tuning fork, the material parameters, and the fluid density and viscosity, but only for fluid with small viscous effects, such as air [12]. In 2011, Waszczuk et al. developed an implicit analytical model using an equivalent circuit approach, relating tuning-fork resonant frequency and quality factor to fluid density and viscosity. The model contained undetermined coefficients related to the material and size of the tuning fork, and the accuracy of the model was affected by the parasitic capacitance of the tuning fork [13]. In 2014, Henisch et al. compared the vibration of a tuning fork in a fluid to the damped vibration of a pendulum–spring system. Based on the forces exerted on the tuning fork in the fluid, they derived an implicit analytical model relating tuning-fork resonant frequency and quality factor to fluid density and viscosity, with the effective area of interaction between the tuning fork and fluid being an undetermined coefficient [14]. In 2015, Henisch et al. studied the feasibility of using an electromagnetic-driven metal tuning fork to measure fluid density and viscosity, and analyzed the sensitivity of tuning fork characteristic parameters to fluid density and viscosity. However, due to the limitation of experimental fluid samples, only the sensitivity of the tuning fork was studied when density and viscosity changed within a small range [15]. In 2020, Zhang et al. used the Sobol global sensitivity analysis method instead of the commonly used finite difference method to analyze the sensitivity of tuning forks to fluid density and viscosity, but did not carry out further research into the relationship between the sensitivity of tuning forks and the large-scale variation of fluid density and viscosity [16].
In order to overcome the limitation of existing explicit analytical models, which are only applicable when the viscous effects of the fluid are small, this paper utilizes finite element analysis to simulate the coupling vibration law between tuning forks and fluids. It compares the results of finite element numerical simulations, analytical model predictions, and experimental measurements. Building upon this comparison, the finite element method is employed to simulate the relationship between tuning-fork resonance characteristics and fluid characteristic parameters. Furthermore, the sensitivity of tuning forks to large-scale variations in fluid density and viscosity is analyzed based on the finite element simulations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analytical Model
Assuming that the cross section of the tuning fork arm is uniform along the length, and the length of the tuning fork arm is much larger than the width and thickness, according to the Euler–Bernoulli cantilever-beam theory, the flexural vibration equation of the tuning fork arm during vibration in an incompressible fluid is as follows [12]:
where represents Young’s modulus; represents the moment of inertia; represents the resonant angular frequency of the tuning fork when it vibrates in the fluid; represents the density of the tuning fork material; represents the width of the tuning fork arm; represents the thickness of the tuning fork; represents the displacement function, where represents the position coordinate along the length direction of the tuning fork arm; represents the external driving force of the tuning fork; and represents the force of the fluid on the tuning fork. is obtained by solving the linear Navier–Stokes equation, and represents hydrodynamic function. When the tuning fork is immersed in the fluid with a small viscous effect, Formula (1) is solved to obtain the resonant frequency of the tuning fork when it is performing first-order in-plane anti-phase flexural vibration [12],
where represents the resonant angular frequency of the tuning fork when it vibrates in vacuum, , is the first positive root of the equation , represents the real part of the hydrodynamic function [16], and represents the Reynolds number.
By substituting Formula (2) into Formula (1), the fluid viscosity quality factor of the tuning fork during the first-order flexural vibration can be obtained:
where represents the imaginary part of the hydrodynamic function [16]. The quality factor of the tuning fork in Formula (3) is related to the resonant frequency of the tuning fork in Formula (2), and Formula (2) is derived under the assumption of small viscous effects of the fluid, which implies that the resonant frequency and quality factor in Formula (2) and Formula (3) are only applicable when the viscous effect of the fluid is small [17,18].
2.2. Finite Element Method
2.2.1. Coupling Relationship between the Tuning Fork and Fluid
The structure of the tuning fork is shown in Figure 1a. The length of the tuning fork arm is , the width of the tuning fork arm is , the thickness of the tuning fork arm is , and the spacing between the tuning fork arms is . The bottom of the tuning fork is fixed, thus the displacement is zero. Figure 1b is a schematic diagram of the tuning fork performing first-order in-plane anti-phase flexural vibration. This paper mainly studies the relationship between the resonant frequency and quality factor of this vibration mode with respect to fluid density and viscosity. The material of the tuning fork is quartz, with a density of , and other material property parameters of quartz are defined by the elastic matrix (the conversion matrix between stress and strain, related to material parameters such as Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio), the coupling matrix (the conversion matrix between charge and stress), and the relative dielectric constant.
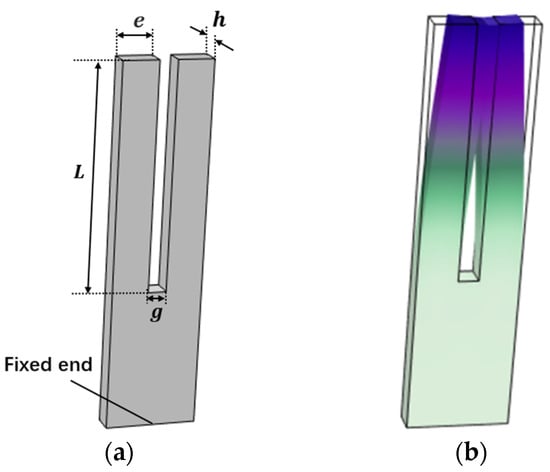
Figure 1.
(a) Tuning fork model in finite element method. (b) The tuning fork performs first-order in-plane reverse flexural vibration.
The governing equations for fluid motion in the finite element method are defined by the linear Navier–Stokes equations, including the momentum equation, the continuity equation, and the constitutive relation equation:
where represents the initial density of the fluid in the absence of disturbance, represents the total acoustic velocity field, represents the initial background acoustic velocity field, and represents the acoustic velocity field generated by tuning fork’s vibration. indicates the total temperature, where indicates the initial background temperature and indicates the temperature change caused by the tuning fork’s vibration. represents the total acoustic pressure, where represents the initial background pressure and represents the acoustic pressure caused by the tuning fork’s vibration. represents the density of the fluid during the propagation of the acoustic wave; represents the coefficient of thermal expansion at constant pressure; represents the dynamic viscosity; and represents the volume viscosity, which is related to the momentum loss caused by the expansion and compression of the fluid. represents the isothermal compression rate; represents the stress; and represents the unit diagonal matrix, .
Fluid in finite element method is compressible fluid, and density, and dynamic viscosity are related to temperature and pressure. and are set to constants in simulation, so that, and are not affected by temperature and pressure.
When the tuning fork and the fluid are in coupled vibration, their displacements are continuous, satisfying the following relationship:
where and represent the displacement of the tuning fork and the velocity of the fluid, respectively, and their relationship in the frequency domain is . This coupling relationship shows that the normal stress on the boundary between the tuning fork and the fluid is also continuous.
To sum up, the equations of fluid motion in the analytical method and the finite element method are both linear Navier–Stokes equations. However, in order to obtain an explicit expression for the resonant frequency and quality factor of the tuning fork with respect to fluid density and viscosity in the process of solving Equation (1), it is assumed that the viscous effect of the fluid is small, providing only an approximate solution. This approximation does not hold well when the fluid viscosity is large. The finite element method gives the relationship between tuning-fork resonance parameters and fluid characteristic parameters by solving Equation (4) to Equation (8), without approximation. Therefore, the finite element method is more in line with the actual situation than the analytical method, and the simulation results are closer to the actual situation.
2.2.2. Comparison of Finite Element Method and Analytical Method
In the finite element simulation, the material and size of the tuning fork are consistent with those of the laboratory quartz tuning fork in literature [19]. The length of the tuning fork arm is 4.05 mm, the width is 0.66 mm, the thickness is 0.4 mm, and the spacing is 0.24 mm. The resonant frequency and quality factor of tuning forks in 19 groups of fluids with different densities and viscosities were measured by experiments in reference [19]. In this paper, the finite element method and the analytical method were used to simulate the model with parameters identical to those in the experiments. Equation (2) and Equation (3) were used for the analytical method, the value of Young’s modulus was , and the value of the material density of the tuning fork was . The comparison of the numerical simulation results, analytical results, and experimental measurement results is shown in Table 1, where fluids of groups 1–19 are arranged in order of viscosity from small to large. The finite element simulation results were obtained through the conductance diagram, with peak value corresponding to the resonant frequency of the tuning fork, quality factor , and is bandwidth. Figure 2 shows the results of group 1 and group 19. The resonant frequency of the tuning fork in fluid of group 1 was and the quality factor was . In fluid of group 19, the resonant frequency of the tuning fork was and the quality factor was .

Table 1.
Comparison of numerical results, analytical results, and experimental results.
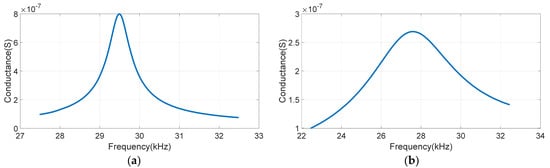
Figure 2.
(a) Conductance diagram of the tuning fork in fluid of group 1. (b) Conductance diagram of the tuning fork in fluid of group 19.
Figure 3 shows the comparison of numerical, analytical, and experimental results of resonant frequency and quality factor. Figure 4 shows the relative differences between numerical results and experimental results, and the relative differences between analytical results and experimental results, respectively. The relative difference of numerical results is , and the relative difference of analytical results is .
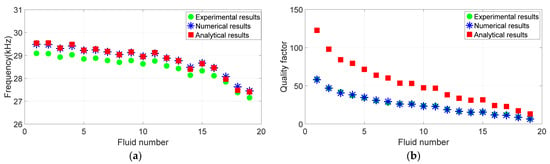
Figure 3.
(a) Numerical, analytical, and experimental results of resonant frequency corresponding to 19 groups of different fluids. (b) Numerical, analytical, and experimental results of quality factor corresponding to 19 groups of different fluids.
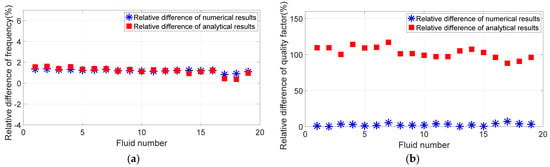
Figure 4.
(a) Relative difference of numerical results and analytical results of resonant frequency corresponding to 19 groups of different fluids. (b) Relative difference of numerical results and analytical results of quality factor corresponding to 19 groups of different fluids.
From Figure 3 and Figure 4, it can be seen that the numerical results and analytical results of the resonant frequency are highly consistent, with a relative difference of less than 2% from the experimental measurement results. The difference between the numerical results and the analytical results of the quality factor is large, the relative difference between the numerical results and the experimental results is less than 4%, and the relative difference between the analytical results and the experimental results can even exceed 110%. This shows that the finite element method includes the influence of fluid viscous effects on tuning-fork resonance parameters, and is closer to the actual situation than the approximate analytical method, and the simulation results are more accurate.
3. Results
3.1. Relationship between Tuning-Fork Resonance Characteristics and Fluid Characteristic Parameters
Based on the above conclusions, the finite element method is used in this paper to simulate the relationship between the tuning-fork resonance characteristics (resonant frequency and quality factor) and the fluid characteristic parameters (density and viscosity) when the fluid density varies from to and the viscosity varies from to . The numerical simulation results are shown in Figure 5.
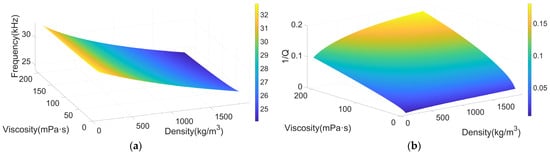
Figure 5.
(a) Resonant frequency in relation to fluid density and viscosity. (b) Quality factor in relation to fluid density and viscosity.
It can be seen from Figure 5 that both the resonant frequency and quality factor of the tuning fork decrease with the increase in fluid density and viscosity. The vibration of the tuning fork in the fluid can be regarded as the damped vibration of a oscillator spring system [20], so the resonant frequency and quality factor can be written as follows [14,21]:
where represents the elastic coefficient of the spring, represents the mass of the oscillator, represents the spring damping, represents the additional mass of the fluid, and represents the fluid damping. When the tuning fork vibrates in the fluid, the additional mass , where is the effective area of the tuning fork, so the resonant frequency of the tuning fork decreases when the density and viscosity increase, with damping coefficient and . Because as the increase in and , the increasing trend of is greater than Therefore, with the increase in and , the quality factor gradually decreases. Also, as and increase, the fluid damping force on the tuning fork increases, leading to greater energy loss in the tuning fork vibration, hence reducing its quality factor.
3.2. Sensitivity Analysis
In the finite element numerical simulation, the calculation formula of relative sensitivity is
where represents or , represents or , and Formula (11) represents the relative change in resonant frequency or quality factor corresponding to a relative change in unit density or viscosity. The higher the sensitivity, the more sensitive the tuning-fork resonance parameters are to the changes of fluid characteristic parameters, resulting in higher measurement accuracy.
The tuning fork size is set to be consistent with that used in the laboratory in the finite element method. Fluid density increases from to , is , viscosity increases from to , and is Figure 6 shows the sensitivity of resonant frequency to density and viscosity, and Figure 7 shows the sensitivity of quality factor to density and viscosity.
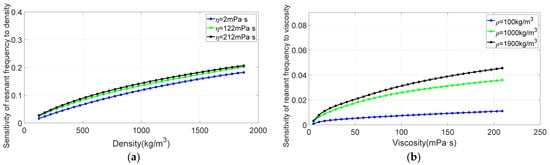
Figure 6.
(a) Sensitivity of resonant frequency to density. (b) Sensitivity of resonant frequency to viscosity.
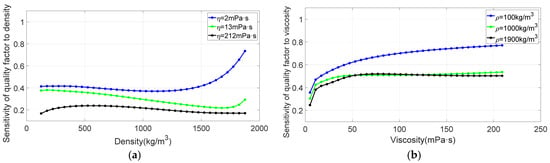
Figure 7.
(a) Sensitivity of quality factor to density. (b) Sensitivity of quality factor to viscosity.
It can be seen from Figure 6 that the sensitivity of tuning-fork resonant frequency to fluid density and viscosity increases with the increase in fluid density and viscosity, and the sensitivity of tuning-fork resonant frequency to fluid density is greater than to viscosity. It can be seen from Figure 7b that the sensitivity of tuning fork quality factor to fluid viscosity generally increases with the increase in fluid viscosity. The sensitivity value of tuning fork quality factor to fluid density is comparable to that of viscosity. But the sensitivity of quality factor to fluid density does not vary monotonically.
Henisch et al. [15] analyzed, through experiments, the sensitivity of the metal tuning fork driven by electromagnetic means. However, this approach required setting up experimental platforms and extensive data-processing work. Moreover, the analysis results were limited by experimental samples and only the sensitivity of the tuning fork within a small range of density and viscosity variations was analyzed. In contrast, the finite element method does not require the construction of experimental platforms and experiments, and can analyze the sensitivity of the tuning fork when the density and viscosity change in a wide range, which can greatly save time and economic costs.
4. Conclusions
Firstly, the existing analytical model of the relationship between tuning-fork resonance characteristics and fluid characteristics based on Euler–Bernoulli’s cantilever-beam theory was analyzed. It has the limitation of being applicable to the small viscous effects of fluid. In this paper, the finite element method was used to establish the simulation model to simulate the coupling vibration law of the tuning fork and fluid, and the influence of the fluid viscous effect on the resonant characteristics of tuning fork was considered. The comparison of the finite element numerical results, analytical results, and experimental measurement results showed that the finite element simulation results and experimental measurement results had a higher agreement, and the relative difference rate of resonant frequency between the two was less than 2%, and the relative difference rate of quality factor was less than 4%. This indicates that, compared with the approximate analytical method, the finite element method can consider the influence of the fluid viscous effect, so it is more in line with the actual situation than the analytical method. Finally, based on the finite element method, the sensitivity of tuning-fork resonance characteristics to fluid characteristic parameters (density and viscosity) was calculated. The results show that the sensitivity of tuning-fork resonant frequency to fluid density and viscosity increases with the increase in fluid density and viscosity, and the sensitivity of tuning fork quality factor to fluid viscosity generally increases with the increase in fluid viscosity. However, the sensitivity of quality factor to fluid density does not change monotonically. Compared with experiments, the established finite element simulation model can be used, conveniently, to analyze the sensitivity change in tuning fork to fluid density and viscosity when the fluid density and viscosity change in a large range, which can greatly save time and economic cost. It provides a theoretical reference for further optimization of the design of the tuning fork sensor to improve the accuracy of measuring fluid characteristic parameters. Next, the finite element simulation model can be optimized into the tuning fork’s vibration in multiphase flow, so as to study the relationship between tuning fork’s resonance parameters and multiphase flow’s characteristic parameters.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.J., D.C. and X.H.; methodology, F.J., Y.D. and M.T.; software, F.J.; validation, F.J.; formal analysis, F.J., D.C. and X.H.; investigation, F.J. and M.Z.; data curation, F.J.; writing—original draft preparation, F.J.; writing—review and editing, D.C. and Y.Z.; visualization, F.J. supervision, D.C.; project administration, D.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 42074174 and funded by Chongqing Natural Science Foundation, grant number CSTB2023NSCQ-MSX0968.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Toledo, J.; Ruiz-Díez, V.; Pfusterschmied, G.; Schmid, U.; Sánchez-Rojas, J.L. Flow-through sensor based on piezoelectric MEMS resonator for the in-line monitoring of wine fermentation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 54, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, J.; Jiménez-Márquez, F.; Úbeda, J.; Ruiz-Díez, V.; Pfusterschmied, G.; Schmid, U.; Sánchez-Rojas, J.L. Piezoelectric MEMS resonators for monitoring grape must fermentation. In Proceedings of the Micromechanics Europe 2016: 27th Micromechanics and Microsystems Europe Workshop, Cork, Ireland, 28–30 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sell, J.K.; Niedermayer, A.O.; Babik, S.; Jakoby, B. Gas density sensor for real-time monitoring in a high pressure reactor. Procedia Chem. 2009, 1, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Voglhuber-Brunnmaier, T.; Niedermayer, A.O.; Feichtinger, F.; Jakoby, B. Fluid sensing using quartz tuning forks—Measurement technology and applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, J.; Manzaneque, T.; Ruiz-Díez, V.; Jiménez-Márquez, F.; Kucera, M.; Pfusterschmied, G.; Wistrela, E.; Schmid, U.; Sánchez-Rojas, J.L. Comparison of in-plane and out-of-plane piezoelectric microresonators for real-time monitoring of engine oil contamination with diesel. Microsyst. Technol. 2016, 22, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Zeng, J.B.; Cai, D.Y.; Zhang, C.G.; Fan, W.T. The research of tight gas reservoir fluid identification in Kuche. Chin. J. Eng. Geophys. 2014, 11, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.X.; Zhai, L.S.; Yan, C.; Wang, H.M.; Jin, N.D. Capacitive phase shift detection for measuring water holdup in horizontal oil–water two-phase flow. Sensors 2018, 18, 2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, M.; Ham, G. Downhole viscosity measurement platform using tuning fork oscillators. In Proceedings of the IEEE SENSORS 2015, Busan, Republic of Korea, 13–15 November 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- González, M.; Seren, H.; Buzi, E.; Deffenbaugh, M. Fast downhole fluid viscosity and density measurements using a self-oscillating tuning fork device. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium, Glassboro, NJ, USA, 13–15 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rocco, D.; Difoggio, R.; Walkow, A.; Bergren, P.; Reittinger, P.W. Downhole Tool for Drilling or Wire Line Operations, Has Flexural Mechanical Resonator Which is Actuated in Response to Sonde Output to Determine Fluid Parameters. EP Patent 1397661 B1, 10 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Matsiev, L.F.; Bennett, J.; Kolosov, O. High precision tuning fork sensor for liquid property measurements. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 18–21 September 2005; pp. 1492–1495. [Google Scholar]
- Sader, J.E. Frequency response of cantilever beams immersed in viscous fluids with applications to the atomic force microscope. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waszczuk, K.; Piasecki, T.; Nitsch, K.; Gotszalk, T. Application of piezoelectric tuning forks in liquid viscosity and density measurements. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinisch, M.; Voglhuber-Brunnmaier, T.; Reichel, E.K. Reduced order models for resonant viscosity and mass density sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 220, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinisch, M.; Voglhuber-Brunnmaier, T.; Reichel, E. Electromagnetically driven torsional resonators for viscosity and mass density sensing applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 229, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, D.H.; He, X.; Wang, X.M. A Hydrodynamic Model for Measuring Fluid Density and Viscosity by Using Quartz Tuning Forks. Sensors 2020, 20, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chon, J.W.M.; Mulvaney, P.; Sader, J.E. Experimental validation of theoretical models for the frequency response of atomic force microscope cantilever beams immersed in fluids. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 3978–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysden, C.A.V.; Sader, J.E. Frequency response of cantilever beams immersed in viscous fluids with applications to the atomic force microscope: Arbitrary mode order. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 044908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M. A study of the Method of Measuring the Density and Viscosity of High Temperature Fluids Using a Tuning Fork. Doctoral Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Du, G.H.; Zhu, Z.M.; Gong, X.F. Fundamentals of Acoustics, 3rd ed.; Nanjing University Press: Nanjing, China, 2012; pp. 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Aoust, G.; Levy, R.; Verlhac, B. Optimal quality factor for tuning forks in a fluid medium. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 243, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).