Research on Microbial Community Structure in Different Blocks of Alkaline–Surfactant–Polymer Flooding to Confirm Optimal Stage of Indigenous Microbial Flooding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
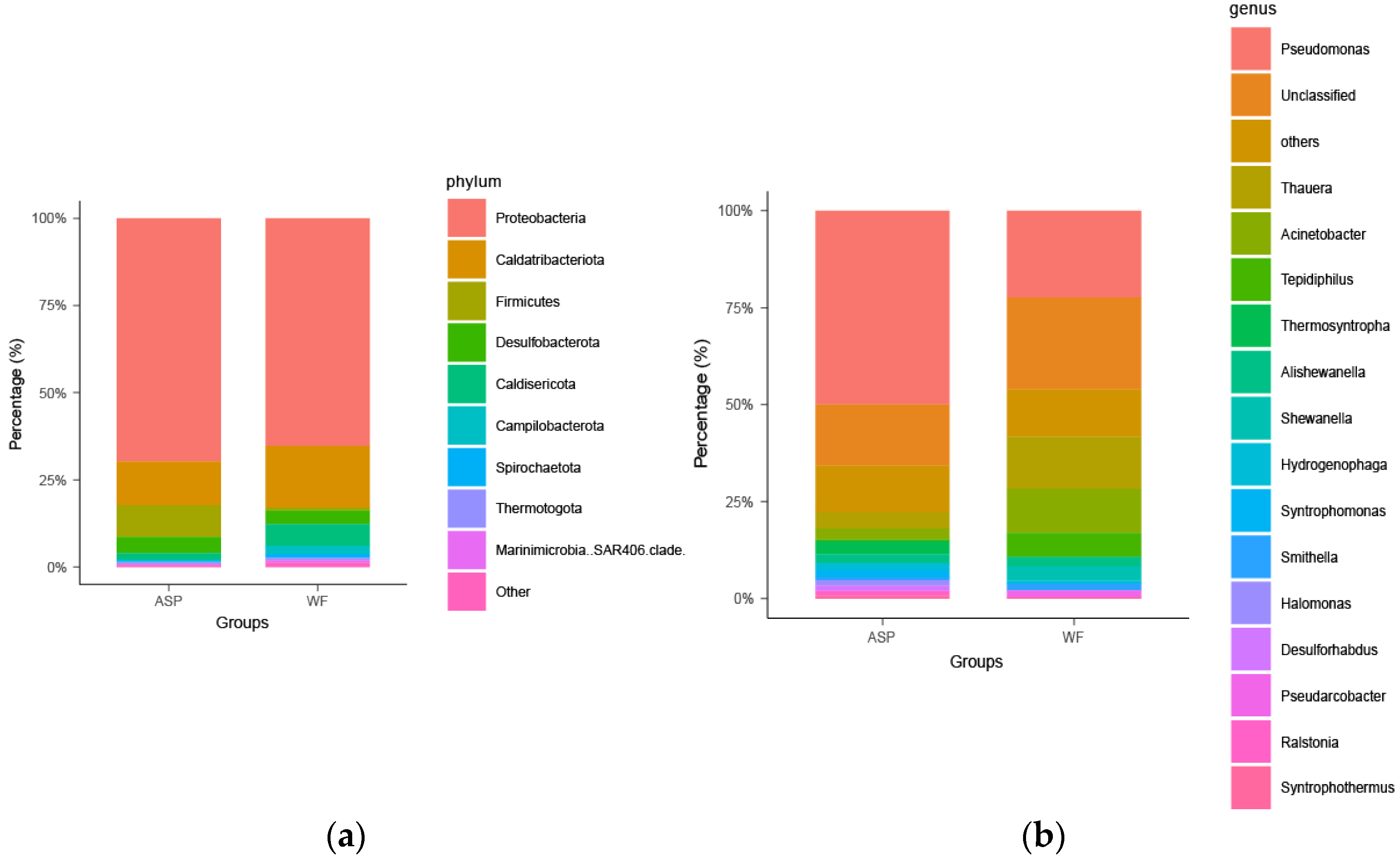
3.1. Composition of Microbial Communities in Different Displacement Blocks
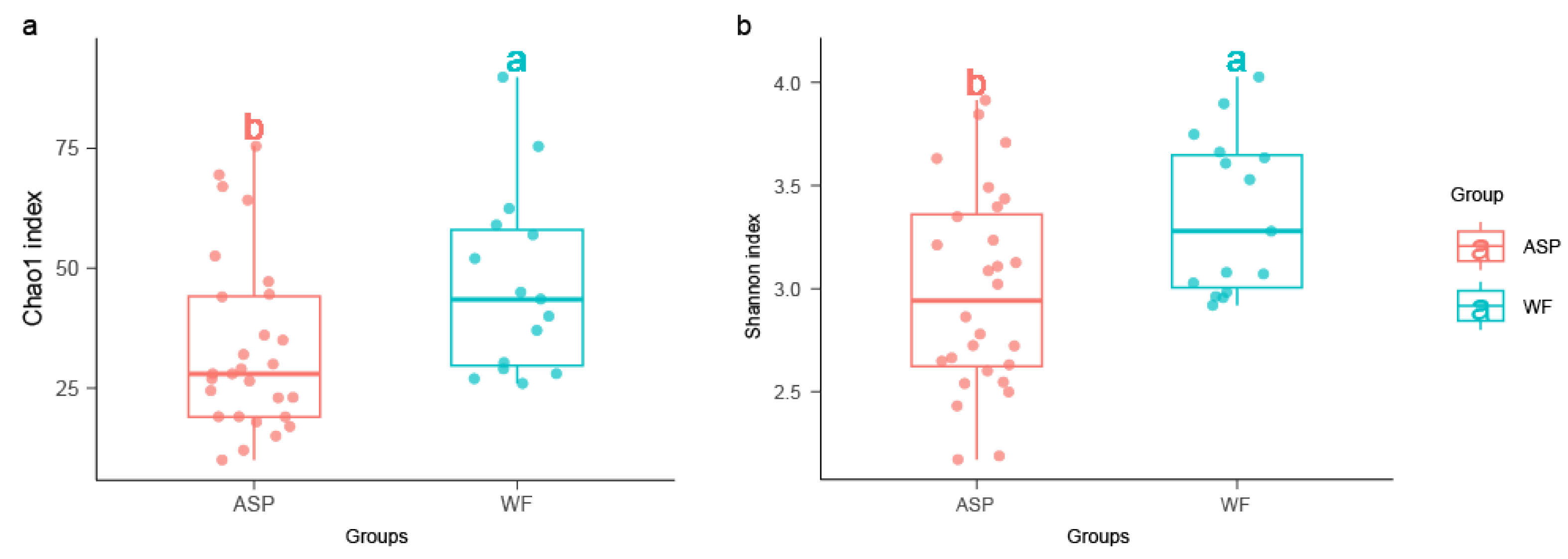
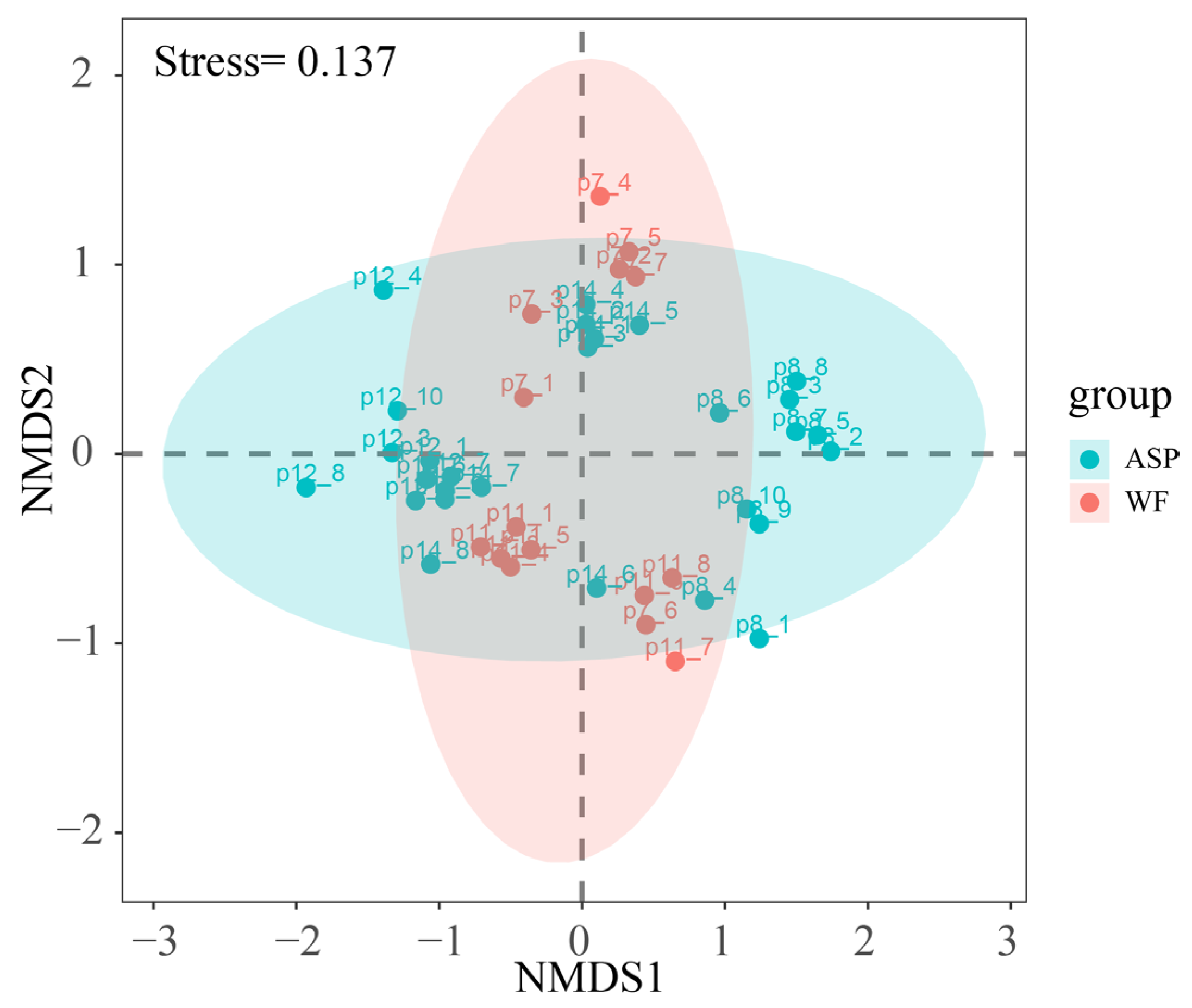
3.2. Diversity of Microbial Communities in Different Displacement Blocks
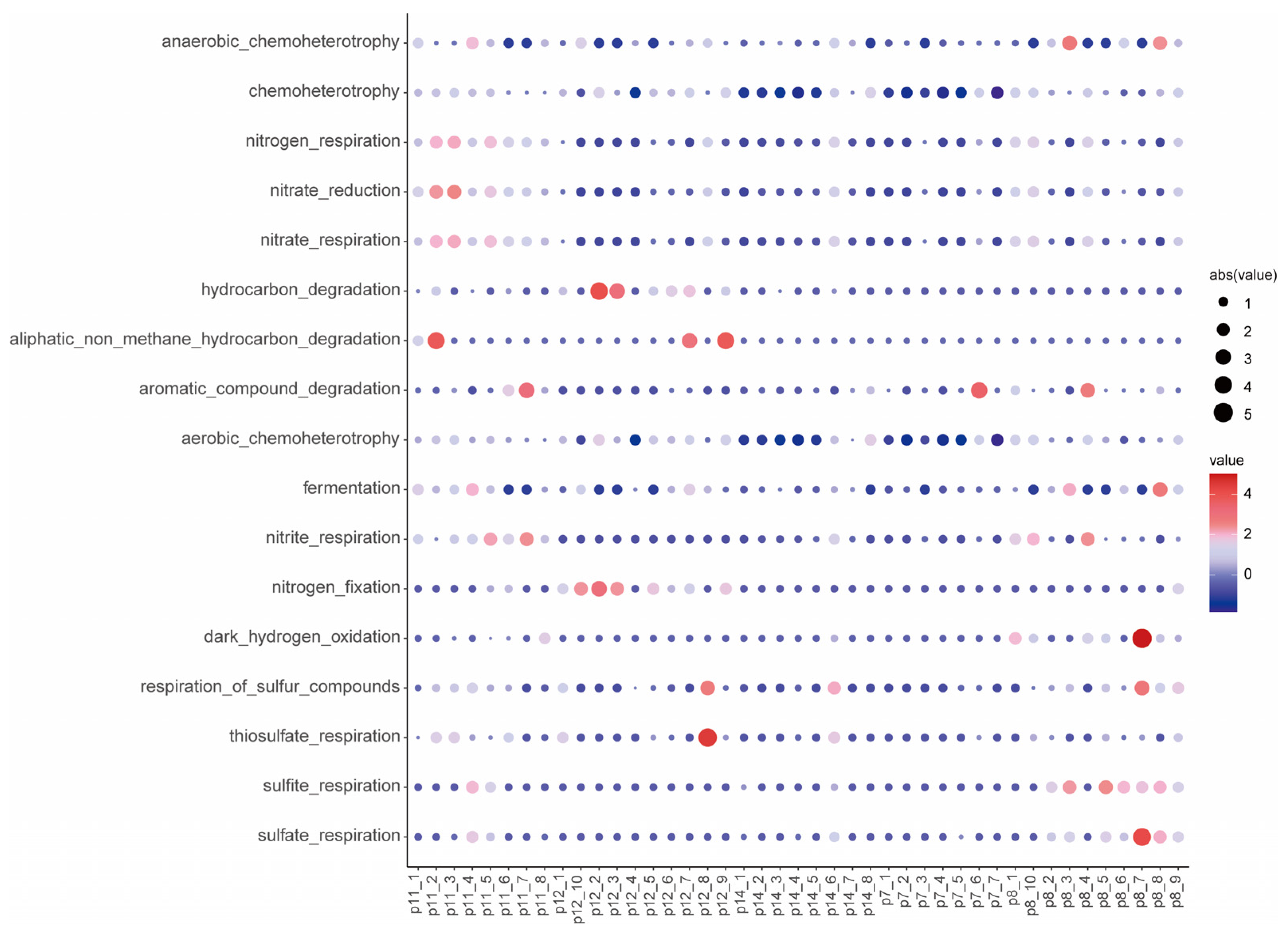
3.3. Analysis of Co-Occurrence Networks and Functional Prediction in Different Displacement Blocks
3.4. Correlation Analysis between Microbial and Environmental Factor of Oil Reservoirs in Different Displacement Blocks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gbadamosi, A.O.; Junin, R.; Manan, M.A.; Agi, A.; Yusuff, A.S. An overview of chemical enhanced oil recovery: Recent advances and prospects. Int. Nano Lett. 2019, 9, 171–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Niu, L.; Lu, X. Performance of ASP compound systems and effects on flooding efficiency. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 178, 1178–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashedi, H.; Yazdian, F.; Naghizadeh, S. Microbial Enhanced Oil Recovery. In Introduction to Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) Processes and Bioremediation of Oil-Contaminated Sites; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stewart, T.L.; Fogler, H.S. Biomass plug development and propagation in porous media. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2001, 72, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.R. Microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR). Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2010, 13, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInerney, M.J.; Nagle, D.P.; Knapp, R.M. Microbially enhanced oil recovery: Past, present, and future. In Petroleum Microbiology; Bernard, O., Michel, M., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 215–237. [Google Scholar]
- Van Hamme, J.D.; Singh, A.; Ward, O.P. Recent advances in petroleum microbiology. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2003, 67, 503–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, P.F.D.; Moreira, R.S.; Almeida, R.C.D.C.; Guimaraes, A.K.; Carvalho, A.S.; Quintella, C.; Esperidiã, M.C.A.; Taf, C.A. Selection and application of microorganisms to improve oil recovery. Eng. Life Sci. 2004, 4, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, J.M.; Roy, M.K.; John, L.C.; Bhupathiraju, V.K.; Coates, J.D. Use of indigenous or injected microorganisms for enhanced oil recovery microbial biosystems: New frontiers. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Microbial Ecology, Halifax, NS, Canada, 9–14 August 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Yernazarova, A.; Kayirmanova, G.; Baubekova, A.; Zhubanova, A. Microbial Enhanced Oil Recovery. In Chemical Enhanced Oil Recovery (cEOR)—A Practical Overview; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khire, J.M.; Khan, M.I. Microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR). Part 2. Microbes and subsurface environment for MEOR. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1994, 16, 258–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R.S.; Lindsey, R.P. World-Wide Applications of Microbial Technology for Improving Oil Recovery. In Proceedings of the SPE/DOE Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, Tulsa, Oklahoma, 21–24 April 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orphan, V.J.; Taylor, L.T.; Hafenbradl, D.; Delong, E.F. Culture-dependent and culture-independent characterization of microbial assemblages associated with high-temperature petroleum reservoirs. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhi, Z.; Wei, L.; Wu, H.; Wu, Y. Comparison of microbial community structures between oil and water phases in a low-permeability reservoir after water flooding. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Ma, F.; Su, J.; Li, W.; Wang, Q. Effect of polymer oil drive process in Daqing oil field on the microorganism community in oil deposit system. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 136, S617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.D.; Hnatow, L.L.; Zhang, S.; Fallon, R.D.; Jackson, S.C.; Tomb, J.; DeLong, E.F.; Keeler, S.J. Characterizing microbial diversity in production water from an Alaskan mesothermic petroleum reservoir with two independent molecular methods. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tully, B.J.; Nelson, W.C.; Heidelberg, J.F. Metagenomic analysis of a complex marine planktonic thaumarchaeal community from the Gulf of Maine. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Huang, L.; Zhang, X.; Gao, X. The Role of the Bacterial Community in Producing a Peculiar Smell in Chinese Fermented Sour Soup. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louca, S.; Jacques, S.M.S.; Pires, A.P.F.; Leal, J.S.; Srivastava, D.S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Farjalla, V.F.; Doebeli, M. High taxonomic variability despite stable functional structure across microbial communities. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 1, 0015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Ren, H.; Li, S.; Leng, X.; Yao, X. Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Co-occurrence Pattern during Vegetation Restoration in Karst Rocky Desertification Area. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Lei, S.; Wu, H.; Liao, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, G.; Wang, G.; Fang, L.; Song, Z. Simplified microbial network reduced microbial structure stability and soil functionality in alpine grassland along a natural aridity gradient. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 191, 109366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Li, J.-L.; Yin, L.-Z.; Luo, X.-Q.; Ahmad, M.; Fang, B.-Z.; Li, S.-H.; Deng, Q.-Q.; Wang, P.; Li, W.-J. Habitat-dependent prokaryotic microbial community, potential keystone species, and network complexity in a subtropical estuary. Environ. Res. 2022, 212 Pt D, 113376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulanowicz, R.E. Biodiversity, functional redundancy and system stability: Subtle connections. J. R. Soc. Interface 2018, 15, 20180367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Obregón, D. Behind Taxonomic Variability: The Functional Redundancy in the Tick Microbiome. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjani, S.J.; Upasani, V.N. Carbon spectrum utilization by an indigenous strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa NCIM 5514: Production, characterization and surface active properties of biosurfactant. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognolo, G. Biosurfactants as emulsifying agents for hydrocarbons. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1999, 152, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrzanowski, Ł.; Dziadas, M.; Ławniczak, Ł.; Cyplik, P.; Białas, W.; Szulc, A.; Lisiecki, P.; Jeleń, H. Biodegradation of rhamnolipids in liquid cultures: Effect of biosurfactant dissipation on diesel fuel/B20 blend biodegradation efficiency and bacterial community composition. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 111, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Chi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Jin, X.; Jin, P. Diversified metabolism makes novel Thauera strain highly competitive in low carbon wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2021, 206, 117742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, K.; Ishihara, M.; Shimauchi, T.; Harayama, S. Physicochemical properties and biodegradability of crude oil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 31, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Li, Y.; Tan, L.; Guo, F.; Ma, T. Composition of Bacterial and Archaeal Communities in an Alkali-Surfactant-Polyacrylamide-Flooded Oil Reservoir and the Responses of Microcosms to Nutrients. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastolla, U.; Fortuna, M.A.; Pascual-García, A.; Ferrera, A.; Luque, B.; Bascompte, J. The architecture of mutualistic networks minimizes competition and increases biodiversity. Nature 2009, 458, 1018–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Luo, F.; Zhou, J. Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Zhang, R.; Zeng, Y.; Dai, T.; Ye, Z.; Gao, Q.; Yang, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, G.; Zhou, J. Petroleum pollution changes microbial diversity and network complexity of soil profile in an oil refinery. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1193189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, P.; Ma, A.; Wei, X.; Chen, X.; Yin, J.; Hu, F.; Zhuang, X.; Song, M.; Zhuang, G. Interaction and spatio-taxonomic patterns of the soil microbiome around oil production wells impacted by petroleum hydrocarbons. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Gonzalez, N.; Huber, J.A.; Vallino, J.J. Microbial Communities Are Well Adapted to Disturbances in Energy Input. mSystems 2016, 1, e00117-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Xia, X.; Guo, S.; Li, J.; Song, Z.; Qu, G. Microscopic oil displacement mechanism of indigenous microorganisms under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions in reservoirs. Acta Pet. Sin. 2014, 35, 528–535. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, M.B.; Martiny, A.C.; Martiny, J.B.H. Global biogeography of microbial nitrogen-cycling traits in soil. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 8033–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.F.; Park, H.; Yeung, C.; Eggleston, B.; Francis, C.A.; Criddle, C.S. Ammonia-oxidizing communities in a highly aerated full-scale activated sludge bioreactor: Betaproteobacterial dynamics and low relative abundance of Crenarchaea. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 2310–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittebolle, L.; Vervaeren, H.; Verstraete, W.; Boon, N. Quantifying Community Dynamics of Nitrifiers in Functionally Stable Reactors. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanwonterghem, I.; Jensen, P.D.; Rabaey, K.; Tyson, G.W. Genome-centric resolution of microbial diversity, metabolism and interactions in anaerobic digestion. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 3144–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaman, K.; Brown, C.T.; Hug, L.A.; Sharon, I.; Castelle, C.J.; Probst, A.J.; Thomas, B.C.; Singh, A.; Wilkins, M.J.; Karaoz, U.; et al. Thousands of microbial genomes shed light on interconnected biogeochemical processes in an aquifer system. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-X.; Mbadinga, S.M.; Liu, J.-F.; Zhou, L.; Yang, S.-Z.; Gu, J.-D.; Mu, B.-Z. Microbiota and their affiliation with physiochemical characteristics of different subsurface petroleum reservoirs. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 120, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Nie, Y.; Chi, C.-Q.; Tang, Y.-Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.-B.; Liu, Z.-S.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wu, X.-L. Crude oil as a microbial seed bank with unexpected functional potentials. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.-Y.; Duan, R.-Y.; Liu, J.-F.; Yang, S.-Z.; Gu, J.-D.; Mu, B.-Z. Molecular analysis of the microbial community structures in water-flooding petroleum reservoirs with different temperatures. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 4645–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenchi, N.; İnceoğlu, Ö.; Kebbouche-Gana, S.; Gana, M.L.; Lliros, M.; Servais, P.; GarcíaArmisen, T. Diversityof microbial communities in production and injection waters of Algerian oilfields revealed by 16S rRNA gene amplicon 454 pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
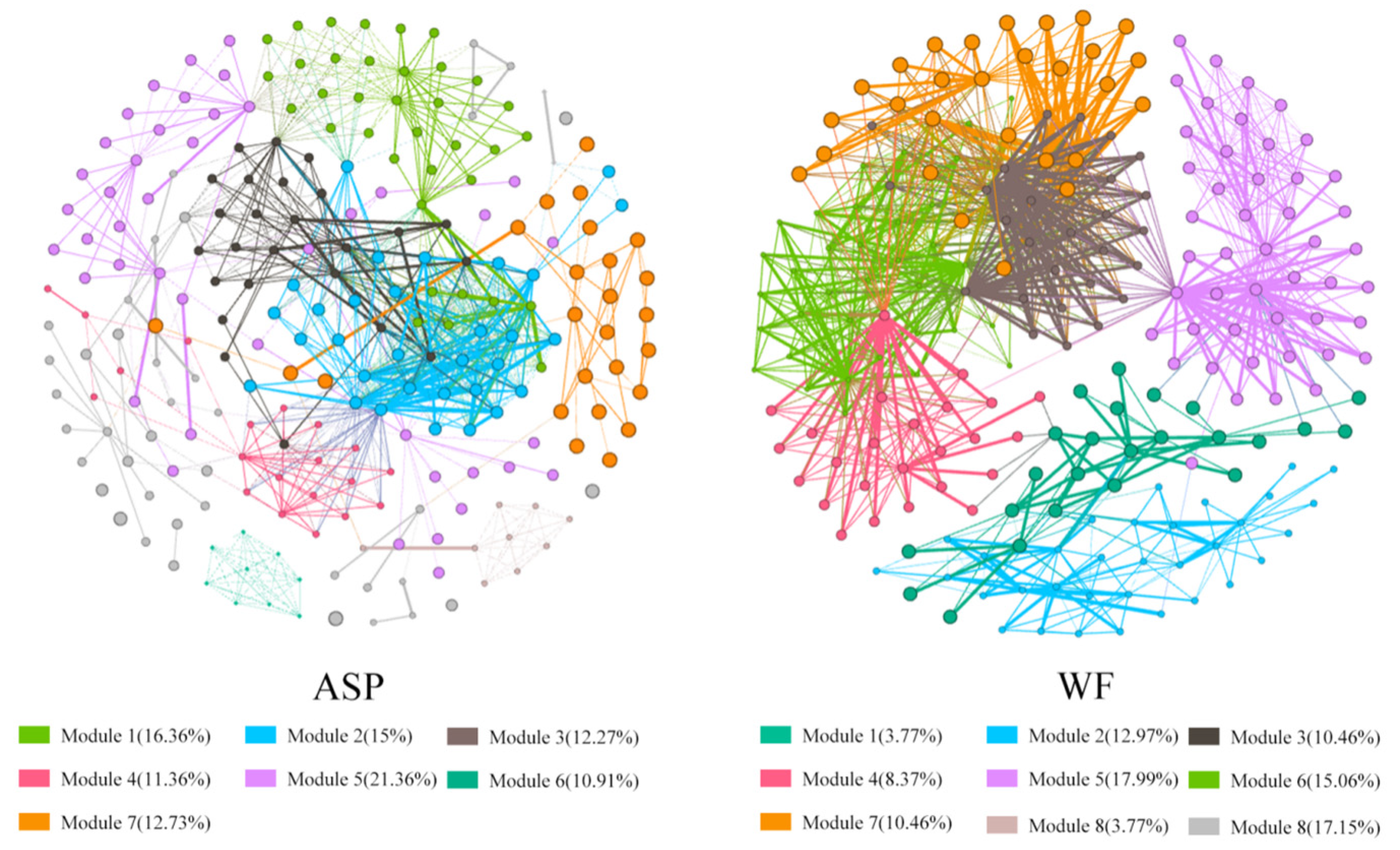

| Topological Properties | ASP | WF |
|---|---|---|
| Total nodes | 220 | 239 |
| Total edges | 944 | 1252 |
| Average degree | 7.9 | 11.382 |
| Average clustering coefficient | 0.258 | 0.363 |
| Average path length | 4.333 | 4.709 |
| Network density | 0.033 | 0.052 |
| Modularity index | 0.606 | 0.647 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Hou, Z.; Wang, M.; Yang, E. Research on Microbial Community Structure in Different Blocks of Alkaline–Surfactant–Polymer Flooding to Confirm Optimal Stage of Indigenous Microbial Flooding. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5243. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125243
Liu Y, Zhang X, Wu X, Hou Z, Wang M, Yang E. Research on Microbial Community Structure in Different Blocks of Alkaline–Surfactant–Polymer Flooding to Confirm Optimal Stage of Indigenous Microbial Flooding. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(12):5243. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125243
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yinsong, Xiumei Zhang, Xiaolin Wu, Zhaowei Hou, Min Wang, and Erlong Yang. 2024. "Research on Microbial Community Structure in Different Blocks of Alkaline–Surfactant–Polymer Flooding to Confirm Optimal Stage of Indigenous Microbial Flooding" Applied Sciences 14, no. 12: 5243. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125243
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhang, X., Wu, X., Hou, Z., Wang, M., & Yang, E. (2024). Research on Microbial Community Structure in Different Blocks of Alkaline–Surfactant–Polymer Flooding to Confirm Optimal Stage of Indigenous Microbial Flooding. Applied Sciences, 14(12), 5243. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125243





